Abstract
The sapwood and heartwood of European larch (Larix decidua Mill.) are both used in industrial applications, but they differ in structure and composition, which may lead to surface property differences. This study compared their surface characteristics (on radial and tangential sections) after sanding with aluminium oxide papers of four grit sizes (P60, P120, P180, P240). Surface roughness (Ra, Rz), wettability (contact angle with two reference liquids: water and diiodomethane, 3 and 30 s after droplet deposition), surface free energy, and colour parameters (L*, a*, b*) were analysed. Microscopic measurements were also performed to assess anatomical differences between sapwood and heartwood. The results showed no significant differences in roughness (Ra, Rz) between sapwood and heartwood. Measurement direction and sandpaper grit accounted for about 80% of variability in roughness parameters. Wettability was mainly influenced by wood area, with its effect ranging from 55% to 89% depending on measurement time. The sapwood was characterised by the lower wettability on the tangential section, while the heartwood was characterised by the lower wettability on the radial section. This was examined for the contact angle tests performed 3 s after the water droplet had been applied to the wood surface. Such dependencies were not observed after 30 s. Sapwood exhibited higher surface free energy (SFE) values than heartwood. The greatest colour change ΔE, at level 2.59, was noted for the heartwood on the radial section after sanding with P240 sandpaper.
Keywords:
anatomical structure; European larch; heartwood; roughness; sanding; sapwood; tracheids; wettability 1. Introduction
Wood has long been valued for its versatility and sustainability. In recent years, its use has gained renewed interest in various industries due to growing environmental awareness. Sanding is a key surface preparation step in the final stages of wood processing. Its main objectives are to ensure the smoothness required for painting, provide the appropriate roughness for effective gluing, and maintain or enhance the aesthetic appearance of the wood [1,2,3,4,5]. However, in order for sanding to effectively improve the surface quality, the sanding parameters must be optimally selected. When planning a technological sanding process, many aspects should be considered. The key aspects of the sanded material that affect the final condition of the surface after sanding are the type of wood, its moisture content, and intended use [6,7,8,9,10,11]. In addition to the properties of the material itself, which is sanded wood, the final appearance of the surface (primarily its roughness, durability, and gluing ability) is significantly influenced by the selection of production equipment, the size and type of abrasive grains, and comprehensive sanding process variables [12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20]. In general, the sanding process is intended to reduce the surface roughness of wood resulting from previous machining operations, depending on the tool used and processing parameters, such as cutting speed or tool pressure [21,22]. In addition, sanding can modify the microstructure of the wood surface, which affects its ability to absorb moisture and therefore its wettability [23,24,25]. Generally, sanding wood results in reduced surface roughness, leading to reduced wettability [26]. Wood wettability, which refers to the tendency of a liquid to spread across and adhere to the wood surface, plays a critical role in how the material interacts with protective coatings such as varnishes and impregnations. Numerous studies have shown that sanding parameters need to be carefully adapted not only to the wood species being processed [27,28,29], but also to the specific anatomical orientation of the surface [30,31]. This is due to the fact that wood is a heterogeneous material (differences in chemical composition, structure, physical properties) even in the case of the same species (genetic diversity, environmental influences). Undoubtedly, the most important properties of wood that influence the selection of appropriate sanding parameters include anatomical feature dimensions [28,29] and wood hardness [32,33,34]. The cited studies show that the sanding parameters must be individually developed for each type of wood in the context of its subsequent finishing, the application of protective coatings, material durability, and aesthetic values. Among the many factors influencing the sanding efficiency and the quality of the obtained surface, the determining factors are the type of wood and the abrasive grain characteristics [4]. Various types of abrasive papers are available, differing in both the kind of abrasive material used and the grain size. However, it is the grain size that has the most significant impact on the resulting surface roughness.
Most research on the sanding process is conducted for species with a wide range of applications in industry, mainly furniture. Larch is the species often used for this [35]. This wood is often used both in construction (building facades, window and door joinery, terrace boards) and in furniture. There is a wealth of information regarding the anatomical structure and chemical, physical, and mechanical properties of this wood. Its surface performance, however, has not yet been thoroughly investigated. In the case of larch, both the sapwood and the heartwood areas are valuable in industry. Although larch wood is composed mainly of a narrow sapwood and the sapwood constitutes a small percentage of the harvested timber (usually 5–10 rings from the bark side), in cases where wood is harvested from younger trees, it can constitute a much larger percentage [36]. In exterior applications and generally as structural wood, larch wood with the smallest possible sapwood share is actually used. Due to the very large number of extractives in larch heartwood (including arabinogalactan and phenolic compounds), it has a much greater resistance to biological factors and better strength parameters than sapwood [37,38]. However, in some applications, larch sapwood can be a cheaper alternative to heartwood, e.g., larch wood intended for impregnation. Impregnated sapwood sometimes outperforms unimpregnated heartwood in biological durability [39,40]. Larch sapwood may also be desirable in the production of veneers, furniture, and various types of woodworking accessories. It is lighter, without dark streaks, and is easier to dye than heartwood. The light colour of the wood and its high degree of smoothness are desirable features in light, elegant arrangements [41,42], and brightness and smoothness are typical features of polished larch sapwood.
Differences in the anatomical structure and chemical composition of the sapwood and heartwood may lead to different reactions of these areas to mechanical processes, including sanding. Heartwood, saturated with extractive substances, usually has higher hardness and lower water absorption compared to sapwood, which may affect the evenness of the processed surface [43,44]. Studies carried out on European larch (Larix decidua Mill.) have shown that sapwood, as an actively conductive layer of wood, is more porous and hydrophobic after treatment, which may affect the absorption of finishing materials [45].
The aim of the research was to investigate the influence of one of the most important sanding factors, which is the size of the abrasive grains, on selected surface parameters of European larch (Larix decidua Mill.) sapwood and heartwood, i.e., roughness, wettability, and colour, in the context of specific properties of this species. This research can contribute to a better understanding of how different processing parameters affect the quality of the wood’s surface, which is of great importance in further processing stages and industrial applications of larch wood.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Wood Preparation
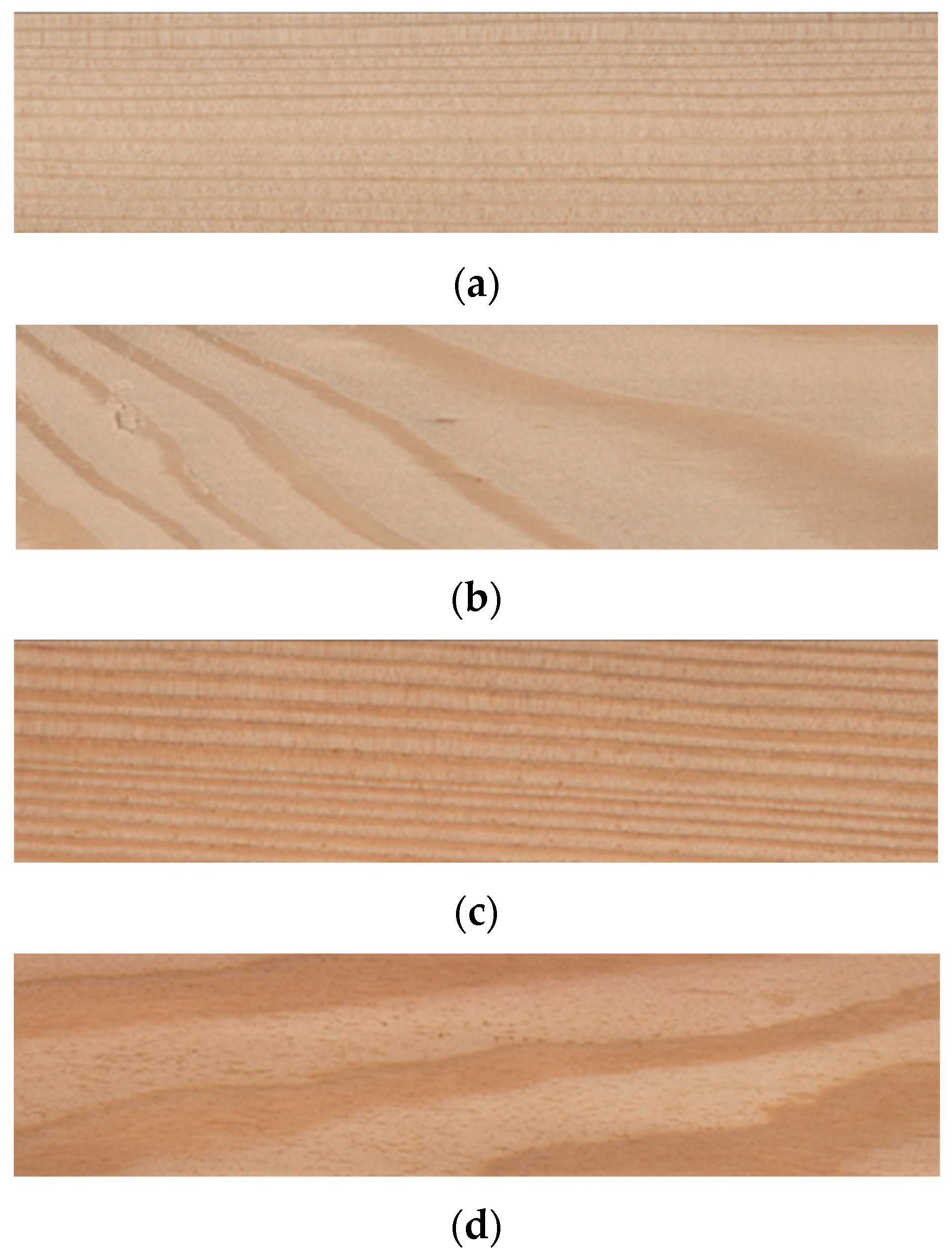
For the study, the sapwood and heartwood of European larch (Larix decidua Mill.) were used (Figure 1). Samples with dimensions of 150 mm × 50 mm × 10 mm were prepared, with the longest side (150 mm) oriented parallel to the fibres. Two types of samples were considered, differing in the anatomical orientation of the analysed surface. In the first variant, the tested surface (150 mm × 50 mm) corresponded to the radial section (Figure 1a,c), while in the second it represented the tangential section (Figure 1b,d).
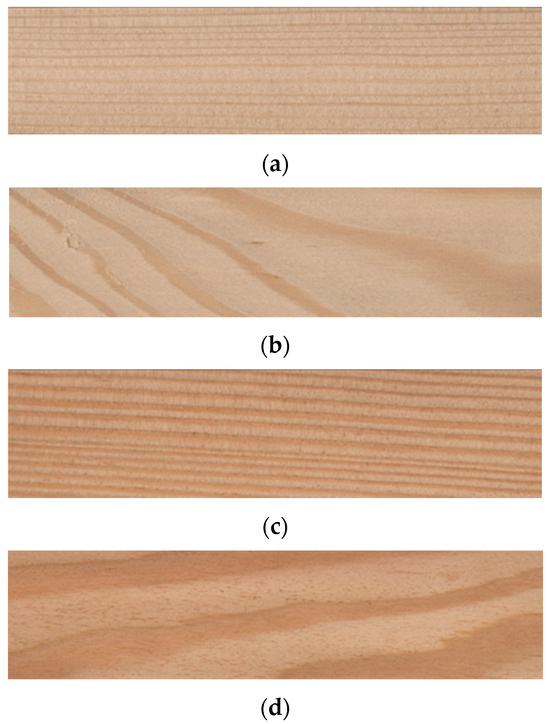
Figure 1.
European larch (a) sapwood—radial section; (b) sapwood—tangential section; (c) heartwood—radial section; (d) heartwood—tangential section.
After cutting, prepared samples were conditioned under standard laboratory conditions (temperature 20 °C ± 2 °C, relative humidity 65% ± 5%) until reaching equilibrium moisture content. Surface treatment was carried out by sanding with aluminium oxide abrasive papers of four grit sizes: P60, P120, P180, and P240. Moisture content was determined in accordance with ISO 13061-1:2014 [46] and remained within the range of 8 %–10%. Wood density was assessed using the stereometric method, following ISO 13061-2:2014 [47]. The average density values for European larch sapwood and heartwood were 458 (±5) kg × m−3 and 587 (±21) kg × m−3, respectively.
2.2. Microscopic Measurements
To investigate the structure of wood, specimens with dimensions of 10 mm (radial) × 10 mm (tangential) × 15 mm (longitudinal, parallel to the fibres) were prepared. The samples underwent maceration in a solution composed of distilled water, 96% ethanol, and glycerol, mixed in a 1:1:1 volume ratio. The soaking process lasted for 3 weeks to ensure the sufficient softening of the tissue. After maceration, thin sections with a thickness of 15–30 µm were obtained using a sledge microtome (Reichert, Vienna, Austria). The sections were stained with a 5% safranin solution prepared in 96% ethanol to enhance contrast between anatomical features. Microscopic examination was performed using an Olympus BX-41 light microscope (Olympus Corporation, Tokyo, Japan) equipped with a digital imaging system and Cell B analytical software (version 3.4). In transverse sections, the diameters of earlywood and latewood tracheids were measured in both radial and tangential directions. For each anatomical element, 30 individual measurements were recorded.
2.3. Roughness Parameters Determination
Surface roughness measurements were carried out using a Surftest SJ-210 portable surface roughness tester (Mitutoyo Corporation, Kawasaki, Japan). The procedure followed the guidelines of ISO 21920-2:2021 [48]. Two parameters were analysed: Ra (arithmetical mean deviation of the assessed profile) and Rz (maximum height of the assessed profile). Measurements were performed both parallel and perpendicular to the fibres, with 12 repetitions in each direction for every sanding variant. The measurement accuracy was 0.001 µm.
2.4. Wettability Measurements
Contact angle measurements were performed using a Phoenix 300 goniometer (Surface Electro Optics Co., Suwon, South Korea) employing the sessile drop method, with a droplet volume of 3 µL. Two standard reference liquids—distilled water and diiodomethane—were used in the analysis. The contact angle was recorded at two time intervals: 3 s and 30 s after droplet deposition. An image analysis system (Image XP, Surface Electro Optics, version 5.8) was used to process and analyse the droplet profiles.
The surface tension components values of the reference liquids: for water, γ = 72.8 mJ × m−2 (dispersive: 21.9 mJ × m−2, polar: 51.0 mJ × m−2); for diiodomethane, γ = 50.8 mJ × m−2 (dispersive: 50.8 mJ × m−2, polar: 0.0 mJ × m−2) [49]. The surface free energy of European larch sapwood and heartwood was calculated using the Owens–Wendt method, based on Young’s equation [50].
2.5. Wood Colour Determination
The colour measurements were conducted using a SPECTROMASTER 565-D spectrophotometer (ERICHSEN GmbH & Co. KG, Hemer, Germany). The analysis was performed under standard lighting conditions using a D65 illuminant (representing average daylight) [51]. The following CIELAB colour parameters were determined: L* (lightness), a* (chromatic coordinate on the red–green axis), and b* (chromatic coordinate on the yellow–blue axis). The total colour difference ∆E was determined in accordance with ISO 7724-3:1984 [52]. Measurements were taken on both radial and tangential surfaces, with 12 replicates recorded for each sanding variant.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analyses were carried out using STATISTICA version-13.3 software (TIBCO Software Inc., Palo Alto, CA, USA). The assumptions for analysis of variance (ANOVA) were verified. The normality of data distribution was assessed using the Shapiro–Wilk test, and the homogeneity of variances was checked with Levene’s test. Both criteria were met, allowing the application of ANOVA (Fischer’s F-test), with a significance level (p) of 0.05. The contribution of each factor to the total variance (Factor Influence %) was calculated based on the ratio of the sum of squares (SS) for that factor to the total SS from the ANOVA model.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. European Larch Tracheids Dimensions
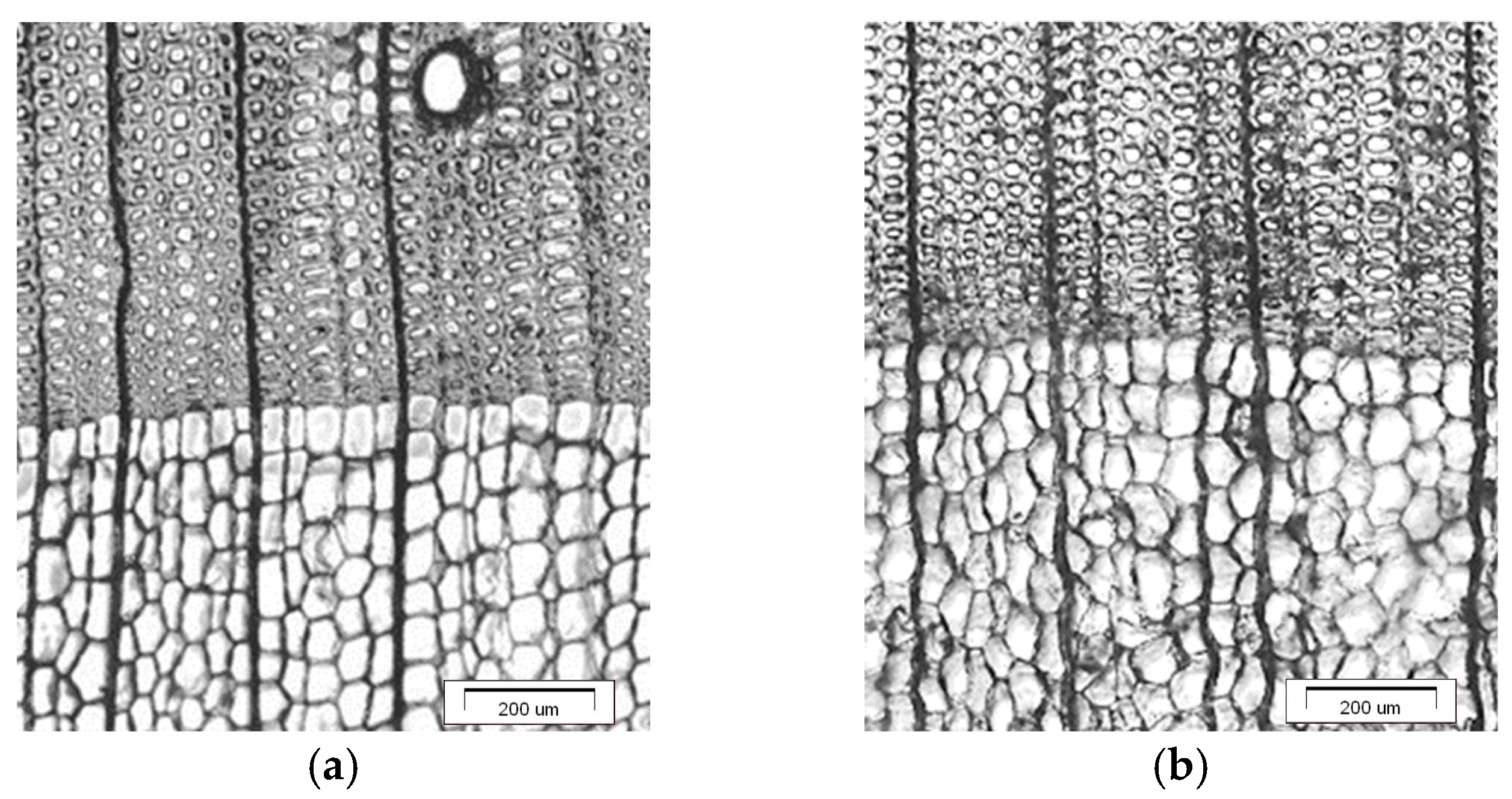
The sapwood of European larch differed in anatomical structure compared to the heartwood (Figure 2a,b). This is a typical feature of softwood [53,54]. These differences depend on a number of factors: genetic conditions, origin, habitat, growth conditions, age, position relative to the height, and diameter of the trunk [55,56].
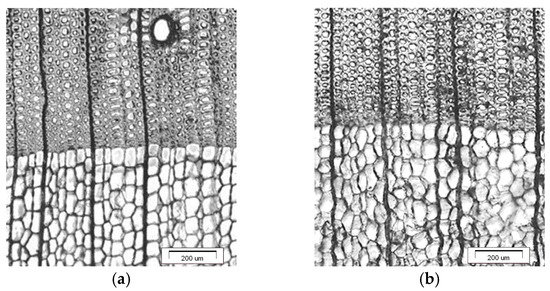
Figure 2.
Transverse section of European larch (a) sapwood and (b) heartwood.
It is generally stated that within a given wood area, earlywood tracheids are characterised by a larger diameter in radial direction than in the tangential direction, which is the opposite of what was found in latewood tracheids (Table 1). This was found both for sapwood tracheids and heartwood tracheids. Latewood tracheids flattened in the radial direction are characteristic of softwood [53,57].

Table 1.
Diameter of European larch tracheids; ±(SD).
In the sapwood zone of the European larch studied, the diameter of the earlywood tracheids in the radial direction was five times larger than that of the latewood tracheids (Table 1). In the tangential direction, the diameter of the earlywood tracheids was about 1.5 times greater than that of the latewood tracheids. In the heartwood zone, these differences were slightly smaller. The diameter of the earlywood tracheids in the radial direction was 7.5 times larger than the diameter of the latewood tracheids. In the tangential direction, the diameter of the earlywood tracheids was about 1.4 times greater than that of the latewood tracheids. In the sapwood zone, the earlywood tracheids had a radial diameter approximately 20% larger than the diameter of the earlywood tracheids in the heartwood. However, the latewood tracheids had a diameter about twice as large in this direction. In the sapwood zone, the earlywood tracheids had a tangential diameter approximately 30% larger than the diameter of the earlywood tracheids in the heartwood, and the latewood tracheids had a diameter approximately 10% larger in this direction.
3.2. Roughness of European Larch Wood
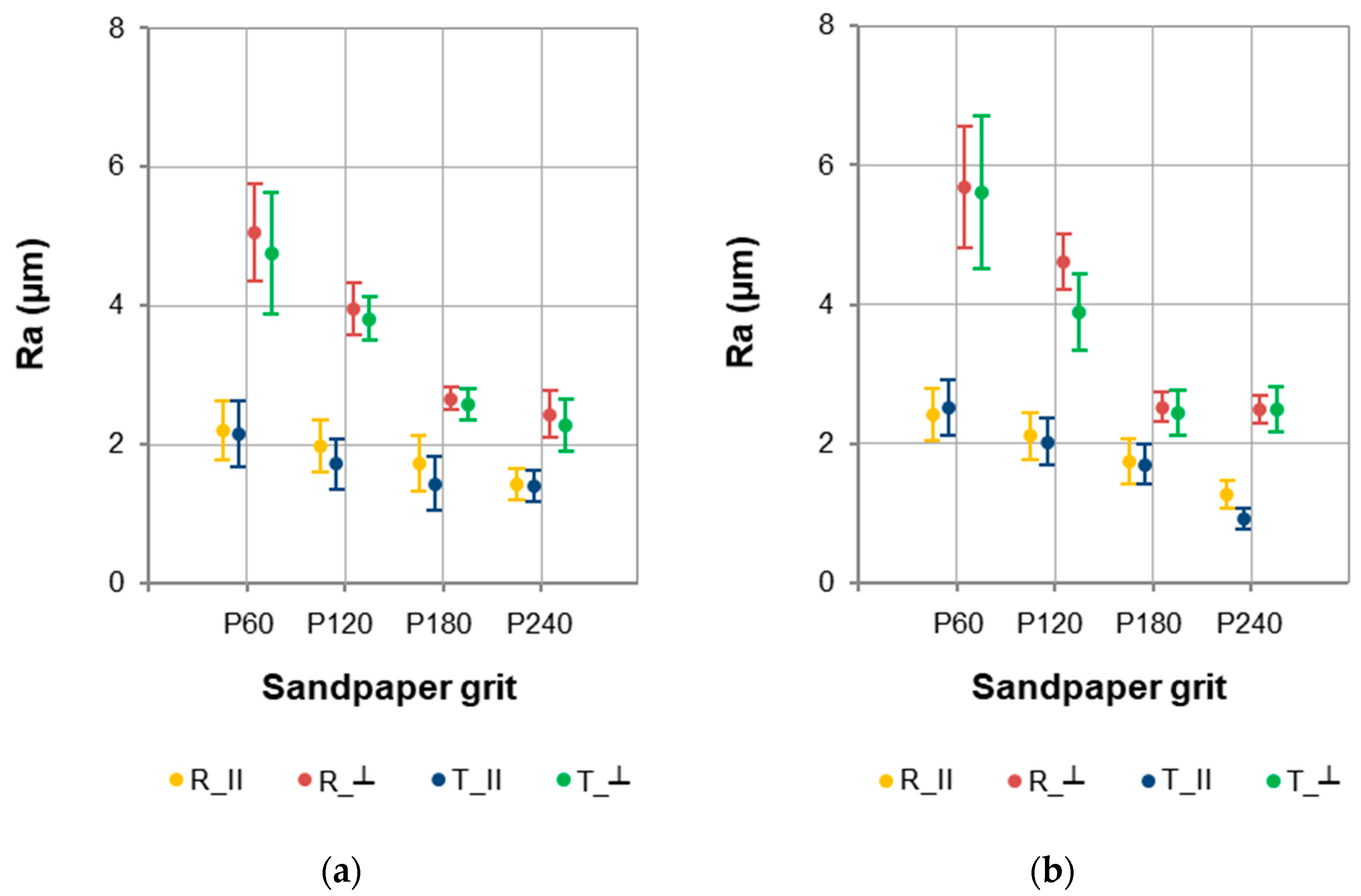
The influence of four factors on the roughness parameters of European larch wood was analysed. The Ra parameter values showed significant variation depending on measurement direction and sandpaper grit size (Figure 3). The sapwood was characterised by lower Ra values (Figure 3a) compared to the heartwood (Figure 3b), but these differences were not significant. Depending on the factors studied, the mean Ra values for sapwood were in the range of 1.401–5.053 µm, and for heartwood in the range of 0.922–5.682 µm.
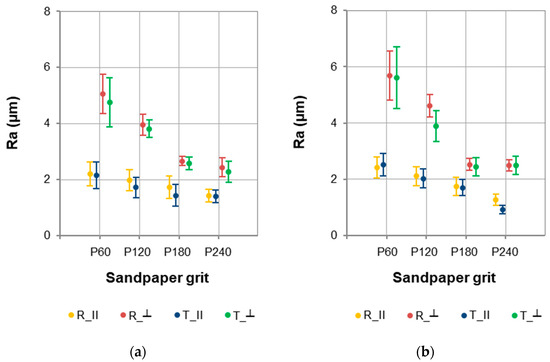
Figure 3.
Ra parameter values for (a) sapwood and (b) heartwood of European larch.
Generally, it can be assumed that sapwood and heartwood of European larch wood on the same anatomical section (R–radial or T–tangential) are characterised by similar roughness. The differentiating factors were measurement direction (parallel to the grain–‖ or perpendicular to the grain–⊥) and sandpaper grit size (in the range P60–P240). The Ra parameter values were higher for measurements conducted perpendicular to the grain, and the finer grit (larger number of sandpaper used), the lower the roughness of the tested wood area. These are typical dependencies, but it is worth noting that a significant decrease in the Ra parameter was examined after sanding sapwood and heartwood with P180 sandpaper. Moreover, for sapwood, no significant differences were found in the Ra parameter values after sanding with P240 paper compared to sanding with P180 sandpaper. However, a significant decrease in roughness parallel to the grain on the radial section (R_‖) and tangential section (T_‖) after sanding with P240 sandpaper was noted for the heartwood.
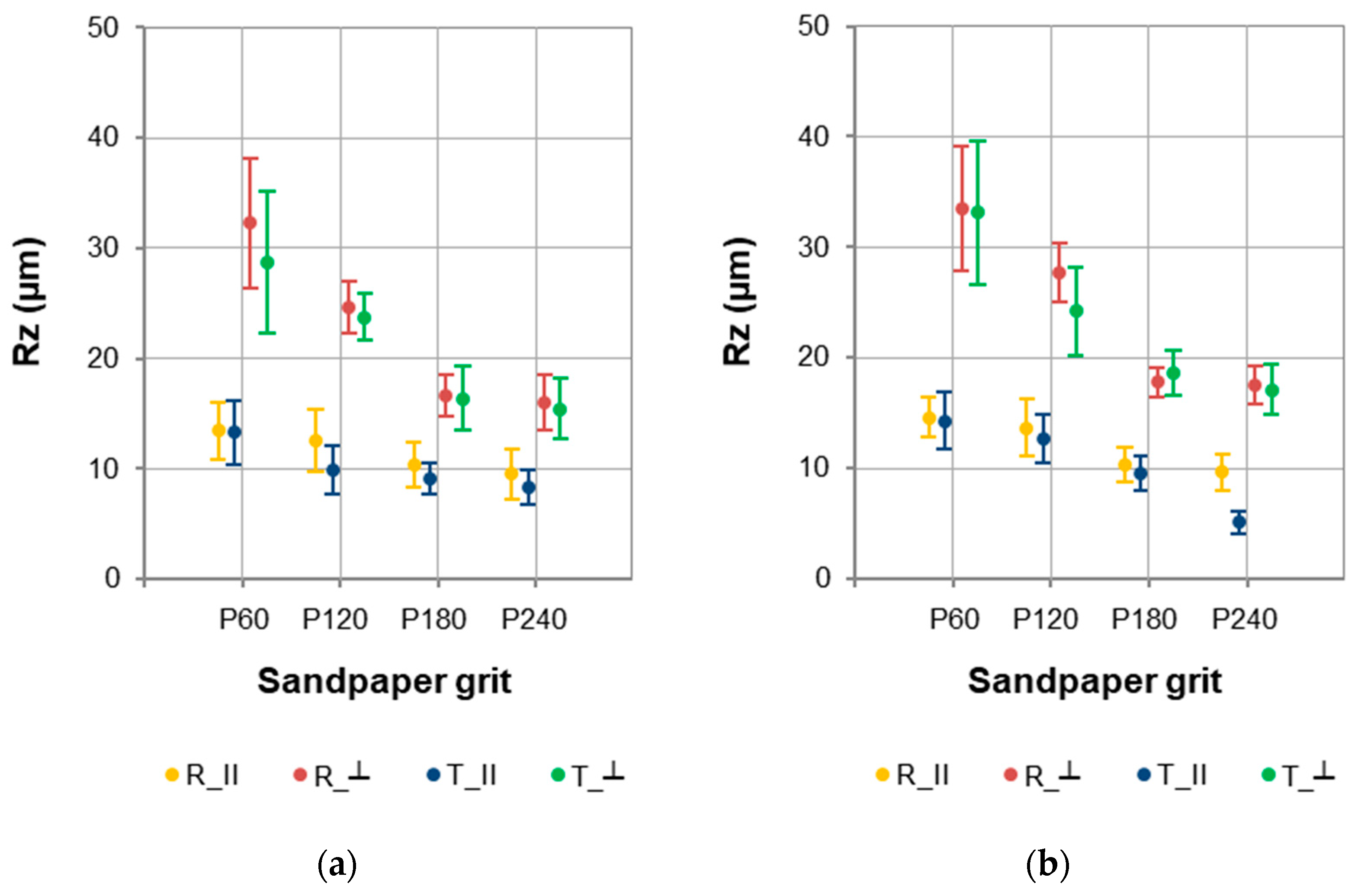
Similar dependencies for Ra were noted for the Rz parameter (Figure 4). However, the values were higher due to the nature of the Rz parameter (maximum height of the assessed profile). Depending on the factors studied, the mean Rz values for sapwood were in the range of 8.294–32.282 µm, and for heartwood in the range of 5.126–33.485 µm.
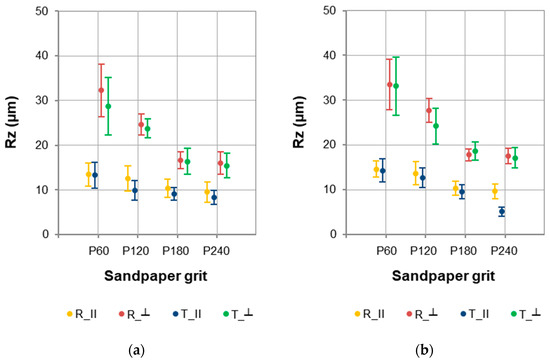
Figure 4.
Rz parameter values for (a) sapwood and (b) heartwood of European larch.
The conducted studies of the anatomical structure of European larch wood indicate differences in the structure of sapwood and heartwood (Section 3.1). However, the differences shown did not translate into a differentiation of roughness parameters (Ra, Rz) depending on the wood area (sapwood, heartwood). The surface roughness of wood is a combination of textures created within many processes such as sawing, planing, and sanding. Each of these processes has its own individual characteristics that lead to a wood surface with different properties [58,59]. It is worth noting that during sanding, randomly located wood anatomical elements are cut at different angles and create depressions, causing a certain roughness, i.e., the anatomical roughness. Surface roughness can also be caused by the random position of cuts in relation to the area of earlywood and latewood [8,10].
The direction of measurement and sandpaper grit had the greatest influence on the roughness parameters value Ra and Rz (Table 2). The measurement direction showed an influence of 47% and sandpaper grit of 30% on Ra. These two factors accounted for 77% of the Ra variability. Similar relationships were found in relation to the Rz parameter. The measurement direction showed an influence of 52% and sandpaper grit of 26%. It is worth noting that the wood area had a minimal, i.e., 1%, impact on roughness parameters. It follows that the sapwood and heartwood of European larch wood on the same anatomical section (radial or tangential) are characterised by similar roughness. The factors differentiating the roughness parameters are the direction of measurement and sandpaper grit. Other factors that were not included in the studies and could be responsible for the variability of roughness parameters constitute a small percentage, i.e., 10%–13%.

Table 2.
Factors influencing the roughness parameters of European larch wood (Fischer’s F-test; p ≤ 0.05).
3.3. Wettability of European Larch Wood
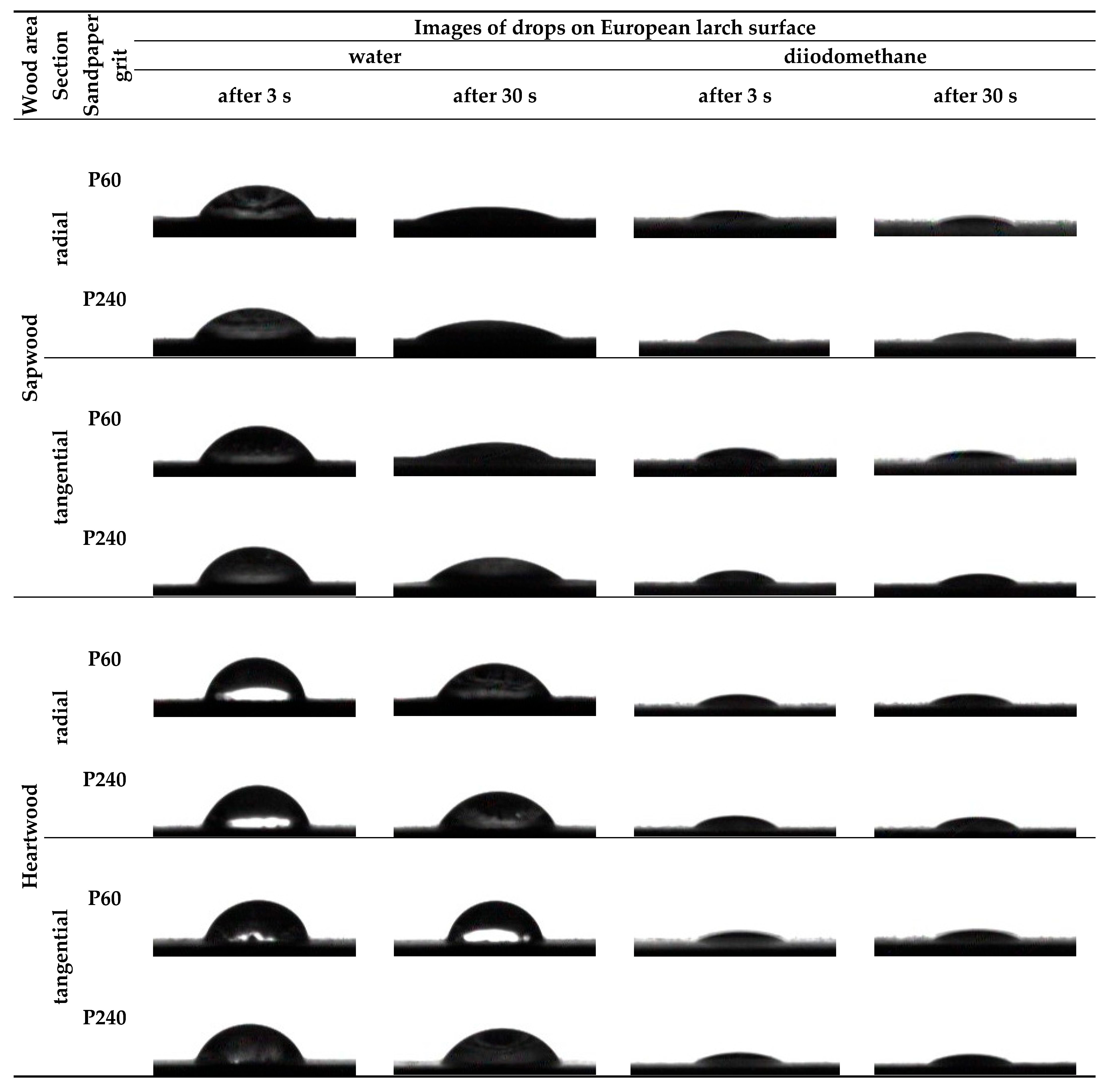
The contact angles at the phase boundary wood–water and at the phase boundary wood–diiodomethane showed significant changes depending on wood area (sapwood, heartwood), anatomical section (radial—R, tangential—T), and sandpaper grit. Images of both water and diiodomethane drops on European larch sapwood and heartwood after sanding with P60 and P240 sandpapers are presented in Figure 5. Sapwood was characterised by greater wettability than heartwood. This is primarily due to differences in the anatomical structure and chemical composition of the sapwood and heartwood [45].
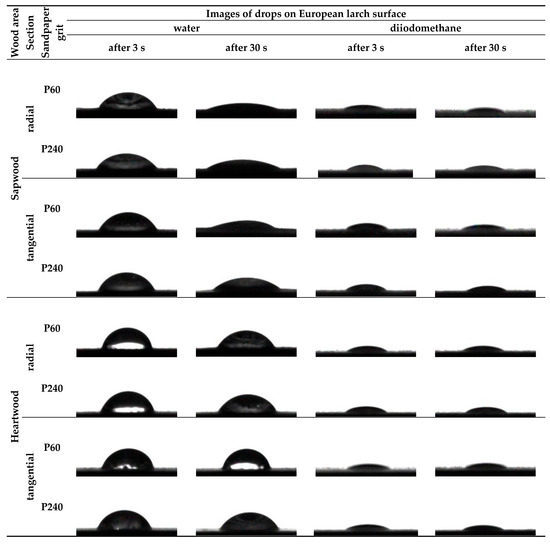
Figure 5.
Images of water and diiodomethane drops on the European larch sapwood and heartwood after sanding.
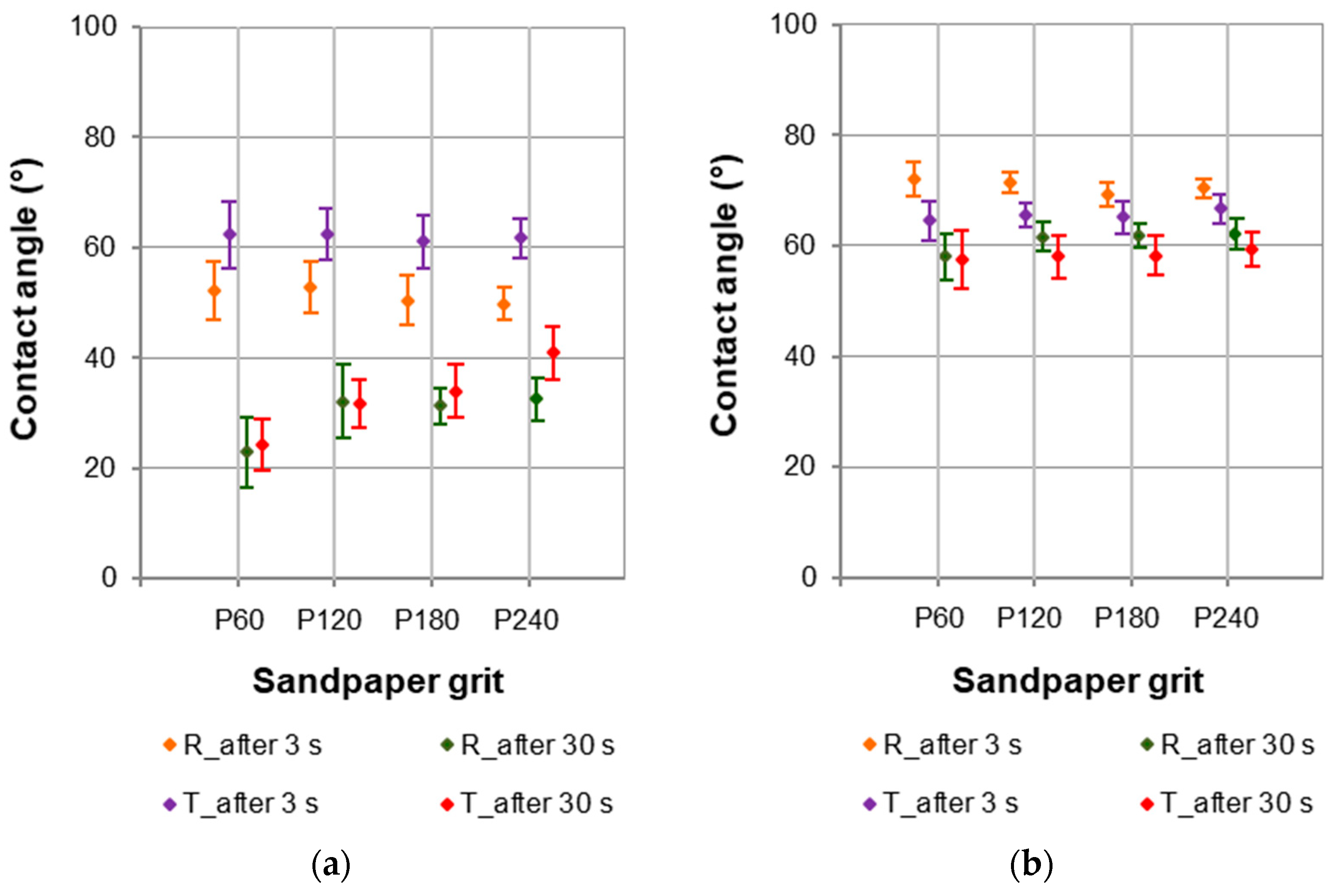
It is worth noting that sapwood was characterised by the lower wettability on the tangential section (Figure 6a), while the heartwood was characterised by the lower wettability on the radial section (Figure 6b). This was found during the contact angle tests performed 3 s after the water droplet had been applied to the wood surface. Such dependencies were not observed after 30 s. The average value of the contact angle after 3 s for the tangential section of the sapwood was approximately 60°, and for the radial section approximately 50°. The higher wettability on the radial section could result from the “availability” of thin-walled parenchyma cells forming the wood rays, the structure of which is particularly visible in the radial section. The average value of the contact angle after 3 s for the tangential section of the heartwood was approximately 65°, and for the radial section approximately 70°. These differences were not as great as in the case of sapwood.
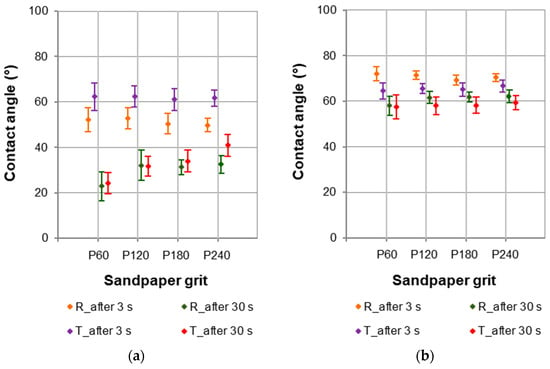
Figure 6.
Contact angles at the phase boundary wood–water for (a) sapwood and (b) heartwood of European larch.
The variation in contact angle between 3 and 30 s reflects the dynamic nature of the wetting process. At the initial stage (3 s), the contact angle predominantly represents the early wetting phase, which is influenced by chemical composition, roughness, and surface energy. During this phase, the liquid droplet mainly interacts with the outermost surface features, including surface roughness, extractives, and microstructure. As time progresses (up to 30 s), the contact angle generally decreases due to liquid penetration into the wood’s porous structure, driven by capillary forces. This deeper interaction involves anatomical elements such as tracheids (in earlywood and latewood) and rays, which significantly influence the rate and extent of liquid absorption. Wood anatomy has a crucial role in this process. Earlywood, characterised by larger lumens and thinner cell walls, typically facilitates faster liquid uptake, resulting in a more rapid decrease in contact angle. In contrast, the denser structure and smaller lumens of latewood tend to restrict penetration, slowing the wetting process. Additionally, the orientation of the wood surface (radial, tangential) affects the availability and direction of capillary pathways. Tangential surfaces may offer less resistance depending on the distribution and orientation of earlywood, which is evident in the case of the contact angle tests for heartwood (Figure 6b). Time-dependent changes in contact angle can also be influenced by the chemical composition of the surface, particularly the presence of natural extractives or modifications introduced through sanding. Extractives may form hydrophobic layers that hinder initial wetting, but over time, these compounds can be displaced or dissolved by the liquid, leading to a further decrease in contact angle.
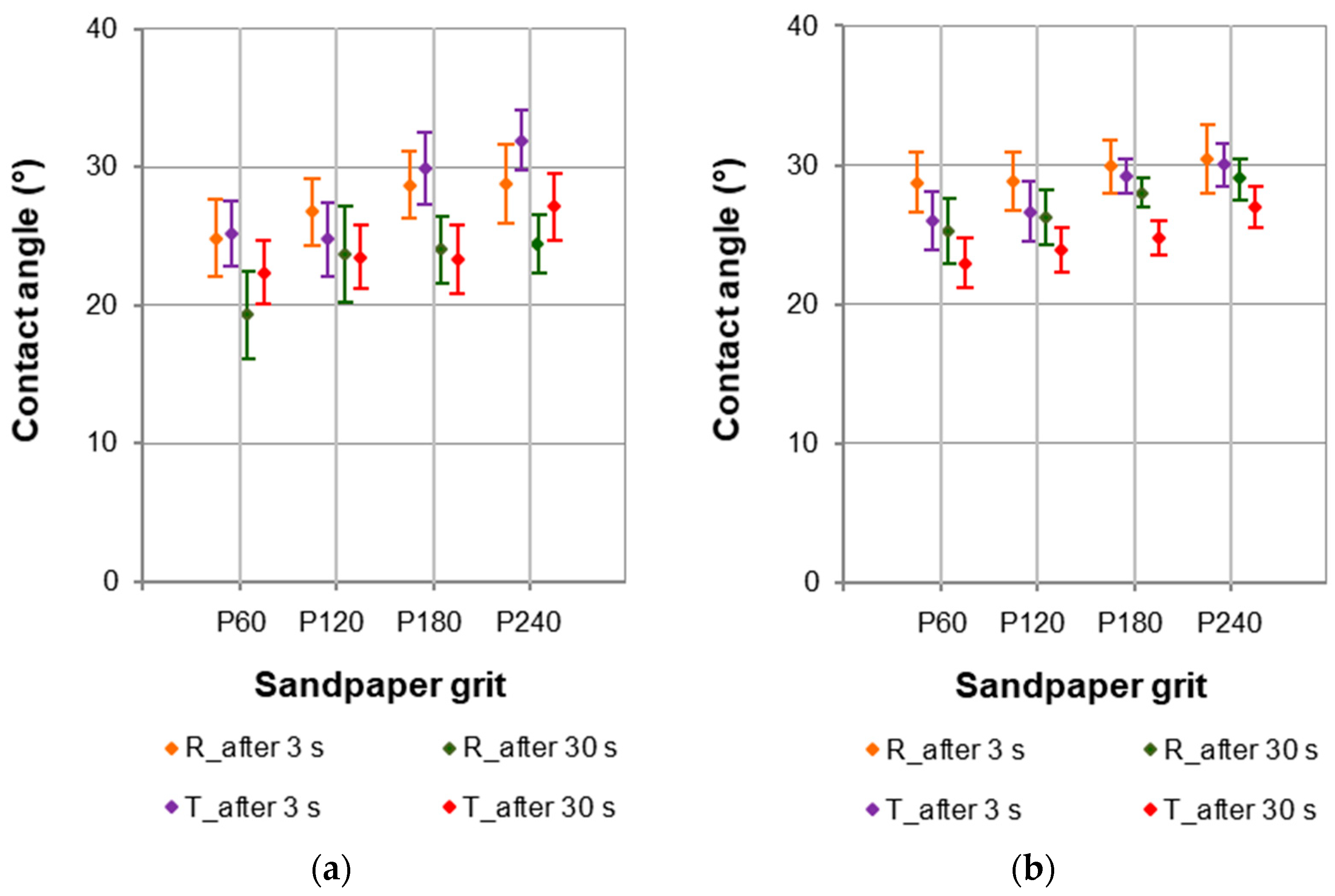
The differences in the contact angle values were much lower when testing European larch surfaces with a nonpolar liquid such as diiodomethane (Figure 7). The contact angles changed to a lesser extent. The values of the contact angles determined with diiodomethane for sapwood ranged from about 19° to 32°, whereas the contact angle values for the heartwood ranged from about 23° to 30°.
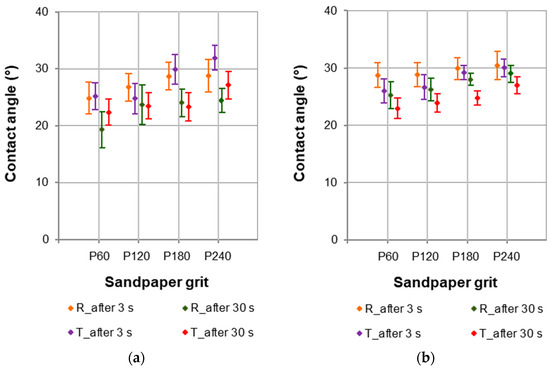
Figure 7.
Contact angles at the phase boundary wood–diiodomethane for (a) sapwood and (b) heartwood of European larch.
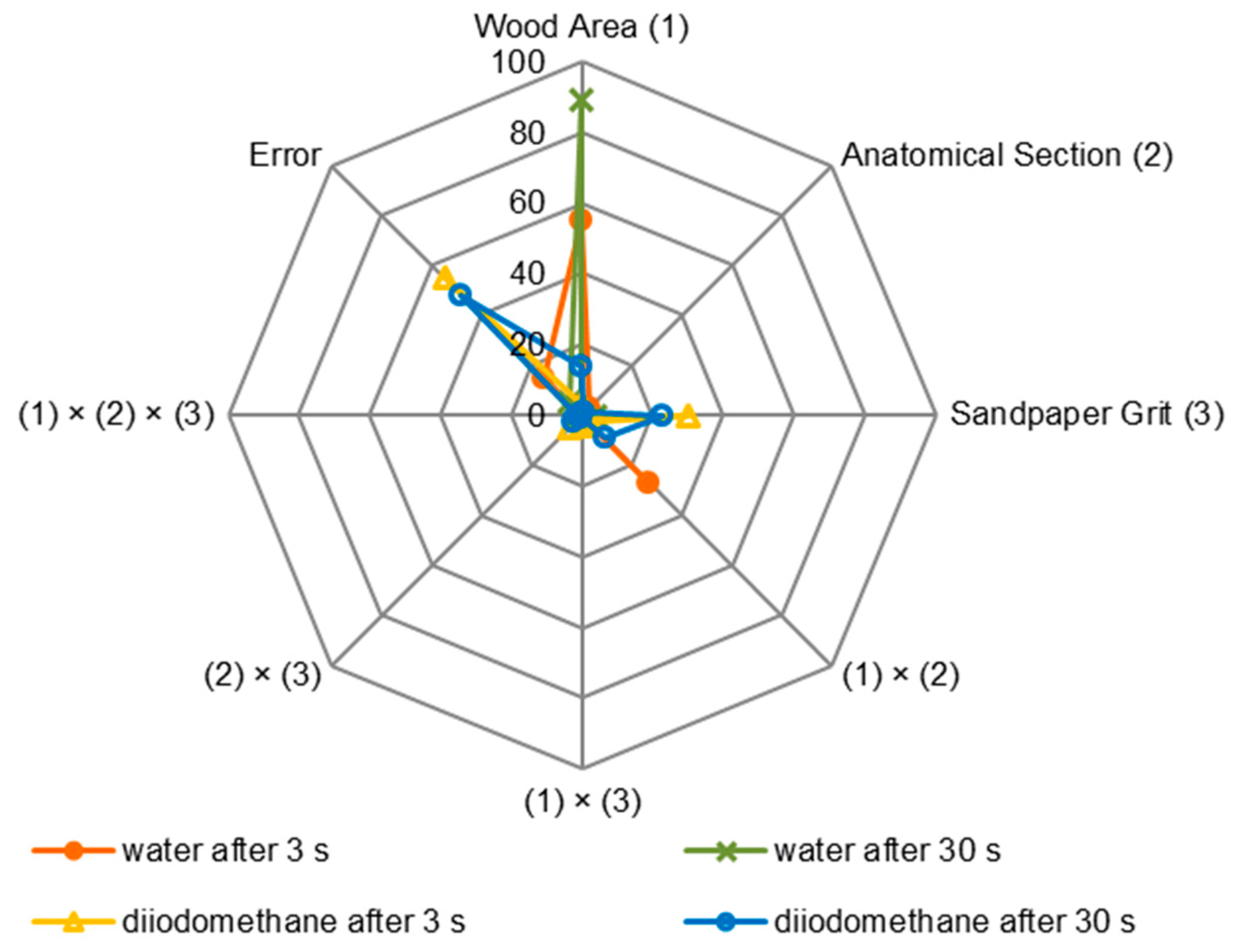
The statistical evaluation of the influence of factors on the contact angles at the phase boundary wood–water (Figure 8) showed that the wood area had the greatest impact. Significantly, this influence increased from 55% to 89% when examining the contact angle after 3 s and 30 s. It was shown that the interaction between the wood area and the wood section significantly influenced the formation of the contact angle determined after 3 s with water. The impact of this interaction was 27%. The percentage impacts of factors on the contact angles at the phase boundary wood–diiodomethane were analysed (Figure 8), and it is worth noting that sandpaper grit showed the greatest impact. This impact was at the level of 30% after determining the contact angles after 3 s and at the level of 23% after determining the contact angles after 30 s.
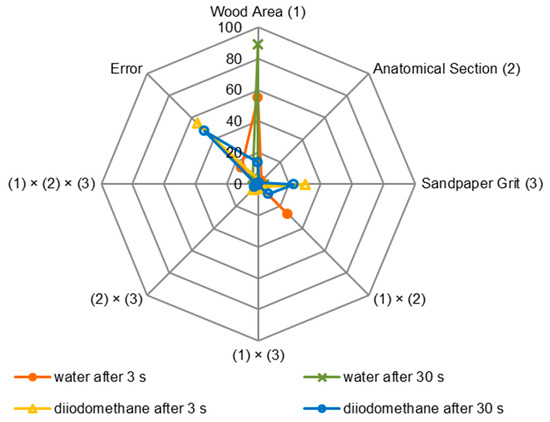
Figure 8.
Statistical evaluation of the factors and interactions between them influencing the contact angle at the phase boundary wood–water and wood–diiodomethane for European larch wood (based on ANOVA, Fischer’s F-test, p ≤ 0.05).
Sapwood typically features larger, more open lumens and a higher proportion of functional tracheids, resulting in greater porosity. After sanding, these anatomical structures become more exposed, increasing the number of accessible capillary pathways on the surface. This enhances the wood’s ability to absorb and distribute liquids, leading to lower contact angles and increased wettability. In contrast, heartwood is denser, with many conduits occluded by extractives. These blockages reduce effective porosity and limit capillary absorption. As a result, liquids interact primarily with the outer surface layer, causing higher contact angles and lower surface energy responses (Figure 9). The chemical composition of heartwood also differs markedly from that of sapwood due to the accumulation of hydrophobic extractives such as phenolic compounds and resins. These substances migrate into cell walls and lumens during heartwood formation, rendering the surface more hydrophobic and less reactive to polar liquids, including water-based coatings. Even after mechanical sanding, which removes the outermost layers and may reduce surface contamination, these extractives can remain embedded within the cell walls or migrate back to the surface, continuing to influence wettability and adhesion behaviour. Sapwood, with its lower extractive content, lacks this hydrophobic barrier, resulting in greater surface receptivity. Sanding alters the microtopography of the wood surface; however, its effect is modulated by the underlying anatomical structure. Sapwood, being softer and more porous, is more easily abraded, potentially resulting in a rougher or more absorbent surface. Conversely, the higher density of heartwood may produce smoother or more compressed surfaces after sanding, depending on factors such as abrasive grit size, the anatomical section, and sanding direction relative to the grain. This interplay between mechanical abrasion and anatomical resistance significantly influences how finishes spread, penetrate, and cure on each wood type. In summary, the interaction between anatomical structure, chemical composition, and sanding-induced surface modification results in distinct and measurable differences in the surface properties of European larch sapwood and heartwood. Understanding these mechanisms is essential for optimising the performance of adhesives, coatings, and finishes, and should be carefully considered in both scientific research and practical woodworking applications.
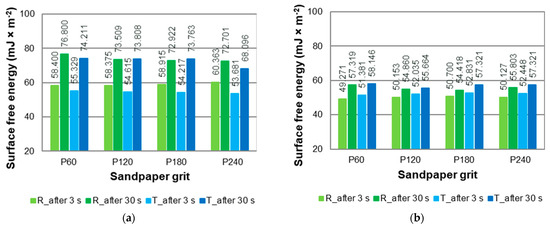
Figure 9.
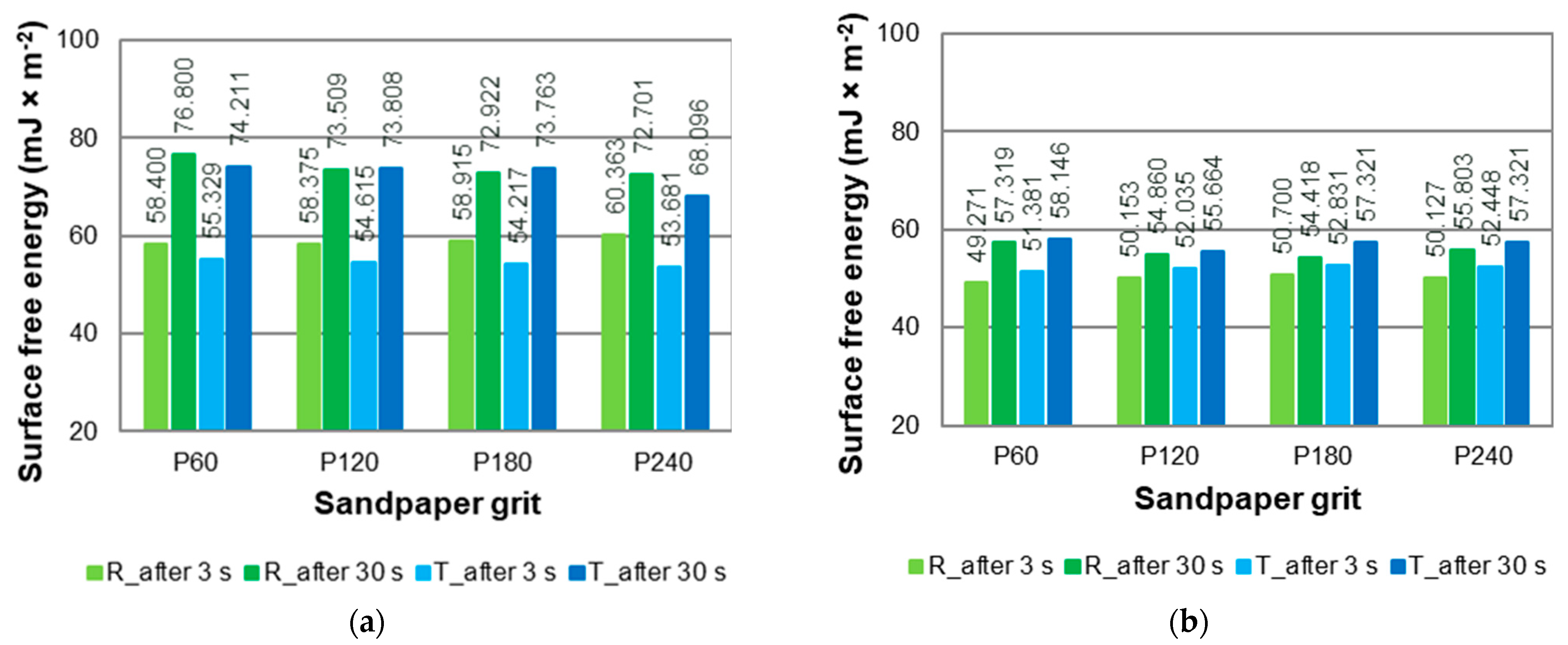
Surface free energy of (a) sapwood and (b) heartwood of European larch (R—radial section, T—tangential section).
Surface free energy (SFE) describes the tendency of a solid surface to interact with liquids and is closely related to wettability. In wood, SFE is influenced by both chemical composition and structural characteristics such as surface roughness. However, as noted by Liptáková and Kúdela [60], interpreting both contact angle and SFE in wood is inherently challenging due to the material’s porous structure and its ability to absorb liquids during measurement. This dynamic interaction can lead to time-dependent changes in wetting behaviour and affect the calculated values.
As shown in Figure 9, sapwood exhibited generally higher SFE values than heartwood. This may be attributed to its higher content of hydrophilic components, such as hemicelluloses and cellulose [45], and smoother surface texture. In contrast, heartwood contains more lignin and hydrophobic extractives, which reduce surface polarity and hinder wetting. The greater difference in contact angle between 3 and 30 s observed in sapwood supports the interpretation of a more active wetting process, while the more stable values in heartwood reflect limited absorption and slower wetting dynamics. Higher SFE values were noted for sapwood in the radial section (R) and for heartwood in the tangential section (T). These relationships were particularly visible after 3 s from applying a drop of liquid to the wood surface. However, after 30 s from the application of the drop to the wood surface, these relationships were not as pronounced. The sapwood consists of a network of dead tracheids (earlywood and latewood) and living parenchyma cells. In contrast, heartwood is the inactive wood fraction devoid of living cells [61]. In European larch wood, the share of parenchyma is in the range 7%–11% [53].
After sanding, the observed differences in surface properties between European larch sapwood and heartwood have practical significance for woodworking and surface finishing processes. Due to its lower extractive content and more open anatomical structure, sapwood generally exhibits higher wettability. As a result, it tends to absorb water-based adhesives, coatings, and finishes more readily, leading to improved adhesion and more uniform surface coverage—beneficial in applications requiring high-quality surface treatment, such as furniture manufacturing. On the other hand, heartwood, characterised by a higher content of hydrophobic extractives and a denser structure, shows reduced wettability. This implies a need for more intensive surface preparation such as finer sanding, chemical pre-treatment, or the application of solvent-based finishes, to achieve satisfactory adhesion and finishing quality. Recognising these anatomical and chemical differences between sapwood and heartwood is essential when selecting sanding methods and finishing systems, helping to enhance product performance, surface aesthetics, and processing efficiency in both artisanal and industrial woodworking contexts.
3.4. Colour of European Larch Wood
Wood colour refers to the natural shade of the colour of dried wood [62]. In the literature, wood colour is usually defined descriptively, so general information is given in describing some types of wood, describing the colour as yellow, brown, reddish brown, etc. [63]. When light affects the wood surface, part of the incident light is reflected directly from the surface, and the other part penetrates the cells of the wood surface. The basic components of wood–cellulose, lignin, and hemicelluloses absorb and reflect light in different ways. Pigments contained in wood also absorb specific wavelengths of light. Part of the light not absorbed by the cell walls is reflected and partly passes through the wood substance. Unabsorbed light is recognised as the colour of the wood, and through the nature of the changes in wavelength, it is perceived as a specific colour of the wood.
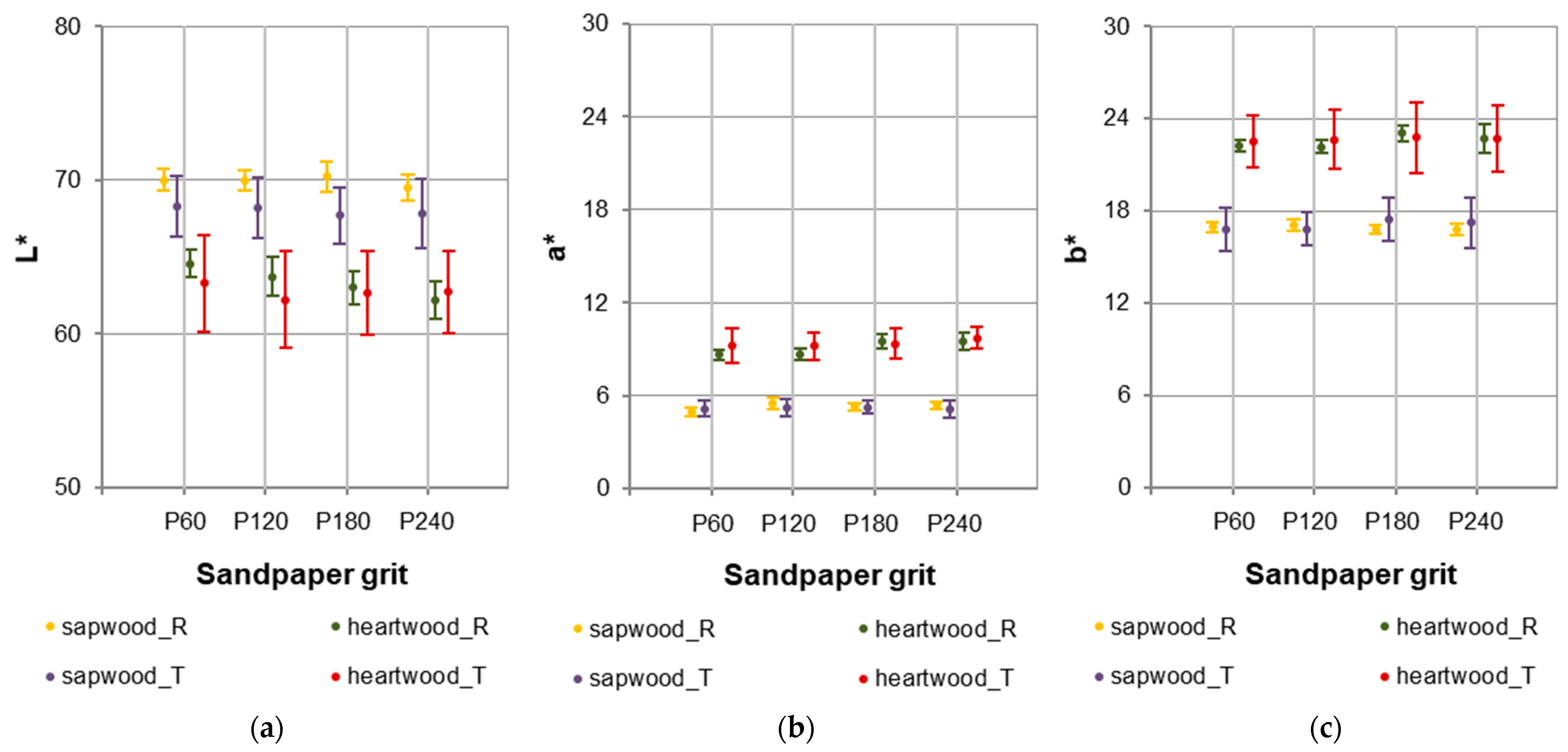
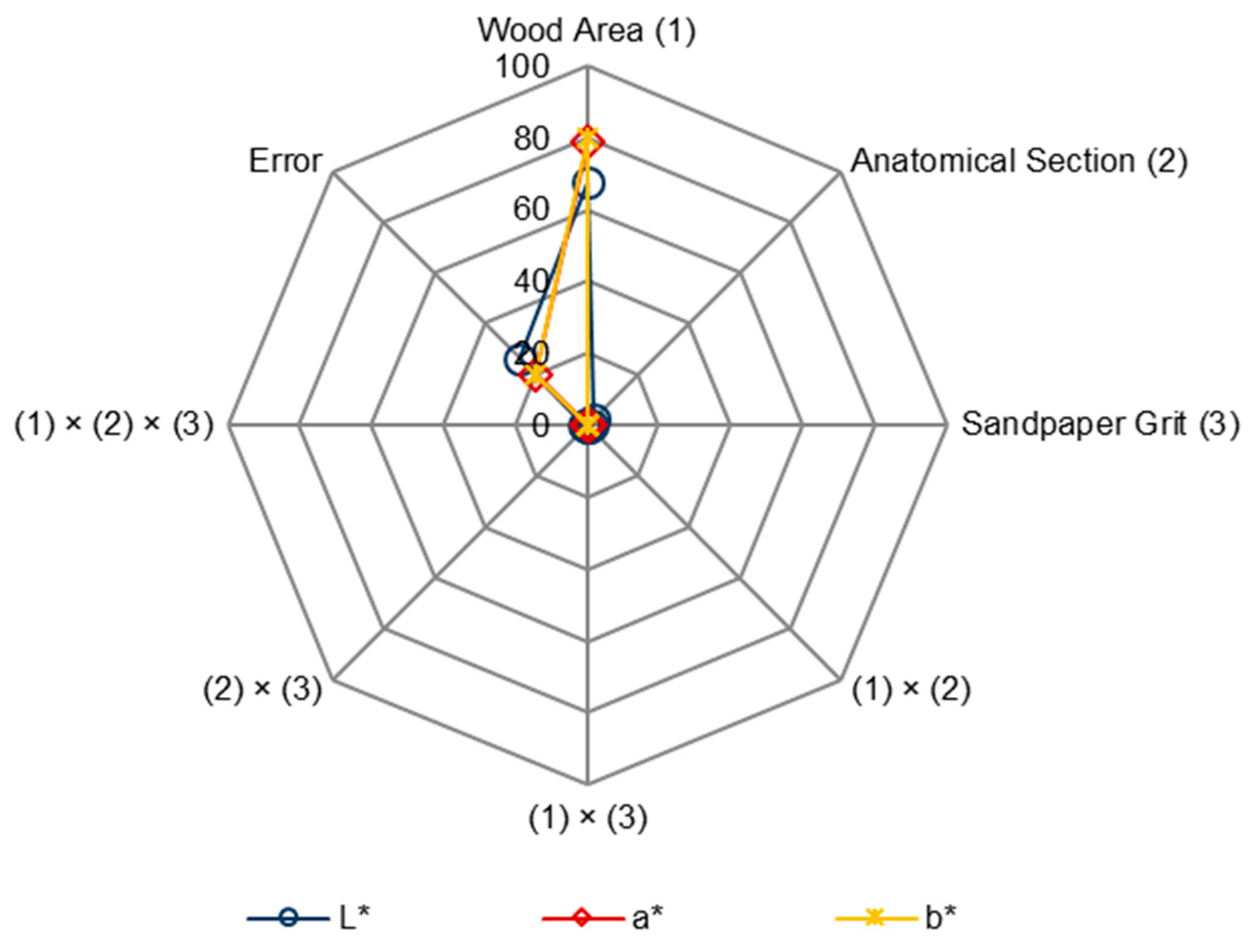
The conducted research showed that sanding the surface of European larch wood with P60–P240 sandpapers changes the texture of the wood, but it does not significantly differentiate the colour parameter values, i.e., L* (Figure 10a), a* (Figure 10b), b* (Figure 10c), after sanding. The only factor differentiating the colour was the wood area. This factor determined the L* parameter values in 68%, the a* parameter values in 79%, and the b* parameter values in 80% (Figure 11). Analysing the statistical evaluation of the factors influencing the colour parameters of European larch, it can be clearly seen that the wood area determined the colour parameters. Differences in the colour parameters values between species resulted from the presence of extractive compounds, i.e., differences in the chemical composition of wood [61]. The influence of sandpaper grit on the L*, a*, and b* parameters values was not statistically significant.
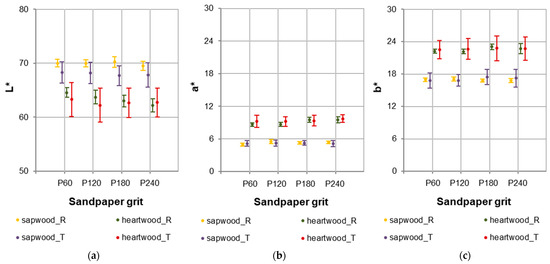
Figure 10.
Colour parameters: (a) L*, (b) a*, (c) b* for European larch wood.
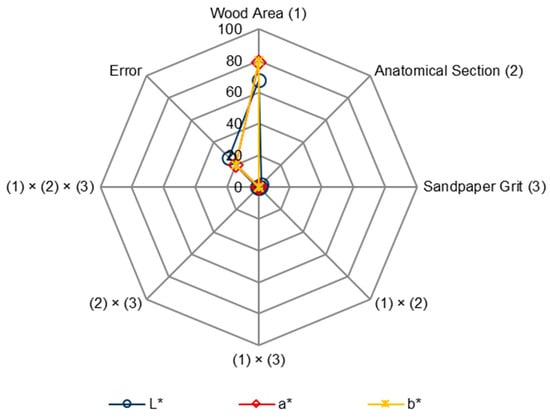
Figure 11.
Statistical evaluation of the factors and interactions between them influencing the colour parameters of European larch wood (based on ANOVA, Fischer’s F-test, p ≤ 0.05).
To quantitatively assess the impact of different sandpaper grits on surface colour, the colour difference value ΔE was used (Table 3). This value represents the difference between colours and is calculated based on the CIELAB colour space model. The greatest colour change ΔE, at level 2.59, was noted for the heartwood on the radial section after sanding with P240 sandpaper. Slightly smaller colour changes, at the level of 1.98, were noted after sanding with P180 grit sandpaper. The reference point was the colour parameters determined for the heartwood radial section after sanding with P60 sandpaper. At a slightly lower level, changes were recorded for sapwood radial section (ΔE = 1.22) after sanding P120 and heartwood tangential section (ΔE = 1.08) after sanding P120. The reference point, in given cases, was the colour parameters determined for sapwood radial section and heartwood tangential section after sanding with P60 sandpaper, respectively. A standard observer does not notice the difference in colour when 0 < ∆E < 1. However, in the case when 1 < ∆E < 2, only an experienced observer can notice the colour difference. An unexperienced observer notices the colour difference when 2 < ∆E < 3.5 [64]. On this basis, it can be assumed that in the four indicated cases, the observer would notice the colour difference. In most of the analysed cases ∆E was below 1, which suggests that the standard observer does not notice the difference in European larch colour after sanding.

Table 3.
The total colour difference value ΔE for European larch wood after sanding.
4. Conclusions
The present study investigated the influence of sanding with different grit sizes of aluminium oxide sandpaper on selected surface properties of European larch sapwood and heartwood. The following conclusions can be drawn:
- The sapwood and heartwood of European larch wood on the same anatomical section (radial or tangential) are characterised by similar roughness. The differentiating factors were measurement direction (parallel to the grain or perpendicular to the grain) and sandpaper grit size (in the range P60–P240).
- The measurement direction showed an influence of 47% and sandpaper grit of 30% on Ra value parameter. Similar relationships were found in relation to the Rz parameter. The measurement direction showed an influence of 52% and sandpaper grit of 26%.
- Sapwood was characterised by greater wettability (contact angle with water) than heartwood. Taking into account the section of the wood, sapwood was characterised by the lower wettability on the tangential section, while the heartwood was characterised by the lower wettability on the radial section. This was examined for the contact angle tests performed 3 s after the water droplet had been applied to the wood surface.
- Wood area had the greatest impact on the contact angles at phase boundary wood–water. This influence increased from 55% to 89% when examining the contact angle after 3 s and 30 s.
- Sapwood exhibited generally higher surface free energy values than heartwood. For sapwood, higher surface free energy values were noted for the radial section, and for heartwood these values were noted for the tangential section. These relationships were particularly visible after 3 s from the application of a drop of liquid to the wood surface.
- Wood colour was predominantly influenced by wood area. Sanding the surface of European larch wood with P60–P240 sandpapers changes the texture of the wood, but does not significantly affect the differentiation of the colour parameters, i.e., L*, a*, b*. The greatest colour change ΔE, at level 2.59, was noted for the heartwood on the radial section after sanding with P240 sandpaper. The reference point was the colour parameters determined for heartwood radial section after sanding with P60 sandpaper.
This study reveals notable differences in the surface properties of European larch sapwood and heartwood after sanding, particularly regarding wettability and its potential impact on adhesion and finishing performance. The results emphasise the need to account for wood type and anatomical variability when selecting surface preparation methods and finishing systems. Future research should investigate the role of environmental and climatic factors such as relative humidity, temperature, and seasonal growth conditions influencing surface wettability. These variables may substantially affect the performance and durability of finishes, particularly in applications exposed to outdoor or fluctuating climatic conditions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualisation, A.L. and A.P.; methodology, A.L., K.L., and P.B.; software, A.L. and K.L.; validation, A.L.; formal analysis, A.L., K.L., and P.B.; investigation, A.L. and K.L.; resources, A.L., A.P., and K.L.; data curation, A.L., A.P., and K.L.; writing—original draft preparation, A.L., A.P., and T.K.; writing—review and editing, K.L. and P.B.; visualisation, A.L.; supervision, A.L., K.L., and P.B.; project administration, A.L. and P.B.; funding acquisition, P.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article; further inquiries can be directed to the authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Richter, K.; Feist, W.C.; Knaebe, M.T. The effect of surface roughness on the performance of finishes. Part 1: Roughness characterization and stain performance. For. Prod. J. 1995, 45, 91–96. [Google Scholar]
- Sandak, J.; Negri, M. Wood surface roughness—What is it. In Proceedings of the 17th International Wood Machining Seminar, Rosenheim, Germany, 26–28 September 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Ugulino, B.; Hernández, R.E. Analysis of sanding parameters on surface properties and coating performance of red oak wood. Wood Mater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 13, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sydor, M.; Mirski, R.; Stuper-Szablewska, K.; Rogoziński, T. Efficiency of machine sanding of wood. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bembenek, M. Researches on influence of wood sanding direction on wood gluing. J. Indian Acad. Wood Sci. 2022, 19, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Maura, L.F.; Hernández, R.E. Evaluation of varnish coating performance for two surfacing methods on sugar maple wood. Wood Fiber Sci. 2005, 37, 355–366. [Google Scholar]
- De Maura, L.F.; Hernández, R.E. Effects of abrasive mineral, grit size and feed speed on the quality of sanded surfaces of sugar maple wood. Wood Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 517–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilera, A.; Zamora, R. Surface roughness in sapwood and heartwood of blackwood (Acacia melanoxylon R. Br.) machined in 90-0 direction. Eur. J. Wood Wood Prod. 2009, 67, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cool, J.; Hernández, R.E. Improving the sanding process of black spruce wood for surface quality and water-based coating adhesion. For. Prod. J. 2011, 61, 372–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, P.L.; Sharif, S.; Sudin, I. Roughness models for sanded wood surfaces. Wood Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, B.; Liu, H.; Xu, M.; Xing, F. Analysis of sanding parameters, sanding force, normal force, power consumption, and surface roughness in sanding wood-based panels. Bioresources 2014, 9, 7494–7503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borkowski, J.A. Uses of Abrasives and Abrasive Tools, 1st ed.; Borkowski, J.A., Szymański, A.M., Eds.; Ellis Horwood Series in Mechanical Engineering; Hardcover; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1992; p. 288. ISBN 978-0-13-932518-2. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, J.B.; Carrano, A.L.; Lemaster, R.L. Quantification of Process Parameters in a Wood Sanding Operation. For. Prod. J. 1999, 49, 41–46. [Google Scholar]
- Očkajová, A.; Sikliena, M. The Influence of Chosen Factors of Wood Sanding upon the Efficiency of Sand Belt. Drev. Vysk./Wood Res. 2000, 45, 33–38. [Google Scholar]
- Carrano, A.L.; Taylor, J.B.; Lemaster, R. Parametric Characterization of Peripheral Sanding. For. Prod. J. 2002, 52, 44–50. [Google Scholar]
- Sinn, G.; Gindl, M.; Reiterer, A.; Stanzl-Tschegg, S. Changes in the Surface Properties of Wood Due to Sanding. Holzforschung 2004, 58, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurau, L.; Mansfield-Williams, H.; Irle, M. Processing Roughness of Sanded Wood Surfaces. Eur. J. Wood Wood Prod. 2005, 63, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilic, M.; Hiziroglu, S.; Burdurlu, E. Effect of machining on surface roughness of wood. Build. Environ. 2006, 41, 1074–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Moura, L.F.; Cool, J.; Hernández, R.E. Anatomical evaluation of wood surfaces produced by oblique cutting and face milling. IAWA J. 2010, 31, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laina, R.; Sans-Lobera, A.; Villasante, A.; Lopez-Espi, P.; Martinez-Rojas, J.A. Effect of the anatomical structure, wood properties and machining conditions on surface roughness of wood. Maderas-Cienc. Y Tecnol. 2017, 19, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Myles, A.; Wright, A.; Mitton, D. The impact of sanding on the surface properties of wood. Wood Fiber Sci. 2015, 47, 29–36. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, S.; Lee, D.; Hwang, T. Influence of sanding on the surface roughness of wood. Wood Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 573–582. [Google Scholar]
- Piao, C.; Winandy, J.E.; Shupe, T.F. From hydrophilicity to hydrophobicity: A critical review: Part I. Wettability and surface behawior. Wood Fiber Sci. 2010, 42, 490–510. [Google Scholar]
- Petrić, M.; Primoz, O. Determination of Wettability of Wood and its Significance in Wood Science and Technology. A Cris. Review. Rev. Adhes. Adhes. 2015, 3, 121–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva Siebra, M.B.; de Lima Fernandes, N.C.; Ribeiro, P.G.; Lobão, M.S. Molhabilidade de duas madeiras amazônicas tratadas com produtos de acabamento. Sci. Nat. 2020, 2, 68–71. [Google Scholar]
- Sinderski, L.G.Z. Ângulo de Contato e Rugosidade de Madeiras, uma breve revisão. Braz. J. Wood Sci. 2020, 11, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Očkajová, A.; Kučerka, M.; Krišťák, L.; Ružiak, I.; Gaff, M. Efficiency of sanding belts for beech and oak sanding. BioResources 2016, 11, 5242–5254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoma, H.; Peri, L.; Lato, E. Evaluation of wood surface roughness depending on species characteristics. Maderas. Cienc. Y Tecnol. 2015, 17, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun-Won, K.; Kazuharu, H.; Eunsuk, J.; Haradhan, K. Relationship between wood anatomical features and surface roughness characteristics. Wood Res. 2023, 68, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslan, S.; Coşkun, H.; Kiliç, M. The Effect of the Cutting Direction, Number of Blades and Grain Size of the Abrasives on Surface Roughness of Taurus Cedar (Cedrus libani A. Rich.). Woods. Build. Environ. 2008, 43, 696–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankowska, A. Understanding of surface roughness of wood based on analysis its structure and density. Ann. WULS—SGGW. For. Wood Technol. 2020, 111, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiziroglu, S.; Anwar, U.M.K.; Hamdan, H.; Paridah, M.T. Evaluation of surface quality of some Malaysian species as function of outdoor exposure. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2008, 199, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim, M.R.S.; Ribeiro, P.G.; Martins, S.A.; Del Menezzi, C.H.S.; De Souza, M.R. Surface wettability and roughness of 11 Amazonian tropical hardwoods. Floresta E Ambiente 2013, 20, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alia-Syahirah, Y.; Paridah, M.T.; Hamdan, H.; Anwar, U.M.K.; Nordhalia, A.S.; Lee, S.H. Effects of anatomical characteristics and wood density on surface roughness and their relation to surface wettability of hardwood. J. Trop. For. Sci. 2019, 31, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwała, M. Drewno w meblarstwie. Leśne Pr. Badaw. 2004, 1, 144–149. [Google Scholar]
- Kopeć, K. Drewno. Właściwości i Zastosowanie. [Wood. Properties and Uses]; Karol Kopeć: Starachowice, Poland, 2017; Volume I, p. 207. ISBN 978-83-946932-1-3. [Google Scholar]
- Gierlinger, N.; Jacques, D.; Schwanninger, M.; Wimmer, R.; Pâques, L.E. Heartwood extractives and lignin content of different larch species (Larix sp.) and relationships to brown-rot decay-resistance. Trees 2004, 18, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabner, M.; Müller, U.; Gierlinger, N.; Wimmer, R. Effects of Heartwood Extractives on Mechanical Properties of Larch. IAWA J. 2005, 26, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.J.; DeGroot, R. Treatability and Durability of Heartwood. In National Conference on Wood Transportation Structures; Ritter, M.A., Duwadi, S.R., Lee, P.D.H., Eds.; Gen. Tech. Rep. FPL-GTR-94; U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Forest Products Laboratory: Madison, WI, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Vek, V.; Balzano, A.; Poljanšek, I.; Humar, M.; Oven, P. Improving Fungal Decay Resistance of Less Durable Sapwood by Impregnation with Scots Pine Knotwood and Black Locust Heartwood Hydrophilic Extractives with Antifungal or Antioxidant Properties. Forests 2020, 11, 1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, M. Influence of Colour and Glossiness on Image of Wood. J. Soc. Mater. Sci. 1985, 34, 972–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindberg, S.; Roos, A.; Kihlstedt, A.; Lindström, M. A product semantic study of the influence of the sense of touch on the evaluation of wood-based materials. Mater. Des. 2013, 52, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowell, R.M. (Ed.) Handbook of Wood Chemistry and Wood Composites, 2nd ed.; CRC Press Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012; p. 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamke, F.A.; Lee, J.N. Adhesive penetration in wood—A review. Wood Fiber Sci. 2007, 39, 205–220. [Google Scholar]
- Bardak, S.; Nemli, G.; Bardak, T. The quality comparison of particleboards produced from heartwood and sapwood of European larch. Maderas. Cienc. Y Tecnol. 2019, 21, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 13061-1; Physical and Mechanical Properties of Wood—Test Methods for Small Clear Wood Specimens—Part 1: Determination of Moisture Content for Physical and Mechanical Tests. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014.
- ISO 13061-2; Physical and Mechanical Properties of Wood—Test Methods for Small Clear Wood Specimens—Part 2: Determination of Density for Physical and Mechanical Tests. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014.
- ISO 21920-2; Geometrical Product Specifications (GPS)—Surface Texture: Profile Part 2: Terms, definitions and Surface Texture Parameters. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021.
- Gindl, M.; Sinn, G.; Gindl, W.; Reiterer, A.; Tschegg, S. A comparison of different methods to calculate the surface free energy of wood using contact angle measurements. Colloids Surf. A—Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2001, 181, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, D.K.; Wendt, R.C. Estimation of the surface free energy of polymers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1969, 13, 1741–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN ISO/CIE 11664-2; Colorimetry—Part 2: CIE standard illuminants. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022.
- ISO 7724-3; Paints and Varnishes—Colorimetry—Part 3: Calculation of Colour Differences. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1984.
- Wagenführ, R. Holzatlas, 6th ed.; Neu Bearbeitete und Erweiteste Auflage; Fachbuchverlag: Leipzig, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Mańkowski, P.; Laskowska, A. Compressive strength parallel to grain of earlywood and latewood of yellow pine. Maderas-Cienc. Y Tecnol. 2021, 23, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazdrowski, W.; Jelonek, T.; Tomczak, A.; Stypuła, I.; Spława-Neyman, S. Proportion of sapwood and heartwood and selected biometric features in larch trees (Larix decidua Mill.). Wood Res. 2007, 52, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Bektaş, İ.; Tutuş, A.; Gültekin, G. The Effect of Sapwood and Heartwood Differences on Mechanical Properties of Fast-Growing Tree Species. Drv. Ind. 2020, 71, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozakiewicz, P.; Życzkowski, W. Physical and mechanical properties and anatomy of common juniper (Juniperus communis L.). wood. Sylwan 2015, 159, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinn, G.; Myesterday, H.; Stanzl-Tschegg, S. Surface properties of wood and MDF after ultrasonic-assisted cutting. J. Mater. Sci. 2005, 40, 4325–4332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendarto, B.; Shayan, E.; Ozarska, B.; Carr, R. Analysis of roughness of a sanded wood surface. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2006, 28, 775–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liptáková, E.; Kúdela, J. Analysis of the Wood-Wetting Process. Holzforschung 1994, 48, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Słupianek, A.; Dolzblasz, A.; Sokołowska, K. Xylem Parenchyma—Role and Relevance in Wood Functioning in Trees. Plants 2021, 10, 1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ugrenović, A. Wood Technology; Croatian Publishing: House, Zagreb, 1950. [Google Scholar]
- Horvat, I.; Krpan, J. Drvnoindustrijski Priručnik; Croatian Publishing: House, Zagreb, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Mokrzycki, W.S.; Tatol, M. Colour difference ∆E—A survey. Mach. Graph. Vis. 2011, 20, 383–411. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).