Abstract
This paper presents a solution for small businesses to gather statistics on the presence of their customers in and around their institutions, using Bluetooth technology. The solution includes a model of a mobile system based on Bluetooth technology that can provide information about the detectable devices’ relative position to create statistics on users’ presence in a specific timeframe. The research conducted shows that Bluetooth technology can be efficiently used to log the user’s relative position. This paper proposes a two-component system, which includes a mobile application and a cloud-based database with a simple online query interface. The prototype was implemented for the Android operating system and confirms the feasibility of the proposed solution. The developed prototype application was designed as a foundation for further commercial development. The proposed solution provides small businesses with an accessible way of collecting data on the presence of people without having to buy specialized equipment.
1. Introduction
Bluetooth technology [1] plays a crucial role in the business world by providing a reliable, low-cost wireless communication solution for a wide range of applications. It enables devices to communicate with each other over short distances, making it ideal for use in small businesses such as retail stores, cafes, and restaurants. One of the critical benefits of Bluetooth technology for businesses [2] is its ability to create location-based services, proximity marketing, and indoor navigation. This allows businesses to engage with customers in a more targeted and personalized way, increasing the likelihood of sales and customer loyalty. Bluetooth beacons, for example, can be placed throughout a store to send location-based notifications and offers to customers’ smartphones, directing them to specific products or areas of the store. In addition to customer engagement, Bluetooth technology can also be used to streamline business operations. Bluetooth-enabled devices [1,3] such as smartphones and tablets can be used for point-of-sale transactions, inventory management, and other business operations, making it a versatile and cost-effective solution for small businesses. Another significant benefit of Bluetooth [4] is its ability to connect with a wide range of devices, from smartphones and tablets to laptops and desktop computers, allowing businesses to easily integrate Bluetooth technology into their existing systems and processes without needing expensive and complex infrastructure.
Bluetooth technology plays an important role in business by providing a reliable and cost-effective wireless communication solution [5]. It enables businesses to engage with customers in a more targeted and personalized way and streamline their operations, improving overall efficiency and profitability.
Collecting statistics on the presence of people in a specific area at a particular time can be of great value to businesses and institutions to help them provide better services and to gain intelligence on how to improve them. Among many possible usages, some need to be conducted only once or on the odd occasion, and they do not require great accuracy. One such example can be improving the coverage and reliability of a Wi-Fi network in a building based on information about places of accumulation of people compared with the router statistics; another could be simply measuring the number of people passing by a shop in a specified timeframe or counting the attendance of students at a lecture. This and similar situations create a need for a solution that does not require buying expensive specialized equipment, which in most cases can prove unprofitable but will provide reliable enough statistics. Logging of the user’s relative position can be performed based on the signal emitted by his mobile device.
The twenty-first century is a time of rapid technological advancement, miniaturization, and wireless devices [3]. The speed of life imposed by modern society’s demands led to a situation when “being offline” became barely possible, resulting in the vast majority of people living in a developed country having a phone. In the second quarter of the year 2017, there were already about 5 billion unique mobile subscribers registered worldwide, and 620 million new subscribers are predicted to be added to that number by 2020 [6] and a forecasted 7.620 million smartphone subscriptions worldwide by 2027 [7]. Considering those numbers, one can assume that counting the presence of people can be simplified to counting the mobile phones in their possession. One mobile device capability can be used to perform this task, such as Bluetooth 802.15.1 technology [8,9].
A growing interest in the internet of things (IoT) [10,11,12,13], smart technologies [14,15,16], and smartphones [17,18,19,20] becoming increasingly connected in general plays a significant role in making people leave their Bluetooth switch turned on [21,22,23]. Current numbers say up to 50% of users already do not turn off their 802.15.1 connectivity [9] at any moment, with younger users more likely to be in this group, and those statistics are increasing [24,25].
The suggested application areas of Bluetooth [9] related to the IoT and smart technologies, particularly for indoor spaces, include:
- Inventory management and emergency management [26];
- Occupancy detection [27];
- Smart grid applications [28];
- Smart energy management [29];
- Location-based services;
- Proximity marketing;
- Indoor navigation;
- Point-of-sale transactions and Bluetooth low-energy technology with point-of-interest [30,31];
- Logging of the user’s relative position.
Considering the nature of the task, a mobile platform seems ideal for running the created solution. Devices with an Android operating system have continually held the most significant global market share of all smartphones sold to end users since the beginning of 2011 and topping up at 88% in the second quarter of 2018. Its only real competitor is iOS (Apple Inc.’s mobile operating system developed for the company’s products) with a less significant 11.9% global market share in 2018 [32], and the market size in 2030 is predicted to be 925.7 billion [33]. Creating an application for this operating system ensures a lack of unnecessary programming effort and a huge base of possible users. One of the free cloud solutions available on the market can be used to store and process data collected by the mobile application. They can run an external database, deliver a backend service needed for communication with the mobile application, and provide a simple query interface that can visualize data.
The main contributions of this work are the following papers:
- The paper proposes an accessible solution for small businesses to gather statistics on the presence of their customers in and around their institutions using 802.15.1 technology [9].
- The paper presents a model of a mobile system based on Bluetooth technology that can provide information about detectable devices’ relative position to create statistics on users’ presence in a specific timeframe.
- The paper discusses the possibility of using Bluetooth technology for logging the user’s relative position and shows that such a solution is feasible.
- The paper presents a two-component system that was designed and a prototype that was implemented to confirm that 802.15.1 technology [9] is efficiently used to log the user’s relative position.
- The paper highlights the modular design of the app, which guarantees that Bluetooth technology can be easily exchanged in favor of other technology if needed.
- The paper presents the developed prototype application as a foundation for further commercial development.
- The paper discusses the importance of Bluetooth technology in the business world by providing a reliable, low-cost wireless communication solution for a wide range of applications, including location-based services, proximity marketing, and indoor navigation.
The purpose of this paper is to design a model of a mobile system based on 802.15.1 technology [9] that can provide information about detectable devices’ relative position to create statistics on users’ presence in a particular area in a specific timeframe. Created solutions should not enforce the buying of any specialized equipment, making a mobile application and a cloud-based database with a simple online query interface the perfect choice.
To sum up, monitoring the presence of people in a particular area in a specific timeframe can provide valuable statistics. This can be simplified by logging the relative position of detectable mobile devices supporting 802.15.1 technology [9].
Limitations. The limitations of this scientific paper are:
- A lack of empirical validation. This paper does not provide any empirical evidence to support the claims made about the efficiency and accuracy of the proposed solution. While the prototype implementation is described, no results of its performance are provided.
- A limited scope. This paper only focuses on the usage of Bluetooth technology and does not consider other technologies that can be used to log the user’s relative position. Additionally, this paper only considers the Android operating system, limiting the potential user base.
- Privacy concerns. This paper does not address the potential privacy concerns that may arise from collecting location data from users’ mobile devices. The implications of collecting and processing personal data should be considered and addressed.
- Generalizability. This paper does not provide information on the generalizability of the proposed solution to different types of small businesses or institutions. The specific context of This study may not be applicable to other settings, and further research is needed to validate its effectiveness in different environments.
2. Materials and Methods
The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) 802.15.1 [9] is a standard that describes media access control and physical layer specifications for devices connecting within a wireless personal area network (WPAN) [33,34]. Issued in 2002, the standard was based on BluetoothTM version 1.1 foundation specifications. It mainly defines the lower transport layers (logical link control and adaptation protocol—L2CAP, Link Manager protocol (LMP), baseband, and radio) but also specifies a clause on the SIM access profile and provides a protocol implementation conformance statement (PICS). A specification and description language (SDL) model for an integrated Bluetooth MAC sublayer is also described [35]. Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) is a wireless personal area network technology based on the IEEE 802.15.1 standard [9]. Bluetooth Low Energy Advertising features, such as adverting channels (37, 38, and 39), are the main benefit of Bluetooth 5.0 and the support for mesh topology. It is designed to provide a low-cost, low-power solution for small businesses looking to improve their connectivity and automation. BLE can connect devices such as smartphones, laptops, and tablets to peripherals such as printers, scanners, and sensors. This allows businesses to easily share information and automate tasks, improving efficiency and reducing costs. Additionally, BLE devices are typically small and easy to install, making them an accessible solution for small businesses with limited resources.
2.1. Bluetooth
IEEE standardized Bluetooth is 802.15.1 [9], but the standard is no longer maintained—the Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG) took over the maintenance and development of the specification. Bluetooth SIG standards must be met to trademark a product as a Bluetooth device [1,21,22,23,36]. The technology is an energy-efficient short-range communication system, and initially, it was meant to replace the old RS-232 cables. It operates at ultra high frequency (UHF) radio waves between 2400 and 2485 MHz and includes a 2 MHz wide part of the spectrum at the bottom end, and 3.5 MHz wide at the top is unused to avoid interference. A 2.4 GHz short-range frequency band is a part of the industrial, scientific, and medical (ISM) radio bands reserved internationally for those purposes. Bluetooth uses a frequency-hopping spread spectrum (FHSS) [37]—frequency channels are rapidly changing (usually 1600 hops/s) using a modulation scheme known to both transmitter and receiver. Transmitted data is divided into packets and sent through one of 79 designated channels, each having a bandwidth of 1 MHz. Initially, the Gaussian frequency-shift keying (GFSK) [38] technique was used, providing speeds of up to 721 kbps in Bluetooth 1.0—this bit rate was called the basic rate (BR). Version 2.0 introduced improvements to GFSK increasing the speed to 1 Mbps in BR mode and featured an enhanced data rate (EDR) that used differential phase-shift keying allowing raw data rates of 2 Mbps in case of π/4 differential phase-shift keying (π/4 DQPSK) or 3 Mbps with 8-point differential phase-shift keying (8DPSK). In Bluetooth 3.0, high-speed transfers via 802.11 using Bluetooth pairing were added [39,40,41,42,43,44]. Later versions mainly concerned Bluetooth Low Energy, designed for sport and fitness devices, accessories, and location services using beacons, control, and automation systems [45].
All core changes to the Bluetooth standard related to the connection speed, typical range, and modes used [46] are presented in the table below (Figure 1). It is also worth noting that the existence of three different power level classes depends on predicted usage and range [40]. A summary of those classes is presented in Figure 2.

Figure 1.
Comparison of Bluetooth standards by connection speed, range, and mode.

Figure 2.
Summary of Bluetooth power classes.
The lowest possible level allowing a reliable link for battery conservation purposes should be chosen. If the power control capability is available, the power level can be adjusted according to a received signal strength indicator (RSSI), a relative value of the power present in a signal received [40,41].
2.2. The Pros and Cons of Using Bluetooth Technology for Positioning
A model of a smart locating application for small businesses, based on Bluetooth 802.15.1 technology [9], is presented. Bluetooth technology allows devices to communicate with each other over short distances, making it ideal for use in small businesses, such as retail stores, cafes, and restaurants. It enables businesses to engage with customers in a more targeted and personalized way and streamline their operations, improving overall efficiency and profitability. The proposed solution logs the relative position of detectable mobile devices supporting 802.15.1 technology [9] to create statistics on users’ presence in a particular area in a specific timeframe.
The advantages of using Bluetooth technology for positioning are its reliability, low cost, and ability to connect with a wide range of devices, making it a versatile and cost-effective solution for small businesses. It also allows for location-based services, proximity marketing, and indoor navigation. Bluetooth beacons can be placed throughout a store to send location-based notifications and offer them to customers’ smartphones, directing them to specific products or areas of the store.
There are some drawbacks to using Bluetooth technology for positioning. The range is limited to about 30 feet, and the accuracy is not as high as some other technologies, such as ultra-wideband (UWB). Bluetooth signals can also be affected by interference from other devices in the area, and the signal strength can vary depending on the type of device and its orientation.
The pros and cons of using Bluetooth technology are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
The pros and cons of using Bluetooth technology for positioning.
These pros and cons vary depending on the specific use case and the implementation of Bluetooth technology.
Bluetooth technology is efficiently used to log the user’s relative position, providing valuable statistics for small businesses without the need for expensive specialized equipment. The modular design of the app also allows for easy exchange of Bluetooth technology in favor of other technologies if needed.
2.3. The Way of Communication
Bluetooth works with a master/slave architecture and is packet-based. A unique 48-bit address is used to distinguish devices. A master can connect to up to seven slaves, forming a piconet; all of them share the master’s clock and the same hopping pattern. The device can change its role, however, starting as a master and subsequently functioning as a slave, allowing for full-duplex communication. The transfer of data can occur between the master and one other device at any given time (does not apply to the broadcast mode) as the former chooses which slave to address, rapidly switching devices in a round-robin style, and all of the slaves should listen to data in each receive slot [41]. Bluetooth standards require devices to pair and be bound for security reasons. Otherwise, some private data could be exposed, or even the control of the device could be taken over [41]. However, for this article, the usage of this process will not be required. Thus, it can be omitted.
2.4. Detecting Devices
Devices using 802.15.1 technology [9,40], if in discoverable mode, respond to broadcasts from other devices.
- A device performing a scan sends a broadcast to find other devices;
- All devices in the range that are in discoverable mode receive the broadcast;
- Recipients knowing the address of the sender respond only to this specific addressee providing the following information:
- Device name;
- Device class;
- List of services;
- Technical information.
The main requirements suggest that these data will be enough to create a fully functional application in the scope of this article. The device name can be used as a friendly display name. The device class will allow the application to recognize whether a device is of a type of interest. Technical information includes the MAC address, which will serve different devices, and RSSI, which can approximate the relative distance from the receiver.
2.5. Relative Position Logging
Position logging can be done by saving the object’s location in set time intervals. It will require fewer resources than continuous tracking while still being sufficient in many use cases. Moreover, such collected data are enough to create a movement model or provide valuable statistics. An RSSI value can be used for this work to determine a device’s relative position. It is represented by a number usually ranging from −100 to 0; where closer to 0 means a stronger received signal [41]. Although RSSI is not directly translatable to metric units and can vary depending on the device, it is measured through experimental proceedings. The distance can be compared and approximated if needed. Deploying more than two receivers will allow trilateration.
2.6. Similar Existing Solutions
There are plenty of Bluetooth location solutions available on the market. They can be divided into two main groups based on principles of operation. The first group contains systems with Bluetooth Low Energy beacons deployed around an area. Companies providing such technologies include Proximi.io, Locatify, and infsoft GmbH. Not having any advanced built-in logic, they serve a purpose similar to a lighthouse.
However, to make broadcasts sent by those devices useful on the tracked device, there must be an operating application, or another means that recognizes them and is in possession of the real-world coordinates of those beacons [42]. A simple representation of this system is shown in Figure 3.
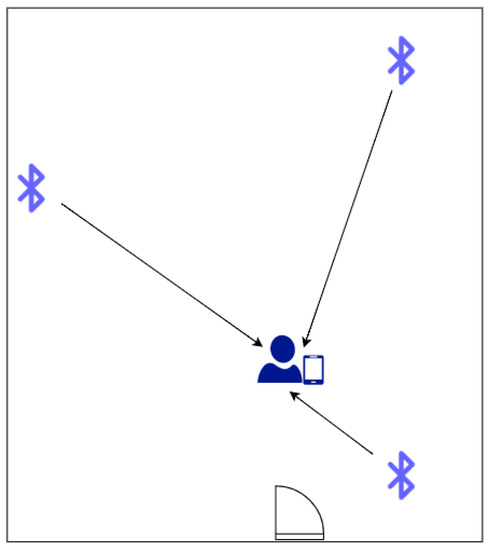
Figure 3.
Representation of Bluetooth localization (own source).
This situation requires the user’s direct interaction with the location service, all of which makes this solution serve a bit of a different purpose than the one described in the article. Moreover, it proves that, in this case, the approach with beacons is inappropriate. Another tactic is represented by a Spanish company Libelium. Their commercial solution involves a sophisticated IoT device called Meshlium.
Apart from being a tool for smart cities, this technology also involves a listener that can precisely monitor shopping and street activity by tracking smartphones in their radius using WiFi and Bluetooth. It detects them without the need to connect to any access point, eliminating the participation of owners of mobile devices [43,44,45,46]. As a commercial solution, Meshlium’s cost varies and can range from around USD 2000 to over USD 5000 for a full kit, including additional sensors [47]. This price range makes the technology highly unaffordable for small companies or people who want to use it only a few times and do not need accurate data. Thus, there is a market gap for a new low-cost solution.
Libelium’s smartphone monitoring solution [48] is a powerful tool that can be used in a variety of industries and applications. One potential use case scenario for this technology is in the retail industry. Imagine a retail store that wants to track customer behavior and gather data on foot traffic patterns, dwell time, and engagement with different products. The store could use Libelium’s solution to place Bluetooth beacons throughout the store and track the movement of customers’ smartphones as they shop. This data could be used to optimize the store layout, identify high-traffic areas, and determine which products are most popular among customers.
Another use case scenario is in the field of smart cities. The solution aided in monitoring the movement of people and vehicles in a city to gather data on traffic patterns, parking occupancy, and crowd density. This data can be used to optimize traffic flow, plan public transportation routes, and improve the overall efficiency and livability of the city. In the industrial sector, Libelium’s solution is applied to monitor the movement of workers and equipment on a factory floor. This data can be used to optimize the production process, identify bottlenecks, and improve overall efficiency.
Libelium’s smartphone monitoring solution provides valuable insights into customer behavior, traffic patterns, and worker movement, which can optimize operations, improve efficiency, and ultimately boost the bottom line for businesses and organizations in various industries.
3. Prototype
In order to prove that such a Bluetooth logging solution is possible, a prototype application was developed. The proposed prototype solution consists of an Android mobile application and a cloud service responsible for storing and processing data. The solution also handles visualization of the statistics on the presence of devices (Bluetooth technology users).
3.1. Technology Overview
Java programming language was chosen for the mobile application implementation as it remains the official language recommended by Google and can be used without the fear of becoming outdated soon [49]. During the development, IntelliJ IDEA integrated development environment was used as it offers full integration with Android tools developed by Google [49]. One of those tools is Android Profiler, a custom resource management monitor. The Gradle building system was used to compile and prepare the Android package. In the development process, a few additional dependencies were used to speed up the process by reducing the boilerplate code and taking care of some Android-related concerns. These include:
- Lifecycle package—for building lifecycle-aware components that automatically adjust to the current state of the application;
- Room Persistence Library—to take care of the SQLite database of the application;
- Azure Mobile SDK—to connect to the REST API provided by the Microsoft Azure cloud service;
- Easy Permissions—to properly ask the end user for needed permissions.
The foundation of the cloud database platform [50,51,52,53,54] is the Microsoft SQL Server database. Around it, the rest of the Azure platform [55,56,57] is built, consisting of an administration web portal (Figure 4).
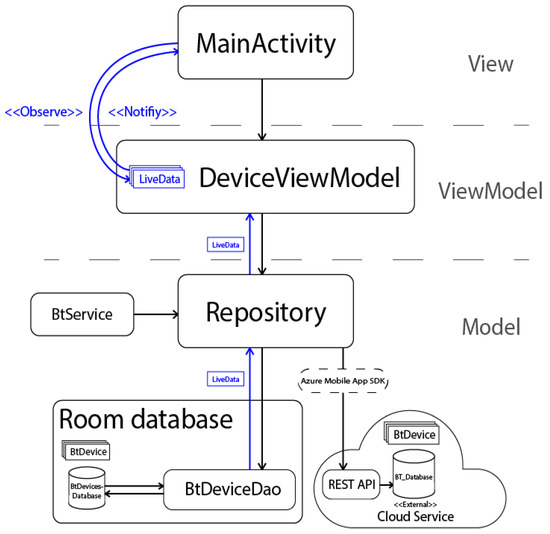
Figure 4.
Simplified diagram of the Smart Locator application structure and data flow (own source).
The Smart Locator application was tested on Bluetooth 5 version, but it can be easily adapted to the other or newest Bluetooth versions.
To locate Bluetooth devices to collect customer information, the following steps can be taken:
- Develop a mobile application: The first step is to develop a mobile application for the Android operating system that is compatible with all system versions from 5.0 Lollipop and above. The application should use Bluetooth 802.15.1 technology [9] to detect nearby Bluetooth-enabled devices and log their relative position.
- Implement a prototype: Once the mobile application is developed, a prototype should be implemented to test its functionality and performance. The prototype should provide a convenient interface for users to view and analyze the collected data.
- Collect data: The mobile application should be deployed on the business premises, and the Bluetooth-enabled devices’ relative position should be logged for a specific timeframe. The collected data should be stored in a cloud-based database for further analysis.
- Analyze data: The collected data can be analyzed to gain insights into customer behavior, such as their presence in specific areas of the business premises at particular times. The data can be used to optimize business operations, such as improving the coverage and reliability of the Wi-Fi network or measuring the number of people passing by a shop.
To improve the proposed solution, the following new methods can be implemented:
- Use machine learning algorithms: Machine learning algorithms can be used to analyze the collected data and provide more in-depth insights into customer behavior. For example, clustering algorithms can be used to group customers based on their presence in specific areas, and regression algorithms can be used to predict future customer behavior.
- Use other wireless communication technologies: the mobile application can be designed to support other wireless communication technologies, such as Wi-Fi or RFID, to provide more accurate location data.
- Integrate with other business systems: the mobile application can be integrated with other business systems, such as point-of-sale systems or inventory management systems, to provide a more comprehensive view of customer behavior.
- Enhance data privacy and security: to protect customer privacy, the mobile application should be designed to collect only anonymous data, and the cloud-based database should be secured using encryption and other security measures.
3.2. Architecture Model
The proposed solution is built according to the MVVM architectural pattern. According to this pattern, the application is divided into three parts [58]:
- The model—is responsible for data, current state, and business logic. It should not be tied to other components so it can be reused in other contexts;
- The view—is in charge of displaying the user interface (UI), taking advantage of data binding, which reduces the amount of code needed to connect the view and the model by being bound to observable variables in the ViewModel;
- The ViewModel—wraps around the model to allow the view to pass events to the model and provide the observable data needed by the view, without actually being tied to it.
Figure 4 presents the general of the application in a simplified manner. It clearly presents the MVVM pattern implemented [58] in the application and two databases: one on the mobile device for storing local data with the SQLite database and the other on the Azure platform that communicates with the mobile application via REST API provided by Microsoft.
View. During the implementation, the emphasis was put strictly on functionality, performance, and resource management. The app launches directly to the screen, where every option is available. Upon pressing the switch, the Bluetooth turns on (if it is off), and the scanning starts. The list is populated with new logs containing the device’s information, such as the name, MAC address, type, RSSI [59], and detection time (Figure 5).
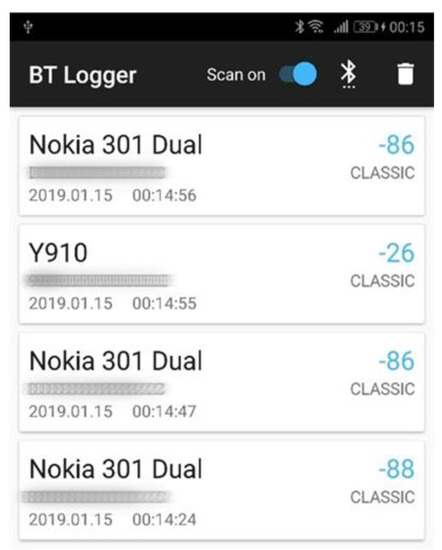
Figure 5.
The main screen of the Smart Locator app presents a list of detected devices and their information (own source).
The instance variable added to every log sent to the cloud database makes it possible to run the application on several devices and distinguish data. This way, more accurate localization data can be gathered after properly arrogating the working environment.
Finally, we can set the minimum signal strength, where the default value is 100, representing a weak strength signal of −100 dBm (Figure 6).
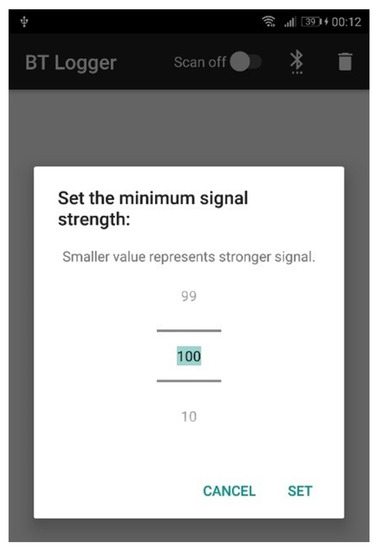
Figure 6.
Dialog window that allows changing the minimum signal strength needed to save a device detection log (own source).
The application remembers the currently set number, so the proper starting value is displayed every time the dialog is opened.
Model. The internal data storage is implemented via an SQLite database, which stores entities named BtDevice. The Data Access Object (DAO) BtDeviceDao is responsible for communication with the Repository class, which connects the ViewModel part of the application. The Room Persistence library was crucial for the implementation and management of the storage, as a big part of the code is auto-generated, leading to a massive reduction of boilerplate code.
In the project, the internal database displays records on the screen as the LiveData class stores the entities inside it and offers convenient notifications whenever data changes. For the external storage, a cloud SQL database named BT_Database is responsible. The communication between the application and the cloud service is implemented using Azure Mobile App SDK. However, it was not necessary to implement a bipolar solution.
The Repository class is the most critical component of the model, which is in possession of the BtDeviceDao and the MobileServiceTable<BtDevice> object that is used to pass data to the cloud database; it handles all the communication with the ViewModel and operates the BtService that is the main element of the application’s functionality.
ViewModel. The ViewModel, in the case of this project, consists of only one class, BtDeviceViewModel, that, as it is supposed to be, is responsible for providing data to the view and for passing events from the user interface to the model. LiveData residing in the class can be accessed through the public method, which exposes data to allow its observation.
3.3. Cloud Configuration
The mobile application service used in the solution is based on Node.js and is automatically created by the Microsoft Azure platform. Most importantly, it could be easily configured through the user-friendly interface available on the website and provides a REST API that can be used to connect the mobile application with the database in the cloud. For the needs of this prototype, a straightforward SQL database consisting of only one table (presented in Figure 7) was enough to provide all the necessary functionality.
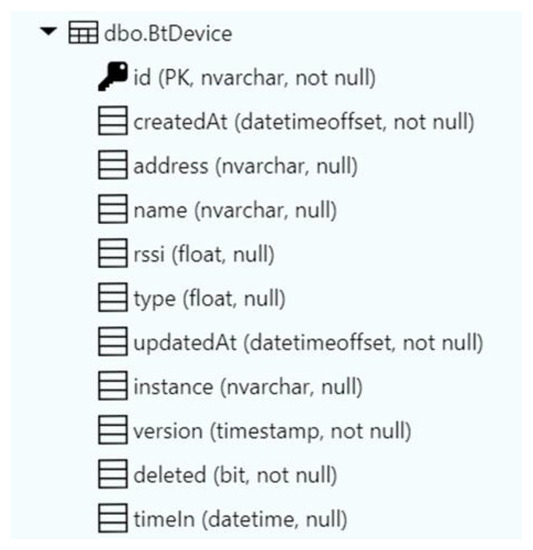
Figure 7.
BtDevice table schema (own source).
Moreover, the application service created it automatically based on the data received from the application on its first connection. If any changes occur in the structure of the data that is being received, the platform will try to alter the database accordingly.
3.4. Resource Management
Mainly thanks to multithreading and a ViewModel, the application is highly resource efficient. According to the Android Profiler resource management tool, the CPU and network usages are marginal (Figure 8), and the performance of the prototype is astonishing owing to the lack of the need to create new Views every time data has to be displayed in the list—instead, they are cached. What is more, no memory leaks were detected.
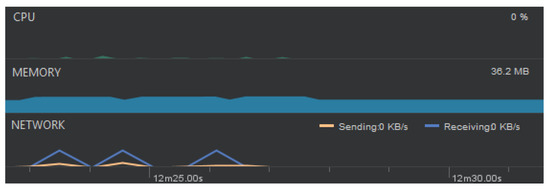
Figure 8.
A fragment of the Android Profiler window showing the resource consumption of the Smart Locator app. Peaks visible in the network section on the bottom represent moments of detection (own source).
4. Testing Procedure for Bluetooth Devices
To test the solution, three devices should be used with nearly identical hardware in terms of Bluetooth. Initially, the environment needed to be appropriately set up. The room where the tests are held has two entrances—next to where each logger was placed. The room is 9 × 6 m. In the beginning, a third device is put at different distances from the first logging smartphone, and real distances between them are measured to link them to corresponding RSSI values. The same action should be repeated with the second logger. During all of the tests, the same database table should be used. However, after each of them, the data is backed up in a separate table to avoid confusing the results, and the main table was cleared. All tests should be repeated at least three times.
4.1. Testing Environment for Smart Locator App’s Presence Detection Using Bluetooth-Enabled Device Logger
In the first stage, only one device is used as a logger. The minimum signal strength should not be limited. Thus, all discoverable devices appearing in the range are registered. This use case is to imitate the situation when the Smart Locator app serves as a means to provide insight into the presence of people in a particular area in a specific timeframe. The schema of the testing environment is shown below (see Figure 9).
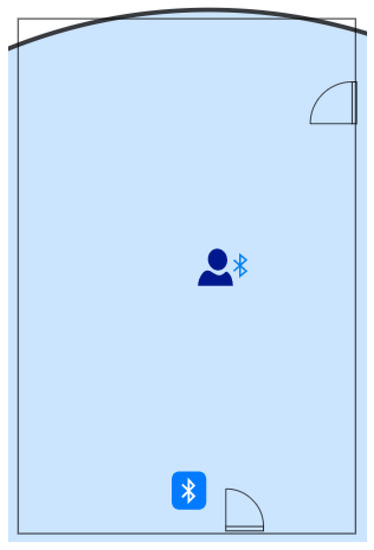
Figure 9.
Schema of the testing environment—first stage (own source).
A user with a Bluetooth-enabled device enters a classroom through the door closer to the logger. Next, he walks towards the opposite side of the room, stopping for 1 min in the middle. Eventually, he leaves through the second door.
4.2. Testing Environment for the Smart Locator App—Second Stage with Two Devices
In the second stage, an additional device with an instance of the Smart Locator app running is added. It should be placed as shown on the schema (Figure 10). The ranges of both devices are not limited. This led to the creation of a “common area” where two loggers should register a user. In order to test the cooperation of two Smart Locator instances, a user’s movement from the previous stage is performed once again. The goal is to obtain more detailed data on the user’s relative position and its change during the test.
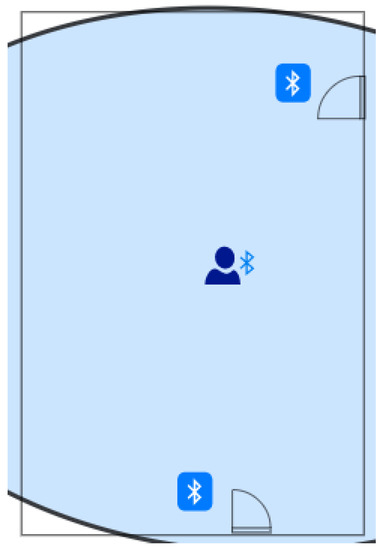
Figure 10.
Schema of the testing environment second stage, an additional device with an instance of the Smart Locator app running (own source).
4.3. Smart Locator for Presence Monitoring and Tracking at a Limited Range
The last test covers a situation when the Smart Locator is used only to check if someone passed through a particular spot or was present next to it. A solution like this could possibly be used in museums to check if people are interested in an exposition or to check the presence of students at a lecture. To achieve the desired effect, the range of the devices is reduced to cover only a small area next to the door, as shown in Figure 11 (all responses with RSSI [59] lower than minus 55 are ignored). A user enters the classroom, stops by the door for a while, walks to the other side of the room, and leaves. This time the aim is to register the time when he enters and if he stands by the door.
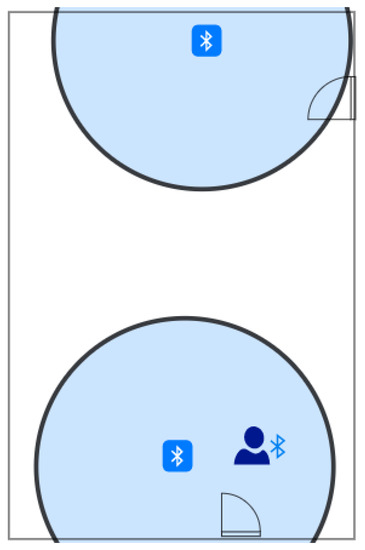
Figure 11.
Comparison schema of the testing environment—third stage; the approximate range of devices marked in bluish color (own source).
5. Discussion
After successfully implementing a simple prototype that works, it is clear that the Smart Locator application has huge potential for further development and deployment. Key features and interesting aspects of Smart Locator are highlighted below.
5.1. Bluetooth Technology
The research has shown that Bluetooth 802.15.1 technology [9] can successfully log the user’s relative position. Moreover, the characteristics of its operation allow the creation of a resource-friendly and nonintrusive solution that does not require any actions to be performed on the examined devices. Thus, it does not disturb their owners.
The basic mechanism of device detection already provides all the necessary information to distinguish devices from one another and approximate the relative location. Furthermore, those features turned out to be easily accessible in the Android operating system making this combination an excellent choice.
5.2. Mobile Application
The Android mobile operating system has proved to be an excellent platform for creating an application using Bluetooth adapters and connecting with external APIs. During the mobile application development, the focus was mainly on functionality and performance (resource management). Although the user interface was designed to be simple and straightforward before the application deployment, some tweaks to the visuals would be recommended.
The performance mentioned above was achieved with great success, after an in-depth examination of the Smart Locator app prototype, both empirically and using the Android Profiler resource monitor, no bugs related to the application were discovered. It was proved that everything works as intended when the app is in the background or foreground or when it gets killed by the system due to a resource shortage.
In order to develop the prototype into a commercial-grade solution, some additional features are required. The most important is the ability to provide its connection string to the database and possibly a login screen with the validation of credentials. It is necessary to allow users to collect data from their personal Microsoft Azure database so they can actually retrieve the statistics. It is not possible in the current application version, as all instances are permanently tied to a single test database. Another feature that could be added is a short tutorial on the first start of the application. It should include information on how to use and configure the whole solution. For this purpose, a step-by-step list of actions, a video, or both could be introduced. Since the system in its current form is dedicated to experienced users with knowledge of SQL, additional links to tutorials on this language could be provided for the rest of the potential users.
5.3. Cloud Service and Data Visualization
The Microsoft Azure Mobile Application Service, which was used in the solution, serves its role exceptionally well. It was straightforward to set up and integrate with the application while offering all the necessary features. It holds the cloud database, handles the app service communication, and provides a query interface for the solution to visualize the data. Regarding the current method for data visualization, a query interface provided by the Azure platform is a very convenient tool for experienced users. It could even be favoured over a visual interface as it provides endless possibilities for inquiry customization. However, for basic users that do not need such flexibility, the final solution should include a custom graphical interface with predefined queries. It could be in the form of a webpage, a separate desktop application, or could be added as a second module of the mobile application.
6. Conclusions
This research was conducted on Bluetooth 802.15.1 technology and its usage. As a result, a model of a smart locating application was designed, and a prototype was implemented. A two-component system was developed to provide information about detectable devices’ relative position to create statistics on users’ presence in a particular area in a specific timeframe. It consists of two components and does not require additional specialized equipment. The first component is a mobile application, a native application designed for the Android operating system. It is compatible with all system versions up to 5.0 Lollipop and was written in Java. The prototype was developed in IntelliJ IDEA. The tool provides a convenient interface, and thanks to the built-in Gradle build toolkit, additional libraries and packages could be easily integrated into the project. Using the MVVM architecture design pattern led to a massive reduction of programming effort and eliminated lots of boilerplate code.
The modular design of the app guarantees that Bluetooth technology can be easily exchanged in favor of other technology if needed. The Android Profiler resource management monitor helped to investigate the application for possible memory leaks, and the GitHub extension allowed fast backups and a method to track changes in the code. The application features all the functionality needed to serve the intended role as a means of collecting data and takes advantage of the provided REST API to connect to a server. The second component of the solution is the Mobile Application Service and the cloud database. The choice of the Microsoft Azure platform proved to be a good one. A straightforward step-by-step guide configured this part of the system relatively quickly. The integration of both components was straightforward, and no problems appeared during this process. The current method involving a simple query editor is sufficient for working with the prototype and provides full control over data.
The created system prototype confirms that, although there are not many solutions working on a similar basis, 802.15.1 technology can already be efficiently used to log the user’s relative position to provide statistics on the presence of people in a particular area in a specific timeframe. Moreover, due to the increasing number of users that leave their Bluetooth adapter active, it will only become more reliable.
An accessible solution for small businesses based on 802.15.1 technology is Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE). BLE is a wireless personal area network technology that allows devices to communicate with each other over short distances [33,34]. It is designed for low power consumption and is suitable for small businesses such as retail stores, cafes, and restaurants. BLE can be used to create location-based services, proximity marketing, and indoor navigation, making it a valuable tool for small businesses looking to improve customer engagement and increase sales. Additionally, BLE-enabled devices such as smartphones and tablets can be used for point-of-sale transactions, inventory management, and other business operations, making it a versatile and cost-effective solution for small businesses.
Future works. Possible future lines of research opened with this research are:
- Integration of other technologies. Although the developed prototype application was based on Bluetooth 802.15.1 technology, the modular design of the app allows for easy integration with other technologies. Future research could explore the integration of other technologies, such as Wi-Fi or GPS, to further improve the accuracy and reliability of the smart locating application.
- Expansion of the application’s functionalities. The smart locating application designed in this research provides valuable statistics on users’ presence in a particular area in a specific timeframe. Future research could focus on expanding the application’s functionalities to include features such as indoor navigation, proximity marketing, and personalized recommendations based on users’ behavior patterns.
- Point-of-interest data. The authors highlighted important future implications of BLE, including location-based services, proximity marketing, etc. By adding on to this point, coupling Bluetooth Low Energy technology with POI data could be very useful for similar future applications, including BLE-POI-based route planning and recommendation. It can also be a good alternative to GPS technology.
- Improving the accuracy of the application. The accuracy of the smart locating application depends on various factors, such as signal strength and interference from other devices. Future research could explore techniques to improve the accuracy of the application, such as machine learning algorithms and signal processing techniques.
- Security and privacy concerns. As the smart locating application collects data on users’ presence and behavior patterns, it is essential to address security and privacy concerns. Future research could focus on developing secure and privacy-preserving solutions to ensure the protection of users’ data.
- Commercialization and real-world deployment. The developed prototype application was designed as a foundation for further commercial development. Future research could focus on the commercialization and real-world deployment of the application, including its integration with existing business systems and processes, and user acceptance testing.
This paper achieves this by stating that the proposed solution was implemented as a prototype, which confirms that 802.15.1 technology can be efficiently used to log the user’s relative position. The modular design of the app ensures that Bluetooth technology can be easily exchanged in favor of other technology if needed. The developed prototype application was designed as a foundation for further commercial development. This paper’s main contribution is proposing a simple and accessible solution for small businesses to gather statistics on the presence of their customers by leveraging Bluetooth technology and a mobile application.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.S. and O.S.; methodology, Y.S., O.S. and M.G.; software, Y.S. and O.S.; validation, Y.S., O.S. and M.G.; formal analysis, Y.S. and O.S.; investigation, Y.S. and O.S.; resources, Y.S. and O.S.; data curation, Y.S. and O.S.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.S. and O.S.; writing—review and editing, Y.S., O.S. and M.G.; visualization, Y.S. and O.S.; supervision, Y.S. and O.S.; project administration, Y.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Fidelis, O.F.; Gbenga, A.T. Bluetooth Technology: Overview and Applications. South East. J. Res. Sustain. Dev. SEJRSD 2019, 1, 9–19. Available online: https://sejrsd.org.ng/index.php/SEJRSD/article/view/2 (accessed on 11 April 2023).
- Alzoubi, H.; Alshurideh, M.; Kurdi, B.; Akour, I.; Aziz, R. Does BLE technology contribute towards improving marketing strategies, customers’ satisfaction and loyalty? The role of open innovation. Int. J. Data Netw. Sci. 2022, 6, 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkanishy, A.; Furth, P.M.; Rivera, D.T.; Badawy, A.H.A. Low-overhead Hardware Supervision for Securing an IoT Bluetooth-enabled Device: Monitoring Radio Frequency and Supply Voltage. ACM J. Emerg. Technol. Comput. Syst. JETC 2021, 18, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthick, S.; Sundramurthy, V.P.; Devaru, S.D.; Narayanaswamy, R.; Mohan, A.; Akkaraju, S.C.; Carmichael, M.J.; Manjunath, T.C. WITHDRAWN: Realization of Industrial Automation Using Bluetooth Technologies. Mater. Today Proc. 2021. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2214785320396048 (accessed on 20 January 2023).
- Chowdhury, M.Z.; Shahjalal, M.; Hasan, M.K.; Jang, Y.M. The role of optical wireless communication technologies in 5G/6G and IoT solutions: Prospects, directions, and challenges. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, D.; Tim Hatt, T. GSMA Intelligence—Research—Global Mobile TrendsSept. 2017. Available online: https://www.gsmaintelligence.com/research/2017/09/global-mobile-trends-2017/639/ (accessed on 12 April 2023).
- Number of Smartphone Subscriptions Worldwide from 2016 to 2021, with Forecasts from 2022 to 2027. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/330695/number-of-smartphone-users-worldwide/ (accessed on 12 April 2023).
- Verma, D.; Shehzad, K.; Khan, D.; Ain, Q.; Kim, S.; Lee, D.; Lee, K. A Design of 8 fJ/conversion-step 10-bit 8MS/s low power asynchronous SAR ADC for IEEE 802.15. 1 IoT sensor based applications. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 85869–85879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEEE 802.15.1-2005—IEEE Standard for Information Technology—Local and Metropolitan Area Networks—Specific Requirements—Part 15.1a: Wireless Medium Access Control (MAC) and Physical Layer (PHY) Specifications for Wireless Personal Area Networks (WPAN). Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/1490827 (accessed on 13 March 2023).
- Poniszewska-Maranda, A.; Matusiak, R.; Kryvinska, N.; Yasar, A.-U.-H. A real-time service system in the cloud. J. Ambient. Intell. Hum. Comput. 2020, 11, 961–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pivoto, D.; de Almeida, L.; da Rosa Righi, R.; Rodrigues, J.; Lugli, A.; Alberti, A. Cyber-physical systems architectures for industrial internet of things applications in Industry 4.0: A literature review. J. Manuf. Syst. 2021, 58, 176–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poniszewska-Maranda, A.; Kaczmarek, D.; Kryvinska, N.; Xhafa, F. Studying usability of AI in the IoT systems/paradigm through embedding NN techniques into mobile smart service system. Computing 2019, 101, 1661–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, S.; Mishra, K.N.; Dutta, S. Sensitive Data Identification and Security Assurance in Cloud and IoT based Networks. Int. J. Comput. Netw. Inf. Secur. IJCNIS 2022, 14, 11–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štefanič, M.; Stankovski, V. A review of technologies and applications for smart construction. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng. Civ. Eng. 2018, 172, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novotný, R.; Kuchta, R.; Kadlec, J. Smart city concept, applications and services. J. Telecommun. Syst. Manag. 2014, 3, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Al Nuaimi, E.; Al Neyadi, H.; Mohamed, N.; Al-Jaroodi, J. Applications of big data to smart cities. J. Internet Serv. Appl. 2015, 6, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojuh, D.; Isabona, J. Empirical and Statistical Determination of Optimal Distribution Model for Radio Frequency Mobile Networks Using Realistic Weekly Block Call Rates Indicator. Int. J. Math. Sci. Comput. IJMSC 2021, 7, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, S.; Enayet, A.; Mouri, I.J. A smart, location based time and attendance tracking system using Android application. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Eng. Inf. Technol. IJCSEIT 2015, 5, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nashwan, S.; Hamarsheh, A. An Extended Approach for Enhancing Packet-Loss of inter-SGSN in 3G Mobile Networks. Int. J. Comput. Netw. Inf. Secur. IJCNIS 2017, 9, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Lee, S.C.; Lee, B.G.; Chung, W. Mobile healthcare system based on Bluetooth medical device. J. Sens. Sci. Technol. 2012, 21, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mane, A.; Khot, U.Q. Improvement for Dynamic Adaptive Streaming of Multimedia in LTE Cellular Network Using Cross-layer Communication. Int. J. Wirel. Microw. Technol. IJWMT 2022, 12, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, K.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Huang, S.; Ning, G.; Pang, W.; Li, B.; Chen, H. A system of portable ECG monitoring based on Bluetooth mobile phone. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Symposium on IT in Medicine and Education, Guangzhou, China, 9–11 December 2011; Volume 2, pp. 309–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin, L.; Xiaoyun, C. Home intelligent sports action automation system based on Bluetooth. Microprocess. Microsyst. 2021, 80, 103335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coombs, J. The Straight Goods on Bluetooth: How Many Consumers Have it on? April 2015. Available online: https://m.rover.io/the-straight-goods-on-bluetooth-how-many-consumers-have-it-on-d0ebe3b5d718 (accessed on 12 April 2022).
- Thompson, D. iBeacon: Is Bluetooth On? And Other Insights from Empatika. March 2014. Available online: http://beekn.net/2014/03/ibeacon-bluetooth-insights-empatika/ (accessed on 12 April 2022).
- Filippoupolitis, A.; Oliff, W.; Loukas, G. Bluetooth low energy based occupancy detection for emergency management. In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Ubiquitous Computing and Communications and International Symposium on Cyberspace and Security (IUCC-CSS), Granada, Spain, 14–16 December 2016; pp. 31–38. [Google Scholar]
- Tekler, Z.D.; Low, R.; Gunay, B.; Andersen, R.K.; Blessing, L. A scalable Bluetooth Low Energy approach to identify occupancy patterns and profiles in office spaces. Build. Environ. 2020, 171, 106681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collotta, M.; Pau, G. A novel energy management approach for smart homes using Bluetooth low energy. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2015, 33, 2988–2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekler, Z.D.; Low, R.; Yuen, C.; Blessing, L. Plug-Mate: An IoT-based occupancy-driven plug load management system in smart buildings. Build. Environ. 2022, 223, 109472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, R.; Tekler, Z.D.; Cheah, L. An end-to-end point of interest (POI) conflation framework. ISPRS Int. J. Geo. Inf. 2021, 10, 779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Luo, A.; Liu, Y.; Xu, J.; Li, Z.; Zhuang, F.; Sheng, V.S.; Zhou, X. Where to go next: A spatio-temporal gated network for next poi recommendation. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2020, 34, 2512–2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Market Share Held by the Leading Smartphone Operating Systems in Sales to End Users from 1st Quarter 2009 to 2nd Quarter 2018. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/266136/global-market-share-held-by-smartphone-operating-systems/ (accessed on 12 April 2023).
- Smartphone Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis, By Operating System (Android, iOS), By Distribution Channel (OEM, Retailer), Region and Forecast Period 2022–2030. Available online: https://marketresearchcommunity.com/smartphone-market/?gclid=CjwKCAiArNOeBhAHEiwAze_nKIREmq0Wg1NDWOkSM-OxOCnOSRdlKlGFR6FuIeGXuRG7ijThP8JrbRoClGMQAvD_BwE (accessed on 13 March 2023).
- IEEE 802.15.10-2017 IEEE Recommended Practice for Routing Packets in IEEE 802.15.4 Dynamically Changing Wireless Networks. Available online: https://standards.ieee.org/ieee/802.15.10/5752/ (accessed on 13 March 2023).
- IEEE 802.11. The Working Group Setting the Standards for Wireless LANs. Available online: http://www.ieee802.org/11/ (accessed on 12 April 2022).
- Bluetooth Technology Website. Available online: https://www.bluetooth.com/ (accessed on 12 April 2019).
- Nallappan, K.; Skorobogatiy, M. Photonics based frequency hopping spread spectrum system for secure terahertz communications. Opt. Express 2022, 30, 27028–27047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goode, S.H. A comparison of Gaussian minimum shift keying to frequency shift keying for land mobile radio. In Proceedings of the 34th IEEE Vehicular Technology Conference, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 21–23 May 1984; Volume 34, pp. 136–141. [Google Scholar]
- The History of Bluetooth. Available online: https://www.androidauthority.com/history-bluetooth-explained-846345/ (accessed on 15 April 2023).
- Bluetooth Radio Interface|Modulation & Channels|Electronics Notes. Available online: https://www.electronics-notes.com/articles/connectivity/bluetooth/radio-interface-modulation-channels.php (accessed on 15 April 2022).
- Sauter, M. From GSM to LTE-Advanced: An Introduction to Mobile Networks and Mobile Broadband; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; 450p. [Google Scholar]
- How to Do Accurate Indoor Positioning with Bluetooth Beacons? July 2017. Available online: https://proximi.io/accurate-indoor-positioning-bluetooth-beacons/ (accessed on 15 April 2023).
- Tiwari, C.; Jha, V. Enhancing Security of Medical Image Data in the Cloud Using Machine Learning Technique. Int. J. Image Graph. Signal Process. IJIGSP 2022, 14, 13–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maduranga, M.W.; Sithara, J.P. Real-Time Animal Location Estimation Using Wearable Sensors and Cellular Mobile Networks. Int. J. Wirel. Microw. Technol. IJWMT 2022, 12, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshlium IOT Gateway. Available online: https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/1386/3791/products/meshlium_iot_gateway_1024x1024.jpg?v=1525581043 (accessed on 15 April 2023).
- Detecting iPhone and Android Smartphones by WiFi and Bluetooth [Cellular-MobileHand Phone Detection]|Libelium. Available online: http://www.libelium.com/products/meshlium/smartphone-detection (accessed on 15 April 2023).
- Meshlium. Available online: http://www.libelium.com/resources/images/content/products/meshlium/smartphones-detection/bluetooth_ street_wifi_bt_shops_big.png (accessed on 18 April 2023).
- Libelium Meshlium Xtreme—Plug&Play Multichannel IoT Gateway. Available online: https://www.iot-store.com.au/products/libelium-meshlium-xtreme-plug-play-multichannel-iot-gateway (accessed on 11 April 2022).
- I Want to Develop Android Apps—What Languages Should I Learn? Available online: https://www.androidauthority.com/develop-android-apps-languages-learn-391008/ (accessed on 11 April 2023).
- Microsoft Azure. Available online: https://portal.azure.com (accessed on 10 May 2022).
- Das, S.; Grbic, M.; Ilic, I.; Jovandic, I.; Jovanovic, A.; Narasayya, V.R.; Chaudhuri, S. Automatically Indexing Millions of Databases in Microsoft Azure Sql Database. Int. Conf. Manag. Data 2019, 666–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guay Paz, J. Introduction to azure cosmos db. In Microsoft Azure Cosmos DB Revealed: A Multi-Model Database Designed for the Cloud; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; p. 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poppe, O.; Guo, Q.; Lang, W.; Arora, P.; Oslake, M.; Xu, S.; Kalhan, A. Moneyball: Proactive auto-scaling in Microsoft Azure SQL database serverless. Proc. VLDB Endow. 2022, 15, 1279–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soh, J.; Copeland, M.; Puca, A.; Harris, M. Microsoft Azure: Planning, Deploying, and Managing the Cloud; Apress: New York, NY, USA, 2020; 560p. [Google Scholar]
- IntelliJ IDEA and Android Studio FAQ|IntelliJ IDEA Blog. en-US. 2020. Available online: https://blog.jetbrains.com/idea/2013/05/intellij-idea-and-android-studio-faq/ (accessed on 11 April 2023).
- Lisowski, M.; Michalska, J.; Kacki, M.; Precht, J. Smart Locator. Modern IT Methodologies and Services; Lodz University of Technology: Lodz, Poland, 2019; Student work. [Google Scholar]
- What Is Azure—Microsoft Cloud Services|Microsoft Azure. Available online: https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/overview/what-is-azure/ (accessed on 13 April 2023).
- MVC vs. MVP vs. MVVM on Android. Available online: http://academy.realm.io/posts/eric-maxwellmvc-mvp-and-mvvm-on-android/ (accessed on 11 April 2023).
- Ramirez, R.; Huang, C.-Y.; Liao, C.-A.; Lin, P.-T.; Lin, H.-W.; Liang, S.-H. A Practice of BLE RSSI Measurement for Indoor Positioning. Sensors 2021, 21, 5181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).