Abstract
The mobile network ecosystem is undergoing profound change driven by Artificial Intelligence (AI), Network Function Virtualization (NFV), and Software-Defined Networking (SDN). These technologies are well positioned to enable the essential transformation of next-generation networks, delivering significant improvements in efficiency, flexibility, and sustainability. AI is expected to impact the entire lifecycle of mobile networks, including design, deployment, service implementation, and long-term management. This article reviews the key characteristics of 5G and the anticipated technology enablers of 6G, focusing on the integration of AI within mobile networks. This study addresses several perspectives, including network optimization, predictive analytics, and security enhancement. A taxonomy is proposed to classify AI applications into 5G and 6G according to their role in network operations and their impact across vertical domains such as the Internet of Things (IoT), healthcare, and transportation. Furthermore, emerging trends are discussed, including federated learning, advanced AI models, and explainable AI, along with major challenges related to data privacy, adaptability, and interoperability. This paper concludes with future research directions, emphasizing the importance of ethical AI policies and cross-sector collaborations to ensure effective and sustainable AI-enabled mobile networks.
1. Introduction
1.1. Motivation
Broadly, Artificial Intelligence (AI) refers to machines that imitate intelligent behaviours that normally require human intervention. These intelligent actions include logical reasoning, personal development, problem solving, learning, etc. The origins of AI date back to 1950, when Alan Turing developed the Turing test, a tool for assessing a machine’s ability to reproduce intelligent behaviour typical of a human being [1]. However, today’s AI is far more advanced than Turing ever imagined. It encompasses a variety of sub-fields, such as machine learning, natural language processing, robotics and computer vision, to name but a few. Whatever the sector of activity concerned, the ultimate objective is generally the same: to build models from data, exploit them and, ultimately, make informed decisions on the basis of these same models. The relationship between AI and mobile networks can be conceptualised as a tree [2]. AI is the main trunk, while various technical fields, such as machine learning and its various offshoots, such as deep learning and reinforcement learning, among others, form the roots [3,4].
AI and modern mobile networks have a mutually beneficial relationship: AI drives network efficiency, automation and security, while advanced mobile connectivity provides the high-speed, low-latency infrastructure needed to manage AI-enabled applications and services [5]. Machine learning, a subset of AI, plays a central role in modern mobile networks. It is applied in advanced systems and devices to optimise virtual reality and Internet of Things (IoT) services. It also helps ensure quality of service, strengthen security, address synchronisation issues, and support many other critical tasks. AI solutions are resource and energy efficient, and do not require specialized hardware requirements such as high computing power or high resolution to be natively integrated into the network. These solutions, when fully integrated into the network, bring real benefits for 5G and future networks. They help tackle key challenges such as the synchronization of advanced multiple access schemes, network security, traffic analysis, IoT device management, and support for virtual reality applications [6,7,8].
Rapidly evolving technologies have also led to advances in the mobile network sector. The evolution of mobile networks is fascinating, from their fundamental versions to contemporary generations. Overall, the evolution of wireless networks is responding to the growing demands of users and their applications. Innovative services come first, followed by the emergence of new network functionalities. Today’s mobile network still requires an operating model that involves manual intervention. For example, network operators monitor radio quality and the associated load, and sometimes have to reconfigure the network.
1.2. State of the Art and Research Gaps
The literature offers insightful, in-depth analyses of particular technological fields, such as AI-enabled digital twins for 6G [9], sophisticated deep learning models [10], and AI frameworks for proactive network management [11], although it is still mainly dispersed. Surveys frequently focus on specific applications, such as satellite-based non-terrestrial networks [12], the Metaverse [13], or security in network slicing [14], leading to a segmented viewpoint. Broader overviews sometimes lack a cohesive, comprehensive framework that integrates these disparate technology strands, even while they address 6G’s prospects and problems [15] or provide basic roadmaps for AI integration [16]. Additionally, an emphasis on discrete AI paradigms, like deep reinforcement learning, limits a lot of research without combining the potential for synergy between convergent paradigms such as edge intelligence, explainable AI (XAI), and federated learning [17].
In order to provide a coherent roadmap for the future of intelligent mobile networks, it is necessary to address these gaps through a multifaceted taxonomy that not only unifies the disparate architectural visions and application domains of 5G and 6G, but also offers a structured framework to navigate the complex interactions between technologies, operational difficulties, and ethical considerations. Several important research gaps that need to be addressed include:
- Lack of a thorough analysis of the network lifetime from 5G to 6G.
- Restricted organized taxonomies that connect operations, applications, and technology.
- Understudied new AI paradigms and their implications for operations and ethics.
- Applications are not fully covered, and there is no cross-domain integration.
- Ignored social and practical factors, such as ethics, energy, and interoperability.
By providing a comprehensive, multifaceted examination of AI for 5G and 6G networks, our survey seeks to close these gaps by bringing to light new paradigms, real-world uses, moral dilemmas, and cross-domain synergies that have not been covered collectively in previous research.
1.3. Contributions of This Survey
Our primary goal is to explore how mobile wireless communications can evolve towards a future where virtual presence becomes a tangible reality, unlocking broad economic and research opportunities. This vision includes not only improved network reliability and much lower latency, which make live virtual reality experiences possible, but also the emergence of transformative applications such as autonomous driving and advanced cellular sensing technologies [18,19].
Building on this vision, our survey offers a comprehensive and systematic examination of AI’s role in shaping 5G and 6G networks. Unlike many studies that concentrate on isolated AI techniques or specific use cases, we adopt a broad, multi-dimensional approach that captures the full spectrum of AI integration in mobile networks. Specifically, we:
- Develop a detailed taxonomy that classifies AI applications across multiple axes from network technology and functionality, through operational impacts, to diverse application domains, integration models, and stages in the network lifecycle. This structure provides clarity in understanding the complex interactions at play.
- Shed light on emerging AI paradigms such as federated learning, which allows for collaborative model training without compromising data privacy; Edge AI, which pushes intelligence closer to users for faster and more efficient processing; and explainable AI, which is critical for transparency and trust in automated network decisions.
- Identify and discuss key challenges including data protection concerns, energy consumption constraints, and interoperability issues, which are crucial for the practical deployment of AI in mobile networks.
- Outline future research directions, emphasizing the ethical considerations involved in AI adoption, as well as the growing convergence of AI with other technological domains like the Internet of Things and immersive reality systems.
Our survey is intended as a valuable resource for researchers, engineers, and decision-makers alike, offering both a panoramic view of the AI landscape in wireless communications and a roadmap for future innovations that will help realize the promise of a truly intelligent and immersive mobile network environment. As summarized in Table 1, a comparative analysis of the literature reveals a field fragmented into highly specialized studies, underscoring the need for a holistic framework.

Table 1.
Comparative analysis of key surveys on AI in 5G and 6G Networks.
1.4. Paper Organization
The structure of this article is as follows: Section 2 details the key concepts of 5G and 6G networks, Section 2.2.3 examines the incorporation of AI into these infrastructures through an in-depth classification, while Section 4 highlights the recent developments, challenges and future prospects of this technological fusion. Figure 1 illustrates the complete visual structure of our paper.
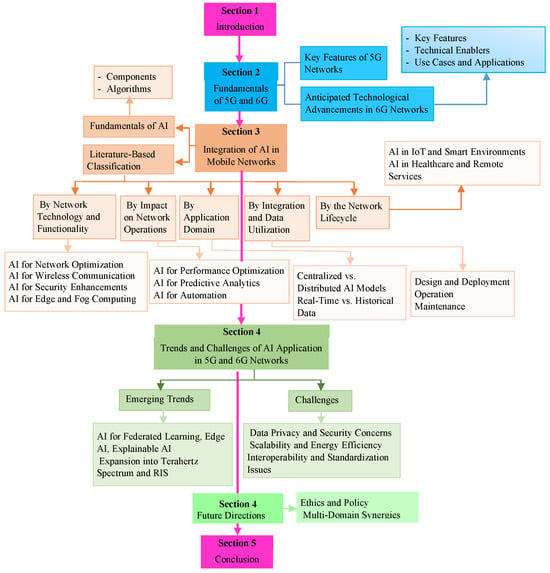
Figure 1.
Structure of the paper.
2. Fundamentals of 5G and 6G Technologies
5G technology has improved network capabilities with evolved radio access and flexibility features, including virtualisation, software-defined networking and cloud-native architecture. With its unique capabilities, 5G has leveraged the network infrastructure to consider future network designs based on cloud-native network functions virtualisation systems. These systems offer more robust deployment and significantly lower operating costs than those based exclusively on physical systems.
In addition, 5G technology has failed to meet the urgent needs of real-time applications, such as tactile internet, real-time assisted driving and telemedicine. To meet these requirements, promising joint operations between 5G technology and intelligence technologies, including artificial intelligence and machine learning, are expected to evolve 5G networks to deliver ultra-reliable low-latency communications and extreme throughput services.
6G technology, currently under development, aims to create an ecosystem where objects can learn, adapt their behaviour to their environment and collaborate to optimise data processing and production without human intervention, by harnessing the intelligence of the network. 6G is expected to bring new breakthroughs due to AI and machine learning technologies, not only for energy-efficient, reliable and scalable communication services, but also for sensing, perceiving, organising, controlling and managing the environment. These specific features will foster the emergence of innovative applications, including the full realisation of intelligent cities, environments and lives, reinforcing the integration of communication technologies into the real world.
2.1. Key Features of 5G Networks
The global mobile communications network has evolved over the past decades through continuous innovation, investment and research. The fifth generation (5G) cellular mobile communications network is the latest globally accepted network standard. It was introduced in 2018 after several years of evolution of mobile communications from 1G to 4G, with significant improvements in performance and applications compared to previous generations. Compared to 4G, 5G offers increased data rates, reduced latency, improved reliability, massive connectivity and increased system capacity through the integration of pre-5G and non-orthogonal multiple access concepts, as well as dense, small and closed cells. 5G has been in the global market on a large scale since early 2019 and continues to grow. Many countries have deployed 5G, and competition is fierce to establish the most extensive 5G network. However, 5G continues to make progress in various areas of research and has many other aspects that require significant advances for its full development. Figure 2 illustrates the use cases of 5G with corresponding Key Performance Indicators: eMBB (Enhanced Mobile Broadband), mMTC (Massive Machine-Type Communications) and URLLC (Ultra-Reliable and Low Latency Communications).
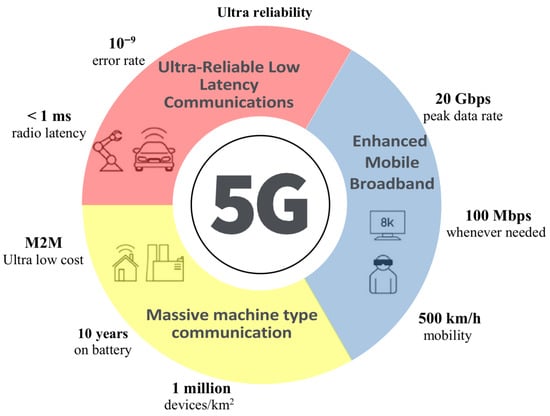
Figure 2.
Illustration of 5G use cases.
2.1.1. Use Cases
Today, several studies recognise that the next step in the evolution of telecommunications worldwide is 5G mobile access technology, which is expected to cover a wide spectrum of applications such as IoT, smart city management, healthcare services, virtual reality and entertainment [20,21,22]. A series of functionalities and requirements have been implemented in the 5G network. The main goals are related to high bit rate, low latency, high density allowing for a large number of devices per km2 and high spectral efficiency.
Due to the diversity of applications that 5G aims to serve and the heterogeneity of their QoS requirements, three main classes of services have been established: eMBB, mMTC and URLLC. eMBB [23], which stands for enhanced Mobile Broadband, aims to guarantee high data rates and increased network capacity compared to previous networks, enabling new entertainment, augmented reality and virtual reality experiences. mMTC [24] which stands for ‘massive Machine-Type Communications’, is a category of services present in Internet of Things applications, mainly used when the network needs to interconnect a large volume of devices to transmit small amounts of data with low energy consumption. URLLC [25] aims to achieve certain unique ultra-reliable machine-type services. The 5G network must offer a wide variety of requirements for multiple different use cases.
2.1.2. Network Slicing
Another key characteristic of the 5G architecture is the network slicing concept [26]. The idea behind network slicing is to build multiple virtual networks on a single physical network. It is possible to create a dedicated network slice according to the user’s needs. For example, for machine-to-machine communications, a slice can be created for automotive, transport, infrastructure, industry or even healthcare. For human-to-human communications, virtual network slices can be created for 3D video, data transfer at best, live video broadcasting, or even voice with minimal quality of service. The functionality of each slice can range from the virtual client function provided to its end customers to real network elements. A network slice consists of three main parts: the connectivity slice, the compute slice and the storage slice. These slices can be instantiated sequentially and in parallel as required. Independent QoS parameters can be used for each slice [27].
2.1.3. Beamforming and Massive MIMO
Massive MIMO and beamforming are two advanced antenna technologies that have become extremely popular in the 5G stringent 5G standards. Beamforming is a technique based on multiple antennas to direct signals to specific users, increasing signal strength and reducing interference with other users. Massive multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) systems operate on the same basic principle of directing signals to intended users, but use a large number of antennas at the base station, increasing spectral efficiency and network capacity. Beamforming has huge potential to improve the quality of the user experience and network performance. One of the main reasons for focusing research on Massive MIMO is the ongoing evolution of the technology. Beamforming and Massive MIMO are fundamental aspects of 5G standards and can offer significant performance benefits [28,29,30].
2.1.4. Edge Computing and Cloud-Native Infrastructure
Edge computing is a network approach aimed at bringing computing and data storage closer to where they are needed, i.e., the source of the data [31]. Wired and wireless networks are used to transmit data between sources and destinations; the aim of edge computing is to process data at the edge of the network, close to the source. This approach has the advantage of reducing latency, which in turn reduces network load and increases response times for real-time applications. Edge computing is enabled by 5G infrastructure; for example, modern 5G small cells installed in streetlights are standard access nodes in the 5G network and provide compute capacity for computation and data storage [32]. Cloud-native infrastructure in 5G refers to a network fabric that leverages cloud concepts, where network functions are implemented as encapsulated microservices, managed by platforms such as Kubernetes. It offers dynamic scalability, sophisticated automation and increased resilience, improving resource management and the efficiency of the 5G network. Integrating Edge Computing with native cloud technology removes the functional boundaries between Edge and logically centralised systems, allowing applications to run on the infrastructure without modification. The benefits of this approach are: dynamic scalability of computing power; development, deployment and management of scalable, high-performance applications; and accelerated time-to-market using a standard 5G network. The key features that differentiate 6G networks from their predecessors are summarised as follows. They include ultra-reliable low-latency communication with latency of 0.1 to 1 ms. The Internet of Behaviour and the Internet of Everything are also fundamental. 6G supports diverse types of communication, including human-machine communication, machine-machine communication, holographic communication, haptic communication, and advanced multimedia. Scalability and adaptability are essential aspects of these networks. Energy efficiency is greatly improved, up to 1000 times higher than previous generations. Finally, 6G networks provide resilience to security attacks and ensure privacy preservation. times improved energy efficiency, resilience to security attacks and privacy preservation [33,34,35,36].
2.2. Anticipated Technological Advancements in 6G Networks
The development of 6G networks is a complex endeavor that encompasses standardization, industrial projects, and infrastructure deployment. These aspects are crucial to harnessing the full potential of 6G in transforming mobile communication systems. In these initiatives, the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) and other global organizations play a central role, with the goal of publishing international standards before 2030. This process requires cross-sector collaboration to ensure that 6G meets the diverse needs of future digital societies. In the following, we discuss the key elements of 6G standardization, industrial initiatives, and reference frameworks. The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) is leading the standardization initiatives for 6G, with the IMT-2030 framework serving as the central component. This framework outlines the technological evolutions and future requirements for terrestrial IMT systems toward 2030 and beyond [37]. Figure 3 summarizes the key milestones and timeline for 6G standardization. Table 2 provides an overview of the key 6G technologies and their benefits, showing how 6G is expected to enhance performance across multiple dimensions and deliver significant value.
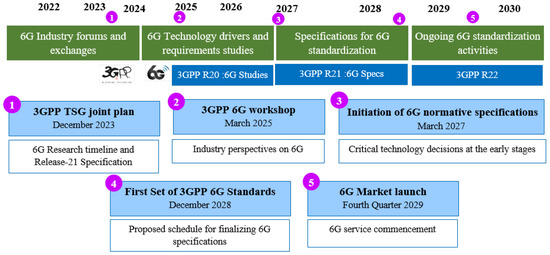
Figure 3.
6G standardization timeline.

Table 2.
Key technologies and benefits for 6G networks.
Several trends are expected to drive this progression, including: the expansion of AI and data analytics; the crucial importance of the network in enabling various applications in society; the future emergence of specific market demands and associated application scenarios; and the gradual trend towards limiting the energy consumption of communications networks. The planned targets for 6G connectivity are ambitious and include a peak user throughput of at least 1 Tbit/s; radio interface latency of no more than 100 μs; provision of spectrum in excess of 1 THz; 100 times higher density of connected devices compared to 5G; and integration of communication, sensing and location technologies [38].
2.2.1. Key Features of 6G Networks
6G networks will be very different from previous generations of communications networks. They are characterised by key features such as ultra-reliable, low-latency communications, throughput improvements of tens of gigabits per second, increased energy efficiency for long battery life, the ability for a trillion devices to meet IoT requirements, support for diverse types of communication, scalability and adaptability to dynamically changing application requirements, resilience to security attacks and privacy protection. Finally, they have the ability to adapt quickly to new trends. To realise these key differentiating characteristics, 6G networks would require fundamental reform of existing technologies, regulatory frameworks and lifestyles [39]. Figure 4 summarises the fundamental characteristics of 6G technology.
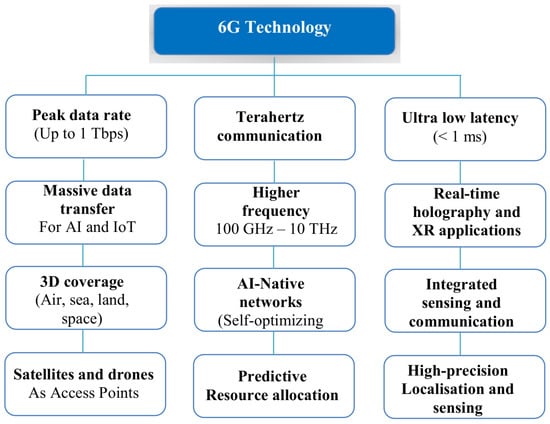
Figure 4.
The fundamental characteristics of 6G technology.
2.2.2. Technical Enablers for 6G Networks
A natural extension of existing 5G networks, 6G networks are expected to offer enhanced connectivity to support innovation in smart applications and the associated industrial sector. A number of technical tools are currently being investigated as part of the research, and are expected to be adopted or deployed in some form to ensure 6G continuity and meet the stringent KPI targets for these systems. The first technical tool that will underpin the functionality of the 6G network is advanced antenna technologies, typically based on smart structures, advanced materials or software-controlled antennas. While some of these antenna technologies are already at an advanced stage of implementation or development, such as smarter MIMO, large smart antennas and visible light communication, related advances are expected to pave the way for further improvements in energy efficiency, radiation pattern control and secure communication [40,41,42].
The second technical enabler supporting future connectivity aims to address several gaps in the current technology infrastructure, while developing advanced 4G and 5G mobile communication systems at lower operating frequencies, known as terahertz communication [43,44].
The third category of enablers for 6G networks is expected to build on trends already visible with current 4G and 5G telecommunications systems. These are essentially network management enablers such as adaptive networks, network virtualisation and slicing. However, for 6G, this will also need to be carried out on a much larger scale, and involve artificial intelligence and machine learning much more strongly and directly in the day-to-day management of the network and the ongoing optimisation of its performance.
So, the applications we hope to be able to run on 6G include: Fully Augmented or virtual reality, but capable of supporting many remote users at the same time [45]; Haptic communication applications [46]; High density wireless networks for downloading or uploading VR/AR content [47]; Social holographic experiences, including concerts or conferences [48]; Cloud gaming to provide the ability to perform computation on the user’s device or to be enabled for part of the gaming experience at the edge of the network [49]; Users and/or industry adopting many more advanced computing applications and services, using wireless connectivity to connect to the advanced cloud [50]; Industries deploying ultra-reliable, low-latency services requiring very low network latency with full service level agreements [51]; Industries using the ability to use the reach of the satellite network for coverage and anchor their own local network with that for a predictable service level agreement [12]; Industries deploying battery-powered Internet of Things devices and/or sensor networks with low power consumption and low bandwidth that can remain operational in poor environmental conditions [52].
2.2.3. Use Cases and Applications of 6G Networks
6G networks require the integration of various advanced technical tools to become a key driver of low latency, high reliability communications. Enhanced AR/VR QoE, intelligent communications for highly automated driving, ambitious long-range communications for rural areas, industrial automation, large-scale robotics, wireless access networks (FANs), self-optimising industrial zones and integrator-driven XR collaborative platforms are essential.
In addition to 6G requirements and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), advances in technical tools and the scientific findings mentioned above will refine the functionality and percentage of communication features required, for example energy and spectrum efficient technologies. The applications associated with 6G technology are numerous, with a plethora of proposals currently being studied.
Immersive holographic communication modalities, encompassing three-dimensional holograms and metaverse applications, represent a significant advance in user interaction [53]. The concept of the Internet of the senses aspires to digitally transmit sensory stimuli such as olfaction, gustation and tactile sensations, generating unprecedented levels of interpersonal engagement [54]. The field of advanced industrial automation is poised to reap substantial benefits from real-time control of collaborative robotics, increasing productivity and precision in the manufacturing sector [55].
Improved telemedicine capabilities will facilitate remote robotic surgery and continuous medical monitoring, improving accessibility to essential health services [56]. Intelligent mobility initiatives will capitalise on vehicle-to-anything (V2X) instant communication frameworks to support autonomous vehicle operations [57]. In the agricultural sector, precision methodologies such as autonomous aerial vehicles and real-time soil evaluation are expected to transform farming practices [58].
Integrated networks encompassing space, air and ground infrastructure promise uninterrupted connectivity across terrestrial boundaries, opening up possibilities for extraterrestrial exploration and communication [59]. Environmental monitoring initiatives will benefit from sophisticated climate data aggregation and disaster prediction systems [60]. Hyper-personalised educational paradigms will provide immersive and interactive learning environments meticulously tailored to individual needs, while digital twins will facilitate real-time simulations for urban landscapes, industrial operations and individual users, fostering informed decision-making processes [48].
Industrial projects around the world are playing a key role in shaping 6G, driving both innovation and global standardization. Several EU-funded projects—including 6G4Society, BeGREEN, COALESCE, IN2CCAM, CENTRIC, 6Green, and 6G-TWIN—are leading efforts to integrate energy efficiency, renewable energy, and ecological resilience into next-generation networks. These initiatives highlight the importance of AI-driven optimization, sustainable infrastructure design, and cross-disciplinary collaboration as strategies to minimize the ecological footprint of 6G systems. Collectively, they emphasize that sustainability must be embedded in 6G design from the outset, with ongoing activities advancing green telecommunications practices [61]. In Europe also, the Joint Undertaking on Smart Networks and Services (SNS JU) actively supports research and innovation, promoting global 6G trends and helping to build a strong, collaborative ecosystem for the next generation of mobile networks [62]. A solid framework is essential to guide the development and deployment of 6G on a global scale. The SNS ICE project, for example, provides a platform to track and report global 6G trends, helping to integrate the advances from the SNS JU into the broader 6G ecosystem [38]. The Sustainable Impact Analysis and Optimization Framework (SIAOF) focuses on reducing energy consumption and enhancing network performance by collecting data across multiple layers and making real-time adjustments [63].
Table 3 provides a detailed comparison between 5G and 6G technologies, highlighting key differences and major advances.

Table 3.
5G vs 6G comparative summary.
3. Integration of AI in Mobile Networks
3.1. Fundamentals of AI: Components, and Algorithms
AI is the rapid development of intelligent computer programs and devices capable of perceiving the environment, acting, drawing conclusions and learning from experience. It focuses on cognition, problem solving, perception, linguistic intelligence and social intelligence. AI improves computing capabilities, manages unpredictable work environments and controls robotic machines [64]. AI is a technical interface combining various knowledge systems, robotic technologies and algorithmic studies. It aims to automate critical activities and overcome real-world obstacles. Despite different definitions in different fields, its vast scope makes an exhaustive definition difficult [65].
3.1.1. Components of AI
AI is made up of several important components that work together to enable AI systems to detect, analyse, understand and process data and its source types. These components can be defined as machine learning (ML), natural language processing (NLP) and computer vision (CV) [66,67]. ML is an AI discipline. It is a set of algorithms using different techniques to learn from data. There are three main types of ML: supervised learning, unsupervised learning and reinforcement learning. ML is primarily used to predict outcomes. Several techniques are used in ML, such as clustering, decision trees, deep learning, regression analysis, support vector machines, random forests, etc. It is used in many fields, including healthcare, banking, e-commerce and video games. NLP is a branch of AI that learns and understands the communication between computers and human language, and implements various strategies.
These tactics include fact extraction, syntactic analysis, semantic understanding, collocation and word sense disambiguation. Natural Language Processing (NLP) is used to convert natural language into computer language and is used in the fields of machine translation and chatbots. CV, which is also an aspect of AI, uses artificial neural networks to interpret digital images and videos. In CV, artificial neural networks extract complex, large-scale images to simplify them for automatic interpretation. It is used in image and photo retouching, 2D object identification, 3D object restoration, identification and classification, and the study of geographical maps [68]. Figure 5 shows the main components of AI.
Figure 5.
AI main components.
3.1.2. Algorithms in AI
Algorithms, the foundation of AI, solve problems by acting as methodologies or mechanisms that enable machines to learn, make choices, produce predictions and extract knowledge from structured and unstructured data. This subsection categorises the different algorithms associated with AI according to their learning paradigms and discusses the concepts of some popular algorithms in each category. Generally, all algorithms used in AI can be divided into three categories: (1) supervised learning algorithms; (2) unsupervised learning algorithms; and (3) reinforcement learning algorithms. Supervised learning is the most common learning paradigm. In this case, the machine learning model is trained on a set of labelled data. Unsupervised learning, as the name suggests, covers algorithms where the machine is trained on an unlabelled dataset. The machine attempts to learn patterns in the dataset without external help.
The final category, reinforcement learning, refers to a particular branch of machine learning where the model is trained to make a series of decisions based on previous results. Reinforcement learning uses a feedback system to guide the model towards its goal. Certain algorithms can be classified into several categories according to their behaviour, and the choice depends on the type of data, the complexity of the problem and the business objective. Supervised learning algorithms include linear regression, logistic regression, decision trees, random forests, support vector machines and neural networks. Unsupervised learning algorithms include clustering, dimensionality reduction, a priori algorithms and anomaly detection. Q-learning and the deep Q-network are among the algorithms used in the reinforcement learning technique [69,70].
3.2. AI Integration and Advancements in 5G and 6G Networks
Building on the discussion of AI fundamentals, recent advances in artificial intelligence for 5G and 6G networks have further reshaped the way networks operate, enabling real-time decision-making, predictive resource allocation, and efficient deployment on edge devices. Innovations in neural network architectures, such as Transformer models, now support traffic prediction, allowing for proactive management of network resources [71]. Lightweight models like MobileNet and TinyML facilitate AI execution directly on edge devices, ensuring low latency and high efficiency in processing data locally [72]. Reinforcement learning algorithms, exemplified by the PRAXIS framework, enhance traffic optimization in URLLC, improving network reliability and responsiveness [73]. Moreover, AI-driven capabilities enable dynamic spectrum control and predictive resource management, maximizing network performance and user experience [74]. These developments illustrate the transition from the more centralized AI applications of 5G, which primarily focus on optimization and support, to the pervasive and autonomous AI-driven paradigm envisioned for 6G, where distributed, collaborative models allow networks to anticipate, adapt, and manage operations in ultra-dense and heterogeneous environments, supporting advanced services such as holographic communications and massive intelligent environments [72]. Table 4 summarizes how AI is applied across different dimensions of 5G and 6G networks, showing its growing role in optimization, automation, edge intelligence, and privacy-aware frameworks. Figure 6 shows an illustration of the role of AI in 5G and 6G Networks.

Table 4.
Classification of AI applications in 5G and 6G networks.
Figure 6.
An Illustration of the role of AI in 5G and 6G networks: From application-driven deployment in 5G to network-wide optimization in 6G.
3.3. Literature-Based Classification of AI Application in 5G and 6G
In cellular networks, AI can be integrated into the foundations of cellular network management to improve network efficiency and functionality in a variety of application contexts. The integration of AI in 5G and 6G networks has been extensively researched, with various studies categorising AI applications from different perspectives. In order to provide a structured understanding, this section proposes a comprehensive classification of AI applications in mobile networks. It takes into account various elements such as network characteristics, influence on operations, usage areas, data management and lifetime. We suggest a multi-dimensional classification in our taxonomy of AI applications for 5G and 6G networks, which offers an organized and repeatable approach.
In order to showcase AI’s significance in network optimization, wireless communication, security, and edge/fog computing, applications are first grouped by network technology and functionality. In order to differentiate between solutions that enhance performance, facilitate predictive analytics, or automate management, they are categorized based on their influence on network operations. Third, applications are categorized by domain, including transportation, healthcare, and IoT and smart environments. Fourth, they are divided into real-time and historical data-driven applications, as well as centralized and distributed AI models, based on integration and data consumption. Lastly, the network lifecycle, which includes design and deployment, operation, and maintenance, is used to classify applications. This taxonomy guarantees clarity and reproducibility by outlining the standards and justification for every category. By reviewing previous work, we highlight the main developments, challenges and multiple roles of AI in enhancing, protecting and automating next-generation mobile networks.
3.3.1. By Network Technology and Functionality
AI applications can be classified according to network technology and certain network characteristics. The application of a different AI model or algorithm brings undeniable benefits to a network. AI dissemination models focus on improving network performance, while targeted dissemination models focus on specific applications or functionalities. Improving network performance, spectral efficiency and resource allocation has always been a concern for any operator or researcher. On the other hand, AI applications in 5G networks may also offer the opportunity to support new use cases from a service perspective. Table 5 presents AI applications by network technology and functionality, detailing their specific roles according to different network types and functions. The analysis of the literature shows that the choice of AI approaches is guided by fundamental trade-offs between accuracy, privacy, latency, computational complexity, and energy efficiency.

Table 5.
AI applications by network technology and functionality.
a. AI for Network Optimization
AI plays a key role in optimising the performance of 5G and 6G networks through intelligent resource management, traffic prediction and mobility management.
The integration of AI techniques, including ML and Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL), enables networks to dynamically adapt to changes in demand, improving efficiency and user experience. AI-based intelligent resource management algorithms facilitate dynamic resource allocation, ensuring fair access between users and devices in congested networks. Techniques such as predictive provisioning and model mining enable real-time adjustments to resource distribution, improving overall network capacity and quality of service. AI-driven resource allocation was explored in [75] where the authors propose AI-powered provisioning and resource allocation for 5G/6G networks, leveraging ML and AI to optimise network performance, ensure fair access and increase capacity through predictive provisioning and model mining of real network traffic data. Paper [83] presents a new resource allocation technique specifically designed for 6G networks, exploiting AI to optimize network resource allocation. This approach aims to overcome the limitations of traditional algorithms used in previous cellular networks. Similarly, ref. [84] addresses dynamic resource allocation in 6G networks, exploiting real mobile user statistics and 5G testbed profiling to improve resource efficiency, which aligns with intelligent resource management and traffic prediction in advanced network systems. While fuzzy logic dynamically optimizes resource allocation according to real-time parameters, AI-based traffic prediction models complement this approach by analyzing historical data to anticipate future network needs. This predictive capability enables proactive resource management, improving network efficiency and user experience. Building on this predictive capability, reinforcement learning-based schedulers, such as the one proposed in [85], further improve network efficiency by dynamically adapting to traffic variations and optimizing resource allocation according to reward functions predefined by network administrators. This innovative scheduler optimally manages IoT traffic and enables mobile networks to support an additional data rate of with negligible effect on current traffic load. A different perspective is offered in [86] where the authors examine emerging 5G wireless network traffic characteristics and elucidate the challenges these pose for effective 5G traffic management. In addition, the use of deep learning for traffic prediction enables bandwidth utilization to be optimized and latency to be reduced, which is crucial for applications such as IoT and augmented reality.
A multitude of AI-based models have been designed to improve the accuracy and efficiency of traffic forecasts, capitalizing on the sophisticated attributes of these cutting-edge networks. Research [87] presents an AI-driven model, Refinished Long Short-Term Memory (RLSTM), for traffic forecasting in intelligent transport systems, exploiting 5G/6G networks. It improves forecast accuracy by dynamically adjusting parameters and using seasonal time differences to stabilize traffic data. Paper [88] presents a federated learning framework for forecasting wireless traffic in 5G-Advanced/6G networks, addressing data security and privacy issues while achieving high accuracy rates (0.80 after 27 rounds, 0.86 after 50 rounds) through regional model training. In [89], the authors discuss traffic forecasting using machine learning and big data for transportation systems to reduce complexity and include image processing for traffic sign recognition in autonomous vehicles.
AI enhances mobility management by enabling intelligent handover processes and optimizing the user experience. Integrating AI into mobility management promotes smooth connectivity and efficient spectrum use, both of which are essential to the requirements expected of 6G networks. However, to fully exploit the potential of AI in 6G environments, challenges such as scaling, real-time decision-making and energy efficiency need to be addressed. To address these issues, the Intelligent Mobility Management (iMM) entity proposed for 6G networks [90] uses user equipment (UE) mobility data to make autonomous decisions, reducing control plane delays by up to owing to a trajectory prediction algorithm (TPA) with accuracy. In the same vein, the authors of [91] introduce an AI multiple linear regression model to optimize mobility management in 5G and 6G networks, correcting suboptimal handover control parameters through the instantaneous indication measurement function, thus improving performance indicators such as handover probability and radio link failure. Following a similar approach, ref. [92] addresses AI-assisted mobility management in 5G and beyond, focusing on UE mobility prediction using models such as LSTM, BiLSTM-attention and ANN. It highlights challenges, solutions and applications in vertical sectors, achieving around accuracy in trajectory prediction. The work in [76] focuses on autonomous mobility management in ultra-dense 5G HetNets using reinforcement learning. It improves the robustness of user mobility while minimizing operational costs, paving the way for advanced mobility management techniques that could be applicable to future 6G networks.
The integration of AI into 5G and 6G network optimization promotes better resource management, traffic forecasting and mobility, based on machine and reinforcement learning methods. These methods promote dynamic resource allocation, reduce latency and optimize the user experience, owing in particular to sophisticated models such as RLSTM and federated learning. However, a number of challenges remain, including scalability, instant decision-making, energy consumption and data protection. To increase the impact of AI, future studies should focus on developing more efficient algorithms, combining AI methods with traditional optimization solutions, and enhancing security through techniques such as federated learning. In addition, it is necessary to promote interoperability between different network technologies in order to facilitate the large-scale deployment of AI.
The main trade-off lies between the computational complexity of DRL [85] and the simplicity with lower adaptability of traditional ML [75]. While DRL enables proactive optimization, it demands significant computational resources.
b. AI for Wireless Communication
A major development in wireless networks is the growing integration of AI to optimize performance. In this type of communication, several technologies influence the proximity of AI applications. One of these is the switch from sub-6 GHz to millimeter waves. The latter require line-of-sight to minimize path loss and increase bandwidth. It is therefore essential to design an antenna gain that can control the location of the receiver. To meet this need, MIMO technology has progressively evolved to offer a large number of antenna systems, known as massive MIMO. As massive MIMO beams are formed simultaneously, speed of beam formation is essential. Using a small-cell method with a beam-forming antenna reduces interference. Owing to these different hardware acceleration technologies unified by application, uplink response time can be reduced, significantly increasing the use of AI in 5G/6G. In this way, each wireless communication technology offers a variety of functionalities owing to its increased intelligence, bringing AI applications closer together.
With this in mind, a large body of research has examined the impact of AI on improving wireless communications, including the optimization of signal distribution, resource allocation and network management. In [77], researchers explore a deep learning-based channel estimation method for massive terahertz MIMO systems, highlighting the need for accurate channel knowledge to ensure efficient beamforming in 6G. They also highlight challenges such as severe path loss and directivity in THz communications. Similarly, ref. [93] focuses on AI applications in MIMO technology for 6G and beyond, notably via the AIDETECT-2 method, improving signal detection efficiency. However, this article does not directly address beamforming or terahertz communication in the context of 5G and 6G. A different perspective is proposed in [94], which focuses on hybrid beamforming in massive non-terrestrial THz broadband MIMO communications, addressing the problem of beam squint and improving spectral efficiency. It highlights the role of intelligent transmission surfaces in reducing hardware costs and improving the energy efficiency of wireless communications. The paper [95] discusses the use of AI in 5G and 6G, focusing on topics such as AI channel estimation, deep reinforcement learning for beamforming and advances such as meta-surfaces and phased array antennas, which increase the efficiency of massive MIMO and terahertz communications. The study in [96] proposes an intelligent self-adaptive beamforming scheme based on deep reinforcement learning for massive MIMO systems in 6G terahertz communications. This enables real-time prediction of spatial phase profiles for efficient beamforming and improves the performance of wireless communications.
The use of network slicing represents another element affecting the viability of AI in wireless communications. AI is essential to 5G and 6G network slicing, enabling efficient and scalable resource allocation, optimizing segment management and guaranteeing quality of service through real-time data analysis and predictive decision-making. A large body of research has explored AI-based methods for optimizing network slicing, focusing on resource maximization, adaptive orchestration and performance enhancement for next-generation wireless networks. To improve network efficiency, ref. [97] focuses on 6G, highlighting AI applications that require network slicing to meet different AI quality of service (QoAIS) requirements. This involves matching users’ QoAIS needs to network capabilities, optimizing resource allocation and orchestrating AI services. Ref. [98] introduces a framework called “semantic slicing”, exploiting AI to optimize resource allocation and data processing in 6G networks. This approach improves wireless communication by intelligently managing resources at the network edge, enabling efficient and responsive applications across the entire computing continuum. Ref. [78] applies AI techniques to 6G network slicing, highlighting its role in network assurance and service delivery. It highlights the advantages of AI over traditional models in addressing complex slicing challenges, particularly in dynamic environments and demanding vertical application scenarios.
c. AI for Security Enhancements
The security technology enhancements likely to be used in 5G and 6G networks define the main deployment modes for these mechanisms. These could include: (1) advanced encryption; (2) different authentication protocols; (3) enhanced NAS layer security, among others. As 5G is designed to meet the requirements of future networks, every effort is made to guarantee the security and confidentiality of data exchanged between end-users, as well as the security of all network segments. Due to the constant evolution of networks, they are becoming increasingly dynamic from one version to the next. Recently, AI has become one of the new security paradigms to adapt to the constant, high-risk changes in 5G and 6G environments. The use of AI, mainly deep learning, for intrusion detection systems (IDS) is showing positive results: AI is able to handle increased complexity and anomalies, and has the characteristic of learning continuously to adapt to massive network changes. At the same time, AI technologies are improving performance owing to their scalability and ongoing efforts to predict, recognize and prevent unknown encryption attacks by machines in electronic environments such as 5G networks. Growing concern about data privacy over the past decade has led to various privacy protection techniques in the 5G and 6G communication paradigms that followed. The following references present key aspects of AI applications to enhance the security of 5G and 6G networks. Ref. [79] examines AI/ML-based detection algorithms that improve the security of 6G IoT networks by enabling the exchange of shared secret keys in real time and protecting against remote eavesdropping to ensure ultra-reliable, low-latency communications while maintaining a low probability of interception. Ref. [99] argues that security features for 5G, using SDN and NFV, must evolve towards 6G networks. It detects new security threats and privacy issues, and suggests 6G-specific defenses to improve security in the integrated AI-driven environment. In [100], the authors investigate an AI-driven security monitoring framework for 5G, using deep learning models for threat detection across network layers. Their work enhances security through real-time traffic analysis, signal classification and an intelligent assistant for incident response, improving overall network security. Paper [101] examines security enhancements to AI-based 6G using federated learning to combat threats such as fraudulent attacks and theft of personal data. It proposes a security system incorporating trust assessment, Q-learning incentives and local differential privacy to protect user data and model integrity. In contrast, ref. [80] proposes a blockchain-based data security system for AI applications in 6G networks to address data processing vulnerabilities. It highlights the integration of AI and blockchain to enhance the security of applications such as indoor positioning and autonomous vehicles.
A critical trade-off emerges between the accuracy of centralized models [100] and the privacy offered by Federated Learning [101]. The latter protects user privacy but introduces challenges in model convergence.
d. AI for Edge and Fog Computing
Edge computing and fog computing have gained in popularity due to their ability to support latency-sensitive scenarios. Unlike traditional cloud architectures, edge computing and fog computing bring calculations closer to data sources, reducing latency and increasing the responsiveness of real-time applications. AI-based algorithms enable predictive resource allocation, adaptive workload distribution and efficient power management, optimizing network performance in dynamic environments. In addition, AI enhances edge computing by enabling intelligent caching, anomaly detection and security threat mitigation. In telecoms networks, AI-driven models can support network slicing, traffic prediction and autonomous system optimization, making edge computing and cloud computing more efficient and scalable for future 5G and 6G networks. Many proposals suggest the use of machine learning models for management and orchestration designed for edge computing or fog computing. Figure 7 illustrates how AI enables resource optimization in 5G Mobile Edge Computing through interactions between cloud, edge nodes, 5G cells, and IoT sensors. AI enhances resource allocation in 5G Mobile Edge Computing by acting as the central decision engine. The AI module processes data from sensors, edge nodes, and 5G cells, then generates adaptive strategies to balance traffic and optimize bandwidth, computing, and storage resources. The cloud complements this process by providing large-scale model training and global coordination. This interaction reduces latency, improves quality of service, and supports energy-efficient network operation. As the authors of [81] point out, advanced AI plays a crucial role in improving 6G communication networks, through the use of decentralized and federated learning models. This work demonstrates the importance of integrating advanced computing technologies to optimize data analysis, reduce latency and guarantee user-configurable network reliability. Building on this approach, ref. [102] discusses advanced AI as a solution for 6G networks to improve effectiveness, safety and efficiency. The article focuses on the integration of training and model inference at the network edge, addressing challenges such as latency and power consumption, relevant to both 5G and 6G. The paper [103] focuses on the deployment of AI tasks in intelligent multi-access edge systems within 6G networks to optimize resource allocation and computation offload, which is crucial for edge and fog computing applications in advanced network environments. The authors of [104] present fog computing as an essential technology for 6G networks to enhance AI applications by providing data storage and computation capabilities. It discusses QoS criteria, enabling efficient management of IoT applications in edge computing and fog computing environments. The article [105] explains how artificial intelligence (AI) enhances mobile edge computing (MEC) and fog computing in 5G and 6G networks, addressing resource allocation, network load and latency requirements, thus improving the computational performance and efficiency of modern applications. The authors of [106] discuss the integration of fog computing into IoT and CPS systems, highlighting its role in latency-sensitive applications such as augmented reality and industrial IoT, essential for improving AI applications in 5G and 6G environments. Paper [82] focuses on proactive caching in 6G cloud-edge collaboration, using distributed deep reinforcement learning to optimize content prediction and decision making, thereby improving edge success rate, minimizing latency and reducing traffic costs in edge computing and fog computing scenarios.
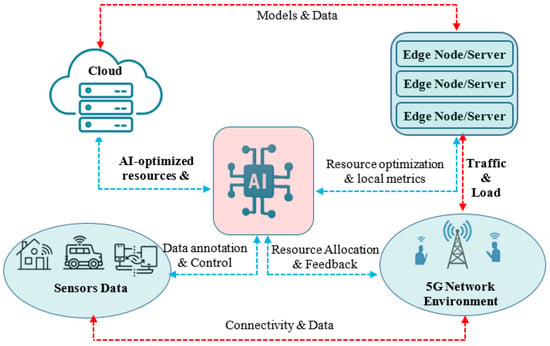
Figure 7.
An illustration of how AI enables resource optimization in 5G Mobile Edge Computing through interactions between cloud, edge nodes, 5G cells, and IoT sensors.
3.3.2. By Impact on Network Operations
a. AI for Performance Optimization
Optimising the performance of 5G and 6G networks focuses on two key aspects: spectral efficiency and energy savings. Spectral efficiency refers to the maximum amount of data transmitted per unit frequency in a given transmission system. It is therefore a common measure for optimising performance and improving capacity. Improving efficiency is particularly important for 5G, a technology characterised by high data rates and volumes, as well as for 6G networks, which are currently expanding their connectivity and coverage [107]. Transmission over a wider range of frequencies is desirable when data traffic increases in order to accelerate throughput and improve network performance. Spectral efficiency not only opens up new areas of spectrum needed to extend the data capacity of wireless networks, but also goes beyond traditional limits and allows more users to connect to the network simultaneously. At the same time, sophisticated modulation techniques can be adopted to avoid errors and faults in the wireless channel and thus ensure reliable data transmissions as far as possible [108]. Licensed protected bands are reserved for licensed spectrum, but specific regions of the licensed spectrum, which are less frequently used, may be allocated to unauthorised users. Spectrum use is not available in some areas, and if there is no primary licensee using that block of spectrum, a secondary user will use it. The terms ‘white space communication’, ‘dynamic spectrum access’, ‘opportunistic spectrum’ and ‘shared spectrum’ describe this usage. Spectrum sharing can occur simultaneously between two licensed users employed by different companies, one licensed and one unlicensed user simultaneously, and two unlicensed users on the same carrier wave [109]. Energy-saving methods are essential for the sustainability and operation of future networks. The massive deployment of mobile networks raises concerns about energy consumption. Several techniques for saving energy in 5G and 6G networks have been published. Source [110] discusses tactics such as traffic distribution or the implementation of power saving modes to periodically turn off base stations with excess capacity, thereby increasing energy efficiency and optimising the use of network resources. Spectrum sharing can occur simultaneously between two licensed users employed by different companies, one licensed user and one unlicensed user simultaneously, and two unlicensed users on the same carrier wave [109]. A trade-off analysis between energy consumption and maximum tolerable packet delay is performed in order to reduce the number of servers and active circuits. Multi-criteria optimisation problems of partition, memory capacity and link capacity are addressed for efficient hardware design with limited power consumption [111]. Renewable energy sources, including solar power, wind turbines and fuel cells, can be used to power small-scale networks and adjust network load. Energy recovery techniques allow energy to be recovered from a variety of sources. Economic and monetary incentives are essential to motivate base stations because of their high proportion of decentralised production. In addition, energy and data collectors can harness energy from cooperative devices [112,113]. Spectrum sharing can occur simultaneously between two licensed users employed by different companies, a licensed user and an unlicensed user simultaneously, and two unlicensed users on the same carrier wave [109]. Appropriate radio resource management techniques can also save energy. Dynamic spectrum management and reordering techniques can improve the efficiency of radio resource management. User behaviour and demand management play a key role in energy savings through the flexibility to exploit large levels of potential demand-side resources [114]. Maximum system throughput is maximised according to user type, and mobile traffic is scheduled. Energy consumption can be analysed as a function of quality of service. Energy consumption must also be high when quality of service is very high, and vice versa. Maximum system throughput is maximised according to user type, and mobile traffic is scheduled. Energy consumption can be analysed as a function of quality of service. The trade-off between quality of service and energy consumption must be analysed under a number of constraints. Service-centric strategies exploit the statistical demand for service to improve service quality and energy savings. An increase in quality of service leads to an increase in the power of the signal transmitted, and therefore an increase in energy consumption. Energy efficiency must be accurately monitored. New monitoring technologies are also considered essential for managing the system as a whole [115].
Real-time monitoring must evolve to improve energy efficiency in a cost-effective way. Instant radio resource management protocols need to be modified to improve network performance. Switching off the power amplifier would degrade the transmitted signal [116].
AI can improve sustainability through spectral efficiency and energy savings in 5G and 6G networks. Many AI techniques are used today to optimise mobile network performance, taking into account network resources, user QoS, service requirements, energy constraints and user and service behaviours [117,118]. AI can be implemented for dynamic spectrum allocation using machine learning techniques to improve resource utilisation in mobile networks, including spectrum efficiency. More efficient use of spectrum can then meet user needs [119,120]. AI predicts energy savings by analysing traffic patterns from previous days stored in the database. This analysis allows mobile network operators to plan when base station controllers should go into sleep mode and when they should be most active to save energy without compromising the quality of experience. Numerous case studies show that AI has been implemented and has contributed to the optimisation of mobile networks [121]. AI will make it possible to adjust the configuration of network resources and allocate the necessary resources to meet the needs of end customers. The virtualised baseband unit (VBU) is currently available. AI allows more network parameters to be adjusted than virtualised radio access networks [122]. AI will further optimise the use of resources and thus contribute more to the sustainability of spectrum efficiency and energy savings in 5G. It will help mobile operators meet the challenge of network sustainability and contribute to the goal of reducing energy consumption and emissions. It will maximise the value and utility of the infrastructure needed to meet growing customer demand in the transition from 4G to 5G networks.
This will also preserve the desired and maximum customer performance and experience [123]. The challenge is to maintain throughput, avoid network congestion and continuously optimise link budget quality and reachability. AI can provide predictive analytics that enable mobile operators to manage resources more efficiently and be a participating and innovative player in sustainability and ecological conservation in 5G [124]. Since AI can operate in a continuous recycling model to adapt to network evolution, it will adapt to 6G and be available for better tuning with more complex training and validation, making it more efficient and reliable. From an ethical and legal point of view, AI should be regulated to guarantee its autonomy. It should comply with the required quality control and key performance indicators and be based on customer-centric models [125].
Case studies providing an overview of the practical application of spectral efficiency and energy conservation are presented in [126,127,128]. Advances in performance optimisation. Leveraging state-of-the-art AI techniques, such as deep learning and effective reinforcement learning, to train the inference policies of radio access networks: improving the signal-to-noise ratio to decode a primary user’s message while inducing an acceptably reduced SNR for a secondary user. In this way, protecting the primary link from eavesdropping while ensuring that the secondary receiver is able to obtain valuable channel observations on demand. Currently, the deployment of such solutions must comply with global regulatory frameworks that limit acceptable stations in the link budget for conventional negative error access without interfering with existing networks, urgent traffic or supporting advanced traffic types. In hostile environments, secure solutions that combine reconfigurability and secure communication with the physical layer and AI can be essential. To enable rapid response and advanced training, these secure solutions require new data-driven concepts [129,130,131].
b. AI for Predictive Analytics
Predictive models enable network traffic patterns and operational problems to be anticipated. Two key elements of predictive analysis are essential: data collection and the development of the analysis model. During data collection, relevant data is gathered from different levels of network operations, such as mobile stations, radio access networks and the core network. Network analysis is performed using predictive analysis tools to build predictive models. Several predictive tools are available and can be used for predictive analysis [132]. The following are some examples of the success of predictive analytics in network operations, using a specific pivotal predictive model to proactively manage the network: (1) predicting network load; for example, a predictive model that estimates the number of simultaneous mobile stations; (2) predictingnetwork failures; for example, a predictive model that anticipates the probability of a base station failure; (3) updating the predictive model; for example, problems can arise when updating a predictive model due to frequent changes in network topology and user services. Consequently, the model would predict the future based on historical observations that are not very relevant for current network scenarios [133]. Therefore, a dynamic prediction model is investigated, in which the software behaves as if it starts learning again as soon as there is any significant change in the network or cell failure. This is particularly important for load and power prediction when navigating a cell in the data centre network environment. Research [75] is investigating the integration of AI and ML with predictive analytics to optimise resource allocation in 5G/6G wireless networks. By exploiting real testbed data, AI models can dynamically allocate resources, improve network capacity and quality of service (QoS). his approach enables efficient network traffic management, guaranteeing fair access for various users and applications, thus addressing the challenges posed by the interconnected nature of modern wireless communication networks. Research paper [87] presents an AI-driven approach for Intelligent Transport Systems (ITS) using predictive analytics in the context of 5G/6G networks. It introduces the Refinite Long Term Memory Model (RLSTM), which improves traffic predictions by dynamically adjusting units and hidden layers for increased accuracy. By analysing the unpredictability of 5G traffic across seasonal time differences, the RLSTM model significantly outperforms conventional methods, enabling accurate predictions that facilitate better decision-making for efficient traffic management in advanced network environments. The paper [134] discusses the integration of AI and data science (DS) in 6G network design and optimisation, which builds on the limitations of 5G. It highlights the use of AI-enhanced mobile edge computing and predictive analytics for intelligent mobility and intelligent spectrum management. This combination aims to improve network performance through automatic adjustments and resource management, addressing the diverse application needs and traffic constraints faced by today’s networks. Ref. [135] highlights the importance of artificial intelligence as a predictive analysis tool in the precision agriculture sector. It proposes a predictive model of apple diseases in orchards in the Kashmir Valley using data analysis and machine learning in an IoT system. The study, which combines artificial intelligence and wireless sensor networks, aims to improve the quality and volume of agricultural production by identifying diseases at an early stage.
c. AI for Automation
Currently, most of the tasks involved in network operations are carried out manually. While routine operations, such as monitoring and fault management, can be automated and systemised to improve operational efficiency, automation remains intermittent. AI-driven automation can be divided into three fundamental frameworks: domain-centric automation, service-centric automation and experience-centric automation. There are also a multitude of tools that can be deployed for the overall automation of network operations, including cognitive analytics, AI orchestration models, AI APIs and AIOps [136]. Computer network and network security issues where AI can be effective include intrusion detection, spam filtering, malware removal and virtual traps to capture hackers. AI has been able to identify signals correlated with the attack phase before it occurs, enabling the system’s self-healing to work as quickly as, or even faster than, a human operator. This can reduce the time between patch availability and system protection by eliminating human determination of the entire patching phase [137]. In [138], the authors explain how AI-enabled deployment automation improves space-air-ground integrated networks (SAGINs) for 6G, improving key performance indicators compared to 5G. They highlight the need for flexible and automated strategies to optimise network functions without manual intervention. Paper [139] explores the integration of distributed AI in 6G networks, improving automation through dynamic decision making. It analyses the performance and architectural impacts, focusing on automatic scaling of virtual resources in network slices, building on existing 5G frameworks for better management. Paper [140] explores the critical role of AI in improving the efficiency and complexity management of 5G networks, proposing intelligent RAN automation. It also explores the extension of these advances to 6G, focusing on AI/ML services and optimising the user experience in cloud virtual reality applications. Examples of automation efforts are diverse, spanning multiple relevant thematic communities that address digital and network systems in a broad sense [141]. In the field of telecommunications, there is a lot of work on how to integrate the benefits of new AI technologies into network operations supporting existing and next-generation network infrastructures [142]. This work requires validation in real telecommunications networks, where the operational state is constantly changing and many operational methods, management systems and network functions hosted in the cloud or at the edge interact. The 5G and 6G telecoms scenarios in the advanced automation studies highlight their potential to transform network operations. Given the hype around 5G and 6G, we see multiple demonstrations of successful AI integration among key collaborators [143]. Table 6 presents the impact of AI on network operations in 5G/6G, detailing the impact areas, corresponding AI applications, their benefits, and relevant references.

Table 6.
AI Impact on network operations in 5G/6G.
3.3.3. By Application Domain
a. AI in IoT and Smart Environments
The application of AI to IoT systems is intimately linked to the mind, as IoT is about devices, people, data and the intelligent exchange between them. AI can make human-based IoT systems more proactive, predictive and preventative by making them smarter, identifying trends and making decisions through data analysis. This predictive analytics allows decisions to be made based on incoming data predicted using algorithms [144]. Other smart domains can make use of data captured by devices from AI algorithms. Intelligent data collection by AI is analysed from smart city behaviour to industrial domain properties and processes [145].
The application domains of smart environmental domains can be divided into manageable spaces or dwellings, such as smart homes, the urban environment combining smart city and smart agriculture, and property management, such as Industry 4.0 or industrial automation. The implementation of commercial products is elementary and involves precise details, with very specific fixed options. In contrast, the area of research into the horizontal transformation of AI in the smart home is more concerned with defining high-performance APIs and building fundamental bricks of AI or machine learning. Care must be taken to apply basic techniques on a large scale and to develop new techniques adapted to specific problems. In Industry 4.0, manufacturers need to produce an interoperable infrastructure to design different automation requirements, and this uses AI learning algorithms to suggest optimal combinations [146,147,148]. The authors of [149] try to understand how AI and IoT can transform urban life. They improve urban life through applications such as air quality forecasting, disaster management, cybersecurity, predictive analytics and energy monitoring, thereby promoting sustainability and resilience. In [150], the authors demonstrate that integrating AI with IoT in smart homes improves automation, efficiency and convenience. Key functionalities of their work include smart energy management, predictive maintenance and personalised experiences, using various AI algorithms for data processing and decision-making in these environments. The paper [151] explains how AI improves IoT-based environmental monitoring by improving data quality, enabling predictive analysis and facilitating decision-making. It highlights the integration of AI with IoT technologies to address environmental challenges and promote sustainable development initiatives. Research [152] highlights the role of AI in the IoT by optimising hardware for energy efficiency and performance, enabling real-time processing and collaborative execution of AI tasks across devices, improving applications in smart cities, industrial automation, healthcare and environmental monitoring.
b. AI in Healthcare and Remote Services
AI has created significant opportunities in the delivery of healthcare and vitality services. AI technology is highly developed at various levels of patient care, diagnostics and personalized medicine. However, the significant development of AI technologies in medical diagnostics is significant, as AI expertise in the technical assessment of diagnosis, patient care and treatment can standardize processes and produce more accurate results. Telemedicine is another area that has attracted a great deal of interest; numerous studies have been carried out into the use of AI to optimize and automate remote consultations, as well as systems for automating online monitoring. In smart healthcare systems, AI is transforming patient data management by enabling more efficient, accurate, and secure handling of medical information. Figure 8 shows how AI can be applied in healthcare to monitor patient data from sensors in portable devices. The system analyzes and classifies the data, sending real-time alerts to healthcare professionals when anomalies are detected. It highlights the potential of AI to support timely and effective medical interventions. Numerous studies have been conducted in this context. Research [153] highlights the role of AI in improving remote healthcare services through deep learning and knowledge graphs, facilitating the efficient analysis of textual data for disease diagnosis, thus improving healthcare accessibility and outcomes despite existing skepticism and difficulties related to symptom similarity. In [154], the authors propose an AI-based healthcare framework that decentralizes patient monitoring, enhances security through authenticated IoT devices and uses predictive analytics for resource optimization, significantly improving data retrieval time, transfer rates and energy efficiency for remote healthcare services. The study [155] highlights the role of AI in healthcare through disease prediction, secure user recognition and consultation options. It focuses on the integration of Aasha workers to improve access to remote healthcare, giving patients self-assessment tools and improving collaboration between healthcare professionals. The article [156] discusses the use of AI in telemedicine via the dynamic adaptive diagnosis and treatment approach, which uses the intelligent symptom analysis algorithm, adaptive treatment recommender and continuous learning diagnostic network for effective remote diagnosis and personalized treatment planning. The article [157] presents an AI-infused telemedicine kiosk that improves remote healthcare through real-time videoconferencing, patient monitoring and IoT-powered drug dispensing, ensuring ethical data management and improved accessibility for underserved regions, transforming healthcare delivery.

Figure 8.
Smart Healthcare: AI-based patient data management.
The impact of medical data compliance regulations, such as the GDPR, on AI model training is profound, shaping the methodologies and frameworks designed to ensure data privacy while advancing healthcare analytics. To meet these regulatory requirements, innovative approaches such as federated learning have emerged, enabling decentralized model training without sharing patients’ raw data, thereby preserving confidentiality in compliance with data protection laws [158,159]. In this paradigm, hospitals train AI models locally and exchange only model updates, significantly reducing the risks associated with centralized data storage. Recent developments like Federated Learning 3.0 integrate blockchain technologies to enable dynamic compliance monitoring through mechanisms such as “data passports,” ensuring real-time adherence to GDPR principles [160]. Furthermore, hybrid privacy-preserving frameworks combine homomorphic encryption and differential privacy to protect sensitive medical data while maintaining analytical performance [161]. In parallel, secure model deployment strategies are increasingly designed to comply with both GDPR and HIPAA standards, reinforcing trust and integrity in AI-driven healthcare applications [162]. While these advancements enhance regulatory compliance and strengthen AI capabilities in the healthcare sector, challenges remain, including the continuous adaptation to evolving data protection frameworks and the trade-offs between model performance and privacy preservation.
c. AI in Transportation and Logistics
Over the past decade, the application of AI in the transport and logistics sector has seen significant advances and is already influencing long-standing industry practices. AI-based technologies are being used in various areas of the sector, such as optimizing delivery routes, adopting predictive maintenance for vehicles and infrastructure, and automating inventory control [163]. The combination of AI and 5G in logistics and transport services offers many advantages. The number of vehicles, users and the Internet of Things (IoT) are increasing rapidly, which should lead transport and logistics companies to generate an abundance of data that can lead to inefficiencies. The combination of AI and 5G can alleviate the real-time traffic function due to faster data processing and reception speeds. Using AI to predict traffic conditions becomes highly beneficial when supported by technologies such as 5G and beyond. In logistics and transportation services, one of the benefits of combining AI and 5G is the realization of fleet efficiency, effectiveness and safety services through the deployment of 5G and 6G. Traffic can regulate network performance in real time with lower latency, higher throughput and better consistency. An obvious effort has been made in this context, and dozens of research studies have been published. The authors of [163] focus on AI in reverse logistics transport routing to reduce CO2 emissions. The authors of [164] discuss the integration of AI and 5G technology in logistics through a new model including smart AGVs for remote monitoring and real-time data transmission, improving warehousing efficiency, reducing costs and improving supply chain transparency and controllability. Similarly, article [165] discusses an integrated communication system for logistics support and security using 5G and artificial intelligence. It highlights its three levels and five functional modules that improve data centralization and operational efficiency, helping to reduce companies’ production costs. Ref. [166] highlights how the integration of AI with 5G technology improves supply chain visibility, operational efficiency and communication in transport and logistics, facilitating real-time processing and decision-making, optimizing port operations and responding to industry challenges. The authors of [87] discuss an AI-driven approach to Intelligent Transport Systems (ITS) in 5G/6G networks, focusing on a tailored prediction model (RLSTM) for traffic forecasting, improving the efficiency of decision-making and traffic management in the face of 5G traffic complexities. Ref. [167] discusses an enhanced traffic management model (ETMM) that integrates artificial intelligence and 5G technology to improve urban traffic, minimize travel time and enhance mobility through real-time data analysis and dynamic signal optimization for efficient transportation management. Table 7 presents a summary of AI applications by application domain, highlighting the AI contributions, associated benefits, and supporting references.

Table 7.
Summary of AI applications by application domain.
The interplay between 5G/6G networks and V2X protocols is central to the advancement of intelligent transportation systems. By combining these technologies, communication becomes more reliable, latency is significantly reduced, and a wide spectrum of applications can be efficiently supported. This integration is particularly critical for the development of autonomous vehicles and smart cities, as it enables rapid data exchange and more informed decision-making. In this context, 5G-V2X introduces notable improvements: URLLC ensures that safety-critical information is transmitted promptly and reliably [168], while the extended communication range enhances both V2V and V2I interactions, improving overall network coverage and stability [169]. Furthermore, the high bandwidth of 5G allows for real-time sharing of high-definition maps and video streams, enhancing navigation and situational awareness [170]. Looking ahead to 6G, emerging technologies such as Non-Terrestrial Networks (NTN) and Integrated Sensing and Communication (ISAC) are expected to further strengthen V2X capabilities by enabling ubiquitous coverage and advanced environmental sensing [171]. In addition, AI-driven optimizations will refine communication protocols and traffic management systems, making them more adaptive and intelligent [169]. Despite these promising developments, challenges remain—particularly in terms of network scalability, security, and the integration of heterogeneous technologies—which must be addressed to achieve reliable and secure deployment of next-generation V2X networks [172].
Overall, the IoT, healthcare, and transportation sectors represent distinct yet increasingly interconnected ecosystems. By leveraging common enablers such as edge intelligence, federated learning, and 5G/6G connectivity, these domains are converging toward a cross-domain AI framework. This integrated approach not only improves scalability and supports real-time processing, but also reinforces compliance, security, and interoperability across these diverse verticals.
3.3.4. By Integration and Data Utilization
Data becomes the priority when AI is applied to a network. AI models offer several modes of integration with existing network architectures, including centralized models where data is sent to a centralized compute layer, distributed models where processing is performed on a device-by-device basis, and a static combination of the two, based on network architecture. AI systems are designed to integrate seamlessly with network systems. In network operations, real-time data is favored over historical data. When AI models are used, any delay in processing data in the pipeline will become a crucial aspect of data storage strategies as network throughput increases.
a. Centralized vs. Distributed AI Models
A fundamental operational difference between centralized and decentralized AI models lies in unified or localized control and decision-making. In centralized AI models, the data and control plan are managed jointly; for distributed AI models, these plans can be managed or supported in a decentralized way, for example by technology segment. The centralized AI model enables unified control of the network, with end-to-end management of the decision-making process, and thus simplified decision-making. On the other hand, application of the distributed AI model promotes resilience and scalability, and enables downstream decisions to be made to tailor these operations to each technology domain or network segment, while offering greater flexibility in decision-making based on localized policies.
The first approach offers excellent visibility and end-to-end control by tracking resource flows from the access layer to the cloud data center. This centralized orchestration of resources defines the system’s feasible operating area, in terms of policies and binding limits, to achieve the adoption target based on concrete options. Significantly lower latency is required to speed up decision making and transmission, thus considerably reducing the implementation time of the overall solution or approach. An obvious disadvantage is the need for actual exchange of infrastructure data, and the greater possibility of third-party data storage. A number of research studies have focused on centralized models, exploring their potential to address key challenges and optimize performance in a variety of areas. Building on the centralized approach, ref. [173] investigates AI-based methods for 5G network optimization, highlighting the role of centralized AI models in resource allocation, traffic management and dynamic network slicing, enabling real-time optimization and efficient bandwidth utilization to meet the demands of modern telecommunications.
On the other hand, the distributed approach has the advantage of leveraging Big Data and transactional data to manage conflicting operations between domains, in a shorter timeframe, owing to data encryption in a secure enclave environment for transition between technologies. Storage space can be provided by the cloud. Offering core and access as two separate products pushes product volume to maximum value, which is negatively correlated with user satisfaction. Consequently, knowledge of core technologies and slice management are included in this particular sequence optimization. Many other combinations are possible and applicable. Slicing also interacts with points, creating a shift in the demand model from a controllable trend to a materialized customer interest model. The distributed AI model is self-protecting and self-healing, but also benefits from holistic orchestration to handle larger volumes of traffic. An interesting advantage developed by distributed systems could be the potential limitation of Big Data generation, based on slices of individual entities within the same product domain.
Each feature can be treated as a separate activity, making it possible to manage internal pricing and investment in a feature, and optimize costs. Numerous studies have explored decentralized AI models, analyzing their potential to overcome challenges and improve efficiency in various applications. The paper [174] focuses on a distributed AI model using federated learning for user mobility classification in 5G networks. It highlights the advantages of local model training in small cells, solving the problems of data distribution and system heterogeneity, in contrast to centralized methods. In paper [175], the authors present federated learning as a distributed AI model for IoT edge devices, improving privacy and reducing data transmission. This contrasts with centralized AI models that require data aggregation, raising issues of security and efficiency. The article [176] examines the combination of federated learning (FL) and edge computing in the context of 5G, highlighting the difference between centralized AI models that rely on a central server and distributed models such as edge AI and FL, which improve data privacy and resource management.
The authors of [177] focus on decentralized Edge intelligence via hierarchical federated learning (HFL), as opposed to centralized AI models. HFL allows data owners to develop models on site, which improves privacy and reduces communication problems, unlike traditional centralized methods that rely on central servers. A combination of centralized and distributed AI models can be provided where centralized orchestration contributes to policy optimization, where both high-level and low-level signaling solutions are considered. On a global scale, both pricing and predictive analytics are taken into account, with the latter helping to uncover potential adaptive strategies. Similarly, much of the functionality and limitations of such an AI system would vary according to the limited and perfect domain information available, whereas a generalist AI system would provide a “sub-optimal” slicing engine. Several recent studies have examined the combination of the two approaches, exploring their integration to exploit their respective strengths. The authors of [178] discuss the advanced integration of computing and communication, highlighting how Networked AI Systems (NAAS) enable the fusion of centralized and distributed AI models across cloud, edge and endpoint. This enhances real-time intelligent services within 5G networks. Ref. [179] presents a federated machine learning architecture that combines centralized and decentralized AI models on the 5G edge. It relies on decentralized nodes to train local models while using a central node to consolidate the results. This process improves confidentiality and performance while addressing computational constraints. Similarly, the authors of [180] suggest a UE-centric traffic management framework that relies on federated learning, merging global centralized models for coordination with locally deployed models for each UE. This improves decision-making while respecting the computational and energy limitations of 5G radio networks.
b. Real-Time vs. Historical Data
Real-world mobile network applications offer many opportunities for advanced AI applications. For example, historical data can be used to generate traffic forecasts for dynamic energy management, load balancing and congestion control. Moving averages, calculated over extended historical periods, and exponential moving averages, which focus on recent periods, can be applied in such cases. For real-time outage management, real-time data is essential to detect whether a network is operating outside a defined policy. Here, short-term variations in detected values can be analyzed, with statistical tests used to identify sudden changes in size or level. In another context, peering forecasts are essential for optimizing link transactions, improving flexibility and mitigating risks associated with map-based management actions. By leveraging AI and forecasting, it is possible to anticipate variations in link throughput as a function of demand, helping to minimize network disruptions. When applying AI to network scenarios, the choice between real-time and historical data depends on learning needs. Combining the two can improve decision-making and response accuracy. Both types of data can define a new feeding/learning mechanism for a network application. The literature lacks rigorous studies on the disadvantages of choosing one or the other. Many experts opt for a combination of the two, but do not study the advantages of either. In our opinion, the choice of the two types of data directly influences the decision to create a new feeding/learning mechanism for a network AI application. Several studies have explicitly highlighted the distinction between real-time and historical data, emphasizing their respective roles and applications in various contexts. The authors of [181] focus on the capabilities of 5G IoT devices to process real-time data, highlighting their advantages over historical data in terms of latency, reliability and scalability, essential for the development of effective AI models in dynamic contexts. In [167], the Enhanced Traffic Management Model (ETMM) combines real-time and historical data to improve traffic forecasting and congestion assessment. It exploits 5G technology for fast information transmission, optimizing traffic flow and effectively promoting urban mobility. The article [182] focuses on real-time prediction in 5G networks, with an emphasis on current traffic analysis for efficient resource distribution. Unlike historical data, real-time data provides instant changes and alerts for network management, improving performance in changing environments. Research [183] focuses on the use of historical and real-time flight data in DQN models, enhanced by 5G technology. This integration enables real-time updates, improving responsiveness to changing conditions and optimizing flight path predictions with increased accuracy and reliability. Table 8 presents AI models categorized by integration and data utilization approach, outlining key features and associated references.

Table 8.
AI models by integration and data utilization.
3.3.5. By the Network Lifecycle
The typical lifecycle of a networked system comprises four main stages: (1) design, (2) deployment, (3) operation and (4) maintenance. AI significantly improves the efficiency of network management at each stage of this lifecycle.
a. Design and Deployment
In each of these phases, the network is transformed as the organization evolves, or as new applications are developed and adopted. It is essential that these transformations are carried out quickly, effectively and efficiently. The use of AI techniques can improve the effectiveness of these activities, reducing the level of human intervention required, alleviating task complexity and, consequently, lowering operational costs and increasing organizational agility. This sub-section focuses on two of these initial phases of activity, where AI can make a significant contribution to greater efficiency and effectiveness.
Combining AI with the design process enables AI tools to generate optimized network architectures that best meet customers’ operational needs. Simulation of these different design possibilities also enables potential future failures to be identified and an action plan to mitigate them to be drawn up. Deployment AI tools simplify the installation of new devices. Using AI in the deployment phase enables configuration errors that could compromise network compliance to be identified, and the necessary steps taken to correct them. AI makes it possible to control the rate at which software or configurations are deployed on a network, without causing instability or loss of redundancy. Automating these functions simplifies parts of the deployment process, dramatically reducing deployment time and improving accuracy, with fewer rollbacks or errors.
In what follows, we explore several papers that focus on 5G/6G network design with reference to AI. Research [184] presents an innovative antenna design model using AI, in particular multi-objective zebra optimization (MOZO), which aims to improve 5G mobile communication by reducing return loss while increasing gain. This improves the performance of a small rectangular patch antenna designed for 30 GHz. The authors of [185] present a distributed deep learning platform in a 5G-oriented framework, focusing on smart devices and mobile networks. It highlights the importance of adapting and extending deep learning models to optimize quality of service (QoS) while reducing energy consumption in mobile cloud computing. Ref. [186] proposes an enriched neuro-fuzzy classifier (ENF) for traffic analysis and a fitness-based reinforcement learning (F-RL) algorithm for controller load balancing, improving the design of a new four-layer software-defined 5G architecture for better QoS provisioning. Ref. [187] explores AI and machine learning techniques for associating users with different 5G communication slices, using neural network-based models and random forests to improve 5G architecture design and efficiency in real-time scenarios. Other approaches focusing on smart antenna design in 5G and beyond have already been discussed in [40,41,42].
b. Operation
AI also improves network management in the operational domain. Its capabilities enable real-time monitoring of the network, traffic, alerts and events. A large volume of monitoring data can be analyzed, enabling real-time multi-knowledge analysis combined with advanced algorithms for reliable and secure network management. AI can quickly report any detected degradation or anomaly, and suggest effective actions to avoid passing them on to customer service. AI then enables effective network control, for example by managing traffic flow, reallocating resources, optimizing paths and balancing load. It can also be used to configure and fine-tune radio parameters, channel allocation and more.
These AI capabilities make it possible to predict certain developments by analyzing historical data: traffic trends, resource utilization and network status. Operational activities, in particular, are impacted by the adoption of AI, with the automation of several parts of the network and the anticipation introduced by predictive analysis.
The literature pertinent to the operational phase of 5G and 6G networks encompasses studies on intelligent resource allocation, traffic forecasting, mobility oversight [75,83,84,85,86,87,88,89,90,91,92], security advancements [79,80,99,100] and those cited in Section 3.3.2 concerning ‘Impact on Network Operations’ [107,108,112,114,119,124].
c. Maintenance
AI is currently playing a key role in improving network maintenance. Its ability to perform network maintenance is growing due to its wide application in monitoring network performance and identifying potential problems, enabling them to be resolved before they become serious. With the rapid development of 5G mobile network technology, the maintenance of these networks, which are far more complex than 4G or earlier networks, is becoming increasingly important. The huge volume of data generated by 5G networks offers the potential to detect and solve network problems using this data. Against this backdrop, further research has been carried out. The paper [188] identifies the main AI models for 5G network maintenance, including decision trees, neural networks and support vector machines. This article examines their advantages, limitations and application methodologies, focusing on predictive maintenance and proactive performance improvement strategies in network management. Similarly, in paper [189], the authors presented AI/ML models for service maintenance in Beyond 5G networks by correcting performance drifts through modifications.
They highlight the importance of network automation and service lifecycle management to improve network optimizations and service delivery. The authors of [100] present specialized deep learning models, including CNNs, RNNs and transformers, for traffic analysis, signal classification and log anomaly detection in 5G networks. These models improve security monitoring and incident response, ensuring robust maintenance of network operations. The authors of [190] propose a 5G-enabled network application (NetApp) using AI for predictive maintenance of energy-related infrastructures, using an automatic encoder for anomaly detection in operational data, facilitating rapid interventions and avoiding equipment failures. Reference [191] uses AI-inspired optimization to manage resources in smart electrical grids. Although focused on power networks, it well illustrates how AI can help dynamically allocate resources in complex systems—an idea that can inspire similar approaches in 5G and 6G networks. Table 9 presents AI applications in key phases of the network lifecycle (deployment, operation and maintenance), highlighting AI contributions and corresponding references.

Table 9.
AI applications across the network lifecycle.
3.4. Synergies and Interdependencies Between AI Application Domains
While the preceding taxonomy provides a structured classification of AI applications in 5G and 6G networks, it is important to note that these domains do not operate in isolation. In practice, AI-driven functionalities often interact, where advancements or data in one area directly enhance capabilities in another. Recognizing these interconnections is essential for realizing a fully intelligent and holistic network ecosystem. Several critical synergies can be highlighted:
- Synergy between Network Optimization and Security Enhancements: The relationship between network performance and security is deeply interconnected. AI models developed for traffic prediction and anomaly detection in network optimization (e.g., [75,87]) can also feed into intrusion detection systems for cybersecurity (e.g., [79,100]). For example, a sudden spike in network traffic flagged by a predictive model as potential congestion can simultaneously indicate a Distributed Denial-of-Service attack. By sharing data and insights between performance monitoring and security operations centers, AI can enable a unified and proactive defense mechanism. In practice, predictive traffic models could automatically trigger security protocols to isolate affected network slices, ensuring service continuity and integrity.
- Synergy between Edge Intelligence and Data-Driven Applications: Edge AI and Federated Learning are fundamentally powered by application-specific data, particularly from IoT and smart environments. Massive real-time data streams from IoT sensors in a smart city, for example, can be processed locally at the edge to train AI models for immediate decision-making. This, in turn, supports automation in network operations. A concrete example is vehicular sensors and traffic cameras feeding data into edge-based AI to dynamically optimize traffic light cycles and manage V2X communication resources. Here, application data not only informs the network but actively drives optimization, creating a continuous feedback loop between data and operations.
- Synergy between Predictive Analytics and the Network Lifecycle: Predictive analytics bridges the design, operation, and maintenance phases of the network. AI models trained on historical and real-time operational data can forecast network demands, guiding the deployment of new infrastructure. Furthermore, predictive models anticipating component failures can inform the design of more resilient network elements, establishing a continuous improvement cycle. This synergy closes the loop between the operational state of the network and its long-term evolution.
In summary, these synergies emphasize that the true power of AI in mobile networks lies not only in addressing discrete challenges but in creating an integrated, self-optimizing, and adaptive ecosystem. Future research and implementation should prioritize cross-domain AI architectures and data-sharing frameworks to fully exploit these interconnected benefits, bridging network optimization, mobility management, edge/fog computing, and security.
4. Trends and Challenges of AI Application in 5G and 6G Networks
4.1. Emerging Trends
The emerging trends outlined below directly address the limitations and trade-offs discussed in the previous section. They represent the evolution of the field aimed at resolving the fundamental conflicts between performance objectives. The integration of AI techniques in the 5G/6G framework is expected to dramatically improve network performance and deliver outstanding data services to their various users. In this section, we discuss increasingly important, but still little explored, aspects of AI in the context of 5G and 6G networks, such as federated learning, edge AI, explainable AI, wireless communication in the terahertz band and reconfigurable smart surfaces. These emerging trends are analyzed in terms of their contribution to improving network performance and capabilities. The following sections detail the associated challenges and design goals for the deployment of AI-driven smart networks. The main obstacle to traditional federated learning lies in the need for a central server to collect and organize model training. Some data cannot be disclosed for reasons of confidentiality, security and other reasons linked to the laws and limits of physics.
Consequently, decentralized training of AI models is required, enabling it to be performed in parallel with the distributed model at different nodes for updating, computing, averaging, etc. Federated learning is becoming increasingly common in a variety of applications, including 5G and 6G networks, IoT systems and wireless sensor networks. In edge networks, federated learning needs to be taken into account in a different way: data traffic, modes, interference, direction of data flow, and so on. These resources generally involve decentralized peripheral networks that place particular emphasis on data distribution. They also provide peripheral intelligence to end devices. Distributed AI development takes place at the edge, where data is processed, distributed and received.
4.1.1. AI for Federated Learning, Edge AI, and Explainable AI
This trend directly addresses the accuracy-privacy trade-off identified in previously, enabling collaborative training without centralizing the data.AI, in its industries, has demonstrated its impact on the intelligent operation and policy mechanisms of telecommunication solutions. Starting with different types of AI, federated learning allows different types of models to learn on decentralized devices and a coordinated server [192]. This approach minimizes the disclosure of individual data models, preserving user data privacy and compliance. Similarly, AI Edge helps to minimize end-to-end network latency by exploiting local data processing at the advanced enablement layer of the mobile telecommunication infrastructure. Among other models, AI can also be applied in a more relevant way; Explainable AI extends monitoring decisions and justifies the automatic predictions made by these models [193].
This has a dual benefit: on the one hand, end-users and stakeholders have greater confidence in implementing these AI-driven functionalities to influence decision-making through acceptable user experiences. On the other, they are also required to ensure compliance with the latest data control regulations.
All these paradigms are commonly considered in emerging 5G and 6G technology environments, as they combine to increase decentralized network intelligence to make functionality more elastic in the context of 5G/6G network slicing for optimal customizations. It’s also worth noting that federated learning includes Edge AI and indicates that this is a form of decentralized AI application, harnessing the power of closer distributed datasets, as illustrated.
In a similar format, principled approaches to vertical de-anonymization in federated learning illustrate the realization of explainable AI concepts and smooth model updates for users. Interaction with this AI and numerous research works also focuses on certain aspects of the AI system relevant to next-generation communication networks in terms of 5G/6G, including security, privacy, energy, quality of service, noise, trust and reliability. Recent works [194,195,196,197] have explored AI in 6G networks, focusing on those three main directions, Federated Learning, Edge AI, and Explainable AI, to enhance privacy, efficiency, and transparency.
4.1.2. Expansion into Terahertz Spectrum and Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces
In efforts to develop wireless communication technologies, wireless data throughput is expected to increase by a factor of 10 to 100. The Terahertz spectrum, which is the wavelength between microwaves and infrared, is recognized as a new frontier for ultra-high-speed wireless communications, with potential data rates of up to Tbps. Terahertz communications offer new capabilities for using the unique characteristics of the Terahertz spectrum to increase the data bandwidth available for communication purposes [44]. Exploration of the Terahertz spectrum is motivated primarily by three considerations: (i) material properties in the Terahertz frequency band, (ii) molecular absorption loss and (iii) widely available frequency bands. The objectives of Terahertz communication systems are to provide compact and affordable Terahertz devices, to reduce device power consumption, and to provide techniques for selectively exploiting Terahertz wireless functionality.
One innovation to overcome the limitations of traditional node deployment is the use of a thin structure, called a Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface (RIS), capable of dynamically adjusting reflected and refracted signals according to controlled variations in the electrical components, such as amplitude and phase, of each of its unit elements. Due to RIS’s capabilities, it can maintain signal quality by directing and/or concentrating energy to a desired terminal, or by diffusing energy from other transmitters to avoid interference between networks. What’s more, RIS implementation can even cover dead zones in feeder areas not covered by existing network nodes by adjusting the energy reflected or transmitted to these dead z ones. The integration of reconfigurable smart surfaces (RIS) with THz communication networks was initially proposed in 2019 [44]. The synergy between THz communications and RIS makes it possible to create networks that are more efficient, safer and more controllable than conventional systems. The hardware implementation of RIS is less complex, more compact and less costly.
This raises the idea of integrating RIS into terahertz communications, which form the frontier of 6G networks. It is capable of operating in the terahertz frequency bands, known to cause atmospheric molecular absorption, but increases information throughput and reduces transmission system coverage. Challenges to implementing RIS in terahertz environments include hardware design considerations, molecular absorption issues and the high costs associated with operating in the terahertz spectrum. RIS is a key technology for enhancing the functionality of terahertz communication networks, enabling them to reach the edge of 6G networks. The terahertz communication network made up of T-CUs can be designed in a compact way, as RIS can focus on certain T-CU signals, increasing coverage and avoiding molecular absorption problems, especially for remote users.
4.2. Challenges
Data confidentiality and security have been widely recognized with 5G and 6G networks, owing to the considerable improvement in the collection process and their intensive use. As a result, misuse of data can cost a fortune, while AI models can be used to degrade communication links and cripple networks. In today’s networks, human operators control decisions, while data is exploited insidiously. These networks only operate in human presence, leaving the system in peace. With AI-driven networks, humans serve mainly as a safety net in exceptional cases. As a result, AI takes over more decision-making processes. The number of users of connected objects and other mobile devices is exploding worldwide, leading to increasing network complexity. Nevertheless, providing adequate network quality of service for every device will be a nightmare for mobile network operators. More efficient network operation is required.
Firstly, an energy-efficient device will often have a much greater transmission range than an energy-hungry one. As a result, a growing number of devices can use the available energy more efficiently, thereby reducing their consumption. Secondly, several designated small cells, operating in unison, can include a megacell or use radio resources. Historical network systems had similar protocols and algorithms using industry standards and new technologies, while neighboring networks require active radio frequency channels using a unique proprietary technology. Slicing relies on orchestration and resource sharing, and can include access to DSP chips, caching, mobile computing mechanisms at the edge and access to data storage. More complex AI would enable the RAN to provide any service, depending on functionality and demand. Overcoming these challenges will be crucial to implementing AI in 5G and 6G networks.
4.2.1. Data Privacy and Security Concerns
The technological enhancement in AI and machine learning techniques improves several fundamental aspects of 5G and 6G networks. AI implementations in these networks contribute to user data profiling, network management, data analysis, predictive traffic engineering, seamless mobility management and security problem solving. The AI-enabled network performs certain actions based on data or context, without human intervention, for the benefit of users. In most of these applications, AI is used to analyze user data. The process of analyzing user data by a neutral, invisible third party often leads to serious security and confidentiality issues. Data protection laws require user data to be treated anonymously and confidentially, on a need-to-know basis. AI can reveal certain underlying properties of user data that have not yet been discovered. This active role of AI can reveal user data, not only threatening its confidentiality, but also reducing the robustness or performance of AI models.
The term cybersecurity requires all components associated, directly or indirectly, with information systems to protect themselves from vulnerabilities and attacks by hackers. The invisible analysis of data by AI, without human coordination, can give rise to a number of internal and external threats to the data security of 5G and 6G systems. Key threats include unauthorized or phishing attackers, capable of intercepting receivers to gain access to confidential information; cyberterrorists or disruptive attacks, capable of launching distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks on network switch hardware resources; jammers, capable of transmitting jamming signals to overload the receiver at just the right moment; and data spoofers, capable of altering real position coordinates and time information, and information thieves, who can decipher encryption to steal or download confidential information. Solving all these problems requires a comprehensive security framework for networks, such as secure encryption, secure access devices and network security systems with integrated, scalable multi-level security covering a range of security functions, covering stateless and stateful, basic and advanced inspections, as well as context-sensitive applications. However, to establish trust between users and service providers, strict security measures must be applied, and data policies and regulations must be complied with. From the point of view of data protection regulations, the data protection laws of several countries oblige companies to obtain the free and informed consent of individuals in order to process their personal data down to the smallest detail. Data confidentiality and security therefore play an essential role in AI design. A secure system and secure user data provide accurate results for the AI-based system. On the other hand, obtaining an unauthenticated data pool or input will constitute a vulnerability not only to the robustness but also to the performance of the AI system. Several achievable promotions can improve 6G networks’ resilience, interoperability, and trust while building upon the suggested comprehensive security framework. Federated Learning (FL), for instance, allows data to remain on user devices or at its source, while only model updates (gradients or weights) are shared with a central server for aggregation. This approach significantly reduces the need to transmit raw data, yet shared model updates can still leak sensitive information through inference attacks. To mitigate these risks, Differential Privacy (DP) introduces carefully calibrated noise to the updates, obfuscating individual contributions without heavily impacting model accuracy. Similarly, Secure Multi-Party Computation (SMPC) and homomorphic encryption enable computation on encrypted data, ensuring that sensitive information remains protected even when processed externally. While these mechanisms enhance privacy, they also introduce computational and communication overheads, which must be carefully managed to meet the low-latency and energy efficiency requirements of edge and 6G networks. Lightweight cryptographic schemes and model compression techniques are therefore actively explored to balance privacy, performance, and energy consumption. The architectural context is also crucial. In hierarchical 6G networks, edge, fog, and cloud layers each play a specific role in privacy preservation. Edge devices can locally process sensitive data using TinyML or lightweight models, minimizing exposure. Fog nodes handle secure aggregation of model updates, while cloud servers perform cross-domain model fusion with encrypted updates. Ensuring smooth interoperability across these layers requires standardized protocols and frameworks. Initiatives such as ETSI’s Experiential Networked Intelligence (ENI) and 3GPP’s SA6 working group define common APIs and security interfaces that enable safe and efficient sharing of AI models and data across multi-operator and multi-platform environments. Adaptive algorithms and adversarial training can further strengthen AI models, allowing networks to dynamically react to new threats and continuously improve robustness. AI can actively assist network security by monitoring traffic, detecting irregularities, and autonomously mitigating specific vulnerabilities, enabling networks to self-heal with minimal human intervention. Finally, the combination of advanced privacy-preserving techniques, hierarchical architecture-aware processing, standardization, and strict regulatory compliance ensures consistent privacy, interoperability, and user confidence. This holistic approach not only safeguards sensitive data but also enhances the accuracy, robustness, and reliability of AI-powered 6G services, complementing and reinforcing existing security architectures while preparing networks for future, more complex AI-driven operations.
4.2.2. Scalability and Energy Efficiency
AI can help to understand and harmonize the ever-increasing volume of communications. As network traffic expands, to extend the impact of AI beyond a few hundred processors, algorithms will need to evolve to tens of thousands or more. This evolution involves the development of distributed and parallel AI architectures, where computation is shared across edge, fog, and cloud layers. Techniques such as model partitioning, pipeline parallelism, and asynchronous training can enable AI to scale efficiently across thousands of nodes while minimizing bottlenecks. At the same time, sensors, the Internet of Things and mobile devices are growing exponentially, and AI needs to be able to process these data sets efficiently. Lightweight AI models, including TinyML and quantized neural networks, can reduce memory footprint and computational demand, making it feasible to deploy AI directly on resource-constrained devices. Federated Learning also allows local processing at the device level, limiting the need to transfer massive raw datasets to centralized servers and reducing both latency and energy consumption. With the development of embedded technologies, network load is increasingly determined by bursty or scheduled downloads. In addition to scalability, energy sustainability is also an issue. Communicating is generally more energy-efficient than processing data, which is usually stored and transmitted by several radios to a single computer. However, emerging energy-efficient AI techniques, such as model pruning, adaptive inference, and event-driven computation, allow AI models to dynamically adjust their complexity according to network conditions, balancing performance and energy use. Similarly, the use of edge-assisted AI reduces the need for long-distance data transfer, further decreasing energy consumption and improving real-time responsiveness. This can lead to high latency, high energy costs and overloaded connections in the event of a sudden surge in traffic. An efficient system for the networks of the future must address both these issues. Scalability and energy efficiency are closely linked: as AI models grow in size and complexity, optimizing computational distribution, minimizing communication overhead, and employing low-power inference strategies are all essential to maintaining both performance and sustainability. So, in addition to the application prospects of AI and networks of the future, it would be useful to categorize the open questions in terms of scalability and energy sustainability. Key research challenges include developing standardized benchmarking for AI energy consumption, designing adaptive algorithms that respond to dynamic network loads, and integrating cross-layer strategies that jointly optimize model accuracy, latency, and power efficiency across heterogeneous 6G architectures.
4.2.3. Interoperability and Standardization Issues
5G and 6G are driven by multiple new technology standards, the integration of different networks and devices, and many other complex network architectures, complicating effective collaboration between different systems. One of the key features of 5G networks is to provide a unifying environment for multiple access network technologies. The integration of 5G with existing cellular networks relies on two main deployment architectures, each with distinct implications for security and network management. The Non-Standalone (NSA) architecture allows for rapid rollout by anchoring 5G New Radio to the 4G Evolved Packet Core. In this hybrid setup, control plane signaling depends on 4G infrastructure, while user plane traffic takes advantage of 5G capabilities. However, this approach also inherits the security limitations of the 4G ecosystem.
By contrast, the 5G Standalone (SA) architecture introduces a fully new Service-Based Architecture (SBA) core with built-in Zero-Trust security principles. The 5G core ensures mutual authentication among all network functions and supports fine-grained security policies through its cloud-native design. This shift fundamentally changes how security and control are handled in heterogeneous network environments.
For AI applications in 5G and future 6G networks, this architectural divide poses significant challenges. AI systems must navigate differing security postures between NSA and SA deployments, adapt to variable latency characteristics, and maintain performance across hybrid environments. As networks evolve toward 6G, addressing these architectural complexities while ensuring backward compatibility and smooth migration paths will be essential. Table 10 summarizes the main differences between these architectures and their implications for AI integration. As 5G technologies proliferate and the transition to 6G takes place, formal approval of network infrastructures and the services provided by 5G remain the norm. Despite continuing interoperability challenges, AI is already playing an increasingly important role in 5G deployment. Standardization issues are a major drawback for the application of AI to 5G networks.

Table 10.
Comparison between NSA and SA architectures and their AI/6G implications.
Although 5G has been developed according to a standardized basic architecture, it also incorporates numerous methods and procedures, such as network slicing, service-oriented architecture for non-autonomous applications and the services and systems aspects of technical specification groups, compatible with enhanced network functions and applicable to numerous artificial intelligence and machine learning applications for autonomous 5G. In addition, specifications for AI-related work and methods within geographically connected networks will be considerably extended and will mark 6G.
5. Future Directions
Several future prospects for the application of AI to 5G/6G networks deserve particular attention. Quantum AI is a promising area where improved AI processes could be exploited to reduce, or even eliminate, excessive processing times owing to existing deep learning models capable of handling noise, thus significantly improving the performance of quantum communication systems. It also influences the optimization paradigm and decision-making approaches used in 5G/6G networks. On the other hand, ethical aspects and, more specifically, the impact of the application of AI decision algorithms on society and the fundamental rights of individuals are potential obstacles to the use of AI in 5G/6G networks. Collaboration between stakeholders is crucial to rapidly determine regulatory measures and guide regulators towards the development of proactive AI-based communication systems.
It is important to discuss synergies in various application areas in order to foster innovation capabilities that bring together research in the field of AI assimilation and research at the intersection of ICT and emerging technologies, in order to develop more advanced infrastructures. This area of research is increasingly focusing on the interaction between AI and two emerging technologies such as the Internet of Things and blockchain, or more recently on their interaction with embedded generation systems, for which major technological advances are expected. AI-based game theory should also be studied in 5G/6G networks, where dynamic user behavior is affected by the cost of technology adoption, including impacts on ecosystems. In summary, the next generation of telecommunications will be continuously and highly adaptive in all aspects of interaction between individuals or groups of communicating devices, software agents or AI systems such as developers, producers and service providers.
5.1. Ethics and Policy
The growing impact of AI on decision-making within networks brings with it many implications in terms of human rights, accountability and transparency. The level of control built into each AI technology can determine whether that technology will qualify as critical or merely impactful. Human rights implications for EU member states include freedom of expression and information; legality, legitimacy, necessity and proportionality; transparency and confidentiality; trust, security and privacy; accountability and strong safeguards; and respect for users’ data rights. It also raises the issue of rigorous law enforcement to ensure responsible AI and stimulate European leadership. A common approach to creating an ethical framework for AI requires AI software to be in tune with societal and cultural values, to avoid harmful and discriminatory misuse, to be transparent, declared and understandable, and to be subject to the strictest accountability and compliance requirements throughout its lifecycle, including post-market and post-use monitoring.
Implementing policies aimed solely at protecting individual interests, rather than adapting them to new knowledge and innovation, can be detrimental to the community. In other words, AI network solutions should take into account, on the one hand, the promotion of competitiveness in innovation and, on the other, the protection of individuals and their fundamental rights.
5.2. Multi-Domain Synergies
Among the different fields of application, there are not only overlaps and opportunities for hierarchical interdependencies. Nurturing synergies between different disciplines is increasingly embraced as a means of fostering innovation and life-centred thinking, which also encourages ‘speaking the same language’ and bridging conceptual gaps. Here, multidisciplinary perspectives encompass telecommunications, data science and artificial intelligence. For example, although telecommunications, data and AI sciences are three distinct fields, effective and efficient collaboration can be established to improve communication networks. This development and its potential to meet the challenges of 5G and 6G are as relevant as they have been overlooked to date.
The rise of a wide range of modern ICTs has brought the world closer to life online, and industries are developing new technologies. The fourth industrial revolution—the roll-out of 5G and then 6G—is expected to be characterised by AI-based applications with autonomous and intelligent functionality. For example, network intelligence and automation should go beyond the management of telecoms infrastructures. A smooth transition to a more efficient intelligent environment is not obvious. It is therefore crucial to ensure an effective exchange of information and knowledge between academia, industry and policy-makers. The communicative nature of networks, which are increasingly data-driven, and the proliferation of use cases have major implications for the various stakeholders. Indeed, while 5G and then 6G are expected to become mainstream technologies in the near future, end-users are likely to benefit from an instantaneous experience owing to increased dense capacity and low-latency communication services.
6. Conclusions
This survey has provided a comprehensive exploration of Artificial Intelligence integration in mobile networks, tracing the evolutionary pathway from 5G’s AI-assisted operations toward 6G’s vision of native AI architectures. Through a multidimensional taxonomy, we have systematically organized and critically evaluated AI applications across domains such as network optimization, security enforcement, and predictive analytics. Beyond mere classification, our analysis brings to light the fundamental compromises that shape AI solutions in next-generation networks—particularly the tensions between accuracy and privacy, between computational complexity and adaptive capability, and between latency requirements and energy efficiency.
Our assessment of the research landscape reveals clear evolutionary trends: a marked shift from centralized to distributed intelligence, from reactive management to proactive prediction, and from opaque models toward explainable AI systems. These transitions represent direct responses to the core challenges examined throughout our study, including data confidentiality concerns, scalability limitations, and interoperability barriers. Emerging paradigms like Federated Learning, Edge AI, and Explainable AI embody the field’s collective effort to navigate and resolve these inherent trade-offs.
For both researchers and industry practitioners, this survey offers more than a taxonomic structure—it provides a practical framework for informed decision-making. When designing AI solutions for specific applications, whether in intelligent transportation, healthcare delivery, or IoT ecosystems, our analysis supports strategic choices: selecting Federated Learning where privacy preservation is critical, employing Deep Reinforcement Learning for highly dynamic environments despite its computational demands, and leveraging Edge AI for latency-sensitive applications while carefully considering its localized energy footprint. As we look toward the future, the convergence of AI with 6G networks will demand continued attention to ethical governance, cross-sector collaboration, and the development of adaptive systems capable of dynamically balancing competing objectives. By understanding both the capabilities and the limitations of different AI approaches detailed in this survey, stakeholders can make judicious decisions that advance toward more secure, efficient, and sustainable mobile networks—systems truly capable of serving society’s evolving communication needs.
Author Contributions
N.O.: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing—Original Draft, Supervision. Responsible for the overall structure of this paper and the integration of AI, NFV, and SDN concepts across the mobile network lifecycle. H.K.: Investigation, Visualization, Writing—Review & Editing. Collected and organized information on 5G and 6G, developed the taxonomy of AI applications, and prepared figures and tables illustrating key findings. F.Z.: Formal Analysis, Validation, Review & Editing. Analyzed AI perspectives including network optimization, predictive analytics, and security enhancement; assessed emerging trends such as federated learning and explainable AI; validated conclusions and proposed future research directions. All authors have contributed to the critical review and discussion. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
| Acronym | Full Form |
| 5G | Fifth Generation |
| 6G | Sixth Generation |
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| AR | Augmented Reality |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
| DL | Deep Learning |
| DRL | Deep Reinforcement Learning |
| DTN | Digital Twin Network |
| eMBB | Enhanced Mobile Broadband |
| FL | Federated Learning |
| IDS | Intrusion Detection System |
| IoT | Internet of Things |
| ITS | Intelligent Transportation Systems |
| KPI | Key Performance Indicator |
| LSTM | Long Short-Term Memory |
| MEC | Mobile Edge Computing |
| MIMO | Multiple-Input Multiple-Output |
| ML | Machine Learning |
| mMIMO | massive MIMO |
| mMTC | massive Machine-Type Communications |
| NFV | Network Function Virtualization |
| NLP | Natural Language Processing |
| NSA | Non-Standalone |
| NTN | Non-Terrestrial Networks |
| QoE | Quality of Experience |
| QoS | Quality of Service |
| RAN | Radio Access Network |
| RIS | Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces |
| RL | Reinforcement Learning |
| RNN | Recurrent Neural Network |
| SA | Standalone |
| SBA | Service-Based Architecture |
| SDN | Software-Defined Networking |
| THz | Terahertz |
| UE | User Equipment |
| URLLC | Ultra-Reliable Low-Latency Communications |
| V2X | Vehicle-to-Everything |
| VR | Virtual Reality |
| XAI | Explainable Artificial Intelligence |
References
- Lee, G.T. History and Future of Artificial Intelligence; Institute for Future Growth: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2024; Volume 10, pp. 127–141. [Google Scholar]
- Raihan, A. An Overview of the Implications of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Sixth Generation (6G) Communication Network. Res. Briefs Inf. Commun. Technol. Evol. 2023, 9, 120–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, I.H.; Hoque, M.M.; Uddin, M.K.; Alsanoosy, T. Mobile data science and intelligent apps: Concepts, AI-based modeling and research directions. Mob. Netw. Appl. 2021, 26, 285–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovira-Sugranes, A.; Razi, A.; Afghah, F.; Chakareski, J. A review of AI-enabled routing protocols for UAV networks: Trends, challenges, and future outlook. Ad Hoc Netw. 2022, 130, 102790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, B. Research paper on artificial Intelligence. Int. J. Sci. Res. Manag. 2024, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.H.H. Applications of machine learning in mobile networking. J. Smart Internet Things 2023, 1, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghag, O.M. Artificial Intelligence and energy efficiency of 5G radio access network. Int. J. Comput. Eng. 2023, 4, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaigandla, K.K. A Systematic Survey on Artificial Intelligence in 6G Wireless Networks: Security, Opportunities, Applications, Advantages, Future Research Directions and Challenges. Babylon. J. Artif. Intell. 2025, 2025, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Z.; Xu, W.; Huang, Y.; Wang, X.; You, X. Wireless network digital twin for 6G: Generative AI as a key enabler. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2024, 31, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, L.; Shao, Y.; Sun, L.; Liu, F.; Yang, S.; Ma, W.; Li, L.; Liu, X.; Hou, B.; Zhang, X.; et al. Advanced deep learning models for 6G: Overview, opportunities, and challenges. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 133245–133314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tshakwanda, P.M.; Arzo, S.T.; Devetsikiotis, M. Advancing 6G network performance: AI/ML framework for proactive management and dynamic optimal routing. IEEE Open J. Comput. Soc. 2024, 5, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahboob, S.; Liu, L. Revolutionizing future connectivity: A contemporary survey on AI-empowered satellite-based non-terrestrial networks in 6G. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2024, 26, 1279–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawish, M.; Dharejo, F.A.; Khowaja, S.A.; Raza, S.; Davy, S.; Dev, K.; Bellavista, P. AI and 6G Into the Metaverse: Fundamentals, Challenges and Future Research Trends. IEEE Open J. Commun. Soc. 2024, 5, 730–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dangi, R.; Jadhav, A.; Choudhary, G.; Dragoni, N.; Mishra, M.K.; Lalwani, P. Ml-based 5G network slicing security: A comprehensive survey. Future Internet 2022, 14, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhammadi, A.; Shayea, I.; El-Saleh, A.A.; Azmi, M.H.; Ismail, Z.H.; Kouhalvandi, L.; Saad, S.A. Artificial intelligence in 6G wireless networks: Opportunities, applications, and challenges. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 2024, 2024, 8845070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letaief, K.B.; Chen, W.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.J.A. The roadmap to 6G: AI empowered wireless networks. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2019, 57, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Liu, Y.; Al-Tahmeesschi, A.; Nag, A.; Soleimanpour-Moghadam, M.; Canberk, B.; Arslan, H.; Ahmadi, H. Advancing 6G: Survey for explainable AI on communications and network slicing. IEEE Open J. Commun. Soc. 2025, 6, 1372–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannou, I.; Christophorou, C.; Vassiliou, V.; Pitsillides, A. A novel Distributed AI framework with ML for D2D communication in 5G/6G networks. Comput. Netw. 2022, 211, 108987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Zhou, C.; Li, M.; Wu, H.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, N.; Shen, X.S.; Zhuang, W. AI-native network slicing for 6G networks. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2022, 29, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Dhar, S.P.; Shanmugasundaram, R.; Chemparathy, J. 5G Networks; River Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Sahu, V.; Sahu, N.; Sahu, R. Challenges and opportunities of 5G network: A review of research and development. Am. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2024, 8, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.; Mishra, A.K. 5G network implementation. In Advances in Systems Analysis, Software Engineering, and High Performance Computing; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2024; pp. 62–88. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H. Enhanced Mobile Broadband Communication Systems. In Design and Optimization for 5G Wireless Communications; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 239–302. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Ma, G. Introduction on Massive Machine-Type Communications (mMTC). In SpringerBriefs in Electrical and Computer Engineering; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Raman, R.; Singh, R.; Gupta, Z.; Verma, S.; Rajput, A.; Parikh, S.M. Wireless communication with extreme reliability and low latency: Tail, risk and scale. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Contemporary Computing and Informatics (IC3I), Uttar Pradesh, India, 14–16 December 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Wijethilaka, S.; Liyanage, M. Survey on Network Slicing for Internet of Things Realization in 5G Networks. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2021, 23, 957–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matencio-Escolar, A.; Wang, Q.; Alcaraz Calero, J.M. SliceNetVSwitch: Definition, Design and Implementation of 5G Multi-Tenant Network Slicing in Software Data Paths. IEEE Trans. Netw. Serv. Manag. 2020, 17, 2212–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khwandah, S.A.; Cosmas, J.P.; Lazaridis, P.I.; Zaharis, Z.D.; Chochliouros, I.P. Massive MIMO systems for 5G communications. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2021, 120, 2101–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreifuerst, R.M.; Heath, R.W. Massive MIMO in 5G: How Beamforming, Codebooks, and Feedback Enable Larger Arrays. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2023, 61, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, B.; Tian, Z.; Mei, W.; Chen, Z.; Han, C.; Li, S.; Yuan, J.; Zhang, R. Beamforming Technologies for Ultra-Massive MIMO in Terahertz Communications. IEEE Open J. Commun. Soc. 2023, 4, 614–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siriwardhana, Y.; Porambage, P.; Liyanage, M.; Ylianttila, M. A Survey on Mobile Augmented Reality with 5G Mobile Edge Computing: Architectures, Applications, and Technical Aspects. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2021, 23, 1160–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jararweh, Y. Enabling efficient and secure energy cloud using edge computing and 5G. J. Parallel Distrib. Comput. 2020, 145, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsabadi, A.A.; Yadav, A.; Gadallah, Y.; Yanikomeroglu, H. Exploring the 6G potentials: Immersive, hyper reliable, and low-latency communication. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2407.11051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thota, S.; Govind, T.R. 6G. In Towards Wireless Heterogeneity in 6G Networks; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2024; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Giménez-Antón, S.; Grasa, E.; Perelló, J.; Cárdenas, A. 6G-RUPA: A flexible, scalable, and energy-efficient user plane architecture for next-generation mobile networks. Computers 2024, 13, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szilagyi, P.; Contreras-Murillo, L.M.; Menéndez, D.R.; Giardina, P.; De la Oliva, A. 6G architecture for enabling predictable, reliable and deterministic networks: The PREDICT6G case. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC), Dubai, United Arab Emirates, 21–24 April 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.; Zhang, L.; Li, R.Y.N.; Di Renzo, M. The itu vision and framework for 6g: Scenarios, capabilities, and enablers. IEEE Veh. Technol. Mag. 2025, 20, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennanen, H.; Hänninen, T.; Tervo, O.; Tölli, A.; Latva-Aho, M. 6G: The Intelligent Network of Everything. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 1319–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Ye, Q.; Zhou, Y. 6G-Empowered Offloading for Realtime Applications in Multi-Access Edge Computing. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2023, 10, 1311–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Talwar, R.; Anand, S.; Bhola, J.; Pandey, D. Advancements and challenges in system on chip antennas (SoC) for 6G communication. In Advances in Wireless Technologies and Telecommunication; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2024; pp. 251–261. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, Y.; Dong, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhu, L.; Hong, Z.; Jiang, Q.; Wang, D.; Jin, S.; Zhang, R. Fixed and movable antenna technology for 6G integrated sensing and communication. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2407.04404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- New, W.K.; Wong, K.K.; Xu, H.; Wang, C.; Ghadi, F.R.; Zhang, J.; Rao, J.; Murch, R.; Ramírez-Espinosa, P.; Morales-Jimenez, D.; et al. A tutorial on fluid antenna system for 6G networks: Encompassing communication theory, optimization methods and hardware designs. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2407.03449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, W.; Yu, H.; Ali, F.; Huang, H. Active RIS-aided terahertz communications with phase error and beam misalignment. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2409.09713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S.; Virdi, J.S.; Babakhani, A.; Roberts, I.P. A survey on advancements in THz technology for 6G: Systems, circuits, antennas, and experiments. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2407.01957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, M.; Long, B.; Liu, H. A survey of extended reality in 3GPP Release 18 and beyond. Highlights Sci. Eng. Technol. 2023, 56, 542–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awais, M.; Ullah Khan, F.; Zafar, M.; Mudassar, M.; Zaigham Zaheer, M.; Mehmood Cheema, K.; Kamran, M.; Jung, W.S. Towards enabling haptic communications over 6G: Issues and challenges. Electronics 2023, 12, 2955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, S.; Wu, J.; Li, J.; Konstantin, K. Information-centric massive IoT-based ubiquitous connected VR/AR in 6G: A proposed caching consensus approach. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 8, 5172–5184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Gao, J.; Li, M.; Zhou, C.; Hu, S.; He, M.; Zhuang, W. Toward immersive communications in 6G. Front. Comput. Sci. 2023, 4, 1068478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phanindra, B.N. A survey of cloud gaming platforms: Architectural design and performance evaluation of major providers. Int. J. Sci. Res. Eng. Manag. 2024, 8, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Batra, R.; Kumar, S.; Bargavi, M. A review of implementing exploring mobile edge computing within the framework of 5G and 6G networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advances in Computation, Communication and Information Technology (ICAICCIT), Faridabad, India, 23–24 November 2023; pp. 1225–1230. [Google Scholar]
- Salama, A.M.; Xie, B.; Debnath, J.; Kumar, A. Low-latency high-reliability industrial MAC protocol for 6G networks. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Performance, Computing, and Communications Conference (IPCCC), Anaheim, CA, USA, 17–19 November 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Fernando, X.; Lăzăroiu, G. Energy-efficient Industrial Internet of Things in green 6G networks. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 8558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friese, I.; Galkow-Schneider, M.; Bassbouss, L.; Zoubarev, A.; Neparidze, A.; Melnyk, S.; Zhou, Q.; Schotten, H.D.; Pfandzelter, T.; Bermbach, D.; et al. True 3D holography: A communication service of tomorrow and its requirements for a new converged cloud and network architecture on the path to 6G. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on 6G Networking (6GNet), Paris, France, 18–20 October 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Kanthavel, R.; Dhaya, R. Research review on AI-powered 6G as sixth-sense technologies. In Advances in Wireless Technologies and Telecommunication; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2024; pp. 373–394. [Google Scholar]
- Pires, R.; Blue, H.; Malinen, J.; De Angelis, M.; Giardina, P.G.; Landi, G.; Laukkanen, M.; Ahola, K.; Porambage, P. Closed-loop automation in 6G for minimum downtime task continuity in surveillance cobots. In Proceedings of the Joint European Conference on Networks and Communications & 6G Summit (EuCNC/6G Summit), Antwerp, Belgium, 3–6 June 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Omkar, J.; Menaka, S.; Praveena, J.; Varshney, N.; Arunkumar, B.; Reddy, G.V. The use of 6G communication technology in healthcare applications for the accurate and better transmission. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Advance Computing and Innovative Technologies in Engineering (ICACITE), Greater Noida, India, 14–15 May 2024; Volume 27, pp. 1993–1999. [Google Scholar]
- Nautiyal, A.P.; Bathla, N. Revolutionizing urban mobility: Smart transportation & vehicle-to-infrastructure communication—A review. Int. J. Multidiscip. Res. 2024, 6, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Kemp, T. Soil Analysis via Remote Sensing and Artificial Intelligence for Precision Regenerative Agriculture. Ph.D. Thesis, Toronto Metropolitan University, Toronto, ON, Canada, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Bithas, P.S. Distributed HAPS-assisted communications in FSO/RF space-air-ground integrated networks. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2024, 56, 1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Li, B.; Guo, N.; Chen, Y.; Su, X.; Lu, Y. Environmental monitoring system with information transmission and acquisition based on ZigBee and 5G combined technology. In Proceedings of the IEEE 6th International Electrical and Energy Conference (CIEEC), Hefei, China, 12–14 May 2023; pp. 4172–4177. [Google Scholar]
- Decorme, R.; Faye, S.; Calisti, M.; Pryor, S.; Dey, I.; Fanti, M.P.; Malandrino, F.; Lombardo, C. Towards sustainable 6G: A collaborative call to action for addressing environmental challenges in (and thanks to) future mobile networks. Open Res. Eur. 2025, 4, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antón-Haro, C.; Trichias, K.; De Majo, C.; Kaloxylos, A.; Beriere, J. 6G Smart Networks and Services: Global Strategies, Main Work Directions & Future Outlook. In Proceedings of the 2024 Joint European Conference on Networks and Communications & 6G Summit (EuCNC/6G Summit), Antwerp, Belgium, 3–6 June 2024; pp. 1115–1120. [Google Scholar]
- Viji, G.J.; Sheeba, L.; Kumar, D.; Sharmila, B.N.; Lukose, B. Eco-Intelligent 6G Deployment: A Data-Driven Multi-Objective Framework for Sustainable Impact Analysis and Optimization. In 6G Impacts on Natural Habitats and Human Life; IGI Global Scientific Publishing: Hershey, PA, USA, 2025; pp. 191–226. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Li, C.; Li, S.; Zhang, P.; Cheng, M. Application research of 6G-based digital twins in smart cities. In Proceedings of the 2024 2nd International Conference on Mechatronics, IoT and Industrial Informatics (ICMIII), Melbourne, Australia, 12–14 June 2024; pp. 30–34. [Google Scholar]
- Bag, S.; Dhamija, P. Role of artificial intelligence in operations environment: A review and bibliometric analysis. TQM J. 2020, 32, 869–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Tao, D. Empowering Things with Intelligence: A Survey of the Progress, Challenges, and Opportunities in Artificial Intelligence of Things. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 8, 7789–7817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; He, H.; He, T.; Lausen, L.; Li, M.; Lin, H.; Shi, X.; Wang, C.; Xie, J.; Zha, S.; et al. GluonCV and GluonNLP: Deep learning in computer vision and natural language processing. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2020, 21, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Kashyap, R.; Senthil Kumar, A.V. (Eds.) Challenges and applications for implementing machine learning in computer vision. In Advances in Computer and Electrical Engineering; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhary, K.R. Fundamentals of Artificial Intelligence; Springer: New Delhi, India, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Bian, Y.; Lu, Y.; Li, J. Research on an artificial intelligence-based professional ability evaluation system from the perspective of industry-education integration. Sci. Program. 2022, 2022, 4478115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, Q.S.; Hussain, S.; Bashir, I. Artificial intelligence and machine learning as pioneers in advancing 5G/6G network capabilities: Evolution, introduction, antecedents, and consequences. In 5G/6G Advancements in Communication Technologies for Agile Management; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2025; pp. 215–232. [Google Scholar]
- Horvath, K.; Tuda, S.; Idrizi, B.; Kitanov, S.; Doko, F.; Kimovski, D. 6G Infrastructures for Edge AI: An Analytical Perspective. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2506.10570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaik, R.B.; Nagaradjane, P.; Ioannou, I.; Vassiliou, V. PRAXIS: Proximal Reinforcement-aided Adaptive eXpert Intelligent System for Efficient Traffic Management in URLLC. In Proceedings of the 2025 IEEE International Conference on Communications Workshops (ICC Workshops), Montreal, QC, Canada, 8–12 June 2025; pp. 2088–2094. [Google Scholar]
- Paul, V. 5G and AI in Telecommunication Engineering: Powering a Smart, Connected Future: A Technical Review. J. Comput. Sci. Technol. Stud. 2025, 7, 669–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaram Mohan, K.; Mathew Fenn, S. Artificial intelligence and its theranostic applications in dentistry. Cureus 2023, 15, e38711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Kwong, C.F.; Zhou, S.; Ye, T.; Li, L.; Ardakani, S.P. Autonomous mobility management for 5G ultra-dense HetNets via reinforcement learning with tile coding function approximation. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 97942–97952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Ahn, Y.; Kim, S.; Shim, B. Deep learning-aided parametric sparse channel estimation for terahertz massive MIMO systems. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.07255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Li, J.; Kato, N. Artificial intelligence-assisted network slicing: Network assurance and service provisioning in 6G. IEEE Veh. Technol. Mag. 2023, 18, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ara, I.; Kelley, B. Secure and ultra-reliable 6G IoT algorithms with AI-enhanced shared key physical layer security. In Proceedings of the IEEE 15th Annual Ubiquitous Computing, Electronics & Mobile Communication Conference (UEMCON), Yorktown Heights, NY, USA, 17–19 October 2024; pp. 148–157. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Su, Z.; Li, R.; Zhang, K.; Wang, Y. Blockchain-based data security for artificial intelligence applications in 6G networks. IEEE Netw. 2020, 34, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nivetha, B.; Selvaprabhu, P.; Menon, U.V.; Rajamani, V.; Chinnadurai, S. 6G vision on edge artificial intelligence. In Towards Wireless Heterogeneity in 6G Networks; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2024; pp. 127–157. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.; Xu, Z.; He, X.; Lou, Q.; Xia, Y.; Huang, S. Proactive caching with distributed deep reinforcement learning in 6G cloud-edge collaboration computing. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 2024, 35, 1387–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaioannou, P.; Pastellas, I.; Tranoris, C.; Karagiorgou, S.; Denazis, S. AI-fuelled dimensioning and optimal resource allocation of 5G/6G wireless communication networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Mediterranean Conference on Communications and Networking (MeditCom), Madrid, Spain, 8–11 July 2024; Volume 23, pp. 413–418. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, R.; Kumar Sagar, P.; Malhotra, S.; Kulshreshtha, K. Improved resource allocation in 6G networks through artificial intelligence. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Disruptive Technologies (ICDT), Greater Noida, India, 15–16 March 2024; pp. 1208–1213. [Google Scholar]
- Chinchali, S.; Hu, P.; Chu, T.; Sharma, M.; Bansal, M.; Misra, R.; Pavone, M.; Katti, S. Cellular network traffic scheduling with deep reinforcement learning. In Proceedings of the Thirty-Second AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Thirtieth Innovative Applications of Artificial Intelligence Conference and Eighth AAAI Symposium on Educational Advances in Artificial Intelligence, AAAI’18/IAAI’18/EAAI’18, New Orleans, LA, USA, 2–7 February 2018; AAAI Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, C.X.; Hong, X.; McLaughlin, S. Artificial Intelligence to Manage Network Traffic of 5G Wireless Networks. IEEE Netw. 2018, 32, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musa, U.I.; Gupta, S.; Mensah, Q.E. AI-Driven Intelligent Transportation Systems in the Age of 5G/6G Networks. Available online: https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-3746665/v1 (accessed on 11 November 2025).
- Nan, J.; Ai, M.; Liu, A.; Duan, X. Regional-union based federated learning for wireless traffic prediction in 5G-Advanced/6G network. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CIC International Conference on Communications in China (ICCC Workshops), Foshan, China, 11–13 August 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Jedhe, A.; Chopade, S. Traffic prediction for intelligent transportation system using machine learning. Int. J. Res. Appl. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2022, 10, 244–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, P.; Schwarzmann, S.; Trivisonno, R. An intelligent entity in 6G networks for advanced mobility management: Analyzing the benefits and accuracy requirements. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Machine Learning for Communication and Networking (ICMLCN), Stockholm, Sweden, 5–8 May 2024; pp. 274–279. [Google Scholar]
- Saad, S.A.; Shayea, I.; Sid Ahmed, N.M.O. Artificial intelligence linear regression model for mobility robustness optimization algorithm in 5G cellular networks. Alex. Eng. J. 2024, 89, 125–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Duan, X.; Sun, W.; Ai, M. Research on mobility prediction in 5G and beyond for vertical industries. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CIC International Conference on Communications in China (ICCC Workshops), Xiamen, China, 28–30 July 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Babu, B.; Daha, M.Y.; Ashraf, M.I.; Khurshid, K.; Hadi, M.U. AIDETECT2: A novel AI-driven signal detection approach for beyond 5G and 6G wireless networks. Electronics 2024, 13, 3821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Xiao, L.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, P.; Jiang, T. Hybrid beamforming design for ITS-aided THz wideband massive MIMO non-terrestrial communication. In Proceedings of the IEEE 98th Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC2023-Fall), Hong Kong, China, 10–13 October 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Tamilarasi, K.; Pavithra, S.; Rangarajan, R.; Venkataraman, V.; Shankar, K. AI-powered optimization: Revolutionizing 6G networks for efficiency and performance. In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Smart Technologies and Systems for Next Generation Computing (ICSTSN), Villupuram, India, 18–19 July 2024; Volume 100, pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, Y.J.; Zhu, C.; Tan, T.C.; Kumar, A.; Wong, L.J.; Chong, Y.; Singh, R. Self-adaptive deep reinforcement learning for THz beamforming with silicon metasurfaces in 6G communications. Opt. Express 2022, 30, 27763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Hua, M.; Chen, T.; Liu, G.; Deng, J.; Li, N. Quality of AI service assurance in 6G native artificial intelligence networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Sensing, Diagnostics, Prognostics, and Control (SDPC), Shijiazhuang, China, 26–28 July 2024; pp. 70–75. [Google Scholar]
- Lovén, L.; Shahid, H.F.; Nguyen, L.; Harjula, E.; Silvén, O.; Pirttikangas, S.; López, M.B. Semantic slicing across the distributed intelligent 6G wireless networks. In Proceedings of the 20th Annual IEEE International Conference on Sensing, Communication, and Networking (SECON), Madrid, Spain, 11–14 September 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Ko, K.M.; Kim, C.L.; Lim, J.S.; Kim, S.W.; Seo, B.S. AI-based security enhancement and personal information protection techniques inherited from 6G networks. In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Soft Computing and Applications, Toronto, ON, Canada, 27–28 September 2023; Academy & Industry Research Collaboration Center: Kyoto, Japan, 2023; pp. 261–269. [Google Scholar]
- Parveen, K. Securing breakneck pace of 5G networks air interfaces through proactive AI monitoring. Int. J. Electron. Crime Investig. 2024, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Su, Z.; Li, R. Security and privacy in artificial intelligence-enabled 6G. IEEE Netw. 2022, 36, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, H.J.; Mishra, A.; Ratchagar, N.P. Advancing 6G networks: The implications of edge AI integration. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Advances in Computation, Communication and Information Technology (ICAICCIT), Faridabad, India, 23–24 November 2023; pp. 1180–1185. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Lin, F.; Yang, L.; Huang, D. AI service placement for multi-access edge intelligence systems in 6G. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2023, 10, 1405–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansar, S.A.; Samriya, J.K.; Kumar, M.; Gill, S.S.; Khan, R.A. Intelligent fog-IoT networks with 6G endorsement: Foundations, applications, trends and challenges. In 6G Enabled Fog Computing in IoT; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 287–307. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, J. Mobile edge computing, metaverse, 6G wireless communications, artificial intelligence, and blockchain: Survey and their convergence. In Proceedings of the IEEE 8th World Forum on Internet of Things (WF-IoT), Yokohama, Japan, 26 October–11 November 2022; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Tran-Dang, H.; Kim, D.S. Applications of fog computing. In Cooperative and Distributed Intelligent Computation in Fog Computing; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 19–31. [Google Scholar]
- Salameh, A.I.; El Tarhuni, M. From 5G to 6G—Challenges, technologies, and applications. Future Internet 2022, 14, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zheng, X. 6G: A survey on technologies, scenarios, challenges, and the related issues. J. Ind. Inf. Integr. 2020, 19, 100158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahraki, A.; Abbasi, M.; Piran, M.J.; Taherkordi, A. A comprehensive survey on 6G networks:Applications, core services, enabling technologies, and future challenges. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2101.12475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Choi, H.; Kang, H.; An, J.; Yeom, S.; Hong, T. A systematic review of the smart energy conservation system: From smart homes to sustainable smart cities. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 140, 110755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almalki, F.A.; Alsamhi, S.H.; Sahal, R.; Hassan, J.; Hawbani, A.; Rajput, N.S.; Saif, A.; Morgan, J.; Breslin, J. Green IoT for Eco-friendly and sustainable smart cities: Future directions and opportunities. Mob. Netw. Appl. 2023, 28, 178–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potrč, S.; Čuček, L.; Martin, M.; Kravanja, Z. Sustainable renewable energy supply networks optimization—The gradual transition to a renewable energy system within the European Union by 2050. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 146, 111186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsamhi, S.; Afghah, F.; Sahal, R.; Hawbani, A.; Al-qaness, M.A.; Lee, B.; Guizani, M. Green internet of things using UAVs in B5G networks: A review of applications and strategies. Ad Hoc Netw. 2021, 117, 102505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karrupusamy, P.; Balas, V.E.; Shi, Y. (Eds.) Sustainable Communication Networks and Application; Lecture Notes on Data Engineering and Communications Technologies; Springer: Singapore, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Danaei Yeganeh, F.; Ebrahimi, A. Dynamic spectrum refarming for GERAN/EUTRAN considering GERAN voice traffic. Telecommun. Syst. 2020, 73, 507–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Guo, H.; Zhang, Z.; Hu, C.; Xu, X.; Lin, P. Performance Analysis of 2.1 GHz FDD Spectrum Re-farming Scheme Based on MOCN Network. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Information Processing and Network Provisioning (ICIPNP), Beijing, China, 15–16 September 2022; pp. 116–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yigitcanlar, T.; Mehmood, R.; Corchado, J.M. Green artificial intelligence: Towards an efficient, sustainable and equitable technology for smart cities and futures. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halhoul Merabet, G.; Essaaidi, M.; Ben Haddou, M.; Qolomany, B.; Qadir, J.; Anan, M.; Al-Fuqaha, A.; Abid, M.R.; Benhaddou, D. Intelligent building control systems for thermal comfort and energy-efficiency: A systematic review of artificial intelligence-assisted techniques. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 144, 110969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, Z.; Al-Turjman, F.; Mostarda, L.; Gagliardi, R. Applications of Artificial Intelligence and Machine learning in smart cities. Comput. Commun. 2020, 154, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Jiang, C.; Wang, J.; Ren, Y.; Debbah, M. Machine Learning for 6G Wireless Networks: Carrying Forward Enhanced Bandwidth, Massive Access, and Ultrareliable/Low-Latency Service. IEEE Veh. Technol. Mag. 2020, 15, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, S.M.; Periyasamy, M.; Kamaludeen, N.A.; Towfek, S.K.; Marappan, R.; Kidambi Raju, S.; Alharbi, A.H.; Khafaga, D.S. Optimizing traffic flow in smart cities: Soft GRU-based recurrent neural networks for enhanced congestion prediction using deep learning. Sustainability 2023, 15, 5949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Challoumis, C. Building a Sustainable Economy–How AI Can Optimize Resource Allocation. In Proceedings of the XVI International Scientific Conference, Copenhagen, Denmark, 17–20 December 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.J.; Raghavendra, R.; Gupta, U.; Acun, B.; Ardalani, N.; Maeng, K.; Chang, G.; Behram, F.A.; Huang, J.; Bai, C.; et al. Sustainable AI: Environmental implications, challenges and opportunities. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2111.00364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishant, R.; Kennedy, M.; Corbett, J. Artificial intelligence for sustainability: Challenges, opportunities, and a research agenda. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2020, 53, 102104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Yan, Z.; Wen, S. Deep Learning and Artificial Intelligence in Sustainability: A Review of SDGs, Renewable Energy, and Environmental Health. Sustainability 2023, 15, 13493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodorakopoulos, L.; Theodoropoulou, A.; Stamatiou, Y. A state-of-the-art review in big data management engineering: Real-life case studies, challenges, and future research directions. Eng 2024, 5, 1266–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharany, S.; Badotra, S.; Sharma, S.; Rani, S.; Alazab, M.; Jhaveri, R.H.; Reddy Gadekallu, T. Energy efficient fault tolerance techniques in green cloud computing: A systematic survey and taxonomy. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2022, 53, 102613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassey, K.E.; Rajput, S.A.; Oladepo, O.O.; Oyewale, K. Optimizing behavioral and economic strategies for the ubiquitous integration of wireless energy transmission in smart cities. World J. Adv. Eng. Technol. Sci. 2024, 13, 482–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhu, D.; Liu, Y. Artificial intelligence empowered physical layer security for 6G: State-of-the-art, challenges, and opportunities. Comput. Netw. 2024, 242, 110255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Zheng, X.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Karjalainen, M.; Dong, S.; Lu, R.; Wang, J.; Hyyppä, J. The effect of artificial intelligence evolving on hyperspectral imagery with different signal-to-noise ratio, spectral and spatial resolutions. Remote Sens. Environ. 2024, 311, 114291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Gao, A.; Wu, W.; Tai, D.I.; Tseng, J.H.; Wu, S.; Tsui, P.H. Parameter estimation of the homodyned K distribution based on an artificial neural network for ultrasound tissue characterization. Ultrasonics 2021, 111, 106308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbasi, M.; Shahraki, A.; Taherkordi, A. Deep Learning for Network Traffic Monitoring and Analysis (NTMA): A Survey. Comput. Commun. 2021, 170, 19–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, D.K.; Das, S. Smart grid architecture model for control, optimization and data analytics of future power networks with more renewable energy. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 301, 126877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nancharaiah, K.R.; Ravi, K.C.; Srivastava, A.K.; Arunkumar, K.; Siddiqui, S.T.; Arun, M.R. Analysis of data science and AI-enabled 6G wireless communication networks. Radioelectron. Commun. Syst. 2023, 66, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhter, R.; Sofi, S.A. Precision agriculture using IoT data analytics and machine learning. J. King Saud Univ. Comput. Inf. Sci. 2022, 34, 5602–5618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaseen, A. Accelerating the SOC: Achieve greater efficiency with AI-driven automation. Int. J. Responsible Artif. Intell. 2022, 12, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Sarker, I.H. AI-based modeling: Techniques, applications and research issues towards automation, intelligent and smart systems. SN Comput. Sci. 2022, 3, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Chen, N.; Xiao, A.; Jia, H.; Jiang, C.; Zhang, P. AI-enabled deployment automation for 6G space-air-ground integrated networks: Challenges, design, and outlook. IEEE Netw. 2024, 38, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumdar, S.; Trivisonno, R.; Poe, W.Y.; Carle, G. Distributing Intelligence for 6G Network Automation: Performance and Architectural Impact. In Proceedings of the ICC 2023—IEEE International Conference on Communications, Rome, Italy, 28 May–1 June 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Q.; Li, N.; Chih-Lin.; Huang, J.; Xu, X.; Xie, Y. Intelligent RAN Automation for 5G and Beyond. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2024, 31, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bécue, A.; Praça, I.; Gama, J. Artificial intelligence, cyber-threats and Industry 4.0: Challenges and opportunities. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2021, 54, 3849–3886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.; Yuan, Q.; Li, J.; Wang, S.; Yang, F. Artificial Intelligence Powered Mobile Networks: From Cognition to Decision. IEEE Netw. 2022, 36, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chander, B.; Pal, S.; De, D.; Buyya, R. Artificial intelligence-based internet of things for industry 5.0. In Internet of Things; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 3–45. [Google Scholar]
- Abouelyazid, M. Advanced Artificial Intelligence Techniques for Real-Time Predictive Maintenance in Industrial IoT Systems: A Comprehensive Analysis and Framework. J. AI-Assist. Sci. Discov. 2023, 3. Available online: https://scienceacadpress.com/index.php/jaasd/article/view/83 (accessed on 11 November 2025).
- Balantrapu, S.S. AI for Predictive Cyber Threat Intelligence. Int. J. Manag. Educ. Sustain. Dev. 2024, 7, 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Hui, C.X.; Dan, G.; Alamri, S.; Toghraie, D. Greening smart cities: An investigation of the integration of urban natural resources and smart city technologies for promoting environmental sustainability. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 99, 104985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omrany, H.; Al-Obaidi, K.M.; Hossain, M.; Alduais, N.A.M.; Al-Duais, H.S.; Ghaffarianhoseini, A. IoT-enabled smart cities: A hybrid systematic analysis of key research areas, challenges, and recommendations for future direction. Discov. Cities 2024, 1, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemanand, D.; Jayalakshmi, D.S.; Ghosh, U.; Balasundaram, A.; Vijayakumar, P.; Sharma, P.K. Enabling Sustainable Energy for Smart Environment Using 5G Wireless Communication and Internet of Things. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2021, 28, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Z.Y.; Shah, S.A.; Draheim, D.; Hameed, S.; Rathore, M.M.U. Guest Editorial: Smart cities 2.0: How Artificial Intelligence and Internet of Things are transforming urban living. IET Smart Cities 2024, 6, 129–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutar, P.; Sarkar, S.A.; Tagare, A.; Pawar, A. A review on IoT-enabled smart homes using AI. In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Computing Communication and Networking Technologies (ICCCNT), Kamand, India, 24–28 June 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Arabelli, R.; Boddepalli, E.; Buradkar, M.; Goriparti, N.V.S.; Chakravarthi, M.K. IoT-enabled environmental monitoring system using AI. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communication and Applied Informatics (ACCAI), Chennai, India, 9–10 May 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, P.V.; Kulkarni, A.; Mendhe, D.; Keshar, D.K.; Tilak Babu, S.B.G.; Rajesh, N. AI-optimized hardware design for internet of things (IoT) devices. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Recent Trends in Computer Science and Technology (ICRTCST), Jamshedpur, India, 9–10 April 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Mah, P.M. Investigating remote healthcare accessibility with AI: Deep learning and NLP-based knowledge graph for digitalized diagnostics. Proc. AAAI Symp. Ser. 2024, 4, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pamulaparthyvenkata, S.; Murugesan, P.; Gottipalli, D.; Palanisamy, P. AI-enabled distributed healthcare framework for secure and resilient remote patient monitoring. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Smart Electronics and Communication (ICOSEC), Tamil Nadu, India, 18–20 September 2024; pp. 2034–2041. [Google Scholar]
- Shaikh, A.J.; Takbhate, S.B.; Gawai, S.; Limbore, A.M.; Patil, V.A. Revolutionizing healthcare: AI-powered solutions, technological integration for accessible and effective medical service. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advances in Computing Research on Science Engineering and Technology (ACROSET), Indore, India, 27–28 September 2024; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Asha.; Sumalatha, I.; Mishra, A.; Thethi, H.P.; Kalra, R.; Almusawi, M. Utilizing artificial intelligence in telemedicine for efficient remote diagnosis and treatment plan. In Proceedings of the IEEE 13th International Conference on Communication Systems and Network Technologies (CSNT), Jabalpur, India, 6–7 April 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Kurpad, N.B.; Dhanyashree, S.; Shivank, V.; Surya Shobith, T.A.S.; Jinny, S.V. AI-infused telemedicine for rural wellness: A comprehensive approach. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Innovative Trends in Information Technology (ICITIIT), Kottayam, India, 15–16 March 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Akinsiku, A.M. A comprehensive survey of federated learning approaches for privacy-preserving machine learning. Tech-Sphere J. Pure Appl. Sci. 2025, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahsavari, Y.; Dambri, O.A.; Baseri, Y.; Hafid, A.S.; Makrakis, D. Integration of federated learning and blockchain in healthcare: A tutorial. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2404.10092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganti, R.; Nellutla, V. Federated Learning 3.0: A Self-Healing Framework for Cross-Cloud AI Training with Provable GDPR Compliance. Eur. J. Comput. Sci. Inf. Technol. 2025, 13, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhinakaran, D.; Sankar, S.; Selvaraj, D.; Raja, S.E. Privacy-preserving data in IoT-based cloud systems: A comprehensive survey with AI integration. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2401.00794. [Google Scholar]
- Srivenkateswaran, C.; Jaya Mabel Rani, A.; Senthil Kumaran, R.; Vinston Raja, R. Securing healthcare data: A federated learning framework with hybrid encryption in cluster environments. Technol. Health Care 2025, 33, 1232–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, J.; Mohammed, I. Implementation of AI transportation routing in reverse logistics to reduce CO2 footprint. Int. J. Supply Chain Manag. 2024, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Huo, M.; Tang, S.; Chen, D.; Du, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, X. Research and application of key technologies of intelligent unmanned warehousing based on 5G. In Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on Next Generation Data-driven Networks (NGDN), Shenyang, China, 26–28 April 2024; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y. Logistics security integrated communication system under the background of 5G artificial intelligence. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Communication Technologies (ICAICT 2023), Shenzhen, China, 9–11 June 2023; Smart Innovation, Systems and Technologies. Springer Nature: Singapore, 2024; pp. 325–334. [Google Scholar]
- Apruzzese, M.; Bruni, M.E.; Musso, S.; Perboli, G. 5G and companion technologies as a boost in new business models for logistics and supply chain. Sustainability 2023, 15, 11846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datey, V.; Prabhu, S. Smart traffic control and prediction model empowered with 5G technology, artificial intelligence and machine learning. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Ambient Intelligence, Knowledge Informatics and Industrial Electronics (AIKIIE), Ballari, India, 2–3 November 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Shabib, S.; Fahoom, E.; Amsheh, M.A.; Shaini, C.; Gharib, A. Toward Safer Roads: Challenges and Solutions for URLLC in Modern Vehicle-to-Everything Networks. In Proceedings of the 2025 IEEE 4th International Conference on Computing and Machine Intelligence (ICMI), Mount Pleasant, MI, USA, 5–6 April 2025; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Kandu, S.S.; Prakash, A.; Tiwari, M.; Tripathi, S.; Gupta, N.; Pal, R. C-V2X and 5G-V2X: Challenges and Improvement Strategies. In Proceedings of the 2025 Third International Conference on Microwave, Antenna and Communication (MAC), Bhopal, India, 27–29 June 2025; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Pawar, V.; Zade, N.; Vora, D.; Khairnar, V.; Oliveira, A.; Kotecha, K.; Kulkarni, A. Intelligent Transportation System with 5G Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X): Architectures, Vehicular Use Cases, Emergency Vehicles, Current Challenges and Future Directions. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 183937–183960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodr, J.; Wei, Z.; Wang, J.; Gutierrez, C.A.; Correia, L.M. 6G-enabled vehicle-to-everything communications: Current research trends and open challenges. IEEE Open J. Veh. Technol. 2025, 6, 2358–2391. [Google Scholar]
- Baccari, S.; Hadded, M.; Touati, H.; Ghazzai, H.; Laouiti, A.; Setti, G. Multi-Technology Integration in Hybrid V2X Networks: A Survey, Challenges, and Open Issues. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 138475–138508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bikkasani, D.C. AI-driven 5G network optimization: A comprehensive review of resource allocation, traffic management, and dynamic network slicing. Am. J. Artif. Intell. 2024, 8, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, S.M.; Kim, S.; Kwon, S. Federated learning for user mobility classification in 5G heterogeneous networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE 99th Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC2024-Spring), Singapore, 24–27 June 2024; pp. 01–06. [Google Scholar]
- Rane, J.; Kaya, Ö.; Mallick, S.K.; Rane, N.L. Federated learning for edge artificial intelligence: Enhancing security, robustness, privacy, personalization, and blockchain integration in IoT. In Future Research Opportunities for Artificial Intelligence in Industry 4.0 and 5.0; Deep Science Publishing: Mumbai, India, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Ekellem, E.A.F. Harnessing the synergy: Federated learning meets edge computing in 5G ecosystems. TechRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, W.Y.B.; Ng, J.S.; Xiong, Z.; Jin, J.; Zhang, Y.; Niyato, D.; Leung, C.; Miao, C. Decentralized edge intelligence: A dynamic resource allocation framework for hierarchical federated learning. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 2022, 33, 536–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Hu, X.; Zhang, G.; Spachos, P.; Plataniotis, K.N.; Wu, H. Networking systems of AI: On the convergence of computing and communications. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 20352–20381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, L.; Silva, L.; Pinho, D.; Morais, F.; Martins, C.M.; Pires, P.M.; Fidalgo, P.; Rodrigues, H.; Cortez, P.; Pilastri, A. A federated machine learning approach to detect international revenue share fraud on the 5G edge. In Proceedings of the 37th ACM/SIGAPP Symposium on Applied Computing, Virtual, 25–29 April 2022; pp. 1432–1439. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Zhou, H.; Elsayed, M.; Bavand, M.; Gaigalas, R.; Ozcan, Y.; Erol-Kantarci, M. On-device intelligence for 5G RAN: Knowledge transfer and federated learning enabled UE-centric traffic steering. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Commun. Netw. 2024, 10, 689–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padmapriya, S.; Patil, T.; Veeraiah, V.; Namdev, A.; Koujalagi, A.; Gupta, A. Investigating scope of real-time data processing for IoT in 5G revolution. In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Computing Communication and Networking Technologies (ICCCNT), Kamand, India, 24–28 June 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, R.; Munoz, Y.; Lipps, C.; Schotten, H.D. Supervised wireless communication: An analytic framework for real-time model inference in the 5G core network. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Balkan Conference on Communications and Networking (BalkanCom), Istanbul, Turkey, 5–8 June 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Srivatsa.; Vivek.; Kusuma. Deep Q-networks and 5G technology for flight analysis and trajectory prediction. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Electronics, Computing and Communication Technologies (CONECCT), Bangalore, India, 12–14 July 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Vasudevan, B.; Vaithianathan, V.; Akshaya, V. A novel artificial intelligence-based antenna designing model for optimizing 5G mobile communication. Internet Technol. Lett. 2025, 8, e586. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Cai, P.; Li, D.; Zhu, B. Artificial Intelligence Cloud Platform for 5G Era. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE 2nd International Conference on Image Processing and Computer Applications (ICIPCA), Shenyang, China, 28–30 June 2024; pp. 1401–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hongvanthong, S. Novel four-layered software defined 5G architecture for AI-based load balancing and QoS provisioning. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Computer and Communication Systems (ICCCS), Shanghai, China, 15–18 May 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Endes, A.; Yuksekkaya, B. 5G Network Slicing with Multi-Purpose AI models. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Black Sea Conference on Communications and Networking (BlackSeaCom), Sofia, Bulgaria, 6–9 June 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Kannan, Y.; Kapil, D. Implementing Machine Learning algorithms for predictive network maintenance in 5G and beyond networks. Int. J. Wirel. Mob. Netw. 2024, 16, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samdanis, K.; Abbou, A.N.; Song, J.; Taleb, T. AI/ML service enablers and model maintenance for beyond 5G networks. IEEE Netw. 2023, 37, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannakidou, S.; Radoglou-Grammatikis, P.; Koussouris, S.; Pertselakis, M.; Kanakaris, N.; Lekidis, A.; Kaltakis, K.; Koidou, M.P.; Metallidou, C.; Psannis, K.E.; et al. 5G-enabled NetApp for predictive maintenance in critical infrastructures. In Proceedings of the 5th World Symposium on Communication Engineering (WSCE), Nagoya, Japan, 16–18 September 2022; pp. 129–132. [Google Scholar]
- Navesi, R.B.; Naghibi, A.F.; Zafarani, H.; Tahami, H.; Pirouzi, S. Reliable operation of reconfigurable smart distribution network with real-time pricing-based demand response. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2025, 241, 111341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qamar, F.; Kazmi, S.H.A.; Siddiqui, M.U.A.; Hassan, R.; Zainol Ariffin, K.A. Federated learning for millimeter-wave spectrum in 6G networks: Applications, challenges, way forward and open research issues. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2024, 10, e2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brik, B.; Chergui, H.; Zanzi, L.; Devoti, F.; Ksentini, A.; Siddiqui, M.S.; Costa-Pérez, X.; Verikoukis, C. Explainable AI in 6G O-RAN: A tutorial and survey on architecture, use cases, challenges, and future research. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2307.00319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, N.; Gupta, L. Securing the 6G–IoT Environment: A Framework for Enhancing Transparency in Artificial Intelligence Decision-Making Through Explainable Artificial Intelligence. Sensors 2025, 25, 854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Chen, X.; Wu, H.; Wang, Z.; Chen, X.; Niyato, D.; Huang, K. Integrated sensing and edge AI: Realizing intelligent perception in 6G. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Qu, G.; Chen, Q.; Chen, X.; Chen, Z.; Huang, K. Pushing large language models to the 6G edge: Vision, challenges, and opportunities. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2025, 63, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nallakaruppan, M.; Dhanaraj, R.K.; Shukla, S.; Krishnamoorthi, S.; Kaushal, R.K.; Goyal, M.K.; Basheer, S.; Quasim, M.T. A Federated Autoencoder Framework with Explainable AI for Intelligent 6G-IoT Infrastructure Optimization. IEEE Internet Things J. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).