Functional Spermatogenesis Across Testicular Developmental Stages in Neomale Large Yellow Croaker (Larimichthys crocea) Revealed by Histology and Gonadal Specific Cellular Markers
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics
2.2. Fish
2.3. Sampling
2.4. Gonadal Histology
2.5. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) Analysis
2.6. Immunofluorescent Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
2.8. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qPCR)
3. Results
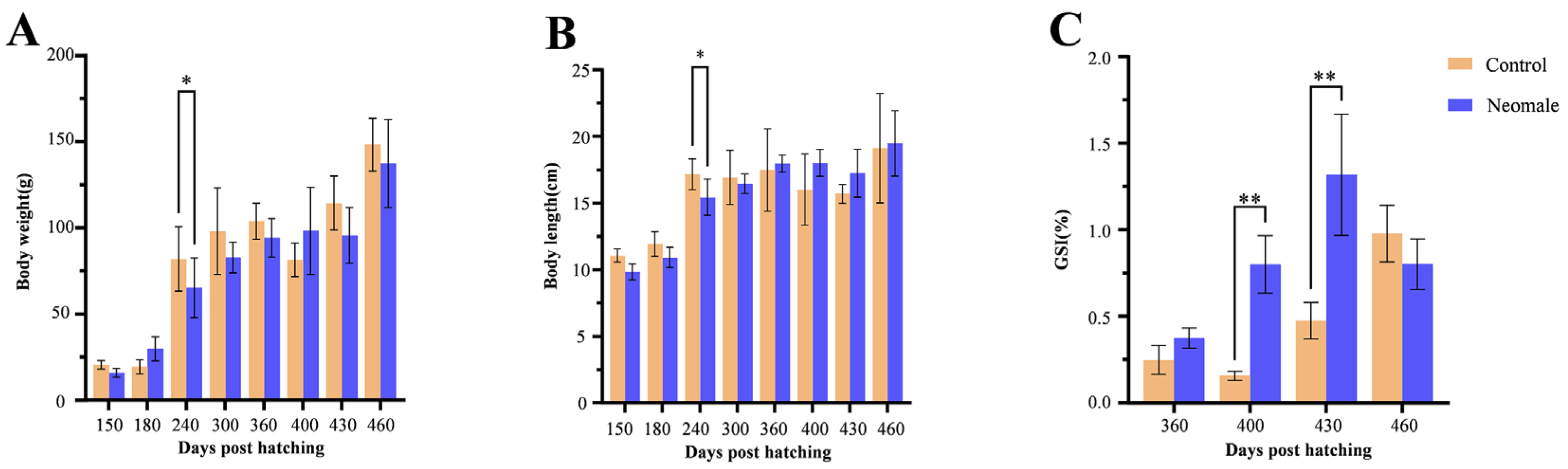
3.1. Growth and GSI
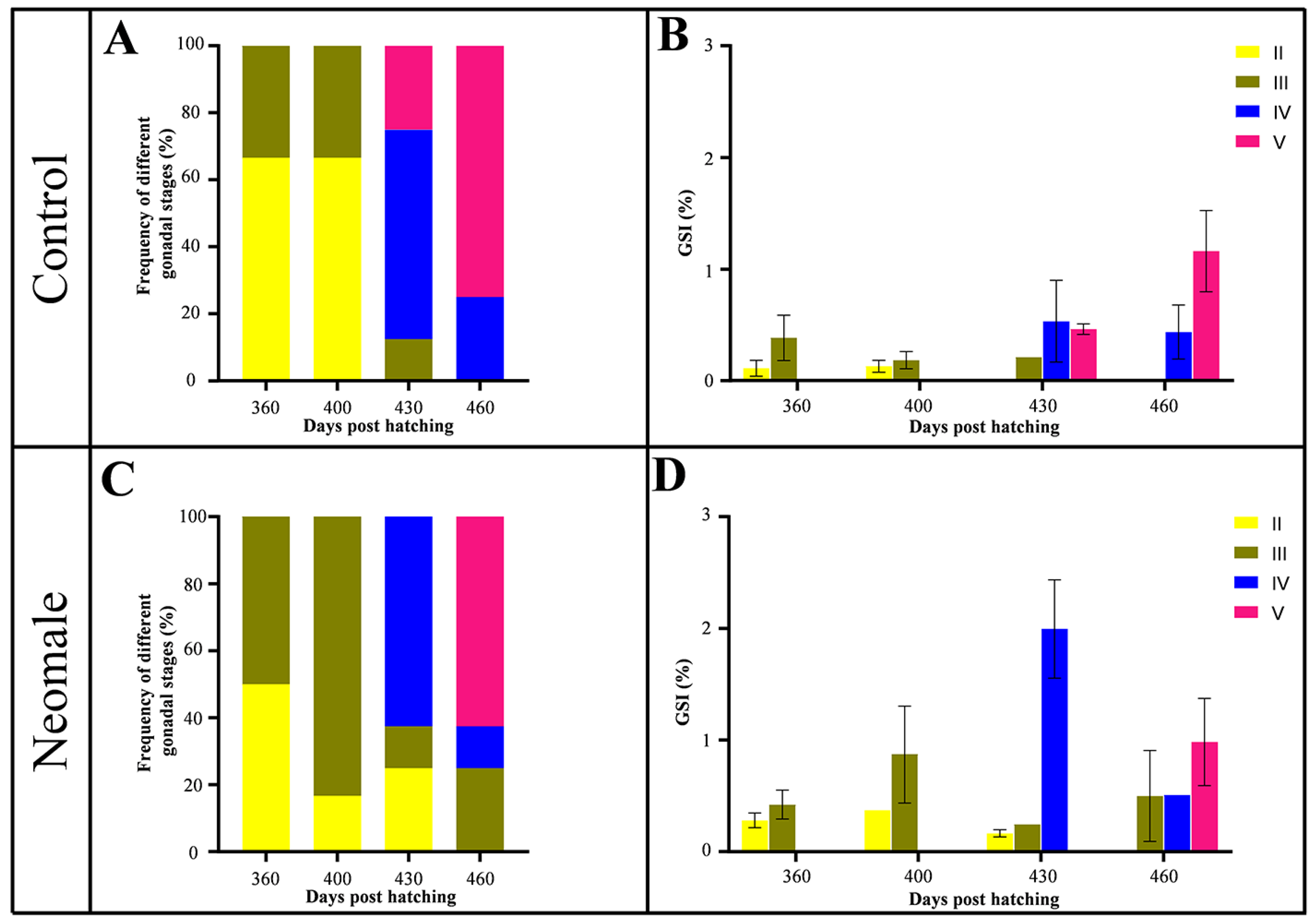
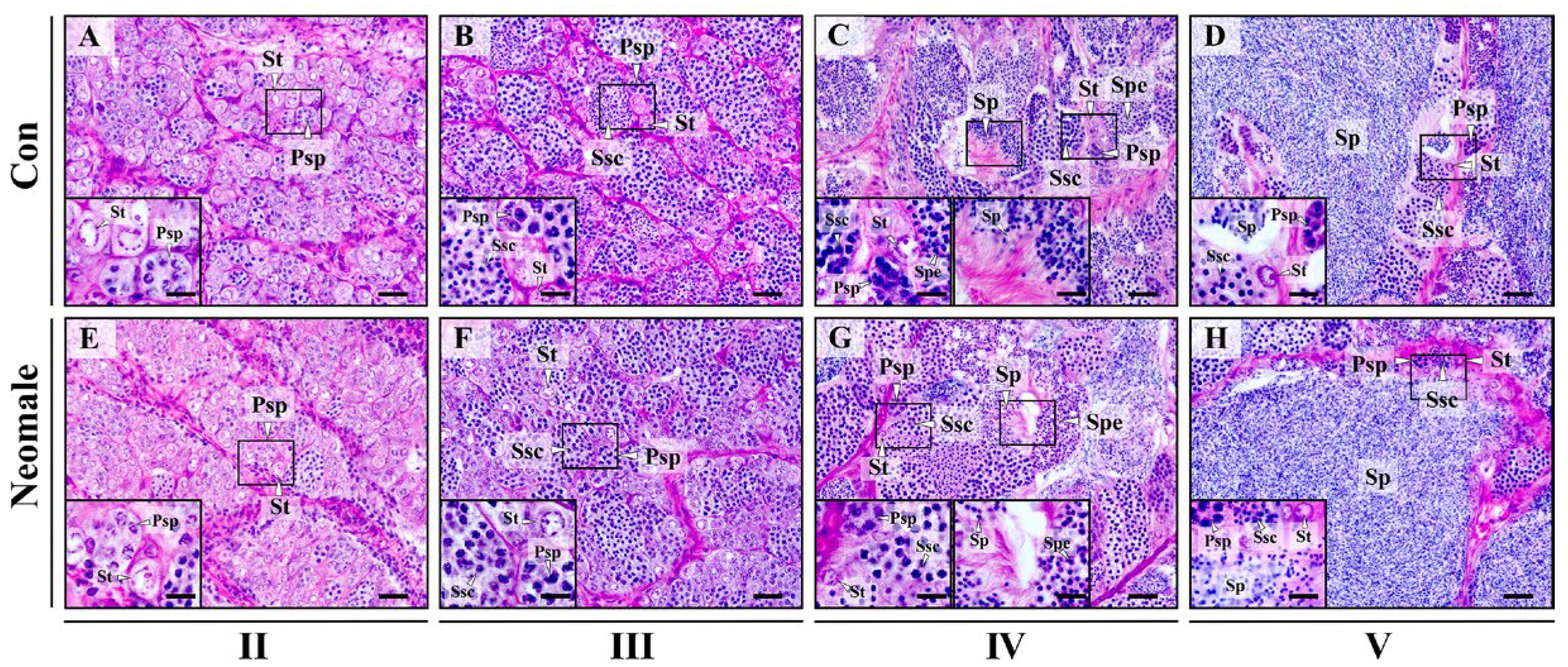
3.2. Gonadal Histology of Neomale Large Yellow Croaker
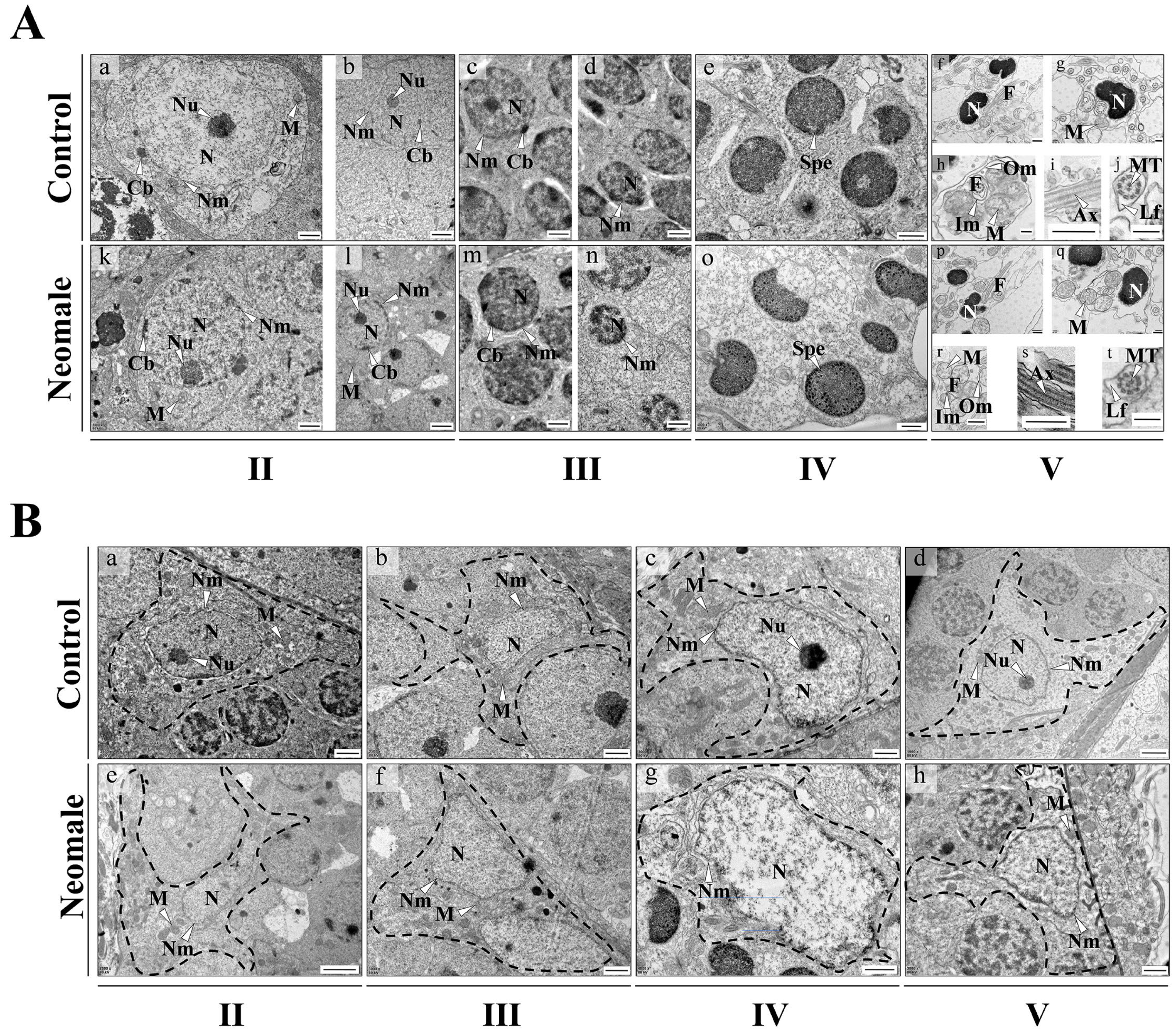
3.3. Ultrastructural Observation of Spermatogenic Cells and Sertoli Cells in Neomale Large Yellow Croaker
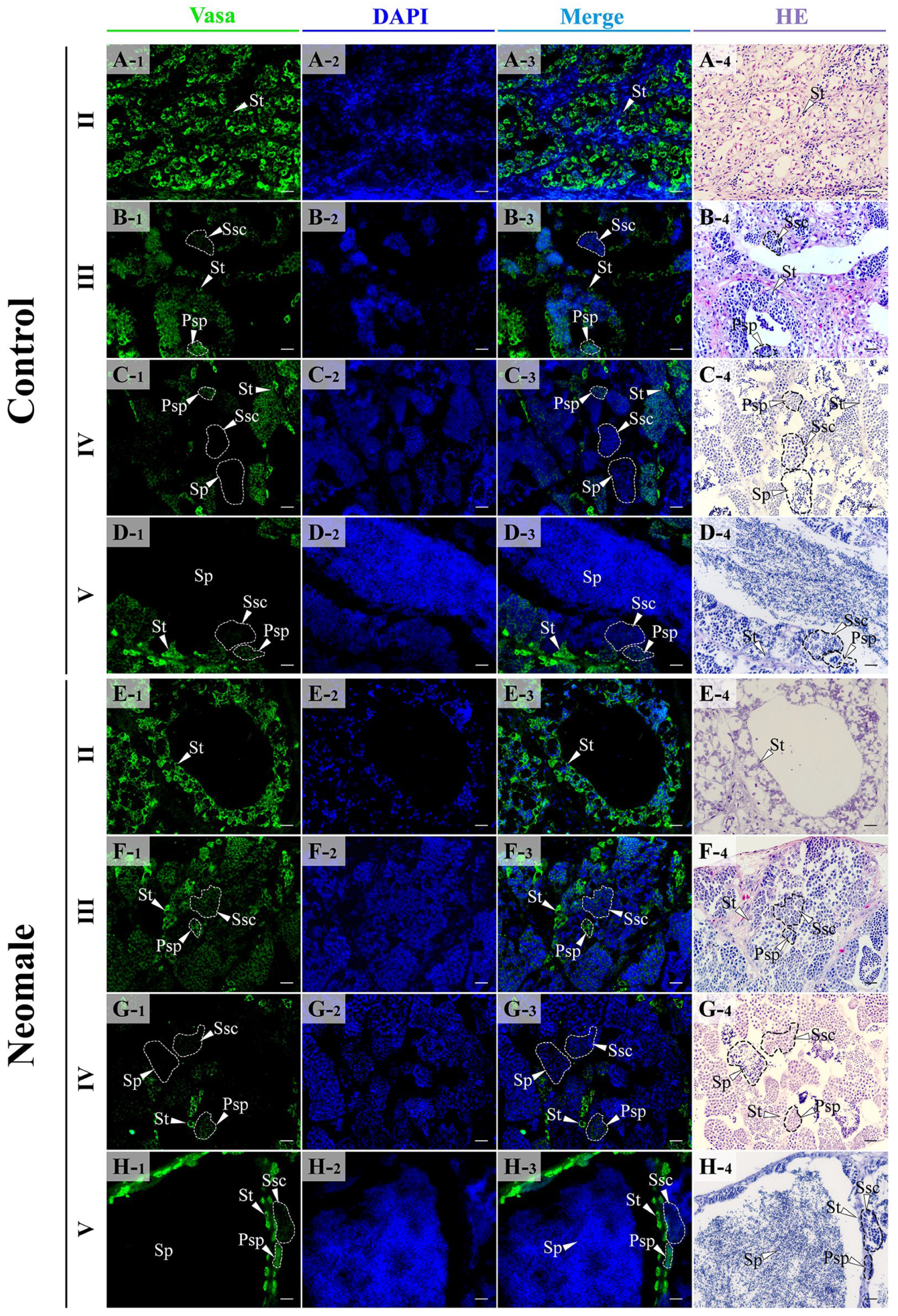
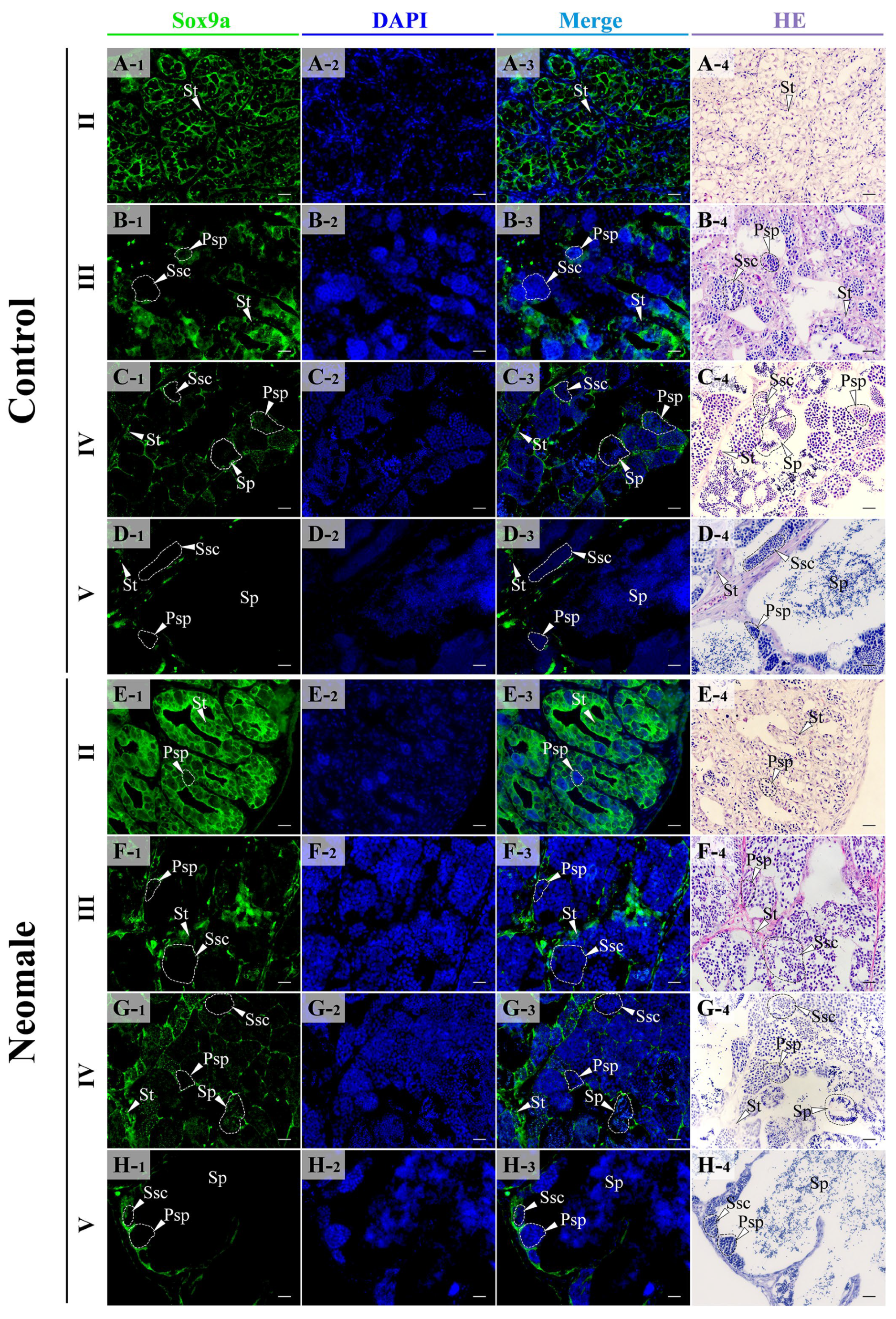
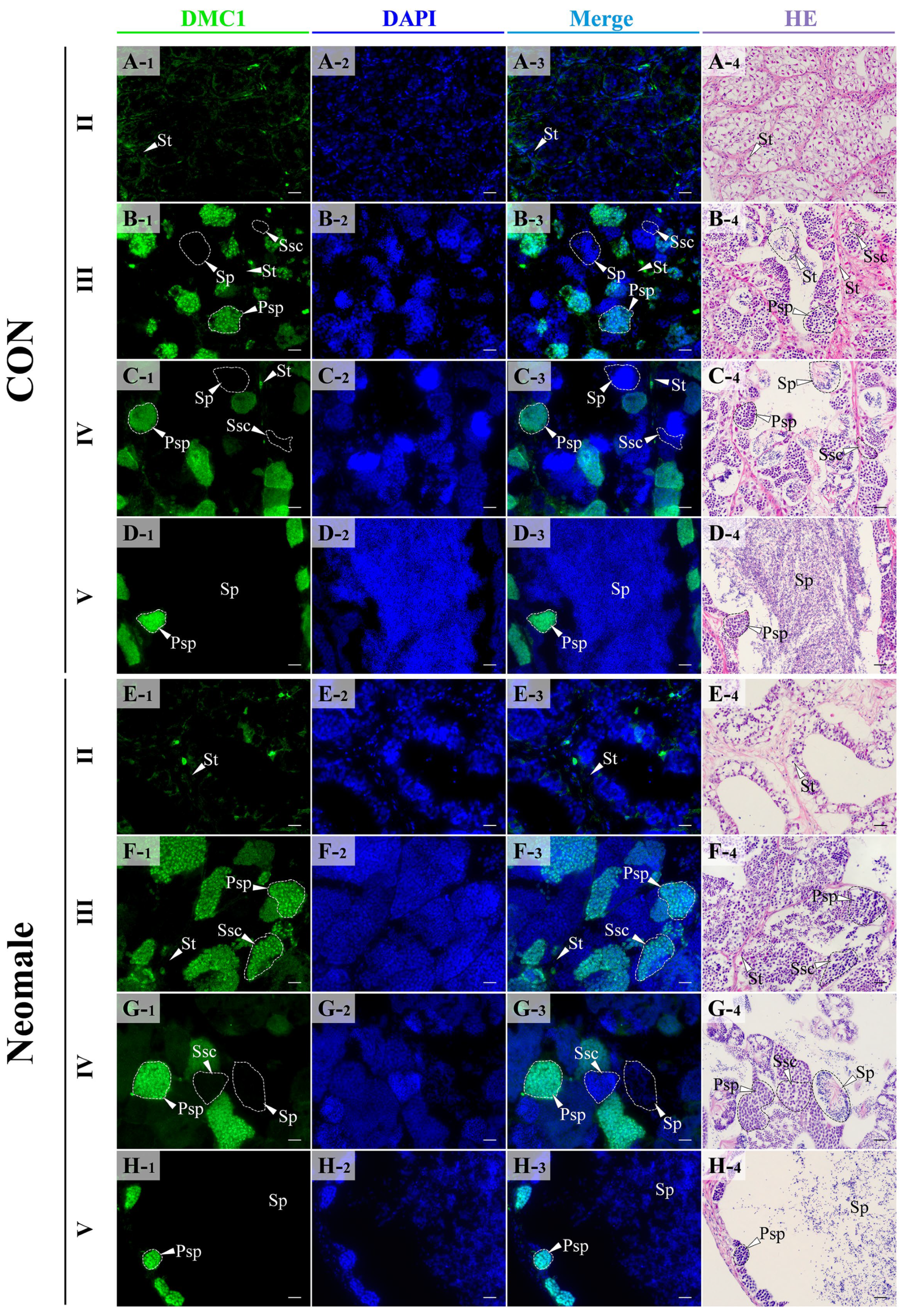
3.4. Localization of Vasa, Sox9a and DMC1 Proteins in the Gonads of Neomale Large Yellow Croaker
4. Discussion
4.1. Growth and GSI Dynamics During Gonadal Maturation in Neomale Large Yellow Croaker
4.2. Testicular Histological and Ultrastructural Integrity with Spermatogenic Synchrony in Neomale Large Yellow Croaker
4.3. Expression Patterns of vasa, sox9a, and dmc1 During Spermatogenesis in Neomale Large Yellow Croaker
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- The Bureau of Fisheries and Fishery Administration, the Ministry of Agriculture. China Fishery Statistical Yearbook; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2024; pp. 21–37. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Fan, S.; Xu, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, W.; Hu, Y.; Deng, X.; Liu, H.; Yang, C.; et al. Germplasm innovation of large yellow croaker and its research progress. Reprod. Breed. 2025, 5, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Cai, M. Artificial Gynogenesis and Sex Control in Large Yellow Croaker. In Sex Control in Aquaculture; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 751–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, X.; Cai, M.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, Z. Histological observation on gonadal sex differentiation in large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea). J. Fish. China 2012, 36, 1057–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; You, F.; Yan, B.; Zhang, P. Effects of ultra-violet irradiation on sperm motility and diploid gynogenesis induction in large yellow croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea) undergoing cold shock. Aquac. Int. 2007, 15, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Wu, Q.; Liu, X.; Yao, C.; Chen, Q.; Wang, Z. Artificial induction of mito-gynogenetic diploids in large yellow croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea) by hydrostatic pressure. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2010, 28, 713–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Xie, Q.; Wei, F.; Wu, X.; Xu, W.-T.; Zhan, W.; Liu, F.; Guo, D.-D.; Niu, B.-L.; Lou, B. Development and identification of a sex-specific molecular marker in Dai-qu stock large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea). Aquaculture 2022, 555, 738172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, A.; Xiao, S.; Xu, S.; Ye, K.; Lin, X.; Sun, S.; Wang, Z. Identification of a male-specific DNA marker in the large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea). Aquaculture 2017, 480, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, J.; Hu, W.; Chen, R.; Yang, Y.; Li, H.; Li, W.; Yin, X.; Xu, D. Production of neomale and neofemale large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea) and establishment of all-female populations. Aquaculture 2024, 590, 741010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piferrer, F. Endocrine Sex Control Strategies for the Feminization of Teleost Fish. In Reproductive Biotechnology in Finfish Aquaculture; Lee, C.-S., Donaldson, E.M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2001; pp. 229–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Yang, F.; Tian, L.; Chen, R.; Xu, D.; Takeuchi, Y. Induction of sex reversal in blue drum (Nibea mitsukurii) and gynogenetic yellow drum (Nibea albiflora) by oral administration of letrozole. Aquac. Res. 2019, 51, 882–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, R.W.; de França, L.R.; Lareyre, J.-J.; LeGac, F.; Chiarini-Garcia, H.; Nobrega, R.H.; Miura, T. Spermatogenesis in fish. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2010, 165, 390–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Guan, Y.; Wang, M.; Liu, D.; Xiong, S.; Li, J.; Yu, X. Research progress on Sertoli cell secretion during spermatogenesis. Front. Endocrinol. 2025, 15, 1456410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Fan, Q.; Yang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H. Effects of 17a-Methyltestosterone and Aromatase Inhibitor Letrozole on Sex Reversal, GonadalStructure, and Growth in Yellow Catfish Pelteobagrusfulvidraco. Biol. Bull. 2015, 228, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syanya, F.J.; Mahadevan, H.; Khanna, A.R.N. The effects of a non-steroid aromatase inhibitor on hybrid red tilapia masculinization, growth, reproductive hormone profile, and economic efficiency in aquaculture. Aquac. Int. 2025, 33, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meena, D.K.; Lal, J.; Biswas, P.; Singh, S.K.; Debbarma, R.; Deb, S.; Yadav, N.K.; Patel, A.B. Effects of dietary aromatase inhibitors on masculinization of rosy barb (Pethia conchonius): Evidence from growth, coloration and gonado-physiological changes. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0287934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Nozu, R.; Nakamura, M. Role of estrogen in spermatogenesis in initial phase males of the three-spot wrasse (Halichoeres trimaculatus): Effect of aromatase inhibitor on the testis. Dev. Dyn. 2010, 240, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Srivastava, P.P.; Verma, R.; Srivastava, S.C.; Kumar, D.; Ansari, A. Effect of dietary administration of letrozole and tamoxifen on gonadal development, sex differentiation and biochemical changes in common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). Reprod. Fertil. Dev. 2015, 27, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Martín, L.; Blázquez, M.; Piferrer, F. Masculinization of the European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) by treatment with an androgen or aromatase inhibitor involves different gene expression and has distinct lasting effects on maturation. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2009, 160, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breton, T.S.; Kenter, L.W.; Greenlaw, K.; Montgomery, J.; Goetz, G.W.; Berlinsky, D.L.; Luckenbach, J.A. Initiation of sex change and gonadal gene expression in black sea bass (Centropristis striata) exposed to exemestane, an aromatase inhibitor. Comp. Biochem. Phys. A 2019, 228, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, M. Morphological and Physiological Studies on Gonadal Sex Differentiation in Teleost Fish. Aqua-Biosci. Monogr. 2013, 6, 1–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Budd, A.; Banh, Q.; Domingos, J.; Jerry, D. Sex Control in Fish: Approaches, Challenges and Opportunities for Aquaculture. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2015, 3, 329–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsumura, K.; Blann, V.E.; Lamont, C.A. Progeny Test of Masculinized Female Rainbow Trout Having Functional Gonoducts. Progress. Fish-Cult. 1991, 53, 45–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatain, B.; Saillant, E.; Peruzzi, S. Production of monosex male populations of European seabass, Dicentrarchus labrax L. by use of the synthetic androgen 17α-methyldehydrotestosterone. Aquaculture 1999, 178, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Yang, F.; Chen, R.; Lou, B.; Zhan, W.; Hayashida, T.; Takeuchi, Y. Production of neo-males from gynogenetic yellow drum through 17α-methyltestosterone immersion and subsequent application for the establishment of all-female populations. Aquaculture 2018, 489, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katare, M.B.; Pai, M.; HS, M. Effect of anastrozole on masculinization in ornamental fish, dwarf gourami, Trichogaster lalius (Hamilton, 1822). Indian J. Exp. Biol. 2021, 59, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazier, C.B.; Langley, S.; Ramsey, N.B.; Wright, J.M. Androgen inhibition of Vitellogenin Gene Expressionin Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 1996, 104, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.; Moon, H.; Yeo, I. Inhibition of sexual maturation inhibition using exemestane and tamoxifen in female olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceous). Res. Sq. 2023. preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malo, A.F.; Gomendio, M.; Garde, J.; Lang-Lenton, B.; Soler, A.J.; Roldan, E.R.S. Sperm design and sperm function. Biol. Lett. 2006, 2, 246–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Shao, J.; Li, P.; Wu, J.; Wei, Q. Morphology and ultrastructure of Brachymystax lenok tsinlingensis spermatozoa by scanning and transmission electron microscopy. Tissue Cell 2016, 48, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.J.; Dixson, A.F. Motility and the midpiece in primates. Nature 2002, 416, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y. Topmouth Culter (Culter alburnus) All-Female Breedingsystem Establishment and Evaluation. Ph.D. Thesis, East China Normal University, Shanghai, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Begum, S.; Gnanasree, S.M.; Anusha, N.; Senthilkumaran, B. Germ cell markers in fishes—A review. Aquac. Fish. 2022, 7, 540–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, C.; Kawakami, K.; Hopkins, N. Zebrafish vasa homologue RNA is localized to the cleavage planes of 2- and 4-cell-stage embryos and is expressed in the primordial germ cells. Development 1997, 124, 3157–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braat, A.K.; van de Water, S.; Goos, H.; Bogerd, J.; Zivkovic, D. Vasa protein expression and localization in the zebrafish. Mech. Dev. 2000, 95, 271–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milani, L.; Cinelli, F.; Iannello, M.; Lazzari, M.; Franceschini, V.; Maurizii, M.G. Immunolocalization of Vasa, PIWI, and TDRKH proteins in male germ cells during spermatogenesis of the teleost fish Poecilia reticulata. Acta Histochem. 2022, 124, 151870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Yang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Li, H.; Chen, R.; Miao, L.; Xu, D. Gametogenesis and vasa expression are seasonally regulated in yellow drum (Nibea albiflora). Aquac. Rep. 2024, 35, 101970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Lu, L.; Chen, R.; Yu, L.; Hu, W.; Xu, D. Production of sterile mono-sex triploid yellow drum (Nibea albiflora): Genotypic females and sex-reversed phenotypic males with emphasis on utilization as surrogate broodstock. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2023, 49, 1277–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, S.S.; Toyooka, Y.; Akasu, R.; Katoh-Fukui, Y.; Nakahara, Y.; Suzuki, R.; Yokoyama, M.; Noce, T. The mouse homolog of Drosophila Vasa is required for the development of male germ cells. Gene Dev. 2000, 14, 841–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardinali, M.; Gioacchini, G.; Candiani, S.; Pestarino, M.; Yoshizaki, G.; Carnevali, O. Hormonal regulation of vasa-like messenger RNA expression in the ovary of the marine teleost Sparus aurata. Biol. Reprod. 2004, 70, 737–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartung, O.; Forbes, M.M.; Marlow, F.L. Zebrafish vasa is required for germ-cell differentiation and maintenance. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2014, 81, 946–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, G.; Shu, T.; Xia, Y.; Jin, X.; He, J.; Yin, Z. Androgen signaling regulates the transcription of anti-Mullerian hormone via synergy with SRY-related protein SOX9A. Sci. Bull. 2017, 62, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Marí, A.; Yan, Y.-L.; BreMiller, R.A.; Wilson, C.; Cañestro, C.; Postlethwait, J.H. Characterization and expression pattern of zebrafish anti-Müllerian hormone (amh) relative to sox9a, sox9b, and cyp19a1a, during gonad development. Gene Expr. Patterns 2005, 5, 655–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhu, Y.; Li, W.; Shen, W.; Wu, X.; Ye, K.; Wang, Z. Cloning and expression of sox9a/b gene in the large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea). J. Fish. China 2019, 43, 1691–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Tang, Y.H.; Deng, W.Y.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, L.S.; He, X.; Xie, Q.P.; Li, Y.Q.; Deng, L.; Wang, D.S.; et al. Involvement of Sox9a in chondrogenesis and gonadal development in teleost Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Zool. Res. 2023, 44, 729–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, S.; Watakabe, I.; Nishimura, T.; Toyoda, A.; Taniguchi, Y.; Tanaka, M. Analysis of Medaka sox9 Orthologue Reveals a Conserved Role in Germ Cell Maintenance. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e29982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Symon, A.; Harley, V. SOX9: A genomic view of tissue specific expression and action. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2017, 87, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kajiura-Kobayashi, H.; Kobayashi, T.; Nagahama, Y. Cloning of cDNAs and the differential expression of A-type cyclins and Dmc1 during spermatogenesis in the Japanese eel, a teleost fish. Dev. Dyn. 2005, 232, 1115–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Zhao, L.; Peng, S.; Chu, H.; Liang, R.; Tian, M.; Connell, P.P.; Li, G.; Chen, C.; Wang, H. Mechanisms of distinctive mismatch tolerance between Rad51 and Dmc1 in homologous recombination. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, 13135–13149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Behery, E.I.; El-Naseery, N.I.; El-Ghazali, H.M.; Elewa, Y.H.A.; Mahdy, E.A.A.; El-Hady, E.; Konsowa, M.M.H. The efficacy of chronic zinc oxide nanoparticles using on testicular damage in the streptozotocin-induced diabetic rat model. Acta Histochem. 2019, 121, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, M.; Liu, S.; Long, Y.; Zeng, C.; Liu, J.; Liu, L.; Zhang, C.; Duan, W.; Liu, Y. The cloning of Dmc1 cDNAs and a comparative study of its expression in different ploidy cyprinid fishes. Sci. China Ser. C 2008, 51, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Cui, X.; Jia, S.; Luo, D.; Cao, M.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, H.; Huang, K.; Zhu, Z.; Hu, W. Disruption of dmc1 Produces Abnormal Sperm in Medaka (Oryzias latipes). Sci. Rep 2016, 6, 30912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Hu, W.; Chen, R.; Yang, Y.; Yang, S.; Xu, D. Functional Spermatogenesis Across Testicular Developmental Stages in Neomale Large Yellow Croaker (Larimichthys crocea) Revealed by Histology and Gonadal Specific Cellular Markers. Biology 2025, 14, 1054. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14081054
Liu X, Hu W, Chen R, Yang Y, Yang S, Xu D. Functional Spermatogenesis Across Testicular Developmental Stages in Neomale Large Yellow Croaker (Larimichthys crocea) Revealed by Histology and Gonadal Specific Cellular Markers. Biology. 2025; 14(8):1054. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14081054
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xu, Weihua Hu, Ruiyi Chen, Yang Yang, Sixian Yang, and Dongdong Xu. 2025. "Functional Spermatogenesis Across Testicular Developmental Stages in Neomale Large Yellow Croaker (Larimichthys crocea) Revealed by Histology and Gonadal Specific Cellular Markers" Biology 14, no. 8: 1054. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14081054
APA StyleLiu, X., Hu, W., Chen, R., Yang, Y., Yang, S., & Xu, D. (2025). Functional Spermatogenesis Across Testicular Developmental Stages in Neomale Large Yellow Croaker (Larimichthys crocea) Revealed by Histology and Gonadal Specific Cellular Markers. Biology, 14(8), 1054. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14081054






