Abstract
Due to COVID-19, many countries implemented emergency plans, such as lockdown and school closures. This new situation has significantly affected families, namely, the involvement required to support children’s learning at home. The current study aimed to analyze Portuguese parents’ perceptions of their home-based parental involvement in their children’s learning during the lockdown and school closures in 2020 due to COVID-19. An online survey, using a closed-ended questionnaire, was employed. Variables included parents’ sociodemographic and COVID-19 related characteristics; students’ sociodemographic characteristics; distance learning context; parental involvement; and students’ autonomy. Data were collected from a sample of 21,333 parents with children from elementary school to secondary education, and statistical data analysis was performed using IBM SPSS Statistics 26. Findings revealed that Portuguese parents supported their children during the pandemic mainly through the monitoring of attention in classes and task realization. However, several variables appear to significantly determine parental involvement time, which is higher when students attend public schools, when they are less autonomous and younger, when parents’ level of education is lower, when the child is a boy (except in secondary education where gender is not relevant), and when the online school time is higher. Findings highlight the need for a significant investment of time from parents, particularly of primary school children, making it difficult to cohere work or telework with school activities. Implications for policies, schools, families are discussed in order to promote children’s learning and success.
1. Introduction
With the spread of COVID-19, countries implemented emergency plans to slow down and limit the virus’s transmission such as the closure of schools, either nationwide, regionally, or in a targeted way [1,2]. Some schools and universities were temporarily closed for face-to-face educational activities [3]. In Portugal, all schools were closed at a national level during the pandemic’s first wave between March and May 2020. In May 2020, some schools provided face-to-face educational activities for secondary students (the last two years of secondary school with final national exams). In September 2020, after the summer holidays, all schools and educational levels re-opened in the country. The interruption of school activities may have affected students, both academically and psychologically. The psychological effects of home schooling and social isolation on the mental health and wellbeing of students, teachers, and families in this pandemic phase are an issue to consider [3,4]. School learning interruption may have contributed to students’ significant academic losses, mostly for those students already at a previous disadvantage [4].
Specific educational measures were implemented to mitigate these learning losses, and different forms of online education and educational resources were mobilized to assure teaching and learning continuity. Consequently, during the pandemic, requirements for digital technology intensified significantly, despite the challenges that this intensification meant for teachers, families, and students to ensure the continuity of learning from home. As most schools and teachers were not used to online teaching, an immediate change was challenging [1,3,5]. Even with the availability of technological resources, both teachers’ qualifications and school practices for using digital devices effectively needed to improve [2]. Other difficulties were identified, such as students’ lack of access to technology and the internet, alternate modes for academic activity supplies such as additional tasks and excessive homework, and limited opportunities for more in-depth explanations from teachers when required [3,5]. Online schooling, therefore, resulted in higher levels of stress for students and families [3].
When schools were closed, companies and institutions had to introduce remote work, which led families into new routines and interaction patterns [6]. This new situation has significantly affected families’ work-family balance, parental support, and school-family modes of collaboration. Necessarily, this imposed changes that affected the entire community of Portuguese parents, students, and schools; and shaped parents’ role in their children’s education and learning during this time, in a form never previously experienced.
Study Objectives and Research Questions
Acknowledging the relevance of parental involvement and simultaneously considering the specific challenges for parents supporting their children at home during the lockdown, this moment in time may have created new challenges for home-based parental involvement, or intensified existing ones. Following Lu [7], the COVID-19 pandemic can open the way for improvements in education, such as the support and promotion of parental involvement. Hence, understanding parents’ perspectives is key during these unprecedented times.
The purpose of this paper is to report Portuguese parents’ perceptions of their home-based parental involvement in their children’s learning and school life during the lockdown and school closures (March to July 2020). The results reported in this paper are part of a broader study where other objectives were also considered (e.g., understanding the perception of parents regarding teachers or the school mission and understanding the main tools that were being used in home-based learning).
Our research questions, focused on the lockdown period, were:
RQ1: How did parents support student’s learning during the pandemic at each level of education? Is this involvement similar for private and public schools?
RQ2: How are parents’ involvement and students’ autonomy related per level of education?
RQ3: Are the determinants of parent’s involvement the same at each level of education?
2. Literature Review
2.1. Parental Involvement
Existing research has called attention to parental involvement’s relevant role in children’s schooling and success [8,9,10,11]. Parental involvement is a complex construct that has been defined in several ways (e.g., [9,10,12,13]). Recently, Antipkina and Ludlow [10] proposed a holistic concept of parental involvement: a “continuum of parenting behaviours ranging from those representing lower levels of involvement to those representing higher levels of involvement” (p. 856). In his meta-synthesis, Wilder [14] found the following parental involvement definitions used in different articles: parent-child communication about school; home-supervision; checking homework; homework assistance; education expectations and aspirations; attendance and participation in school activities; reading with children; communication with schools; parenting style; and parental attitudes toward education. Parental homework involvement, for instance, is a commonly found operationalization of parental involvement, which can be seen as a form of quantitative help (e.g., doing homework, helping with questions) or qualitative help (e.g., organizing the tasks, helping with the creation of a no-distraction environment, supporting the search for answers) [8].
Often in the literature, studies of parental involvement are focused on involvement at home (home-based involvement, meaning parents’ behavior towards school life and practicing activities related to school learning with their children at home, such as parents helping their children with homework, parents discussing schooling with their children, parental monitoring of school tasks and rule-setting), involvement with the school (school-based involvement related to parents’ various forms of participation in the schools’ activities), or acknowledge both places for the analysis of involvement behaviors and activities (home-school communication, such as parents interacting with teachers) [15,16]. Some studies also establish a difference between school-initiated parental involvement and parent-initiated involvement [17].
For several years now, the literature has emphasized the relevance of different variables in mediating the level of parental involvement, from parental/family characteristics to student variables, and school characteristics. Some examples of parental/family variables that are associated with parental involvement include [18]: sociodemographic factors (e.g., more education seems to relate to higher levels of involvement at school; being a father or mother has mixed results in the literature—some studies show non-significant influence of students’ level of education [19], others mention that mothers show higher levels of involvement [20]); parents’ perceptions of their child’s academic competency and need for their support (perception of lower learning autonomy usually increases the frequency of parents’ involvement); and parents’ time to support (having more work demands or family responsibilities, such as more children, is negatively associated with involvement). As for students’ characteristics, their age is one variable which influences parental involvement [21], mostly because it tends to decrease from primary to middle school and even more during secondary school, mostly related to parents’ perceptions that their involvement is less necessary/less welcomed by their adolescents and lower parental self-efficacy on the learning topics during high school; parental perceptions of their child’s needs/efficacy in different subjects mediates their involvement [18]. Schools’ actions to promote parental involvement are considered one of the main predictors of parental involvement: when parents consider that schools are promoting their involvement, parental involvement is generally higher [18] and there appears to be higher parental involvement in private schools then in public schools [22].
2.2. Parental Home-Based Involvement during the Pandemic
Considering the COVID-19 pandemic and the changes it brought to students’ learning, parental home-based involvement was particularly crucial. Parents’ role in supervising their children’s learning was reinforced, mostly through accompanying their children’s study and developing self-regulation strategies related to online learning [23].
Several barriers to distance and home-learning have been identified from parents’ perspectives [24,25,26,27], such as personal barriers, technical barriers, logistical barriers, and financial barriers. Personal barriers included low technical expertise to support their children in accessing online learning and the materials/tools used in this environment. Technical barriers were mainly related to the lack of adequate internet access or technology to follow learning activities properly. Logistical barriers were related to the perception that online learning did not meet pupils’ individual needs/learning rhythm, and parents also found that it was not an effective substitute for face-to-face learning process. As for financial barriers, these are highly related to the logistical ones (not being able to afford better technological tools and internet access).
Spinelli and colleagues [28] showed that more stressed parents were less involved in their children’s learning activities during the pandemic. Dong and colleagues [25] reported that the majority of parents felt the need to be present with their children during online learning activities at least once per day.
Even though hurdles did exist, parental involvement in children’s learning may also have increased during lockdown home learning [29]. The literature highlighted how parents of children of all ages, from primary to secondary pupils, felt closer to their children’s learning by acknowledging a more in-depth insight into their learning and that created opportunity to contribute more to their learning [30]. Additionally, most parents, mainly of younger pupils, found that the home-learning situation improved parent-teacher relationships, augmenting parents’ appreciation for teachers and this perception was shared by the teachers [30].
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Instruments and Measures
The current study employed an online survey using a closed-ended questionnaire developed by the researchers and administrated through Google Forms from the 1st of June 2020 to the 13th of July 2020, sent to a national sample of parents. Variables included in this study were organized into several groups: parents’ sociodemographic and COVID-19 related characteristics; students’ sociodemographic characteristics; distance learning context; parental involvement; and students’ autonomy. Variables are described in Table 1.

Table 1.
Description of the main variables of the study.
COVID-19 related characteristics were selected from the broader study referred to in the purpose of the study, and were aimed at describing some dimensions related to the pandemic situation: contact with COVID-19 in the family; adequate technologies; difficulties in accompanying the school tasks in the context of online learning.
It is important to mention that there are different instruments in the literature to collect data on parental involvement, including home-based parental involvement, school-based parental involvement, and home-school communication [14]. However, the circumstances of the data collection for this study demanded a more focused questionnaire, adjusted to the specific behaviors and activities of parental involvement during the COVID-19 lockdown of schools. For instance, activities relevant to “regular” parental involvement such as parents attending school meetings or going to museums with children were not possible during this time. For this reason, these specific items were excluded. Other items were included to explore home-based parental involvement, such as parents supporting children’s study behaviors or time spent on supporting children’s school activities. Monitoring child attention in the classes and school task realization is an example of an item that was prepared specifically for this pandemic time, since this kind of monitoring is usually done by teachers in the classroom. Ensuring that deadlines are accomplished turned out to be a relevant item in a time characterized by a significant number of assignments and school tasks with different and challenging deadlines to accomplish. Thus, the items developed for this study are derived from the literature review and also from the previous work of the authors in the field of educational intervention, with intense interaction between school contexts, teachers, students and parents (before COVID-19 and during pandemic). Since there was a lack of adequate instruments to measure parental engagement in pandemic times, we have chosen to use different forms of measuring the same variable so that we could have a more complete picture of the phenomenon and could inter-relate the variables.
Parental involvement was also operationalized through the amount of time dedicated by parents to supporting children’s school activities, as seen in the literature in this domain.
Student’s autonomy was operationalized through the perceived degree of children’s autonomy, on a 5-point Likert scale. However, we have chosen to measure the involvement of parents in task realization as an additional indicator of autonomy, since this variable relates to parents’ reported behavior and the other relates to a more abstract perception of autonomy.
3.2. Participants and Sample Sociodemographic Characteristics
Data were collected from a sample of 21,333 parents (89% mothers and 11% fathers), with children in various stages of schooling, from the 1st level of basic education (primary school) to secondary education. The first level of education includes children from 6 to 10 years old, the second level of education from 10 to 12 years old, the third level of education from 12 to 15 years old, and the secondary from 15 to 18 years old.
The distribution of responses through each level of schooling, the respective average age of students, and the % of girls is shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Distribution of students per level of education, average age, and gender.
This distribution implies that the 1st level of education is the best represented in our sample, with 50.4% of the parents having children in this level of education. 22.2% of parents had children in the 2nd level of education, 20% in the 3rd level of education, and 7.4% in the secondary. In total, 48.8% of the students were girls, 92.6% of the students were enrolled in public schools and 7.4% in private schools. The percentage of students in private education in our sample is lower than the actual percentage in the population (according to Pordata (www.pordata.pt, (accessed on 15 June 2021)), in 2019 the % of students attending private schools in Portugal was 12.5% in the 1st, 2nd and 3rd levels of education, and 21.2% in the secondary).
In total, 32.7% of the sampled parents reported they have a bachelor’s degree and 13.2% reported having a level of education higher than a bachelor’s degree. This implies that our sample is constituted of highly educated parents. According to Pordata (www.pordata.pt, (accessed on 15 June 2021)), the proportion of people between 15 and 64 years of age that have a bachelor’s or higher education level is 27% of the Portuguese population. In our case, in spite of the different range of ages, that percentage was 47.1%, clearly above population values. This implies that our sample, despite its size, is not completely representative of the education level of parents in Portugal (however, for other variables the sampled percentages are similar to population percentages).
In total, 89.6% of the parents were between 31 and 50 years old and they were distributed throughout the country in a representative way (e.g., 30% of parents were from the central region, 25% from the north, 10% from the Lisbon metropolitan area, 5% were from Madeira, and 5% were from Azores). A total of 43.5% of parents have one child, 47.5% have two children, and 9% have three or more children. Most of the confined parents did not have any contact with COVID-19 in their families (99.1% reported 0 cases). This is explained by the fact that the first wave in Portugal was quickly contained, and the pandemic was clearly under control, contrary to what happened in the second wave that started around October 2020.
A total of 67.6% of parents reported having technologies that allow all members of the household to work simultaneously. When we cross this variable with the parents’ educational level, we realize that this percentage was higher in families where the parents have a higher level of education. This implies that the national reality regarding the existence of technologies may be over-estimated in this sample.
3.3. Procedures
Responses from parents were collected from the 1st of June 2020 to the 13th of July 2020 through a Google Forms questionnaire. In cases with multiple children, parents were asked to focus on one child only.
Questionnaires were administered through contact with diverse schools across the country and parents’ associations. Respondents were recruited through an email list of Leya Education (a group of the editorial company Leya that has very close contacts with school stakeholders, in particular CONFAP—the National Confederation of Parents’ Associations—had an important role in helping spreading the questionnaire via email through registered parents all over the country). Respondents had no incentive for their participation.
The current study followed the recommendations from the ethics committee of the Universidade Católica Portuguesa. All parents participated voluntarily and gave informed consent to participate in the research, in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. Participants were informed about the aims of the research, and confidentiality and anonymity were assured.
3.4. Data Analysis
The analysis of the data was performed using IBM SPSS Statistics 26. We employed various statistical techniques from descriptive analysis to inferential statistics. Various tests were performed on the data and their selection related to the types of data at hand. For the overall analysis of the full list of determinants of parental involvement, an ordinal regression analysis was chosen. The need for an ordinal regression was related to the nature of the dependent variable—time of involvement—that is a categorical variable, since we have categories for involvement time but not the exact amount of time spent by parents in supporting their children. Note that for ease of analysis and presentation of results, in some parts of this paper we compute averages for this variable; therefore, treating it as continuous. We will signal throughout the paper where and how this practice was undertaken.
4. Results
4.1. Descriptive Data
Some descriptive data for the full sample of participants are shown next.
4.1.1. Parental Involvement
Regarding the predominant form of parental involvement, the possible answers and the respective percentages in each category are shown in Table 3, where 3.4% of parents indicated that they are unable to support their children, 36.5% monitored child attention in the classes and school task realization and 23.8% provided support in the realization of school tasks.

Table 3.
Descriptive data for predominant form of parental involvement.
Concerning parental involvement time, 66.9% of parents spent 1 or more hours per day supporting their student’s learning (Table 4).

Table 4.
Descriptive data for parental involvement time.
If we convert this variable to continuous (considering the value 0.25 for less than 30 min and the value 3 for more than 2 h) we can observe that on average parents spent 1.5 h per day supporting their child’s school activities. The scale used asks for the actual time in some alternatives (“1 h”, “2 h”, etc.) but also asks for time intervals in others (“Less than 30 min”, “More than 2 h”). In one case or the other, parents’ answers were just an approximation of the exact time that is generally unknown, and therefore the approximation to a continuous variable provides an alternative way of analysis.
It is interesting to verify that the time of involvement seems to be directly related to the form of involvement (Table 5). In fact, the forms of parental involvement that represent more temporal intensity are the support in task realization, and the monitoring of child attention in the classes and school tasks realization. When the child is seen as autonomous or the parent cannot help, the average time of involvement is less than one hour.

Table 5.
Relationship between parental involvement form and parental involvement time.
A qui-square test between the two variables (forms of parental involvement and the time of involvement, considered as categorical) results in a statistically significant relationship between the two variables (Pearson qui-square of 9084.95 and p-value of 0.000) and a phi value of 0.635.
Regarding parental involvement difficulties during the pandemic (Table 6), the predominant difficulty was conciliation between supporting the student’s school activities and telework (24.4%). Tiredness and mental disposition was the second most chosen option, with 20.3% of parents providing this answer.

Table 6.
Descriptive data for parental involvement difficulties.
4.1.2. Distance Learning Context
A total of 89.1% of parents reported that their children took online classes, and in the majority of cases these classes were for all subjects (only in 15% of the cases was some absence of classes reported, mainly in subjects related to arts or physical activity). This percentage was around 88% in the 1st level of education, but it was 91% in secondary. So, in general, distance learning was a reality for a great percentage of Portuguese students in this sample. Regarding the time that children spent on online classes (see Table 7), most students spent between 2 and 6 h per day in online classes.

Table 7.
Time of online classes and parental involvement time.
Note that the proportion of public schools in each interval of online classes’ time decreased, meaning that in general students from private schools tended to have a higher number of online classes.
4.1.3. Student’s Autonomy
Regarding the perception of the child’s autonomy, 36.9% of the parents reported that their children were very autonomous or totally autonomous (Table 8).

Table 8.
Descriptive data for the perception of the child’s autonomy.
Concerning school tasks and how the student usually performed them, in 41.4% of the cases the student frequently needed the presence of an adult (Table 9).

Table 9.
Descriptive data for how the child performs school tasks.
4.2. Inferential analysis
RQ1: How did parents support student’s learning during the pandemic in each level of education? Is this involvement similar for private and public schools?
As seen in the previous section, the most prevalent form of parents’ involvement in the full sample was monitoring the child’s attention in the classes and school tasks realization, followed by supporting task realization. The involvement of the parents is, however, largely dependent on the age of the children and on the level of education. Dividing the involvement variable per level of education, we have the following data (Table 10).

Table 10.
Level of education of studies and involvement form.
In the first level of education the prevalent form is the monitoring of attention in classes and tasks realization, but the support in the actual realization of tasks was also very prevalent. In the second and third levels of education the prevalent forms were the monitoring of attention in classes and tasks realization, and ensuring deadlines were accomplished, and in secondary education students were mostly autonomous.
The average time of parental involvement decreased and the average time of online classes increased from the first level of education to the secondary, as can be seen in the last two columns of Table 10. In these columns, we used continuous scales for parental involvement time, as explained before, and also for the time of online classes (obtained by using the value of the center of the intervals in Table 7 as an estimate of the online class time to convert it into a continuous scale). In Figure 1 we show the values in the last two columns of Table 10 disaggregated per school type.
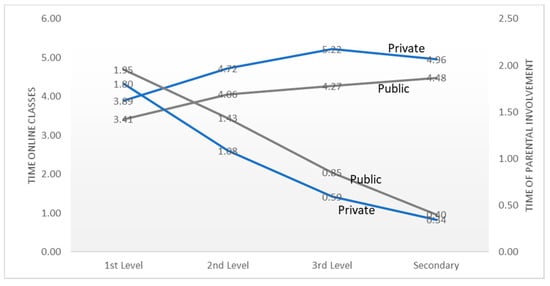
Figure 1.
Time of online classes and parental involvement time per level and type of school.
The involvement of the parents and the online classes’ time is also related to the type of school attended, with public schools’ parents spending more time supporting their children than private schools’ parents, and with private schools providing more online classes time in all levels of education. The higher time spent in online classes in private schools may be an explanatory factor for the lower parental involvement in this type of school. The differences observed in the graph (for the two time variables) are statistically significant as concluded from an ANOVA test for two factors.
In conclusion, we can say that Portuguese parents supported their children during the pandemic mainly through the monitoring of attention in classes and task realization, except for the secondary schools where students are predominantly autonomous. In the first level of education, parents’ involvement frequently implied their support in the actual realization of the school tasks; whereas in the second and third levels, parents tended to pay more attention to the accomplishment of deadlines. The parents’ involvement time is higher when students attend public schools and in public schools the time of online classes is on average lower than in private schools.
RQ2: How are parents’ involvement and students’ autonomy related per level of education? Are involvement and autonomy similar for private and public schools?
This research question is the first step towards deciding which of the two variables that capture the autonomy of the students is better for the analysis.
First, it is important to note that there is a certain mismatch between the two questions on autonomy (the perception of student’s autonomy and how students perform tasks). Figure 2 shows the percentage of students in each category.
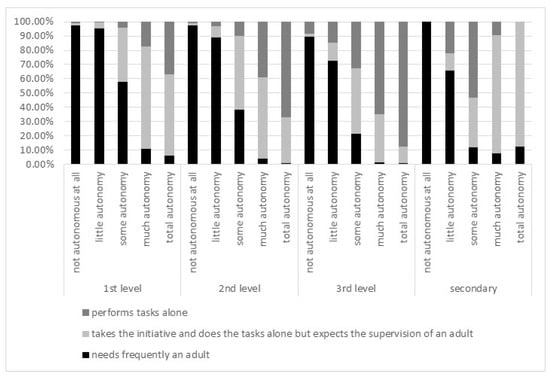
Figure 2.
Percentage of students in each category when cross comparing the two autonomy variables.
If the variables ‘student autonomy’ and ‘how students perform tasks’ were in full agreement, one would expect, within each level of education, a reduction in the black columns’ (frequently needs an adult) percentages when the perception of autonomy increases. On the other hand, one would expect the dark grey column (performs tasks alone) to be the maximum for the level of perception of ’total autonomy’. While the former indeed happens, the latter does not happen for all levels of education. Indeed, secondary education students perceived as totally autonomous by their parents are also perceived as still needing the supervision of an adult. Only in the third level of education does the dark grey column dominate the total autonomy category.
There is therefore some misconception between the perception of autonomy and the way tasks are performed. Given this misconception we have chosen to use the involvement of parents in the task realization as an indicator of autonomy, since this variable relates to parents’ actual behavior and the other relates to a more subjective perception of autonomy.
Using the variable of how school tasks are performed as a surrogate for the autonomy of the children, and crossing this variable with the parents’ involvement time, we have the following (Table 11).

Table 11.
Autonomy versus parents’ involvement time.
In the first level of education, parents spend more than 2.17 h on average supporting their children when they are less autonomous. In the secondary, less autonomous students require on average 1.22 h per day of parents’ time, while more autonomous students require just 0.29 h.
Figure 3 shows the above values taking into account the type of school.
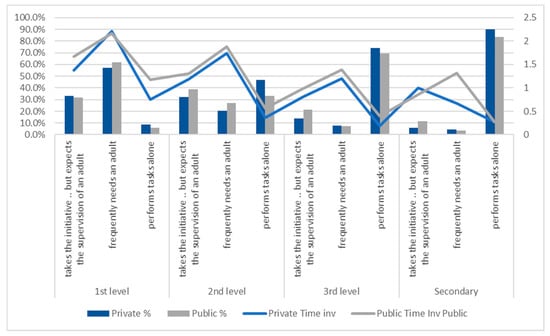
Figure 3.
Autonomy and involvement time per level of education and per type of school.
In the columns, we see the percentage of students in each of the groups of autonomy, in each level of education, and each school type. Interestingly, more autonomous students dominate in private schools in all levels of education. In terms of parental involvement time, it is always larger in public than in private schools and decreasing with the degree of autonomy of the student, as expected. Only in secondary education does it appear that more autonomous students from private schools require a larger involvement time from their parents, but this finding should not be highlighted since the sample size for private schools in secondary education is small. Note that the level of education, the type of school and the student autonomy are all considered statistically significant in explaining parental involvement (a generalized linear model showed the significance of all factors).
In conclusion, we can say that the autonomy of the student is related to parents’ involvement, with more autonomous students requiring a lower amount of parental involvement time—at each level of education we found that more autonomous students required at least one hour less of parental involvement, on average. From the first level of education to secondary, the expected reduction in parental involvement time in all classes of autonomy is less than 1 h, meaning that although significantly different, the time of parental involvement is not, in absolute terms, much reduced over all the levels of education.
Regarding public and private schools, it appears clear that parents of students from private schools report a higher autonomy for their children, and therefore the time of involvement is generally higher for public school students in all classes of autonomy (with the exception of the secondary schools). This may be related to the amount of online schooling, which tended to be higher in private schools.
RQ3: Are the determinants of parent’s involvement the same in each level of education?
Taking the variable of parents’ involvement time as the proxy variable for parents’ involvement, we ran a regression model to explain involvement time through the set of variables discussed above, including the socio-demographic characteristics of students and their parents. An ordinal regression was performed for each level of education given the previous findings that the level of education of studies is a determinant in explaining the time of parental involvement, and therefore the determinants of this involvement may differ per level.
The results from Table 12 indicate that many variables are consistently relevant in explaining parents’ involvement, in all levels of education. The main conclusions that can be inferred from the analysis of Table 12 are as follows.

Table 12.
Coefficients for the Ordinal Regression per level of education (non-significant values in bold).
Parents involvement time tended to increase when the parent is the mother and all else is constant; it tended to decrease when the level of education of the parent increased (meaning that more educated parents on average have less time of involvement with their children); students attending public schools tended to require more involvement time from their parents than students from private schools; girls tended to require less involvement time than boys; the number of children in the household has a negative effect on the individual involvement time with a specific child; children who are less autonomous (frequently need an adult or can take their own initiative but then wait for supervision) require more involvement time from parents than autonomous children; and the involvement time varies positively with school activities’ time. That is, with all else constant, parental involvement time was always lower for students with fewer than 6 h of school activities than for students with more than 6 h of school activities (the base case for the nominal variable school time). This seems to suggest that the more school time, the more involvement is required from parents (probably in helping their children with homework and online classes follow up). Note that this happens within each level of education, although as seen previously, as the level of education increased the mean school time increased and mean parental involvement time decreased.
Regarding factors that are only relevant to some level of education, it is interesting to note that the number of children is a relevant factor only for parents whose children are in the first level of education, since after that level of education this variable loses its statistical significance. The gender of the parent is only relevant in the first and second levels, suggesting that in these levels of education respondent women tended to report more involvement time than men, but afterwards the difference between genders is not statistically significant (note however, that the small number of male respondents may bias our results). In secondary education, probably due to a reduced sample size, many variables lose their statistically significant status. The type of school is not a factor in determining parents’ involvement in secondary education, nor the gender of the student. In addition, there is no difference in parents’ involvement when school online time lies between 4 and 6 h or more than 6 h.
5. Discussion
As mentioned, this study focused on parental involvement during the first Portuguese confinement related to the pandemic which enforced schools’ closure. Considering the changes that this situation brought to students’ learning, parental home-based involvement was particularly significant, with parents’ supervision of schoolwork being reinforced [23] and requested by online teaching.
In general, for the sample analyzed, we can say that online classes were a reality for most students since more than 92% of the students attended more than 2 h of online classes daily. Likewise, parental involvement was also generalized (and unavoidable) since in about 80% of the cases, parents reported being involved in supporting their children’s study for at least 30 min per day. Although it may be true that parents devoted daily time to support children, they also reported specific difficulties, the most prevalent of which was the conciliation of school support with telework, and the second of which was the tiredness and mental disposition that affected all in quarantine. Despite the significant number of variables that can be related to parental involvement (e.g., students, family, and school variables) [18,19,20], it is of note that in this sample, parental/family variables related to parents’ time and parent’s health gained relevance, which may be due to the specific nature of the pandemic and the imposed changes.
The research questions posed in this paper allowed us to understand the prevalent form of support that Portuguese parents used, which is the monitoring of attention in classes and task realization in all levels of education except for secondary, where students are predominantly autonomous. When analyzing the parents’ involvement time, we found that it is, as expected, decreasing with the level of education, but we also found significant differences between public and private schools, with parents of students from public schools spending more time on supporting the learning of their children. It is important to realize that, in Portugal, private schools have had more synchronous activities during schools’ closure than public schools, for all levels of education, which may contribute to a reduction in the need of attention from parents of children in private schools. Even at a distance, teachers at private schools have supported and guided children’s study more. As expected, we also found that the autonomy of children clearly reduced the involvement time of parents [18], but differences in involvement time between the first level of education and the secondary are generally lower than 1 h (for all classes of autonomy).
Finally, we attempted to analyze the determinants of parents’ involvement time in a model with all the variables and performed this per level of education. Interestingly some determinants varied per level of education. For example, the number of other children at home determines the time parents spend with their children only when they attend the first level of education, which is the level where there is less autonomy. As in other studies, e.g., [18], children’s age is one variable which influences parental involvement, as it tends to decrease from primary to middle school and even more during secondary school, mostly related to parents’ perceptions that their involvement is less necessary. The gender of the parent that answered the questionnaire also loses significance when the level of education increases, as also reported in other studies [19,20]. Female parents show a higher time of parental involvement than male parents in the first and second levels, but then that factor is no longer significant. Most importantly, several variables appear to significantly determine parental involvement time, which is higher when students attend public schools, when they are less autonomous and younger, when parents level of education is lower, when the child is a boy (except during secondary education where gender is not relevant), and when the online school time was higher. In part, this is surprising, considering previous research where parental involvement was higher when students attend private schools and parents’ level of education is higher [18,22]. Different results may be explained by the specific situation of schools’ closure during pandemic, the diversity of educational measures defined by different schools, and the related consequences on parents’ behaviors.
These findings are useful for supporting governmental decisions owing to the pandemic prevalence, which required many government measures in 2020 that are still required in the current 2021 year. In case of a new period of online classes, it is important to know that this implies a significant investment of time for parents, particularly for parents with lower levels of education, for whom it is difficult to conciliate work or telework with school activities. This is particularly relevant for families with many children (where the lower involvement of parents may put learning at risk) and/or students attending public schools who require more time from their parents. Governmental measures should pay special attention to large families with young children where learning may indeed become compromised.
As we have seen, COVID-19 brought significant challenges to families, to students, and to teachers, including school-stress; difficulties in managing time and personal resources; and lack of technical, logistical, and financial conditions.
Opportunities could also be identified, such as the greater presence and involvement of parents in their children’s school life. New forms of parental involvement have emerged during the pandemic that can be addressed as useful methods of involvement even after pandemic, particularly referring to home-based parental involvement and home-school communication. So, we can ask: what can be harnessed for the post-pandemic era? What new forms of parental involvement may remain after the pandemic? We suggest moments of sharing and deep reflection about this question in schools with all stakeholders, identifying critical aspects that should be maintained and lessons learned, both during and after the pandemic: How to improve students’ learning and autonomy? How to involve parents and promote their development? How to involve teachers in attitudes and behaviors that promote a true partnership between school and family?
Interventions to promote parental involvement should be designed considering multiple factors, as we could see in this study. Therefore, multilevel interventions are welcome, involving school leaders, teachers, parents, and students in the promotion of students’ learning and success; in the analysis of the needs of parents, teachers and students; and thus the development of action plans. Another relevant question refers to the direction of the relationship between parental involvement and students’ autonomy. Do more involved parents make their children less autonomous? Do less autonomous children require more involved parents? These are questions that could be analyzed in the family and school contexts, trying to figure out the best options for students’ learning and development.
Some limitations of the study should be acknowledged. Data were collected through an on-line questionnaire, which may have contributed to the difficulty of access for parents with lower educational qualifications or lack of information technology resources. Additionally, self-reported measures of parents’ perceptions were used. We also point out the lack of comparison with similar studies during the lockdown. Future studies might analyze the adaptations of other types of parental involvement in times of a pandemic, namely, school-initiated parental involvement or home-school communication. Taking into account the context of online and distance learning, it would be useful to have a specific question measuring parents’ digital and information literacy skills, since it could influence parental support of their children.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization and methodology, all authors; formal analysis, M.C.A.e.S.; investigation, M.L.V.; writing–original draft, M.C.A.e.S., R.S.C., M.C. and L.M.R.; writing–review & editing, L.M.R. and M.C.A.e.S.; project administration, M.C.A.e.S.; funding acquisition, L.M.R. and M.C.A.e.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki, and according to the Catholic University Ethical Code.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- OECD. Education Responses to Covid-19: Embracing Digital Learning and Online Collaboration; OECD: Paris, France, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- UNESCO. Distance learning strategies in response to COVID-19 school closures. UNESCO COVID-19 Educ. Response 2020, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Wajdi, M.B.N.; Kuswandi, I.; Faruq, U.; Zulhijra, Z.; Khairudin, K.; Khoiriyah, K. Education Policy Overcome Coronavirus, A Study of Indonesians. EDUTEC J. Educ. Technol. 2020, 3, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimers, F.; Schleicher, A. A Framework to Guide an Education Response to the COVID-19 Pandemic of 2020; OECD: Paris, France, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho, M.; Azevedo, H.; Cruz, J.; Fonseca, H. Inclusive education on pandemic times: From challenges to changes according to teachers’ perceptions. In Proceedings of the ICERI2020: 13th Annual International Conference of Education, Research and Innovation, Seville, Spain, 9–11 November 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Markowska-Manista, U.; Zakrzewska-Olędzka, D. Family with children in times of pandemic—what, where, how? Dilemmas of adult-imposed prohibitions and orders. Soc. Regist. 2020, 4, 89–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S. School + Family Community Learning Model of PE Course under COVID-19 Epidemic Situation. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Learn. 2020, 15, 218–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dettemers, S.; Yotyodying, S.; Jonkmann, K. Antecedents and Outcomes of Parental Homework Involvement: How Do Family-School Partnerships Affect Parental Homework Involvement and Student Outcomes? Front. Psychol. 2019, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gugiu, P.C.; Gugiu, M.R.; Barnes, M.; Gimbert, B.; Sanders, M. The Development and Validation of the Parental Involvement Survey in their Children’s Elementary Studies (PISCES). J. Child Fam. Stud. 2019, 28, 627–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antipkina, I.; Ludlow, L.H. Parental Involvement as a Holistic Concept Using Rasch/Guttman Scenario Scales. J. Psychoeduc. Assess. 2020, 38, 846–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punter, R.A.; Glas, C.A.W.; Meelissen, M.R.M. Psychometric Framework for Modeling Parental Involvement and Reading Literacy, 1st ed.; Springer One: Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 5–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoover-Dempsey, K.V.; Walker, J.M.T.; Sandler, H.M.; Whetsel, D.; Green, C.L.; Wilkins, A.S.; Closson, K. Why Do Parents Become Involved? Research Findings and Implications. Elem. Sch. J. 2005, 106, 105–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoover-Dempsey, K.V.; Sandler, H.M. Why do parents become involved in their children’s education? Rev. Educ. Res. 1997, 67, 3–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, J.L. School and Family Partnerships. Report No. 6; Center on Families, Communities, Schools & Childrens’ Learning: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1992; pp. 3–25. Available online: https://eric.ed.gov/?id=ED343715 (accessed on 15 June 2021).
- Wilder, S. Effects of parental involvement on academic achievement: A meta-synthesis. Educ. Rev. 2014, 66, 377–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, J.; Denessen, J.; Brus-Laeven, M. Socio-economic background, parental involvement and teacher perceptions of these in relation to pupil achievement. Educ. Stud. 2007, 33, 177–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driessen, G.; Smit, F.; Sleegers, P. Parental Involvement and Educational Achievement. Br. Educ. Res. J. 2005, 31, 509–532. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/30032581 (accessed on 15 June 2021). [CrossRef]
- Eccles, J.S.; Harold, R.D. Family involvement in children’s and adolescents’ schooling. In Family-School Links: How Do They Affect Educational Outcomes? Booth, A., Dunn, J.F., Eds.; Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1996; pp. 3–34. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.W.; Hill, N.E. Including fathers in the picture: A meta-analysis of parental involvement and students’ academic achievement. J. Educ. Psychol. 2015, 107, 919–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleischmann, F.; Haas, A. Explaining parents’ school involvement: The role of ethnicity and gender in the Netherlands. J. Educ. Res. 2016, 109, 554–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, K.D.; Lambert, M.C.; January, S.A.; D’Angelo, J.F. Confirmatory factor analyses comparing parental involvement frameworks with secondary students. Psychol. Sch. 2017, 54, 947–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Institute for Research. Available online: https://www.air.org/resource/public-vs-private-parental-involvement-k-12-education (accessed on 1 March 2021).
- Kong, Q. Practical Exploration of Home Study Guidance for Students during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Case Study of Hangzhou Liuxia Elementary School in Zhejiang Province, China. Sci. Insigt Edu. Front. 2020, 5, 557–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuhammad, S. Barriers to distance learning during the COVID-19 outbreak: A qualitative review from parents’ perspective. Heliyon 2020, 6, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donga, C.; Caob, S.; Lia, H. Young children’s online learning during COVID-19 pandemic: Chinese parents’ beliefs and attitudes. Child. Youth Serv. Rev. 2020, 118, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhamani, S.; Makhdoom, A.Z.; Bharuchi, V.; Ali, N.; Kaleem, S.; Ahmed, D. Home Learning in Times of COVID: Experiences of Parents. J. Educ. Educ. Dev. 2020, 7, 09–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbe, A.; Ogurlu, U.; Logan, N.; Cook, P. COVID-19 and Remote Learning: Experiences of Parents with Children during the Pandemic. Am. J. Qual. Res. 2020, 4, 45–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinelli, M.; Lionetti, F.; Setti, A.; Fasolo, M. Parenting Stress during the COVID-19 Outbreak: Socioeconomic and Environmental Risk Factors and Implications for Children Emotion Regulation. Fam. Process 2020, 2–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bubb, S.; Jones, M. Learning from the COVID-19 home-schooling experience: Listening to pupils, parents/carers and teachers. Improv. Sch. 2020, 23, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozkurt, A.; Jung, I.; Xiao, J.; Vladimirschi, V.; Schuwer, R.; Egorov, G.; Lambert, S.R.; Al-Freih, M.; Pete, J.; Olcott, D., Jr.; et al. A global outlook to the interruption of education due to COVID-19 pandemic: Navigating in a time of uncertainty and crisis. Asian J. Distance Educ. 2020, 15, 1–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).