Text Correction
There was an error in the original publication [1]. Data was incorrectly extracted from Table 3 of Juan et al. [53], where we had taken the value for % body fat in the post-probiotic group and compared it to body weight in the post-placebo group. Data has been reanalyzed using the correct value for % body fat in the post-placebo group.
A correction has been made to Section 3.8.
3.8. Percentage Change in Body Fat
Three studies assessed percentage change in body fat (BF%) after probiotics intervention. Use of probiotics reduced BF% in both breast cancer patients and survivors (MD = −1.81; 95% CI: −5.22 to 1.61; p = 0.30; Figure 4A). Subgroup analysis demonstrated that ProLBE supplements significantly reduced the elevation of BF% in breast cancer patients (MD = −4.20; 95% CI: −7.59 to −0.81; p = 0.02) while a smaller decrease in BF% occurred in breast cancer survivors with use of ProLBS capsules (Figure 4B).
As such, a correction has also been made to Table 4 and Figure 4 to reflect the revised analysis.
The corrected Table 4 appears below:

Table 4.
Quantitative subgroup analysis for all the included trials.
Table 4.
Quantitative subgroup analysis for all the included trials.
| Subgroup/Sensitivity Analysis | Number of Trials | SMD (95% CI) | p-Value | Heterogeneity (I2, p-Value) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BMI | |||||
| Probiotics ± prebiotics | Probiotics only | 2 | 0.00 (−0.76, 0.77) | 0.99 | 73% (0.05) |
| Combined with FOS | 3 | −0.05 (−0.29, 0.20) | 0.72 | 0% (0.99) | |
| Intake duration | 10 weeks | 3 | −0.06 (−0.30, 0.19) | 0.65 | 0% (1.00) |
| 8 weeks | 2 | 0.14 (−0.30, 0.58) | 0.53 | 19% (0.27) | |
| 3 weeks | 1 | −0.34 (−0.75, 0.07) | 0.11 | N/A | |
| Body weight | |||||
| Probiotics ± prebiotics | Probiotics only | 2 | 0.10 (−1.08, 1.28) | 0.87 | 88% (0.004) |
| Combined with FOS | 2 | −0.01 (−0.32, 0.30) | 0.93 | 0% (0.54) | |
| Intake duration | 10 weeks | 1 | 0.08 (−0.34, 0.49) | 0.73 | N/A |
| 8 weeks | 2 | 0.27 (−0.57, 1.10) | 0.53 | 75% (0.04) | |
| 3 weeks | 1 | −0.47 (−0.88, −0.06) | 0.03 | N/A | |
| BF% | |||||
| Probiotics ± prebiotics | Probiotics only | 1 | −0.51 (−0.93, −0.09) | 0.02 | N/A |
| Combined with FOS | 2 | −0.03 (−0.34, 0.28) | 0.85 | 0% (0.86) | |
| Intake duration | 10 weeks | 1 | −0.00 (−0.42, 0.41) | 0.98 | N/A |
| 8 weeks | 1 | −0.06 (−0.52, 0.40) | 0.80 | N/A | |
| 3 weeks | 1 | −4.50 (−5.28, −3.72) | <0.00001 | N/A | |
| Waist circumference | |||||
| Probiotics ± prebiotics | Probiotics only | 1 | 4.0 (−1.44, 9.44) | 0.15 | N/A |
| Combined with FOS | 2 | −1.10 (−4.52, 2.31) | 0.53 | 0% (0.84) | |
| Intake duration | 10 weeks | 1 | −0.14 (−0.56, 0.28) | 0.36 | 0% (1.00) |
| 8 weeks | 2 | 0.19 (−0.24, 0.63) | 0.39 | 18% (0.27) | |
Abbreviations: BMI, body mass index; BF%, percentage change in body fat; FOS, fructo-oligosaccharides; N/A, not available.
The corrected Figure 4 appears below:
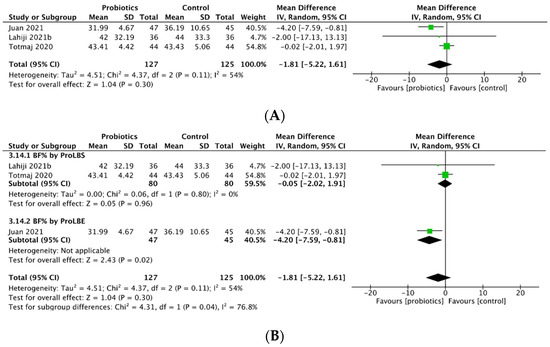
Figure 4.
Meta-analysis for (A) percentage change in body fat (BF%) percent and (B) BF% by probiotic type.
The authors state that the scientific conclusions are unaffected. This correction was approved by the Academic Editor. The original publication has also been updated.
Reference
- Thu, M.S.; Ondee, T.; Nopsopon, T.; Farzana, I.A.K.; Fothergill, J.L.; Hirankarn, N.; Campbell, B.J.; Pongpirul, K. Effect of Probiotics in Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Biology 2023, 12, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).