Prediction Analysis of Integrative Quality Zones for Corydalis yanhusuo W. T. Wang Under Climate Change: A Rare Medicinal Plant Endemic to China
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
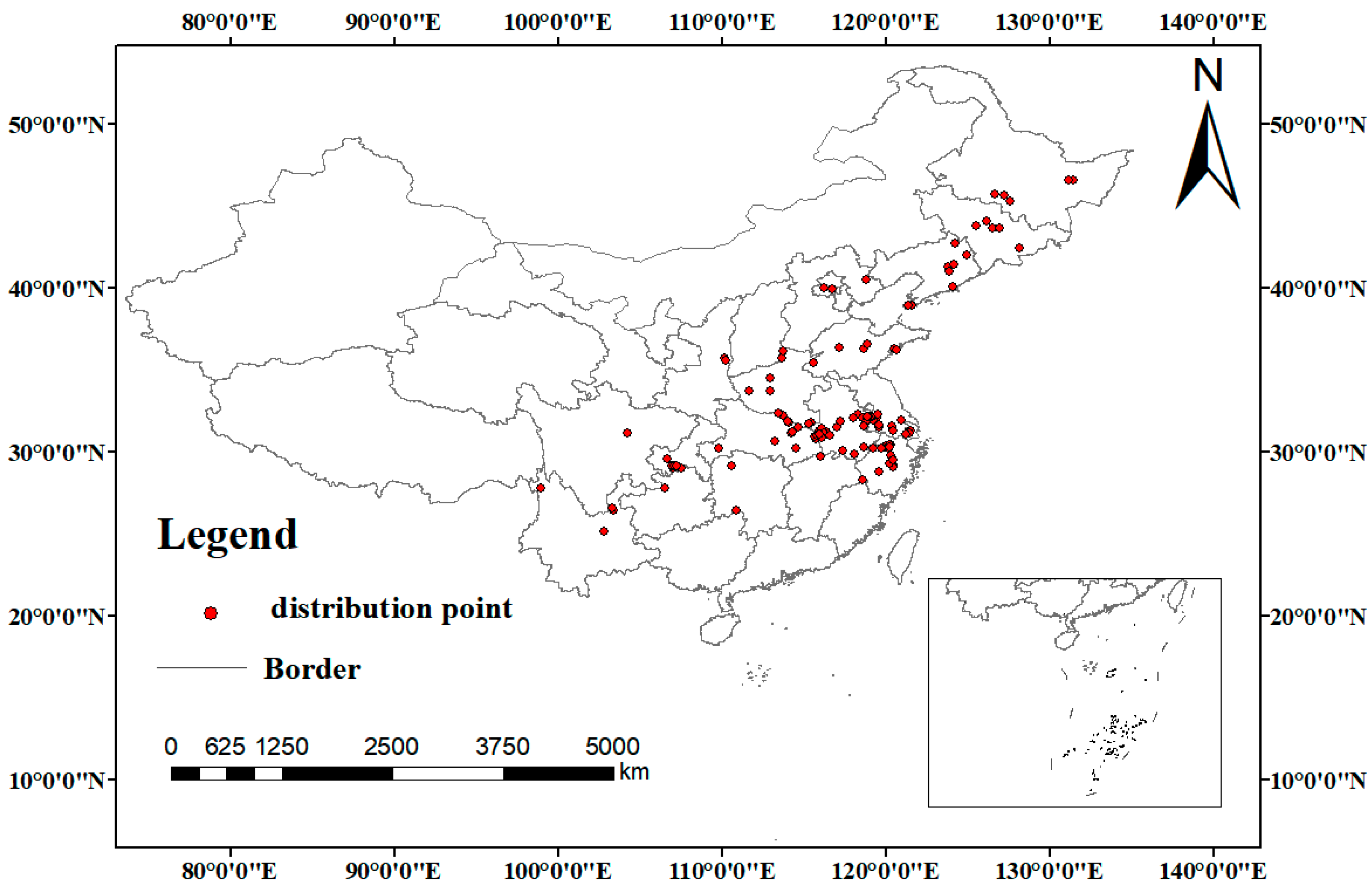
2.1. Species Data Acquisition and Processing
2.2. Environmental Variables Acquisition and Processing
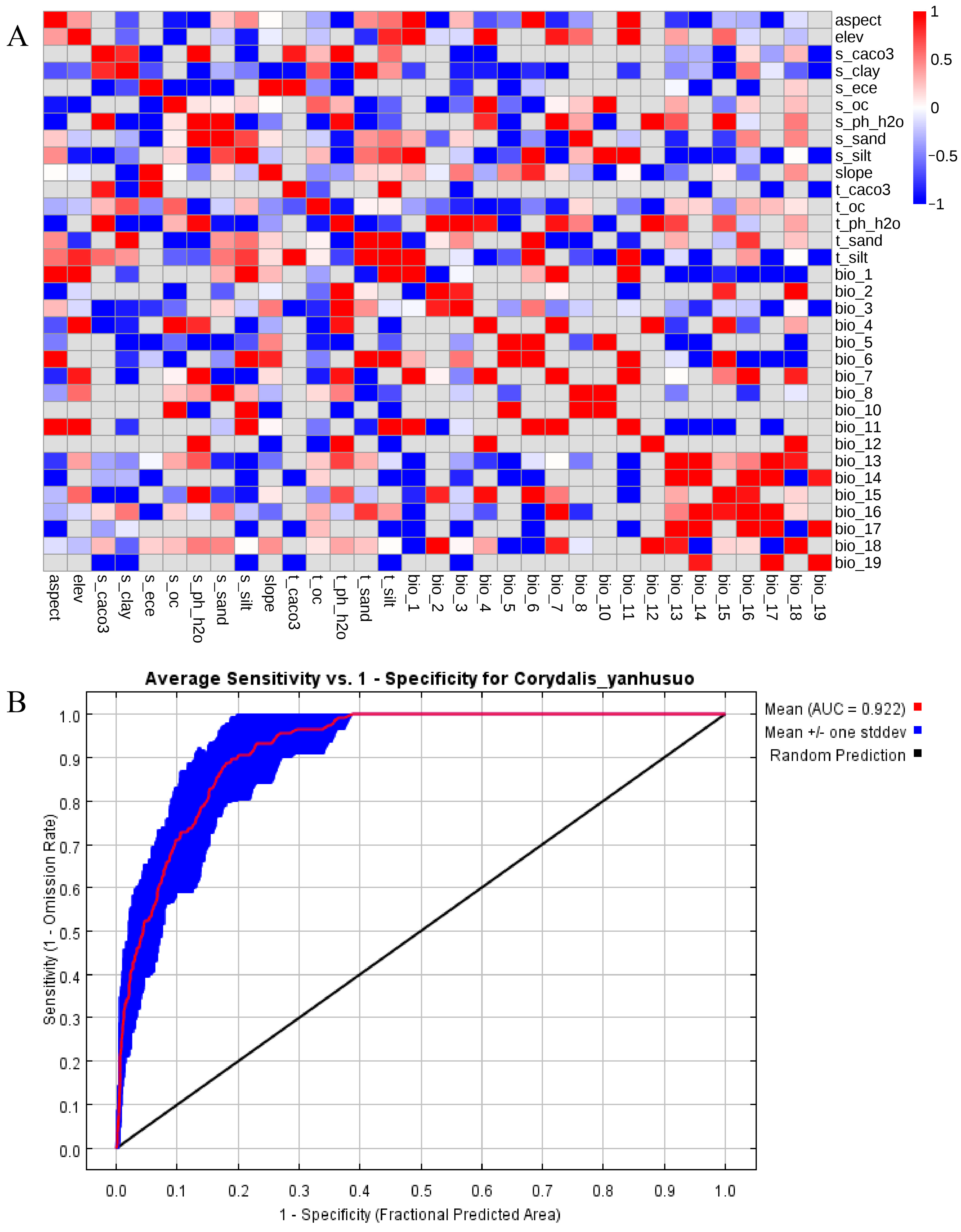
2.3. Predictive Modeling Implementation
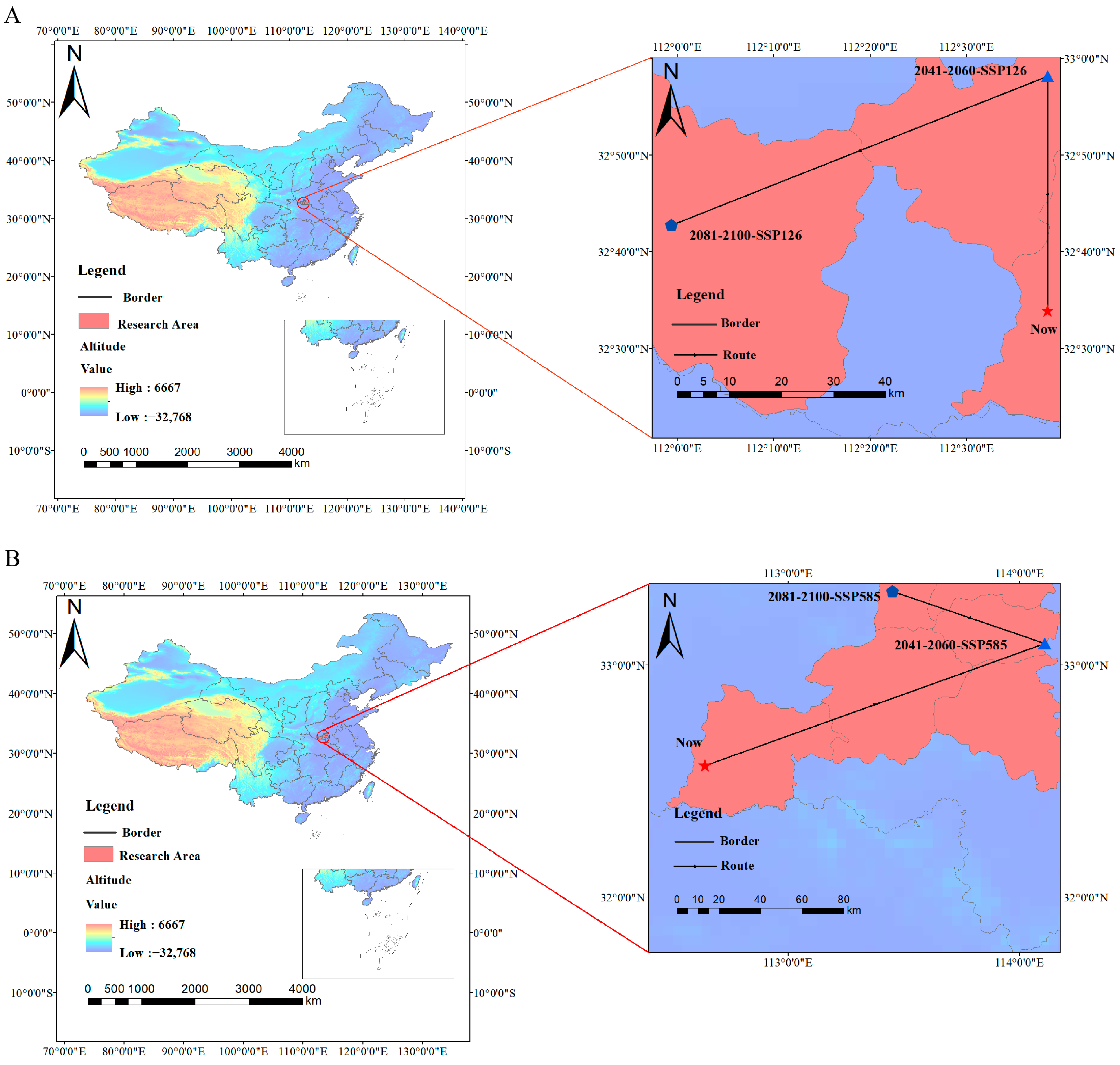
2.4. Centroid Migration
2.5. Integrative Quality Zonation
3. Results
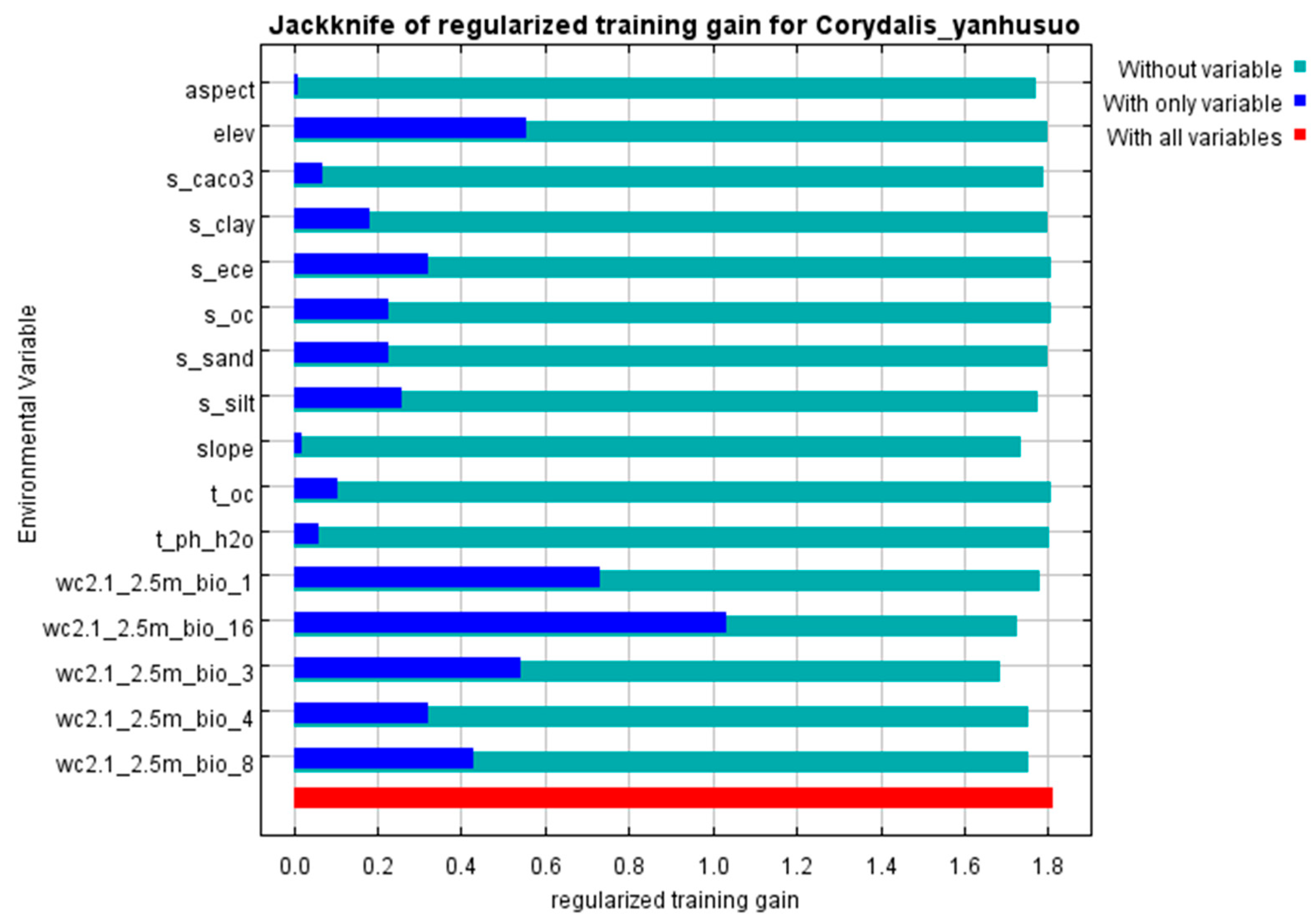
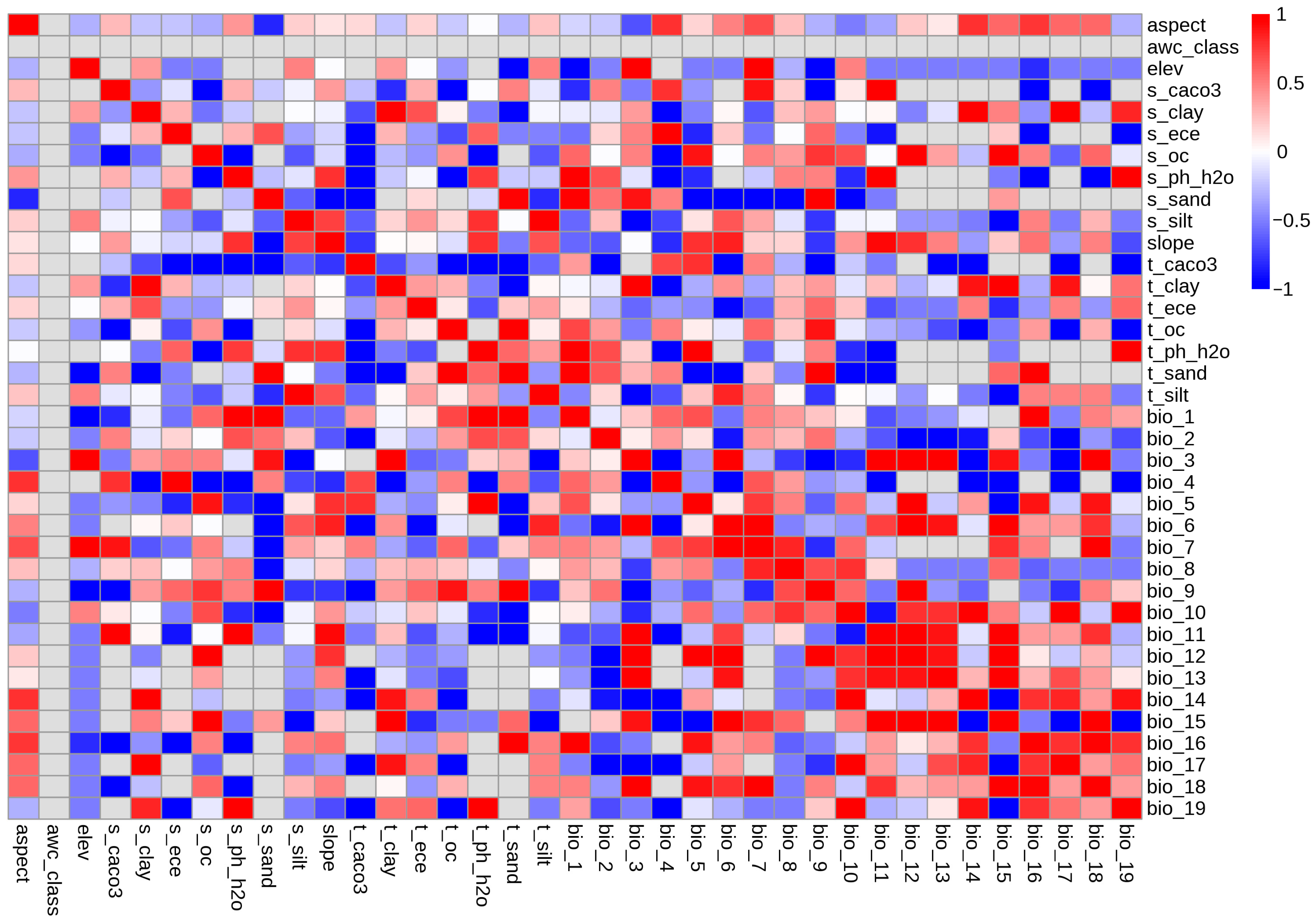
3.1. Model Construction and Screening of Dominant Environmental Variables
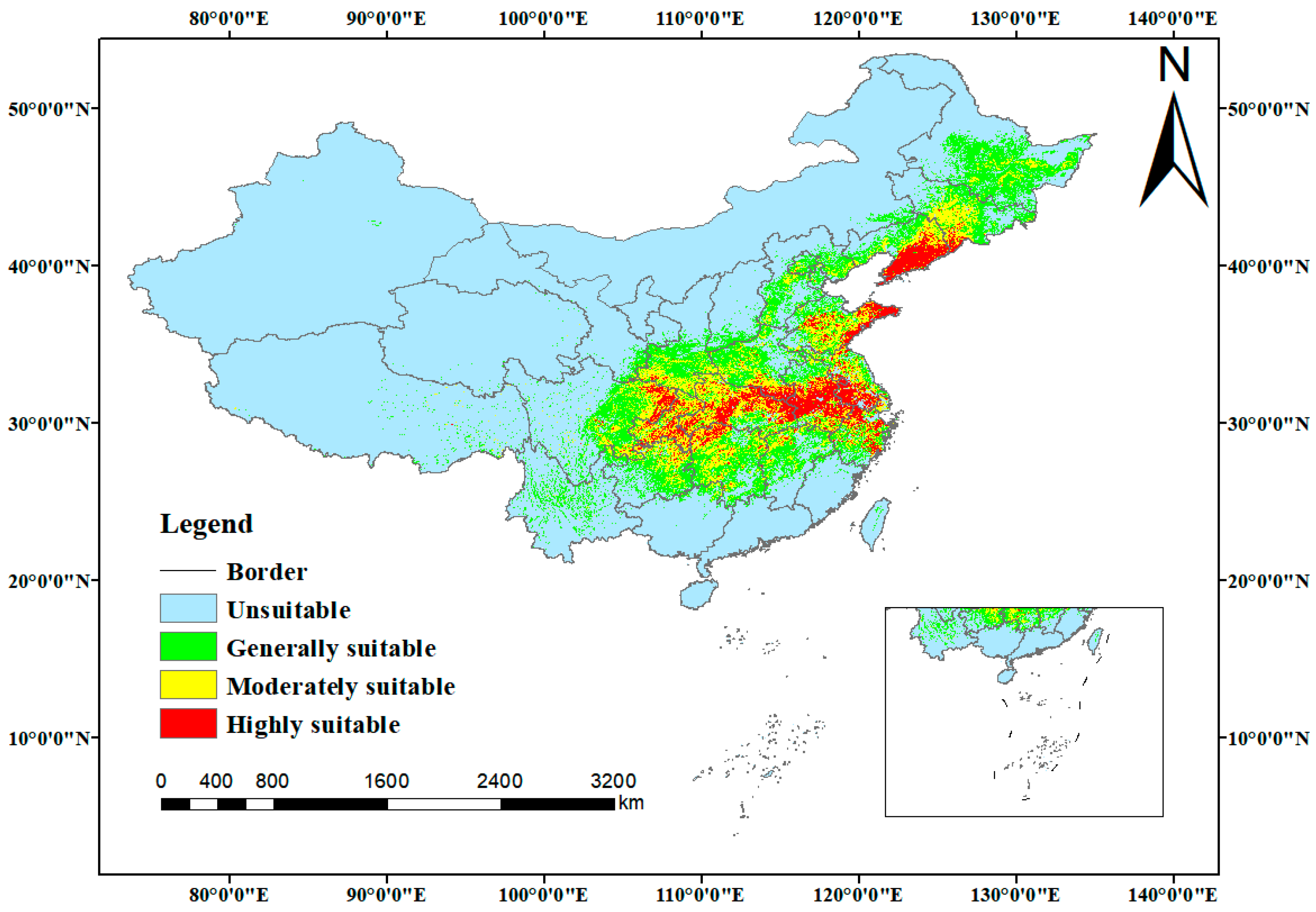
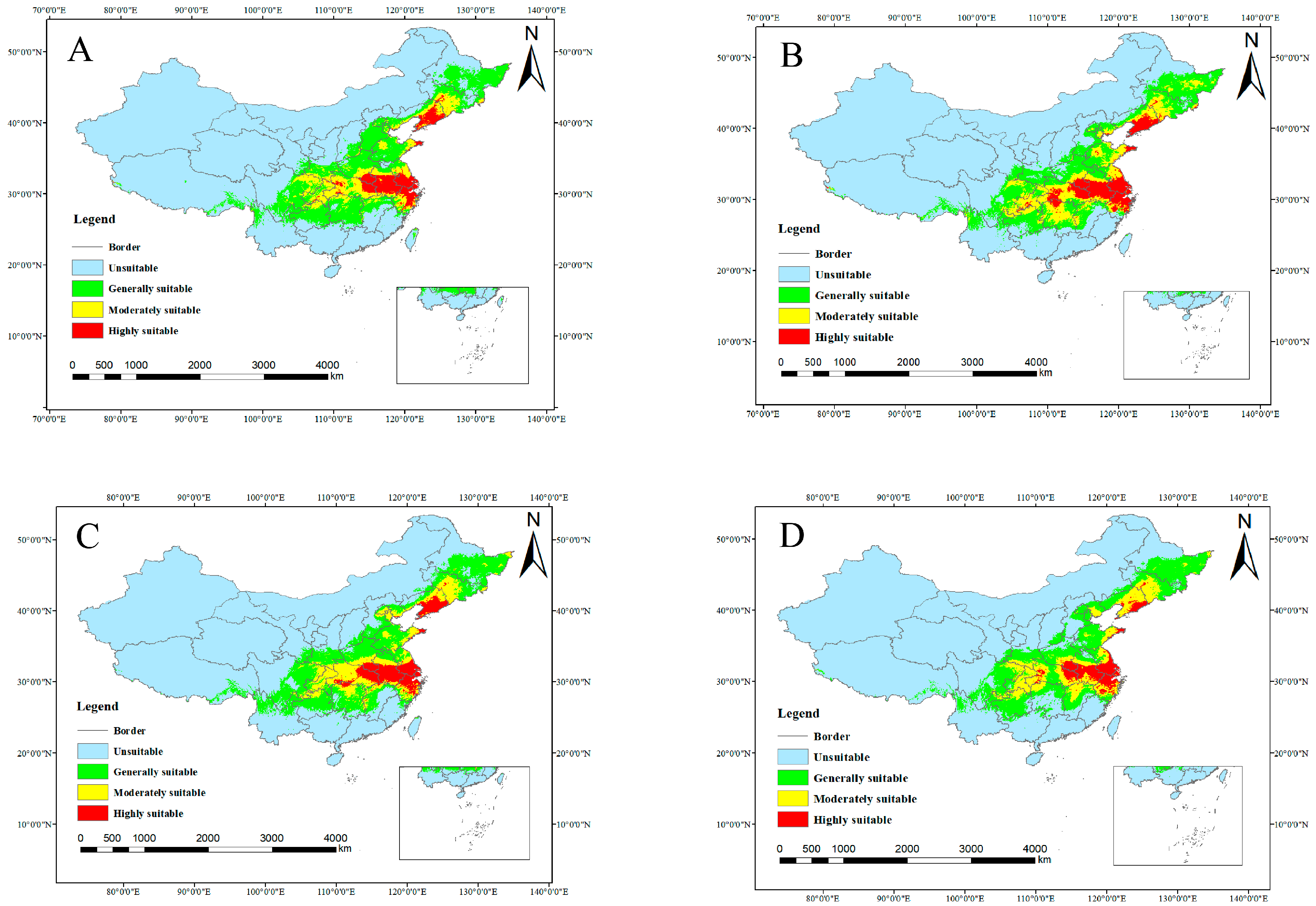
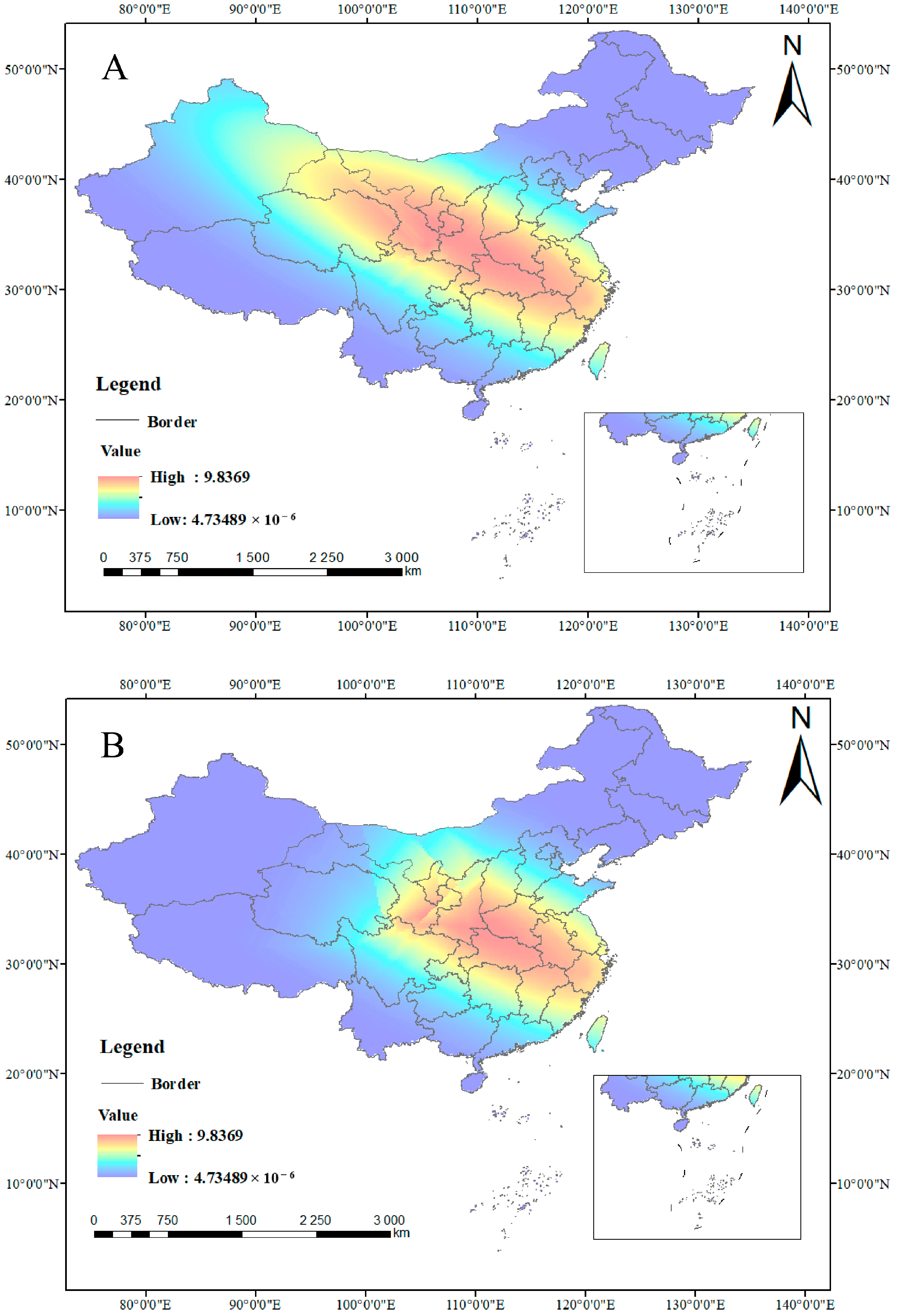
3.2. Spatiotemporal Distribution and Changes in Suitable Habitats of C. yanhusuo
3.3. Evaluation of Key Environmental Variables Influencing THP Accumulation and Construction of Integrative Quality Zonation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, D.; Yang, C.G.; Xiao, C.H.; Wu, Z.; Ren, S.; Yang, Y. First report of Botrytis cinerea causing grey mold on Corydalis yanhusuo in Panan, China. Plant Dis. 2024, 108, 2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Guan, H.; Wang, X.; He, Y.; Sun, H.; Tan, W.; Luo, X.; Su, M.; Shi, Y. Fingerprint-efficacy study of the quaternary alkaloids in Corydalis yanhusuo. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 207, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, H.; Yang, X.; Wang, Z.; Li, G.; Li, L.; Huo, S.; Zhang, B.; He, R.; Chen, K.; Xu, B.; et al. Tetrahydropalmatine triggers angiogenesis via regulation of arginine biosynthesis. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 163, 105242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Lu, X.; Lu, C.; Wang, C.; Xu, H.; Xu, X.; Gou, H.; Zhu, B.; Du, W. 13-Methyl-palmatrubine induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in A549 cells in vitro and in vivo. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 36, 2526–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, S.Q.; Liu, S.M.; Chen, Z.L.; Guo, K.; Yang, X.X.; Zhang, L.H.; Yan, Y.F.; Zhang, T.T.; Zhao, P. Extraction, Structural Analysis, and Bioactivity of a Novel Polysaccharide from Corydalis yanhusuo Residues. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2025, 105, e70115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Cao, J.; Li, R.; Yu, J.; Peng, Y.; Huang, Q.; Zuo, W.; Chen, J. Tetrahydropalmatine ameliorates peripheral nerve regeneration by enhancing macrophage anti-inflammatory response. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2025, 147, 114000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Deng, J.; Liang, J.; Li, S.; Yang, D.; Yan, B. Corydalis yanhusuo Polysaccharides regulates HPA-axis mediated microglia activation and inhibits astrocyte A1 transformation to improve depression-like behavior. Brain Res. 2025, 1864, 149780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Pan, Y.; Tan, J.; Lv, H.; Wang, Y.; Chen, D.X. Metabolomics and transcriptomics reveal the mechanism of alkaloid synthesis in Corydalis yanhusuo bulbs. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0304258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Luo, Y.; Chen, K.; Shen, S.; Duan, Z.; Nuerlan, K.; Hu, Y.; Tong, Y. Functional characterization of oxidosqualene cyclases and CYP716As associated with triterpene biosynthesis from Corydalis yanhusuo. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 318, 145332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Lin, H.; Tang, Y.; Huang, L.; Xu, J.; Nian, S.; Zhao, Y. Integration of full-length transcriptomics and targeted metabolomics to identify benzylisoquinoline alkaloid biosynthetic genes in Corydalis yanhusuo. Hortic. Res. 2021, 8, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Pan, Y.; Jiang, H.; Chen, Y.; Hu, L.; Zhang, H.; Yan, J. A comprehensive quality evaluation method of Corydalis yanhusuo by HPLC fingerprints, chemometrics, and correlation analysis. J. Sep. Sci. 2021, 44, 2054–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.H.; Wu, D.L.; Gao, L.Y.; Fang, Y.; Ge, W.H. L-Tetrahydropalmatine alleviates mechanical hyperalgesia in models of chronic inflammatory and neuropathic pain in mice. Neuroreport 2016, 27, 476–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.Y.; Wang, T.X.; Zhou, J.C.; Qu, W.M.; Huang, Z.L. Dopamine D(1) and D(2) receptors mediate analgesic and hypnotic effects of l-tetrahydropalmatine in a mouse neuropathic pain model. Psychopharmacology 2019, 236, 3169–3182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, H.; Lu, D.; Chen, H.; Zhu, Y.; Xie, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, Z. Tetrahydropalmatine induces the polarization of M1 macrophages to M2 to relieve limb ischemia-reperfusion-induced lung injury via inhibiting the TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3 signaling pathway. Drug Dev. Res. 2022, 83, 1362–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.H.; Yu, G.D.; Wang, Z.T. Resource investigation and quality evaluation on wild Corydalis yanhusuo. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2004, 29, 399–401. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Zhou, X.; Yan, M.; Wang, Z.; Zhong, X.; Li, X.; Zhu, J.; Kong, Y.; Zhu, W.; Geng, R.; et al. Metabolomic and evolutionary integration unveils medicinal potential in six Corydalis species. Mol. Hortic. 2025, 5, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Li, Y.; He, B. Efficient Cultivation Techniques of Corydalis yanhusuo and Strategies to Enhance Alkaloid Content. Med. Plant Res. 2024, 14, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins-Taylor, I.E.; Frey, J.K. Predicting the distribution of a rare chipmunk (Neotamias quadrivittatus oscuraensis): Comparing MaxEnt and occupancy models. J. Mammal. 2020, 101, 1035–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, P.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, X.; Chen, H.; Si, Q.; Wu, J. Potential geographical distribution and environmental explanations of rare and endangered plant species through combined modeling: A case study of Northwest Yunnan, China. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 11, 13052–13067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Li, A.; Luo, X.; Wang, J.; Xie, Y.; Lin, Z.; Hua, D. Climate change impacts on the predicted geographic distribution of Betula tianschanica Rupr. Front. Plant Sci. 2025, 16, 1528255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiang, X.; Lei, Y.; Wu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Shi, X. Potentially suitable distribution areas of Populus euphratica and Tamarix chinensis by MaxEnt and random forest model in the lower reaches of the Heihe River, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, J.; Zhao, Q.; Yan, P.; Sun, M.; Sun, H.; Liang, H.; Zhang, D.; Qian, Z.; Cui, L. Environmental factors influencing potential distribution of Schisandra sphenanthera and its accumulation of medicinal components. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1302417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Fan, G.; He, Y. Predicting the current and future distribution of three Coptis herbs in China under climate change conditions, using the MaxEnt model and chemical analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 698, 134141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; He, J.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, J.; Zeng, L.; He, R.; Guiang, M.M.; Li, Y.; Wu, H. Assessment of Chinese suitable habitats of Zanthoxylum nitidum in different climatic conditions by Maxent model, HPLC, and chemometric methods. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 196, 116515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Sun, X.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, X.; Miao, Y.; Zhang, M.; Feng, Z.; Zeng, R.; Pei, J.; Huang, L. Potential Global Distribution of the Habitat of Endangered Gentiana rhodantha Franch: Predictions Based on MaxEnt Ecological Niche Modeling. Sustainability 2023, 15, 631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zongci, L.Y.Z. New generation of scenarios of greenhouse gas emission. Adv. Clim. Change Res. 2012, 8, 305. [Google Scholar]
- O’Neill, B.C.; Kriegler, E.; Riahi, K.; Ebi, K.L.; Hallegatte, S.; Carter, T.R.; Mathur, R.; Van Vuuren, D.P. A new scenario framework for climate change research: The concept of shared socioeconomic pathways. Clim. Change 2014, 122, 387–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, S.; Zhang, D.; Wen, Y. Potential Geographical Distribution of Lagerstroemia excelsa under Climate Change. Agriculture 2024, 14, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Zagortchev, L.; Ma, J.; Yan, M.; Li, J. Predicting the potential distribution of the parasitic Cuscuta chinensis under global warming. BMC Ecol. 2020, 20, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Li, Q.; He, S.; Liu, Y.; Wang, M.; Jiang, G. Modeling and mapping the current and future distribution of Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae under climate change in China. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0192153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brismar, J. Understanding receiver-operating-characteristic curves: A graphic approach. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 1991, 157, 1119–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Wang, C.; He, J.; Zhang, Z. Analysis of geographical distribution of Abies in China under climate change. Bull. Bot. Res. 2018, 38, 37–46. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.B.; Jiang, S.Y.; Sun, H.; Wang, H.L.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, W.T. Cultural regionalization for Notopterygium incisum based on 3S technology platform Ⅲ. Functional regionalization for cultivation based on suitability evaluation of growth and production quality. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2017, 42, 2639–2644. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Michalet, R.; Guo, X.; Xie, H.; He, M. Variation in biomass and nutrients allocation of Corydalis hendersonii on the Tibetan Plateau with increasing rainfall continentality and altitude. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 132, 108244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Guo, X.; Niu, J.; Duojie, D.; Li, X.; Opgenoorth, L.; Zou, J. Molecular Phylogeography and Evolutionary History of the Endemic Species Corydalis hendersonii (Papaveraceae) on the Tibetan Plateau Inferred from Chloroplast DNA and ITS Sequence Variation. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, S.; Ali, H.; Baharanchi, O.G.; Sher, H.; Yousefpour, R. Investigating endemic species conservation hotspots based on species distribution models in Swat Region, Hindu Kush Pakistan. Land 2024, 13, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Editorial Committee of the Flora of China of Chinese Academy of Science. Flora of China; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1999; Volume 32, p. 475. [Google Scholar]
- Nematollahi, S.; Fakheran, S.; Kienast, F.; Jafari, A. Application of InVEST habitat quality module in spatially vulnerability assessment of natural habitats (case study: Chaharmahal and Bakhtiari province, Iran). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Longzhu, D.; Lu, X.; Songzha, C.; Miao, Q.; Sun, F.; Suonan, J. Habitat suitability of Corydalis based on the optimized MaxEnt model in China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2023, 43, 10345–10362. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, Y.; Shi, J.; De, K.; Wang, X.; Wang, W.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, H.; He, M.; Liu, Q. The current distribution of Carex alatauensis in the Qinghai–Tibet plateau estimated by MaxEnt. Agronomy 2023, 13, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.Y.; Kan, S.L.; Wang, J.L.; Cao, Y.N.; Li, J.M. Complete chloroplast genome sequences of Corydalis edulis and Corydalis shensiana (Papaveraceae). Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2021, 6, 257–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandelook, F.; Van Assche, J.A. Temperature conditions control embryo growth and seed germination of Corydalis solida (L.) Clairv., a temperate forest spring geophyte. Plant Biol. 2009, 11, 899–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qaderi, M.M.; Martel, A.B.; Strugnell, C.A. Environmental Factors Regulate Plant Secondary Metabolites. Plants 2023, 12, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, M.J.; Wu, S.; Duan, M.; Wang, L. Antioxidant Metabolites in Primitive, Wild, and Cultivated Citrus and Their Role in Stress Tolerance. Molecules 2021, 26, 5801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zu, Y.G.; Tang, Z.H.; Yu, J.H.; Liu, S.G.; Wang, W.; Guo, X.R. Different responses of camptothecin and 10-hydroxycamptothecin to heat shock in Camptotheca acuminata seedlings. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2003, 45, 809–814. [Google Scholar]
- Jansen, G.; Jürgens, H.U.; Ordon, F. Effects of temperature on the alkaloid content of seeds of Lupinus angustifolius cultivars. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2009, 195, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, A.; Sen, J.; Deswal, R. Downregulation of terpenoid indole alkaloid biosynthetic pathway by low temperature and cloning of a AP2 type C-repeat binding factor (CBF) from Catharanthus roseus (L). G. Don. Plant Cell Rep. 2007, 26, 1869–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Liu, X.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, S.; Yang, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, M.; Xu, Y. Prediction and verification of potential lead analgesic and antiarrhythmic components in Corydalis yanhusuo W. T. Wang based on voltage-gated sodium channel proteins. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 216, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.H.; Chen, K.; Shen, S.Y.; Luo, Y.F.; Liu, X.H.; Chen, X.; Gao, W.; Tong, Y.R. The composition, pharmacological effects, related mechanisms and drug delivery of alkaloids from Corydalis yanhusuo. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 167, 115511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Sun, J.; Li, W.; Zhang, S.; Yang, L.; Teng, Y.; Lv, K.; Liu, Y.; Su, Y.; Zhang, J.; et al. Analgesic effect of the main components of Corydalis yanhusuo (yanhusuo in Chinese) is caused by inhibition of voltage gated sodium channels. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 280, 114457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variables | Name | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Aspect | Aspect | / |
| Elev | Elevation | m |
| Slope | Slope | ◦ |
| Bio_3 | Isothermality | / |
| Bio_1 | Annual mean temperature | °C |
| Bio_4 | Temperature seasonality | / |
| Bio_16 | Precipitation of the wettest quarter | mm |
| Bio_8 | Mean temperature of the wettest quarter | °C |
| T_ph_h2o | Topsoil pH | −log(H+) |
| T_oc | Topsoil organic carbon content | % weight |
| S_silt | Subsoil silt content | % weight |
| S_clay | Subsoil clay content | % weight |
| S_sand | Subsoil sand content | % weight |
| S_caco3 | Subsoil carbonate or lime content | % weight |
| S_oc | Subsoil organic carbon content | % weight |
| S_ece | Subsoil electrical conductivity | ds/m |
| Environmental Variables | Name | Percent Contribution (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Bio_16 | Precipitation of wettest quarter | 50.3 |
| Bio_3 | Isothermality | 11.6 |
| Bio_1 | Annual mean temperature | 9.1 |
| Bio_4 | Temperature seasonality | 8.3 |
| Environmental Variables | Suitable Range | Adaptive Threshold |
|---|---|---|
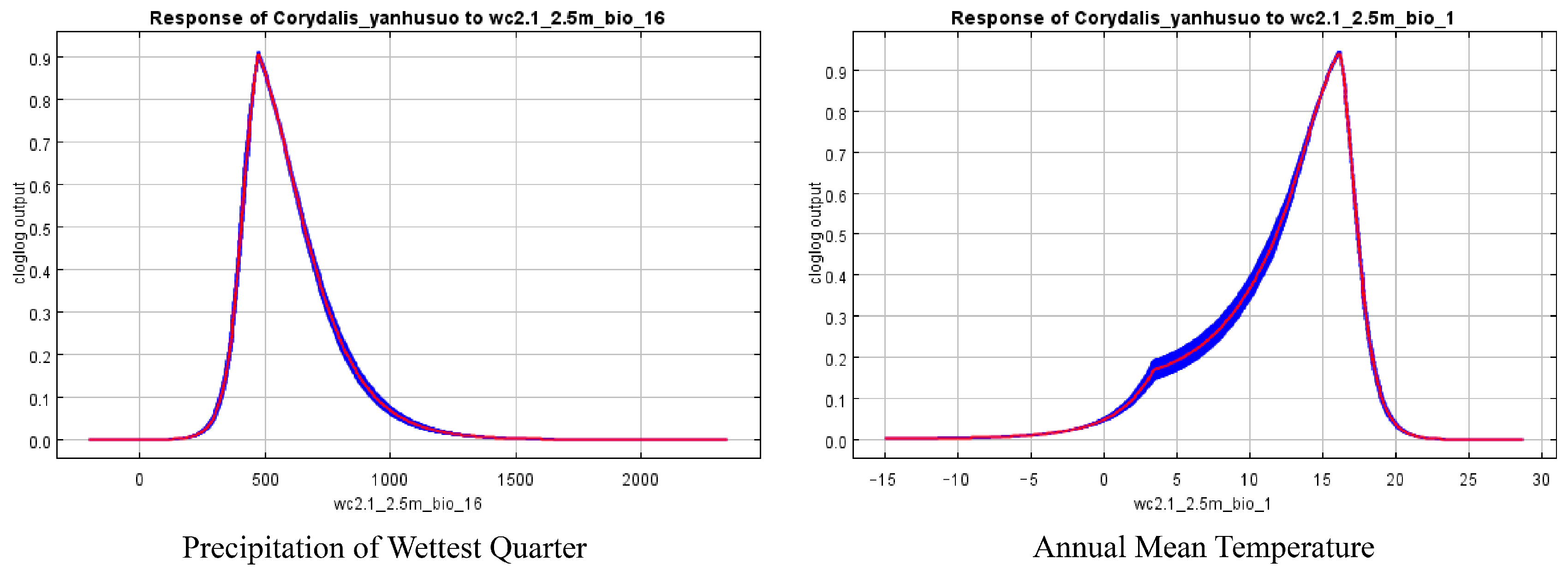
| Bio_16 | 404.8~654.5 mm | 473.6 mm |
| Bio_1 | 11.8~17.4 °C | 16.2 °C |
| Climate Scenarios | Periods | Longitude (°E) | Latitude (°N) | Migration Distance (km) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Present | 112.64 | 32.56 | ||
| SSP126 | 2050s | 112.26 | 32.97 | 53.33 |
| SSP126 | 2090s | 111.99 | 32.71 | 79.88 (2050s → 2090s) |
| SSP585 | 2050s | 114.11 | 33.09 | 177.59 |
| SSP585 | 2090s | 113.45 | 33.32 | 78.96 (2050s → 2090s) |
| Variables | Tetrahydropalmatine |
|---|---|
| Mean diurnal temperature range (Bio_2) | 0.768 ** |
| Temperature seasonality (Bio_4) | 0.842 ** |
| Mean temperature of the wettest quarter (Bio_7) | 0.842 ** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Huang, B.; Xu, L.; Chen, T. Prediction Analysis of Integrative Quality Zones for Corydalis yanhusuo W. T. Wang Under Climate Change: A Rare Medicinal Plant Endemic to China. Biology 2025, 14, 972. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14080972
Wang H, Huang B, Xu L, Chen T. Prediction Analysis of Integrative Quality Zones for Corydalis yanhusuo W. T. Wang Under Climate Change: A Rare Medicinal Plant Endemic to China. Biology. 2025; 14(8):972. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14080972
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Huiming, Bin Huang, Lei Xu, and Ting Chen. 2025. "Prediction Analysis of Integrative Quality Zones for Corydalis yanhusuo W. T. Wang Under Climate Change: A Rare Medicinal Plant Endemic to China" Biology 14, no. 8: 972. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14080972
APA StyleWang, H., Huang, B., Xu, L., & Chen, T. (2025). Prediction Analysis of Integrative Quality Zones for Corydalis yanhusuo W. T. Wang Under Climate Change: A Rare Medicinal Plant Endemic to China. Biology, 14(8), 972. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14080972





