Highlights
Main findings
- Electrospun polyacrylonitrile (ESPAN) nanofibers were coated with polyaniline (PANI) through in situ polymerization.
- The PANI-coated ESPAN nanofibrous adsorbent (PANI-ESPAN) demonstrated excellent adsorption capabilities for a short-chain PFAS (GenX) and could remove nearly all GenX (>98%) from a 100 ppb aqueous solution at pH = 6 and 0.6 g/L loading, with a contact time of 12 h.
Implications of findings
- The GenX adsorption mechanism of PANI-ESPAN at pH = 6 can mainly be attributed to non-Coulomb interactions (hydrophobic, dipole–dipole, and hydrogen bonding), while Coulomb interactions (electrostatic interaction) also played a role in the adsorption.
- By coupling the unique properties of PANI with ESPAN nanofibers, this research demonstrated a versatile and efficient solution to address current short-chain PFAS contamination issues in the practice of water purification.
Abstract
A 6-carbon short-chain per- and polyfluoroalkyl substance (PFAS), GenX, also known as hexafluoropropylene oxide dimer acid (HFPO-DA) and its ammonium salt, has been manufactured in recent years as a replacement for perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA), a traditional long-chain PFAS, due to the increasing environmental regulation of PFAS compounds in recent years. GenX has received significant attention because of the fact that it is more toxic than people originally thought, and it is now one of the six PFAS compounds that are placed under legally enforceable restrictions in drinking water, i.e., 10 ppt, by the United States Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA). In this research, we extended the use of polyacrylonitrile (PAN) nanofibers from electrospinning for GenX removal from water by coating them with polyaniline (PANI) through in situ polymerization. The obtained PANI-coated electrospun PAN nanofibrous adsorbent (PANI-ESPAN) demonstrated excellent GenX adsorption capability and could remove nearly all GenX (>98%) from a 100 ppb aqueous solution. This research provided valuable insights into short-chain PFAS remediation from water by designing and developing high-performance adsorbent materials.
1. Introduction
Per- and poly-fluoroalkyl substances (PFASs), as emerging contaminants, have become a pressing environmental concern due to their exceptional stability, hazardous nature, and widespread presence in various water bodies [1]. In recent years, traditional long-chain PFAS compounds such as perfluorooctane sulfonic acid (PFOS) and perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) have been gradually phased out and replaced by short-chain PFASs due to increasing environmental regulation. However, short-chain PFASs have faster transport through soil and more mobility in water, while they share similarities with their long-chain counterparts in terms of persistence and toxicity, warranting significant attention and targeted removal efforts [2].
In practice, an effective method for removing PFASs from water is adsorption [3,4]. The primary mechanism governing PFAS adsorption is attributed to electrostatic and/or hydrophobic interactions between adsorbent materials and PFAS molecules [5]. Many PFASs have low acid dissociation constants (pKa) and thus exist in an anion form in water, even at a pH that is close to neutral [6]. The electrostatic interaction between adsorbent materials and the head groups of PFAS molecules such as sulfonate or carboxylate groups can facilitate both long- and short-chain PFAS adsorption in these cases [7]. Previous studies also highlighted that the hydrophobic groups (C-F) in PFAS molecules greatly promote their adsorption onto adsorbent materials through hydrophobic interaction [8]. Nonetheless, the hydrophobic interaction for short-chain PFAS adsorption is significantly reduced because of their intrinsically weaker hydrophobic nature.
Among the various short-chain PFAS compounds, GenX, a 6-C short-chain PFAS that is also known as hexafluoropropylene oxide dimer acid (HFPO-DA) and its ammonium salt, has received significant attention since its detection in 2017 in the Cape Fear River of the State of North Carolina (U.S.), followed by statewide investigations. Traditional methods for water treatment have been shown to be inefficient in remediating GenX from water, highlighting the need for novel technologies to address this challenge [9]. Amine (-NH2) surface-functionalized adsorbent materials have demonstrated good GenX removal abilities from water with both electrostatic attractions and hydrophobic interactions [10,11]. For instance, Ji et al. explored the use of amine-functionalized covalent organic framework (COF) materials, which provided a highly porous structure with a tunable surface chemistry, for GenX removal from water. The presence of positively charged amine groups (-NH3+) within the COF not only allowed for strong electrostatic interactions between the COF adsorbent and GenX molecules but also offered a large surface area for the GenX molecules to interact with [10].
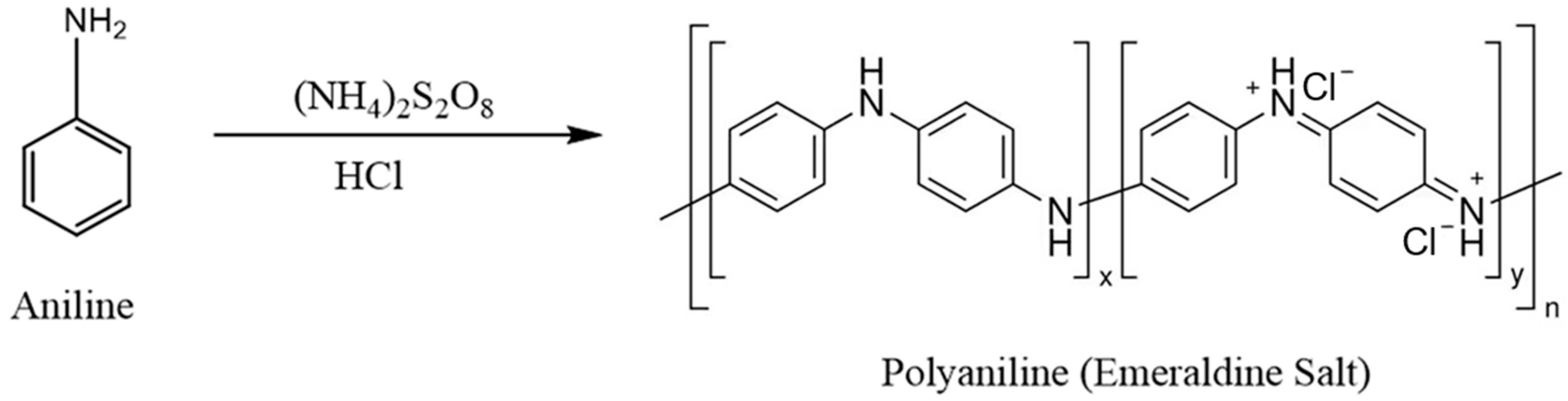
Polyacrylonitrile (PAN) is a popular polymer material for water filtration [12]. It is inexpensive and physically/chemically stable. In our previous work, we studied the removal of GenX from water by utilizing electrospun PAN (ESPAN) nanofibrous adsorbent/filter materials, taking advantage of the small size and concomitant large specific surface area of nanofibers, as well as their easy application in aqueous systems. From our previous research, ESPAN nanofibrous adsorbent demonstrated its potential to remove GenX from water, and surface-modified ESPAN nanofibrous adsorbent with amidoxime functional groups exhibited improved and significant capacity for GenX removal from aqueous solutions at pH = 4 [13]. However, there is still room for us to develop ESPAN-based nanofibrous adsorbent materials with enhanced GenX adsorption performance in water at a neutral pH. In recent years, polyaniline (PANI), a conducting polymer, and its derivatives have shown excellent adsorption capacities towards various organic pollutants, including long-chain PFAS compounds [14], while ESPAN nanofibers with PANI coatings have been reported for heavy metal ions and dye removal from water [15,16], as well as for oil/water separation [17]. In this research, we prepared a PANI-coated ESPAN nanofibrous material (PANI-ESPAN) through an aniline polymerization reaction (Figure 1) on the ESPAN nanofiber surface and explored its brand new application as a novel short-chain PFAS adsorbent material for effective removal of GenX from water. The GenX adsorption performance of PANI-ESPAN and corresponding removal mechanism were studied.
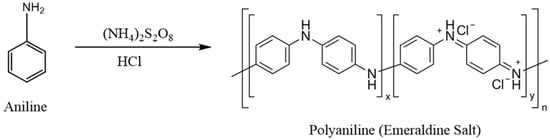
Figure 1.
The polymerization reaction of aniline to synthesized polyaniline.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
N,N-Dimethylformamide (DMF) and polyacrylonitrile (PAN, MW = 150,000) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). Anhydrous acetone, aniline, ammonium persulfate (APS), and 1M hydrochloric acid were purchased from Fisher Scientific (Waltham, MA, USA). GenX was purchased from SynQuest Laboratories. All materials were used as received. Deionized (DI) water was acquired from an in-house Millipore DI water system.
2.2. Preparation of ESPAN and PANI-Coated ESPAN Nanofibrous Adsorbents
The ESPAN nanofibers were prepared by electrospinning a 10 wt.% PAN solution in DMF [13]. The electrospinning was performed in a Spinbox (Nanoscience Instruments, Phoenix, AZ, USA) with a voltage of 13 kV, feeding ratio of 1 mL/h, and collector distance of 15 cm. The PANI-coated ESPAN nanofibrous adsorbent (PANI-ESPAN) was prepared by immersing the as-spun ESPAN nanofibers in an aniline solution (1 mL of aniline in 40 mL of 1M HCl solution), followed by the dropwise addition of an APS solution (0.9 g of APS in 10 mL of 1M HCl solution). This formula was selected to create a relatively homogeneous emeraldine salt PANI coating on the ESPAN nanofiber surface, as indicated by its emerald-green color. To avoid overheating, the reaction system was placed in an ice bath from the beginning and then stirred for 2 h. The obtained PANI-ESPAN was then filtered and washed with 1M HCl three times, followed by being thoroughly washed with DI water and acetone. The final PANI-ESPAN nanofibrous adsorbent was dried in a vacuum oven for 12 h at 80 °C.
2.3. Characterization of PANI-ESPAN
The surface morphology of the prepared PANI-ESPAN was examined using a Zeiss Auriga FIB scanning electron microscope (SEM). Prior to the SEM examination, the samples were sputter-coated with a layer of gold-palladium (~7 nm thick) to prevent surface charge buildup. The average fiber diameter was determined by measuring 40 randomly chosen nanofibers from the SEM images using ImageJ software (version 1.53t). The chemical bonding within the nanofibrous adsorbent was analyzed by an Agilent (Santa Clara, CA, USA) Varian 670 FTIR-ATR spectrometer with a resolution of 4 cm−1. The surface charges of the PANI-ESPAN nanofibers were evaluated by zeta potential analysis with 1 mg/L of nanofiber in DI water via a Malvern (Malvern, UK) Zetasizer ultra-dynamic light-scattering (DLS) instrument. The surface elemental composition and bonding of the nanofiber samples were characterized using an X-ray photoelectron spectrometer (XPS, Thermo Scientific Escalab Xi+, Waltham, MA, USA). The acquired XPS data were processed with the Avantage software (Version V5.9925). The curve fitting for individual elements was performed through a combination of Gaussian–Lorentzian functions. All XPS spectra were charge-corrected based on the 284.8 eV C1s binding energy. The specific surface area and porosity of the PANI-ESPAN nanofibrous adsorbent were evaluated by a Micromeritics (Norcross, GA, USA) ASAP 2020 BET analyzer.
2.4. GenX Adsorption
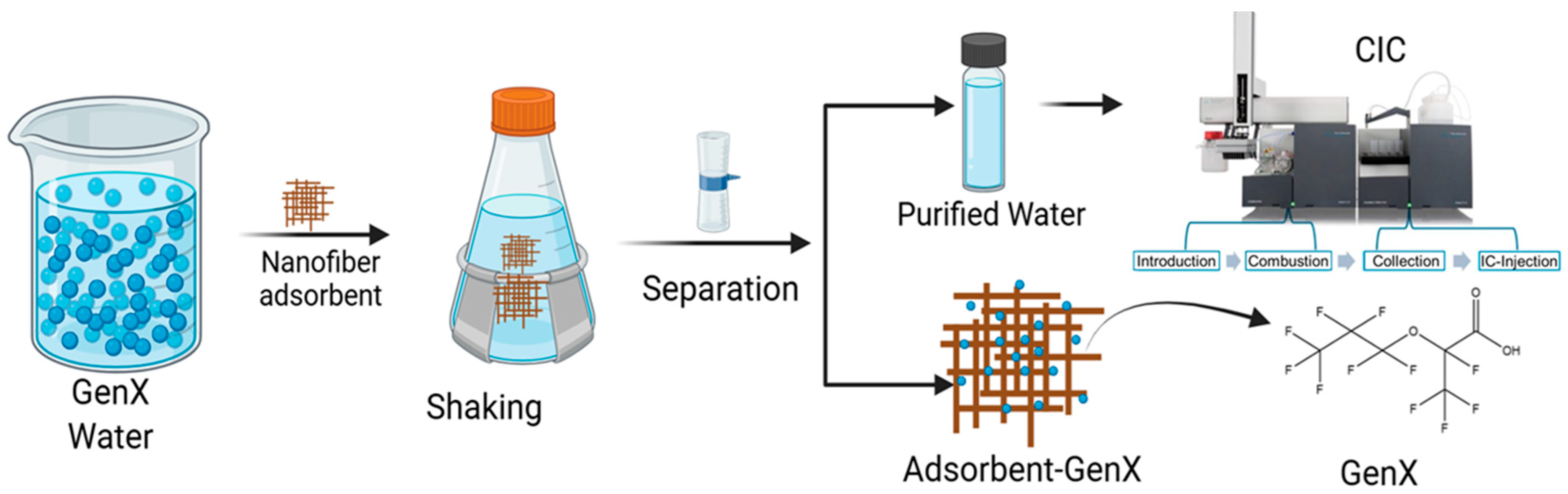
To investigate the performance of PANI-ESPAN on GenX removal (Figure 2), 0.02 g, 0.04 g, 0.06 g, and 0.08 g of PANI-ESPAN nanofibrous adsorbents were added to four individual Erlenmeyer flasks containing 100 mL of 100 ppb (µg/L) GenX water at pH = 3 and 6, respectively. The pH of the GenX water was adjusted using a diluted HCl or NaOH aqueous solution and monitored with an Orion pH meter. These Erlenmeyer flasks were shaken at room temperature for 12 h at 140 rpm using a rotatory shaker. To assess the effect of the GenX concentration on the adsorption efficiency of PANI-ESPAN, 0.06 g of nanofibrous adsorbent was added to 100 mL of GenX water with concentrations in the range of 20 ppb to 100 ppb, respectively, followed by being shaken for 12 h at 140 rpm. The effect of the contact time with the PANI-ESPAN nanofibrous adsorbent on the adsorption of GenX was measured using the batch kinetic reactor method with 200 mL of 100 ppm (mg/L) GenX aqueous solution and 0.06 g of PANI-ESPAN nanofibrous adsorbent, and the contact time ranged from 10 min to 6 h.
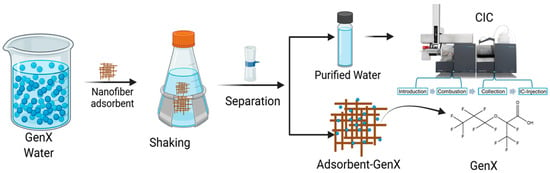
Figure 2.
Schematic diagram of GenX adsorption test.
2.5. GenX Analysis
After adsorption, the nanofibrous adsorbent was removed from the GenX water by being filtered with a 0.45 µm glass microfiber membrane. The concentration of GenX was determined by using a TE Instruments (Houston, TX, USA) XPREP Combustion–Ion Chromatography (C-IC) combustion module coupled with a Metrohm 930 Compact IC Flex system. In this C-IC analysis, the GenX solution sample was first absorbed onto activated carbon and subsequently combusted at 1000 °C in a stream of oxygen/argon. The resulting gaseous hydrogen fluoride was then absorbed into reagent water, and the produced fluoride ions were separated by the IC and identified by comparing the retention time with the calibration standard under identical IC conditions. The GenX concentration was calculated from the fluoride ion (F−) concentration using Equation (1).
where CGenX is the concentration of GenX solution in ppb (μg/mL), CF is the total concentration of fluoride ion in the sample solution from C-IC in ppb, MWGenX is the molecular weight of GenX in g/mol, MWF is the atomic weight of fluorine in g/mol, and nF is the number of fluorine atoms in the GenX molecule.
CGenX = CF × MWGenX/(nF × MWF)
The GenX removal percentage was calculated using Equation (2).
where Ci and Cf are the initial and final GenX concentration, respectively, before and after adsorption. For each nanofiber sample, the adsorption test was carried out three times. The final results were reported as an average ± standard deviation.
The GenX adsorption capacity of the PANI-ESPAN nanofibrous adsorbent was determined using Equation (3).
where Ci and Cf are the initial and final GenX concentrations before and after adsorption, w is the weight of the adsorbent in g, and V is the volume of the GenX solution in L.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of PANI-ESPAN Nanofibrous Adsorbent
3.1.1. PANI Coating
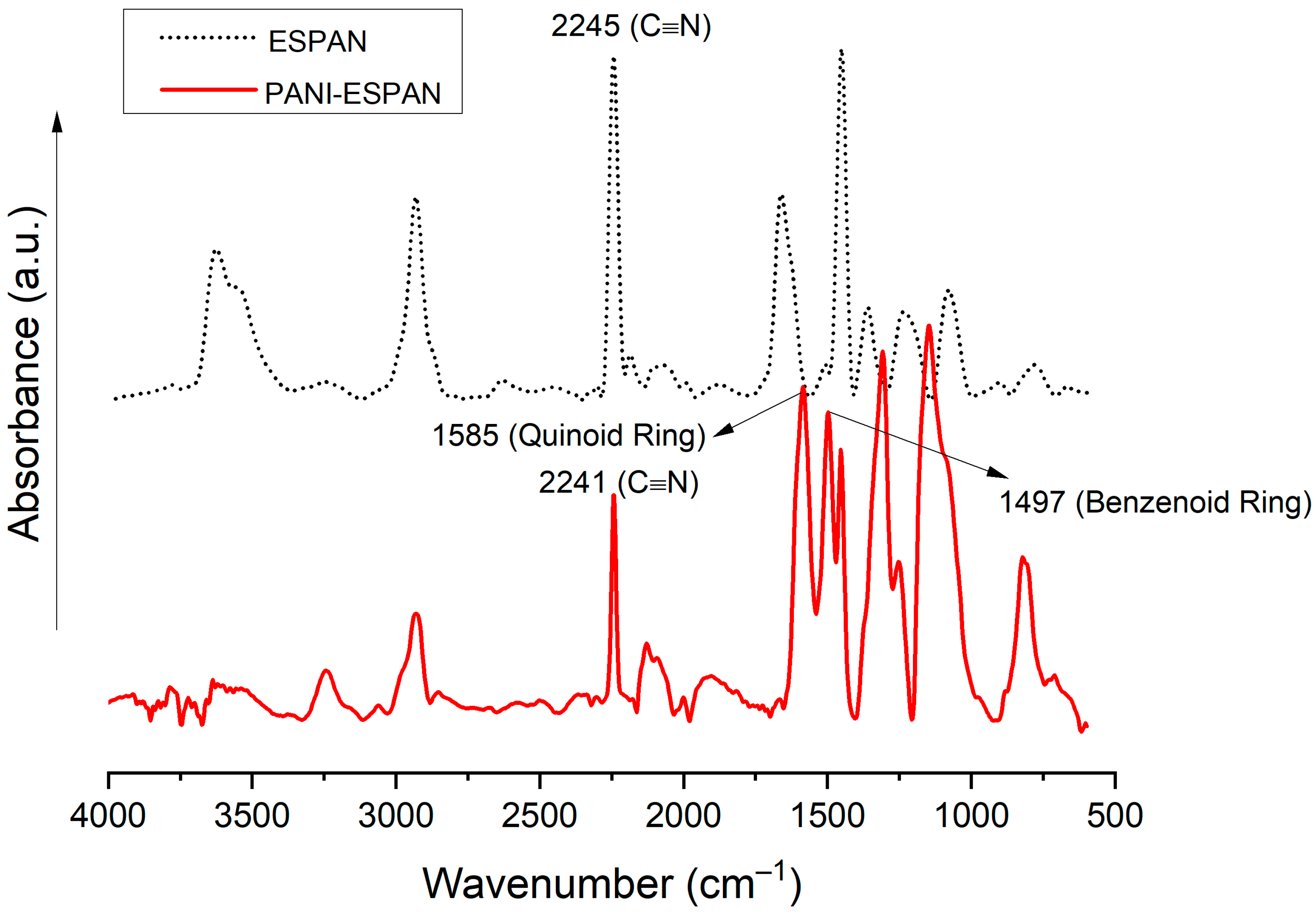
FTIR was used to verify PANI coating formation on the ESPAN nanofibers (Figure 3). The characteristic IR peak of PAN is the one centered at ~2240 cm−1, which is attributed to the stretching vibration of the nitrile groups (-C≡N). The characteristic IR peaks of PANI are the two peaks centered at ~1585 cm−1 and 1497 cm−1, which are attributed to the quinoid and benzenoid ring stretching deformation, respectively [18,19]. The PANI-ESPAN nanofibrous adsorbent showed both characteristic peaks of PAN and PANI, indicating a successful coating of PANI on ESPAN nanofibers. In the meantime, the characteristic IR peaks of the nitrile groups shifted to a lower wavenumber in the coated nanofibers, indicating a dipole–dipole interaction between the PANI and ESPAN.
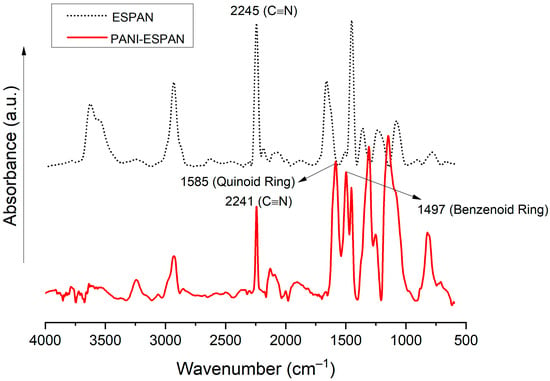
Figure 3.
FTIR spectra of ESPAN and PANI-ESPAN nanofibers.
3.1.2. Morphology
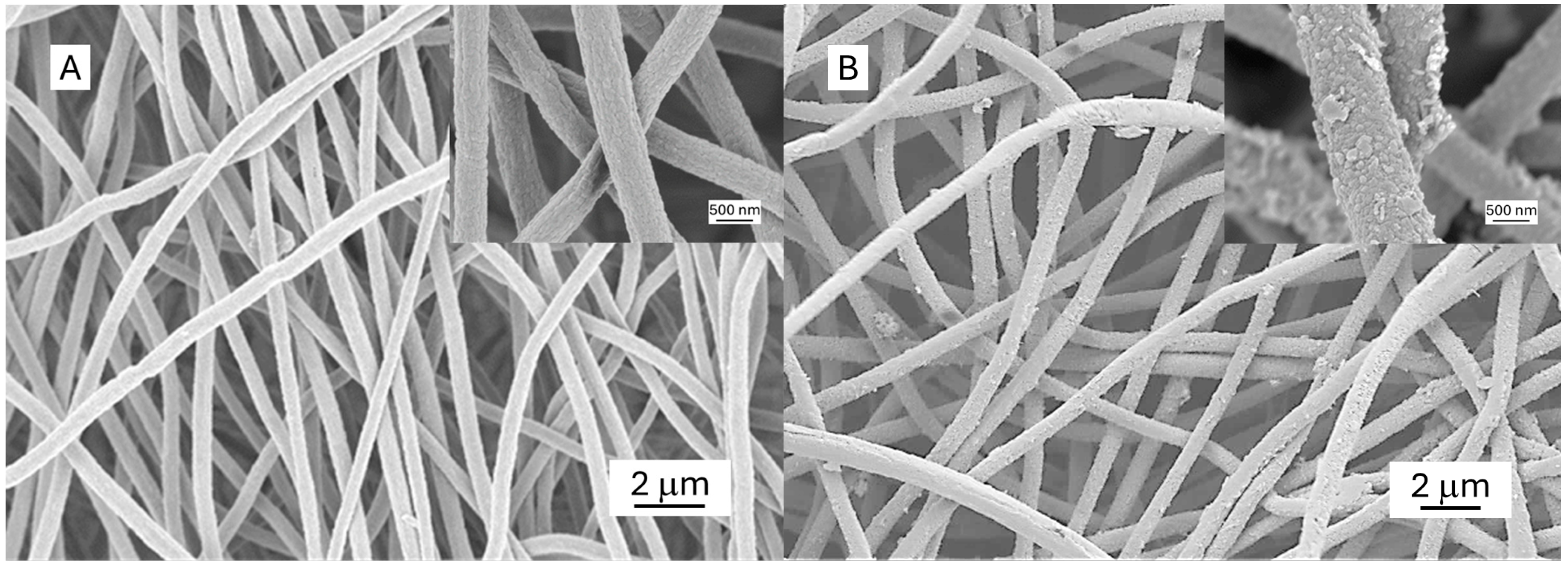
The morphology of the ESPAN and PANI-ESPAN nanofibrous adsorbents was characterized by SEM (Figure 4). The ESPAN nanofibers showed an average diameter of ~430 nm and a relatively smooth surface. After being coated with PANI, the average diameter of the ESPAN nanofibers increased to ~600 nm, indicating a ~85 nm thick PANI coating on the ESPAN nanofibers. In addition, the surface of the ESPAN nanofibers became very rough.
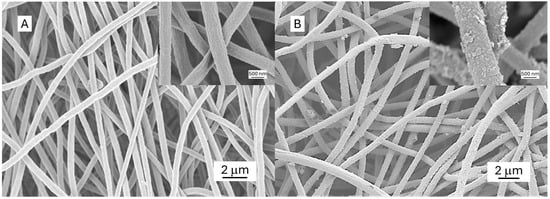
Figure 4.
Representative SEM images of the ESPAN (A) and PANI-ESPAN (B) nanofibrous adsorbents. The inserts are high-magnification images.
3.1.3. Specific Surface Area and Pore Volume
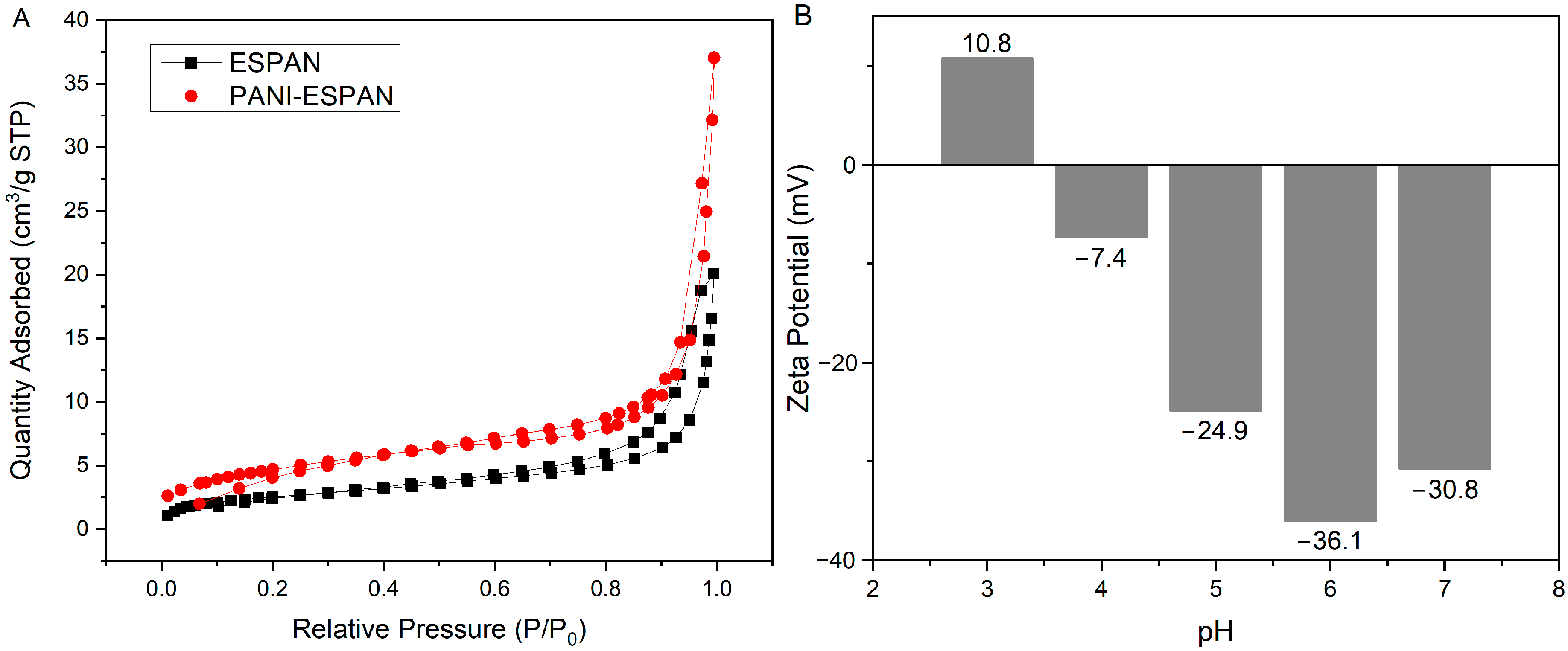
Nitrogen adsorption–desorption isotherms were used to determine the specific surface area and average pore diameter of the ESPAN and PANI-ESPAN nanofibrous adsorbents (Figure 5A). Both ESPAN and PANI-ESPAN exhibited a type IV isotherm, as indicated by the sharp increase in adsorption at higher relative pressures (P/P0 > 0.8). This is a characteristic of mesoporous materials. The presence of a hysteresis loop further confirmed the mesoporous nature of these materials. The ESPAN/PANI nanofibers showed significantly more N2 adsorption at higher relative pressures compared to ESPAN, indicating a higher surface area and a larger total pore volume. The ESPAN nanofibrous adsorbent showed a BET specific surface area of 9.1 m2/g, an average pore size of 18.4 nm, and an average pore volume of 0.028 cm3/g. As expected, the PANI-ESPAN nanofibrous adsorbent exhibited a higher BET specific surface area (16.8 m2/g), a reduced average pore size (13.7 nm), and a doubled pore volume (0.057 cm3/g). This is consistent with the rough surface of ESPAN nanofibers after PANI coating (Figure 4B).
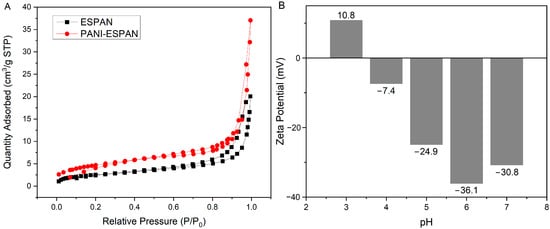
Figure 5.
N2 adsorption/desorption isotherms of ESPAN and PANI-ESPAN nanofibers (A) and zeta potential of PANI-ESPAN nanofibers at different pHs in DI water (B).
3.1.4. Surface Charge
The zeta potentials of the PANI-ESPAN nanofibers were measured at pH = 3, 4, 5, 6, and 7 and used to evaluate the corresponding surface charges (Figure 5B). It was observed that at a low pH (pH = 3), the PANI-ESPAN nanofibers possessed positive zeta potential. In this acidic environment, the protonation of nitrogen atoms in the PANI molecules resulted in a positive surface charge on the nanofibers. The PANI-ESPAN nanofibers possesed a negative zeta potential at pH = 4 and beyond and reached the maximum value (36.1 mV) at a near neutral condition (pH = 6) due to the combined effect of the reduction in the PANI’s positive zeta potential along with the value increase in the ESPAN’s negative potential [13] with the increase of pH.
3.2. Performance of PANI-ESPAN Nanofibrous Adsorbent in GenX Removal
3.2.1. GenX Adsorption on PANI-ESPAN Nanofibrous Adsorbent
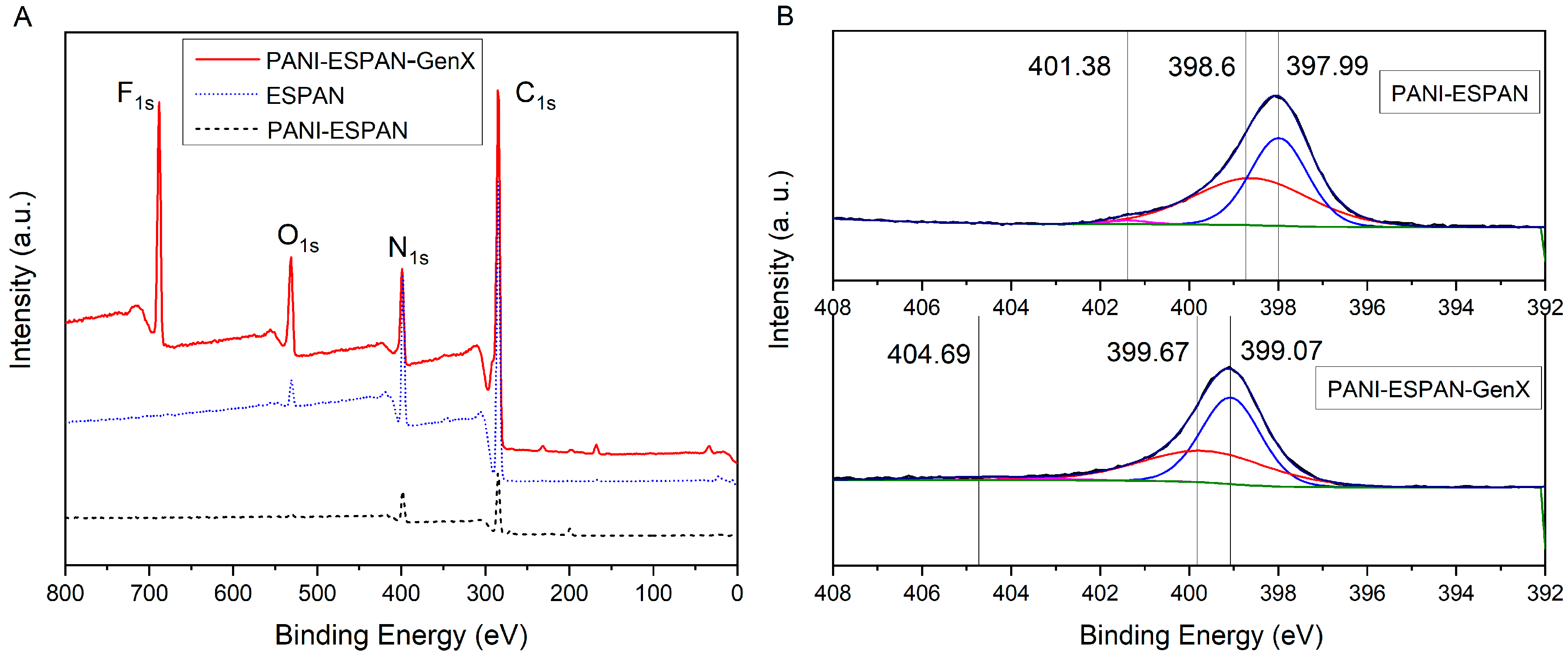
To evaluate the GenX adsorption on the PANI-ESPAN nanofibrous adsorbent, XPS was conducted before and after GenX adsorption. When using 0.06 g of PANI-ESPAN nanofibrous adsorbent in contact with 100 mL of 100 ppb GenX water at pH = 6 for 12 h, the PANI-ESPAN nanofibrous adsorbent showed a significant F1s peak after GenX adsorption (Figure 6), confirming that GenX was adsorbed on the nanofibrous adsorbent. Specifically, element F was 13.13 atom% in this case, and the binding energies of F1s were 688.48 eV and 688.73 eV according to the high-resolution XPS, indicating the presence of organic fluorine molecules. This is consistent with the C-F structure in GenX molecules. The high-resolution XPS spectrum of the PANI-ESPAN nanofibrous adsorbent exhibited three N1s deconvoluted peaks at 397.99 eV, 398.6 eV, and 401.38 eV, corresponding to imine (=N-), amine (-NH-), and protonated imine (-N+=), respectively [20,21]. After GenX adsorption, the N1s peaks shifted to 399.07 eV, 399.67 eV, and 404.69 eV, with increases of +1.07 eV, +1.08 eV, and +3.31 eV, respectively. The shift in the N1s binding energy towards the higher end indicated a change in the chemical environment of PANI-ESPAN due to the adsorption of GenX molecules, which could be ascribed to the inductive effect of nearby F atoms from GenX because F atoms are highly electronegative and can withdraw electron density from adjacent atoms. This result confirmed the GenX adsorption on the PANI-ESPAN nanofibrous adsorbent.
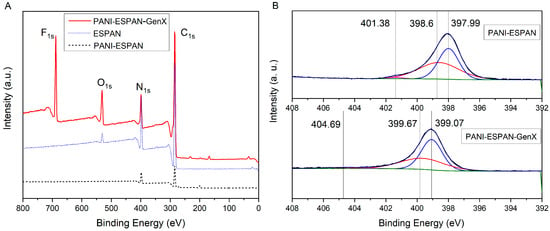
Figure 6.
XPS survey spectra of ESPAN, PANI-ESPAN, and PANI-ESPAN after GenX adsorption (PANI-ESPAN-GenX) (A) and high-resolution XPS spectra showing N1s deconvoluted peaks of PANI-ESPAN before and after GenX adsorption (B).
To acquire a full picture of the PANI-ESPAN nanofibrous adsorbent’s performance in GenX removal from water, we studied the effects of the pH, GenX concentration, adsorbent loading, and contact time on the GenX adsorption performance of PANI-ESPAN.
3.2.2. Effect of pH
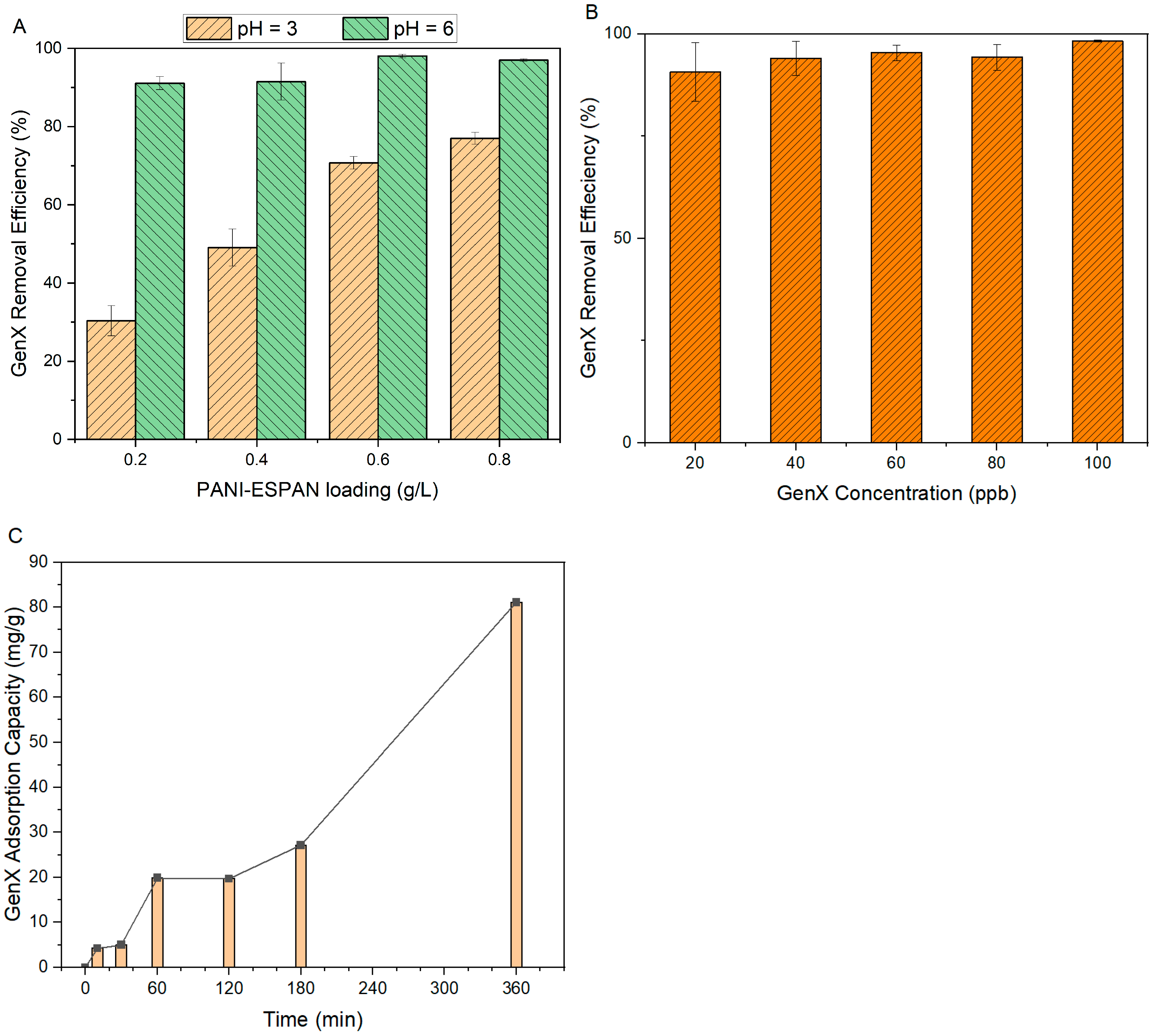
As shown earlier, the surface charge of the PANI-ESPAN varied with the pH of the solution (Figure 5B). At a low pH, PANI was more protonated, leading to a positively charged PANI-ESPAN surface. Conversely, at a high pH, PANI became less protonated, reducing PANI-ESPAN’s positive charge or even showing negative charge. Thus, the GenX adsorption capacity of the PANI-ESPAN nanofibrous adsorbent should be pH-dependent. Based on the pKa of GenX (3.82) [22], as well as the pH of the GenX water (pH = 6), two pHs, i.e., pH = 3 and pH = 6, were studied as representatives. A higher GenX adsorption capacity was observed for the PANI-ESPAN nanofibrous adsorbent at pH = 6 than at pH = 3 (Figure 7A). For example, the PANI-ESPAN nanofibrous adsorbent showed 98% GenX adsorption from 100 mL of 100 ppb GenX water at pH = 6 and 0.6 g/L loading with a contact time of 12 h. The corresponding efficiency of GenX adsorption dropped to 78% at pH = 3. For comparison, the ESPAN nanofibrous adsorbent (without PANI coating) only showed ~1% GenX removal at pH = 6 under the same conditions, indicating a greatly improved GenX adsorption efficiency with a PANI coating.
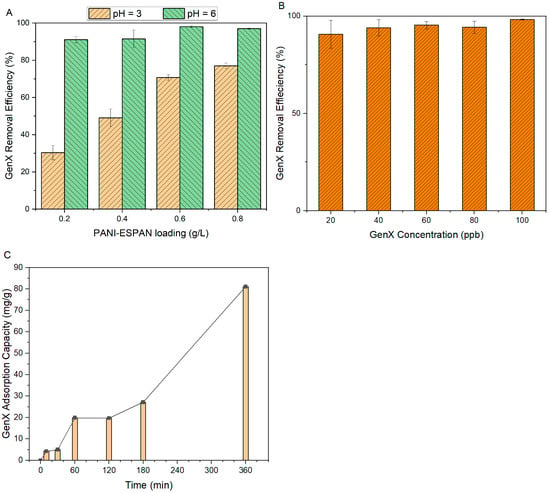
Figure 7.
GenX adsorption efficiency of PANI-ESPAN nanofibrous adsorbent: (A) pH and nanofibrous adsorbent loading effect; (B) GenX concentration effect; (C) contact time effect.
3.2.3. Effect of Adsorbent Loading
The nanofibrous adsorbent loading, essentially the amount of nanofibrous adsorbent that was used per unit volume of water, significantly influenced its GenX removal efficiency. An increase in adsorbent loading led to higher levels of GenX removal. With 100 mL of 100 ppb GenX water at a pH of 6 under a 12 h contact time, as the loading of PANI-ESPAN increased from 0.02 g to 0.06 g, the removal efficiency of GenX increased steadily (Figure 7A). At 0.06 g and beyond, the GenX removal efficiency of PANI-ESPAN appeared to reach a plateau, remaining close to 100%. The larger adsorbent loading was, the more adsorption sites there were. Once a certain amount of nanofibrous adsorbent was reached, nearly all GenX in the solution could be captured/adsorbed.
3.2.4. Effect of GenX Concentration
The GenX removal efficiency of the PANI-ESPAN nanofibrous adsorbent did not change significantly with the change in GenX concentration in the range of 20–100 ppb (Figure 7B) under the conditions of 100 mL of GenX water at pH = 6, 0.6 g/L of PANI-ESPAN loading, and a 12 h contact time. The GenX removal efficiency of PANI-ESPAN remained quite high, nearly reaching 100%. This indicated that under these concentrations, the 0.6 g/L loading of the PANI-ESPAN nanofibrous adsorbent had sufficient adsorption capacity to remove almost all the GenX from the water and not yet reach the maximum adsorption capacity.
3.2.5. Effect of Contact Time
The effect of the contact time on the GenX adsorption of the PANI-ESPAN nanofibrous adsorbent was evaluated in 200 mL of 100 ppm GenX aqueous solution with 0.06 g of PANI-ESPAN nanofibrous adsorbent (Figure 7C). The contact time ranged from 10 min to 360 min (6 h). There was a fast increase in the adsorption of GenX in the first 60 min, indicating a rapid uptake of GenX molecules by PANI-ESPAN at the beginning of GenX adsorption as abundant adsorption sites were available. Afterwards, the GenX adsorption leveled off, suggesting that most of the easily accessible surface adsorption sites of the PANI-ESPAN became occupied. Then, the GenX adsorption increased significantly again. This could have been caused by the deep diffusion of GenX molecules into the nanofibrous adsorbent. After 6 h, the GenX adsorption of the PANI-ESPAN nanofibrous adsorbent reached 81.1 mg of GenX/g PANI-ESPAN.
3.3. GenX Adsorption Mechanism
It was observed that the PANI-ESPAN nanofibrous adsorbent showed better adsorption of GenX at pH = 6 than at pH = 3. The pKa of GenX is known to be 3.82. At pH = 3, the GenX molecules stayed largely in a neutral/molecular form (>87% according to the Henderson–Hasselbalch equation). At the same time, the PANI existed in an emerald salt form, and the PANI-ESPAN nanofibers possessed positive charges, as shown in Figure 5B. Although the positive charges on the PANI-ESPAN nanofibers were in favor of a Coulomb interaction with the GenX anions (COO−) at this pH, due to the relatively small amount of GenX anions, the interaction between the GenX molecules and PANI-ESPAN nanofiber surface should be mainly non-Coulomb interactions, including hydrophobic interactions and dipole–dipole interactions/hydrogen bonding. However, the efficiency of these non-Coulomb interactions was weakened by the positively charged PANI-ESPAN surface. Under this pH, there were not enough Coulomb interactions or non-Coulomb interactions between the GenX molecules and PANI-ESPAN nanofibers for a better adsorption performance. Furthermore, the PANI-ESPAN nanofibers possessed positive charges at pH = 3 but negative charges at pH = 4 (Figure 5B). Therefore, the PANI-ESPAN nanofibers have an isoelectric point in the range of pH = 3 and pH = 4. At pH = 3, the PANI-ESPAN nanofibers were prone to be in a compact conformation [23], which could limit the access of GenX molecules to the adsorption sites on the nanofiber surface and significantly reduce its GenX adsorption performance.
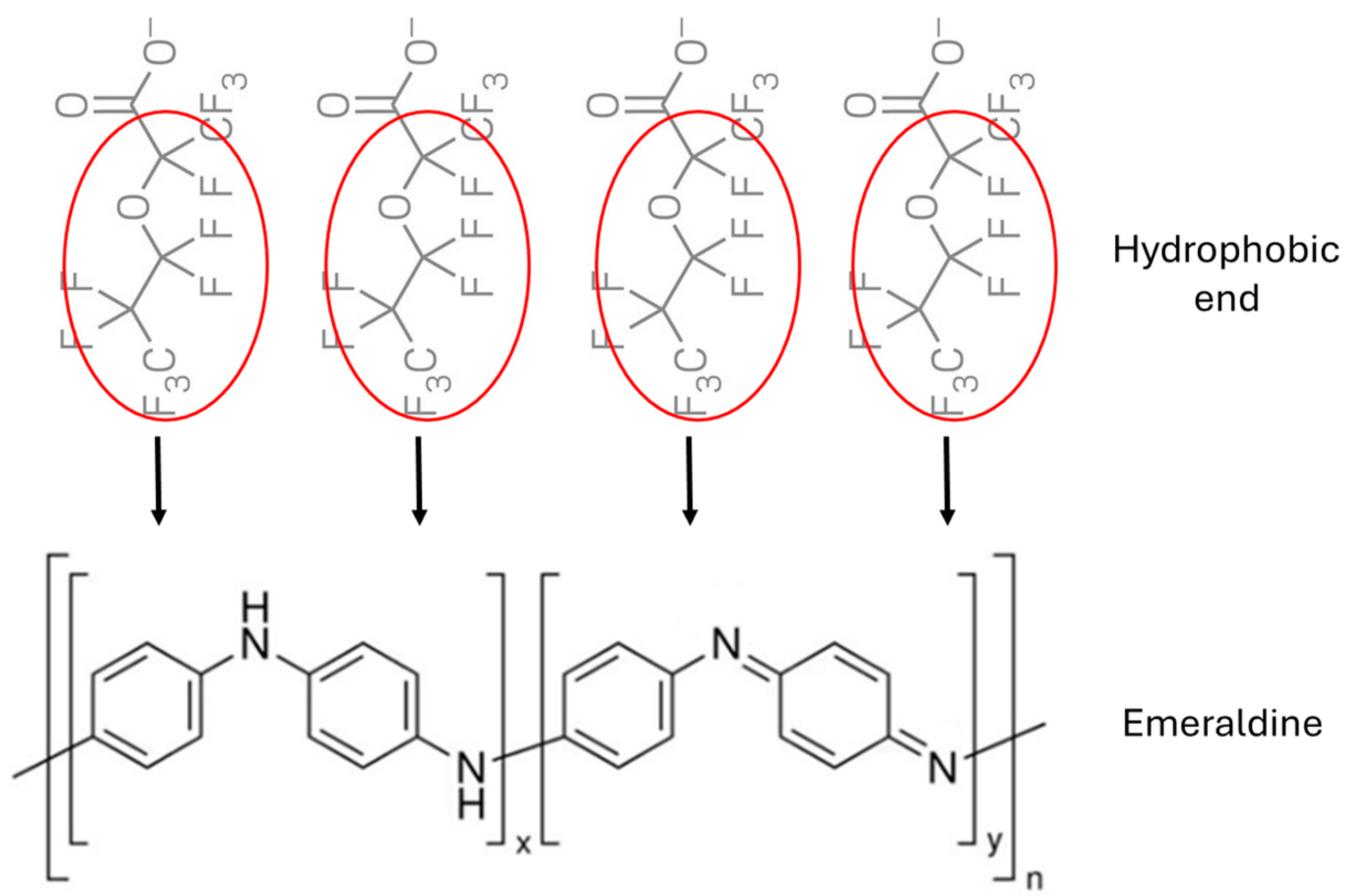
At pH = 6, the ionization of GenX molecules in water was more than 99% based on the pKa of GenX and the Henderson–Hasselbalch equation. In this instance, nearly all GenX molecules existed with an ionic end of -COO−. In the meantime, PANI lost its emeraldine salt form and existed mainly in a neutral emeraldine form. The PANI-ESPAN nanofibers bore a relatively large negative charge (Figure 5B). Although the repulsive force between GenX anions (-COO−) and negative surface charges of PANI-ESPAN nanofibers was not in favor of GenX adsorption, the much larger nanofibers could allow the small GenX anions to approach the surface of the nanofibers through their relatively much bigger hydrophobic parts (Figure 8). More importantly, the PANI-ESPAN nanofibers were prone to be in an extended conformation at pH = 6 due to intra-fiber repulsive forces with a simultaneous reduction in nanofiber agglomeration due to inter-fiber repulsive forces, which could expose more available adsorption sites to GenX molecules in water and thus facilitate GenX adsorption.
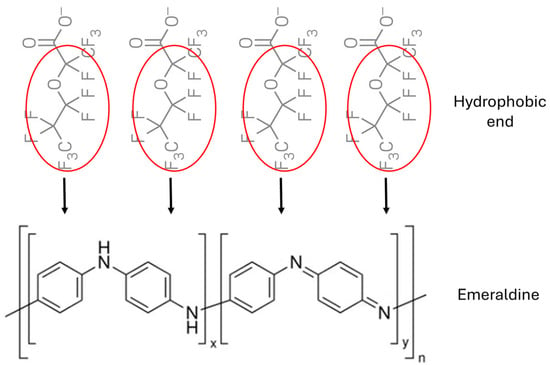
Figure 8.
Schematic diagram of GenX adsorption on PANI-ESPAN nanofibrous adsorbent at pH = 6.
To check the Coulomb interaction between the PANI-ESPAN and GenX, a GenX adsorption test was implemented, following the same procedure as described earlier (0.06 g of PANI-ESPAN nanofibrous adsorbent in contact with 100 mL of 100 ppb GenX water at pH = 6 for 12 h), but with the addition of NaCl to the GenX water. Specifically, NaCl was added to 100 ppb GenX water at a concentration of 5.84 ppm. Then, the PANI-ESPAN nanofibrous adsorbent exhibited a reduced GenX removal efficiency from 98% to 82%. The 16% reduction in GenX removal efficiency of PANI-ESPAN in the presence of NaCl could be ascribed to the shielding effect from Na+ and Cl− ions, which reduced the Coulomb interaction between the GenX anions and PANI-ESPAN nanofibers. The lasting GenX removal capacity of PANI-ESPAN should come from non-Coulomb interactions, including hydrophobic interactions, dipole–dipole interactions, and possible hydrogen bonding, based on the chemical structures of PANI and GenX.
To estimate the maximum GenX adsorption capacity of the PANI-ESPAN nanofibrous adsorbent, we carried out a GenX adsorption test with 0.06 g of PANI-ESPAN in 50 mL of 520 ppm GenX water at pH = 6. After 12 h of contact, the nanofibrous adsorbent material reached equilibrium and showed a GenX adsorption efficiency of 33.7%. Thus, the PANI-ESPAN nanofibrous adsorbent had a GenX adsorption capacity of ~146 mg GenX/g or ~0.42 mmol GenX/g at pH = 6.
It is worth noting that the ESPAN nanofibrous adsorbent exhibited a significantly reduced GenX adsorption efficiency at a 100 ppb concentration compared with at a 100 ppm concentration at pH = 6 [13]. The main reason could be attributed to the ESPAN’s surface hydrophobicity and the electrostatic repulsion between the negatively charged ESPAN surface and GenX anions at this pH under an ultralow concentration gradient. In contrast, the PANI-ESPAN nanofibrous adsorbent had a hydrophilic surface due to the PANI coating, more extended nanofiber conformation due to the larger value of zeta potential, as well as less electrostatic repulsion between the GenX molecules and nanofiber surface with the PANI coating (Figure 8), which facilitated GenX adsorption even at a much lower concentration.
Overall, the PANI-ESPAN nanofibrous adsorbent exhibited excellent adsorption capability for GenX removal from water through the combination of non-Coulomb interactions and Coulomb interactions, with non-Coulomb interactions being predominant. As PANI is inherently stable under various environmental conditions, the risk of secondary pollution is minimized. The coupling of unique properties of PANI with the ESPAN nanofibers offers a versatile and efficient solution to address current short-chain PFAS (e.g., GenX) contamination in the practice of water purification and holds promise for ensuring clean and safe water for communities worldwide.
4. Conclusions
A polyaniline (PANI)-coated polyacrylonitrile (PAN) nanofibrous adsorbent (PANI-ESPAN) was successfully developed by electrospinning a PAN in a DMF solution, followed by an in situ polymerization of aniline on the surface of electrospun PAN (ESPAN) nanofibers. Compared to ESPAN, the prepared PANI-ESPAN nanofibers showed a rougher surface morphology, larger fiber size (+170 nm), and higher specific surface area (+85%). From the GenX adsorption test, it was found that the PANI-ESPAN nanofibrous adsorbent at a loading of 0.6 g/L could nearly removal all GenX molecules from 100 ppb GenX water (>98%) at pH = 6 with a contact time of 12 h, which greatly outperformed ESPAN under these conditions. The GenX adsorption mechanism of the PANI-ESPAN nanofibrous adsorbent was found to be mainly through non-Coulomb interactions (hydrophobic, dipole–dipole, and hydrogen bonding), while Coulomb interactions (electrostatic interaction) also played a role in the adsorption.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: L.Z.; Methodology: I.J., E.A.T. and H.V.P.; Validation: I.J. and L.Z.; Formal Analysis: I.J.; Investigation: I.J., E.A.T. and H.V.P.; Resources: L.Z. and R.Z.; Writing—Original Draft Preparation: I.J.; Writing—Review and Editing: L.Z.; Supervision: L.Z. and R.Z.; Project Administration: L.Z.; Funding Acquisition: L.Z. and R.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was partially funded by North Carolina Collaboratory Funds ID: Collab_245 and Collab_397.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author(s).
Acknowledgments
This work was conducted at the Joint School of Nanoscience and Nanoengineering of North Carolina A&T State University, a member of the Southeastern Nanotechnology Infrastructure Corridor (SENIC) and National Nanotechnology Coordinated Infrastructure (NNCI), which is supported by the National Science Foundation (ECCS-2025462).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Amen, R.; Ibrahim, A.; Shafqat, W.; Hassan, E.B. A Critical Review on PFAS Removal from Water: Removal Mechanism and Future Challenges. Sustainability 2023, 15, 16173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brendel, S.; Fetter, E.; Staude, C.; Vierke, L.; Biegel-Engler, A. Short-Chain Perfluoroalkyl Acids: Environmental Concerns and a Regulatory Strategy Under REACH. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2018, 30, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucharzyk, K.H.; Darlington, R.; Benotti, M.; Deeb, R.; Hawley, E. Novel Treatment Technologies for PFAS Compounds: A Critical Rreview. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 204, 757–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagliano, E.; Sgroi, M.; Falciglia, P.P.; Vagliasindi, F.G.A.; Roccaro, P. Removal of Poly- and Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) from Water by Adsorption: Role of PFAS Chain Length, Effect of Organic Matter and Challenges in Adsorbent Regeneration. Water Res. 2020, 171, 115381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaleshtari, Z.A.; Foudazi, R. A Review on Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) Remediation: Separation Mechanisms and Molecular Interactions. ACS ES&T Water 2022, 2, 2258–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.; Lian, Q.; Zhang, X.; Karsili, T.K.; Holmes, W.; Chen, Y.; Zappi, M.E.; Gang, D.D. A Review of PFAS Adsorption from Aqueous Solutions: Current Approaches, Engineering Applications, Challenges, and Opportunities. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 321, 121138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.B.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Kim, K.-Y.; Won, S.W. Removal of Short- and Long-Chain PFAS from Aquatic Systems Using Electrostatic Attraction of Polyethylenimine-Polyvinyl Chloride Electrospun Nanofiber Adsorbent. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 326, 124853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, C.T.; Wu, T. Recent Progress in Adsorptive Removal of Per- and Poly-Fluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) from Water/Wastewater. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 52, 90–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Maimaiti, A.; Shi, H.; Wu, R.; Wang, R.; Li, Z.; Qi, D.; Yu, G.; Deng, S. Adsorption Behavior and Mechanism of Emerging Perfluoro-2-Propoxypropanoic Acid (GenX) on Activated Carbons and Resins. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 364, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, W.; Xiao, L.; Ling, Y.; Ching, C.; Matsumoto, M.; Bisbey, R.P.; Helbling, D.E.; Dichtel, W.R. Removal of GenX and Perfluorinated Alkyl Substances from Water by Amine-Functionalized Covalent Organic Frameworks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 12677–12681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.-J.; Hwangbo, M.; Chen, Z.; Liu, Y.; Kameoka, J.; Chu, K.-H. Reusable Functionalized Hydrogel Sorbents for Removing Long- and Short-Chain Perfluoroalkyl Acids (PFAAs) and GenX from Aqueous Solution. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 17447–17455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maske, V.A.; Kokate, A.M.; More, P.A.; Salunkhe, R.S.; More, A.P. A Comprehensive Review of Polyacrylonitrile Membranes: Modifications and Applications. Polym. Bull. 2024, 81, 16415–16455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantripragada, S.; Deng, D.; Zhang, L. Remediation of GenX from Water by Amidoxime Surface-Functionalized Electrospun Polyacrylonitrile Nanofibrous Adsorbent. Chemosphere 2021, 283, 131235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olshansky, Y.; Gomeniuc, A.; Chorover, J.; Abrell, L.; Field, J.A.; Hatton, J.; He, J.; Sierra-Alvarez, R. Tailored Polyanilines Are High-Affinity Adsorbents for Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances. ACS EST Water 2022, 2, 1402–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, N.; Atassi, Y. Enhancement of Removal Efficiency of Heavy Metal Ions by Polyaniline Deposition on Electrospun Polyacrylonitrile Membranes. Water Sci. Eng. 2021, 14, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, N.; Atassi, Y. Adsorption of Methylene Blue onto Electrospun Nanofibrous Membranes of Polylactic Acid and Polyacrylonitrile Coated with Chloride Doped Polyaniline. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakiba, M.; Nabavi, S.R.; Emadi, H.; Faraji, M. Development of a Superhydrophilic Nanofiber Membrane for Oil/Water Emulsion Separation via Modification of Polyacrylonitrile/Polyaniline Composite. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2021, 32, 1301–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trchova, M.; Sedenkova, I.; Tobolkova, E.; Stejskal, J. FTIR Spectroscopic and Conductivity Study of the Thermal Degradation of Polyaniline Films. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2004, 86, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Hu, X.B.; Wang, J.Y.; Boughton, R.I. Structure, Conductivity, and Thermopower of Crystalline Polyaniline Synthesized by the Ultrasonic Irradiation Polymerization Method. Macromolecules 2022, 35, 9414–9419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graves, D.A.; Thodoroviez, L.B.; de Oliveira, T.C.; Cividanes, L.S.; Ferreira, N.G.; Almeida, D.A.L.; Goncalves, E.S. Enhanced electrochemical properties of polyaniline (PANI) films electrodeposited on carbon fiber felt (CFF): Influence of monomer/acid ratio and deposition time parameters in energy storage applications. Electrochim. Acta 2023, 454, 142388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Chen, Y.; Luo, X.; Guo, H.; Wang, N.; Su, D.; Zhang, C.; Liu, T.; Wang, G.; Cui, L. Polyaniline engineering defect-induced nitrogen doped carbo-supported Co3O4 hybrid composite as a high-efficiency electrocatalyst for oxygen evolution reaction. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 526, 146626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantripragada, S.; Dong, M.; Zhang, L. Sustainable filter/adsorbent materials from cellulose-based electrospun nanofibrous membranes with soy protein coating for high-efficiency GenX fluorocarbon remediation from water. Cellulose 2023, 30, 7063–7078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olshansky, Y.; Gomeniuc, A.; Chorover, J.; Abrell, L.; Field, J.A.; Hatton, J.; Sierra-Alvarez, R. Synthesis and Characterization of Customizable Polyaniline-Derived Polymers and Their Application for Perfluorooctanoic Acid Removal from Aqueous Solution. ACS EST Water 2021, 1, 1438–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).