Abstract
Dissolved Gas Analysis (DGA) is a diagnostic strategy that monitors oil-immersed transformers by correlating their health status with various insulation degradation by-products, where the Health Index (HI) offers a unified metric for asset evaluation. Existing studies frequently emphasize classification accuracy or single-model regression, overlooking interpretability, feature reduction, and systematic benchmarking. This paper introduces a feature-enhanced multi-experimental methodology for HI prediction incorporating SHapley Additive exPlanations (SHAP) in a dual role—as both an interpretability and a feature selection tool. Models from four algorithmic families (linear, kernel/tree-based, boosting, and hybrid ensembles) were systematically benchmarked using a publicly available dataset. Results demonstrate that the proposed LightGBM–CatBoost hybrid ensemble, enhanced by SHAP-guided feature pruning, achieves superior predictive accuracy while reducing model complexity and improving transparency. Unlike prior works carried out using the same dataset, the proposed framework not only provides a balanced approach that combines interpretability and reduced complexity, but also surpasses previous regression-based approaches, reducing MAE and RMSE by 4.93% and 2.31%, respectively, and enhancing HI predictive accuracy by 1.45%.
1. Introduction
The global energy landscape is experiencing significant transitions, driven by the simultaneous demand for sustainable development and grid modernization [1]. With the growing integration of electrified transportation and penetration of renewables [2,3,4,5] new demands are placed on the power grids with new dynamics. The transition toward a low-carbon future brings new challenges, particularly in maintaining grid stability and power quality, while also creating a pressing need for intelligent energy management systems to ensure effective asset monitoring [6]. Among the most affected components in electrical power systems are power transformers, which are regarded as critical nodes in transmission and distribution networks [7,8]. Factors such as thermal and [1] mechanical stresses, overloading, over-voltage, and short circuits [9,10] expedite their aging mechanisms by releasing certain by-products in their oil. Consequently, intelligent energy management strategies and advanced asset monitoring are essential for the reliable, economical, and efficient operation of power transformers within today’s modern grids [11].
In oil-immersed transformers, dissolved gas analysis (DGA) is a predominant technique that monitors the internal health of these assets via analyzing specific concentrations of combustible gases in their oil caused by the degradation of oil–paper insulation under electrical and thermal stresses [12,13]. Despite the existence of several standards-based approaches, such as IEC Ratios and Duval Triangle [14,15], these techniques often rely on fixed thresholds or expert judgment, which limit their accuracy and scalability [16]. Consequently, the concept of the Health Index (HI) was introduced to provide a more quantified assessment of transformers’ health through a unified, scalable metric that aids in asset maintenance prioritization and to overcome the shortcomings of existing methods.
HI models typically incorporate lab tests from insulation system testing, including the concentration of key gases such as hydrogen (H2), methane (CH4), ethylene (C2H4), acetylene (C2H2), ethane (C2H6), and carbon dioxide (CO2). A weighted score assessment is performed, wherein each parameter is first compared against a standardized scoring table and subsequently assigned a weight according to expert judgments of its performance [17,18]. After that, individual scores are combined into a single index that reveals the overall health condition of the transformer [19]. Table 1 shows the HI classification criteria through mapping the health status of power transformers to their expected remaining years of service according to [20,21]. Although this technique provides a systematic framework, the HI is fundamentally derived as a linear combination of different scores and weighted measurement data. As a result, its practical application may be limited due to the difficulty of capturing nonlinear interactions among all operating conditions parameters.

Table 1.
Transformer health index [20,21].
To address these limitations and with the growing complexity of modern systems, Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) techniques have begun to emerge across diverse domains like vehicle navigation systems [22,23], robotics [24,25], and energy management [26,27,28,29], demonstrating superior capabilities in solving complex nonlinear patterns. This provides a strong precedent for their application in diagnosing similarly intricate signs of transformer faults. Accordingly, AI and ML models have been widely adopted in the field, which have consistently demonstrated superior performance in interpreting DGA data and enhancing HI evaluation [30,31]. AI’s initial efforts focused mainly on models such as Support Vector Regression (SVR), Artificial Neural Networks (ANN), and Fuzzy Logic systems [32,33], followed by subsequent advancements in ensemble learning [34], deep learning [35], and hybrid techniques [36]. These methodologies surpass the limitations of conventional approaches, providing enhanced transformer fault diagnostics with higher accuracy, robustness, and reliability. However, as models become more complex, a clear understanding of the algorithm’s inner workings is often required instead of treating the model as a black box [37]. Accordingly, more attention shifted to explainability and interpretability, where models are assessed not only for their high predictive accuracy but also for their capacity to provide transparent insights into how predictions are made. In this regard, utilizing SHapley Additive exPlanations (SHAP)-based approaches offers a promising direction for model interpretability and transparency. SHAP decomposes each prediction into the contribution of individual features, enabling quantification of how much each input influences the final output [38]. In this way, not only are the most influential features behind transformer health predictions highlighted, but also less relevant ones can be pruned, thus simplifying the model complexity.
To address the identified research gaps, this study offers a dual-scope SHAP-based comprehensive framework for the evaluation of transformer HI prediction. This work systematically benchmarks several models, including linear, kernel, and tree-based, and hybrid-ensemble state-of-the-art models. The proposed framework is implemented in three progressive phases in an attempt to provide a balanced model in terms of predictive accuracy, model complexity, and interpretability. The main contributions of this paper can be summarized as follows:
- A structural unified comparative framework is presented that categorizes models into four families and evaluates them under a multi-experimental pipeline, thus offering a broader assessment than prior single-model studies for a publicly available dataset.
- A dual role for SHAP is presented, serving both as an interpretability and as a feature selection mechanism. When combined with Pearson statistical correlation, this hybrid strategy enables effective feature-pruning that enhances transparency, reduces dimensionality, and improves model efficiency.
- In contrast with other studies using the same dataset, whose main scope was either focused on classification, single regression algorithms, or knowledge-graph reasoning with no feature selection, this work offers improved accuracy while maintaining interpretability at a reduced model complexity.
- The results indicate that high predictive accuracy can be attained without the need for complex deep learning architectures, which are frequently unjustifiable for datasets with non-temporal dependencies.
This paper is divided into seven sections. Section 1 introduces the main paper scope and objectives; then, in Section 2, a literature review is presented, with emphasis on the addressed gap and contributions of this paper. In Section 3, the methodology is detailed, covering the approach used in this paper and what sets it apart from the current literature. Then, the results are presented in Section 4. In Section 5, the data is analyzed under the effect of noise, and the model robustness is tested at different levels of cross-validation, followed by a discussion in Section 6. Finally, a conclusion is added in Section 7.
2. Literature Review and Related Work
Table 2 shows a related literature review concerning the investigation of transformer health condition, fault diagnosis, and dissolved gas forecasting using DGA and oil quality parameters in recent studies.
Early research has focused on employing linear, nonlinear, and statistical modeling for HI prediction. The authors in [39] incorporated multiple linear regression (MLR), artificial neural network (ANN), and adaptive neuro fuzzy inference system (ANFIS), while [40] applied Lasso regression for HI prediction. Although [40] applied change-point detection and Maximal Information Coefficient (MIC)-based feature selection, the analysis was limited to linear models only. The work in [41] applied a probabilistic framework and introduced a risk-oriented statistical perspective on HI evaluation; however, the study relied only on probabilistic statistical fitting without regression or classification benchmarks.

Table 2.
Summary of related work.
Table 2.
Summary of related work.
| Ref | Task Type | ML Models | Interpretability/Explainability | Feature Selection | Dataset |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [42] | Classification | Multi-model | ✓ | x | 470 transformer records |
| [40] | Regression | Single model | x | ✓ | 38 transformers |
| [39] | Regression | Multi-model | x | ✓ | 336 transformers |
| [41] | Regression | Single model | x | x | DGA datasets |
| [43] | Classification | Single model | ✓ | x | 470 transformer records |
| [44] | Causal Reasoning | Single model | ✓ | x | 470 transformer records |
| [45] | Regression | Multi-model | ✓ | ✓ | Substation data |
| [46] | Classification | Multi-model | x | ✓ | 594 samples |
| [47] | Classification | Single model | x | ✓ | 381 DGA records |
| [48] | Regression | Single model | x | x | Utility datasets |
| [49] | Regression | Single model | ✓ | x | 470 transformer records |
| [50] | Classification | Multi-model | x | ✓ | 470 transformer records |
| [51] | Regression | Single model | ✓ | x | 940 transformer records |
| [52] | Classification | Single model | ✓ | ✓ | DGA dataset |
| Proposed | Regression | Multi-model | ✓ | ✓ | 470 transformer records |
✓ means it is covered in this reference, and x means it is covered in this reference.
Other work emphasized dimensionality reduction and optimization techniques, with a shift to transformer fault classification using advanced ML techniques. The work in [46] combined Principal Component Analysis (PCA) with ensemble classifiers for DGA-based fault classification, while [47] proposed LightGBM for improved diagnostic accuracy and IRM + filter/wrapper for feature selection. On the contrary, [48] integrated expectation–maximization-based missing value imputation with LightGBM for HI regression. However, these studies prioritized accuracy within a single model scope while neglecting interpretability or reproducibility. The use of deep learning models has also been explored in [45] for hierarchical attention for gas concentration forecasting. However, the approach remained essentially a black box, offering little interpretability while demanding significant computational resources.
More recently, explainability and interpretability-driven approaches have emerged in order to understand the effects of various DGA variables on model predictions. Focusing on fault classification and using deep learning and optimization techniques, the authors in [52] used SHAP for feature selection, reducing 19 input features to the most relevant 13. This pruning improved diagnostic efficiency and enhanced transparency by quantifying the contribution of each gas variable to the classification outcome. However, as their study was limited to classification tasks, it did not extend to regression-based health index prediction or systematic benchmarking across diverse algorithmic families—areas that our proposed SHAP-enhanced regression framework explicitly addresses. In contrast, the work in [51] work applied SHAP and LIME but only for post hoc explanation of regression outputs, without integrating them into the modeling framework.
The work in this paper is based on a publicly available dataset of 470 transformer records for a wide variety of analytical purposes, which were also used in the work of [42,43,44,49,50]. In [49], CatBoost regression was applied to the dataset, leveraging its ability to handle categorical variables and reduce overfitting through ordered boosting, which makes it particularly effective for complex fault data. However, while this approach achieved strong predictive accuracy, it primarily emphasized single-model regression and offered limited interpretability, leaving gaps in systematic benchmarking and feature reduction that our proposed SHAP-enhanced framework seeks to address. In [50], oversampling was incorporated with RF, SVM, XGBoost, and KNN with PCA for dimensionality reduction for transformer fault HI classification. Knowledge-driven studies also leveraged the same dataset, including [42,44], as well as [43]. While these works provided directly comparable baselines, they were limited either by a single-model orientation, classification-only focus (RF, SVM, XGBoost, KNN), or qualitative reasoning. Thus, this paper pushes these boundaries by systematically benchmarking classical and advanced HI predictive models and by enhancing interpretability through SHAP explainability analysis while also reducing model complexity via SHAP-guided feature selection.
In the highlights presented above, DGA was used in a plethora of studies for transformer condition assessment, spanning tasks from fault classification to health index regression and gas concentration forecasting. Previous works have explored models ranging from traditional linear approaches and handcrafted statistical distributions to nonlinear and ensemble-based methods, and more recently, to black-box complex deep learning architectures. However, the use of highly complex deep learning models is not fully justifiable due to the absence of temporal dependencies that would necessitate such architecture. In contrast to the work carried out in this study, which is focused on predicting HI through regression analysis, many of the related works were limited to root cause analysis, fault classification, and diagnosis, with a lack of interpretability, and primarily focused on predictive accuracy optimization. Although some studies have integrated model interpretability, they were typically confined to post hoc analysis. Moreover, SHAP has either been applied as a feature selection tool or has been used solely for interpretation without influencing the model development pipeline. Additionally, none of the reported work combined two feature selection strategies: Pearson correlation as a statistical filter and SHAP as an embedded method. Nevertheless, the pursuit of a model that achieves both high predictive accuracy and interpretable performance, while simultaneously reducing feature dimensionality, has not been realized in any of the related works summarized in Table 2.
Building on a plethora of research that spans linear, nonlinear, statistical, and ensemble-based modeling for transformer HI prediction, this paper introduces a dual-scope SHAP-based framework that systematically benchmarks four model families—linear, kernel, tree-based, and hybrid state-of-the-art ensemble—using a publicly available dataset of 470 transformer records. Unlike earlier studies that focused on single-model scopes, fault classification, or post hoc interpretability, this work integrates SHAP both as a feature selection and interpretability tool within the modeling pipeline, thereby enhancing transparency and reducing dimensionality. The use of SHAP in conjunction with Pearson statistical correlation provides a complementary feature-selection strategy that captures both the model-driven importance and the linear statistical relevance of each input feature, thereby ensuring that the feature pruning process is robust and significant. The methodology is implemented in three progressively sequential phases to balance model complexity, predictive accuracy, and interpretability, thus surpassing prior work that relied on black-box deep learning models and statistical fitting. Conclusively, this work offers a unified comparative structure via multi-experimental evaluation analysis, offering high predictive HI accuracy without the need for computationally intensive architecture, and extending the boundaries of the existing literature by presenting an interpretable and efficient solution for transformer HI prediction.
3. Methodology
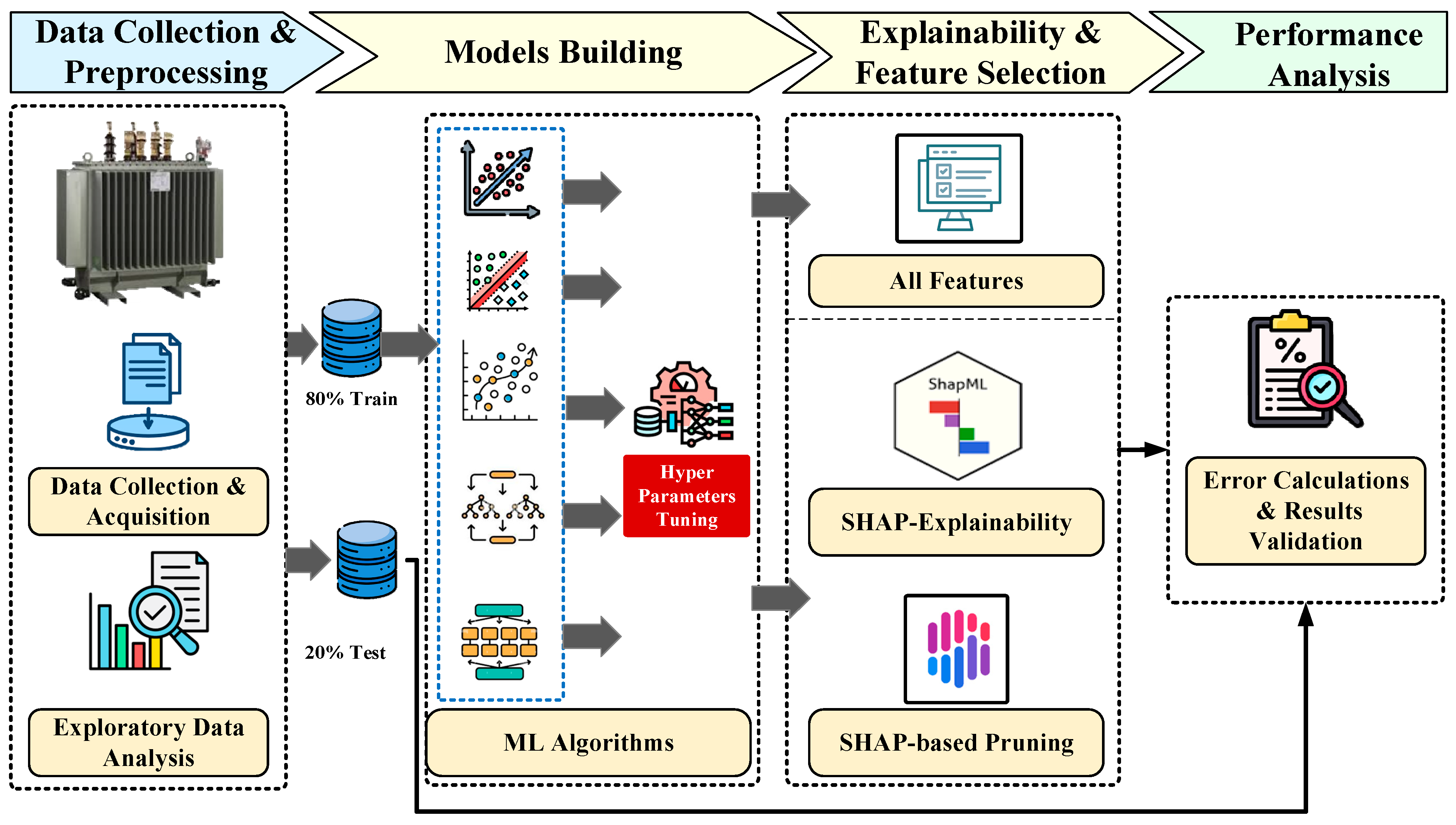
The proposed framework follows a progressive pipeline, as demonstrated in Figure 1, and is structured around a regression-based approach to balance predictive accuracy, model complexity, and interpretability for transformer HI prediction. The pipeline is divided into four main phases, including (a) data collection and preprocessing, (b) model building, (c) explainability and feature selection, and (d) performance analysis. These steps are discussed in Section 3.1, Section 3.2, Section 3.3 and Section 3.4, respectively, followed by the results and performance analysis in Section 4. All simulations and modeling are implemented in the Python platform 3.12.12, using standard libraries such as NumPy, pandas, and Scikit-learn.
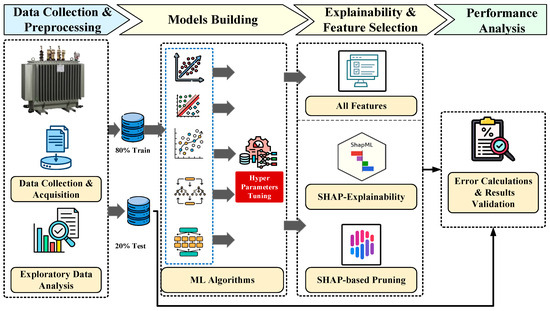
Figure 1.
The proposed three-stage methodology pipeline.
Accordingly, this study consists of three experiments conducted progressively to identify the most effective model in terms of accuracy, decreased complexity, and transparent interpretability, as follows:
- Baseline model evaluation (Experiment I): Multiple models are assessed, including linear regressors, tree and kernel-based learners, boosting, classical, and hybrid ensemble methods. The purpose is to establish baseline performance and select the top 4 best-performing models in terms of highest accuracy and lowest error scores.
- Model optimization (Experiment II): building on the findings of Experiment I, the top performers undergo refinement through hyperparameter tuning and cross-validation to improve predictive accuracy and robustness.
- Feature Selection and Pruning (Experiment III): after model optimization in Experiment II, a SHAP analysis was applied for explainability and feature selection, in combination with Pearson correlation to identify and eliminate the lowest impactful features, thereby reducing the dimensionality and complexity of the model without affecting the model’s accuracy. These two feature selection tools ensure that feature elimination is both statistically justified and aligned with the model’s inherent learning behavior.
3.1. Data Collection and Preprocessing
This step is divided into (a) data description and specification, (b) data exploration, and (c) data preparation, as described in the following sections.
3.1.1. Dataset Description and Specification
This work is based on a publicly accessible dataset provided for power transformer health condition assessments, found in [53] and originally published in [42]. The dataset consists of oil quality samples of power transformers (e.g., methane, nitrogen, hydrogen, etc.) with a corresponding HI and life expectancy. Transformer oil quality is assessed through parameters such as water content, dielectric rigidity, water, and interfacial tension. In addition, power factor is taken into consideration as it is often used as an indication of oil dielectric loss [51]. The DGA data captures the accumulation of critical gases and chemical by-products generated during transformer operation and is compiled from oil samples collected across different resources and locations, and units of varying ages and specifications [21,54].
According to the IEC standard [55] and the data in Table 1, HI calculations are used to determine whether a transformer is in “very good” condition, with a score of 100 corresponding to over 15 years of remaining life. A score of 30 indicates a “good” condition with 5 to 15 years remaining; a “fair” condition is represented by a score of 20 and indicates 2 to 5 years of life expectancy, and a “poor” condition indicates 1 to 2 years remaining and is represented by a score of 10. Accordingly, a score of 0 indicates a “very poor” condition, requiring urgent attention within a less than 1-year period. Since the life expectancy feature does not originate from direct transformer condition measurement, it has been excluded from any further analysis to prevent biased predictions due to data leakage.
3.1.2. Data Exploration
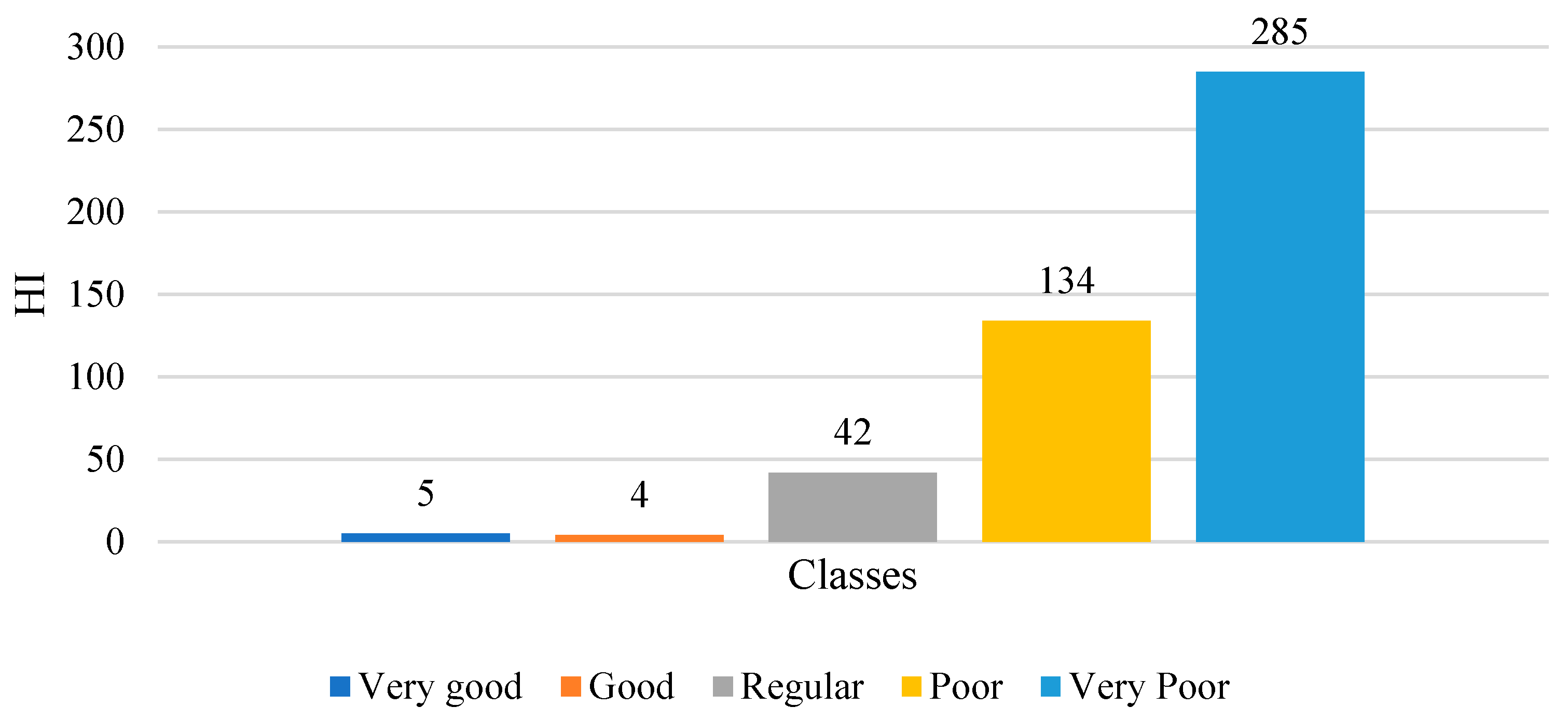
In order to fully understand the dataset, the data exploration phase was carried out before analysis. Thus, a statistical analysis, data visualization, and correlational analysis are carried out in this section. Table 3 presents the descriptive statistics of the numerical features in the dataset, which helps in fully comprehending the data and determining data quality. Accordingly, Hydrogen and Methane’s large ranges suggest that the dataset contains various health stages, ranging from normal operation to faulty development, particularly with partial discharges or corona. Nitrogen gas dominates the gas content, averaging 47,760 ppm, followed by oxygen, which implies that both are consistently present across most data samples. Gases with moderate concentration, such as carbon monoxide (CO), ethane, and methane, can be a sign of paper insulation, thermal degradation, and sustained overheating. In addition, it can be concluded that out of the 470 samples, 285 transformers fall into the ‘very poor’ category with corresponding HI < 30, 134 samples were labeled as the ‘poor’, 42 transformers were ‘regular’, and 4 were labeled as ‘good’, while only 5 samples were ‘very good’ transformers with HI > 70.

Table 3.
Descriptive statistics of the numerical features in the dataset.
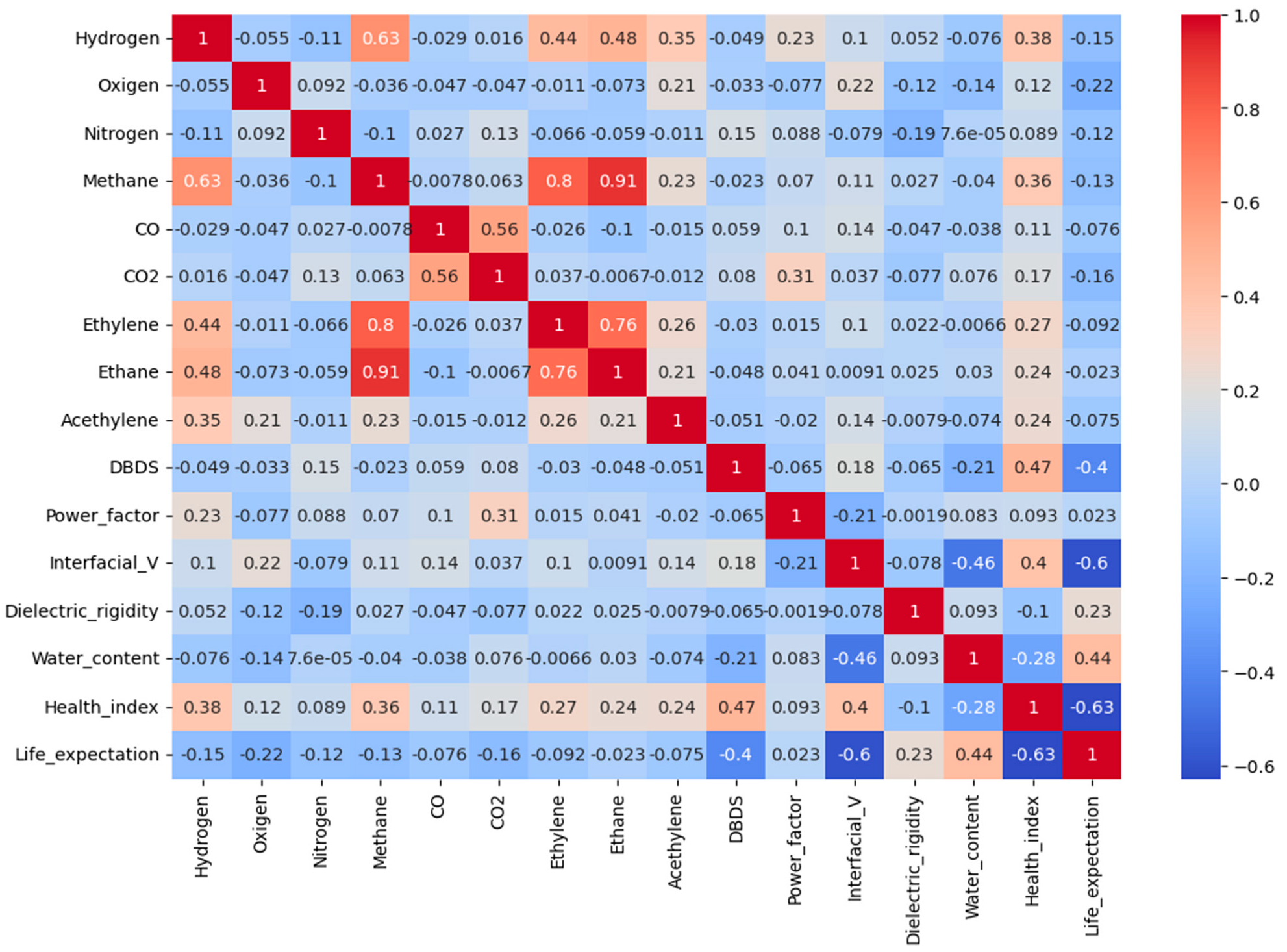
It can be observed from the correlational heat matrix of Figure 2 that the dependent variable HI correlates strongly with some dissolved gases and condition parameters, as quantified by the Pearson coefficient . Moderate correlation ( > 0.3) can be observed with some variables, such as DBDS, hydrogen, methane, and interfacial value, which are positively correlated with HI. Conversely, a negative correlation ( < 0) can be detected with water content and electric rigidity, reflecting that a higher water contamination and reduced dielectric strength contribute to a lower level of transformer health. Other gases, such as CO2, ethylene, acetylene, and ethane, have weaker positive relationships with HI ( < 0.3), suggesting a minor influence on HI.
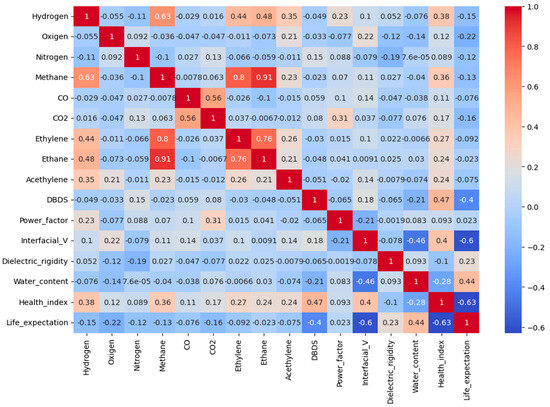
Figure 2.
Correlation analysis of the main transformer health condition parameters.
3.1.3. Data Preparation
In this phase, the dataset undergoes a series of preprocessing steps to enhance predictive quality and ensure the model’s readiness. Accordingly, all numerical features were standardized using z-score normalization to eliminate any scale differences among variables and ensure fair weight distribution across features. Finally, the processed dataset of all models for all experiments was split into an 80:20 ratio for training and testing subsets, respectively.
3.2. Model Building
As mentioned earlier, three sets of experiments are carried out in this work: Experiment I utilizes baseline models, while Experiment II evaluates hyperparameter-tuned versions of the top-performing models from the initial stage. Then, a further analysis of model interpretability is carried out in Experiment III, where redundant variables are excluded using SHAP-based feature selection.
In this study, a diverse set of classical and state-of-the-art ML models was employed to estimate the transformer HI using different algorithmic families for transformer HI prediction. Linear models such as Linear Regression, Ridge, and Lasso were evaluated as foundational, non-complex models. Kernel-based and tree-based models, represented by SVR and Decision Trees (DT), were tested for their reputed ability to model nonlinear patterns. In addition, bagging/boosting strategies, including Random Forest (RF), Gradient Boosting (GB), XGBoost, LightGBM, and CatBoost, were also tested as state-of-the-art approaches due to their ability to handling features’ nonlinearities and complex interactions.
After individual model evaluations, the best model performers underwent the process of hyperparameter tuning using GridSearchCV [49], followed by three-fold cross-validation to avoid overfitting. Furthermore, averaged ensemble approaches were also considered as a hybridization of regressors, where multiple weaker models are combined to produce a stronger model to achieve the highest predictive accuracy in Experiment II.
3.3. Explainability and Feature Selection
Although performance and statistical metrics offer valuable insight into the model’s performance, they do not always provide a comprehensive assessment of feature importance in the constructed model on their own. The SHAP technique assesses an ML model’s output by identifying the features that mostly influence the model’s prediction. In this context, SHAP employs the game theory concept by merging optimal credit allocation with a local explanation through SHAP values [56]. For each sample, the impact of individual features on the output is represented by SHAP values and their relevance is defined as the average marginal contribution across all feature permutations while accounting for orderings and correlations, thereby enabling transparent interpretation of complex ML models.
To offer the model more interpretability and guide feature reduction, SHAP was utilized in this analysis for two functions [57]. SHAP values were generated to evaluate how each feature contributes to the HI prediction in the dataset, where features with high SHAP values were retained and low-SHAP-value features were pruned. Accordingly, SHAP served dual functions in this work: first as a feature explainability tool, and second as a systematic feature selection mechanism when integrated with Pearson statistical correlation. This hybrid feature-selection strategy facilitates the capturing of model-driven importance via SHAP and linear multicollinearity among features via Pearson coefficients. Combining these techniques will simplify the feature’s input space and model’s architecture, yet maintain high prediction accuracy for transformer HI. Thus, this framework contributes beyond conventional approaches in the previous literature, which often focus only on accuracy or fault classification, by additionally providing an interpretable, efficient, and less complex predictable model version.
3.4. Performance Analysis
To ensure consistent comparisons across models, a model’s performance is assessed utilizing some metrics, including Mean Absolute Error (MAE), Root Mean Square Error (RMSE), Mean Squared Error (MSE), and R2 score. Thus, the most suitable modeling strategy should represent the best trade-off for predicting the transformer health index. These performance metrics can be computed using (1)–(4):
Such that n is the total number of samples, is the actual value, is the model’s predicted value, and is the mean of the actual target values.
4. Results
In this paper, model performance in HI prediction was assessed across three modeling experiments. Experiment I involved testing multiple ML algorithms with all features in Section 4.1. Then, in Section 4.2, Experiment II focused on hyperparameter tuning of the best models. Finally, in Section 4.3, Experiment III investigated complexity and interpretability by retraining the optimized models on a reduced, SHAP-identified feature set. Details of the three experiments will be shown in the following sections, followed by a discussion of the results.
4.1. Experiment I: Baseline
In Experiment I, all features in the dataset, except for life expectancy, were used to assess the multi-model’s HI prediction performance using ML regressors. After the pre-processing step, individual linear, tree, kernel-based, and classical ensemble regressors were then evaluated, where all models were trained and tested on an 80:20 split and evaluated using the same performance metrics shown in Table 4. The models tested in this experiment were linear, Ridge, Lasso, SVR, DT, RF, GB, AdaBoost, XGBoost, LightGBM, and CatBoost regressors. In addition to individual model results, hybrid ensemble predictions were generated by averaging outputs from the highest-performing individual models (e.g., RF + GB, LightGBM + CatBoost).

Table 4.
Experiment I regression analysis results.
As demonstrated by Table 4, foundational regressors offered the lowest predictive ability compared to others. Lasso regression scored the highest error metrics among all, with an MAE of 10.82, an RMSE of 13.77, and an R2 value of 0.552. Linear and Ridge regression followed as the second worst with an MAE score of 9.63 and 9.62, MSE values of 172.76 and 172.17, an RMSE of 13.14 and 13.13, and an R2 score of 0.492 and 0.509, respectively.
Nonlinear kernel and tree-based regressors were the second category of ML algorithms in Experiment I. Kernel-based SVR exhibited the lowest predictive accuracy in this group, with an MAE score of 9.82, RMSE of 14.07, MSE of 197.86, and a low R2 score of 0.43, thus indicating poor generalization performance. DT’s slightly better performance is noted in its MAE, scoring 7.64; however, a score of 197.86 was obtained for MSE and 14.07 for RMSE, and a low value of 0.421 as R2. On the contrary, RF substantially improved, achieving 6.42 for MAE, 82.2 for MSE, 9.06 for RMSE, and a strong performance R2 of 0.749. This validates that ensembled bagging performance on RF can effectively capture nonlinearity in the data.
Next, the performance of boosting ensembles was explored, using GB, AdaBoost, XGboost, LightGBM, and CatBoost, where GB recorded the best performance among all individual models. Low error scores of 6.29 for MAE and 53.29 for MSE, an RMSE of 7.29, and an R2 of 0.759 for GB evidenced its strength in error correction and handling nonlinear interactions. Conversely, AdaBoost performed poorly, achieving the highest MAE of 11.70 and a low R2 of 0.450. Similarly, XGBoost, LightGBM, and CatBoost exhibited strong performances and low error scores, with XGBoost achieving the highest R2 score of 0.766 and a strong MAE of 6.917. However, its MSE and RMSE recorded values of 180.86 and 10.42, respectively, indicating possible sensitivity to outliers. A balanced performance was exhibited in LightGBM performance, with an MAE of 6.25, MSE of 80.85, RMSE of 8.99, and R2 of 0.749. Finally, CatBoost, which inherently supports categorical feature handling, recorded an MSE of 94.03, an MAE of 6.39, an RMSE of 9.74, and an R2 of 0.728.
Following the evaluation of individual models’ performance, the hybridization phase took place, where pairwise combinations were created to form averaged ensembles, and the two best-performing hybrids were selected for further analysis. Accordingly, the (LightGBM + CatBoost) and (RF + GB) ensembles achieved the highest performance, scoring an MAE of 6.09, an MSE of 83.01, an RMSE of 9.11, and an R2 score of 0.757 for the (LightGBM + CatBoost) ensemble, whereas the (RF + GB) ensemble achieved an MAE of 6.2, a score of 85.81 for MSE and 9.26 for RMSE, and an R2 score of 0.745. These findings confirm that the (LightGBM + CatBoost) ensemble is the best-performing model among all possible combinations.
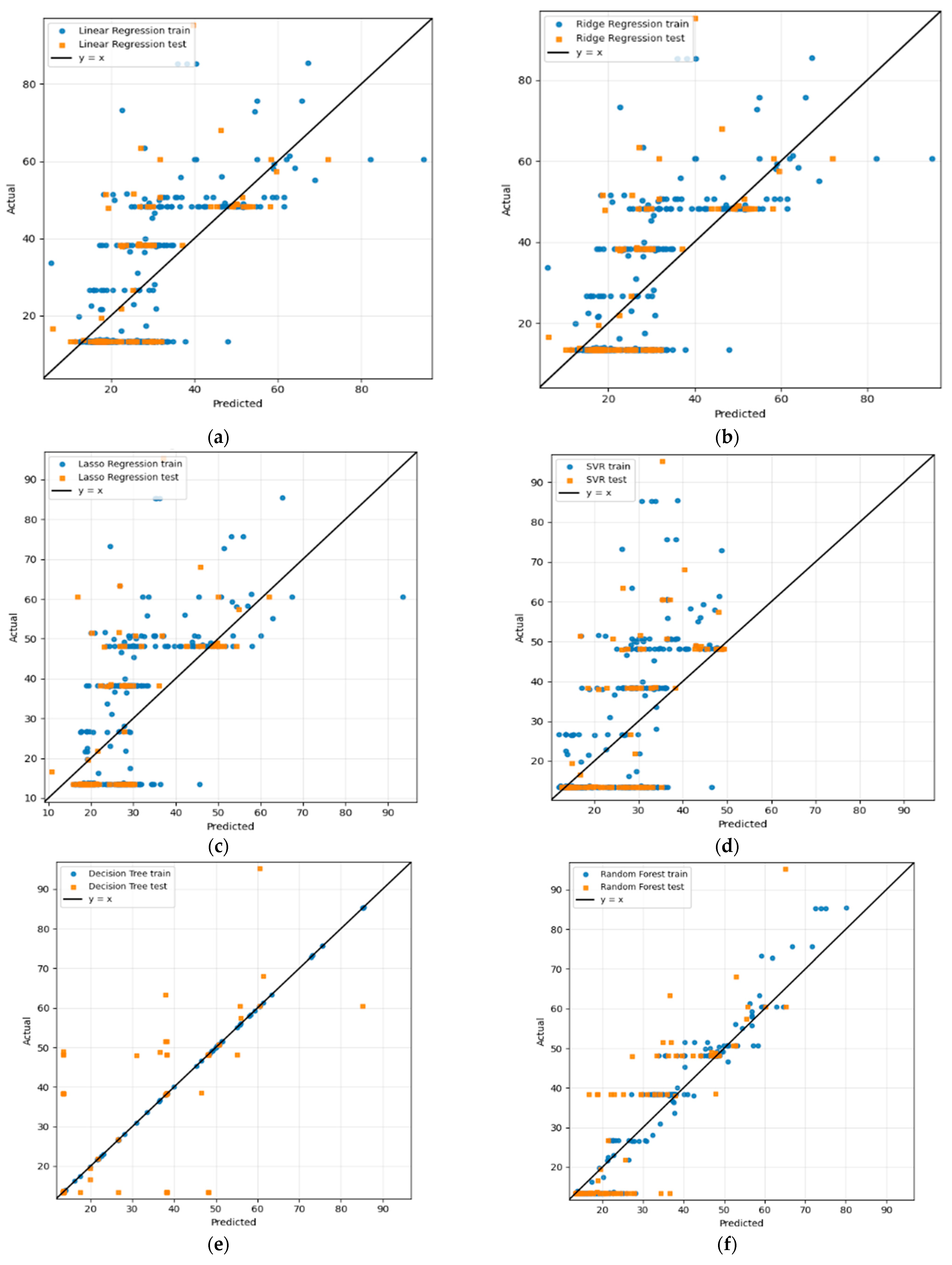
The parity plots presented in Figure 3 provide a visual representation of actual and predicted HI, confirming the findings of Table 4 and offering further insights into each model’s performance, especially regarding overfitting. For foundational ML regressors (Linear, Ridge, and Lasso), as shown in Figure 3a–c, large scatter deviations are exhibited for predicted values from the 1:1 reference line, thus resulting in high error scores, as depicted by the performance metrics in Table 4.
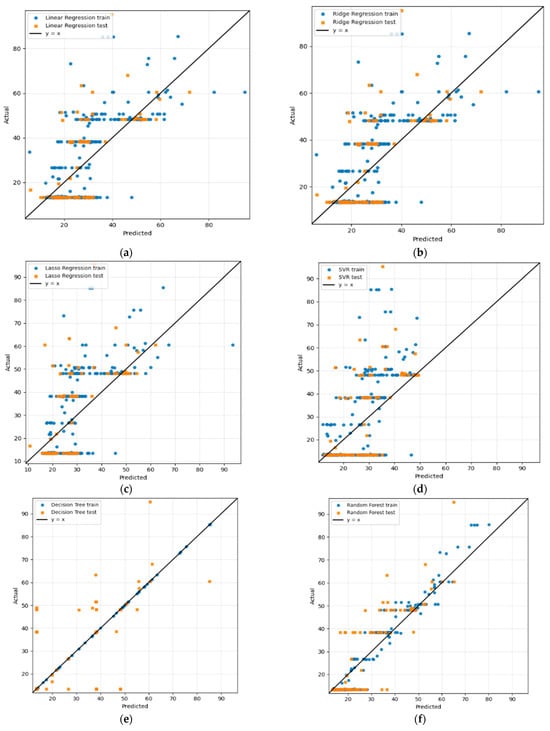
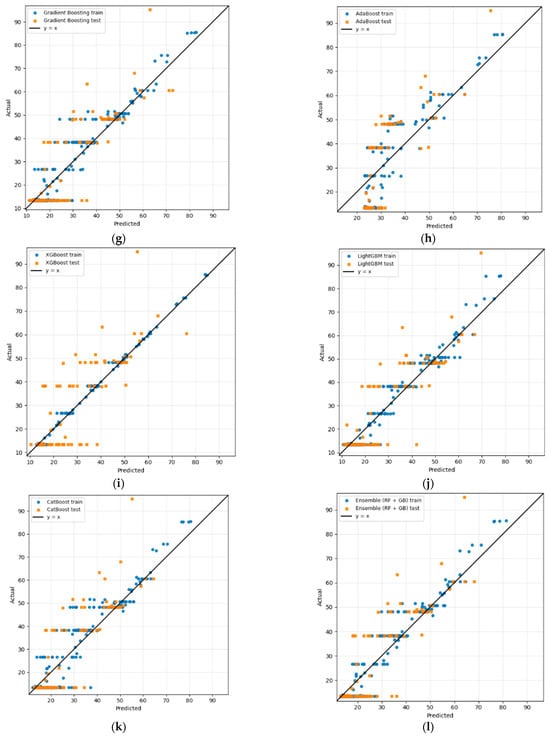
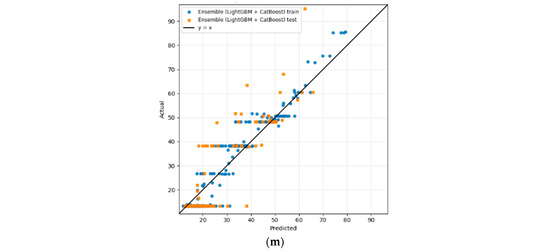
Figure 3.
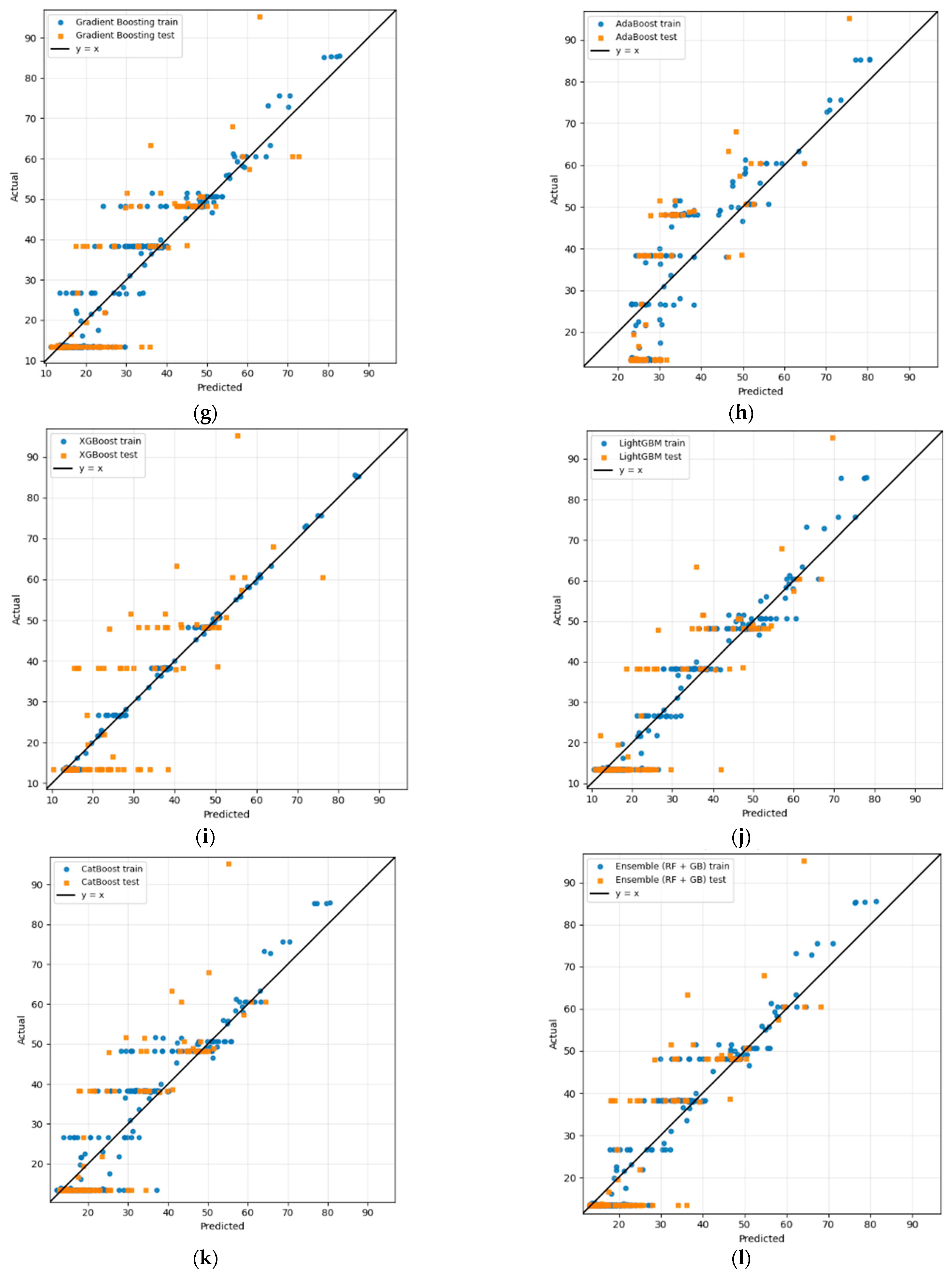
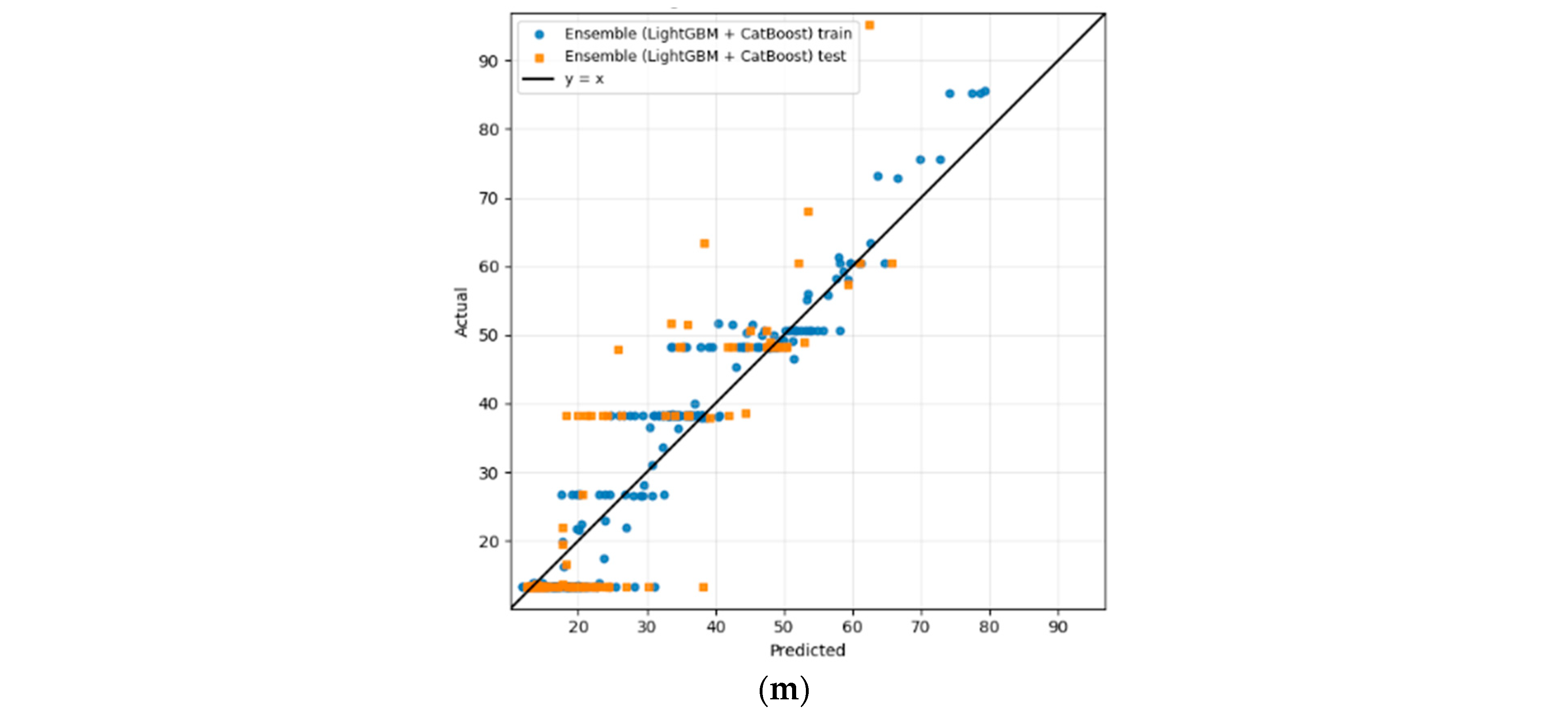
Regression analysis of the proposed methodology of experiment I: (a) Linear, (b) Ridge, (c) Lasso, (d) SVR, (e) DT, (f) RF, (g) Gradient Boosting, (h) AdaBoost, (i) XGBoost, (j) LightGBM, (k) CatBoost, (l) ensemble (RF + GB), and (m) ensemble (LightGBM + CatBoost).
However, nonlinear kernel regressors (SVR) exhibit poor generalized behavior, with test predictions being widely dispersed around the parity line. Conversely, for tree-based regressors, the DT demonstrates strong overfitting with perfect alignment with the training data but scattered test predictions, while the RF demonstrates improved generalization, with test points more closely aligned along the 1:1 line.
Regarding the boosting-based techniques, Figure 3g–k, the parity plots illustrate a better alignment with the 1:1 line. GB exhibits the closest clustering of predictions around the parity line among all individual models, in line with its superior numerical performance. However, AdaBoost demonstrates a broader spread, confirming its poor generalization. XGBoost, LightGBM, and CatBoost display competitive predictive performances, with their points nearer to the diagonal line compared to other models, with CatBoost showing less alignment.
Finally, the hybrid ensembled approach’s parity plot shown in Figure 3l,m, based on a combination of individual learners, demonstrates the strongest visual agreement with the parity trend line. In the (LightGBM + CatBoost) ensemble, both training and test predictions are concentrated close to the diagonal, leading to the lowest overall errors. Likewise, the RF + GB ensemble attained improved alignment relative to its constituent models.
These findings further confirm not only that the (LightGBM + CatBoost) ensemble delivers the best performance among all tested models in terms of accuracy and errors, but also that the average ensemble combination exhibits no signs of overfitting, indicating stronger generalization capabilities. In addition, from a model architectural point of view, this combinational effect could lead to promising complementary results. LightGBM combines two cutting-edge features that increase its accuracy and speed through gradient-based one-sided sampling (GOSS) and exclusive feature bundling (EFB). While GOSS prioritizes samples with larger gradients, EFB reduces the feature dimensionality by merging mutually exclusive features, thereby accelerating the search for optimal split points as well as computational efficiency [57]. On the other hand, Catboost is designed to overcome overfitting problems effectively by applying regularization and early stopping through adopting ordered target statistics and ordered boosting [58,59]. In contrast to LightGBM, Catboost, the ordered boosting and symmetric tree architecture provides unbiased learning, making it ideal when dealing with categorical and noisy datasets [60]. By incorporating these structurally dissimilar learners via model averaging, the ensemble combination achieves improved robustness and generalization across the HI spectrum.
4.2. Experiment II: Tuned Models
Experiment II is based on optimizing the performance of the top-performing algorithms of Experiment I. For this reason, hyperparameter tuning is crucial, since the predictive capability of each base model depends strongly on the choice of its internal configuration. In addition, tuning reduces the chances of over- and under-fitting, thereby ensuring that each model is systematically optimized for fair comparison. At this stage, hyperparameter tuning is carried out for the top four performers, namely, RF, GB, LightGBM, and CatBoost.
To ensure fairness and reproducibility, all constituent models were optimized using an explicit hyperparameter tuning strategy prior to the models’ hybridization. Each model was tuned independently using a structured grid search, where a predetermined set of hyperparameter ranges was systematically evaluated under five-fold cross-validation. Each model was trained on nine folds and validated on the remaining fold, and this process was repeated over all folds. The mean validation score was used to select the best-performing configuration. This procedure was applied separately to the RF, GB, LightGBM, and CatBoost regressors, ensuring that each base learner operated under its optimal settings before combining predictions in the ensemble. The model’s key aspects, such as tree depth, learning rate, and number of estimators, for parameter hyper-tuning can be found in Table 5. In addition, a fixed random seed (random_state = 42) was assigned for all models equally throughout the tuning and training to ensure reproducibility of the optimization path and final results. As a result of this tuning process, models were retained and further integrated into an ensemble hybrid model combination.

Table 5.
ML models’ hyperparameter values.
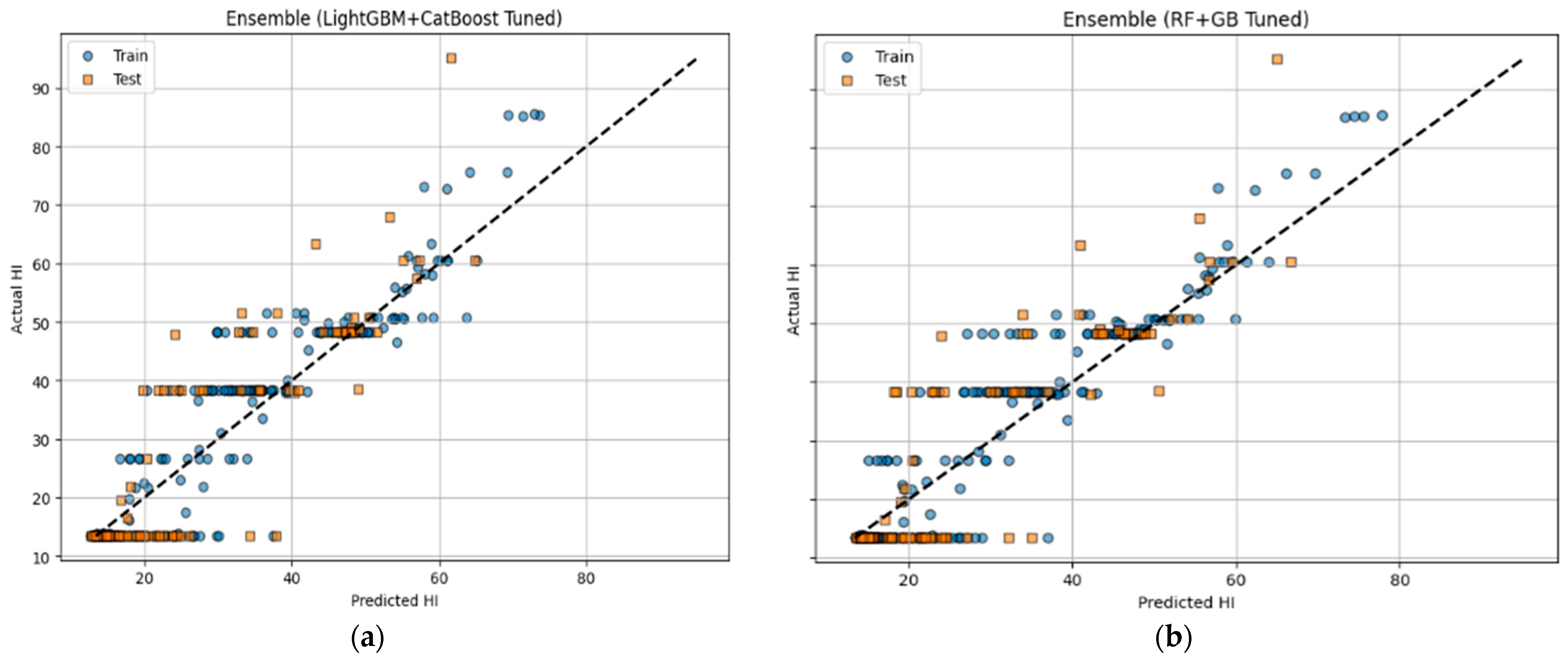
Similarly to Experiment I, another ensemble was formed from the tuned versions in Experiment II, whose performance is demonstrated in the parity plots of Figure 3g and error metrics in Table 6. Two combinations were formed: the first combined the tuned LightGBM and CatBoost models, while the second was built by combining the average outputs of the tuned RF and GB models.

Table 6.
Experiment II regression analysis results and comparison with the best performers from Experiment I.
As illustrated in Table 6 and shown in Figure 4, the tuned (LightGBM + CatBoost) ensemble achieved the best overall performance, with a cross-validated MAE of 5.70, a value of 77.31 for MSE, an RMSE value of 8.793, and an R2 score of 0.774. In comparison, the tuned RF-GB ensemble also demonstrated a slightly lower performance, with a score of 6.17 for MAE, a score of 80.2 for MSE, an RMSE of 8.95, and an R2 of 0.766. Compared to Experiment I, where the highest R2 was 0.766 with XGBoost, this also came at the cost of a high RMSE. These results confirm that combining tuned models results in an elevated model performance with more accurate predictions, better generalizability, and improved fitting.
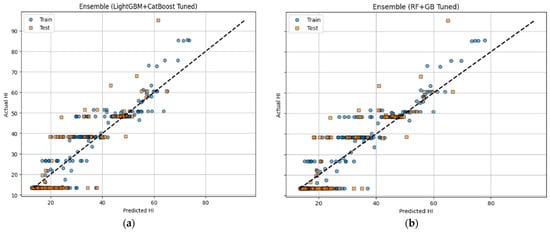
Figure 4.
Regression analysis for tuned, hybrid ensemble models in experiment II: (a) (LightGBM + CatBoost Tuned) and (b) (RF + GB Tuned).
4.3. Experiment III: Tuned and Interpretable Models
The aim of Experiment III was to test whether feature reduction would maintain a balance between interpretability and maintained model performance or not. For this reason, Experiment III introduced SHAP-based explainability and feature selection compared to Experiments I and II. Instead of using a full set of features, SHAP values were computed in Experiment III to identify the most influential features impacting the HI prediction, thus offering a more interpretable predictive tool. Based on SHAP analysis and insights, low-contributing features were omitted from the model, resulting in a reduced feature space. The best-tuned ensemble models from Experiment II—namely the (LightGBM + CatBoost) combination—were reused in this experiment but trained on the refined feature set after SHAP.
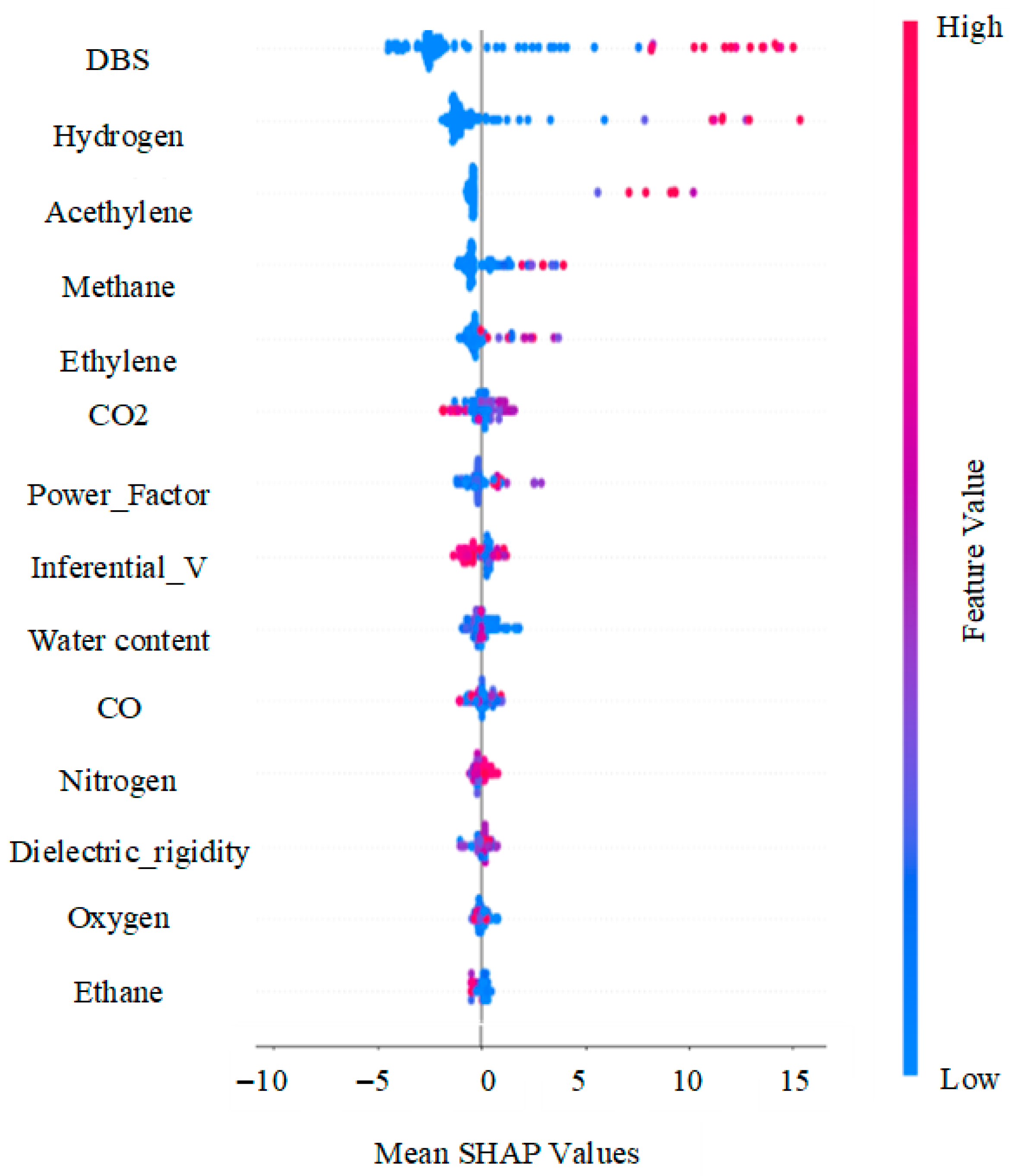
Figure 5 presents the SHAP analysis, and Figure 6 shows the feature ranking summary plot. These two plots were used to rank the input variables according to their average absolute impact across all samples on the model output, as well as visualize their directional contribution. In this work, a combination of two feature selection tools was employed: SHAP, acting as an embedded approach that evaluates feature relevance based on their contribution to the trained model, and the Pearson correlation, used as a complementary filter technique to assess the statistical relationships between individual variables and the target. This combination ensures that feature pruning was not based solely on model-based importance, but also included statistical correlation, thus providing a more rigorous selection mechanism.
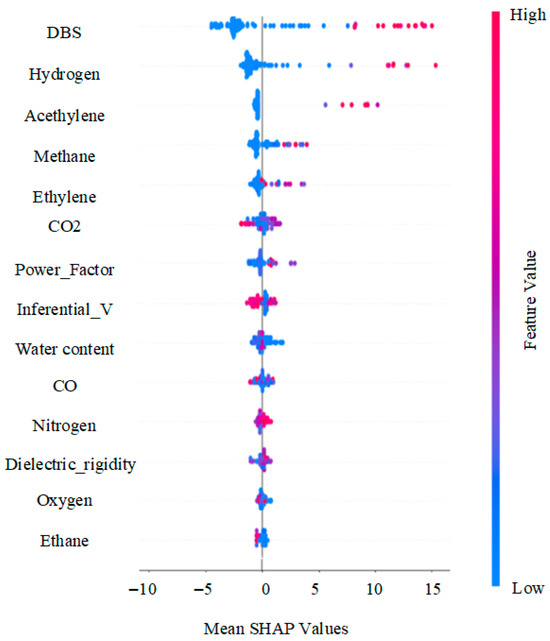
Figure 5.
SHAP analysis and feature importance summary plot.
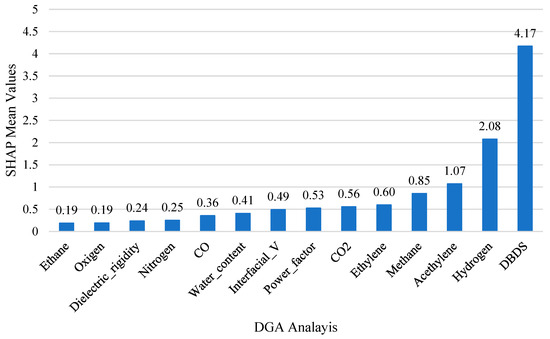
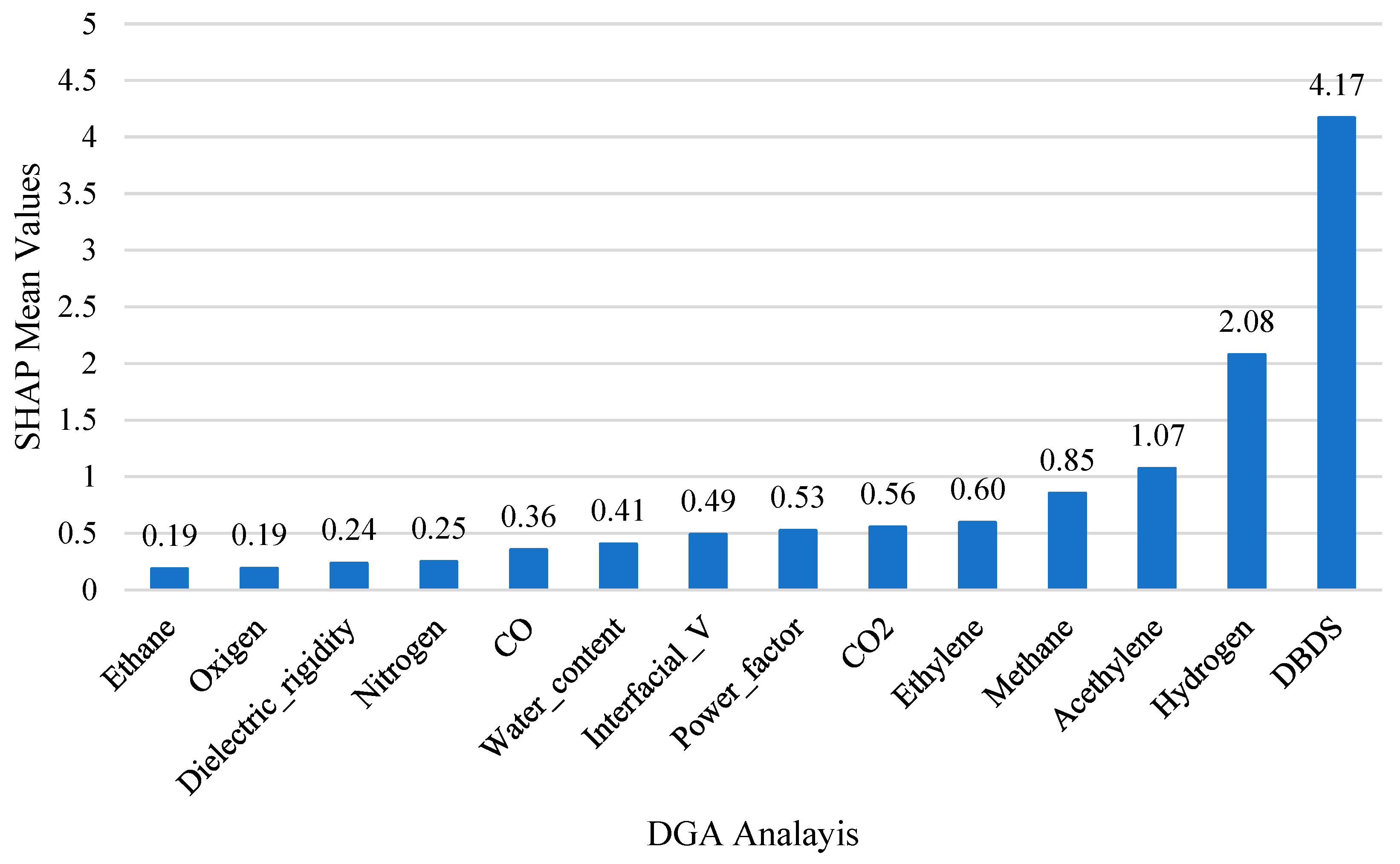
Figure 6.
SHAP importance ranking.
As shown in Figure 6, DBDS was identified as the dominant variable, with a mean SHAP value of 4.17, which was also confirmed by the correlational heat map of Figure 2, where DBDS exhibited a positive relationship with HI ( = 0.47). A group of moderately important features to HI followed, including hydrogen (SHAP 2.08, = 0.39), acetylene (1.07, = 0.42), methane (0.85, = 0.36), ethylene (0.60, = 0.27), CO2 (0.53, = 0.24), power factor (0.49, = 0.23), interfacial value (0.41, = −0.28) and water content (0.36, = −0.10).
On the contrary, the lowest SHAP scores, as shown in Figure 6, were associated with nitrogen (0.25), dielectric rigidity (0.24), oxygen (0.19), and ethane (0.19). Correspondingly, these features showed weak or inconsistent statistical relationships with the target variable, which is shown in their corresponding Pearson heatmap in Figure 2. Oxygen had a near-zero correlation with HI ( = 0.01) and dielectric rigidity ( = −0.12), and nitrogen also showed a very minor association ( = 0.16). In addition to the model-based and statistical evidence, domain knowledge from DGA supports limited diagnostic value for ethane, oxygen, and nitrogen on HI in real operational conditions, further reinforcing their exclusion from the final feature set [61,62].
For a valid comparative assessment of the model’s performance before and after feature pruning, Experiments I and II were conducted using the full set of 14 input features, whereas Experiment III applied a reduced feature set by removing the four least-contributing variables. This pruning action was performed in a manual, iterative manner such that, after each removal, the model was retrained, the corresponding error performance metrics were recorded, and the process was halted once additional feature elimination produced a noticeable decline in performance. Conclusively, this feature elimination approach was guided by both SHAP and statistical correlation evidence. The results of Experiment III are summarized in Table 7, confirming that the removal of the fewest contributing features did not compromise the overall predictive accuracy, and the reduced model achieved comparable performance with a less complex configuration.

Table 7.
Experiment III regression analysis results.
Notably, the tuned (LightGBM + CatBoost) ensemble, when retrained on a SHAP-guided reduced feature count, still maintained strong predicting performance, as indicated by Table 7. With a cross-validated score of 5.79 for MAE, an MSE of 79.36, an RMSE of 8.9, and an R2 score of 0.767, it is still highly competitive compared to its counterpart in Experiment II. The results of Experiment III indicate that eliminating low-impact features did not significantly compromise accuracy, while improving model interpretability and computational efficiency without sacrificing predictive reliability.
4.4. Cross-Validation Analysis of Experiment III
In this section, the effectiveness and robustness of the selected tuned and reduced hybrid ensemble (LightGBM + CatBoost) are investigated via cross-validation and different numbers of folds are examined. In this way, it is possible to identify whether the ensemble’s predictive behavior is consistent and less subject to changes in data partitioning, thus confirming the model’s robustness and generalizability.
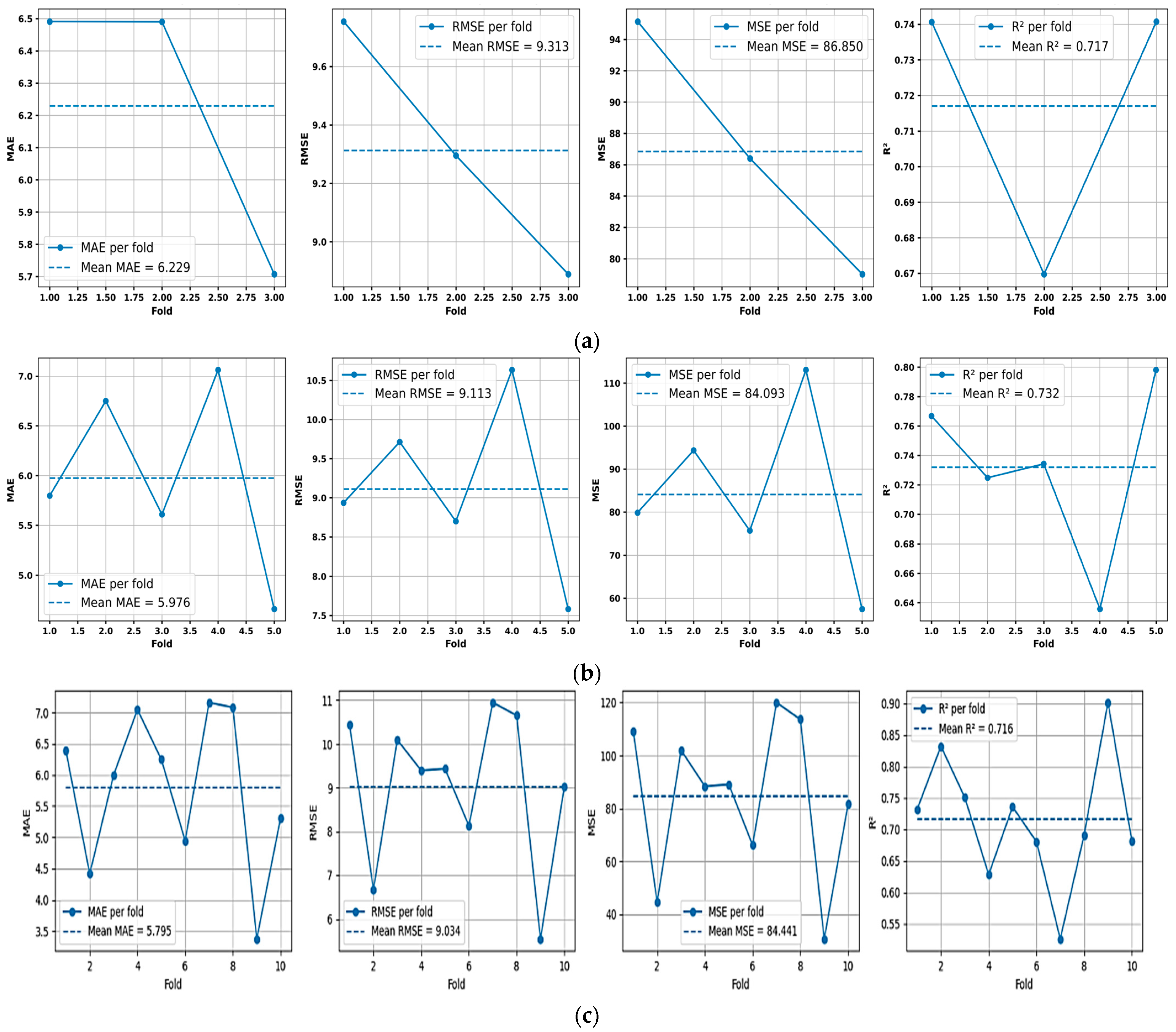
Figure 7 shows the model’s performance with 3, 5, and 10 folds, respectively, which are commonly used values that eliminate any chance of errors from extremely high bias or very high variance [63]. At a value of 3, the tuned hybrid ensemble (LightGBM + CatBoost) showed a consistent performance, with an average MAE of 6.229, an RMSE of 9.313, and an R2 score of 0.717, as observed in Figure 7a. With five folds, the hybrid ensemble performance can be depicted from Figure 7b, with a slightly better average performance than the three-fold case. At five folds, the average MAE was depicted at 5.976, with an RMSE value of 9.113, and an R2 value of 0.732. Finally, at 10 folds, Figure 7c illustrates that the tuned and reduced hybrid ensemble achieves the strongest average predictive performance, with a mean MAE of 5.795, an RMSE value of 9.034, and an average R2 value of 0.716.
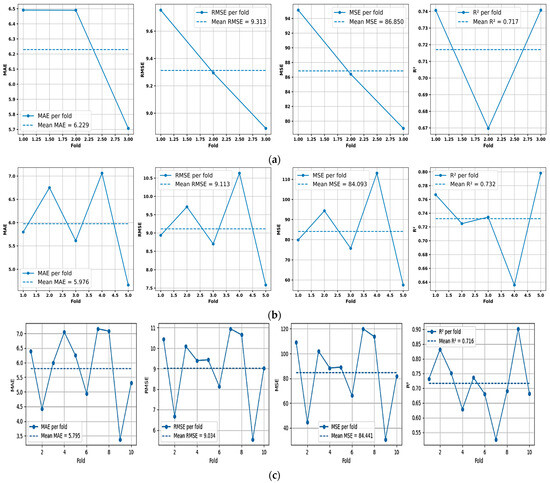
Figure 7.
Tuned and reduced (LightGBM + CatBoost) cross-validation performance, showing, from left to right, MAE, RMSE, MSE, and R2 at (a) 3 folds, (b) 5 folds, and (c) 10 folds.
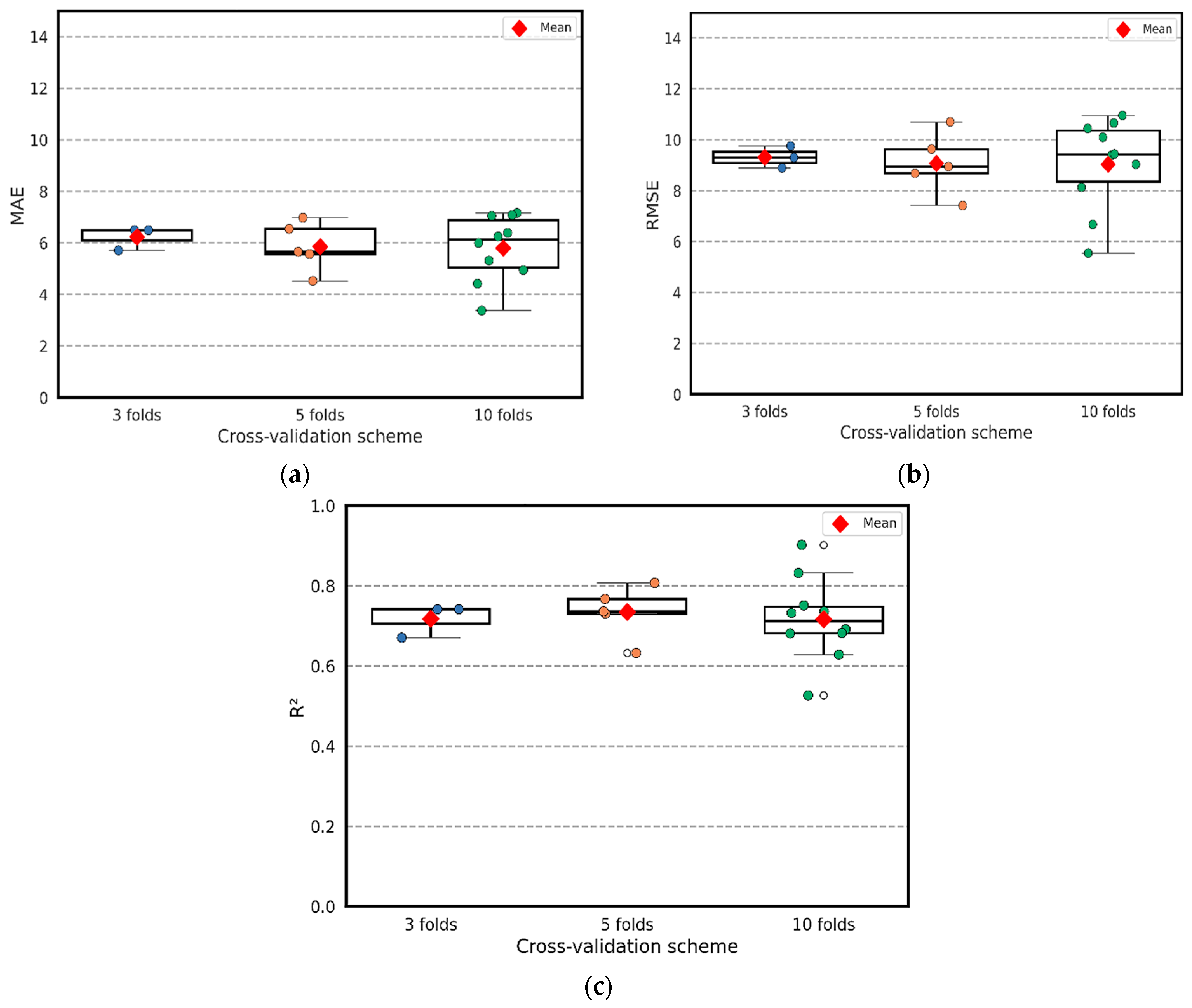
Figure 8 illustrates box-and-whisker plots for the MAE, RMSE, and R2 of multiple seed examinations across the 3-, 5-, and 10-fold configurations. Each jittered dot represents the performance of an individual fold, whereas the box captures the median and interquartile range associated with each CV configuration. It is clear that, across all metrics, the fold-level distributions remain compact, showing no irregular spikes or any unstable behavior in model performance, even with small folds. For MAE, the standard deviations were 0.356, 0.922, and 1.200, corresponding to the 3-, 5-, and 10-fold CV, respectively; RMSE showed moderate variability, with standard deviations of 0.355, 1.201, and 1.650; whereas R2 exhibited tighter dispersion, with standard deviations of 0.033, 0.067, and 0.115. These values demonstrate that even as the number of folds increases, and the training subsets become slightly smaller, the variability across folds remains controlled and well within acceptable limits. In addition, the 10-fold configuration central tendencies remain aligned with those of the 3- and 5-fold schemes. These findings confirm that the tuned and reduced (LightGBM + CatBoost) ensemble is not sensitive to a specific choice of cross-validation scheme, even with a small dataset size. This statistical evidence strongly supports the robustness and repeatability of the proposed hybrid framework.
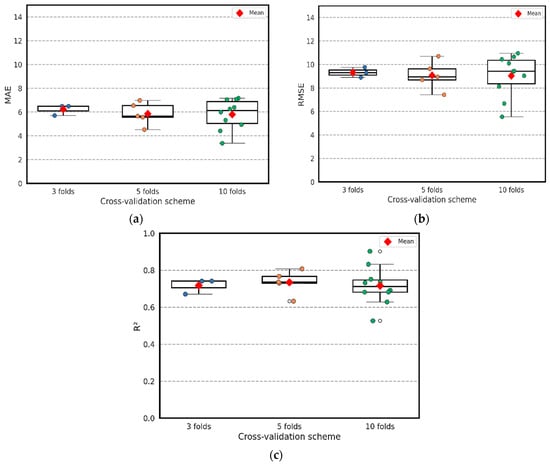
Figure 8.
Per-fold cross-validation performance boxplot for tuned and reduced framework (LightGBM + CatBoost) at (a) MAE, (b) RMSE, (c) R2.
5. Evaluating Model Robustness to Data Imbalance and Noise Injection
This section evaluates the model’s performance robustness and resilience to imbalance in the dataset and noise conditions. These two factors are critical in real-world DGA-based HI prediction, where data scarcity and measurement variability can significantly affect model generalization.
5.1. Data Imbalance
Despite advances in data availability and ML methods, some challenges remain active research topics, one of which is learning from unbalanced datasets, where predictive models must be trained on data in which some values are rarely presented or observed. Although in practice, imbalanced data is a very common problem in field testing, it often causes the learning process to prioritize the majority class and underperform on the minority ones. This leads to poor predictive accuracy for the minority class, which might be the class of the greatest interest. Although data imbalance is a major issue in classification and regression tasks, the former is extensively researched, while the latter is still comparatively underexplored [64]. Although several techniques exist, applying those techniques to continuous variables in regression analysis often imposes several challenges. Commonly, class imbalance regression problems can be handled using algorithm and data-level techniques [65]. The algorithm-level methods involve modifying the learning algorithm itself, in which higher penalties are assigned for minority class samples. Data level approaches often take place during the pre-processing and before the training stage, which can be divided into (i) upsizing the minority class, (ii) downsizing the majority class, and (iii) using a weighted relevance-based combination strategy [66,67]. However, under-sampling is unfavorable as it risks discarding informative samples due to the reduction in data, especially in small, severely imbalanced datasets [67].
Through observation of the studies dataset for transformers DGA, it is shown that the class distribution in Figure 9 demonstrates that the dataset is heavily skewed to the “poor” and “very poor” scores, which can be beneficial for learning degradation patterns and early-warning indicators. However, this skew also introduces a different form of imbalance challenges, in which the model could be naturally biased toward lower HI values and may underperform when estimating higher HI levels (healthy transformers) due to the very low number of samples for very good and good states.
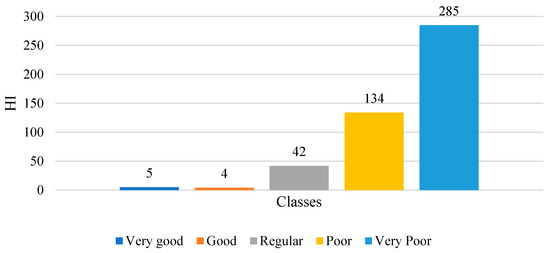
Figure 9.
Distribution of transformer dataset HI classes.
To mitigate this issue and ensure that the model generalizes well across all HI classes, this work explores the utilization of two data imbalance approaches using an adapted synthetic minority over-sampling technique (SMOTE) and weighted sampling technique. These two approaches were conducted on the tuned and reduced hybrid ensemble (LightGBM + CatBoost) of Experiment III, with the aim of determining which strategy effectively improves model performance across underrepresented HI intervals.
5.1.1. Adapted Synthetic Minority Over-Sampling Technique
To address the imbalance across different HI ranges, an adapted regression-based version of SMOTE was implemented in this work, since SMOTE was originally designed for classification tasks. To be able to process the continuous target HI, HI values were discretized into five quantile-based bins, each representing a different segment of the health spectrum, as shown in Table 8. Next, SMOTE was applied to the scaled feature matrix using the binned labels, and synthetic samples were generated in the HI intervals where the number of samples was low (very good and good). When bins contained few samples, the number of nearest neighbors decreased to ensure numerical stability, which thereby balanced the feature space across all five HI intervals. After oversampling, the synthetic samples’ labels were converted back into continuous HI values. Table 8 summarizes the error metrics after five-fold cross-validation for the tuned and reduced hybrid ensemble (LightGBM + CatBoost) model with and without the application of adapted SMOTE for handling imbalances.

Table 8.
Tuned and reduced hybrid ensemble (LightGBM + CatBoost) performance with and without adapted SMOTE.
It can be observed from Table 8 that a substantial degradation in model performance took place after applying the adapted SMOTE. While the baseline hybrid ensemble (LightGBM + CatBoost) achieved an MAE score of 5.81 and a RMSE value of 8.94, the application of SMOTE led to an increase in prediction error MAE ≈ 26.77, RMSE ≈ 30.78, and MSE ≈ 947.419. These indices indicate that the oversampling model obtained a lower and significantly worse performance than the original, non-oversampled version. Possible reasons for this include the introduction of synthetic data, which can lead to class overlap, thus reducing model performance. This degraded performance suggests that the resulting oversampled dataset appears to have distorted the underlying distribution of the features relative to the continuous HI values by forcing the model to learn from synthetic points that may not accurately reflect the true relationships present in the true physical transformer degradation process.
5.1.2. Weighted Regression Technique
To avoid creating synthetic data, a weighted regression strategy was tested on the tuned and reduced hybrid ensemble model (LightGBM + CatBoost). Unlike adapted SMOTE, weighted regression does not alter the dataset by generating any artificial samples; instead, it adjusts the training and learning itself, allowing the model to pay more attention to underrepresented HI regions while still training it entirely on real data. After examining how samples are distributed across the whole HI spectrum, HI values were divided into multiple bins, similar to adapted SMOTE. To compensate for the imbalance, each sample was assigned a weight such that rare HI intervals (good, very good) received higher weights, while frequent intervals (poor, very poor) received lower weights. Thus, weights were inversely assigned according to the HI bin frequency, ensuring that underrepresented health states made higher contributions to the model’s loss function. After that, the calculated weights were passed into the model during training. This allowed for the incorporation of the weighting scheme into the model’s loss calculations, split decisions, and gradient updates. As a result, prediction errors associated with rare HI ranges had a stronger influence on model optimization, while errors in the majority (poor and very poor) ranges received less weight. Table 9 summarizes the error metrics after five cross-validations for the tuned and reduced hybrid ensemble (LightGBM + CatBoost) model with and without the application of the weighted regression technique for imbalance handling.

Table 9.
Tuned and reduced hybrid ensemble (LightGBM + CatBoost) performance with and without weighted regression technique.
Table 9 demonstrates the effectiveness of applying weighted regression on the performance of the tuned and reduced hybrid ensemble model. As mentioned earlier, the model achieved an MAE of 5.811 and an RMSE of 8.938 without any weighting or imbalance handling mechanism. After incorporating sample weights, the model achieved error scores of MAE = 5.943, MSE = 77.140, and RMSE = 8.783, with a corresponding coefficient of determination reaching a value of 0.775. These results indicate that the weighted model enhanced the model’s ability to generalize across the full HI spectrum, particularly in the underrepresented higher-HI ranges, without sacrificing performance in the majority low-HI region. Additionally, since the model was trained on actual, non-synthetic observations, the physical relationships between dissolved gas features and transformer degradation were fully preserved. This led to a more stable learning process and avoided the distortion observed in the SMOTE experiment.
5.2. Noise Injection
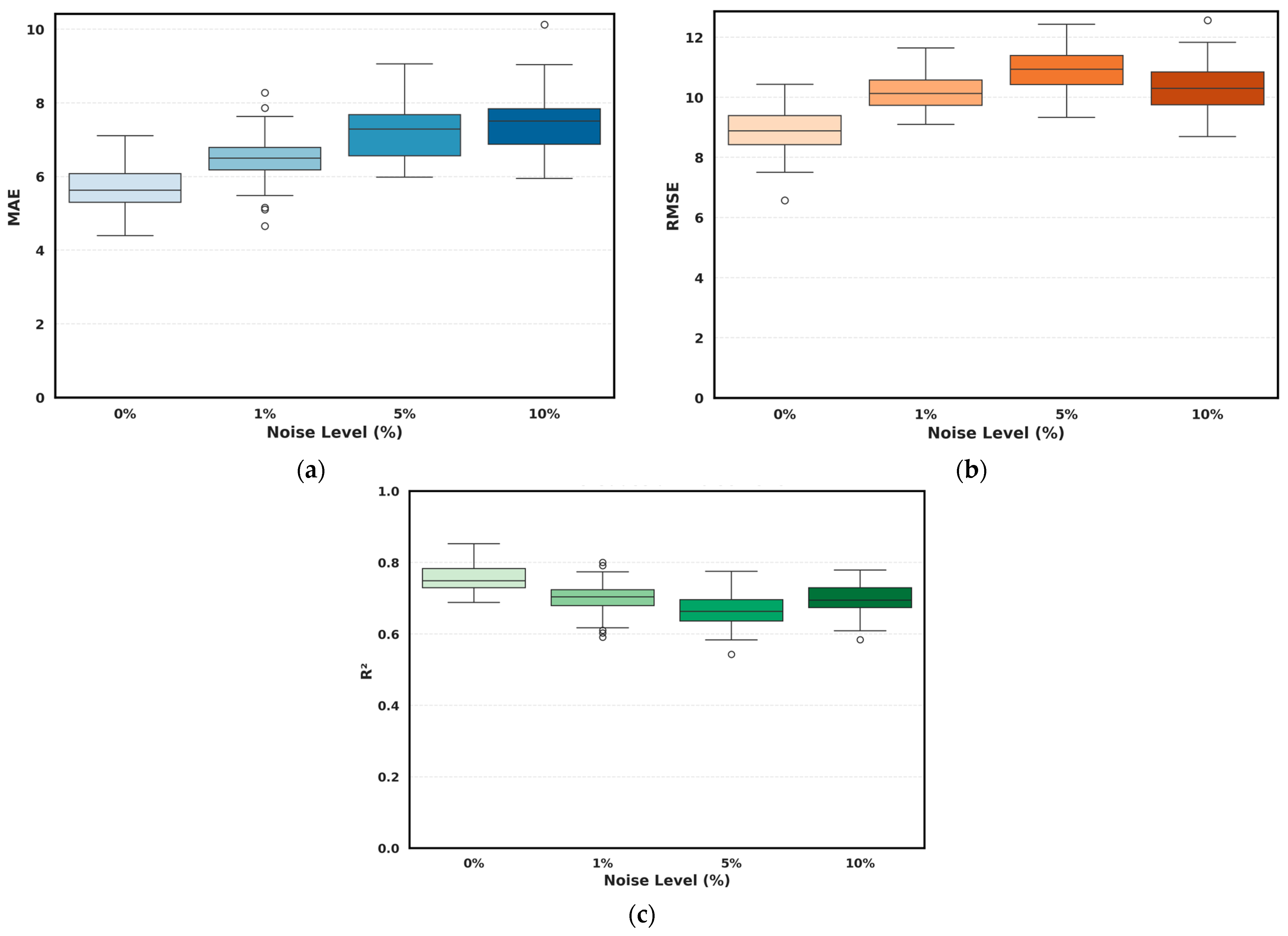
To test the resilience of the proposed framework under different noise levels, the top-performing tuned and reduced hybrid ensemble (LightGBM + CatBoost) model was re-evaluated by introducing Gaussian noise to the input features and analyzing the resulting changes in model accuracy. Gaussian noise was selected to represent random variability from a normal distribution that typically occurs in dissolved gas measurements due to sampling, sensor precision, and laboratory mishandling. Four noise levels were investigated between 10 and 15% in an increasing manner (0%, 1%, 5%, and 10%), with a typically reported range as shown in [68], where 10% noise was chosen as a realistic upper bound. At each noise level, the model was re-trained and evaluated under each noise level, followed by 10 cross-fold validation.
The results in Table 10 show the values for MAE, RMSE, and R2 for HI prediction after adding 1%, 5% and 10% Gaussian noise versus the noise-free condition. An increase in MAE and RMSE is noted, where MAE changed from 5.79 at 0% noise to 7.39 at 10% noise. Similarly, the RMSE score increased from a value of 8.90 at the noise-free condition to 10.347 at the upper noise boundary level of 10%. Additionally, the R2 score dropped from 0.768 to 0.70.

Table 10.
Effect of Gaussian noise on DGA prediction accuracy.
As per Figure 10, the standard deviation, across noise conditions, remained relatively small, reaching a value of 0.711 for MAE, 0.718 for RMSE, and 0.044 for R2, indicating that the predictive performance was largely preserved even under severe noise conditions. The results also confirm that the selected model is robust to realistic levels of random measurement uncertainty.
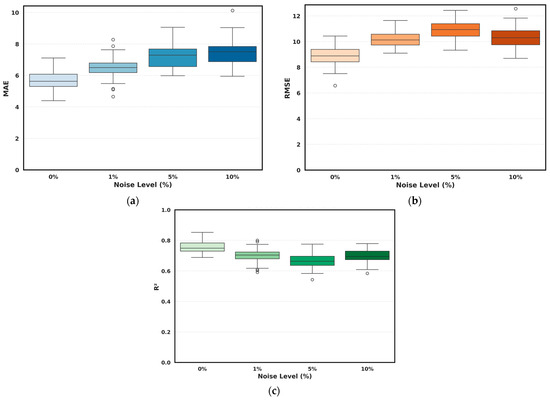
Figure 10.
Effect of Gaussian noise injection on the performance of the tuned and reduced hybrid ensemble (LightGBM + CatBoost) at at (a) MAE, (b) RMSE, (c) R2.
Conclusively, the reported results indicate that while the framework maintains adequate performance, its predictive accuracy declined compared to the original noise-free settings. This underlines the influence of noise on the framework’s performance and highlights the role of measurement uncertainty in practical DGA applications. The model’s performance remained stable across all tested noisy conditions and cross-folds, without any signs of error divergence, which confirms that the approach is not prone to overfitting in the presence of stochastic perturbations. In addition, the consistent trends across noise levels further indicate that the model generalizes reasonably well to imperfect and simulated real-world data. While the analysis was limited to Gaussian perturbations, it confirms that random measurement fluctuations alone do not critically destabilize the model. Further studies and future work should extend the uncertainty beyond Gaussian noise, using larger and more diverse datasets, thereby reflecting multiple transformers in different operating environments, which can be applied to strengthen the framework’s applicability to real field conditions.
6. Discussion
Measuring power transformers HI provides a quantitative evaluation of the overall transformer’s health condition, which can be employed as a viable tool for asset management based on a single index. Through incorporating DGA into HI calculations, the complex chemical byproduct substances due to insulation degradation, overheating, and electrical discharges are translated into a standardized score. The relative concentration and generation rates of these gases provide diagnostic information that reflects the severity and type of fault occurring for a single unit or fleet of transformers. This can provide a robust way to evaluate the asset’s condition, thus supporting maintenance activities and leading to breakdown prevention and system losses.
6.1. Comparison of Performance Among All Experiments
In this work, three sets of experiments were conducted in a progressive manner to evaluate transformer HI prediction. Experiment I served as the baseline for comparative purposes, where a wide range of ML models were applied using all dataset features. This serves as a foundational benchmark of performance across different algorithms. Experiment II improved the model performance through refining the top-performing models from the baseline case via optimized hyperparameter tuning in order to improve generalization, robustness, and predictive accuracy. Finally, Experiment III incorporated SHAP-based feature selection and explainability, thus reducing the model’s complexity while maintaining the model’s accuracy.
Table 11 summarizes all errors, model accuracies, and changes exhibited among the three experimental stages. Experiment I established the reference point for subsequent comparison, utilizing 14 features, and yielding an MAE of 6.09, an RMSE of 9.11, and an R2 score of 0.757 with the hybrid (LightGBM + CatBoost) model. As a result, all subsequent changes recorded in Table 11 were calculated relative to this baseline. Experiment II demonstrated substantial improvement when optimized hyperparameter tuning to the same 14 features took place, reducing the MAE and RMSE by 6.40% and 3.51%, respectively, and improving R2 by 2.25%.

Table 11.
Comparative performance metrics and percentage changes in the three experiments.
Experiment III, which combined tuning with SHAP-based feature reduction with a reduced feature space of 10 features, maintained competitive accuracy with an MAE by 4.93% and with an RMSE by 2.31%, and improved R2 by 1.45% relative to Experiment I, obtaining values very close to those of the tuned full-feature model. Despite a slight RMSE increase relative to Experiment II, the results indicate that feature pruning did not significantly degrade predictive capability. Although these results indicate that the hyperparameter tuning of Experiment II provided the strongest improvements, the reduced 10-feature model in Experiment III preserves most of the gains in accuracy with fewer inputs, demonstrating a favorable balance between predictive performance, complexity, and interpretability.
6.2. Comparisons with Related Studies
Table 12 shows several studies that were conducted using the same dataset, although they differ in modeling scope and methodological objectives. As discussed in Section 2, several studies were conducted using the same transformer dataset, though they vary in their modeling scope and objectives. A number of these works, including [42,43,44], primarily emphasized fault classification or causal reasoning frameworks without reporting quantitative regression performance metrics or any feature selection. Although these approaches provide valuable insights into fault diagnostics and interpretability, their lack of systematic regression benchmarking limits their comparability with quantitative HI predictive models. In contrast, although the work in [50] focused on classification-oriented health index assessment, a PCA for dimensionality reduction was used as a feature selection tool. Alternatively, the authors of [49] present the only work applying regression analysis for the same dataset with a specific focus on CatBoost algorithm and using hyperparameter tuning. With the best recorded performance achieved at a 75:25 split, comparably, their 80:20 results show an error of 6.064 for MAE, an error of 0.755 for R2, an error of 83.989 for MSE, and an RMSE of 9.165. Comparably, the work presented in this study surpasses the results in [49] through achieving better error metrics, higher accuracy, fewer feature counts, and increased model interpretability.

Table 12.
Comparison with related work.
Building on the previous outlook for the same literature utilizing the same dataset, this study provides a more comprehensive evaluation of HI prediction by categorizing models into four families—foundational, kernel-based and tree-based, boosting, and ensembles—and testing them systematically through three structured experiments. In contrast to earlier studies using the same dataset, this work adopts a more balanced approach in terms of accuracy, interpretability, and complexity. The proposed framework was designed to progressively enhance experimental performance by integrating ensembled algorithms, particularly the hybrid (LightGBM + CatBoost) ensemble, with hyperparameter tuning, while reducing model complexity through SHAP-guided feature pruning and ensuring interpretability by utilizing SHAP as an explainability tool and as a feature selection mechanism.
Such methodological advances align with broader sustainability concerns in transformer research, as highlighted in [69], which demonstrate that operational energy losses quickly surpass production-related emissions within 2–3 years of service.
7. Conclusions
Power transformers are critical assets in the transmission sector, and ensuring a reliable electricity supply requires continuous monitoring to detect aging and incipient faults. To bridge the gap between predictive performance and practical usability, this study introduced a progressive multi-experimental framework for transformer HI prediction, combining baseline benchmarking, hyperparameter tuning, and SHAP-guided feature pruning across linear, kernel/tree-based, boosting, and hybrid ensemble models. SHAP was complemented by Pearson correlation to form a dual-stage feature selection strategy, to ensure that the feature pruning process was both statistically relevant and model-driven in its contribution to HI estimation. Among all tested algorithms, the proposed hybrid (LightGBM + CatBoost) ensemble, enhanced through SHAP- and Pearson-based dimensionality reduction, achieved higher accuracy while lowering model complexity and improving interpretability. Compared with the state-of-the-art, which has largely emphasized classification pipelines, single-model regression, or knowledge-graph reasoning without systematic feature pruning, the proposed framework offers both transparency and dimensionality reduction. In addition, while prior studies utilizing the same dataset emphasized classification pipelines, single-model regression, or knowledge-graph reasoning without systematic feature pruning, this work provides superior error metrics, with transparent explanations of model behavior compared to its counterparts. Beyond accuracy improvements, this study also examines how data imbalance and Gaussian noise injection affect HI prediction, thus offering a more realistic representation of real-world DGA measurements, which opens avenues for future research on uncertainty quantification and robustness enhancement. Moreover, by extending transformer lifetime, reducing failures, and minimizing energy losses, improved HI assessment contributes to sustainability-oriented asset management, aligning with recent European LCA findings that highlight the significant environmental impact of transformer operation.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.A.I.; methodology, R.A.I.; software, R.A.I.; validation, R.A.I.; formal analysis, R.A.I.; investigation, R.A.I.; resources, R.A.I.; data curation, R.A.I.; writing—original draft preparation, R.A.I. and A.H.; writing—review and editing, R.A.I. and A.H.; visualization, R.A.I. and A.H.; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work received no funding.
Data Availability Statement
The original data presented in the study are openly available in https://data.mendeley.com/datasets/rz75w3fkxy/1 (accessed on 1 November 2025), DOI: 10.17632/rz75w3fkxy.1.
Acknowledgments
During the preparation of this manuscript, the authors used [ChatGPT-5.2 and Quillbot v38.43.2] for the purposes of [text editing]. The authors have reviewed and edited the output and take full responsibility for the content of this publication.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| ANN | Artificial Neural Networks |
| DGA | Dissolved Gas Analysis |
| DT | Decision Tree |
| GB | Gradient Boosting |
| HI | Health Index |
| MAE | Mean Absolute Error |
| MSE | Mean Squared Error |
| ML | Machine Learning |
| RF | Random Forest |
| RMSE | Root Mean Square Error |
| SHAP | SHapley Additive exPlanations |
| SMOTE | Synthetic Minority over Sampling Technique |
| SVR | Support Vector Regression |
References
- Hebala, A.; Kamel, M.M.; Hamad, M.S. Sustainability-Driven Energy Management Strategies for Reducing Carbon Footprints in Higher Education. Energy Sustain. Dev. 2025, 88, 101783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uniyal, V.; Karn, A.; Singh, V.P. Parametric Optimization of Archimedes Screw Turbine by Response Surface Methodology and Artificial Neural Networks. Renew. Energy Sustain. Dev. 2024, 10, 306–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyo, R.T.; Dewa, M.; Romero, H.F.M.; Gómez, V.A.; Aragonés, J.I.M.; Hernández-Callejo, L. An Adaptive Neuro-fuzzy Inference Scheme for Defect Detection and Classification of Solar Pv Cells. Renew. Energy Sustain. Dev. 2024, 10, 218–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makadia, R.N.; Dave, M.R. Statistical Analysis of Industry Scale Up Draft Coal Gasifier Using Response Surface Methodology for Sustainable Development. Renew. Energy Sustain. Dev. 2024, 10, 294–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, R.A.; Hamad, M.S.; Dessouky, Y.G.; Williams, B.W. A Novel Topology for Enhancing the Low Voltage Ride through Capability for Grid Connected Wind Turbine Generators. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), Raleigh, NC, USA, 15–20 September 2012; pp. 2389–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaber, I.M.; Ibrahim, R.A. Data-Driven Optimal Generation Scheduling Applying Uncertainty in Microgrid. In Proceedings of the 2024 8th International Conference on Green Energy and Applications (ICGEA), Singapore, 14–16 March 2024; pp. 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanfak, A.; Samuel, E.; Fofana, I.; Meghnefi, F.; Ngaleu, M.G.; Kom, C.H. Traditional Fault Diagnosis Methods for Mineral Oil-Immersed Power Transformer Based on Dissolved Gas Analysis: Past, Present and Future. IET Nanodielectrics 2024, 7, 97–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Kim, D.; Chan, K.Y.; Abu-Siada, A. Deep Machine Learning-Based Asset Management Approach for Oil- Immersed Power Transformers Using Dissolved Gas Analysis. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 27794–27809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakzouk, N.E.; Ibrahim, R.A. DC Current-controlled Transductor for Fault Current Limitation in Utility-interfaced PV Systems. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 11th International Conference on Smart Energy Grid Engineering (SEGE), Oshawa, ON, Canada, 13–15 August 2023; pp. 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, R.A.; Zakzouk, N.E. Bi-Functional Non-Superconducting Saturated-Core Inductor for Single-Stage Grid-Tied PV Systems: Filter and Fault Current Limiter. Energy 2023, 16, 4206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, R.A.; Gaber, I.M. Electric Vehicles: From Charging Infrastructure to Impacts on Utility Grid; IOS Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faiz, J.; Soleimani, M. Dissolved Gas Analysis Evaluation in Electric Power Transformers Using Conventional Methods a Review. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2017, 24, 1239–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liao, R.; Yang, L.; Zheng, H.; Sun, C. An Assessment Method for Insulation Condition of Power Transformer Based Upon Cloud Model. Diangong Jishu Xuebao/Trans. China Electrotech. Soc. 2012, 27, 13–20. [Google Scholar]
- Duval, M.; Lamarre, L. The Duval Pentagon-A New Complementary Tool for the Interpretation of Dissolved Gas Analysis in Transformers. IEEE Electr. Insul. Mag. 2014, 30, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoneim, S.S.M.; Farrag, T.A.; Rashed, A.A.; El-Kenawy, E.-S.M.; Ibrahim, A. Adaptive Dynamic Meta-Heuristics for Feature Selection and Classification in Diagnostic Accuracy of Transformer Faults. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 78324–78340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velásquez, R.M.A. A Comprehensive Analysis for Wind Turbine Transformer and Its Limits in The Dissolved Gas Evaluation. Heliyon 2024, 10, e39449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamma, W.R.; Prasojo, R.A.; Suwarno. High Voltage Power Transformer Condition Assessment Considering the Health Index Value and its Decreasing Rate. High. Volt. 2021, 6, 314–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamma, W.R.; Prasojo, R.A.; Suwarno, S. Assessment of High Voltage Power Transformer Aging Condition Based on Health Index Value Considering Its Apparent and Actual Age. In Proceedings of the 2020 12th International Conference on Information Technology and Electrical Engineering (ICITEE), Yogyakarta, Indonesia, 6–8 October 2020; pp. 292–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rediansyah, D.; Prasojo, R.A.; Suwarno; Abu-Siada, A. Artificial Intelligence-based Power Transformer Health Index for Handling Data Uncertainty. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 150637–150648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeinoddini-Meymand, H.; Vahidi, B. Health Index Calculation for Power Transformers using Technical and Economical Parameters. IET Sci. Meas. Technol. 2016, 10, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velásquez, R.M.A.; Lara, J.V.M.; Melgar, A. Converting Data into Knowledge for Preventing Failures in Power Transformers. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2019, 101, 215–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eweda, M.M.; ElNaggar, K. Reinforcement learning for autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs): Navigating challenges in dynamic and energy-constrained environments. Robot. Integr. Manuf. Control. 2024, 1, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fawzy, H.; Elbrawy, A.; Amr, M.; Eltanekhy, O.; Khatab, E.; Shalash, O. A Systematic Review: Computer Vision Algorithms in Drone Surveillance. Robot. Integr. Manuf. Control. 2025, 2, 3009–7967. [Google Scholar]
- Elagan, S.A.; Elkhodary, G.E.; Amer, S.K.; Elsayed, Z.M.; Hesham, O.A.; Hanafy, H. RAFEQI Design and Implementation of a Cost- Effective Personal Assistant Robot. Robot. Integr. Manuf. Control. 2025, 2, 11–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Den, M.B.; Hebala, A. Challenges in Closing the Gap between Software and Hardware in Robotics. Robot. Integr. Manuf. Control. 2024, 1, 11–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrauf, A.A.; Saad, W.W.; Hebala, A.; Galea, M. Model Predictive Control Based PID Controller for PMSM for Propulsion Systems. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Electrical Systems for Aircraft, Railway, Ship Propulsion and Road Vehicles & International Transportation Electrification Conference (ESARS-ITEC), Nottingham, UK, 7–9 November 2018; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Recalde, A.A.; Lukic, M.; Hebala, A.; Giangrande, P.; Klumpner, C.; Nuzzo, S.; Connor, P.H.; Atkin, J.A.; Bozhko, S.V.; Galea, M. Energy Storage System Selection for Optimal Fuel Consumption of Aircraft Hybrid Electric Taxiing Systems. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2020, 7, 1870–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebala, A.; Abdelkader, M.I.; Ibrahim, R.A. Comparative Analysis of Energy Consumption and Performance Metrics in Fuel Cell, Battery, and Hybrid Electric Vehicles Under Varying Wind and Road Conditions. Technologies 2025, 13, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebala, A. Battery Electric Vehicle Performance Analysis Under Varying Wind and Road Slope Conditions. In Proceedings of the 2025 IEEE Workshop on Electrical Machines Design, Control and Diagnosis (WEMDCD), Valletta, Malta, 9–10 April 2025; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, U.M.; Fofana, I.; Rajesh, K.N.V.P.S.; Picher, P. Identification and Application of Machine Learning Algorithms for Transformer Dissolved Gas Analysis. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2021, 28, 1828–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, S.A.; Rana, A.S.; Sohail, S.; Rahman, O.; Parveen, S.; Khan, S.A. Advances in DGA based condition monitoring of transformers: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 149, 111347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, I.B.M.; Hoballah, A.; Ghoneim, S.S.M. Optimal Ratio Limits of Rogers’ Four-Ratios and IEC 60599 Code Methods Using Particle Swarm Optimization Fuzzy-Logic Approach. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2020, 27, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacha, K.; Souahlia, S.; Gossa, M. Power Transformer Fault Diagnosis Based on Dissolved Gas Analysis by Support Vector Machine. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2012, 83, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.C.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, M. Transformer Dissolved Gas Analysis for Highly-Imbalanced Dataset Using Multiclass Sequential Ensembled ELM. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2023, 30, 2353–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoneim, S.S.M.; Taha, I.B.M.; Elkalashy, N.I. Integrated ANN-based Proactive Fault Diagnostic Scheme for Power Transformers using Dissolved Gas Analysis. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2016, 23, 1838–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, S.A.; El-Faraskoury, A.; Badawi, M.; Ibrahim, S.A.; Mahmoud, K.; Lehtonen, M.; Darwish, M.M.F. Towards Precise Interpretation of Oil Transformers via Novel Combined Techniques Based on DGA and Partial Discharge Sensors. Sensors 2021, 21, 2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matzka, S. Explainable Artificial Intelligence for Predictive Maintenance Applications. In Proceedings of the 2020 Third International Conference on Artificial Intelligence for Industries (AI4I), Irvine, CA, USA, 21–23 September 2020; pp. 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, W.; Wang, T.; Wu, Y.; Chen, L.; Zeng, M.; Yang, J.; Hu, N.; Zhang, B.; Xuan, F.; Yang, Z. Robust Odor Detection in Electronic Nose Using Transfer-Learning Powered Scentformer Model. ACS Sens. 2025, 10, 3704–3712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeinoddini-Meymand, H.; Kamel, S.; Khan, B. An Efficient Approach with Application of Linear and Nonlinear Models for Evaluation of Power Transformer Health Index. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 150172–150186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Chen, R.; Zhang, C.; Chen, M.; Li, X.; Ma, G. Dynamic Fault Prediction of Power Transformers Based on Lasso Regression and Change Point Detection by Dissolved Gas Analysis. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2020, 27, 2130–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Wu, Z.; Liu, C. Health index prediction of dissolved gases in transformer oil based on statistical distribution model. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Energy, Power and Electrical Engineering (EPEE2021), Jilin, China, 24–26 September 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velásquez, R.M.; Lara, J.V. Root Cause Analysis Improved with Machine Learning for Failure Analysis in Power Transformers. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2020, 115, 104684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Gil, J.; Buchgeher, G.; Gabauer, D.; Freudenthaler, B.; Filipiak, D.; Fensel, A. Root Cause Analysis in the Industrial Domain using Knowledge Graphs: A Case Study on Power Transformers. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2022, 200, 944–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhetri, T.R.; Aghaei, S.; Fensel, A.; Göhner, U.; Gül-Ficici, S.; Martinez-Gil, J. Optimising Manufacturing Process with Bayesian Structure Learning and Knowledge Graphs. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics; Springer Science and Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 594–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, M.; Cao, Y.; He, G.; Feng, L.; Tan, Z.; Mo, W.; Fan, J. Dissolved gas in transformer oil forecasting for transformer fault evaluation based on HATT-RLSTM. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2023, 221, 109431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hechifa, A.; Dutta, S.; Lakehal, A.; Illias, H.A.; Nanfak, A.; Labiod, C. Enhancing power transformer health assessment through dimensional reduction and ensemble approaches in Dissolved Gas Analysis. IET Nanodielectrics 2024, 7, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Zhang, M.; Chen, W.; Wang, Z. Transformer Fault Diagnosis Utilizing Feature Extraction and Ensemble Learning Model. Information 2024, 15, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogos, A.S.; Liang, X.; Chung, C.Y. Enhancing Transformer Health Index Prediction Using Dissolved Gas Analysis Data Through Integration of LightGBM and Robust EM Algorithms. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 108472–108483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalla, K.R.; Rao, B.; Prasanth, G.T.; Harshavardhini, R.; Keertana, P.; Palle, S. Advanced Health Index Prediction for Transformers Using CatBoost Algorithm. Cuest. Fisioter. 2024, 53, 2161–2176. [Google Scholar]
- Emme, S.S.; Moola, P.R. Application of Data Science Techniques and Machine Learning based classifiers for Transformer Health Assessment. Iraqi J. Sci. 2025, 66, 2581–2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Rashidy, N.; Sultan, Y.A.; Ali, Z.H. Predicting Power Transformer Health Index and Life Expectation based on Digital Twins and Multitask LSTM-GRU Model. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yang, W. Transformer Fault Diagnosis using Machine Learning: A Method Combining SHAP Feature Selection and Intelligent Optimization of LGBM. Energy Inform. 2025, 8, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, J.M.L.R. Mendeley Data. Data for: Root Cause Analysis Improved with Machine Learning for Failure Analysis in Power Transformers. Available online: https://data.mendeley.com/datasets/rz75w3fkxy/1 (accessed on 17 September 2025).
- Velásquez, R.M.; Lara, J.V. Corrosive Sulphur effect in power and distribution transformers failures and treatments. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2018, 92, 240–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEEE. IEEE Guide for Acceptance and Maintenance of Insulating Mineral Oil in Electrical Equipment; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, I.; Liu, K.; Yamamoto, T.; Zahid, M.; Jamal, A. Modeling of Machine Learning with SHAP Approach for Electric Vehicle Charging Station Choice Behavior Prediction. Travel. Behav. Soc. 2023, 31, 78–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, S.; Huang, S.; Bu, W.; Ge, X.; Chen, H.; Liu, J.; Luo, J. LightGBM Low-Temperature Prediction Model Based on LassoCV Feature Selection. Math. Probl. Eng. 2021, 2021, 1776805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.M.; Kim, J.; Kim, K. Ensemble Machine Learning of Gradient Boosting (XGBoost, LightGBM, CatBoost) and Attention-Based CNN-LSTM for Harmful Algal Blooms Forecasting. Toxins 2023, 15, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancock, J.T.; Khoshgoftaar, T.M. CatBoost for Big Data: An Interdisciplinary Review. J. Big Data 2020, 7, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muqtadir, A.; Li, B.; Ying, Z.; Songsong, C.; Kazmi, S.N. Nowcasting the Next Hour of Residential Load using Boosting Ensemble Machines. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 7157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, N. Power Transformer Health Condition Evaluation: A deep Generative Model Aided Intelligent Framework. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2023, 218, 109201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, X.; Cui, Y.; Li, H. Review of Transformer Health Index from the Perspective of Survivability and Condition Assessment. Electronics 2023, 12, 2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nti, I.K.; Nyarko-Boateng, O.; Aning, J. Performance of Machine Learning Algorithms with Different K Values in K-fold CrossValidation. Int. J. Inf. Technol. Comput. Sci. 2021, 13, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavas, R.D.; Das, M.; Ghosh, S.K.; Pal, A. Spatial-SMOTE for Handling Imbalance in Spatial Regression Tasks. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2023, 83, 14111–14132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husain, G. SMOTE vs. SMOTEENN: A Study on the Performance of Resampling Algorithms for Addressing Class Imbalance in Regression Models. Algorithms 2025, 18, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avelino, J.G.; Cavalcanti, G.D.C.; Cruz, R.M.O. Resampling Strategies for Imbalanced Regression: A Survey and Empirical Analysis. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2024, 57, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocksieker, S.; Pommeret, D.; Pommeret, D.A. A Comprehensive Survey on Imbalanced Regression: Definitions, Solutions, and Future Directions. Available online: https://huggingface.co/datasets/samgohan/Tabular_Imbalanced_Regression (accessed on 1 November 2025).
- Bouzar, M.; Fofana, I.; Rebaïne, D. Improving the Reliability of Dissolved Gas Analysis (DGA) Diagnostics Through Consideration of Measurement Device Uncertainty. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2025, 32, 2424–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piotrowski, T.; Markowska, D. Carbon Footprint of Power Transformers Evaluated Through Life Cycle Analysis. Energies 2025, 18, 1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.