Uptake and Translocation of Heavy Metals in Maize Leaves Exposed to Atmospheric Fallout
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
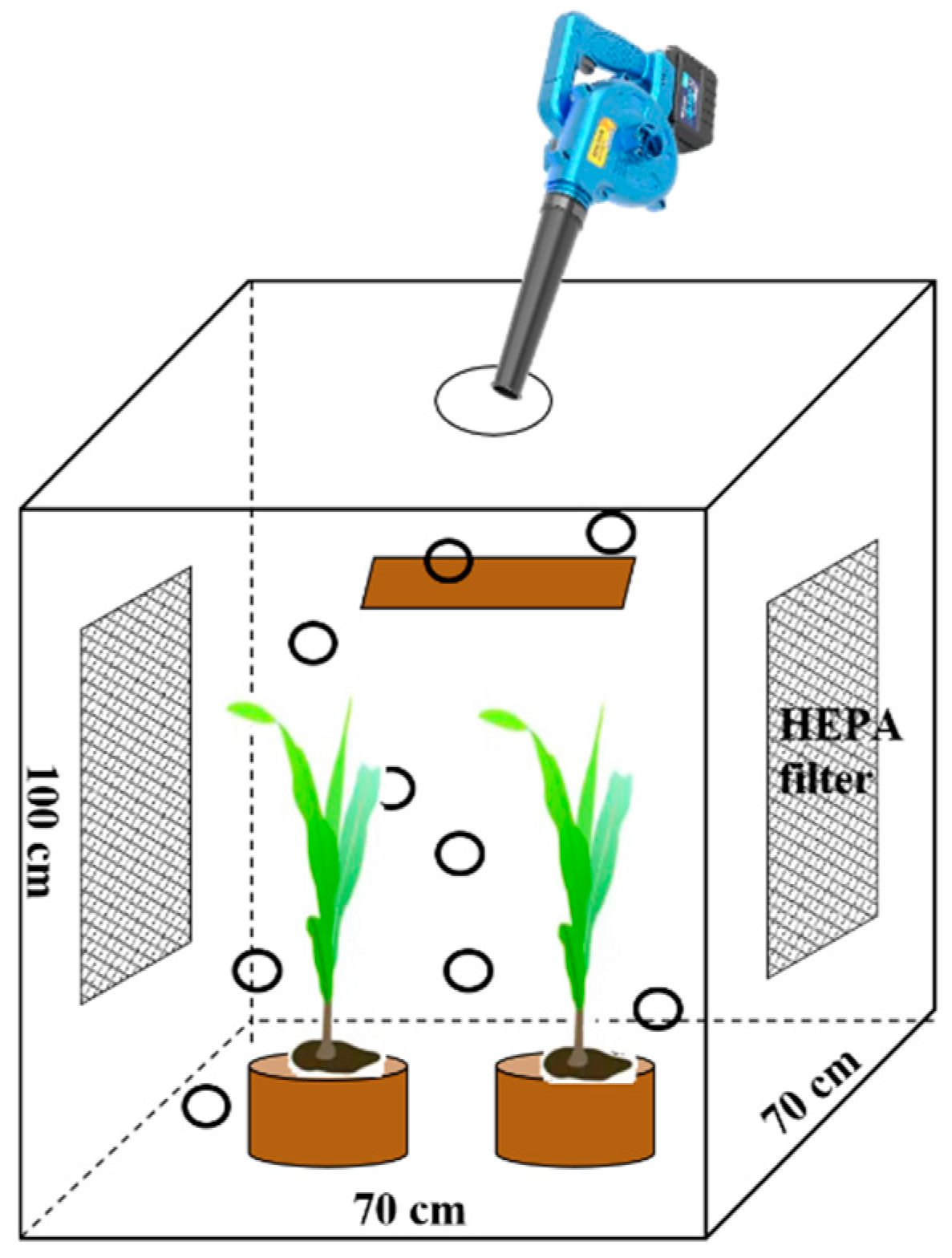
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Maize Growth Parameter
2.3. Sample Collection and Heavy Metal Analysis
2.4. Measurement of Antioxidant System Parameters
2.5. Scanning Electron Microscopy with Energy-Dispersive X-Ray Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Growth of Maize and Antioxidant System Parameters
3.2. Contents of Heavy Metals in Maize
3.3. Distribution of Heavy Metals in Maize
3.4. Bioconcentration Abilities of Heavy Metals
3.5. Morphology of Maize Leaves
4. Discussion
4.1. Pathway of Heavy Metal Uptake and Translocation in Leaves
4.2. Variations in Heavy Metal Accumulation Between Cultivars
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shao, X.; Cheng, H.G.; Li, Q.; Lin, C.Y. Anthropogenic atmospheric emissions of cadmium in China. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 79, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, M.; Fagel, N.; Van Rampelbergh, M.V.; Baldini, J.; Riotte, J.; Cheng, H.; Edwards, R.L.; Gillikin, D.; Quinif, Y.; Verheyden, S. Lead concentrations and isotope ratios in speleothems as proxies for atmospheric metal pollution since the industrial revolution. Chem. Geol. 2015, 401, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, D.Y.; O’Connor, D.; Igalavithana, A.D.; Alessi, D.S.; Luo, J.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Sparks, D.L.; Yamauchi, Y.; Rinklebe, J.; Sik Ok, Y. Metal contamination and bioremediation of agricultural soils for food safety and sustainability. Nat. Rev. 2020, 1, 366–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goix, S.; Mombo, S.; Schreck, E.; Pierart, A.; Lévêque, T.; Deola, F.; Dumat, C. Field isotopic study of lead fate and compartmentalization in earthworm–soil–metal particle systems for highly polluted soil near Pb recycling factory. Chemosphere 2015, 138, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.; Choi, B.; Kang, M. Assessment of mobility and bio-availability of heavy metals in dry depositions of Asian dust and implications for environmental risk. Chemosphere 2015, 119, 1411–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Stein, A.F.; Castell, N.; Gonzalez-Castanedo, Y.; Sanchez de la Campa, A.M.; de la Rosa, J.D. Modeling and evaluation of urban pollution events of atmospheric heavy metals from a large Cu-smelter. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 539, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubier, A.; Wilkin, R.T.; Pichler, T. Cadmium in soils and groundwater: A review. Appl. Geochem. 2019, 108, 104388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Chen, Y.L.; Weng, L.P.; Ma, J.; Ma, Y.L.; Li, Y.T.; Islam, M.S. Comparisons of heavy metal input inventory in agricultural soils in North and South China: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 660, 776–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Geng, L.P.; Gao, P.P.; Dong, J.W.; Zhou, C.; Li, H.B.; Chen, M.M.; Xue, P.Y.; Liu, W.J. Bioimaging of Pb by LA-ICP-MS and Pb isotopic compositions reveal distributions and origins of Pb in wheat grain. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 802, 149729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Athanasios, V.; Konstantinos, F.; Thomais, V. Airborne particulate matter and human health: Toxicological assessment and importance of size and composition of particles for oxidative damage and carcinogenic mechanisms. J. Environ. Sci. Health C Environ. Carcinog. Ecotoxicol. Rev. 2008, 4, 339–362. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.; Kabir, E.; Kabir, S. A review on the human health impact of airborne particulate matter. Environ. Int. 2015, 74, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.P.; Liu, J.; Zhang, L.; Cao, J.; Hu, J.B.; Tian, S.L.; Li, X.Y.; Xu, W. Bulk deposition and source apportionment of atmospheric heavy metals and metalloids in agricultural areas of rural Beijing during 2016–2020. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Liang, H.; Zhu, S. Mercury emission from spontaneously ignited coal gangue hill in Wuda coalfield, Inner Mongolia, China. Fuel 2016, 182, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.L.; Zhou, J.; Li, M.; Hu, Y.M.; Liu, X.L.; Zhou, J. Study of the bioavailability of heavy metals from atmospheric deposition on the soil-pakchoi (Brassica chinensis L.) system. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 362, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.L.; Zhou, J.; Li, M.; Xia, R.Z.; Wang, X.Z.; Zhou, J. Dynamic behaviors of newly deposited atmospheric heavy metals in the Soil-Pak choi system. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 12734–12744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhuang, Z.; Yu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wan, Y.N.; Li, H.F. Arsenic transfer and accumulation in the soil-rice system with sulfur application and different water managements. Chemosphere 2021, 269, 128772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, Z.; Niño-Savala, A.G.; Mi, Z.D.; Wan, Y.N.; Su, D.C.; Li, H.F.; Fangmeier, A. Cadmium accumulation in wheat and maize grains from China: Interaction of soil properties, novel enrichment models and soil thresholds. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 275, 116623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Z.; Wang, Q.Q.; Huang, S.Y.; Niño-Savala, A.G.; Wan, Y.N.; Li, H.F.; Schweiger, A.H.; Fangmeier, A.; Franzaring, J. Source-specific risk assessment for cadmium in wheat and maize: Towards an enrichment model for China. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 125, 723–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, C.; Liu, F.Y.; Yang, J.; Liu, N.; Zhang, K.; Berrettoni, M.; Zhang, H.Z. The newly absorbed atmospheric lead by wheat spike during filling stage is the primary reason for grain lead pollution. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 870, 161965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, R.Z.; Zhou, J.; Zeng, Z.; Sun, Y.F.; Cui, H.B.; Liu, H.L.; Zhou, J. Cadmium isotope fractionations induced by foliar and root uptake for rice exposed to atmospheric particles: Implications for environmental source tracing. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 10, 1096–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, R.Z.; Zhou, J.; Mi, Y.Z.; Cui, H.B.; Liu, H.L.; Hu, K.X.; Zhou, J. Chemical fractions of trace metals in atmospheric wet and dry deposition and contribution to rice root and foliar uptake. Plant Soil 2024, 494, 285–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.L.; Liu, C.Q.; Yang, Y.G.; Bi, X.Y.; Liu, T.Z.; Zhao, Z.Q. Natural and anthropogenic lead in soils and vegetables around Guiyang city, southwest China: A Pb isotopic approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 431, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreck, E.; Foucault, Y.; Sarret, G.; Sobanska, S.; Cécillon, L.; Castrec-Rouelle, M.; Uzu, G.; Dumat, C. Metal and metalloid foliar uptake by various plant species exposed to atmospheric industrial fallout: Mechanisms involved for lead. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 427–428, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Yang, X.D.; Xu, Z.Q.; Fei, J.C.; Peng, J.W.; Rong, X.M.; Huang, Y.; Yang, X.E. Foliar uptake, translocation and accumulation of heavy metals from atmospheric deposition in crops. Plant Nutr. Fert. Sci. 2021, 27, 332–345. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.Q.; Huang, S.Y.; Jiang, R.Q.; Zhuang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Q.; Wan, Y.N.; Li, H.F. Phytoremediation strategies for heavy metal-contaminated soil by selecting native plants near mining areas in Inner Mongolia. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 94501–94514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 15618-2018; Soil Environmental Quality Risk Control Standard for Soil Contamination of Agricultural Land. Ministry of Ecology and Environment: Beijing, China, 2018.
- Uzu, G.; Sobanska, S.; Sarret, G.; Muñoz, M.; Dumat, C. Foliar lead uptake by lettuce exposed to atmospheric fallouts. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 3, 1036–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, T.T.; Leveque, T.; Austruy, A.; Goix, S.; Schreck, E.; Dappe, V.; Sobanska, S.; Yann Foucault, Y.; Dumat, C. Foliar uptake and metal(loid) bioaccessibility in vegetables exposed to particulate matter. Environ. Geochem. Health 2014, 36, 897–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Xu, Z.Q.; Peng, J.W.; Fei, J.C.; Yu, P.Y.; Wang, M.D.; Tian, Y.F.; Huang, Y.; Zhran, M.; Fahmy, A. The contribution of atmospheric deposition of cadmium and lead to their accumulation in rice grains. Plant Soil 2022, 477, 373–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinnersley, R.P.; Scott, L.K. Aerial contamination of fruit through wet deposition and particulate dry deposition. J. Environ. Radioact. 2001, 52, 191–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P.; Yadav, P.; Ghosh, C.; Singh, B. Heavy metal capture from the suspended particulate matter by Morus alba and evidence of foliar uptake and translocation of PM associated zinc using radiotracer (65Zn). Chemosphere 2020, 254, 126863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Khashman, O.A.; Al-Muhtaseb, A.A.H.; Ibrahim, K.A. Date palm (Phoenix dactylifera L.) leaves as biomonitors of atmospheric metal pollution in arid and semi-arid environments. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 1635–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turan, D.; Kocahakimoglu, C.; Kavcar, P.; Gaygısız, H.; Atatanir, L.; Turgut, C.; Sofuoglu, S.C. The use of olive tree (Olea europaea L.) leaves as a bioindicator for environmental pollution in the Province of Aydın, Turkey. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2011, 18, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speak, A.F.; Rothwell, J.J.; Lindley, S.J.; Smith, C.L. Urban particulate pollution reduction by four species of green roof vegetation in a UK city. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 61, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, F.; Wang, L.H.; Sun, F.B.; Li, G.; Yu, L.; Wang, Y.J.; Zeng, X.R.; Yan, H.; Dong, L.; Bao, Z.Y. Study on different particulate matter retention capacities of the leaf surfaces of eight common garden plants in Hangzhou, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 652, 939–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahid, M.; Dumat, C.; Khalid, S.; Schreck, E.; Xiong, T.T.; Niazi, N.K. Foliar heavy metal uptake, toxicity and detoxification in plants: A comparison of foliar and root metal uptake. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 325, 36–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avellan, A.; Yun, J.; Morais, B.P.; Clement, E.T.; Rodrigues, S.M.; Lowry, G.V. Critical review: Role of inorganic nanoparticle properties on their foliar uptake and in planta translocation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 13417–13431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, M.; Natasha; Dumat, C.; Niazi, N.K.; Xiong, T.T.; Farooq, A.B.U.; Khalid, S. Ecotoxicology of heavy metal(loid)-enriched particulate matter: Foliar accumulation by plants and health impacts. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 253, 65–113. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, P.P.; Zhang, X.M.; Xue, P.Y.; Dong, J.W.; Dong, Y.; Zhao, Q.L.; Geng, L.P.; Lu, Y.; Zhao, J.J.; Liu, W.J. Mechanism of Pb accumulation in Chinese cabbage leaves: Stomata and trichomes regulate foliar uptake of Pb in atmospheric PM2.5. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 293, 118585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Kwak, M.J.; Woo, S.Y. Adsorption of particulate matter and uptake of metal and non-metal elements from PM in leaves of Pinus densiflora and Quercus acutissima: A comparative study. Front. For. Glob. Change 2024, 6, 1301533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Lin, L.; Yang, J.; Zhang, H.Z. The relative contributions of different wheat leaves to the grain cadmium accumulation. Toxics 2022, 10, 637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.Q.; Zhu, Z.; Zhao, Y.H.; Huang, Z.; Fei, J.C.; Han, Y.L.; Wang, M.D.; Yu, Y.P.; Peng, J.W.; Huang, Y.; et al. Foliar uptake, accumulation, and distribution of cadmium in rice (Oryza sativa L.) at different stages in wet deposition conditions. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 306, 119390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.Q.; Peng, J.W.; Zhu, Z.; Yu, Y.P.; Wang, M.D.; Huang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Li, Z.J. Screening of leafy vegetable varieties with low lead and cadmium accumulation based on foliar uptake. Life 2022, 12, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth-Nebelsick, A. Computer-based studies of diffusion through stomata of different architecture. Ann. Bot. 2007, 100, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.P.; Xue, P.Y.; Dong, J.W.; Zhang, X.M.; Sun, H.X.; Geng, L.P.; Luo, S.X.; Zhao, J.J.; Liu, W.J. Contribution of PM2.5-Pb in atmospheric fallout to Pb accumulation in Chinese cabbage leaves via stomata. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 407, 124356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.P.; Chen, R.Q.; Xue, P.Y.; Guan, P.B.; Dong, Y.; Liang, H.; Geng, L.P.; Zhao, Q.L.; Ma, W.; Zhao, J.J.; et al. Combined μ-XRF and XANES track the behavior of Pb from PM2.5 entering Chinese cabbage leaves. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2025, 59, 4025–4035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larue, C.; Castillo-Michel, H.; Sobanska, S.; Trcera, N.; Sorieul, S.; Cécillon, L.; Ouerdane, L.; Legros, S.; Sarret, G. Fate of pristine TiO2 nanoparticles and aged paint-containing TiO2 nanoparticles in lettuce crop after foliar exposure. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 273, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larue, C.; Castillo-Michel, H.; Sobanska, S.; Cécillon, L.; Bureau, S.; Barthès, V.; Ouerdane, L.; Carrière, M.; Sarret, G. Foliar exposure of the crop Lactuca sativa to silver nanoparticles: Evidence for internalization and changes in Ag speciation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 264, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schönherr, J.; Luber, M. Cuticular penetration of potassium salts: Effects of humidity, anions, and temperature. Plant Soil 2001, 236, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schönherr, J.R.; Schreiber, L. Size selectivity of aqueous pores in astomatous cuticular membranes isolated from Populus canescens (Aiton) Sm. leaves. Planta 2004, 219, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birbaum, K.; Brogioli, R.; Schellenberg, M.; Martinoia, E.; Stark, W.J.; Günther, D.; Limbach, L.K. No evidence for cerium dioxide nanoparticle translocation in maize plants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 8718–8723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, L.; Ma, Z.Y.; Xu, Y.S.; Sun, F.B.; Lun, X.X.; Liu, X.H.; Chen, J.G.; Yu, X.X. Assessing the capacity of plant species to accumulate particulate matter in beijing, china. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e140664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.; Zhang, Y.X.; Kleinstiver, B.P.; Guo, J.A.; Aryee, M.J.; Miller, J.; Malzahn, A.; Zarecor, S.; Lawrence-Dill, C.J.; Joung, J.K.; et al. Activities and specificities of CRISPR/Cas9 and Cas12a nucleases for targeted mutagenesis in maize. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2019, 17, 362–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnatam, K.S.; Mythri, B.; Nisa, W.U.; Sharma, H.; Meena, T.K.; Rana, P.; Vikal, Y.; Gowda, M.; Dhillon, B.S.; Sandhu, S. Silage maize as a potent candidate for sustainable animal husbandry development—Perspectives and strategies for genetic enhancement. Front. Genet. 2023, 14, 1150132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.X.; Sun, Z.M.; Saud, S.; Fahad, S.; Nawaz, T. Exploring the deleterious effects of heavy metal cadmium on antioxidant defense and photosynthetic pathways in higher plants. Plant Stress 2025, 15, 100716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.Y.; Lin, B.G.; Wu, L.; Pan, P.; Liu, B.B.; Li, R.L. Antagonistic effect of polystyrene nanoplastics on cadmium toxicity to maize (Zea mays L.). Chemosphere 2022, 307, 135714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, S.K.; Naimuzzaman, M.; Rahman, F. Glutathione: A key frontier of heavy-metal detoxification and tolerance in plants. Plant Trends. 2023, 1, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daud, M.K.; Mei, L. Leaf-based physiological, metabolic, and ultrastructural changes in cultivated cotton cultivars under cadmium stress mediated by glutathione. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 15551–15564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajbhiye, T.; Pandey, S.K.; Kim, K.; Szulejko, J.E.; Prasad, S. Airborne foliar transfer of PM bound heavy metals in Cassia siamea: A less common route of heavy metal accumulation. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 573, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lhotská, M.; Zemanová, V.; Pavlík, M.; Pavlíková, D.; Hnilička, F.; Popov, M. Leaf fitness and stress response after the application of contaminated soil dust particulate matter. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 10046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Wang, L.; Sun, Y.P.; Zhao, L.J.; Niu, G.H.; Tan, W.J.; Rico, C.M.; Peralta-Videa, J.R.; Gardea-Torresdey, J.L. Foliar applied nanoscale and microscale CeO2 and CuO alter cucumber (Cucumis sativus) fruit quality. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 563–564, 904–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burzyński, M.; Kłobus, G. Changes of photosynthetic parameters in cucumber leaves under Cu, Cd, and Pb stress. Photosynthetica 2004, 42, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kardel, F.K.; Wuyts, K.; Babanezhad, M.; Vitharana, U.W.A.; Wuytack, T.; Potters, G.; Samson, R. Assessing urban habitat quality based on specific leaf area and stomatal characteristics of Plantago lanceolata L. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 788–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uzu, G.; Sobanska, S.; Sarret, G.; Sauvain, J.J.; Pradère, P.; Dumat, C. Characterization of lead-recycling facility emissions at various workplaces: Major insights for sanitary risks assessment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186, 1018–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahid, M.; Pinelli, E.; Dumat, C. Review of Pb availability and toxicity to plants in relation with metal speciation; Role of synthetic and natural organic ligands. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 219–220, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahid, M.; Dumat, C.; Pourrut, B.; Sabir, M.; Pinelli, E. Assessing the effect of metal speciation on lead toxicity to Vicia faba pigment contents. J. Geochem. Explor. 2014, 144, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomašević, M.; Vukmirović, Z.; Rajšić, S.; Tasić, M.; Stevanović, B. Characterization of trace metal particles deposited on some deciduous tree leaves in an urban area. Chemosphere 2005, 61, 753–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Element | BCF | |
|---|---|---|
| B909 | Q932 | |
| Cd | 0.0003 ± 0.0000a | 0.0004 ± 0.0001a |
| Pb | 0.0003 ± 0.0001a | 0.0007 ± 0.0001a |
| As | 0.0003 ± 0.0000a | 0.0002 ± 0.0000a |
| Zn | 0.0004 ± 0.0002a | 0.0004 ± 0.0000a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Q.; Qi, H.; Zhuang, Z.; Huang, S.; Wang, Q.; Wan, Y.; Li, H. Uptake and Translocation of Heavy Metals in Maize Leaves Exposed to Atmospheric Fallout. Plants 2025, 14, 3418. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14223418
Wang Q, Qi H, Zhuang Z, Huang S, Wang Q, Wan Y, Li H. Uptake and Translocation of Heavy Metals in Maize Leaves Exposed to Atmospheric Fallout. Plants. 2025; 14(22):3418. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14223418
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Qiqi, Hao Qi, Zhong Zhuang, Siyu Huang, Qi Wang, Yanan Wan, and Huafen Li. 2025. "Uptake and Translocation of Heavy Metals in Maize Leaves Exposed to Atmospheric Fallout" Plants 14, no. 22: 3418. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14223418
APA StyleWang, Q., Qi, H., Zhuang, Z., Huang, S., Wang, Q., Wan, Y., & Li, H. (2025). Uptake and Translocation of Heavy Metals in Maize Leaves Exposed to Atmospheric Fallout. Plants, 14(22), 3418. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14223418








