Abstract
In this work, we present an integrated read and programming circuit for Resistive Random Access Memory (RRAM) cells. Since there are a lot of different RRAM technologies in research and the process variations of this new memory technology often spread over a wide range of electrical properties, the proposed circuit focuses on versatility in order to be adaptable to different cell properties. The circuit is suitable for both read and programming operations based on voltage pulses of flexible length and height. The implemented read method is based on evaluating the voltage drop over a measurement resistor and can distinguish up to eight different states, which are coded in binary, thereby realizing a digitization of the analog memory value. The circuit was fabricated in the 130 nm CMOS process line of IHP. The simulations were done using a physics-based, multi-level RRAM model. The measurement results prove the functionality of the read circuit and the programming system and demonstrate that the read system can distinguish up to eight different states with an overall resistance ratio of 7.9.
1. Introduction
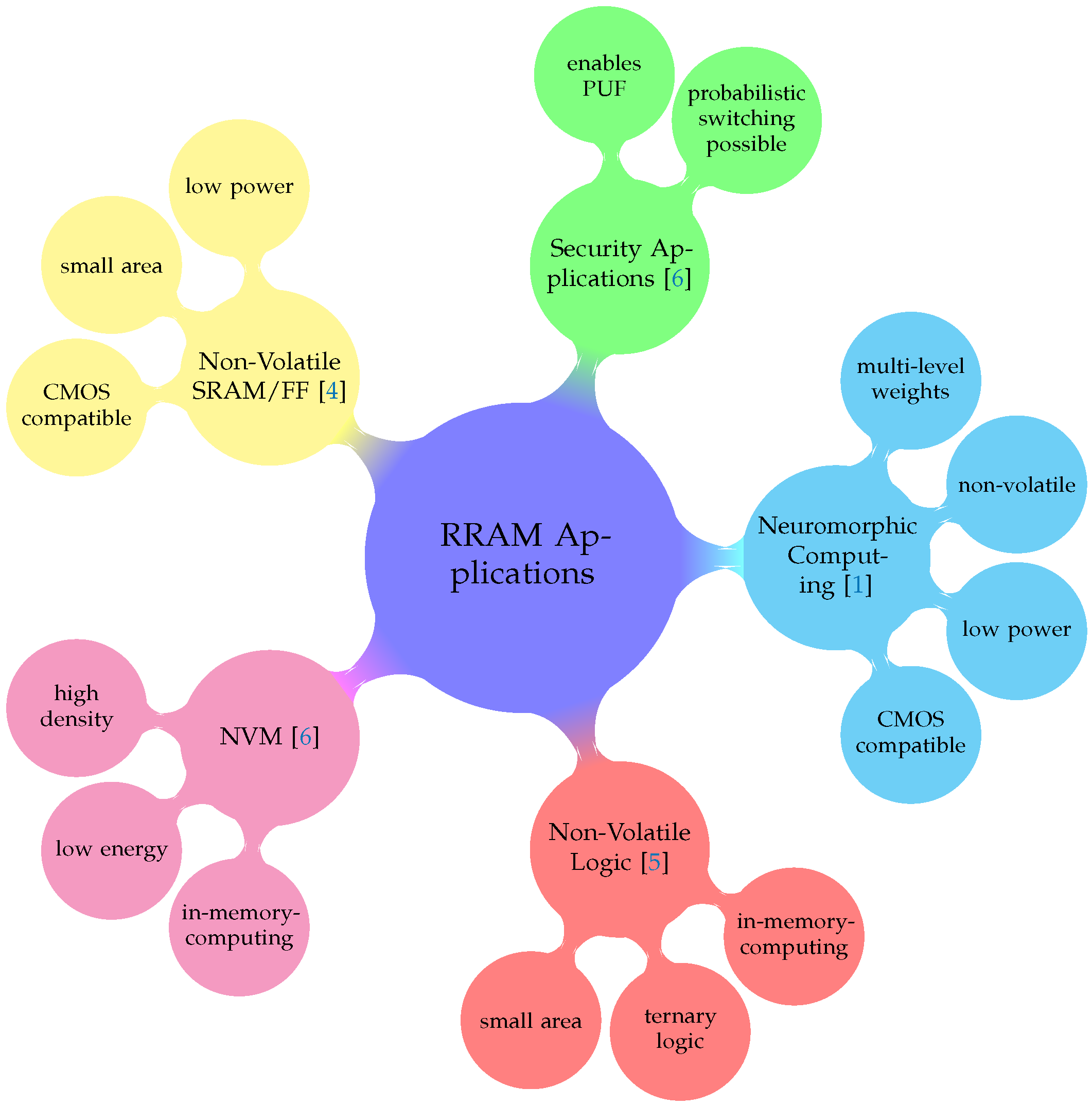
Resistive Random Access Memory (RRAM) is an emerging memory technology with a lot of potential in analog and digital applications. Recently, resistive switching devices gained a lot of focus in several different applications, where the strengths of this memory technology can be taken advantage of. Several of those fields of application are shown in Figure 1. They are used as analog elements in neuromorphic circuits [1], used as a general non-volatile memory device [2,3] or in non-volatile logic gates [4]. Those last two applications can also be combined to realize in-memory computing, one prominent way to overcome the von Neumann bottleneck, one of the major challenges for further improvements of modern computing systems [5]. Furthermore, due to the probabilistic nature of the physical switching inside the RRAM devices, they can also be used in security applications to enable the generation of physical unclonable functions (PUFs) [6].
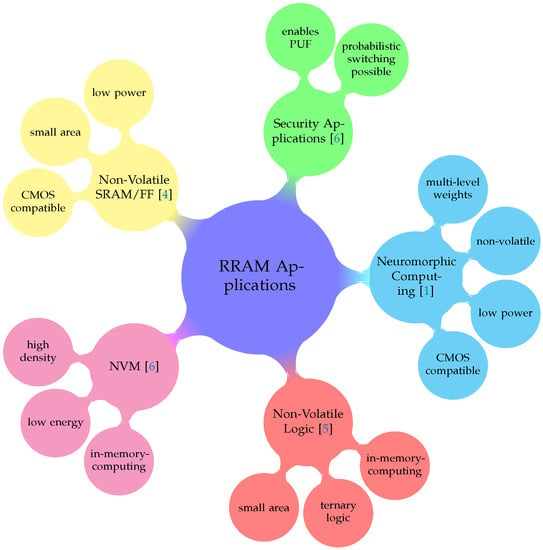
Figure 1.
Resistive Random Access Memory (RRAM) applications.
RRAM devices are interesting for the applications mentioned above because of their advantages as a memory technology, which are also shown in Figure 1. Since most RRAM technologies rely on switching in thin, dielectric layers, the area of individual cells can be kept very small compared to other memory technologies like SRAM or even flash memory. Some RRAM technologies can even surpass the area of , where is the minimum feature size, due to 3D integration [7]. This goes along well with the further scaling in modern semiconductor processes. Because the physical effect used to store the data relies on a structural change in the crystal lattice of the dielectric material, RRAM cells can keep their stored value after shut down of the supply voltage. This non-volatility is a key feature, especially for data storage and logical operations in low-power applications. These applications usually use batteries or energy harvesting, since they operate in circumstances where the energy supply cannot always be guaranteed. Therefore, data loss can be prevented by the non-volatility of the RRAM cells, when power runs low. The ability to adopt more than two resistive states permits the storage of several bits in one RRAM cell, therefore allowing a higher memory density. These three key advantages, small area, non-volatility and multi-state capability, ensure a promising future for RRAM devices in a wide variety of memory, Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) applications [6,7,8].
However, besides those key advantages, there are several issues regarding this technology, which have to be addressed in order to make it competitive as a data storage device. Reliability is one of the biggest concerns in order to avoid data loss [8]. The CMOS compatibility is a necessity to make it economically competitive in the future, but this is not the case with every RRAM technology. Another issue is cell-to-cell and cycle-to-cycle variability [9]. Besides technological improvements, this matter can also be addressed by peripheral circuitry, which take the variability of the cells into account. The presented circuit explores one way to control this cell variability. By introducing several versatile aspects into the circuit, the read and programming systems can strut cell variability in order to secure reliable read and programming operations. Furthermore, with a few adjustments in the device values, the functional principle of the circuit is suitable to other RRAM technologies as well.
The article is organized as followed: In Section 2, the RRAM technology, the circuit was designed for is introduced. Section 3 provides a system overview and the overall principle of the circuit operation, while Section 4 explains the read circuit. In Section 5, the simulation and measurement results are presented and Section 6 gives a conclusion for the proposed circuit.
2. RRAM Technology
In this section, the RRAM technology is introduced. Furthermore, the used programming algorithm based on voltage pulses is described. In the last subsection, the expected cell variability of the technology is derived from previous measurement data.
2.1. 1T1R RRAM Cells
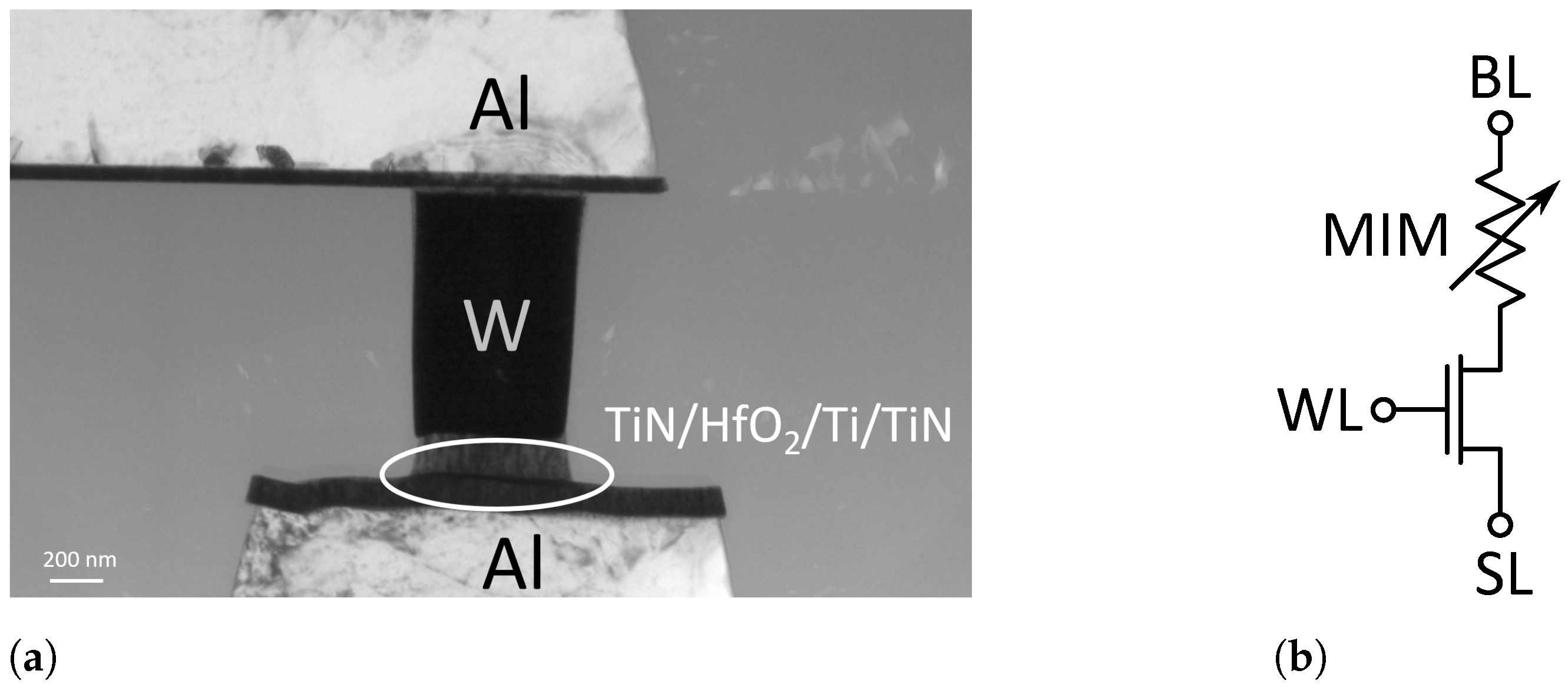
The circuit is designed for usage with the RRAM technology developed by IHP-Leibniz Institut fuer innovative Mikroelektronik (IHP), but the concept is not restricted to this technology and can be adapted for other RRAM technologies. This technology utilizes a Metal-Insulator-Metal (MIM) stack as resistive switching cell and a transistor as the selection device. The MIM stack is located between Metal2 and Metal3 layer in the back end of line (BEOL) of the fabrication process. A SEM picture is shown in Figure 2a. The selection transistor is connected in series with the MIM stack. This configuration is commonly known as one-transistor/one-resistor (1T1R) configuration. Figure 2b shows a schematic of this configuration with the conventional nomenclature of the three available terminals. The terminal connected to the upper electrode of the MIM stack is called Bitline (BL), while the terminal at the source of the selection transistor is called Sourceline (SL). The Wordline (WL) terminal sets the gate voltage of the transistor, therefore selecting the cell.
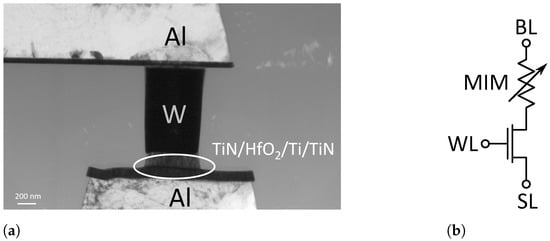
Figure 2.
Structure of a 1T1R cell [10]: (a) SEM picture of the Metal-Insulator-Metal (MIM) stack. (b) Schematic representation of the 1T1R configuration.
The MIM stack consists of a top and a bottom electrode of 150 thick TiN with a scavenging layer of 7 Ti and a dielectrical switching layer of 8 HfO2. The area of the MIM stack is 600 × 600 . During the forming process, the 7 Ti scavenging layer is oxidized to TixNyOy, therefore bringing the oxygen vacancies into the MIM stack, which can then form the conductive filaments (CFs) in the dielectric layer. Those CFs can be built or ruptured by applying voltage pulses of the according polarity, thus changing the overall resistance of the cell [11].
The selection transistor is fabricated using the IHP 130 CMOS process SG13S. For this transistor, the minimal NMOS transistor with a gate length of 130 and a gate width of 150 is used. In previous publications of this technology, the RRAM cells were fabricated in the 250 process SGB25V from IHP, containing a selection transistor of different dimensions [11,12]. For scaling reasons, the cells were migrated to the SG13S process.
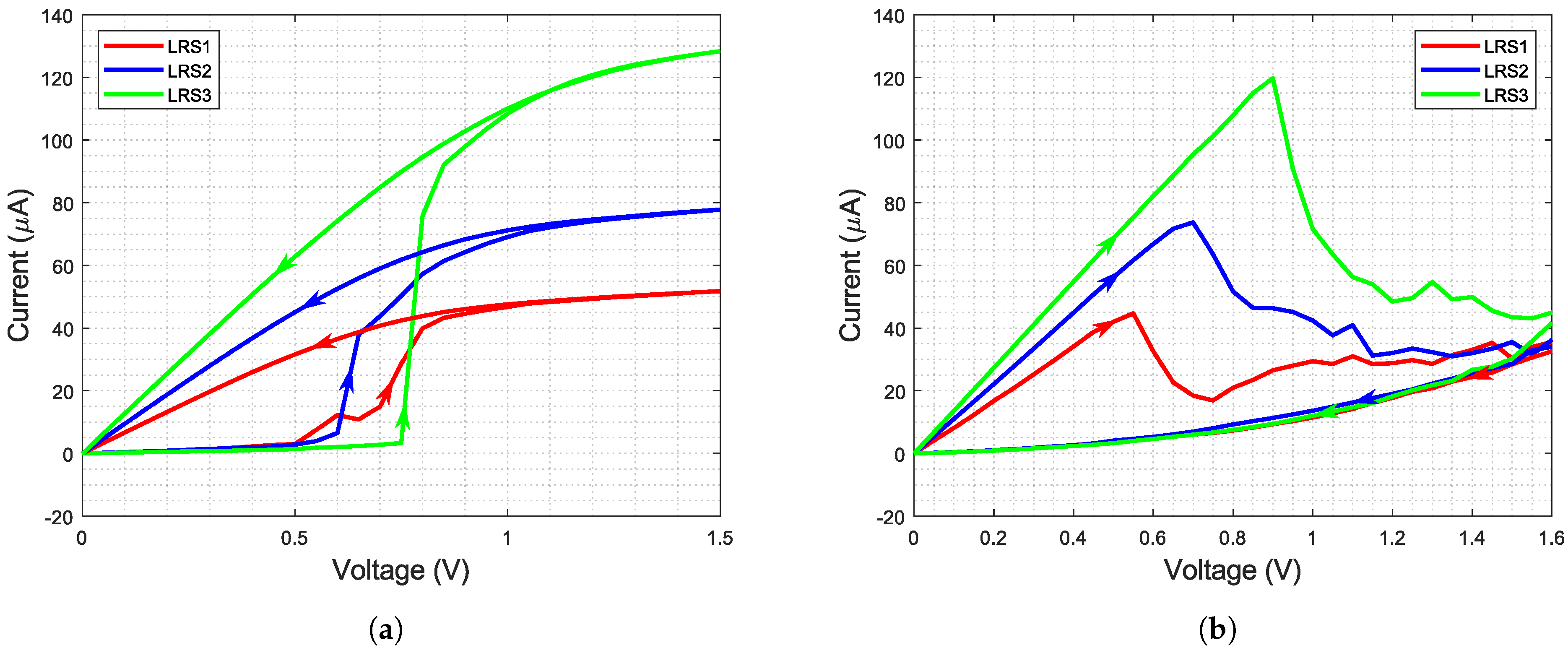
Figure 3a,b shows the measured I-V curves of the RRAM cells. The measurements were done by performing a DC sweep from 0 to for set and reset operation. During the set of the BL voltage and during reset, the SL voltage was swept while the other line was grounded, respectively. Clearly, three different low resistance states (LRS) can be distinguished. It has to be pointed out that the shown curves are the median of the measurement of several cells located in an array and not of a single RRAM cell. During the set process, the LRS, to which the cell is programmed, is determined by the gate voltage applied at the WL. This WL voltage limits the programming current, therefore selecting the programmed state. Table 1 shows the four states (three LRS and one high resistance state (HRS)) and their corresponding resistance values as well as the WL voltages used during programming of the respective state. The WL voltage during reset has to be higher since the pulse is applied to the SL, which means neither drain or source of the selection transistor are grounded. Therefore, the gate voltage has to be raised to achieve sufficient voltage between gate and source to switch the transistor on.
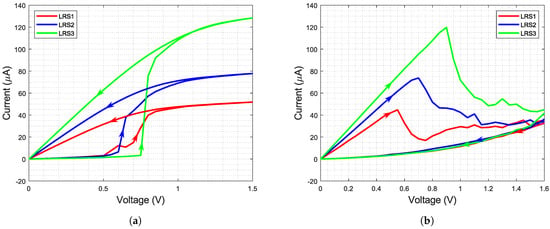
Figure 3.
I-V curves of programming the IHP RRAM cells: (a) Set. (b) Reset.

Table 1.
RRAM cell states.
2.2. Programming Algorithm
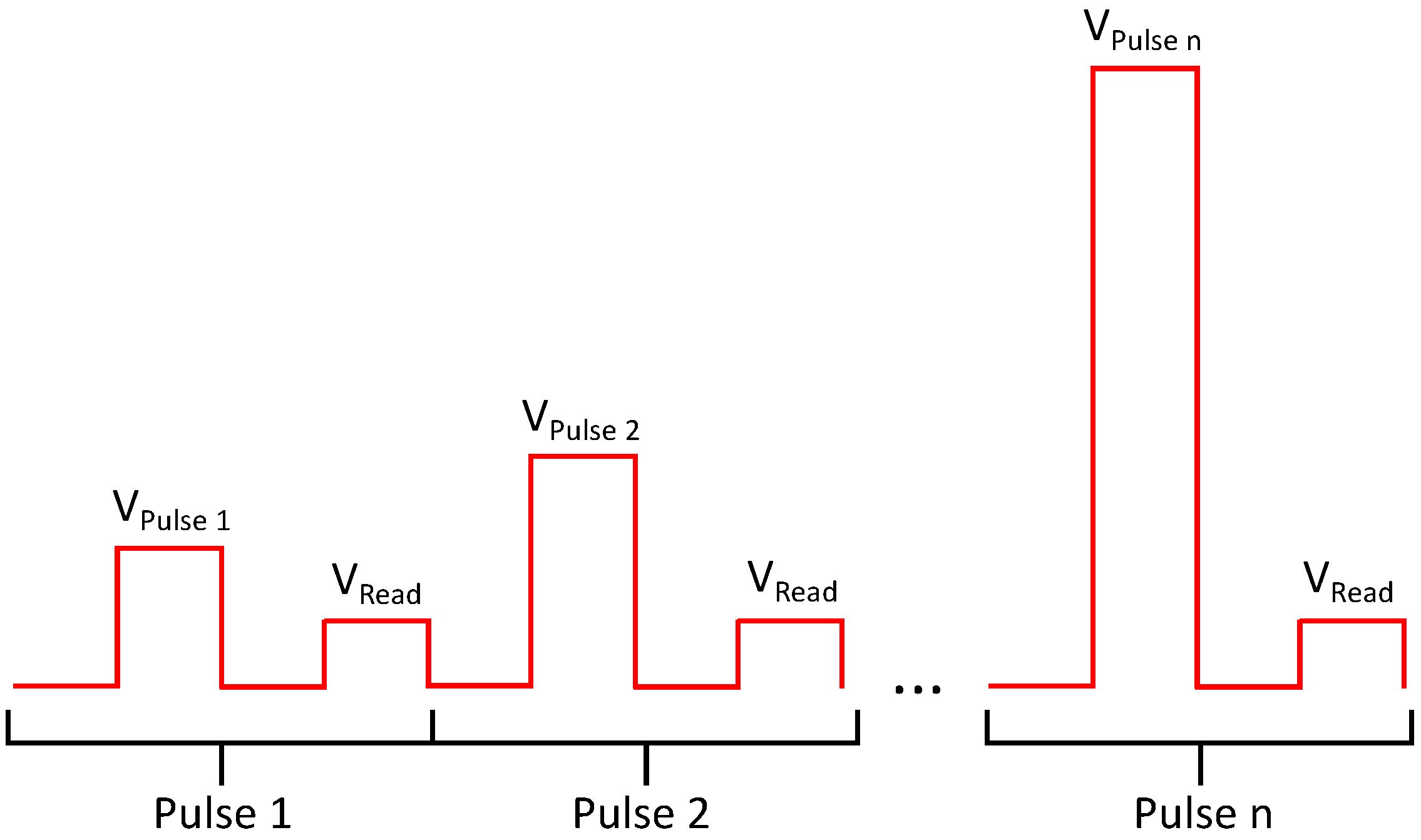
The memory cells are read and programmed by voltage pulses of different height, length and polarity. The programming is done using the “Incremental Step Pulse and Verify Algorithm” (ISPVA) [13,14]. Figure 4 illustrates the algorithm. To control the cell-to-cell variability, the algorithm applies a voltage pulse and reads the cell resistance after the pulse. If the cell resistance corresponds to the desired value, the algorithm is ended, if not, a slightly higher pulse is applied next before the cell resistance is read again. This process is continued until the desired resistance value is read by a read pulse. In this way, the programming of the correct value is secured.
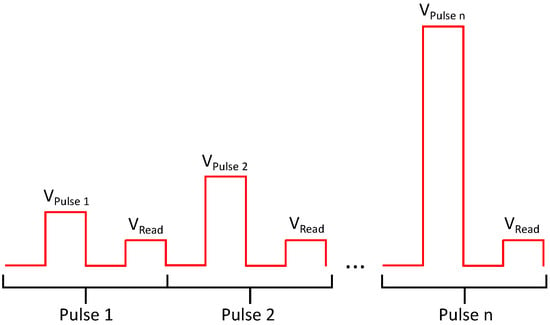
Figure 4.
Illustration of programming algorithm (modified from [14]).
Read pulses usually have a pulse height between and . By using such small voltages, it is assured that a read pulse does not change the resistance of the cell, for which usually higher voltages are needed. For the calculation of the corresponding resistances in Table 1, a read voltage of was assumed. The programming pulses can reach values up to . Current compliance is realized by limiting the gate voltage of the selection transistor during a programming pulse, thereby limiting the maximum current through the transistor and consequently through the MIM stack. In order to take the cell from a higher to a lower resistance state (set process), the voltage pulse is applied to the BL of the cell while the SL is grounded. To take the cell from a lower to a higher resistance state (reset process), the voltage pulse is applied to the SL while the BL is set to ground potential. The forming process mimics the set process, using smaller voltage steps compared to the set process [13].
2.3. Cell Variability
The circuit was designed to offer a great degree of flexibility. This was done in order to be able to control the variability of the used RRAM cells and to have the ability to gather more measurement data than just the pure high or low resistive state. As stated before, the I-V curves shown in Figure 3a,b are median values. Previous measurements of this RRAM technology indicate a non-negligible amount of variability [9,15]. Especially the set and reset voltages can vary up to 1 . Furthermore, the change of the electrical properties can be observed during cycling and temperature variations.
The RRAM technology is an ongoing research topic. The optimal layer dimensions are still under investigation and there is further research going on in the composition of the materials used in the MIM stack. The size of the selection transistor was reduced as well, which inherits different electrical properties compared to the former selection transistor. Therefore, the electrical behavior of the current physical configuration of the technology is not precisely foreseeable. This is the main reason to design the proposed circuit with a higher degree of versatility to be able to control RRAM cells with different electrical properties and get inside knowledge of the switching behavior during forming and programming. Besides that, there are a lot of different RRAM technologies in development with very different properties [16]. A versatile read and programming system will also be able to operate with other technologies due to its adaptability.
3. Circuit Overview
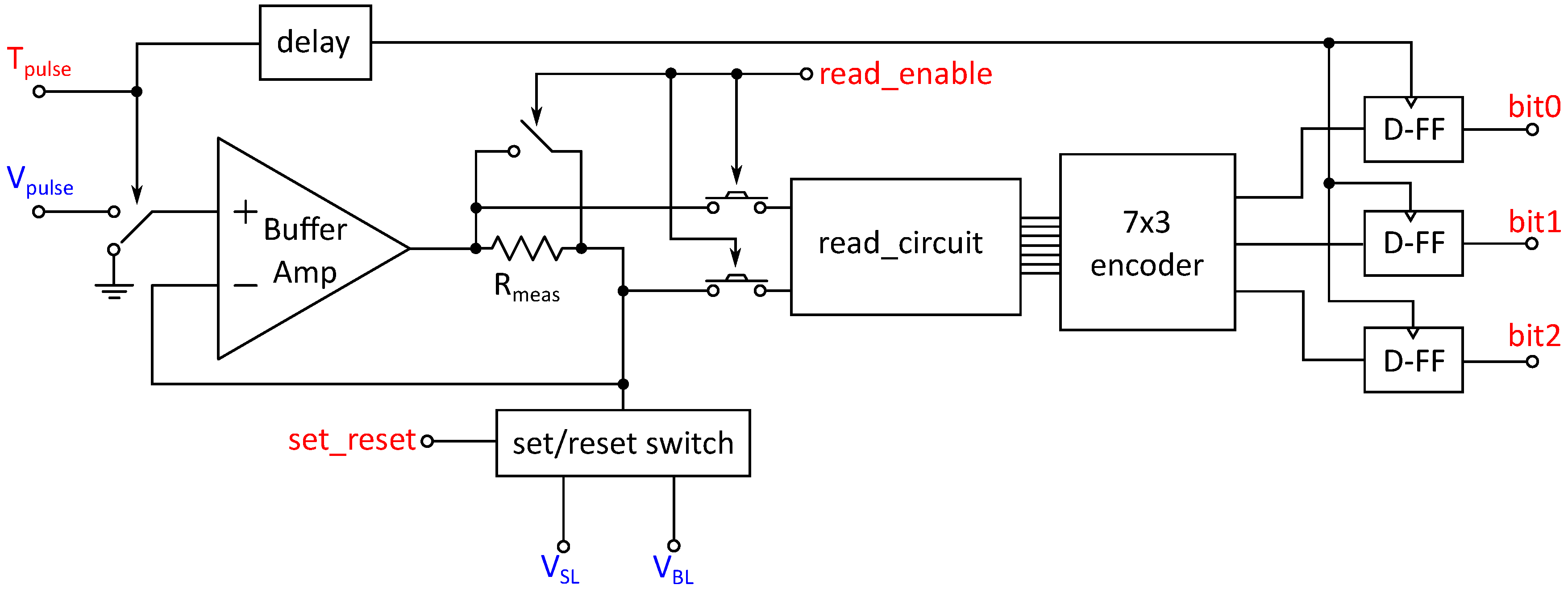
In this section, the overall circuit is introduced and its functionality is explained. An overview of the circuit is given in Figure 5 as well as a summary of the in- and output signals in Table 2. In general, two main modes of operation can be distinguished: read and programming operations. The respected mode of operation can be selected by setting the read_enable input to high for a read operation or to low for a programming operation. In the following subsections, both modes of operation are explained.
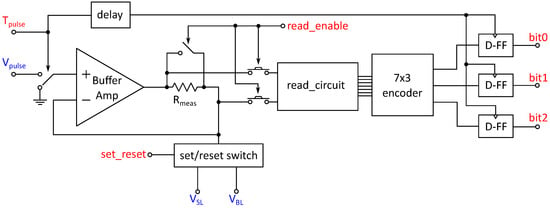
Figure 5.
Overview of the circuit: Digital signals are marked red, while analog voltages are marked blue. The 1T1R cell is connected to the VBL and VSL terminals, where the corresponding voltages are applied. The switches are realized as transmission gates, the arrows signify the digital control signal of the transmission gate. The analog voltage level Vpulse determines the height of the voltage pulse, while the length of the digital Tpulse signal sets its length. The read_enable signal enables the read operation and connects or disconnects the read circuit, while the D flip-flops hold the output values bit0, bit1 and bit2 after the pulse is over and are triggered by the delayed Tpulse signal.

Table 2.
System signals.
3.1. Programming Operation
To perform a programming operation, the read_enable input has to be set to low. This will disconnect the read circuit as well as the encoder and the D-Flipflops from the signal path and bypasses the measurement resistor Rmeas. Therefore, the buffer amplifier is in a voltage follower configuration, where the output is directly connected to the negative input of the operational amplifier. As long as the input signal is low, the positive input of the operational amplifier is grounded. If the signal is moved to high potential, the positive input of the amplifier is connected to the input, where an analog voltage level, corresponding to the pulse height, is applied. By this configuration, a voltage pulse with the height of and the length of the digital signal is created at the input of the amplifier. Since the buffer amplifier is in a voltage follower configuration during programming operations, this input pulse is buffered by the amplifier and applied at the input of the set/reset switch. The set/reset switch bypasses the input to either the BL or SL and puts the other line on ground potential, depending on the value of the set_reset input. If set_reset is on high, the input is bypassed to the BL and the SL is grounded and vice versa.
The outputs bit<0:2> of the read circuit are not relevant during programming operations and will be low since the inputs of the read circuit are grounded, if read_enable is set to low.
For the buffer amplifier, a two stage CMOS operational amplifier was designed. It consists of a rail-to-rail input stage with tail current switching in a folded cascode configuration as the summation stage. This input stage fulfills the condition mentioned above since the inputs are realized with a PMOS and a NMOS differential pair, delivering a high input impedance and preventing current flow into the amplifier. A class-AB output stage provides rail-to-rail output. The amplifier was designed after [17] and contains a floating current source in the second stage. It occupies an area of 92 80 and has a simulated DC voltage gain of dB. It can buffer a voltage pulse with a pulse height of 3 with a rise time of less than 30 with a load of 1 and 10 . Furthermore, the amplifier can deliver output currents up to . Therefore it would be suitable for forming operations as well as programming several cells simultaneously. This amplifier configuration contributes to the high flexibility of the system, since it was designed for general purpose usage in order to be able to fulfill a wider variety of requirements that could occur with different RRAM technologies or applications. The price we pay for this flexibility is in the power efficiency of the amplifier, since an amplifier designed for a more specific application could be optimized. Here we deliberately choose flexibility over specification to enable usage with a wider variety of technologies, systems and applications.
To summarize, during a programming operation, the length of the voltage pulse is determined by the length of the digital input pulse , while the height is set by the voltage level applied to . The voltage pulse is buffered by the operational amplifier in voltage follower configuration. By setting the set_reset signal to high or low, the pulse is either applied to the BL or SL, while the other output is set to ground by the set/reset switch. The forming of the cell can also be done using this mode of operation due to the drive capability of the buffer amplifier.
3.2. Read Operation
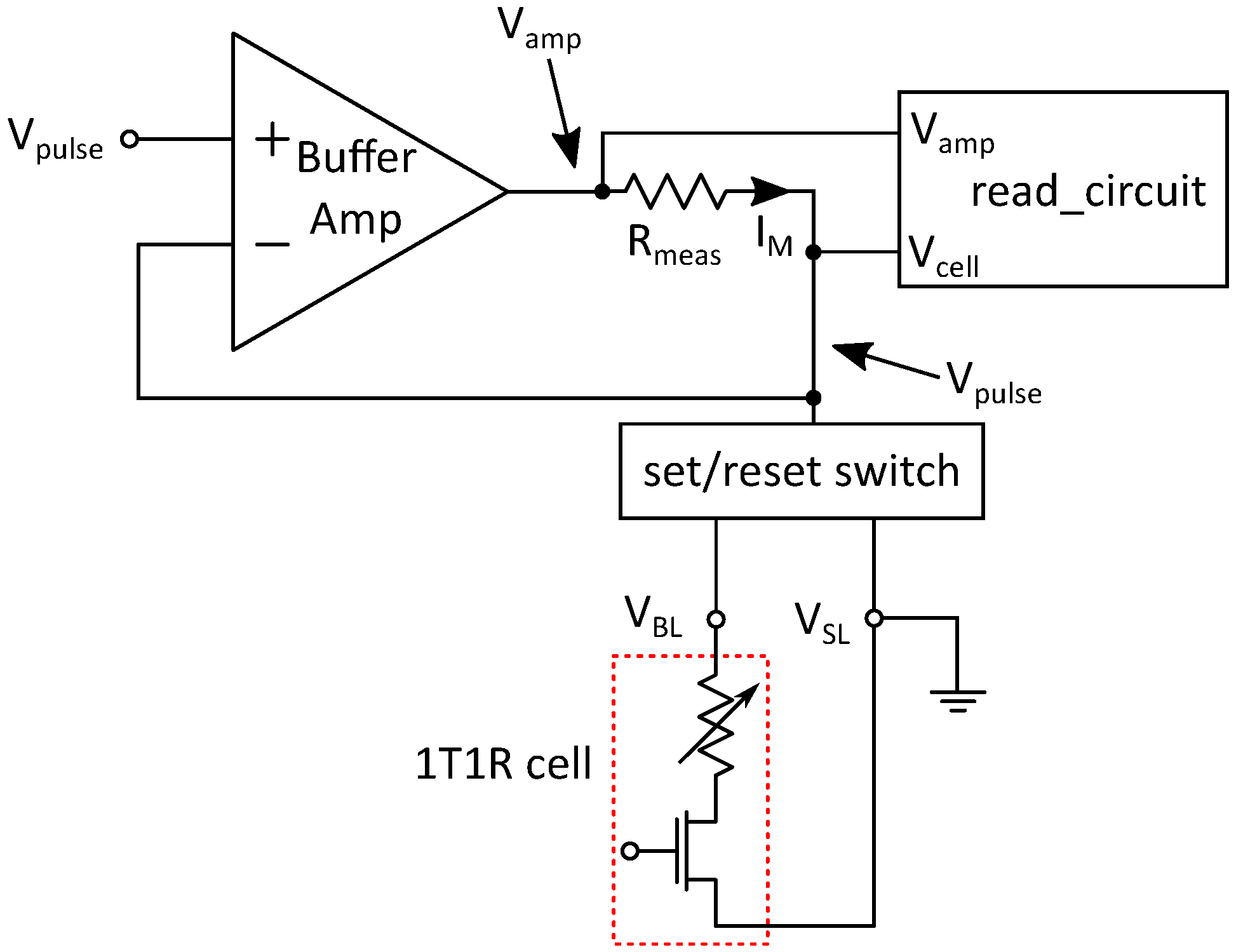
A read operation is set up by putting the read_enable signal to high. This switches the transmission gates in order to include the measurement resistor Rmeas into the feedback path of the buffer amplifier as well as connecting the read circuit to the system. This results in a circuit configuration shown in Figure 6. The read pulse is applied to the positive input of the buffer amplifier in the same way as described during the programming operation. Since the negative feedback is applied after Rmeas, the buffer amplifier raises its output voltage until the voltage at the feedback point corresponds to the input voltage. As a result, the applied voltage pulse to the 1T1R cell has the same length and height as the input pulse.
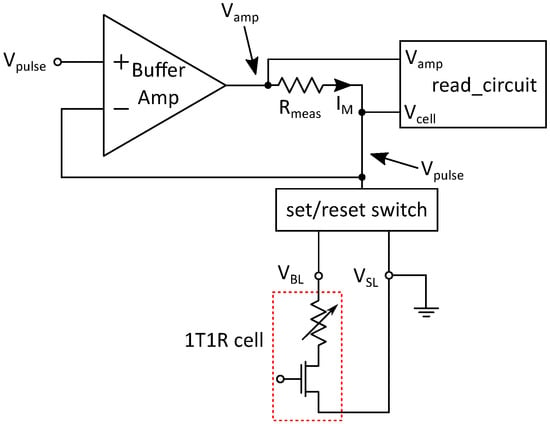
Figure 6.
System configuration during read operation.
The voltage drop over Rmeas depends on the current through the resistor. is directly dependent on the resistance of the memory cell Rcell and the height of the voltage pulse :
Rcell is the analog value that holds the memory information to be extracted. is independent from Rmeas since the buffer amplifier regulates the voltage over the cell according to the input voltage. With Equation (1), the voltage drop over Rmeas can be calculated:
Since the voltage at the output of the buffer amplifier is the voltage drop over the resistor added to , this results in a dependency between the cell resistance Rcell and . By using Equations (1) and (2), this dependency is given as:
Two major conditions have to be fulfilled for Equation (3) in order to be valid: First, the buffer amplifier must be able to regulate the input voltage in the feedback path. If the voltage drop over the measurement resistor is too high, the amplifier goes into saturation at its output and cannot be reached at the cell. The second condition is that no current must flow into the read circuit or the negative input of the buffer amplifier. In order to satisfy Kirchhoff’s current law, the output current of the amplifier has to be the current flowing through the cell.
Since the read operation is usually done with very low voltage pulses in order not to change the state of the memory cell, the first condition is not critical. In the extreme situation of a short in the MIM stack, the on-resistance of the selection transistor is still about 1 kΩ. Given a read pulse of , this would result in a cell current of 300 , thereby corresponding to a 3 voltage drop over the measurement resistor, since a 10 kΩ resistor is used. Therefore, the output voltage of the buffer amplifier is , which is the supply voltage of the circuit. If the circuit is to be used with other RRAM technologies, that show different resistance values for their states, the value of the measurement resistor can be adapted to the corresponding current values. Alternatively, the input voltage can be tuned to achieve a similar read current.
The second condition requires a very high input impedance of the read circuit and the buffer amplifier, compared to the measurement resistor and the cell resistance. In order to fulfill this requirement, the input stage of the read circuit is designed as a common drain amplifier with unity gain.
The reading is performed by evaluating the voltage difference between and , where should correspond to the input voltage . This is done by the read circuit further described in Section 4.
Since the reading operation is based on voltage pulses, the output of the read circuit would only be present for the time the pulse is applied to the memory cell. In order not to influence the 1T1R cell when no operation is performed, the input is grounded, so the output of the read circuit would go to the low level as well. Therefore, the D flip-flops are triggered by the rising edge of the delayed input pulse in order to capture the read output, so the read values will still be available after the pulse is over. The delay is necessary to allow the signals to settle in the system and is programmed to 150 . Measurement data show that this time can be reduced to 50 in order to reduce the minimum possible pulse length and to speed up the read operation.
4. Read Circuit
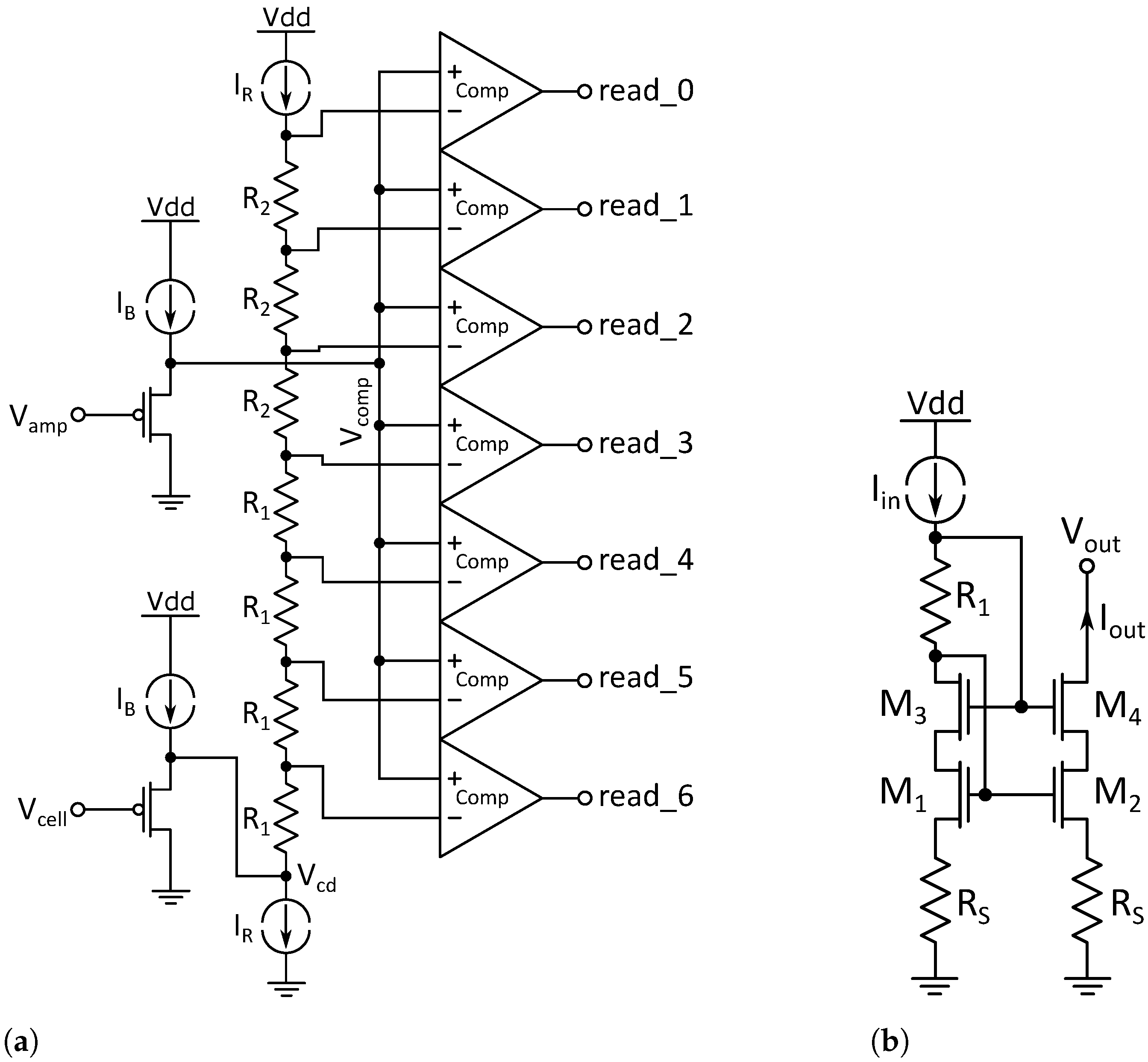
A schematic of the read circuit is shown in Figure 7a. The basic principle to evaluate the difference between and is to systematically raise and compare it to by comparators, so a digital value of the difference of the two input voltages in thermometer code is obtained.
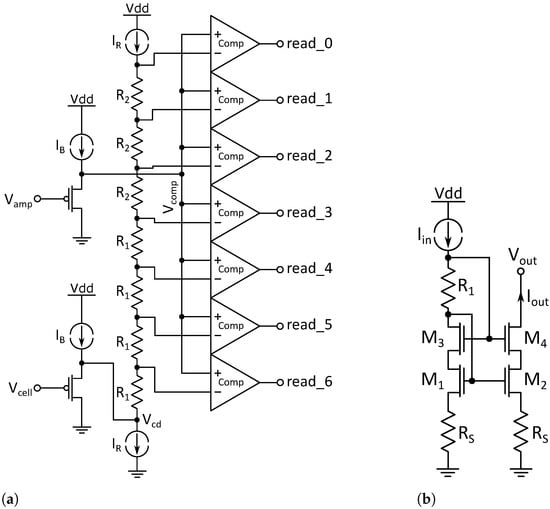
Figure 7.
Components of the read circuit: (a) Read stage with resistor tree and comparators. The shifted cell voltage is raised step by step using the voltage drops over the resistors R1 and R2 in the resistor tree and compared with the shifted voltage from the output of the amplifier. (b) Precision current mirror used for IR in Figure 7.
At the input stage, both input voltages are shifted by two identical common drain stages, which have the same W/L ratio and are biased by . This serves two main purposes:
- Provide a high input impedance to decouple the read circuit from the measurement resistor. This is necessary to prevent current flow into the read circuit
- Shift the relatively low input voltage of away from ground supply, therefore providing a voltage headroom for the current source
In order not to change the voltage difference, is shifted by the same voltage as .
The second stage consists of seven resistors in series through which the current is driven by two current sources. This results in a defined voltage drop over each of the resistors given by Ohm’s law. This stage will further be called resistor tree. The shifted cell voltage, in Figure 7a marked as , is connected below the first resistor and then systematically raised by the voltage drop over the resistors. Therefore, seven different voltages are obtained for comparison with the shifted output voltage of the buffer amplifier, here labeled as .
Since corresponds to the height of the read pulse, it can serve as a reference point. As shown in Equation (3), , and therefore as well, is dependent on the cell resistance and contains the memory information. If the reference voltage is systematically raised and compared with by comparators, the thermometer code of the output bits read<0:6> is a measure of the cell resistance. The thermometer code is then encoded into a three bit binary value.
The value of the resistors is dependent on the voltage range expected for as well as the current . Two different resistance values of and 4 were chosen in order to achieve a higher resolution for higher cell resistance states. Other resistance distributions are possible, for example, a logarithmic or a square function, contributing to the versatility of this method, but resistor matching has to be taken into account. The voltage limitations of the resistor values are the saturation voltages of both current sources near the upper and lower supply rail.
The precision of the current sources is a critical design point since their precision in matching and absolute values directly influence the voltage comparison and therefore the output values. To increase the precision, the self-biased cascoded current mirrors with source degeneration shown in Figure 7b in their respective NMOS and PMOS versions were used. The cascode increases the output resistance while the source degeneration improves matching and noise [18].
Here, the versatility of the read system becomes clear once more. Rmeas, the resistance values to raise as well as the current through the resistors , can be tuned according to the cell conditions during the design process. can even be made tunable after IC fabrication, for example, by including switching of the current sources. Even from an algorithmic perspective, the height of the read pulse can be adapted after the design process.
5. Simulation and Measurement Results
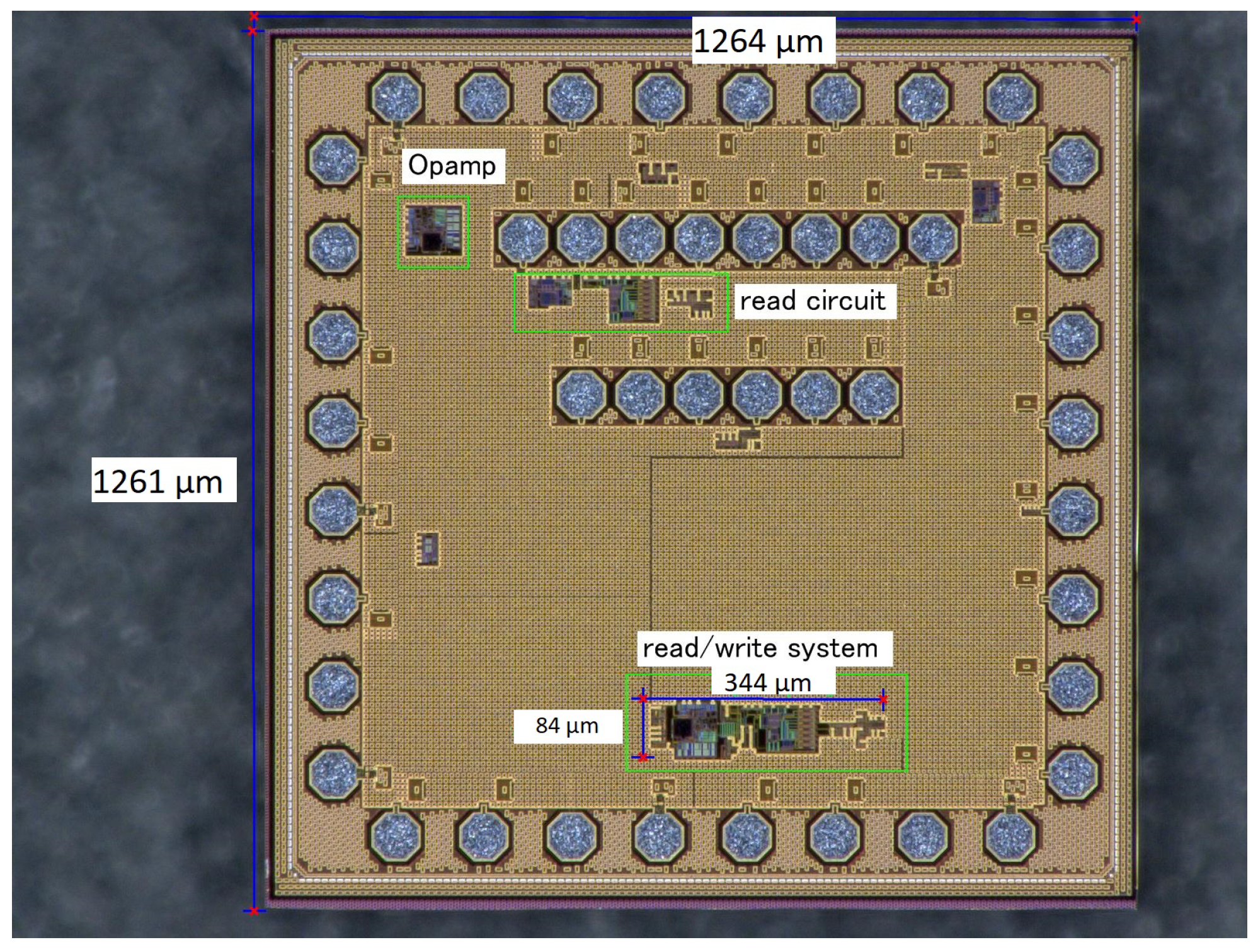
The integrated circuit was designed and fabricated in the 130 SG13S CMOS process by IHP and operates at a supply voltage. A photograph of the chip is shown in Figure 8.
Figure 8.
Picture of the integrated circuit.
5.1. Simulation Results
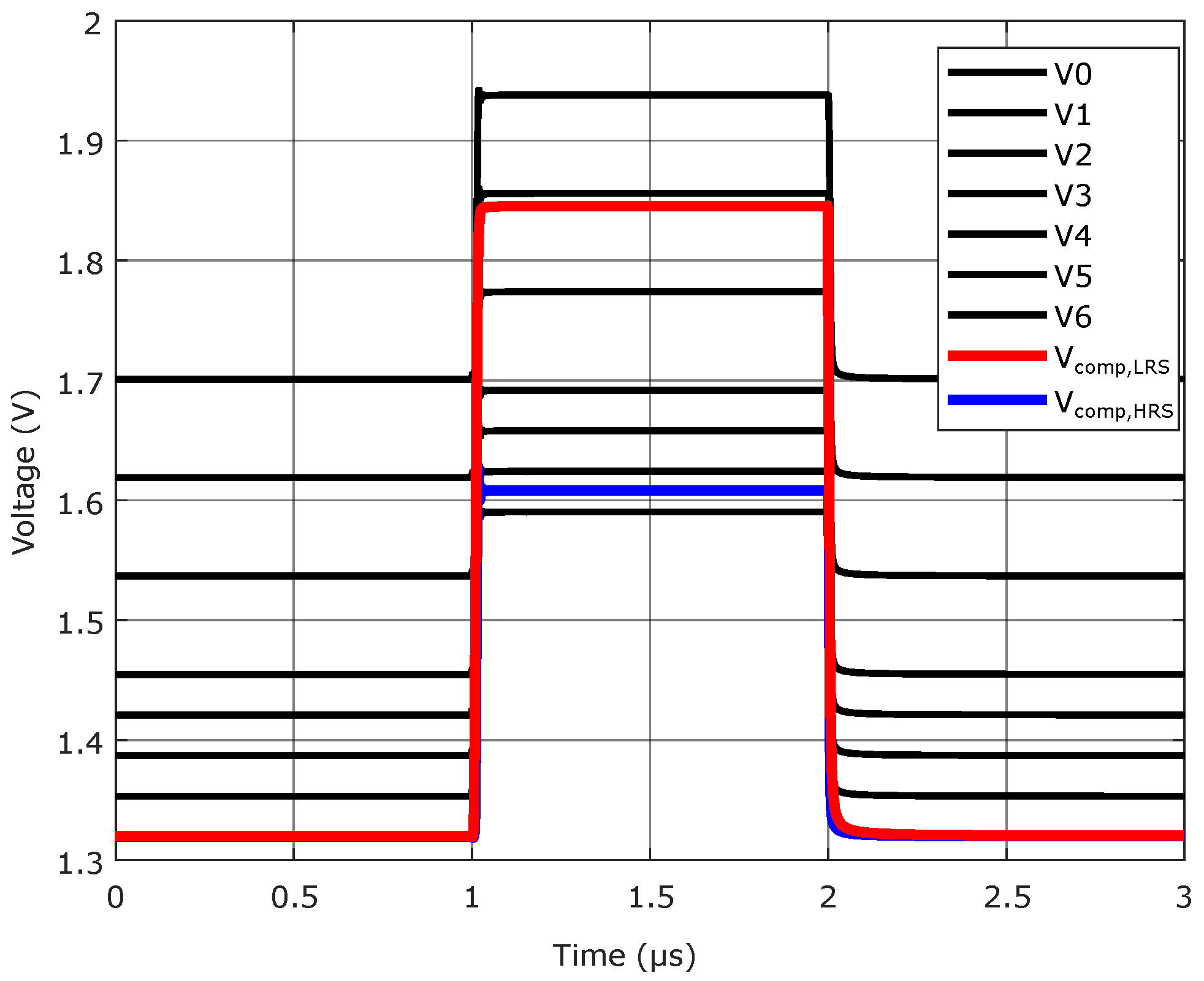
In Figure 9 the simulated voltages inside the read circuit during a read operation are shown. Here, a pulse width of 1 was chosen. The pulse width has an influence on the necessary switching voltage as well as cell variability [19]. A pulse width of 1 is a compromise between programming speed and the necessary pulse height for programming. The voltages V0 to V6 are the systematically raised voltages of in Figure 7a, which are applied at the negative inputs of the comparators. The red line shows for a measurement of a cell in LRS, while the blue line represents for a HRS cell. It can be observed that is significantly lower, since the cell current and therefore the voltage drop over the measurement resistor and is lower. The voltage conditions for the HRS cell will lead to a thermometer code of 0000001, since is greater than the first raised voltage in the resistor tree. This results in a read value of 001 in binary. For the measurement of a LRS cell, the lower cell resistance generates a higher and more comparators are switching. The thermometer code at the output is 0011111 or 101 in binary.
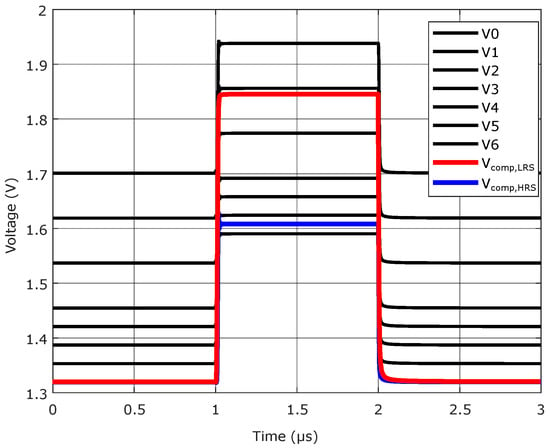
Figure 9.
Simulation results read circuit with two different states.
It can also be observed that before and after the read pulse, when the input of the buffer amplifier is set to ground, is lower than all the negative comparator inputs. Therefore, the output will always be 000 when the read circuit is not active and its inputs are set to ground. This prevents unexpected data output.
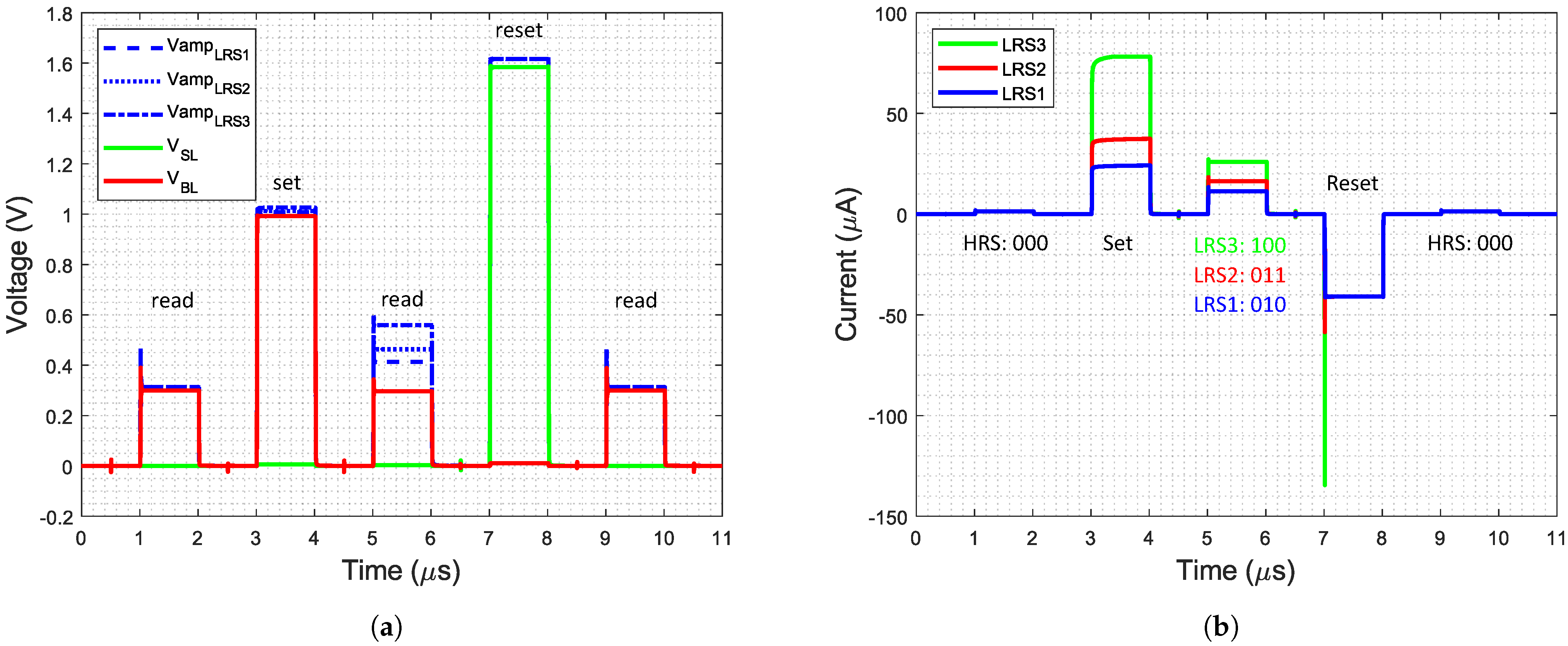
The simulation results of the complete system as depicted in Figure 5 are shown in Figure 10a,b. For simulation, the Spectre-based Virtuoso® Analog Design Environment (ADE) was used. At the ports and , a RRAM model fitted to the IHP RRAM technology based on [20] was used. The model can distinguish between four different states and is based on the physics-based Stanford-PKU model for switching in metal oxide RRAM devices. A sequence of one set and one reset operation was simulated. At the beginning as well as after the set and reset operation, the status of the cell was read using the read operation of the circuit. Figure 10a shows the BL and SL voltages as well as the output voltages of the amplifier , while Figure 10b shows the current flowing through each of the simulated RRAM cells. The simulation was done by programming each of the three different LRS to the model during the set operation. The read values during the read operations are also marked in Figure 10b. In general, a pulse width of 1 was used. The read pulses had a pulse height of 300 , while the set pulses had a height of 1 and the reset pulse a height of . The different LRS were programmed by varying the WL voltage during the set operations.
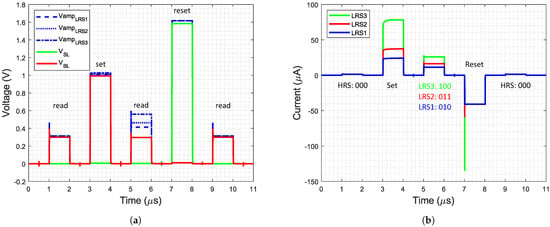
Figure 10.
Simulation results of the system: (a) Voltages and (b) currents. The first read pulse, where all cells are in high resistance state (HRS), is followed by a writing pulse, that sets all cells to different low resistance states (LRS). This is verified by the second read pulse. After the reset pulse, all cells are back in HRS.
It can clearly be observed that the system can program each of the three LRS to the cell and perform a reset operation to program the HRS back into the cell from every LRS. During read operation, the three LRS and the HRS are distinguished by the read system with different read values for the four states:
- LRS3: 100
- LRS2: 011
- LRS1: 010
- HRS: 000
During reset, the polarity of the pulse has to be reversed, therefore, the pulse is applied to the SL while the BL is grounded, depicted in Figure 10a. This results in a current in the other direction, shown in Figure 10b. The switching was realized by the set_reset switch and controlled using the digital set_reset signal. During the set and reset operations, the measurement resistor is bypassed, so the output voltages of the amplifier and the BL/SL voltage are similar. The small difference is a result of the voltage drops over the transmission gates that are used in the set_reset switch and to bypass the measurement resistor. During the read operations, the voltage difference between the amplifier voltage and the BL voltage is evaluated by the read circuit and the three different LRS are visible. While reading the HRS, the voltage drop over the measurement resistor is very small, since the current through the cell in HRS is small.
5.2. Measurement Results Read Circuit
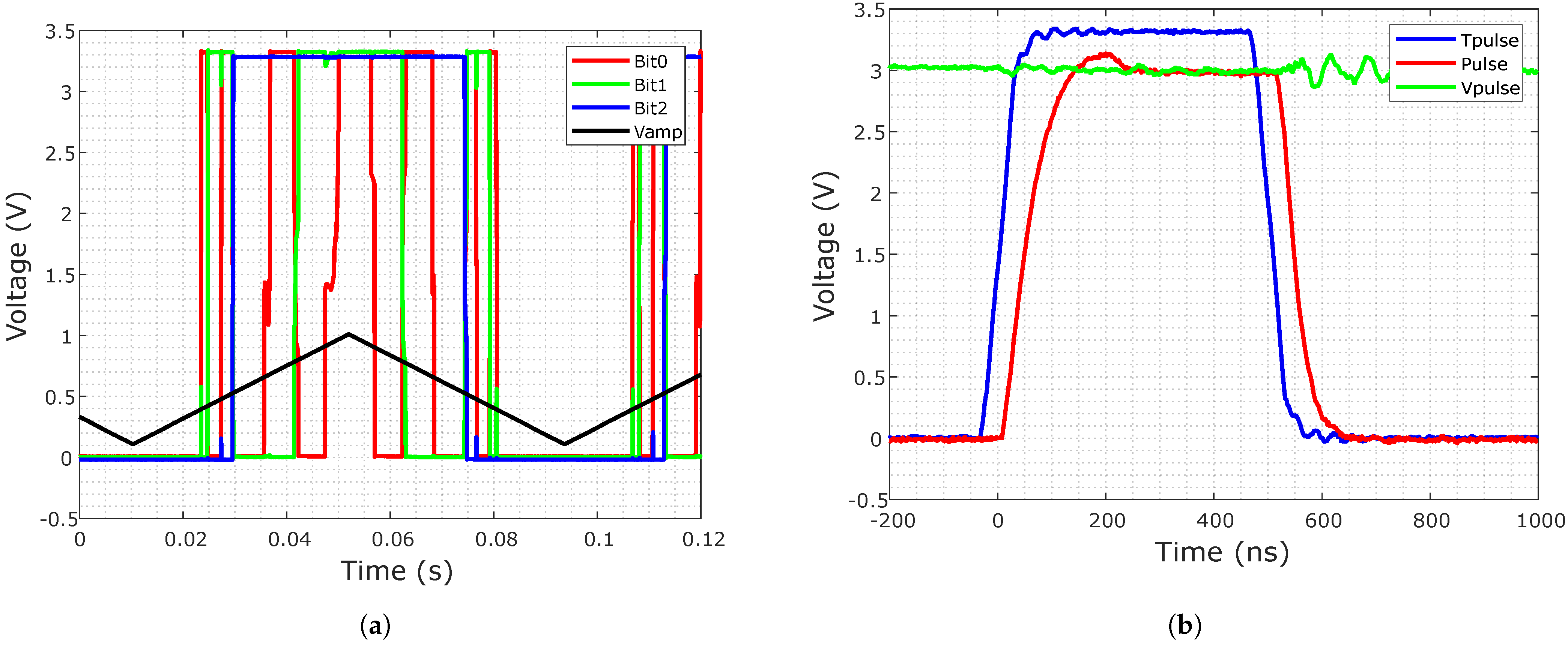
Figure 11a shows the measurement results of the read circuit shown in Figure 7a, where the thermometer output code is encoded as binary. was set to 300 , which corresponds to the realistic pulse height of a read pulse. A rectangular signal between 200 and 1 is fed to the input. Utilizing Equation (3), this represents a cell resistance between kΩ for 1 and basically an open circuit for 200 , since it is below the read voltage. The red, green and blue signals represent the digital output bits, coded in binary, while bit0 in red represents the least significant bit (LSB) and bit2 in blue the most significant bit (MSB). With this setup, the switching voltages of the bits can be observed, thereby determining the range of the read circuit.
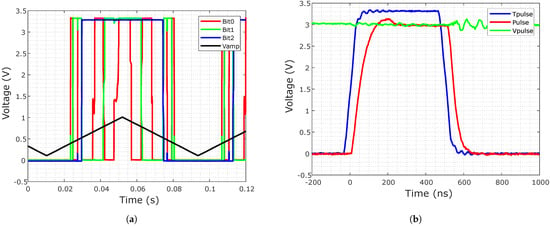
Figure 11.
Measurement results: (a) Read circuit: The input voltage is swept and the switching of the three output bits can be observed. (b) Programming system: The digital pulse Tpulse and the analog voltage level Vpulse together form the buffered voltage pulse at the output of the buffer amplifier.
The switching from 000 to 001 occurs at an input voltage of 380 , which, at a measurement resistance of 10 kΩ and a cell voltage of 300 , means a memory cell resistance of kΩ. The switch from 110 to 111 is triggered at an input voltage of 930 , corresponding to a cell resistance of kΩ. The two different resistance values in the resistance tree, shown in Figure 7a, can clearly be observed, resulting in a smaller difference in voltage between the switching of the values 000 until 100 of about 30 to the switching from 100 to 111 of about 130 .
Table 3 shows the switching voltages of the read circuit with its corresponding resistance values and outputs. The two different resistance values in the resistance tree, shown in Figure 7a, can clearly be observed in the difference of the voltage intervals for the output values between 000 and 100 and between 100 and 111. By changing the height of the read pulse, this range can be adapted to other RRAM technologies. For this configuration, which is suited for the IHP RRAM technology, a resistance ration of 7.9 can be distinguished with a resolution of 3 Bit.

Table 3.
Read circuit measurement results.
This however is the theoretical limit, the practical limitations are dictated by the matching of the resistors in the resistor tree as well as the accuracy of the comparators. As a comparison, the switching voltages marked in Table 3 are shifted by a maximum of +/− 20 during a measurement of another dielectric layer with the same system and measurement configuration.
5.3. Measurement Results System
The evaluation of the whole system by measurement is separated into the two modes of operation.
5.3.1. Programming System
In order to measure the functionality of the programming operation, pulses of different height and length are generated, buffered by the system and evaluated via oscilloscope. As described in Section 3.1, the pulses are generated by applying the height of the pulse at the terminal continuously and then activating the transmission gate by applying a digital pulse of the desired length at the terminal. This results in the buffered output pulse. Here, a pulse length of 500 and a pulse height of 3 were chosen. A delay between the digital input pulse and the buffered pulse at the output of about 50 can be observed. This determines the minimum possible pulse length of about 100 . The functionality of the set/reset switch was measured and no remarkable difference between applying the pulse to the BL or SL could be observed, therefore confirming the correct operation of the set/reset switch.
5.3.2. Read System
The read system was tested by connecting the and pads of the chip via probes off-chip with discrete resistors of different values. Then 25 read operations per resistance value were executed, tracking the different output bits. The off-chip resistors were necessary because the RRAM cells were not available in the semiconductor process during the design of the chip due to the migration to the new process.
The measurements were done using corresponding resistance values to the measured I-V curves from Table 1. The results are shown in Table 4. As read voltage, a voltage pulse of 300 was used. The four different states can clearly be distinguished. The corresponding resistances to the read values are smaller than the calculated resistance values from the measurement results of the read circuit in Section 5.2. This can be explained by the additional resistances added by the probing system and the wire connections as well as the additional set/reset switch and transmission gates in the signal path between the resistor under test and the measurement resistor on the chip at the output of the buffer amplifier. Therefore, the corresponding resistances are shifted to lower values.

Table 4.
Read system measurement results.
6. Discussion and Comparison with Other Read and Programming Circuits
The presented simulation and measurement results show that the circuit is capable of applying the necessary programming pulses as well as distinguishing the four proposed states of the IHP RRAM technology. In order to improve the performance, some adjustments should be made in future versions of the circuit: Due to the measurement setup with off-chip resistors, the accuracy of the whole system is decreased. States in between the resistance levels measured in Table 3 overlap in their output values over a longer series of measurements. Therefore, the resolution of the whole system can be increased by integrating the RRAM cells on the chip, when available, thereby minimizing parasitics. Furthermore, the voltage room of the resistor tree from Figure 7a can be used more efficiently by adapting the resistances of R1 and R2.
Although the circuit is fitted to the IHP RRAM technology, there are several possibilities to adapt the concept to other RRAM technologies. Since it operates with voltage pulses, their length and height can be varied. Especially the height of the voltage pulse can be adjusted to other RRAM technologies, that have different resistance values. By that, the voltage drop over the measurement resistor can be tuned to the necessary resistance window. By changing the values of the current source IR or the resistor values R1 and R2 in Figure 7a, the switching voltages and therefore the resolution of the sensing scheme can be tuned. For different cell resistances, Rmeas can be changed to tune the voltage drop. Due to the set/reset switch, it is possible to use the concept with bipolar and unipolar switching RRAM technologies. By adding more resistors and comparators to the read circuit, more states could possibly be distinguished, although this corresponds with higher requirements for the comparators as well as resistor precision.
In Table 5, the presented circuit is compared to other publications in the field of RRAM or Memristor read and programming circuits. It is compared by the capability to read and program with the same circuitry, the measured or respectively simulated resistance ratio during the read process and the multi-bit capability of the circuits.

Table 5.
Comparison of different read and programming circuits.
The proposed circuit can perform read and programming operations and has the capability of reading up to eight different states, depending on the read circumstances. Four states are proven by measurement for the whole system. The resistance ratio of the read cells are harder to define for the proposed circuit since the output values are dependent on the chosen read voltage. However, it is shown that the circuit can distinguish several states of cells that have a resistance ratio of only 7.9. Here the values of the proposed states from the read system measurement in Table 3 were used for calculation of the resistance ratio.
The circuit in [22] combines the capability of reading and programming as well as being able to perform multi-bit read operations, but a much higher resistance ratio is used. In [21], the read operation is done by a time-to-digital conversion and takes advantage of a much higher resistance ratio as well. Furthermore, it has no programming capability. The proposed circuit in [23] can read and program but lacks the multi-bit capability.
7. Conclusions
This paper presents a read and programming circuit based on voltage pulses for resistive memory cells. During programming it can execute set and reset operations with various pulse heights and widths. The reading is done by evaluating the cell current using the voltage drop over a measurement resistor. The read circuit realizes a digitization, using several comparators to convert the analog voltage drop over the measurement resistor to digital data.
It is shown that the read circuit can distinguish up to eight resistance states between a cell resistance from to , corresponding to a resistance ratio of 7.9. The whole system is reliably capable of distinguishing the four different states of the IHP RRAM technology and has potential to increase the resolution to eight different states by using integrated RRAM cells. It is adaptable to other RRAM technologies by varying the read and programming pulses in height and length, suiting the measurement resistor to the read current range of the technology or tuning the resistor and current values inside the read circuit, therefore showing a high degree of flexibility.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.P., T.M., M.V., M.R. and A.H.; methodology, S.P., T.M., M.V., M.R. and A.H.; validation, all authors; formal analysis, S.P., M.K.M., E.P. and E.P.-B.Q.; investigation, S.P., M.K.M., E.P. and E.P.-B.Q.; resources, M.R., C.W. and A.H.; data curation, S.P., M.V., M.K.M., E.P. and E.P.-B.Q.; writing—original draft preparation, S.P.; writing—review and editing, all authors; visualization, S.P., M.K.M., E.P. and E.P.-B.Q.; supervision, M.R., C.W. and A.H.; project administration, M.R., C.W. and A.H.; funding acquisition, M.R., C.W. and A.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) through the joint research in the project IMBRA and the University of Bayreuth in the funding program Open Access Publishing.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Simulation and measurement data are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the IHP-Leibniz Institut fuer innovative Mikroelektronik for fabricating the integrated circuits.
Conflicts of Interest
The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| RRAM | Resistive Random Access Memory |
| PUF | Physical unclonable function |
| SRAM | Static Random Access Memory |
| FF | Flip Flop |
| NVM | Non-volatile Memory |
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| ML | Machine Learning |
| BL | Bitline |
| SL | Sourceline |
| WL | Wordline |
| MIM | Metal-Insulator-Metal |
| 1T1R | One-Transistor/One-Resistor |
| BEOL | Back end of line |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscope |
| HRS | High resistive state |
| LRS | Low resistive state |
| ISPVA | Incremental Step Pulse and Verify Algorithm |
| LSB | Least significant bit |
| MSB | Most significant bit |
References
- Covi, E.; Lin, Y.; Wang, W.; Stecconi, T.; Milo, V.; Bricalli, A.; Ambrosi, E.; Pedretti, G.; Tseng, T.; Ielmini, D. A Volatile RRAM Synapse for Neuromorphic Computing. In Proceedings of the 2019 26th IEEE International Conference on Electronics, Circuits and Systems (ICECS), Genoa, Italy, 27–29 November 2019; pp. 903–906. [Google Scholar]
- Kawahara, A.; Azuma, R.; Ikeda, Y.; Kawai, K.; Katoh, Y.; Hayakawa, Y.; Tsuji, K.; Yoneda, S.; Himeno, A.; Shimakawa, K.; et al. An 8 Mb Multi-Layered Cross-Point ReRAM Macro With 443 MB/s Write Throughput. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2013, 48, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Gaba, S.; Wheeler, D.; Cruz-Albrecht, J.M.; Hussain, T.; Srinivasa, N.; Lu, W. A Functional Hybrid Memristor Crossbar-Array/CMOS System for Data Storage and Neuromorphic Applications. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biglari, M.; Lieske, T.; Fey, D. High-Endurance Bipolar ReRAM-Based Non-Volatile Flip-Flops with Run-Time Tunable Resistive States. In Proceedings of the 14th IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Nanoscale Architectures NANOARCH ’18, Athens, Greece, 17–19 July 2018; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuben, J.; Pechmann, S. A Parallel-friendly Majority Gate to Accelerate In-memory Computation. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 31st International Conference on Application-specific Systems, Architectures and Processors (ASAP), Manchester, UK, 6–8 July 2020; pp. 93–100. [Google Scholar]
- Zahoor, F.; Zulkifli, T.Z.A.; Khanday, F.A. Resistive Random Access Memory (RRAM): An Overview of Materials, Switching Mechanism, Performance, Multilevel Cell (mlc) Storage, Modeling, and Applications. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Chen, P. Emerging Memory Technologies: Recent Trends and Prospects. IEEE Solid-State Circuits Mag. 2016, 8, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhao, M.; Liu, Y.; Yao, P.; Xi, Y.; Li, X.; Wu, W.; Zhang, Q.; Tang, J.; Gao, B.; et al. Reliability Perspective on Neuromorphic Computing Based on Analog RRAM. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Reliability Physics Symposium (IRPS), Monterey, CA, USA, 31 March–4 April 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, E.; Maldonado, D.; Acal, C.; Ruiz-Castro, J.; Alonso, F.; Aguilera, A.; Jiménez-Molinos, F.; Wenger, C.; Roldán, J. Analysis of the statistics of device-to-device and cycle-to-cycle variability in TiN/Ti/Al:HfO2/TiN RRAMs. Microelectron. Eng. 2019, 214, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossi, A.; Perez, E.; Zambelli, C.; Olivo, P.; Wenger, C. Performance and reliability comparison of 1T-1R RRAM arrays with amorphous and polycrystalline HfO2. In Proceedings of the 2016 Joint International EUROSOI Workshop and International Conference on Ultimate Integration on Silicon (EUROSOI-ULIS), Vienna, Austria, 25–27 January 2016; pp. 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milo, V.; Zambelli, C.; Olivo, P.; Pérez, E.; Mahadevaiah, M.K.; Ossorio, O.G.; Wenger, C.; Ielmini, D. Multilevel HfO2-based RRAM devices for low-power neuromorphic networks. APL Mater. 2019, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, E.; Grossi, A.; Zambelli, C.; Olivo, P.; Roelofs, R.; Wenger, C. Reduction of the Cell-to-Cell Variability in Hf1-xAlxOyBased RRAM Arrays by Using Program Algorithms. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2017, 38, 175–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crupi, F.; Filice, F.; Grossi, A.; Zambelli, C.; Olivo, P.; Perez, E.; Wenger, C. Implications of the Incremental Pulse and Verify Algorithm on the Forming and Switching Distributions in RERAM Arrays. IEEE Trans. Device Mater. Reliab. 2016, 16, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, E.; Grossi, A.; Zambelli, C.; Olivo, P.; Wenger, C. Impact of the Incremental Programming Algorithm on the Filament Conduction in HfO2-Based RRAM Arrays. IEEE J. Electron Devices Soc. 2017, 5, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, E.; Zambelli, C.; Kalishettyhalli Mahadevaiah, M.; Olivo, P.; Wenger, C. Towards Reliable Multi-Level Operation in RRAM Arrays: Improving Post-Algorithm Stability and Assessing Endurance/Data Retention. IEEE J. Electron Devices Soc. 2019, 7, 740–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S. Overview of resistive switching memory (RRAM) switching mechanism and device modeling. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Melbourne, VIC, Australia, 1–5 June 2014; pp. 2017–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciocoveanu, R.; Bahr, A.; Krautschneider, W. Design of a Rail-to-Rail Folded Cascode Amplifier with Transconductance Feedback Circuit. In Proceedings of the ITC Open Conference, Amersfoort, The Netherlands, 14–16 September 2016; pp. 21–24. [Google Scholar]
- Gray, P. Analysis and Design of Analog Integrated Circuits, 5th ed.; Wiley Global Education: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez, E.; Ossorio, O.G.; Dueñas, S.; Castán, H.; García, H.; Wenger, C. Programming Pulse Width Assessment for Reliable and Low-Energy Endurance Performance in Al:HfO2-Based RRAM Arrays. Electronics 2020, 9, 864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuben, J.; Fey, D.; Wenger, C. A Modeling Methodology for Resistive RAM Based on Stanford-PKU Model With Extended Multilevel Capability. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 2019, 18, 647–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossam, H.; Mamdouh, G.; Hussein, H.H.; El-Dessouky, M.; Mostafa, H. A New Read Circuit for Multi-Bit Memristor-Based Memories based on Time to Digital Sensing Circuit. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 61st International Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems (MWSCAS), Windsor, ON, Canada, 5–8 August 2018; pp. 1114–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manem, H.; Rose, G.S. A read-monitored write circuit for 1T1M multi-level memristor memories. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Symposium of Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 15–18 May 2011; pp. 2938–2941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshamy, M.; Mostafa, H.; Ghallab, Y.H.; Said, M.S. A Novel Nondestructive Read/Write Circuit for Memristor-Based Memory Arrays. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 2015, 23, 2648–2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).