Bisphenol E Neurotoxicity in Zebrafish Larvae: Effects and Underlying Mechanisms
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemical Substances
2.2. Zebrafish Cultivation and Maintenance
2.3. Acute Toxicity Test and General Developmental Toxicity Test of BPE
2.4. Behavioral Testing of Zebrafish Larvae
2.5. Studies on the Neurodevelopmental Toxicity of Zebrafish Larvae
2.6. Target Identification for BPE-Induced Neural Damage and PPI Network Construction
2.7. GO and KEGG Pathway Analysis
2.8. Molecular Docking
2.9. Fluorescence Quantitative PCR in Real Time
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
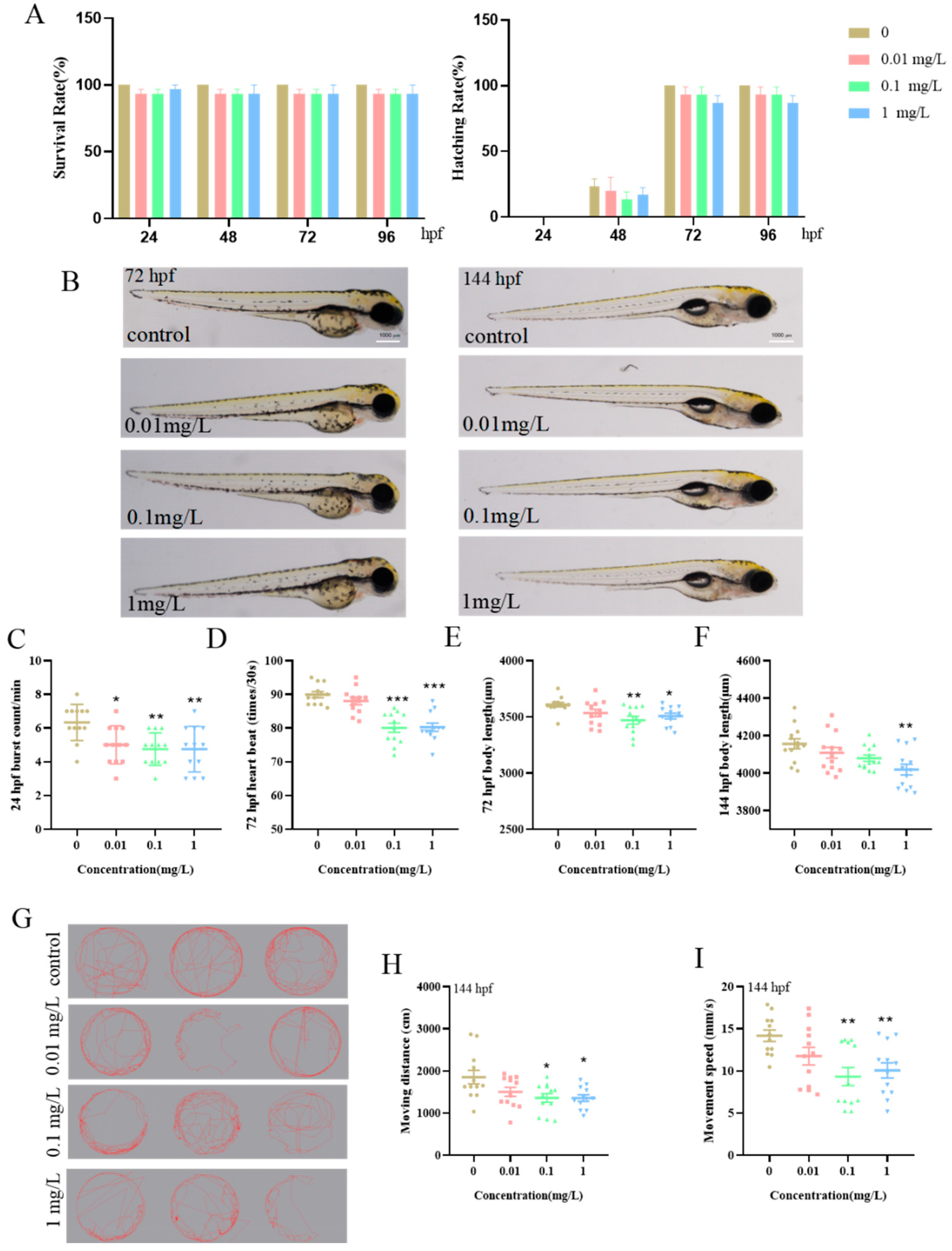
3.1. Impact of BPE Exposure on Zebrafish Larvae’s Early Development and Motor Behavior
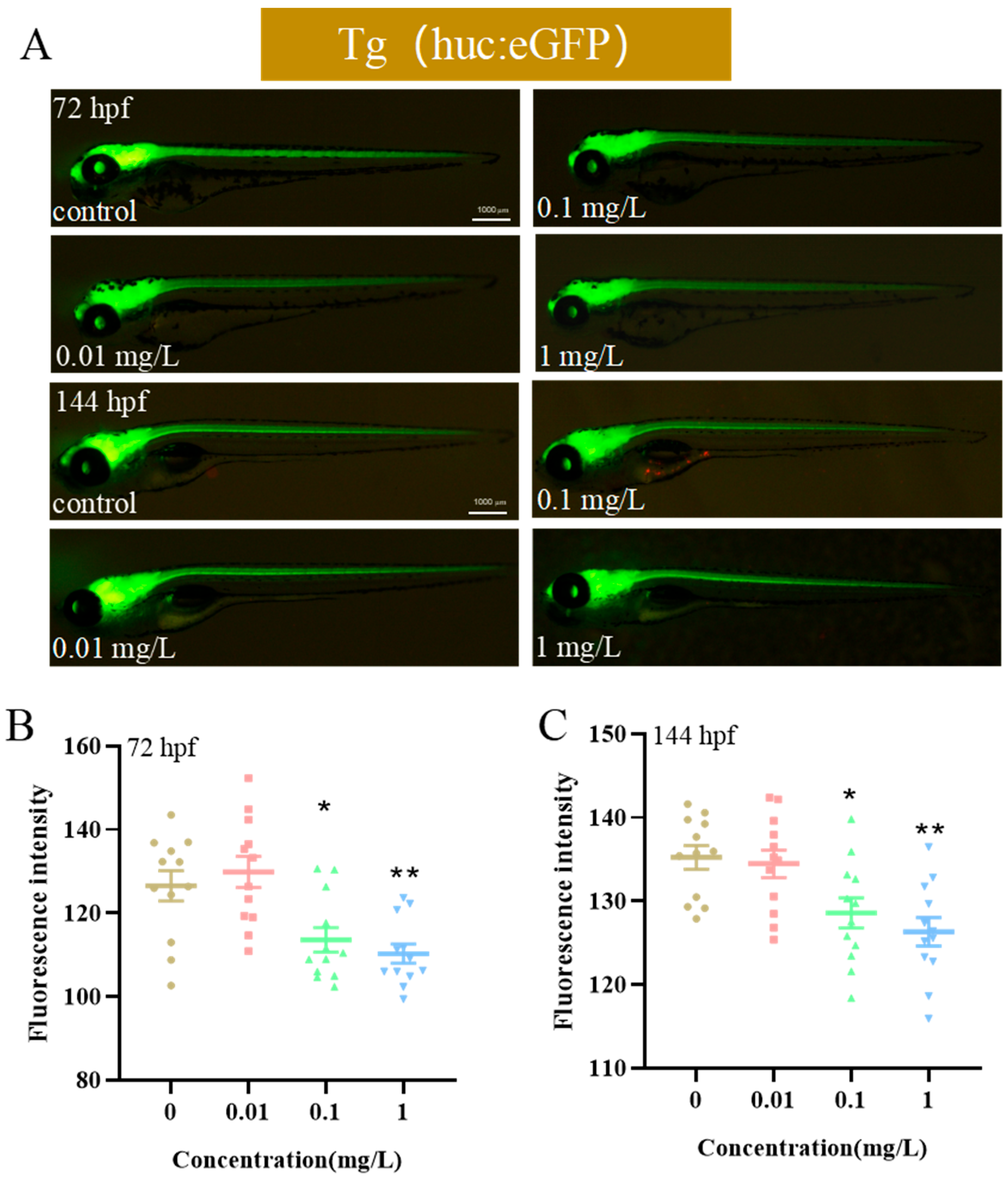
3.2. Effects of Exposure to BPE on Neurodevelopment of Zebrafish Larvae
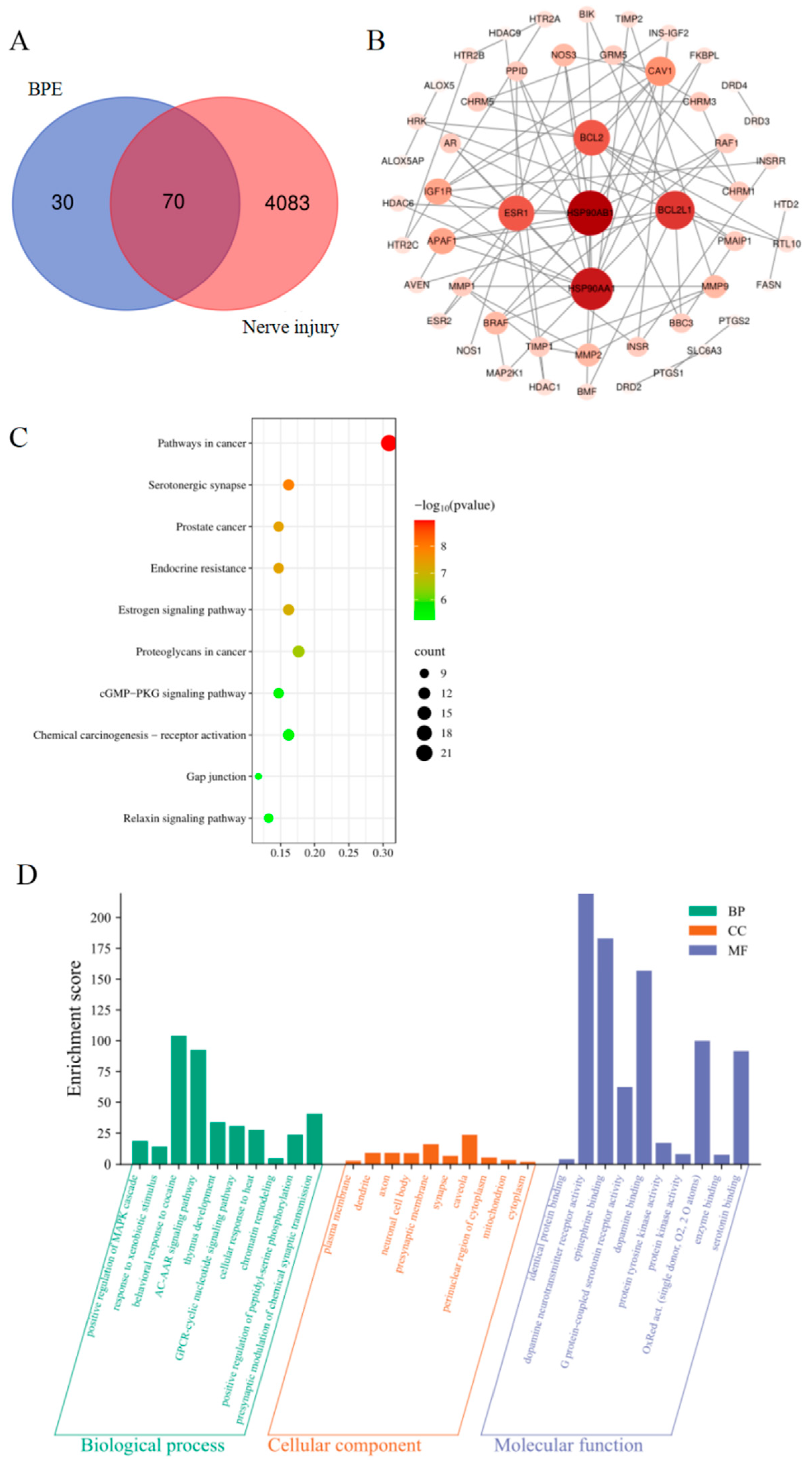
3.3. Potential Targets for BPE-Induced Neurotoxicity
3.4. Major Interaction Networks and Core Genes of Potential Targets
3.5. Functional Analysis of Targets and Pathway Enrichment Analysis
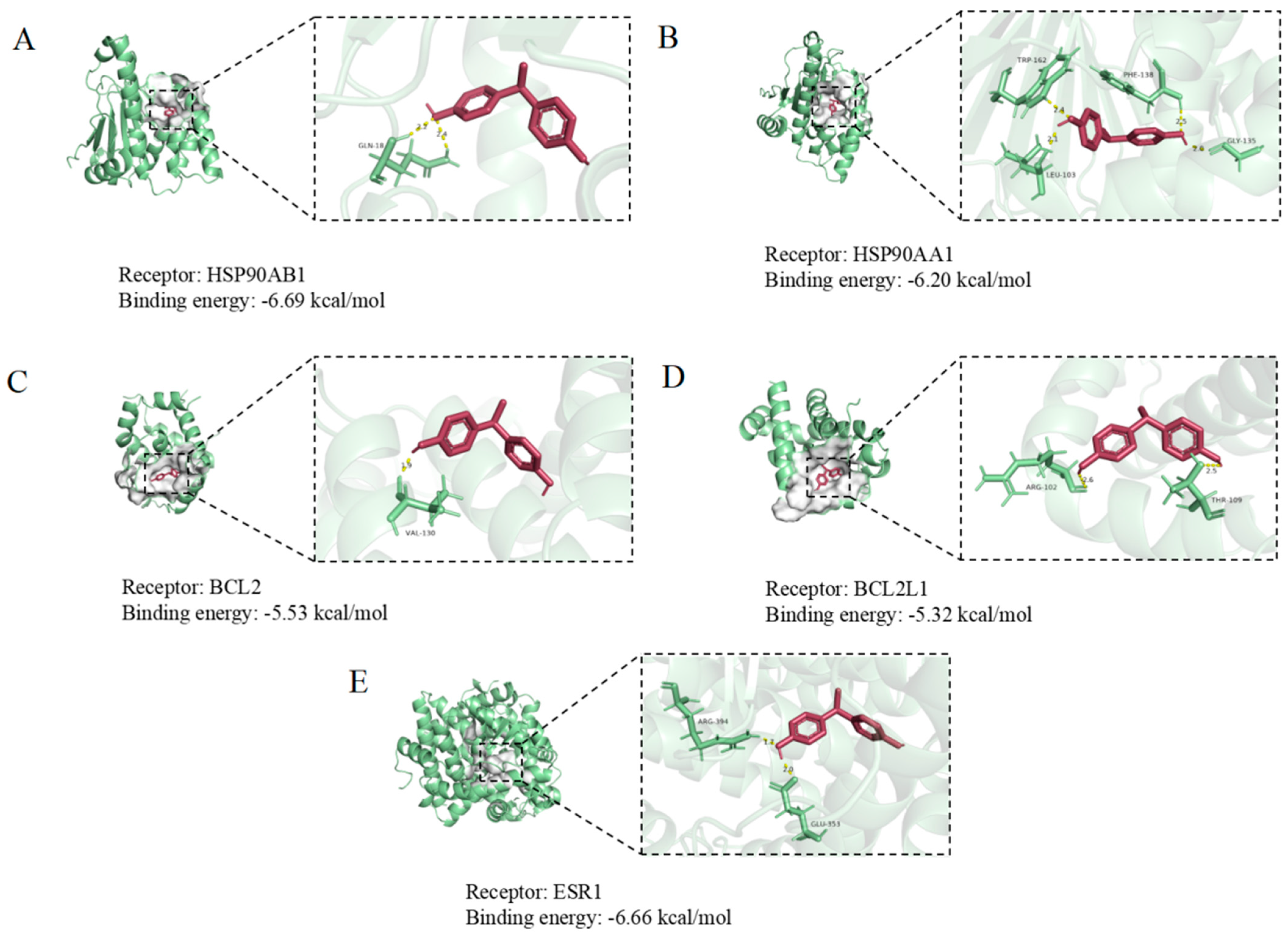
3.6. Molecular Docking of BPE with Core Target Proteins in Neural Damage
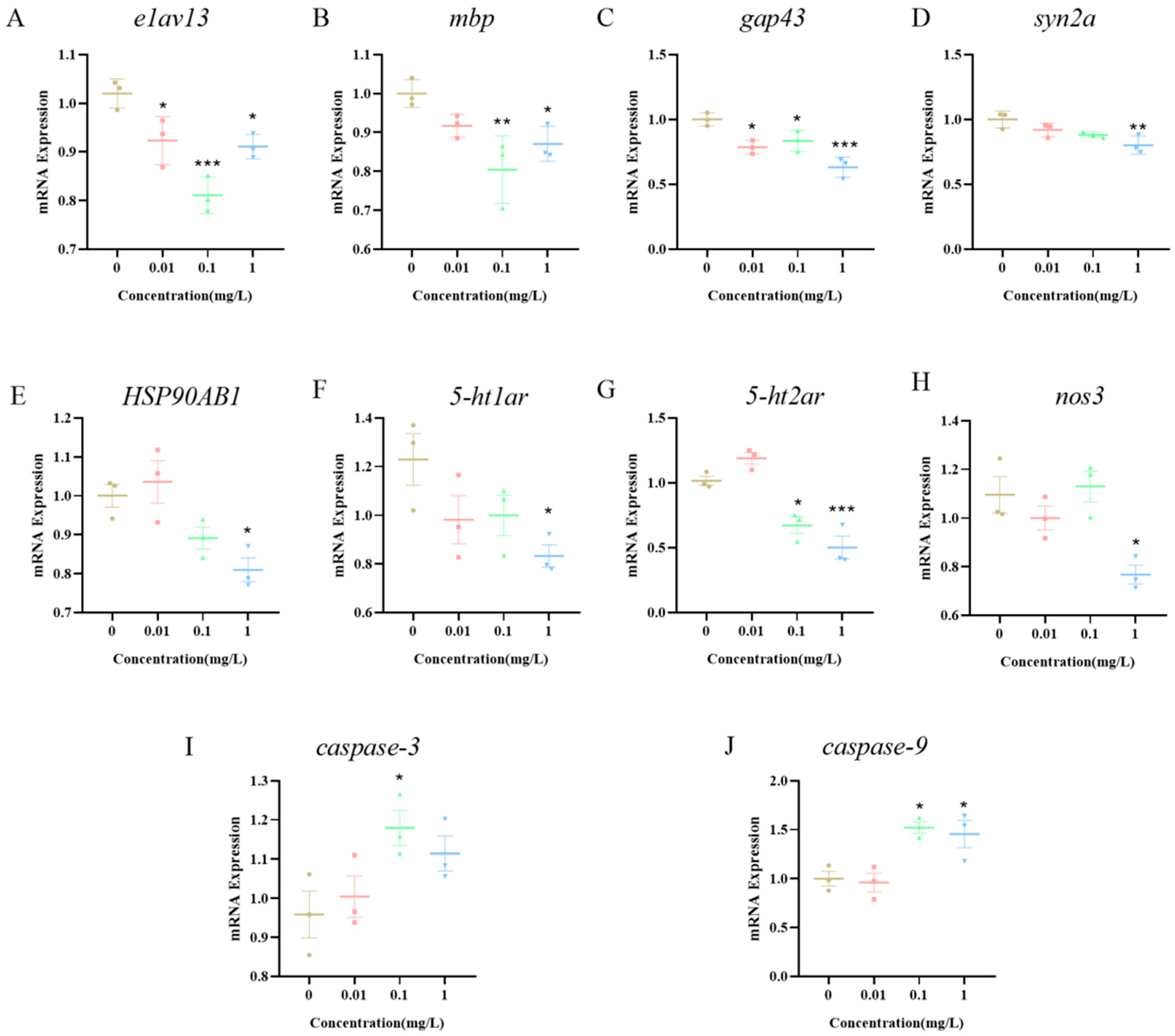
3.7. Expression of Neurotoxicity-Related Pathway Genes in Zebrafish Larvae Induced by BPE Exposure
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, D.; Kannan, K.; Tan, H.; Zheng, Z.; Feng, Y.L.; Wu, Y.; Widelka, M. Bisphenol Analogues Other Than BPA: Environmental Occurrence, Human Exposure, and Toxicity—A Review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 5438–5453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, B.; Wu, N.; Pan, X.; Wang, Z.; Yan, C.; Sharma, V.K.; Qu, R. Ferrate(VI) oxidation of bisphenol E-Kinetics, removal performance, and dihydroxylation mechanism. Water Res. 2022, 210, 118025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, M. Occurrence and exposure assessment of bisphenol analogues in source water and drinking water in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 655, 607–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, S.; Song, M.; Zeng, L.; Wang, T.; Liu, R.; Ruan, T.; Jiang, G. Occurrence and profiles of bisphenol analogues in municipal sewage sludge in China. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 186, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coha, M.; Dal Bello, F.; Fabbri, D.; Calza, P.; Medana, C. Structural elucidation of bisphenol E and bisphenol S photoinduced by-products by high-resolution electrospray ionisation mass spectrometry and tandem mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2021, 35, e9039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesen, M.; Lenarcic, K.; Mislej, V.; Levstek, M.; Kovacic, A.; Cimrmancic, B.; Uranjek, N.; Kosjek, T.; Heath, D.; Dolenc, M.S.; et al. The occurrence and source identification of bisphenol compounds in wastewaters. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 616–617, 744–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucarini, F.; Gasco, R.; Staedler, D. Simultaneous Quantification of 16 Bisphenol Analogues in Food Matrices. Toxics 2023, 11, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, Y.P.; Ma, Q.G.; Hayat, W.; Liu, Z.H.; Dang, Z. Ten bisphenol analogues in Chinese fresh dairy milk: High contribution ratios of conjugated form, importance of enzyme hydrolysis and risk evaluation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30, 88049–88059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Zhao, R.; Tian, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, X.W.; Ma, J.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Geng, S.; Liu, M. Simple high-performance liquid chromatography-ultraviolet method for simultaneous separation and detection of 14 bisphenol pollutants in building materials. J. Sep. Sci. 2023, 46, e2300006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Gao, C.; Fan, Y.J.; Zhuang, T.; Li, Y.; Li, C.A.; Lv, J.; Hu, Z.W.; Tao, L.; Gibson, R.; et al. Perinatal Bisphenol Exposure and Small-for-Gestational-Age Neonates: The Evolving Effect of Replacements Then and Now. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2025, 59, 5983–5993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Li, A.; Zhang, W.; Pang, S.; Liang, Y.; Song, M. Assessing the toxicity of bisphenol A and its six alternatives on zebrafish embryo/larvae. Aquat. Toxicol. 2022, 246, 106154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wu, C.; Zhang, X.; Song, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhang, K.; Sun, M. Developmental neurotoxic effects of bisphenol A and its derivatives in Drosophila melanogaster. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 260, 115098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.; Yin, N.; Liang, S.; Yang, R.; Liu, S.; Lu, Y.; Jiang, L.; Zhou, Q.; Jiang, G.; Faiola, F. Bisphenol A and several derivatives exert neural toxicity in human neuron-like cells by decreasing neurite length. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 135, 111015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, M.; Deng, J.; Gu, J.; Yang, J.; Ge, F.; Huang, C.; Wu, W. TMBPF-induced neurotoxicity and oxidative stress in zebrafish larvae: Impacts on central nervous system development and dopamine neurons. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 268, 115710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Ren, Y. Investigating the neurotoxicity of environmental pollutants using zebrafish as a model organism: A review and recommendations for future work. Neurotoxicology 2023, 94, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S. Analysis of environmental pollutant Bisphenol F elicited prostate injury targets and underlying mechanisms through network toxicology, molecular docking, and multi-level bioinformatics data integration. Toxicology 2024, 506, 153847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.; Li, M.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, X.; Gao, W.; Zhang, S.; Liu, J. Exploring the mechanism of PPCPs on human metabolic diseases based on network toxicology and molecular docking. Environ. Int. 2025, 196, 109324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Jin, H.; Hu, J.; Wang, J.; Yin, D. Mechanistic Insights into 3-Isopropylphenol-Induced Neurotoxicity in Zebrafish: A Network Toxicology and Molecular Docking Approach. Toxics 2025, 13, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Zhu, X.; Xu, K.; Li, Y.; Zhou, J. Network toxicological and molecular docking to investigate the mechanisms of toxicity of agricultural chemical Thiabendazole. Chemosphere 2024, 363, 142711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swisstargetprediction. Available online: http://www.swisstargetprediction.ch/ (accessed on 20 April 2025).
- GeneCards®: The Human Gene Database. Available online: http://www.genecards.org/ (accessed on 21 April 2025).
- Calculate and Draw Custom Venn Diagrams. Available online: http://bioinformatics.psb.ugent.be/webtools/Venn/ (accessed on 24 April 2025).
- STRING. Available online: https://string-db.org/ (accessed on 5 May 2025).
- DAVID. Available online: https://david.ncifcrf.gov/ (accessed on 7 May 2024).
- RCSB Protein Data Bank (RCSB PDB). Available online: https://www.rcsb.org (accessed on 7 May 2025).
- Wallwork, S.B.; Bellan, V.; Catley, M.J.; Moseley, G.L. Neural representations and the cortical body matrix: Implications for sports medicine and future directions. Br. J. Sports Med. 2016, 50, 990–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bambino, K.; Chu, J. Zebrafish in Toxicology and Environmental Health. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 2017, 124, 331–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Lee, J.S.; Kho, Y.; Ji, K. Effects of methylisothiazolinone and octylisothiazolinone on development and thyroid endocrine system in zebrafish larvae. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 425, 127994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Zheng, S.; Shi, X.; Luo, C.; Huang, W.; Lin, H.; Peng, J.; Tan, W.; Wu, K. Neurodevelopmental toxicity of organophosphate flame retardant triphenyl phosphate (TPhP) on zebrafish (Danio rerio) at different life stages. Environ. Int. 2023, 172, 107745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsushima, A.; Ryan, K.; Shimohigashi, Y.; Meinertzhagen, I.A. An endocrine disruptor, bisphenol A, affects development in the protochordate Ciona intestinalis: Hatching rates and swimming behavior alter in a dose-dependent manner. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 173, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, O.; Green, J.M.; Tyler, C.R. Transgenic fish systems and their application in ecotoxicology. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2015, 45, 124–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, D.; Hankin, M.; Li, Z.; Dai, X.; Ding, J. Transgenic zebrafish for studying nervous system development and regeneration. Transgenic. Res. 2001, 10, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millet, V.; Marder, M.; Pasquini, L.A. Adult CNP::EGFP transgenic mouse shows pronounced hypomyelination and an increased vulnerability to cuprizone-induced demyelination. Exp. Neurol. 2012, 233, 490–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Liu, C.; Wang, J.; Zou, L.; Yang, F.; Chi, X.; Zhu, J. Nano-TiO2 aggravates bioaccumulation and developmental neurotoxicity of difenoconazole in zebrafish larvae via oxidative stress and apoptosis: Protective role of vitamin C. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 251, 114554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, J.; Guo, L.; Zhu, Y.; Qian, L.; Shi, L.; Zhang, H.; Ji, G. Neurodevelopmental Toxicity of Emamectin Benzoate to the Early Life Stage of Zebrafish Larvae (Danio rerio). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.C.; Kim, C.H.; Bae, Y.K.; Yeo, S.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Hong, S.K.; Shin, J.; Yoo, K.W.; Hibi, M.; Hirano, T.; et al. Analysis of upstream elements in the HuC promoter leads to the establishment of transgenic zebrafish with fluorescent neurons. Dev. Biol. 2000, 227, 279–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Guo, M.; Yin, X.; Huang, C.; Qian, L.; Zhou, L.; Wang, Z.; Wang, L.; Shi, L.; Ji, G. A systematic comparison of neurotoxicity of bisphenol A and its derivatives in zebrafish. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 805, 150210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogawa, Y.; Kakumoto, K.; Yoshida, T.; Kuwako, K.I.; Miyazaki, T.; Yamaguchi, J.; Konno, A.; Hata, J.; Uchiyama, Y.; Hirai, H.; et al. Elavl3 is essential for the maintenance of Purkinje neuron axons. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pullaguri, N.; Grover, P.; Abhishek, S.; Rajakumara, E.; Bhargava, Y.; Bhargava, A. Triclosan affects motor function in zebrafish larva by inhibiting ache and syn2a genes. Chemosphere 2021, 266, 128930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benowitz, L.I.; Routtenberg, A. GAP-43: An intrinsic determinant of neuronal development and plasticity. Trends Neurosci. 1997, 20, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanba, R.; Fujita, N.; Nagata, S. Structure and expression of myelin basic protein gene products in Xenopus laevis. Gene 2010, 459, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenberg, L.N. Non-monotonic dose responses in studies of endocrine disrupting chemicals: Bisphenol a as a case study. Dose-Response 2014, 12, 259–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeLong, K.; Sheu, S.H. Serotonin signaling at cilia synapses. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2025, 92, 102994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyotani, Y.; Zhao, J.; Nakahira, K.; Yoshizumi, M. The role of antipsychotics and other drugs on the development and progression of neuroleptic malignant syndrome. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 18459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eghan, K.; Lee, S.; Kim, W.K. Cardiotoxicity and neurobehavioral effects induced by acrylamide in Daphnia magna. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 242, 113923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoval, A.; Duran, P.; Gandini, M.A.; Andrade, A.; Almanza, A.; Kaja, S.; Felix, R. Regulation of L-type CaV1.3 channel activity and insulin secretion by the cGMP-PKG signaling pathway. Cell Calcium 2017, 66, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, H.; Werner, M.; Heppenstall, P.A.; Henning, M.; More, M.I.; Kuhbandner, S.; Lewin, G.R.; Hofmann, F.; Feil, R.; Rathjen, F.G. cGMP-mediated signaling via cGKIalpha is required for the guidance and connectivity of sensory axons. J. Cell Biol. 2002, 159, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Sang, C.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, S.; Gao, H. Effects of bisphenol A and bisphenol analogs on the nervous system. Chin. Med. J. 2023, 136, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertotto, L.B.; Richards, J.; Gan, J.; Volz, D.C.; Schlenk, D. Effects of bifenthrin exposure on the estrogenic and dopaminergic pathways in zebrafish embryos and juveniles. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2018, 37, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Hernandez, O.T.; Martinez-Mota, L.; Herrera-Perez, J.J.; Jimenez-Rubio, G. Role of Estradiol in the Expression of Genes Involved in Serotonin Neurotransmission: Implications for Female Depression. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2019, 17, 459–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardozo Pinto, D.F.; Pomrenze, M.B.; Guo, M.Y.; Touponse, G.C.; Chen, A.P.F.; Bentzley, B.S.; Eshel, N.; Malenka, R.C. Opponent control of reinforcement by striatal dopamine and serotonin. Nature 2025, 639, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haase, M.; Fitze, G. HSP90AB1: Helping the good and the bad. Gene 2016, 575, 171–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Li, Y.; Jiang, W.; Li, Y.; Zhou, L.; Song, B.; Liu, X. Inhibition of HSP90 Promotes Neural Stem Cell Survival from Oxidative Stress through Attenuating NF-kappaB/p65 Activation. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 3507290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, D.; Xu, Z.; Zhong, W.; Peng, S. Parallelization of Molecular Docking: A Review. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2018, 18, 1015–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.J.; Yue, Y.X.; Shi, S.J.; Xue, J.Z. Investigation on toxicity mechanism of halogenated aromatic disinfection by-products to zebrafish based on molecular docking and QSAR model. Chemosphere 2023, 341, 139916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, J.; Peng, J.; Wu, M.; Zhan, X.; Wang, D.; Zhu, G.; Wang, W.; An, N.; Pan, X. Analyzing the potential targets and mechanisms of chronic kidney disease induced by common synthetic Endocrine Disrupting Compounds (EDCs) in Chinese surface water environment using network toxicology and molecular docking techniques. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 958, 177980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, D.; Yuan, Q.; Yang, Z.; Deng, C. Assessing male reproductive toxicity of environmental pollutant di-ethylhexyl phthalate with network toxicology and molecular docking strategy. Reprod. Toxicol. 2024, 130, 108749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Lin, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, B.; Chen, L. Insight into the molecular recognition of human and polar bear pregnane X receptor by three organic pollutants using molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulations. Environ. Int. 2024, 190, 108926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerges, N.Z.; Tran, I.C.; Backos, D.S.; Harrell, J.M.; Chinkers, M.; Pratt, W.B.; Esteban, J.A. Independent functions of hsp90 in neurotransmitter release and in the continuous synaptic cycling of AMPA receptors. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 4758–4766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straub, V.A.; Grant, J.; O’Shea, M.; Benjamin, P.R. Modulation of serotonergic neurotransmission by nitric oxide. J. Neurophysiol. 2007, 97, 1088–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saura, M.; Marquez, S.; Reventun, P.; Olea-Herrero, N.; Arenas, M.I.; Moreno-Gomez-Toledano, R.; Gomez-Parrizas, M.; Munoz-Moreno, C.; Gonzalez-Santander, M.; Zaragoza, C.; et al. Oral administration of bisphenol A induces high blood pressure through angiotensin II/CaMKII-dependent uncoupling of eNOS. FASEB J. 2014, 28, 4719–4728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, H.; Mercer, G.V.; Stapleton, D.; Dawson, L.; MacCallum, P.E.; Spring, S.; Sled, J.G.; Blundell, J.; Cahill, L.S. Structural brain abnormalities in endothelial nitric oxide synthase-deficient mice revealed by high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging. Brain Behav. 2022, 12, e2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuida, K. Caspase-9. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2000, 32, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhat, A.A.; Thapa, R.; Afzal, O.; Agrawal, N.; Almalki, W.H.; Kazmi, I.; Alzarea, S.I.; Altamimi, A.S.A.; Prasher, P.; Singh, S.K.; et al. The pyroptotic role of Caspase-3/GSDME signalling pathway among various cancer: A Review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 242, 124832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inserte, J.; Garcia-Dorado, D. The cGMP/PKG pathway as a common mediator of cardioprotection: Translatability and mechanism. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 1996–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gu, K.; Yang, L.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chen, J. Bisphenol E Neurotoxicity in Zebrafish Larvae: Effects and Underlying Mechanisms. Biology 2025, 14, 992. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14080992
Gu K, Yang L, Jiang Y, Wang Z, Chen J. Bisphenol E Neurotoxicity in Zebrafish Larvae: Effects and Underlying Mechanisms. Biology. 2025; 14(8):992. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14080992
Chicago/Turabian StyleGu, Kaicheng, Lindong Yang, Yi Jiang, Zhiqiang Wang, and Jiannan Chen. 2025. "Bisphenol E Neurotoxicity in Zebrafish Larvae: Effects and Underlying Mechanisms" Biology 14, no. 8: 992. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14080992
APA StyleGu, K., Yang, L., Jiang, Y., Wang, Z., & Chen, J. (2025). Bisphenol E Neurotoxicity in Zebrafish Larvae: Effects and Underlying Mechanisms. Biology, 14(8), 992. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14080992






