Analysis of the Impact for Mixed Traffic Flow Based on the Time-Varying Model Predictive Control
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Research on Leading Cruise Control
2.2. Quantitative Description and Impact Analysis of Mixed Traffic Flow
3. Quantitative Description of Mixed Traffic Flow
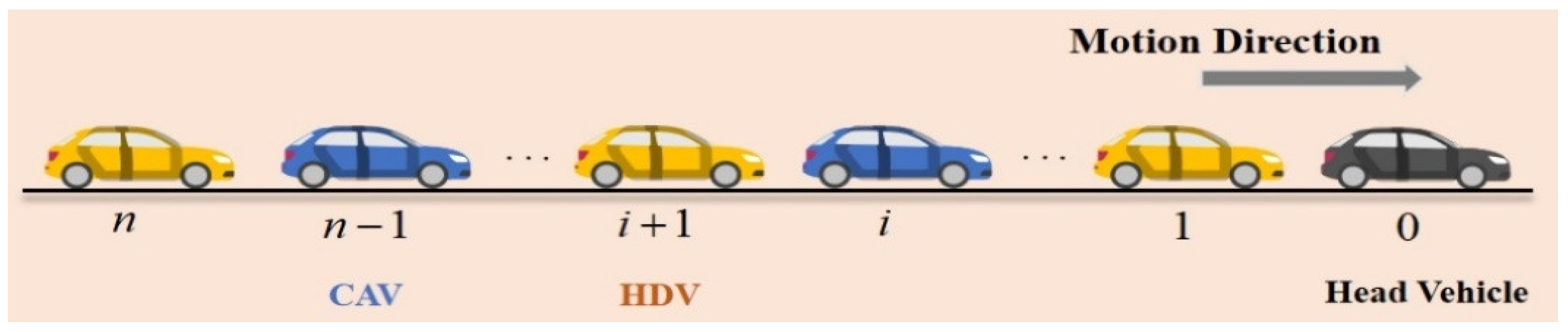
3.1. Problem Statement
3.2. Markov Chain Model
3.3. Linear Time-Varying MPC for Mixed Traffic Flow
4. Performance Metrics
5. Experimental Results and Analysis
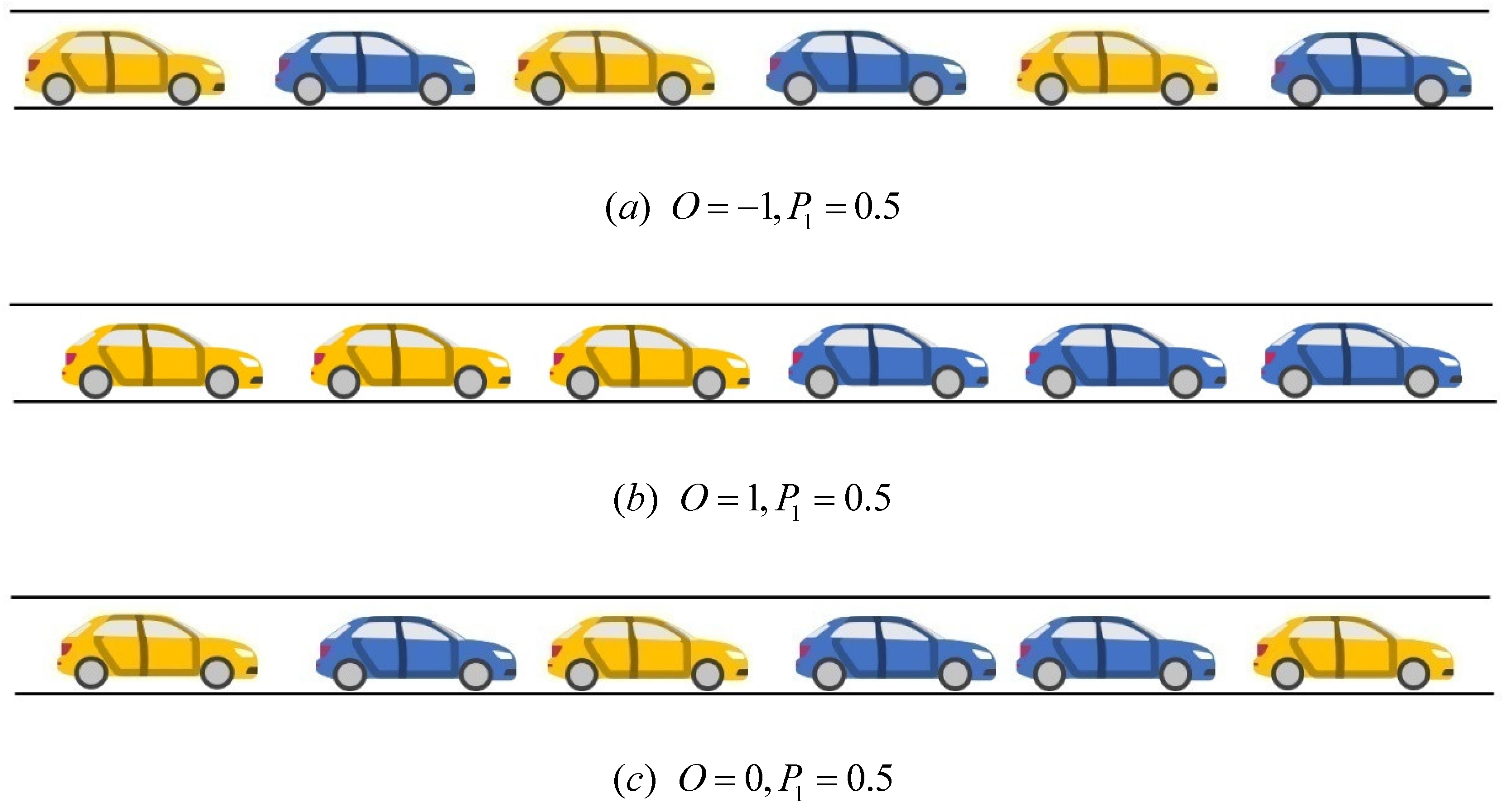
5.1. Experiment 1: CAV in Different Position
5.2. Experiment 2: Platoon Intensity
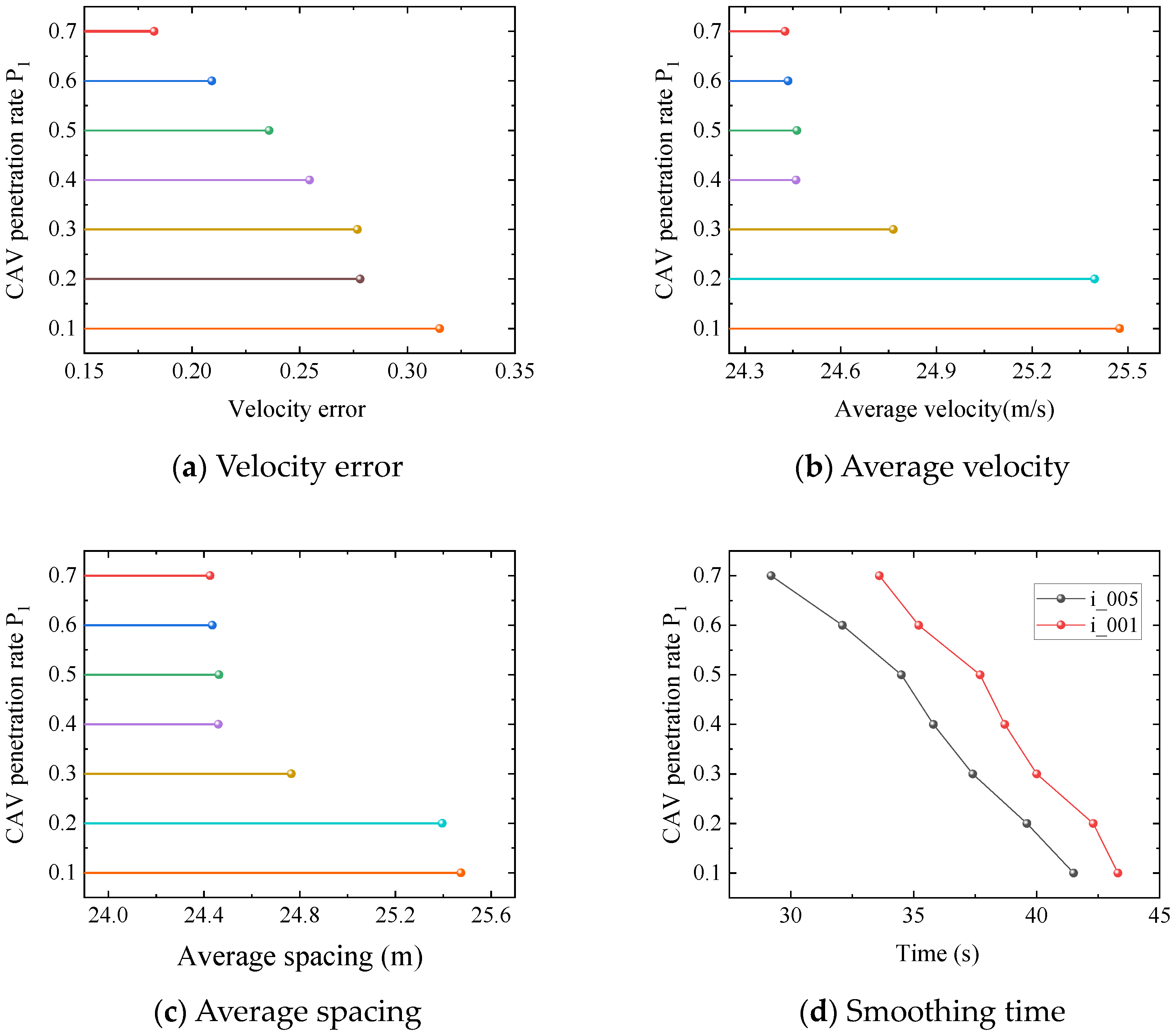
5.3. Experiment 3: CAV Penetration Rates
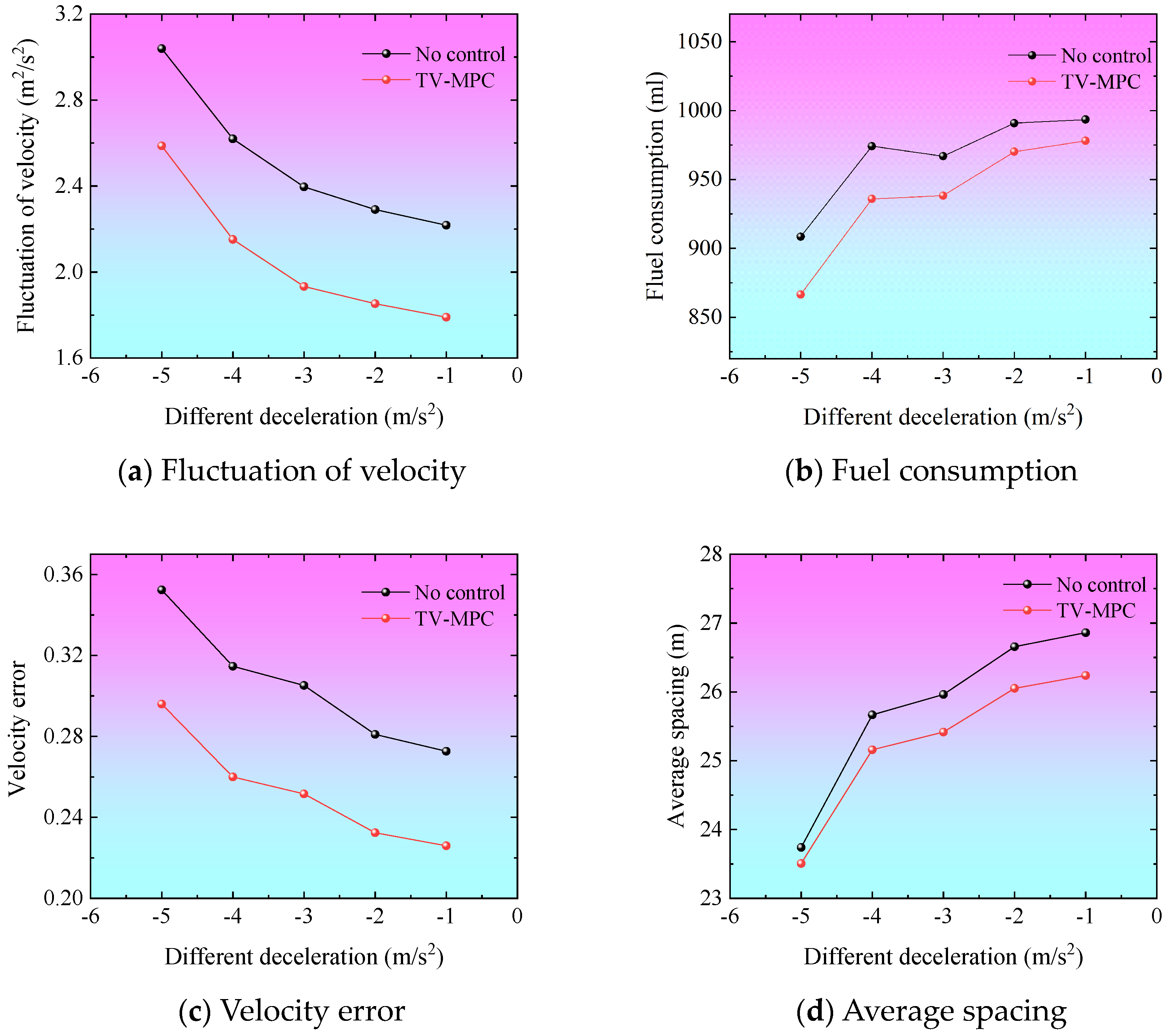
5.4. Experiment 4: Degree of Perturbation
6. Suggestion and Application for TV-MPC
7. Conclusions and Discussion
7.1. Conclusions
7.2. Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, F.; Li, X.; Ma, J. Parsimonious shooting heuristic for trajectory design of connected automated traffic part I: Theoretical analysis with generalized time geography. Transp. Res. Part B Methodol. 2017, 95, 394–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Q.; Lyu, H.; Yang, H.; Wei, Q.; Cheng, R. Bifurcation control of solid angle car-following model through a time-delay feedback method. J. Zhejiang Univ.-Sci. A 2023, 24, 828–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, B.; Jiang, Y. Analysis of the impact of maximum platoon size of CAVs on mixed traffic flow: An analytical and simulation method. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2023, 147, 103989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wu, X.; Bai, X.; Liu, Y.; Xu, M. Intelligent Eco-Driving Control for Urban CAVs Using a Model-Based Controller Assisted Deep Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2025, 26, 7624–7639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, T.; Ferdowsi, A.; Semiari, O.; Saad, W.; Hong, C.S. Convergence of communications, control, and machine learning for secure and autonomous vehicle navigation. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2024, 31, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummins, L.; Sun, Y.; Reynolds, M. Simulating the effectiveness of wave dissipation by FollowerStopper autonomous vehicles. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2021, 123, 102954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Cao, Z.; Li, Z. A reinforcement learning-based vehicle platoon control strategy for reducing energy consumption in traffic oscillations. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2021, 32, 5309–5322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Dong, J.; Chen, C.; Cai, M.; Li, K.; Xu, Q. Implementation and experimental validation of data-driven predictive control for dissipating stop-and-go waves in mixed traffic. IEEE Internet Things J. 2023, 11, 2327–4662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Wang, S.; Wu, C.; Xiao, X.; Lyu, N. A longitudinal velocity CF-MPC model for connected and automated vehicle platooning. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 24, 6463–6476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Li, X.; Hu, J.; Hu, W. Modeling and optimization of connected and automated vehicle platooning cooperative control with measurement errors. Sensors 2023, 23, 9006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhou, B.; Xu, M. Longitudinal car-following control strategy integrating predictive collision risk. Appl. Math. Model. 2023, 121, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, H.; Guo, Y.; Liu, P.; Wang, T. Uncertainty-Aware Dynamics Modeling and Data-Driven Robust Predictive Control for Mixed Vehicle Platoon. IEEE Internet Things J. 2025, 12, 17948–17963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Cheng, R. A real-time adaptive signal control method for multi-intersections in mixed connected vehicle environments. J. Zhejiang Univ.-Sci. A 2025, 1, 189. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, H.; Wang, L.; Zheng, N.; Cheng, Z.; Zheng, X.; Li, J. A novel hierarchical perimeter control method for road networks considering boundary congestion in a mixed CAV and HV traffic environment. Transp. Res. Part B Methodol. 2025, 195, 103219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Zhao, W.; Song, G.; Nie, Z.; Han, X.; Liu, Y. DDPG-based decision-making strategy of adaptive cruising for heavy vehicles considering stability. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 59225–59246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Yu, Y.; Zhou, M.; Lin, C.T.; Wang, X. Jointly dampening traffic oscillations and improving energy consumption with electric, connected and automated vehicles: A reinforcement learning based approach. Appl. Energy 2020, 257, 114030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wabersich, K.P.; Hewing, L.; Carron, A.; Zeilinger, M.N. Probabilistic model predictive safety certification for learning-based control. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2021, 67, 176–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Pant, Y.V.; Jiang, Z. Learning-based modeling of human-autonomous vehicle interaction for improved safety in mixed-vehicle platooning control. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2024, 162, 104600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Chen, D.; Zheng, N.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Ran, B. A deep reinforcement learning based distributed control strategy for connected automated vehicles in mixed traffic platoon. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2023, 148, 104019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, G.; Yue, W. Sampled-data cooperative adaptive cruise control of vehicles with sensor failures. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2014, 15, 2404–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akram, M.A.; Liu, P.; Wang, Y.; Qian, J. Gnss positioning accuracy enhancement based on robust statistical mm estimation theory for ground vehicles in challenging environments. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munigety, C.R. A spring-mass-damper system dynamics-based driver-vehicle integrated model for representing heterogeneous traffic. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 2018, 32, 1850135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munigety, C.R. Conformity and stability analysis of a modified spring–mass–damper system dynamics-based car-following model. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 2019, 33, 1950025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wildhagen, S.; Pezzutto, M.; Schenato, L.; Allgöwer, F. Self-triggered MPC robust to bounded packet loss via a min-max approach. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 61st Conference on Decision and Control (CDC), Cancun, Mexico, 6–9 December 2022; pp. 7670–7675. [Google Scholar]
- Bongard, J.; Berberich, J.; Köhler, J.; Allgöwer, F. Robust stability analysis of a simple data-driven model predictive control approach. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2022, 68, 2625–2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jin, P.J. Model predictive control policy design, solutions, and stability analysis for longitudinal vehicle control considering shockwave damping. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2023, 148, 104038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwenkel, L.; Köhler, J.; Müller, M.A.; Allgöwer, F. Model predictive control for linear uncertain systems using integral quadratic constraints. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2022, 68, 355–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirrer, A.; Haniš, T.; Klaučo, M.; Thormann, S.; Hromčík, M.; Jakubek, S. Safety-extended explicit MPC for autonomous truck platooning on varying road conditions. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2020, 53, 14344–14349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Xie, L.; Xie, L.; Lu, S.; Xu, W.; Su, H. Distributed model predictive control for vehicle platoon with mixed disturbances and model uncertainties. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 17354–17365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Ren, Y.; Yu, H.; Li, Z.; Jiang, H. Connected and automated vehicle platoon maintenance under communication failures. Veh. Commun. 2022, 35, 100467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Li, K.; Xu, Q. DeeP-LCC: Data-enabled predictive leading cruise control in mixed traffic flow. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2023, 31, 2760–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talebpour, A.; Mahmassani, H.S. Influence of connected and autonomous vehicles on traffic flow stability and throughput. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2016, 71, 143–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Lyu, H.; Wang, T.; Cheng, R. STdi4DMPC: Distributed Model Predictive Control for Connected and Automated Truck Platoon with Mixed Traffic Flow Based on Spatiotemporal Trajectory Prediction. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2024, 73, 14563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; He, B.Y.; Ma, J. Connected automated vehicle impacts in Southern California part-II: VMT, emissions, and equity. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2022, 109, 103381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Chen, Y.; Hao, R. An Integrated Optimization Framework for Connected and Automated Vehicles and Traffic Signals in Urban Networks. Systems 2025, 13, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, F.; Yue, S. Carbon emission impacts of longitudinal disturbance on low-penetration connected automated vehicle environments. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2023, 123, 103911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Wang, J.; Zheng, Y. Cooperative formation of autonomous vehicles in mixed traffic flow: Beyond platooning. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 15951–15966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Q.; Chen, H. Enhancing Freeway Traffic Capacity: The Impact of Autonomous Vehicle Platooning Intensity. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghiasi, A.; Hussain, O.; Qian, Z.S.; Li, X. A mixed traffic capacity analysis and lane management model for connected automated vehicles: A Markov chain method. Transp. Res. Part B Methodol. 2017, 106, 266–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Ahn, S.; Chitturi, M.; Noyce, D.A. Towards vehicle automation: Roadway capacity formulation for traffic mixed with regular and automated vehicles. Transp. Res. Part B Methodol. 2017, 100, 196–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Sun, S.; Zhu, F.; Wu, Y.; Yao, Z. A mixed capacity analysis and lane management model considering platoon size and intensity of CAVs. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2023, 615, 128557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, H.; Lyu, H.; Cheng, R. A time-varying driving style oriented model predictive control for smoothing mixed traffic flow. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2024, 637, 129606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowyer, D.P.; Akçelik, R.; Biggs, D.C. Guide to fuel consumption analyses for urban traffic management. Syd. Aust. Aust. Road Res. Board 1984, 21, 485. [Google Scholar]




| parameters | |||||
| value | 1.50 m/s2 | 1.67 m/s2 | 33.30 m/s | 2.00 m | 1.60 s |
| The Position of CAV | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The emission of CO2 (g) | 1307.16 | 1302.75 | 1274.13 | 1281.87 | 1294.33 |
| The fuel consumption (mL) | 997.46 | 991.21 | 932.94 | 945.42 | 966.12 |
| The velocity error | 0.54 | 0.54 | 0.53 | 0.59 | 0.62 |
| The average spacing (m) | 33.44 | 33.43 | 33.00 | 33.45 | 33.66 |
| Fluctuations in velocity (m2/s2) | 24.76 | 24.41 | 20.91 | 21.53 | 22.64 |
| Order of Actions | Scheme |
|---|---|
| deceleration- uniform- acceleration | The head vehicle accelerates from V = 15.0 m/s to V = 5.0 m/s with a = −1.0 m/s2, −2.0 m/s2, −3.0 m/s2, −4.0 m/s2, −5.0 m/s2. After driving at a constant velocity for 5 s and then accelerates from V = 5.0 m/s to V = 15.0 m/s with a = 2.0 m/s2. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, R.; Lou, H.; Wei, Q. Analysis of the Impact for Mixed Traffic Flow Based on the Time-Varying Model Predictive Control. Systems 2025, 13, 481. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems13060481
Cheng R, Lou H, Wei Q. Analysis of the Impact for Mixed Traffic Flow Based on the Time-Varying Model Predictive Control. Systems. 2025; 13(6):481. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems13060481
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Rongjun, Haoli Lou, and Qi Wei. 2025. "Analysis of the Impact for Mixed Traffic Flow Based on the Time-Varying Model Predictive Control" Systems 13, no. 6: 481. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems13060481
APA StyleCheng, R., Lou, H., & Wei, Q. (2025). Analysis of the Impact for Mixed Traffic Flow Based on the Time-Varying Model Predictive Control. Systems, 13(6), 481. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems13060481






