Abstract
Estimating heterogeneous treatment effects plays a vital role in many statistical applications, such as precision medicine and precision marketing. In this paper, we propose a novel meta-learner, termed RXlearner for estimating the conditional average treatment effect (CATE) within the general framework of meta-algorithms. RXlearner enhances the weighting mechanism of the traditional Xlearner to improve estimation accuracy. We establish non-asymptotic error bounds for RXlearner under a continuity classification criterion, specifically assuming that the response function satisfies Hölder continuity. Moreover, we show that these bounds are achievable by selecting an appropriate base learner. The effectiveness of the proposed method is validated through extensive simulation studies and a real-world data experiment.
Keywords:
conditional average treatment effect; heterogeneous treatment effect; causal inference; minimax optimality; Hölder continuous MSC:
62-08; 62P99
1. Introduction
Causal inference plays a pivotal role across a wide range of scientific disciplines. With the rapid advancement of big data technologies, researchers now have access to more information than ever before, enabling more accurate estimation of causal effects. A central task in this field is the estimation of heterogeneous treatment effects (HTEs), which seeks to quantify how treatment effects vary across individuals or subpopulations. This is particularly critical in domains such as precision medicine and targeted policy-making, where practitioners—such as doctors, policymakers, and researchers—aim to determine whether newly developed treatments or interventions produce the desired outcomes for different groups.
As research in causal inference has progressed, it has become increasingly clear that average treatment effects (ATEs) may mask significant heterogeneity at the individual level. As a result, growing attention has been devoted to the estimation of conditional average treatment effects (CATEs), which aim to capture individual-level causal effects conditional on observed covariates.
Early approaches to estimating CATEs include semi-parametric models, such as partial linear models [1,2] and additive models [3], as well as classical non-parametric methods [4]. In addition, several weighting-based methods have been proposed, including inverse probability weighting (IPW), augmented IPW (AIPW) [5,6,7], and propensity score optimization techniques [8]. These traditional methods are supported by mature theoretical foundations but often rely on restrictive modeling assumptions, which limit their flexibility in capturing complex real-world data structures.
With the rise of machine learning, researchers have developed a variety of flexible, data-driven methods for estimating CATEs. Ref. [9] introduced a model-free meta-learning algorithm, which was further extended by [10] through a general framework that includes the Slearner and Tlearner [11,12], and later the Xlearner. Other notable contributions include the Rlearner based on Robinson decomposition [13], Athey’s Causal Forest [14], and the Double Machine Learning (DML) framework [15], which utilizes Neyman orthogonality and cross-fitting to reduce sensitivity to nuisance parameters. The Doubly Robust Learner (DRL) [16] and the unifying framework proposed by [17]—which incorporates the L1 loss to enhance robustness—further broaden the scope of meta-learning-based estimators.
These modern approaches leverage the flexibility of machine learning to model complex functional relationships and have demonstrated strong empirical performance. However, despite their practical success, most theoretical analyses of these methods rely on strong smoothness assumptions, such as requiring the response function to lie in a reproducing kernel Hilbert space (RKHS) or satisfy Lipschitz continuity. While these assumptions facilitate theoretical derivations, they may not hold in many real-world applications.
Among the existing meta-learning methods, the Xlearner has demonstrated strong empirical performance, particularly in scenarios with covariate unbalance and unequal treatment assignment rates. Its design leverages different base learners for treated and control groups, which allows it to adapt well to unbalanced datasets and heterogeneous response surfaces [10]. These features make Xlearner one of the most widely used and practically effective methods in CATE estimation. However, despite its strengths, Xlearner still faces two main challenges. First, as noted by [10], its reliance on propensity scores as weighting functions can limit its flexibility, particularly in complex or high-dimensional data settings. Second, most of its theoretical guarantees rely on the assumption that the underlying response functions are Lipschitz continuous, which may not hold in many practical scenarios where the functions are less smooth or exhibit discontinuities.
To address the limitations of fixed-weight designs and the error accumulation inherent in the Xlearner, while preserving its structural advantages, we propose a novel meta-learning method called RXlearner. This method incorporates a data-driven, covariate-dependent weighting mechanism that adaptively combines pseudo-treatment effect estimates. By doing so, RXlearner enhances the model’s flexibility in capturing complex response patterns and mitigates cumulative errors across estimation stages.
We rigorously establish the theoretical properties of RXlearner by deriving a non-asymptotic error bound under the assumption that the response function satisfies Hölder continuity, a milder and more general condition than those typically assumed in the existing literature. The effectiveness of RXlearner is further demonstrated through extensive simulation studies and a real-world application. While the inherent variability in the data makes the identification of a universally optimal estimator elusive, our results show that RXlearner delivers consistently competitive and robust performance across a broad range of scenarios.
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows. Section 2 introduces the model assumptions and presents the RXlearner algorithm. Section 3 develops the theoretical analysis of the estimator, where we derive non-asymptotic error bounds under Hölder continuity. To evaluate the practical effectiveness of the proposed method, Section 4 reports results from simulation studies, and Section 5 applies RXlearner to a real-world dataset. Section 6 concludes the paper with further discussions and directions for future research. Technical proofs are provided in Appendix A.
2. Methodology
2.1. Models and Assumptions
We consider the estimation of the conditional average treatment effect (CATE) under the potential outcomes framework of Neyman–Rubin [18,19]. Let be a binary treatment indicator, and for each unit i, let and denote the potential outcomes under treatment and control, respectively. Let represent the p-dimensional covariates. We assume that the data are generated independently from a distribution , such that
Under the Stable Unit Treatment Value Assumption (SUTVA) [20], the observed outcome is given by
where denotes the indicator function. The observed dataset is denoted as
We define the response functions as
and the corresponding conditional average treatment effect (CATE) function is
To simulate observed outcomes, we further adopt an additive noise model
The variance parameter controls the noise level and is varied across simulation scenarios.
The propensity score, i.e., the probability of receiving treatment conditional on covariates, is defined as
Our goal is to estimate with an estimator , and to evaluate its performance under the expected mean squared error (EMSE), defined as
Here, we follow the EMSE definition proposed in [10], where and is assumed to be independent of . In our implementation, this assumption is addressed via a sample-splitting strategy: the estimator is trained on one subset of the data, and EMSE is evaluated on an independent test sample drawn from the same distribution. This design ensures that is independent of at evaluation time. Consequently, corresponds to the marginal distribution of the evaluation sample.
To establish the theoretical properties of the estimator, we make the following standard assumptions.
Assumption 1
(Ignorability). The treatment assignment is independent of the potential outcomes conditional on the covariates , i.e.,
Assumption 2
(Positivity). The propensity score is bounded away from 0 and 1, i.e., for all .
Assumption 3
(Conditionally Independent Errors). The errors are independent of treatment assignment given the covariates, i.e., . We further assume that and that the conditional variance of the errors exists.
Remark 1.
Assumption 3 states that the error term is conditionally independent of the treatment assignment given the covariates . This assumption ensures that the estimation of nuisance functions (such as the outcome regressors and the imputed treatment effect differences in the first stage) is unbiased. It is a standard condition in many meta-learner frameworks, including the Xlearner. In our RXlearner, this assumption supports the consistency of the refined weighting strategy. While the assumption may be restrictive in practice, it provides a clean theoretical foundation. We acknowledge this limitation and leave the relaxation of this assumption for future exploration.
2.2. Meta-Algorithms
In this section, we begin by reviewing representative models within the meta-learner framework for CATE estimation. Meta-learners are a class of model-agnostic methods that reduce the problem of causal effect estimation to a series of supervised learning tasks, enabling the use of flexible machine learning algorithms as base learners. We briefly describe three widely used approaches: the Slearner, Tlearner, and Xlearner, which form the foundation for our proposed RXlearner.
The Slearner estimates treatment effects using a single predictive model, where “S” stands for “single”. It incorporates the treatment indicator as one of the input features, treating it on an equal footing with other covariates. The response function is modeled as
where .
The estimated conditional average treatment effect (CATE) at the covariate value x is then given by
While the Slearner uses a single model incorporating the treatment indicator, the Tlearner fits two models independently for each treatment group.
The Tlearner estimates treatment effects by splitting the dataset into treated and control groups and fitting separate models to each subgroup. The “T” stands for “two”, reflecting the use of two distinct models, one for each treatment condition.
The response function for the treated group is modeled as
and for the control group as
The estimated CATE is then computed as the difference between the two fitted models:
A limitation of the Tlearner is that it estimates treatment effects separately for each group without borrowing strength from the other. The Xlearner improves upon this by incorporating cross-group information through imputation.
The Xlearner builds upon the Tlearner and proceeds in three main steps. The first step mirrors the Tlearner: the response functions for the treated and control groups, and , are estimated as in Equations (2) and (3).
In the second step, pseudo-treatment effects are imputed by leveraging the estimated response functions from the opposite group. Specifically, the imputed treatment effects are computed as
These imputed differences are then used to estimate the treatment effects conditional on covariates:
If the response functions are correctly estimated, i.e., and , then
Any supervised learning or regression method can be employed to estimate by regressing the imputed treatment effects on the covariates within each treatment arm. This yields two estimators: from the treated group and from the control group.
In the third step, the final CATE estimate is obtained by combining the two pseudo-effect estimates using a weighting function :
where typically depends on the propensity score, e.g., as in [10].
2.3. RXlearner
To improve upon the standard Xlearner framework while retaining its structural advantages, we propose a novel meta-learning method termed RXlearner (Refitting Xlearner). This method enhances the traditional weighting strategy by incorporating a data-driven mechanism to adaptively combine the two pseudo-treatment effect estimators, and , based on covariate information.
The procedure begins with a standard Xlearner step, wherein we estimate and on the training set, as well as the propensity score . Using these quantities, we construct a pseudo-response variable:
which serves as a proxy for the unobserved individual-level treatment effect.
Instead of relying on the fixed weight function as in the original Xlearner, we adopt a two-stage refitting strategy. In the first stage, we fit a powerful regression model (e.g., Random Forest) to predict using x as input, effectively capturing complex nonlinear relationships between covariates and treatment heterogeneity. However, direct use of this refitted model may lead to instability, especially when the learned is noisy in regions with limited overlap.
To mitigate this, we employ a second stage that recasts the refitted predictions into a convex combination form, aligning with the Xlearner’s structure. Specifically, we aim to learn a new weighting function by minimizing the squared error between the first-stage prediction and a convex combination of and :
where denotes the pseudo-treatment effect from the refitting step, and denotes the test set.
To approximate , we frame this optimization as a supervised regression problem and adopt gradient boosted regression trees (GBRT) [21] implemented via the xgboost package. GBRT minimizes squared loss through functional gradient descent, providing explicit convergence guarantees under standard conditions and offering strong empirical stability in practice.
The final estimate of the CATE is then given by the following:
Remark 2.
It is important to note that the learned weighting function is defined on the test set , rather than on the entire covariate space . This is because the optimization objective in Equation (6) is constructed only over the test points.
Remark 3.
To construct pseudo-outcomes, we apply propensity-score-based weighting similar to the Xlearner framework [10], assigning weights to treated units and to control units. However, our RXlearner differs from the standard Xlearner in that the weight function is not fixed to . Instead, it is refined through a second-stage regression step, where the optimal weights are learned in a data-driven manner by minimizing a squared loss objective (Equation (6)). This allows RXlearner to adaptively learn context-specific weights that may improve performance.
This two-stage design leverages the flexibility of machine learning models to fit pseudo-response values while preserving the interpretable structure of the Xlearner. Specifically, RXlearner can be viewed as a data-driven generalization of the Xlearner: instead of using the propensity score as a fixed weighting function, it learns a flexible weight by minimizing a squared loss with respect to a pseudo-target. This allows RXlearner to adaptively combine the two pseudo-treatment effect estimators and , depending on their relative reliability across the covariate space. Such adaptivity improves estimation robustness and accuracy, especially in the presence of covariate imbalance or heterogeneous noise, making RXlearner well-suited for complex causal inference tasks.
We emphasize that RXlearner can be viewed as a data-driven generalization of Xlearner. In particular, when the optimization problem in (6) is solved with a fixed weight function , the RXlearner reduces exactly to the original Xlearner formulation. That is, if the refitted model perfectly recovers the pseudo-response , then the optimal solution to (6) is attained when . This establishes the Xlearner as a special case of RXlearner.
To facilitate implementation, we summarize the RXlearner procedure in Algorithm 1 as follows.
| Algorithm 1 RXlearner Algorithm |
|
Remark 4.
To ensure reproducibility, we specify the base regression models and tuning parameters used in our implementation of the RXlearner. For the pseudo-target refitting model in Step 3, we use a random forest regressor (R package:
randomForest,
ntree = 100). For learning the weighting function in Step 4, we adopt gradient boosted regression trees (GBRT) using the
xgboostpackage, with squared error loss,
nrounds = 100,
max_depth = 3, and
learning_rate = 0.1. These choices balance flexibility and convergence stability across all experimental settings.
3. Asymptotic Properties
Assuming that only the weighting function is altered, the convergence analysis of RXlearner largely parallels that of Xlearner. Reference [10] established the convergence rate of the Xlearner under the assumption that the response function satisfies Lipschitz continuity. In this work, we generalize this assumption to Hölder continuity and derive the corresponding convergence rate for the RXlearner under this broader condition.
3.1. Fundamental Definitions and Results
To proceed, we begin by reviewing several fundamental definitions and results in the minimax nonparametric regression literature. Definition 1 introduces the concept of Hölder continuity, while Definitions 2 and 3, and Lemma 1 are adapted from [22].
It is worth noting that Hölder continuity provides a broader notion of smoothness than Lipschitz continuity, allowing for a controlled, potentially nonlinear rate of change in the function.
Definition 1.
Let be a function defined on a metric space X. f is referred to as Hölder continuous if there exist constants and such that for any , the following inequality holds:
The constant L is called the Hölder constant, and α is called the Hölder exponent. When , Hölder continuity reduces to Lipschitz continuity.
Definition 2.
Let under the conditions and , and let . A function is called -smooth if, for every , where and , the k-th order partial derivative exists and satisfies
Let denote the collection of all -smooth functions . When , the functions in as defined in Definition 2 satisfy the Hölder continuity condition.
Definition 3.
Let be a class of distributions on such that:
- 1.
- The features are identically distributed in ;
- 2.
- , where X and N are independent, and N follows a standard normal distribution;
- 3.
- .
In the Lemma 1, we derive a lower minimax rate of convergence for this class of distributions.
Lemma 1.
For the class , the sequence
is the minimax lower bound rate of convergence. Specifically, for some constant independent of C,
3.2. RXlearner Convergence Rate in General
To demonstrate the convergence level of the RXlearner, some preparatory work is also requisite. We give the following definitions.
Definition 4.
Let be a class of distributions on such that
- 1.
- The features are independent and identically distributed (i.i.d.) and uniformly distributed in ;
- 2.
- The observed outcomes are , where each is independent and follows a normal distribution with mean 0 and variance ;
- 3.
- and are independent;
- 4.
- The response function μ is Hölder continuous with parameters L and α.
Definition 5.
Let be a family of distributions on such that
- 1.
- ;
- 2.
- The features are i.i.d. and uniformly distributed in ;
- 3.
- There are n treated units such that ;
- 4.
- The observed outcomes are , where each is independent and follows a normal distribution with mean 0 and marginal variance ;
- 5.
- X, W, and are mutually independent;
- 6.
- The response functions and are Hölder continuous with parameters L and α.
Remark 5.
We consider that for a fixed n with , we have the distribution of given that we observe n treated units and control units. We denote this distribution by .
We note that under the are identical in distribution, but not independent.
Next, we will derive a lower bound on the best achievable convergence rate for . The following theorem establishes the minimax lower bound on the rate of convergence for any estimator under Hölder continuity.
Theorem 1
(Minimax Lower Bound). Let be an arbitrary estimator of τ, and let and be constants such that for all ,
then the convergence exponents must satisfy
We prove through Theorem 1 that the optimal rate of RXlearner is .
Proof of Theorem 1.
See Appendix A.1. □
3.3. The Convergence Rate of RXlearner When the Base Learner Is KNN
We now show that RXlearner attains the minimax lower bound by choosing KNN as the base learner.
Theorem 2.
Let , and assume , where the response functions and are Hölder continuous with parameters L and α, satisfying
where , , and .
Furthermore, let be the RXlearner constructed using the KNN base learner with the following specifications
- 1.
- ;
- 2.
- The first-stage base learner for the control group is a KNN estimator with ;
- 3.
- The second-stage base learner for the treated group is a KNN estimator with .
Then, attains the minimax optimal convergence rate stated in Theorem 1. Moreover, there exists a constant such that
Proof of Theorem 2.
See Appendix A.2. □
4. Simulation
In this section, we consider several settings for the data-generating process, where the generation of follows the approach of [17]. Here, p denotes the dimension of covariates:
In the following simulations, we set the training sample sizes to , with a fixed test set size of , and conduct independent replications for each setting. An exception is Simulation 5, which involves a highly imbalanced treatment assignment. Since a training size of results in an insufficient number of treated units, we consider only training sizes from 500 to 5000 in this case.
We use MSE to evaluate the performance of each estimator. With the number of simulation replication T, we have
where is the observed value of the test set in the t replicate, and is the estimator of in the tth replicate.
We present our simulation results in both tabular and graphical formats. In the tables, the best-performing method under each setting is highlighted in bold for ease of comparison.
4.1. Different Response Functions
To evaluate the performance of the proposed estimator and validate the effectiveness of the theoretical framework, we first examine the performance of various estimators under different rates of change in the response function.
Simulation 1: Hölder Continuous Response Function
Simulation 2: Lipschitz Continuous Response Function
Simulation 1 reflects the Hölder continuity structure (with exponent ), which aligns with the theoretical analysis in Section 3. We choose the form to introduce a moderate level of nonlinearity and limited smoothness, which is representative of real-world settings where the underlying structural functions are often non-differentiable or exhibit sharp curvature changes. Such Hölder-type structures have been observed in various domains, including economics and biology (e.g., Kleiber’s law and related metabolic scaling theory; see [23]). This choice also allows us to examine the sensitivity of different estimators to non-smoothness. To further assess robustness under alternative smoothness conditions, we include a Lipschitz continuous setting in Simulation 2.
For these two types of simulations, we consider , , and .
4.2. Cases in Special Situations
We next examine three specially designed simulation settings to evaluate the robustness and adaptability of different estimators under practically challenging conditions. These scenarios are intended to assess the performance of our proposed RXlearner when key identification assumptions are weakened. Specifically, Simulation 3 introduces confounding by violating the unconfoundedness assumption to evaluate the estimator’s robustness under model misspecification. Simulation 4 focuses on the null treatment effect case, where the true conditional treatment effect is uniformly zero across all covariate profiles, highlighting the ability of each method to avoid spurious heterogeneity. Simulation 5 investigates an extremely unbalanced treatment assignment scenario, in which the treated group constitutes a very small proportion of the sample. Given that the Xlearner is known to perform well in such settings, we aim to examine whether RXlearner can inherit or improve upon this advantage. The response function in Simulation 3 is constructed following the specification of [24].
Simulation 3: Confounding
We consider , and .
Simulation 4: No Treatment
We consider , , and .
Simulation 5: Extremely Unbalanced Data
To evaluate the tendency of each method to spuriously detect heterogeneity when the true treatment effect is absent, we compute the false positive rate (FPR) as the proportion of units with estimated CATE values exceeding a fixed threshold where is a pre-specified constant. These thresholds reflect varying levels of tolerance for deviations from zero. The FPR results are reported in Table 1, while the MSE results of Simulations 1–5 are presented in Table 2, Table 3 and Table 4.

Table 1.
False Positive Rates under Simulation 4 where the true CATE is zero.

Table 2.
Simulation results of Simulation 1.

Table 3.
Simulation results of Simulation 2.

Table 4.
Simulation results of Simulations 3–5.
4.3. Cases with Different Correlations and Noise
We further consider two scenarios: one concerning the impact of correlations among variables, and the other involving variations in the noise term.
Simulation 6: Different variable correlations and noise terms
We consider , , and . The corresponding MSE results are summarized in Table 5.

Table 5.
Simulation results of Simulation 6.
4.4. Summary of the Results
To visually compare the performances of different methods across all simulation settings, the corresponding results are presented below in Figure 1, Figure 2, Figure 3, Figure 4, Figure 5, Figure 6 and Figure 7.
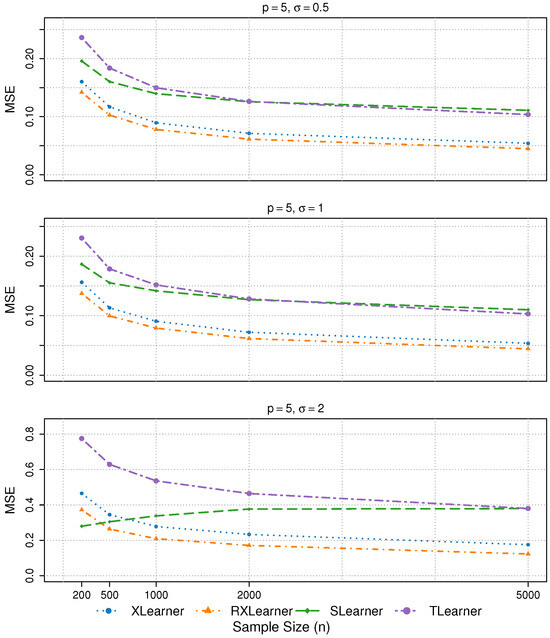
Figure 1.
The results of Simulation 1 are presented, with p = 5.
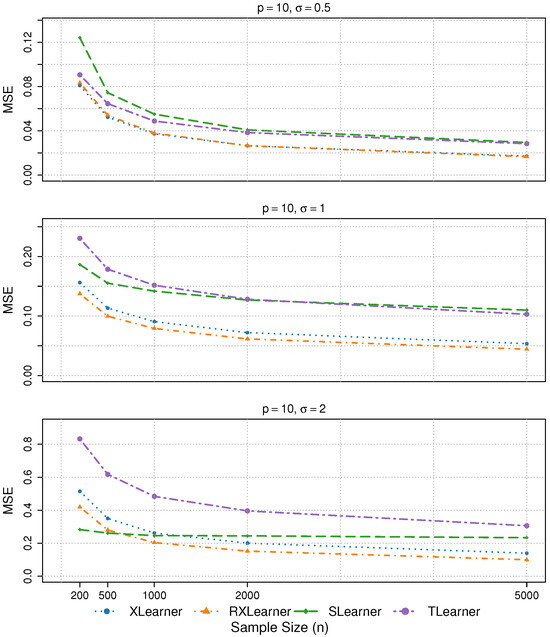
Figure 2.
The results of Simulation 1 are presented, with p = 10.
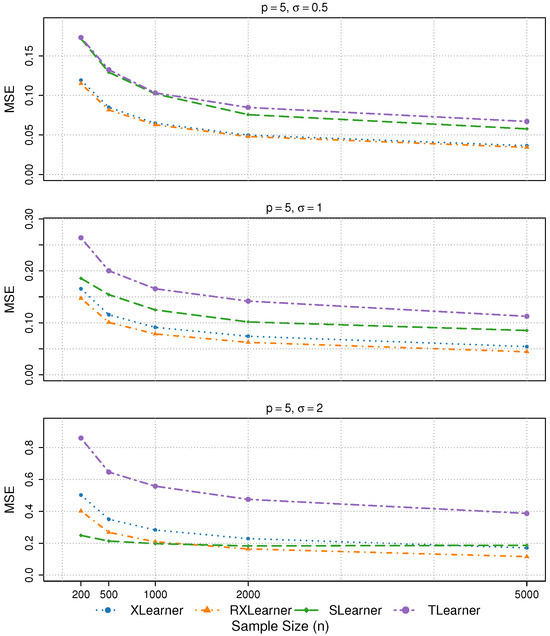
Figure 3.
The results of Simulation 2 are presented, with p = 5.
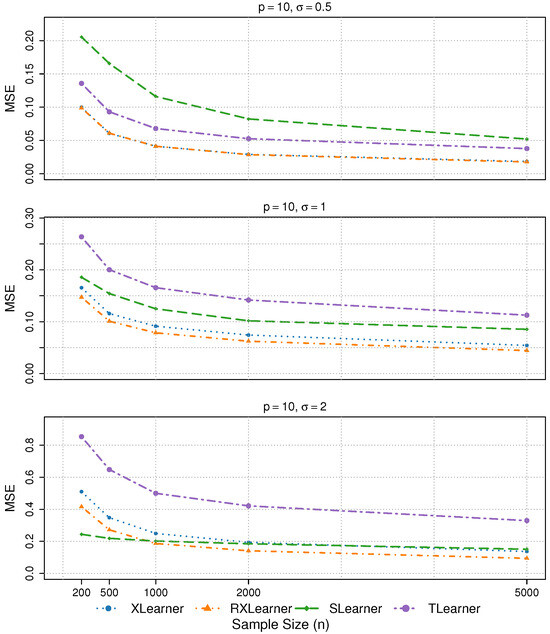
Figure 4.
The results of Simulation 2 are presented, with p = 10.

Figure 5.
Results of Simulations 3–5.
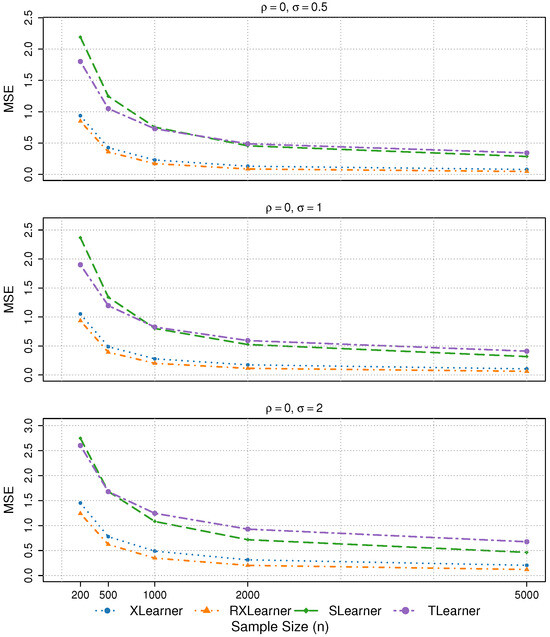
Figure 6.
The results of Simulation 6 are presented, with = 0.
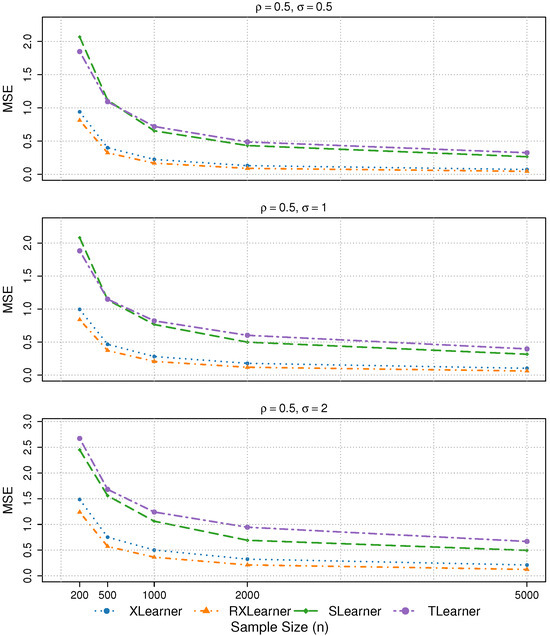
Figure 7.
The results of Simulation 6 are presented, with = 0.5.
Based on the simulations discussed above and the empirical results shown in the figures and tables, we summarize the key findings as follows:
- 1.
- In Simulations 1 and 2, both the Xlearner and RXlearner outperform the Slearner and Tlearner, with RXlearner achieving the best overall performance. Simulation results consistently demonstrate the superior performance of RXlearner across various noise levels (), covariate dimensions (), and sample sizes ( to 5000). As the sample size increases, all methods improve, but RXlearner benefits the most, achieving the lowest MSE in nearly all settings. Its adaptive weighting mechanism proves particularly effective under high-noise and small-sample scenarios, where fixed-weight methods like Xlearner tend to suffer. Notably, RXlearner maintains strong performance even in higher dimensions, highlighting its robustness and favorable convergence behavior compared to traditional meta-learners.
- 2.
- In Simulation 3, under confounded treatment assignment, the Tlearner exhibits the highest estimation error, followed by the Slearner. In contrast, the Xlearner and RXlearner maintain robust performance.
- 3.
- In Simulation 4, where the treatment effect is null, the Slearner performs the best, consistent with its underlying model assumptions. Furthermore, our quantitative evaluation of the false positive rate (FPR) under this setting reveals that the Slearner maintains the lowest FPR across varying thresholds and sample sizes, followed by RXlearner, while Xlearner and Tlearner tend to produce spurious heterogeneity more frequently. This underscores the importance of cautious model selection when the true effect is absent.
- 4.
- In Simulation 5, which involves extremely unbalanced treatment assignment, the RXlearner successfully inherits the strength of the Xlearner, while the Tlearner performs the worst due to its separate modeling for each treatment group.
- 5.
- In Simulation 6, the four learners exhibit similar performance across different levels of variable correlation. The estimation accuracy remains stable under noise levels and , with only a slight deterioration observed when .
In summary, the RXlearner consistently demonstrates the best performance across various scenarios. By enhancing the weighting mechanism of the Xlearner, RXlearner maintains equal or superior accuracy in nearly all settings.
5. Applications
To illustrate our proposed method, we analyze a large-scale Get-Out-the-Vote (GOTV) experiment, which is the same experiment used by [10] to test the Xlearner. This experiment investigates whether social pressure can be used to increase voter turnout in U.S. elections. The authors considered all voters who participated in the 2004 general election as registered voters, randomly selected a subset, and assigned them to either the treatment or control group. Households in the treatment group were sent a mailer with the message “DO YOUR CIVIC DUTY—VOTE!”, and the outcomes were observed during the 2006 primary election. We follow the method of [10] for simulation, but differ in the selection of covariates. While social pressure is typically transmitted through nearby neighbors, it is also influenced by the number of household members. Therefore, we include eight covariates, adding the number of household members as the eighth covariate, in contrast to [10], who used gender, age, and voting history in the 2000, 2002, and 2004 primary elections and the 2000 and 2002 general elections.
A common challenge in evaluating the accuracy of heterogeneous treatment effect estimators on real data is the lack of ground truth. To address this, we introduce synthetic treatment effects into the original dataset. We use the CATE estimates generated by the random forest-based Slearner, Tlearner, Xlearner and RXlearner as the ground truth. This allows us to assign potential outcomes to each sample and create a complete dataset. We can then verify whether different methods successfully recover the true effects and investigate whether the CATE estimates from different estimators significantly impact the results. We select 1000 and 10,000 samples from the full dataset as training sets, with the remaining data used as test sets. The proportion of treated and control groups in the selected samples matches the full dataset with . Figure 8 and Figure 9 present the results of this experiment. We find that the CATE estimates from different methods have a relatively minor impact on the overall model performance. However, in smaller samples , the Slearner outperforms the Tlearner, while the opposite is true for larger samples (n = 10,000).
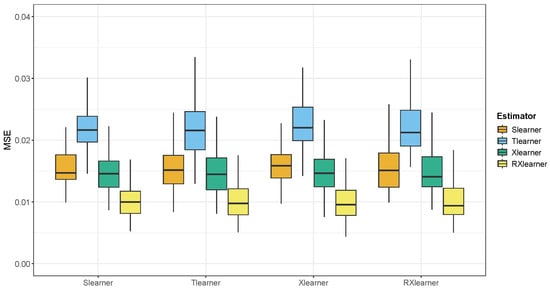
Figure 8.
The boxplots of MSE of estimated CATE for each method when the training sample size is , based on synthetic data generated using the fitted CATE from Slearner, Tlearner, Xlearner and RXlearner, respectively.
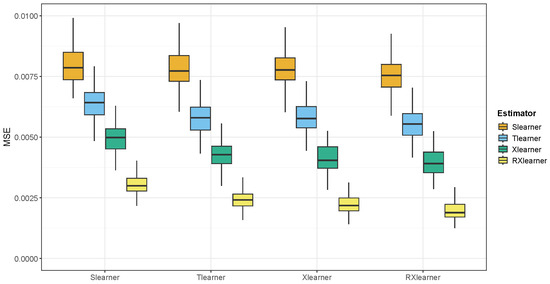
Figure 9.
The boxplots of MSE for each method when the training sample size is n = 10,000, based on synthetic data generated using the fitted CATE from Slearner, Tlearner, Xlearner and RXlearner, respectively.
Notably, we observe that RXlearner achieves a significantly lower MSE compared to other methods when . For the other meta-learners, the performance trends are consistent with those reported in [10], where the performance gaps between methods become more pronounced in low-sample regimes. We believe that in this case, there is still room for improvement in how Xlearner selects the weighting function , and the optimization of in RXlearner leads to a more effective combination of pseudo-responses, resulting in superior performance.
Overall, the RXlearner demonstrates significantly better performance compared to the other estimators.
6. Conclusions
This paper reviews CATE estimation methods under the meta-learner framework, including the Slearner, Tlearner, and Xlearner. Additionally, we propose a new algorithm, the RXlearner. The RXlearner retains the advantages of the Xlearner in handling unbalanced data while being more robust and effective. We conduct extensive simulation studies and real-data experiments, demonstrating that the RXlearner performs excellently in most scenarios. The error bounds of the estimator vary depending on the continuity of the response function. We establish error bounds for the case where the response function is Hölder continuous and show that using KNN as the base learner can achieve these bounds.
There are still many potential improvements for the RXlearner, such as incorporating ideas from DML by applying cross-fitting to (8) [25], or adopting a more direct approach by adding structure to (8), as explored in the works of [26,27]. Another promising direction is to incorporate regularization or complexity control into the second-stage optimization in order to further mitigate the risk of overfitting. We leave the extension of the RXlearner to future work.
Author Contributions
Methodology, Z.Z.; Software, C.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the Youth Academic Innovation Team Construction project of Capital University of Economics and Business, grant number QNTD202303.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Appendix A
Appendix A.1
Proof of Theorem 1.
Many ideas in this proof are inspired by [10]; however, our analysis is conducted under the weaker assumption of Hölder continuity. We proceed by contradiction.
Let , and suppose . Denote by the class of Hölder continuous functions . For any , define as the joint distribution where , , and . Then, Equation (8) implies the following:
Let denote the marginal distribution of the control group under . We then have
where the last inequality follows from Jensen’s inequality.
Now, let be a sequence such that . Define
and observe that
Hence, we can derive
which contradicts the minimax lower bound for nonparametric regression under Hölder continuity when . This completes the proof. □
Appendix A.2
To prove Theorem 2, we first introduce the following two auxiliary results.
Lemma A1.
Let , and suppose with . Let denote the nearest neighbor of x among . Then there exists a constant , independent of n, such that
Proof of Lemma A1.
Observe that
for some constant . Hence,
for some constant , which completes the proof. □
Lemma A2.
Let be the k-nearest neighbors (kNN) estimator with fixed , computed using only the control group, and let be the kNN estimator with fixed , computed using only the treated group. Under the assumptions in Theorem 2, we have
Proof of Lemma A2.
We provide the proof for the first bound; the argument for is analogous.
We decompose the mean squared error as follows
For the variance term , we have
For the squared bias term , using Hölder continuity of , we have
To bound this expression, let , and divide the dataset into disjoint subsets. Define to be the nearest neighbor to x in the j-th subset. Then, are independent and satisfy
By Jensen’s inequality
Integrating over the distribution of x (with as its density function) and applying Lemma A1, we obtain:
Combining the bounds for and completes the proof. □
Proof of Theorem 2.
We begin by decomposing the RXlearner estimator as
where the stage-one estimators are defined as
We evaluate the mean squared error as follows
From Lemma A2, we have
To bound , we decompose it into two terms
Term (A2) can be bounded by
using the fact that .
Term (A1) is bounded via Hölder continuity and Jensen’s inequality
Applying Lemma A1 to each of the above terms yields
Putting all pieces together, we obtain
for a constant . □
References
- Robins, J.M.; Mark, S.D.; Newey, W.K. Estimating Exposure Effects by Modelling the Expectation of Exposure Conditional on Confounders. Biometrics 1992, 48, 479–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, P.M. Root-N-Consistent Semiparametric Regression. Econometrica 1988, 56, 931–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravikumar, P.; Lafferty, J.; Liu, H.; Wasserman, L. Sparse Additive Models. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Stat. Methodol. 2009, 71, 1009–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robins, J.; Li, L.; Tchetgen, E.; Vaart, A. Higher Order Influence Functions and Minimax Estimation of Nonlinear Functionals. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2008, 2, 335–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvitz, D.G.; Thompson, D.J. A Generalization of Sampling Without Replacement from a Finite Universe. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1952, 47, 663–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, K.; Imbens, G.W.; Ridder, G. Efficient Estimation of Average Treatment Effects Using the Estimated Propensity Score. Econometrica 2003, 71, 1161–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robins, J.M.; Rotnitzky, A. Semiparametric Efficiency in Multivariate Regression Models with Missing Data. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1995, 90, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, K.; Ratkovic, M. Covariate Balancing Propensity Score. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Stat. Methodol. 2014, 76, 243–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Laan, M.J. Statistical Inference for Variable Importance. Int. J. Biostat. 2006, 2, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Künzel, S.R.; Sekhon, J.S.; Bickel, P.J.; Yu, B. Metalearners for Estimating Heterogeneous Treatment Effects Using Machine Learning. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 4156–4165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athey, S.; Imbens, G.W. Machine Learning Methods for Estimating Heterogeneous Causal Effects. Stat 2015, 1050, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Athey, S.; Imbens, G. Recursive Partitioning for Heterogeneous Causal Effects. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 7353–7360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, X.; Wager, S. Quasi-Oracle Estimation of Heterogeneous Treatment Effects. Biometrika 2021, 108, 299–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athey, S.; Tibshirani, J.; Wager, S. Generalized Random Forests. Ann. Stat. 2019, 47, 1148–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernozhukov, V.; Chetverikov, D.; Demirer, M.; Duflo, E.; Hansen, C.; Newey, W.; Robins, J. Double/Debiased Machine Learning for Treatment and Structural Parameters. Econom. J. 2018, 21, C1–C68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, E.H. Towards Optimal Doubly Robust Estimation of Heterogeneous Causal Effects. Electron. J. Stat. 2023, 17, 3008–3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wang, H.; Tu, W. Robust Estimation of Heterogeneous Treatment Effects Using Electronic Health Record Data. Stat. Med. 2021, 40, 2713–2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neyman, J. Sur les Applications de la Théorie des Probabilités aux Expériences Agricoles: Essai des Principes. Rocz. Nauk Rol. 1923, 10, 1–51. [Google Scholar]
- Rubin, D.B. Estimating Causal Effects of Treatments in Randomized and Nonrandomized Studies. J. Educ. Psychol. 1974, 66, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, D.R. The Interpretation of the Effects of Non-Additivity in the Latin Square. Biometrika 1958, 45, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, J.H. Greedy Function Approximation: A Gradient Boosting Machine. Ann. Stat. 2001, 29, 1189–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Györfi, L.; Kohler, M.; Krzyzak, A.; Walk, H. A Distribution-Free Theory of Nonparametric Regression; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- White, C.R.; Seymour, R.S. Mammalian Basal Metabolic Rate is Proportional to Body Mass2/3. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 4046–4049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, J.H. Multivariate Adaptive Regression Splines. Ann. Stat. 1991, 19, 1–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schick, A. On Asymptotically Efficient Estimation in Semiparametric Models. Ann. Stat. 1986, 14, 1139–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibshirani, R. Regression Shrinkage and Selection via the Lasso. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B (Methodol.) 1996, 58, 267–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, K.; Ratkovic, M. Estimating Treatment Effect Heterogeneity in Randomized Program Evaluation. Ann. Appl. Stat. 2013, 7, 443–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).