Differential Role of NKG2A/HLA-E Interaction in the Outcomes of Bladder Cancer Patients Treated with M. bovis BCG or Other Therapies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples and Study Groups
2.2. HLA-A, -B and -C and KIR Genotyping
2.3. Expression of NK Cell Receptors in Peripheral Blood Lymphocytes
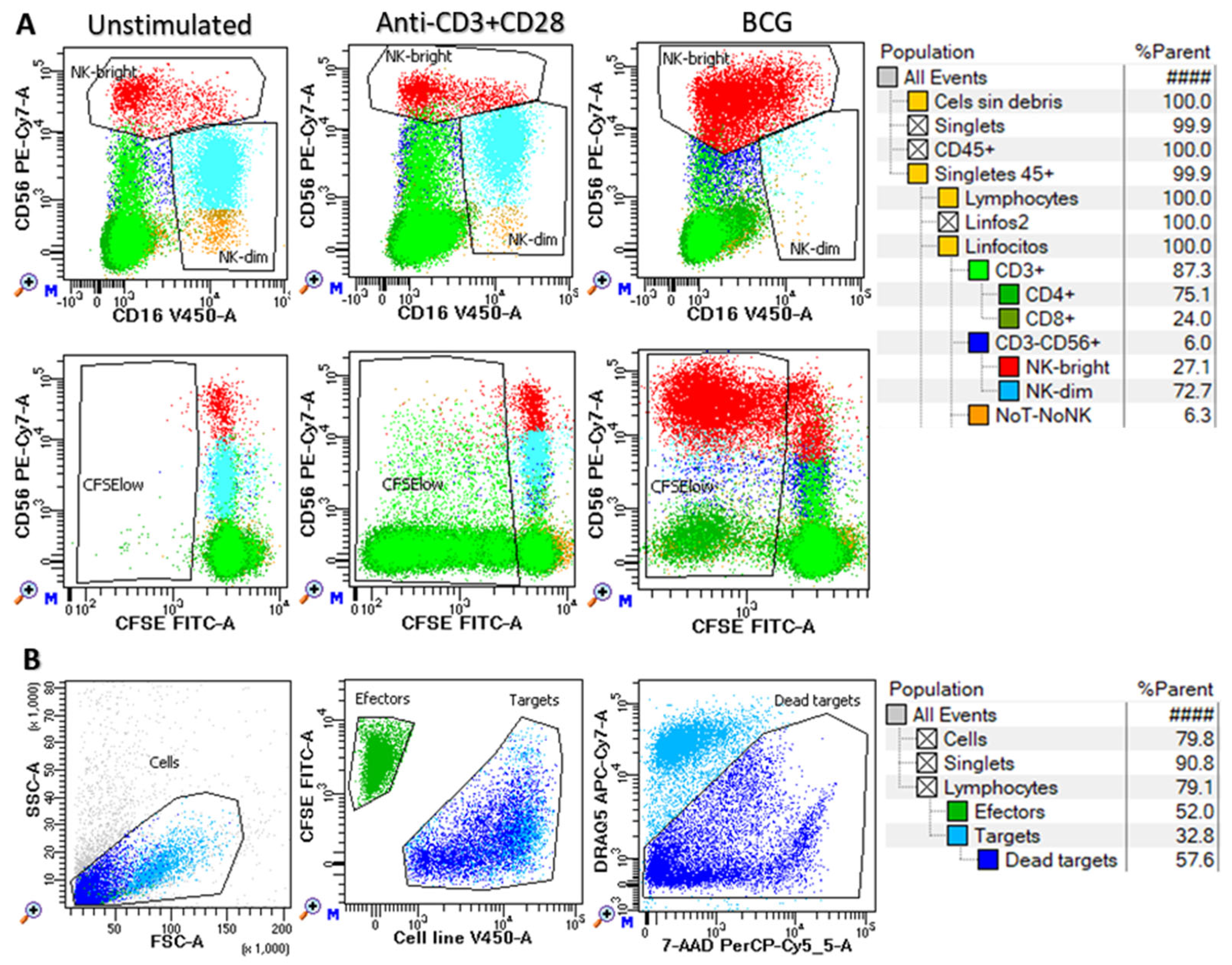
2.4. In Vitro Functional Assays
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical, Biological, Therapeutic and Evolutionary Characteristics of the Study Groups
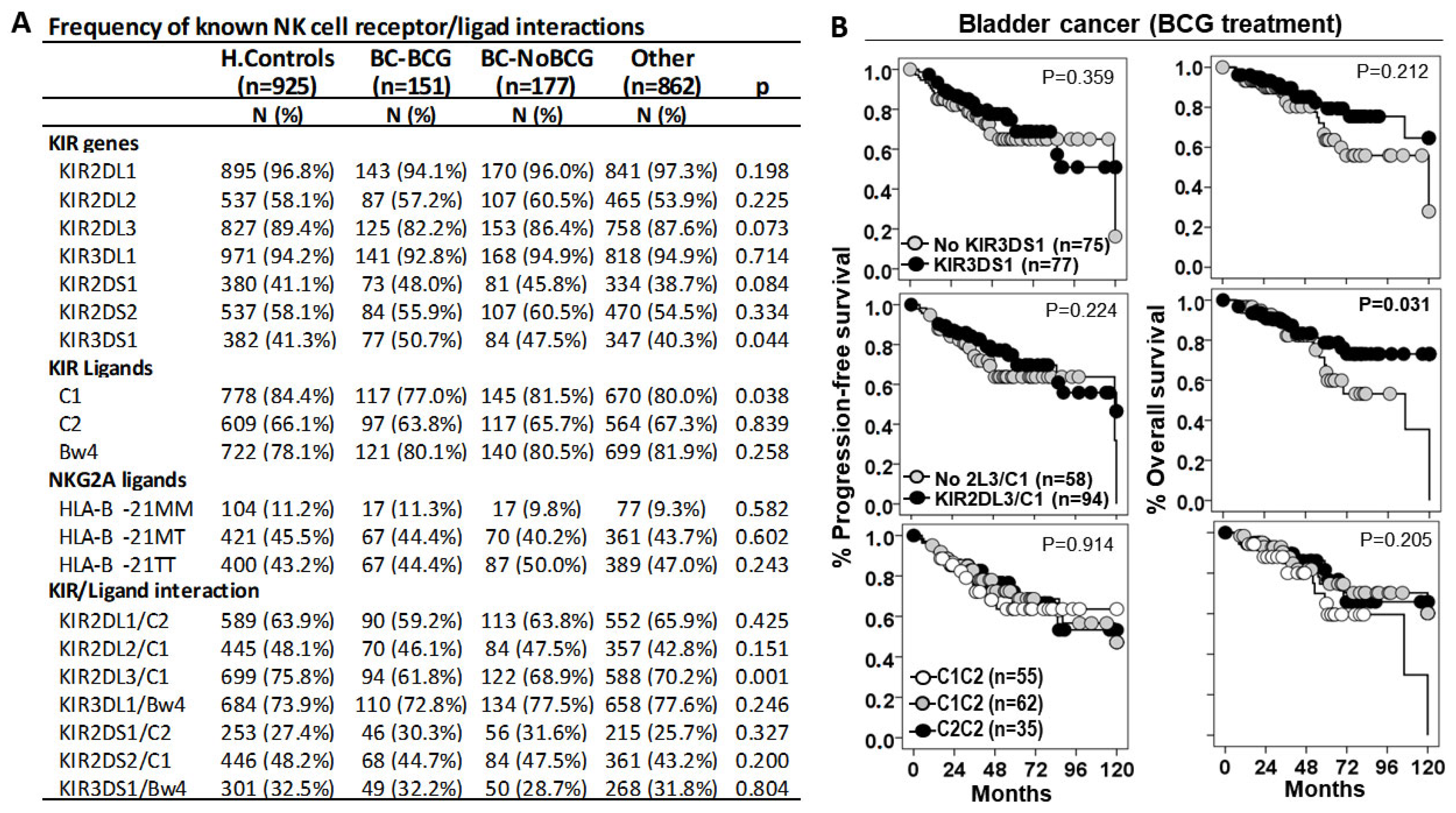
3.2. KIR2DL3/C1 Was the Only Interaction Associated with Susceptibility to BC and Patient Outcome
3.3. HLA-B −21M/T Genotype Is an Independent Predictive Parameter of the Progression-Free and Overall Survival in BC Patients Treated with BCG
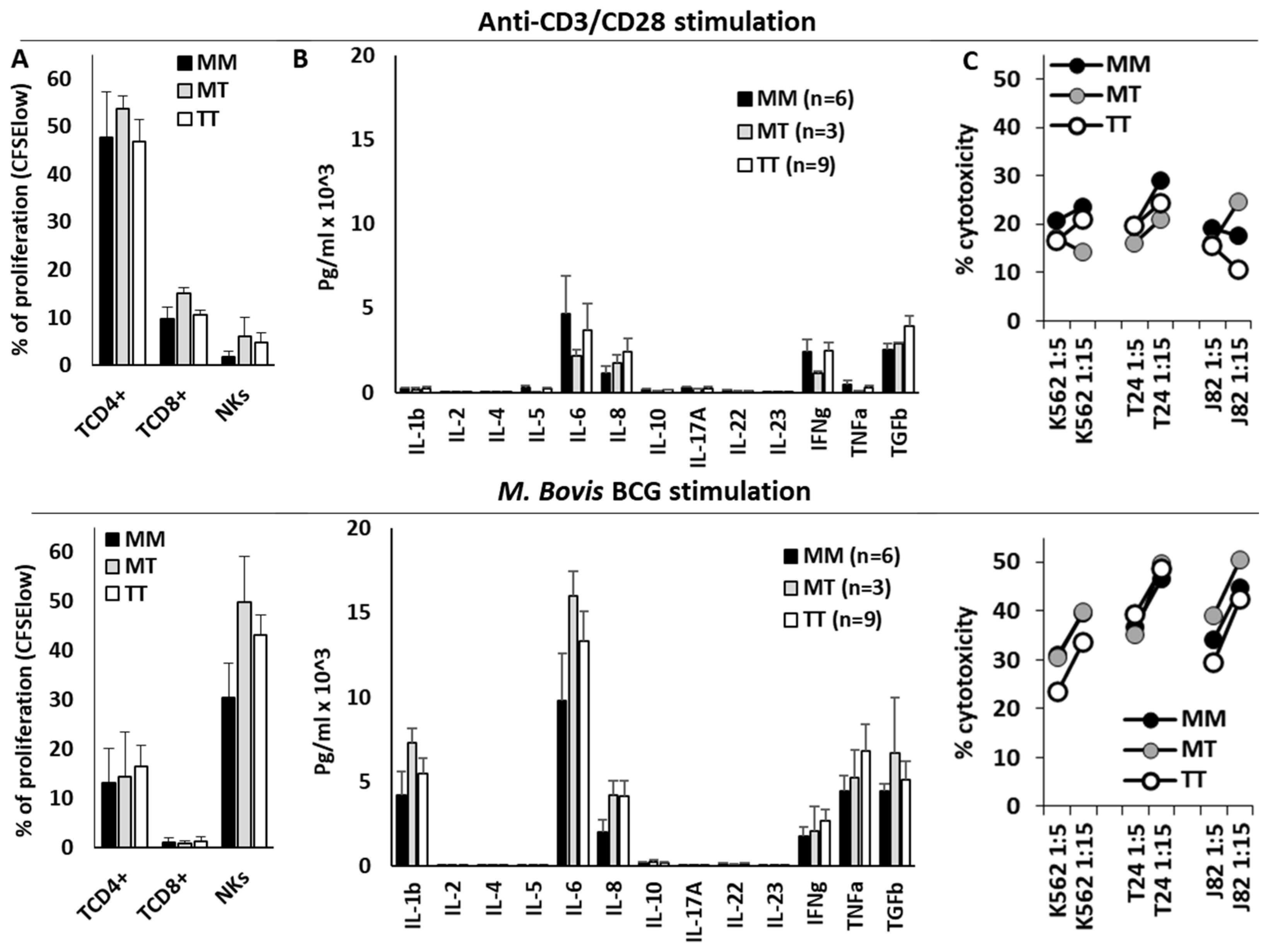
3.4. HLA-B −21M/T Genotype Is Associated with Differential Repertoire of KIR+ NK Cells and Expression of NKG2A in CD56bright NK Cells
3.5. HLA-B −21M/T Genotype Was Not Associated with Differential NK Cell Functionality In Vitro
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Babjuk, M.; Burger, M.; Capoun, O.; Cohen, D.; Compérat, E.M.; Dominguez Escrig, J.L.; Gontero, P.; Liedberg, F.; Masson-Lecomte, A.; Mostafid, A.H.; et al. European Association of Urology Guidelines on Non-muscle-invasive Bladder Cancer (Ta, T1, and Carcinoma in Situ). Eur. Urol. 2022, 81, 75–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flaig, T.W.; Spiess, P.E.; Abern, M.; Agarwal, N.; Bangs, R.; Boorjian, S.A.; Buyyounouski, M.K.; Chan, K.; Chang, S.; Friedlander, T.; et al. NCCN Guidelines® Insights: Bladder Cancer, Version 2.2022. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2022, 20, 866–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieczorek, E.; Garstka, M.A. Recurrent bladder cancer in aging societies: Importance of major histocompatibility complex class I antigen presentation. Int. J. Cancer 2021, 148, 1808–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardoll, D.M. The blockade of immune checkpoints in cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darvin, P.; Toor, S.M.; Sasidharan Nair, V.; Elkord, E. Immune checkpoint inhibitors: Recent progress and potential biomarkers. Exp. Mol. Med. 2018, 50, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Beltran, A.; Cimadamore, A.; Blanca, A.; Massari, F.; Vau, N.; Scarpelli, M.; Cheng, L. Montironi, R.Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors for the Treatment of Bladder Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, M.; Enting, D. Immune Responses in Bladder Cancer-Role of Immune Cell Populations, Prognostic Factors and Therapeutic Implications. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germanà, E.; Pepe, L.; Pizzimenti, C.; Ballato, M.; Pierconti, F.; Tuccari, G.; Ieni, A.; Giuffrè, G.; Fadda, G.; Fiorentino, V.; et al. Programmed Cell Death Ligand 1 (PD-L1) Immunohistochemical Expression in Advanced Urothelial Bladder Carcinoma: An Updated Review with Clinical and Pathological Implications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Lorente, I.; Gimeno, L.; López-Abad, A.; López Cubillana, P.; Fernández Aparicio, T.; Asensio Egea, L.J.; Moreno Avilés, J.; Doñate Iñiguez, G.; Guzmán Martínez-Valls, P.L.; Server, G.; et al. Exploring the Immunoresponse in Bladder Cancer Immunotherapy. Cells 2024, 13, 1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellmann, M.D.; Paz-Ares, L.; Bernabe Caro, R.; Zurawski, B.; Kim, S.-W.; Carcereny Costa, E.; Park, K.; Alexandru, A.; Lupinacci, L.; de la Mora Jimenez, E.; et al. Nivolumab plus Ipilimumab in Advanced Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 2020–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rini, B.I.; Plimack, E.R.; Stus, V.; Gafanov, R.; Hawkins, R.; Nosov, D.; Pouliot, F.; Alekseev, B.; Soulières, D.; Melichar, B.; et al. Pembrolizumab plus Axitinib versus Sunitinib for Advanced Renal-Cell Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 1116–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranti, D.; Yu, H.; Wang, Y.A.; Bieber, C.; Strandgaard, T.; Salomé, B.; Houghton, S.; Kim, J.; Ravichandran, H.; Okulate, I.; et al. HLA-E and NKG2A Mediate Resistance to M. bovis BCG Immunotherapy in Non-Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer. BioRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Cuesta, E.M.; Esteso, G.; Alvarez-Maestro, M.; López-Cobo, S.; Álvarez-Maestro, M.; Linares, A.; Ho, M.M.; Martínez-Piñeiro, L.; Reyburn, H.T.; Valés-Gómez, M. Characterization of a human anti-tumoral NK cell population expanded after BCG treatment of leukocytes. Oncoimmunology 2017, 6, e1293212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouanne, M.; Adam, J.; Radulescu, C.; Letourneur, D.; Bredel, D.; Mouraud, S.; Goubet, A.G.; Leduc, M.; Chen, N.; Tan, T.Z.; et al. BCG therapy downregulates HLA-I on malignant cells to subvert antitumor immune responses in bladder cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 132, e145666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouanne, M.; Roumiguié, M.; Houédé, N.; Masson-Lecomte, A.; Colin, P.; Pignot, G.; Larré, S.; Xylinas, E.; Rouprêt, M.; Neuzillet, Y. Development of immunotherapy in bladder cancer: Present and future on targeting PD(L)1 and CTLA-4 pathways. World J. Urol. 2018, 36, 1727–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maas, M.; Hilsendecker, A.; Pertoll, A.; Stühler, V.; Walz, S.; Rausch, S.; Stenzl, A.; Tsaur, I.; Hennenlotter, J.; Aufderklamm, S. PD-L1 Expression in High-Risk Non-Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer Is Influenced by Intravesical Bacillus Calmette–Guérin (BCG) Therapy. Cancers 2024, 16, 1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masson, D.; Jarry, A.; Baury, B.; Blanchardie, P.; Laboisse, C.; Lustenberger, P.; Denis, M.G. Overexpression of the CD155 gene in human colorectal carcinoma. Gut 2001, 49, 236–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triki, H.; Charfi, S.; Bouzidi, L.; Ben Kridis, W.; Daoud, J.; Chaabane, K.; Sellami-Boudawara, T.; Rebai, A.; Cherif, B. CD155 expression in human breast cancer: Clinical significance and relevance to natural killer cell infiltration. Life Sci. 2019, 231, 116543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.J.; Martinet, L.; Gilfillan, S.; Souza-Fonseca-Guimaraes, F.; Chow, M.T.; Town, L.; Ritchie, D.S.; Colonna, M.; Andrews, D.M.; Smyth, M.J. The receptors CD96 and CD226 oppose each other in the regulation of natural killer cell functions. Nat. Immunol. 2014, 15, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rousseau, A.; Parisi, C.; Barlesi, F. Anti-TIGIT therapies for solid tumors: A systematic review. ESMO Open 2023, 8, 101184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandau, S.; Riemensberger, J.; Jacobsen, M.; Kemp, D.; Zhao, W.; Zhao, X.; Jocham, D.; Ratliff, T.L.; Böhle, A. NK cells are essential for effective BCG immunotherapy. Int. J. Cancer 2001, 92, 697–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Secanella-Fandos, S.; Noguera-Ortega, E.; Olivares, F.; Luquin, M.; Julián, E. Killed but metabolically active mycobacterium bovis bacillus Calmette-Guérin retains the antitumor ability of live bacillus Calmette-Guérin. J. Urol. 2014, 191, 1422–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suttmann, H.; Jacobsen, M.; Reiss, K.; Jocham, D.; Böhle, A.; Brandau, S. Mechanisms of bacillus Calmette-Guerin mediated natural killer cell activation. J. Urol. 2004, 172, 1490–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maasho, K.; Opoku-Anane, J.; Marusina, A.I.; Coligan, J.E.; Borrego, F. Cutting Edge: NKG2D is a costimulatory receptor for human naive CD8+ T cells. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 4480–4484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naoe, M.; Ogawa, Y.; Takeshita, K.; Morita, J.; Iwamoto, S.; Miyazaki, A.; Yoshida, H. Bacillus Calmette-Guérin-pulsed dendritic cells stimulate natural killer T cells and gammadeltaT cells. Int. J. Urol. 2007, 14, 532–538; discussion 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Cuesta, E.M.; López-Cobo, S.; Álvarez-Maestro, M.; Esteso, G.; Romera-Cárdenas, G.; Rey, M.; Cassady-Cain, R.L.; Linares, A.; Valés-Gómez, A.; Reyburn, H.T.; et al. NKG2D is a key receptor for recognition of bladder cancer cells by IL-2-activated NK cells and BCG promotes NK cell activation. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Béziat, V.; Hilton, H.G.; Norman, P.J.; Traherne, J.A. Deciphering the killer-cell immunoglobulin-like receptor system at super-resolution for natural killer and T-cell biology. Immunology 2017, 150, 248–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anfossi, N.; André, P.; Guia, S.; Falk, C.S.; Roetynck, S.; Stewart, C.A.; Breso, V.; Frassati, C.; Reviron, D.; Middleton, D.; et al. Human NK Cell Education by Inhibitory Receptors for MHC Class I. Immunity 2006, 25, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Heller, G.; Chewning, J.; Kim, S.; Yokoyama, W.M.; Hsu, K.C. Hierarchy of the Human Natural Killer Cell Response Is Determined by Class and Quantity of Inhibitory Receptors for Self-HLA-B and HLA-C Ligands. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 5977–5989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, L.M. Current perspectives on natural killer cell education and tolerance: Emerging roles for inhibitory receptors. ImmunoTargets Ther. 2015, 4, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horowitz, A.; Djaoud, Z.; Nemat-Gorgani, N.; Blokhuis, J.; Hilton, H.G.; Béziat, V.; Malmberg, K.-J.; Norman, P.J.; Guethlein, L.A.; Parham, P. Class I HLA haplotypes form two schools that educate NK cells in different ways. Sci. Immunol. 2016, 1, eaag1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enqvist, M.; Ask, E.H.; Forslund, E.; Carlsten, M.; Abrahamsen, G.; Béziat, V.; Andersson, S.; Schaffer, M.; Spurkland, A.; Bryceson, Y.; et al. Coordinated Expression of DNAM-1 and LFA-1 in Educated NK Cells. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 4518–4527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillamón, C.F.; Martínez-Sánchez, M.V.; Gimeno, L.; Mrowiec, A.; Martínez-García, J.; Server-Pastor, G.; Martínez-Escribano, J.; Torroba, A.; Ferri, B.; Abellán, D.; et al. NK Cell Education in Tumor Immune Surveillance: DNAM-1/KIR Receptor Ratios as Predictive Biomarkers for Solid Tumor Outcome. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2018, 6, 1537–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schafer, J.R.; Salzillo, T.C.; Chakravarti, N.; Kararoudi, M.N.; Trikha, P.; Foltz, J.A.; Wang, R.; Li, S.; Lee, D.A. Education-dependent activation of glycolysis promotes the cytolytic potency of licensed human natural killer cells. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 143, 346–358.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodridge, J.P.; Jacobs, B.; Saetersmoen, M.L.; Clement, D.; Hammer, Q.; Clancy, T.; Skarpen, E.; Brech, A.; Landskron, J.; Grimm, C.; et al. Remodeling of secretory lysosomes during education tunes functional potential in NK cells. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kärre, K. Natural killer cell recognition of missing self. Nat. Immunol. 2008, 9, 477–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parham, P. MHC class I molecules and KIRS in human history, health and survival. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 5, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pende, D.; Falco, M.; Vitale, M.; Cantoni, C.; Vitale, C.; Munari, E.; Bertaina, A.; Moretta, F.; Del Zotto, G.; Pietra, G.; et al. Killer Ig-Like Receptors (KIRs): Their Role in NK Cell Modulation and Developments Leading to Their Clinical Exploitation. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilton, H.G.; Parham, P. Missing or altered self: Human NK cell receptors that recognize HLA-C. Immunogenetics 2017, 69, 567–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braud, V.M.; Allan, D.S.; O’Callaghan, C.A.; Söderström, K.; D’Andrea, A.; Ogg, G.S.; Lazetic, S.; Young, N.T.; Bell, J.I.; Phillips, J.H.; et al. HL-E binds to natural killer cell receptors CD94/NKG2A, B and C. Nature 1998, 391, 795–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Botet, M.; Llano, M.; Navarro, F.; Bellón, T. NK cell recognition of non-classical HLA class I molecules. Semin. Immunol. 2000, 12, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.; Goodlett, D.R.; Ishitani, A.; Marquardt, H.; Geraghty, D.E. HLA-E surface expression depends on binding of TAP-dependent peptides derived from certain HLA class I signal sequences. J. Immunol. 1998, 160, 4951–4960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yunis, E.J.; Romero, V.; Diaz-Giffero, F.; Zuñiga, J.; Koka, P. Natural Killer Cell Receptor NKG2A/HLA-E Interaction Dependent Differential Thymopoiesis of Hematopoietic Progenitor Cells Influences the Outcome of HIV Infection. J. Stem Cells 2007, 2, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Merino, A.M.; Song, W.; He, D.; Mulenga, J.; Allen, S.; Hunter, E.; Tang, J.; Kaslow, R.A. HLA-B signal peptide polymorphism influences the rate of HIV-1 acquisition but not viral load. J. Infect. Dis. 2012, 205, 1797–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merino, A.M.; Sabbaj, S.; Easlick, J.; Goepfert, P.; Kaslow, R.A.; Tang, J. Dimorphic HLA-B signal peptides differentially influence HLA-E- and natural killer cell-mediated cytolysis of HIV-1-infected target cells. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2013, 174, 414–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallner, A.; Bernson, E.; Hussein, B.A.; Ewald Sander, F.; Brune, M.; Aurelius, J.; Martner, A.; Hellstrand, K.; Thorén, F.B. The HLA-B-21 dimorphism impacts on NK cell education and clinical outcome of immunotherapy in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2019, 133, 1479–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamiya, T.; Seow, S.V.; Wong, D.; Robinson, M.; Campana, D. Blocking expression of inhibitory receptor NKG2A overcomes tumor resistance to NK cells. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 2094–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, S.; Narita, S.; Fujiyama, N.; Hatakeyama, S.; Kobayashi, T.; Kato, R.; Naito, S.; Sakatani, T.; Kashima, S.; Koizumi, A. Impact of germline HLA genotypes on clinical outcomes in patients with urothelial cancer treated with pembrolizumab. Cancer Sci. 2022, 113, 4059–4069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moch, H.; Humphrey, P.A.; Ulbright, T.M.; Reuter, V.E. WHO Classification of Tumours of the Urinary System and Male Genital Organs, 4th ed.; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Gimeno, L.; González-Lozano, I.; Soto-Ramírez, M.F.; Martínez-Sánchez, M.V.; López-Cubillana, P.; Fuster, J.L.; Martínez-García, J.; Martínez-Escribano, J.; Campillo, J.A.; Pons-Fuster, E.; et al. CD8+ T lymphocytes are sensitive to NKG2A/HLA-E licensing interaction: Role in the survival of cancer patients. Oncoimmunology 2021, 10, 1986943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretta, L.; Moretta, A. Killer immunoglobulin-like receptors. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2004, 16, 626–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillamón, C.F.; Gimeno, L.; Server, G.; Martínez-Sánchez, M.V.; Escudero, J.F.; López-Cubillana, P.; Cabezas-Herrera, J.; Campillo, J.A.; Abellan, D.J.; Martínez-García, J.; et al. Immunological Risk Stratification of Bladder Cancer Based on Peripheral Blood Natural Killer Cell Biomarkers. Eur. Urol. Oncol. 2021, 4, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamat, A.M.; Li, R.; O’Donnell, M.A.; Black, P.C.; Roupret, M.; Catto, J.W.; Comperat, E.; Ingersoll, M.A.; Witjes, W.P.; McConkey, D.J.; et al. Predicting Response to Intravesical Bacillus Calmette-Guérin Immunotherapy: Are We There Yet? A Systematic Review. Eur. Urol. 2018, 73, 738–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.S.; Shan, B.L.; Shan, L.L.; Chin, P.; Murray, S.; Ahmadi, N.; Saxena, A. A systematic review and meta-analysis of quality of life outcomes after radical cystectomy for bladder cancer. Surg. Oncol. 2016, 25, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedke, J.; Black, P.C.; Szabados, B.; Guerrero-Ramos, F.; Shariat, S.F.; Xylinas, E.; Brinkmann, J.; Blake-Haskins, J.A.; Cesari, R.; Redorta, J.P. Optimizing outcomes for high-risk, non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer: The evolving role of PD-(L)1 inhibition. Urol. Oncol. 2023, 41, 461–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salomé, B.; Sfakianos, J.P.; Ranti, D.; Daza, J.; Bieber, C.; Charap, A.; Hammer, C.; Banchereau, R.; Farkas, A.M.; Ruan, D.F.; et al. NKG2A and HLA-E define an alternative immune checkpoint axis in bladder cancer. Cancer Cell 2022, 40, 1027–1043.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbst, R.S.; Majem, M.; Barlesi, F.; Carcereny, E.; Chu, Q.; Monnet, I.; Sanchez-Hernandez, A.; Dakhil, S.; Camidge, D.R.; Winzer, L.; et al. COAST: An Open-Label, Phase II, Multidrug Platform Study of Durvalumab Alone or in Combination With Oleclumab or Monalizumab in Patients With Unresectable, Stage III Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 3383–3393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zuo, F.; Song, J.; Tang, L.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, H.; Yang, Z.; Jing, J.; Ma, X.; et al. Immune checkpoints HLA-E:CD94-NKG2A and HLA-C:KIR2DL1 complementarily shield circulating tumor cells from NK-mediated immune surveillance. Cell Discov. 2024, 10, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manduca, N.; Maccafeo, E.; De Maria, R.; Sistigu, A.; Musella, M. 3D cancer models: One step closer to in vitro human studies. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1175503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ruiz-Lorente, I.; Gimeno, L.; López-Abad, A.; López Cubillana, P.; Fernández Aparicio, T.; Asensio Egea, L.J.; Moreno Avilés, J.; Doñate Iñiguez, G.; Guzmán Martínez-Valls, P.L.; Server, G.; et al. Differential Role of NKG2A/HLA-E Interaction in the Outcomes of Bladder Cancer Patients Treated with M. bovis BCG or Other Therapies. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 156. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13010156
Ruiz-Lorente I, Gimeno L, López-Abad A, López Cubillana P, Fernández Aparicio T, Asensio Egea LJ, Moreno Avilés J, Doñate Iñiguez G, Guzmán Martínez-Valls PL, Server G, et al. Differential Role of NKG2A/HLA-E Interaction in the Outcomes of Bladder Cancer Patients Treated with M. bovis BCG or Other Therapies. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(1):156. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13010156
Chicago/Turabian StyleRuiz-Lorente, Inmaculada, Lourdes Gimeno, Alicia López-Abad, Pedro López Cubillana, Tomás Fernández Aparicio, Lucas Jesús Asensio Egea, Juan Moreno Avilés, Gloria Doñate Iñiguez, Pablo Luis Guzmán Martínez-Valls, Gerardo Server, and et al. 2025. "Differential Role of NKG2A/HLA-E Interaction in the Outcomes of Bladder Cancer Patients Treated with M. bovis BCG or Other Therapies" Biomedicines 13, no. 1: 156. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13010156
APA StyleRuiz-Lorente, I., Gimeno, L., López-Abad, A., López Cubillana, P., Fernández Aparicio, T., Asensio Egea, L. J., Moreno Avilés, J., Doñate Iñiguez, G., Guzmán Martínez-Valls, P. L., Server, G., Ferri, B., Campillo, J. A., Martínez-Sánchez, M. V., & Minguela, A. (2025). Differential Role of NKG2A/HLA-E Interaction in the Outcomes of Bladder Cancer Patients Treated with M. bovis BCG or Other Therapies. Biomedicines, 13(1), 156. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13010156






