1. Introduction
The two-volume Special Issue “Advances in Surface Engineering and Biocompatible Coatings for Biomedical Applications” has brought together a comprehensive collection of 26 peer-reviewed articles, reflecting the rapid scientific progress and sustained global interest in advanced surface modification strategies for biomaterials. Across both volumes, the contributions have accumulated over 73,000 views and over 170 citations in less than two years, a clear indication of the strong and growing impact of this collection within the biomaterials and surface engineering community.
Volume I established the scientific foundation of the collection by presenting advances on innovative surface treatments, antibacterial and bioactive coatings, and tribological and corrosion analyses, including two highly cited review articles that helped shape the broader landscape of biomaterial surface modification. Building on this momentum, Volume II expanded the scope with new contributions including on micro-arc oxidation systems, hybrid ceramic–polymeric coating architectures, multifunctional antibacterial surfaces, corrosion and wear mechanisms in biomedical alloys, and advanced in vitro and in vivo assessment models. Together, these two volumes reveal the evolution of the field from more traditional single-purpose coatings toward more innovative multifunctional and mechanistically engineered surface systems designed to address complex clinical challenges such as osseointegration, infection control, biodegradation, and long-term implant reliability.
The overarching premise of this Special Issue is that while the bulk material provides structural support, it is ultimately the surface and its chemistry, topography, charge, energy, and biological interactions that govern the clinical performance of implants. By presenting advances in physical, mechanical, chemical, electrochemical, and bioactive surface engineering, this two-volume collection offers an integrated, forward-looking perspective on emerging concepts, methodologies, and design principles in biomaterial surface science.
To provide a coherent and structured overview of these contributions, the articles published across both volumes have been thematically classified according to their underlying surface engineering strategies and targeted biological or functional outcomes. The subsequent sections of this editorial highlight five major scientific themes that have emerged from this collection: (i) mechanical and physical surface treatments; (ii) bioactive and ceramic-based coatings; (iii) antibacterial and multifunctional hybrid surfaces; (iv) biological response, biomechanics, and implant–tissue interface studies; and (v) high-impact review papers defining the state of the art. The distribution of the 23 original research articles across the four scientific categories is visually summarized in Figure 1, while Table 1 provides a detailed mapping of only the research articles, categorized by material system, surface modification technique, and biomedical focus. Review papers are discussed separately in Section 2.5 and are not included in Figure 1 and Table 1. This structured synthesis sets the stage for a critical discussion of the key advances, mechanistic insights, and emerging research directions identified throughout the Special Issue.
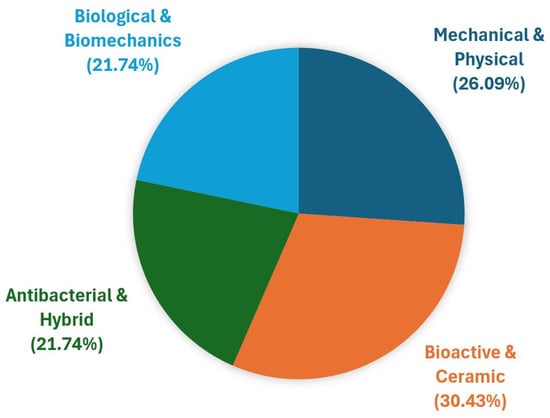
Figure 1.
Distribution of the 23 original research articles published across the two-volume Special Issue according to four scientific categories: (i) mechanical and physical surface treatments (n = 6); (ii) bioactive and ceramic-based coatings (n = 7); (iii) antibacterial and multifunctional hybrid surfaces (n = 5); and (iv) biological response, biomechanics, and implant–tissue interface studies (n = 5).

Table 1.
Research articles included in this Special Issue (Volume I and II) categorized by material system, surface modification technique, and biomedical function.
2. Thematic Overview and Scientific Trends
The research articles included in this Special Issue span a spectrum of surface engineering approaches aimed at improving the biological, mechanical, and functional performance of biomaterials. For clarity and coherence, the content of this Special Issue has been grouped into four major scientific themes: (i) mechanical and physical surface treatments; (ii) bioactive and ceramic-based coatings; (iii) antibacterial and multifunctional hybrid surfaces; and (iv) biological response, biomechanics, and implant–tissue interface studies. Each theme represents a distinct yet interconnected dimension of modern surface engineering, reflecting ongoing efforts to address challenges such as osseointegration, infection control, degradation, wear, and long-term implant stability. In the following subsections, we highlight representative studies within each thematic group and critically discuss the mechanistic insights and emerging trends that arise from their combined findings.
2.1. Mechanical and Physical Surface Treatments
Mechanical and physical surface treatments remain central to the development of high-performance biomaterials, particularly for metallic implants where surface integrity, microstructural stability, and near-surface functionalization govern clinical outcomes [24]. Several contributions in this Special Issue demonstrate how severe plastic deformation, grain refinement, residual stress modulation, and controlled topographical changes can be strategically combined to enhance corrosion resistance, wear behavior, and biological performance.
Shot peening (SP) features prominently among these approaches, with multiple studies reporting its capacity to induce near-surface nanocrystallization, refine grains, and improve mechanical and electrochemical stability in titanium-based systems [25,26]. Conventional SP and fine-particle SP were comparatively investigated for biomedical Ti6Al4V, revealing substantial differences in roughness-driven wettability and antibacterial behavior, attributed to particle size-dependent impact energies and topology alterations [5]. These findings align with prior work on powder metallurgical Ti6Al4V [2] and Cp-Ti [4], where SP generated hardened subsurface layers and improved wear resistance through the formation of highly deformed α-Ti grains. Together, these studies reinforce the versatility of SP as a microstructural engineering tool for tailoring both mechanical durability and cell–surface interactions.
Physical surface modification beyond SP was also explored. Ion implantation of Zr/Nb into ZrO2 films produced strengthened, wear-resistant surfaces, supported by first-principle calculations revealing improved bonding states and defect energetics [3]. Similarly, mechanical pre-tensioning via {332} twinning followed by aging treatment in Ti-15Mo altered grain boundary character and passivation behavior, concurrently enhancing corrosion resistance and wear stability through deformation-assisted microstructural reorganization [6]. These mechanistic insights highlight how controlled plastic deformation pathways, whether impact-driven or deformation-induced, can be exploited to optimize surface reactivity, oxide stability, and long-term implant robustness.
Overall, the mechanical and physical treatments presented across the Special Issue demonstrate a shared theme: altering surface and subsurface microstructure provides a powerful route to tuning implant performance, with SP-induced strain gradients, ion implantation-modified chemistries, and twinning-assisted microstructural evolution offering complementary strategies for advancing next-generation biomedical alloys.
2.2. Bioactive and Ceramic-Based Coatings
Bioactive and ceramic-based coatings represent one of the most intensively explored strategies for enhancing osseointegration, corrosion resistance, and biological performance of metallic biomaterials. Across the contributions in this Special Issue, hydroxyapatite (HA), calcium–phosphate (CaP), bioactive glass, and ceramic–oxide systems are engineered through sol–gel, micro-arc oxidation (MAO), electrophoretic deposition (EPD), liquid-phase deposition, and atomic layer deposition, each offering a distinct pathway for surface functionalization.
Low-temperature synthesis routes were successfully employed to deposit substituted HA coatings incorporating antibacterial ions such as Cu and Zn, yielding surfaces that combine apatite-like bioactivity with improved microbial suppression [7]. Similarly, ZnO-modified CaP layers fabricated via MAO displayed tailored zeta potential and enhanced antibacterial capability, underscoring the synergy between ceramic chemistry, nanoscale surface charge, and microbial interactions [9]. These findings highlight the importance of chemical doping and ionic substitution for modulating both biological and antibacterial responses in HA-based systems.
Complementary strategies using composite approaches were also widely represented. Bioactive glass coatings with ZnO nanoparticles deposited on stainless steel demonstrated enhanced bioactivity and structural integrity, driven by nanoparticle-mediated control of dissolution kinetics and apatite formation [8]. In parallel, Ga-doped HA coatings on β-Ti–45Nb alloys provided dual benefits by supporting osteogenic potential while introducing Ga-mediated antibacterial effects, illustrating how multi-ion engineering can drive multifunctional performance [10].
Magnesium-based biomaterials received particular attention, with several studies addressing their intrinsic challenges related to degradation. Superhydrophobic HA coatings produced through MAO followed by liquid-phase deposition significantly reduced corrosion rates and improved in vitro bioactivity on AZ31 Mg alloys [11]. A complementary approach using MAO ceramic layers combined with ALD TiO2 demonstrated that ultrathin, conformal oxide films can effectively seal MAO porosity, yielding superior corrosion resistance and improved cytocompatibility under physiological conditions [12]. A systematic study on MAO CaP coatings further showed that increasing TiO2 nanoparticle concentration alters surface morphology and oxide layer composition, enhancing passivation and supporting favorable cell responses [13].
Collectively, these contributions reveal a consistent mechanistic theme: bioactive ceramic coatings serve as tunable platforms where chemistry, crystallography, and hierarchical microstructure work in concert to regulate degradation behavior, protein adsorption, cellular attachment, and antibacterial activity. The integration of dopants, composite layers, and hybrid processing routes (e.g., MAO + ALD, MAO + LPD) demonstrates the shift toward multimodal coating architectures that bridge mechanical durability with biological functionality.
2.3. Antibacterial and Multifunctional Hybrid Surfaces
Preventing bacterial adhesion and biofilm formation remains one of the most persistent challenges in implantology. As demonstrated across several studies in this Special Issue, hybrid antibacterial surfaces, engineered through metallic ion incorporation, polymer–nanoparticle composites, or carbon-based lubricating films, offer promising routes to simultaneously enhance antimicrobial activity, interfacial stability, and tribological performance.
Silver-based systems are particularly prominent due to their broad-spectrum antibacterial activity. Powder coatings incorporating silver nanoparticles within different carrier matrices showed that antimicrobial effectiveness can be highly dependent on nanoparticle dispersion and carrier–silver compatibility, highlighting the need for controlled microstructural integration within polymeric systems [14]. Silver–chitosan nanocomposites developed for dental remineralization applications further illustrated multifunctionality, combining strong antibacterial action with the ability to promote surface remineralization, a dual benefit attributed to chitosan’s inherent bioactivity and silver’s bactericidal properties [17].
Gold coatings offer an additional design strategy. Electrodeposited gold layers on dental abutments effectively reduced microgaps and bacterial leakage, demonstrating that even nanoscale modifications to implant–abutment interfaces can influence microbial colonization and mechanical sealing behavior [15]. Similarly, ZnO-containing CaP coatings produced through micro-arc oxidation offered antibacterial function coupled with favorable surface charge characteristics, demonstrating a synergistic response where ionic release, microstructure, and surface energy collectively determine bactericidal efficacy [9]
Carbon-based thin films also emerged as a powerful antibacterial and tribological platform. Diamond-like carbon (DLC) coatings applied to implant abutments improved reverse torque performance while reducing wear and friction at internal conical connections, factors that directly affect implant longevity and mechanical stability [18]. The low surface energy and dense carbon network of DLC not only inhibit bacterial adhesion but also act as a solid lubricant, representing a distinct mechanistic pathway compared to metal-ion or ceramic-based antibacterial strategies.
Further multifunctional behavior was demonstrated in nanostructured antibacterial surfaces for spinal fixation screws, where engineered nano-architectures effectively suppressed biofilm formation and improved mechanical robustness under physiological loading conditions [16]. These results emphasize the importance of integrating textural and chemical cues to disrupt bacterial colonization on load-bearing orthopedic devices.
Taken together, the antibacterial and multifunctional hybrid surfaces presented here highlight a clear trend toward multi-mechanism antimicrobial strategies, where ion release, polymer–nanoparticle synergy, surface energy reduction, and nanoscale architectural control converge to combat biofilm formation while supporting mechanical and biological stability.
2.4. Biological Response, Biomechanics, and Tissue–Implant Interface
Biological interactions at the implant surface ultimately determine the success of biomedical devices, influencing early osseointegration, inflammatory response, long-term stability, and tissue regeneration. Several contributions in this Special Issue address these aspects through experimental, in vivo, and computational approaches, providing mechanistic insight into how surface modifications and biological environment jointly regulate tissue response.
Biomechanics-oriented analyses reveal how implant geometry and stress distribution affect clinical performance. Finite element simulations applied to different miniplate designs demonstrated that geometric optimization can substantially reduce stress concentrations at skeletal anchorage sites, with direct implications for implant stability and patient-specific orthodontic planning [19]. Such models highlight the fundamental link between surface treatment, structural design, and mechanical loading pathways in vivo.
Biochemical and pharmacological modulation of the tissue–implant interface was also explored. An in vivo study examining losartan, an angiotensin II receptor blocker commonly prescribed for hypertension, showed that systemic medication can influence bone–implant integration, enhancing osseointegration in hypertensive rat models [21]. This work underscores the need to consider patient-specific systemic factors when evaluating implant performance and demonstrates that implant success cannot be isolated from systemic biological context.
Biologically driven surface responses were further examined through natural extracts and tissue-level structural analyses. Cranberry extract exhibited osteogenesis-stimulating potential in vitro, attributed to phenolic and anthocyanin compounds that promote osteoblastic activity and modulate oxidative responses [20]. Similarly, the hierarchical orientation of hydroxyapatite fibers in enamel was shown to play a critical role in resisting wear and crack propagation, providing valuable biomimetic insights for engineering high-durability ceramic and CaP coatings [23]. These findings collectively emphasize the importance of microstructural anisotropy and natural hierarchical design principles in informing the next generation of bioinspired surface treatments.
Tissue engineering approaches further expanded the biological scope. An acellular spinal cord scaffold functionalized with VEGF and processed using ultrasound-assisted crosslinking demonstrated enhanced regenerative potential, offering a multifunctional platform for neuroregenerative applications [22]. The ability to modulate vascularization and support axonal growth highlights the broader relevance of surface engineering beyond classical orthopedic and dental implants.
Overall, these studies reinforce that biological response cannot be decoupled from surface chemistry, mechanical environment, or systemic physiology. By integrating biomechanical modeling, pharmacological effects, natural biomolecules, and tissue engineering strategies, this Special Issue provides a multidimensional perspective on how surface engineering influences, and is influenced by, the complex biological milieu surrounding implanted materials.
2.5. Review Articles: Current Landscape and Future Challenges
The Special Issue includes some impactful review papers that collectively frame the broader scientific context of surface engineering for biomedical applications. These reviews synthesize emerging trends, identify persistent challenges, and outline future research directions that resonate strongly with the findings reported in the research articles.
A comprehensive review on surface modification techniques for 3D-printed titanium implants emphasized the transformative role of additive manufacturing in biomedical device design and the necessity of surface treatments to overcome issues such as microstructural heterogeneity, surface roughness artifacts, and reduced osseointegration associated with as-printed components [27]. The authors highlighted a wide range of post-processing strategies, from mechanical treatments to biochemical coatings, thereby aligning closely with many of the experimental studies reported in this Special Issue. Their synthesis reinforces the view that AM-derived implant surfaces require tailored multi-step modification routes to achieve clinically reliable performance.
A second systematic review focused on multifunctional coatings across orthopedic, dental, and soft-tissue implant applications, consolidating the current state of antibacterial, osteogenic, and corrosion-resistant surface technologies [28]. This work underscored the rising importance of multifunctionality, a theme echoed in hybrid coatings incorporating ZnO, Ag–chitosan, DLC films, and complex ceramic dopants across several contributions in this Special Issue. The review argues for integrated solutions capable of addressing the simultaneous demands of mechanical durability, biological compatibility, and infection control, thereby providing a conceptual framework for the multifunctional surface systems identified in Section 2.3.
In addition, an editorial-style review summarizing advances in implant alloys and coatings provided a broader materials-oriented perspective, discussing emerging alloy systems, bioactive ceramics, and next-generation functional coatings [29]. This framework complements the mechanistic insights in Section 2.1 and Section 2.2, reinforcing the need for surface engineering strategies that integrate microstructural control, chemical functionality, and biomimetic design principles.
Together, these reviews exemplify the multidimensional landscape of surface engineering research. Their collective perspective highlights several future challenges, including the need for predictive modeling of biological outcomes, improved synergistic multifunctional coatings, and integrated processing–performance correlations, that are reflected upon and further advanced in the research articles featured in this Special Issue.
3. Emerging Trends and Future Perspectives
Across the two volumes of this Special Issue, several overarching trends have emerged, collectively defining the current direction of surface engineering research for biomedical applications. The first major trend is the shift toward multifunctional and hierarchical surface systems, where a single coating or treatment integrates antibacterial, osteogenic, corrosion-resistant, and tribological functions. Hybrid approaches, such as MAO combined with ALD sealing layers, multi-ion substituted HA coatings, and polymer–nanoparticle composites, reflect a growing emphasis on synergistic mechanisms that simultaneously address the diverse clinical demands placed on implants.
A second trend is the increasing focus on microstructural and chemical precision, made possible through techniques such as ion implantation, ALD, fine-particle shot peening, and controlled ceramic deposition routes. These methods enable nanometer-to-micrometer scale control over grain structure, oxide chemistry, and surface energy, offering predictable pathways for tuning cell behavior, antibacterial activity, and mechanical reliability. As demonstrated in both titanium- and magnesium-based systems, optimized subsurface deformation and oxide stabilization are becoming key parameters for extending implant longevity. Recent progress in plasma-based ceramic oxidation (PEO) processes, particularly electrochemical oxidation (ECO) variants designed to suppress micro-arc instability and reduce coating porosity, further illustrates this trend. Such approaches have demonstrated improved adhesion, reduced surface defects, and enhanced corrosion resistance in magnesium-based systems, positioning ECO/PEO technologies as promising candidates for the next generation of structurally controlled oxide coatings [30,31].
Biologically oriented approaches continue to gain momentum. The incorporation of bioactive molecules, natural extracts, and pharmacological agents points to a growing recognition that implant performance is strongly influenced by the surrounding biological and systemic environment. Studies examining osteogenic stimulation, drug–implant interactions, and bioinspired hierarchical architectures illustrate the field’s increasing movement toward bio–materials integration, where biological signaling and surface design are treated as interconnected components rather than separate domains.
Finally, several contributions highlight the need for predictive and personalized implant design, driven by biomechanics-informed evaluations and computational simulation. As implants become more complex and applications more patient-specific, integrating predictive modeling with advanced surface treatments will become essential for designing next-generation devices that balance mechanical robustness with favorable biological outcomes.
Together, these trends indicate a rapidly evolving landscape in which multi-functionality, microstructural precision, biological integration, and predictive modeling converge to shape future research. The insights collected through this Special Issue underscore the need for continued interdisciplinary efforts aimed at bridging materials science, biology, and biomechanics to engineer surfaces capable of meeting the increasingly complex requirements of modern biomedical implants.
4. Conclusions
The two-volume Special Issue “Advances in Surface Engineering and Biocompatible Coatings for Biomedical Applications” brings together a diverse yet thematically coherent collection of studies that collectively advance our understanding of how engineered surfaces can transform the performance of biomedical materials. Across 26 research and review articles, the contributions demonstrate that the interplay between surface chemistry, microstructure, mechanical integrity, and biological response is central to the success of modern implants.
The research findings highlight several overarching points. Mechanical and physical treatments continue to provide powerful pathways for tailoring near-surface microstructures, modulating residual stress, and enhancing mechanical durability. Bioactive and ceramic-based coatings offer finely tunable chemical and structural platforms for improving corrosion resistance, osteoconductivity, and antibacterial function, particularly through hybrid, doped, and multi-layer architectures. Antibacterial and multifunctional surfaces illustrate a broader trend toward integrated strategies that combine chemical, topographical, and nanostructural cues to control microbial behavior while enhancing tribological performance. Complementing these materials-focused advances, biological and biomechanical investigations demonstrate that systemic factors, cellular signaling, hierarchical structural organization, and mechanical loading pathways must be considered as integral components of implant design.
Together, the collective insights gained through this Special Issue underscore a unifying message: effective surface engineering requires a holistic, interdisciplinary approach that bridges materials science, mechanics, chemistry, and biology. As biomedical applications become increasingly demanding—spanning load-bearing orthopedic devices, bioactive dental interfaces, biodegradable magnesium systems, and regenerative scaffolds—the need for multifunctional, biologically informed, and predictively designed surface solutions will only continue to grow.
We hope that the research and perspectives presented across these two volumes will serve as a valuable resource for the community and stimulate further innovation in the engineering of advanced surfaces for next-generation biomedical implants and devices.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.A. and M.G.; writing—original draft preparation, E.A.; writing—review and editing, E.A., M.G., Y.Y.A. and B.Y.; visualization, E.A.; supervision, E.A. and M.G.; project administration, E.A.; funding acquisition, E.A. and M.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The Guest Editors thank Kocaeli University Scientific Research Projects Coordination Unit (BAP) for project support under Project ID: 3749, Project Code: FKA-2024-3749.
Acknowledgments
The Guest Editors would like to express their sincere appreciation to all authors who contributed their high-quality research and review articles to this two-volume Special Issue, as well as to the reviewers for their timely and constructive evaluations. We also extend our gratitude to the Coatings editorial team for their continuous support throughout the organization and publication process. We would additionally like to acknowledge Mustafa Armağan and Eray Abakay for their assistance during the coordination of the second volume of the Special Issue. Their support in managing submissions and communication workflows is gratefully recognized.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| SP | Shot Peening |
| Ti6Al4V | Titanium Alloy Grade 5 (Ti-6Al-4V) |
| PM | Powder Metallurgy/Powder Metallurgical |
| Cp-Ti | Commercially Pure Titanium |
| ZrO2 | Zirconium Dioxide |
| HA | Hydroxyapatite |
| CaP | Calcium Phosphate |
| ZnO | Zinc Oxide |
| MAO | Micro-Arc Oxidation |
| EPD | Electrophoretic Deposition |
| ALD | Atomic Layer Deposition |
| LPD | Liquid-Phase Deposition |
| BG | Bioactive Glass |
| DLC | Diamond-Like Carbon |
| VEGF | Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor |
| SCI | Spinal Cord Injury |
| FEA | Finite Element Analysis |
| TiO2 | Titanium Dioxide |
| β-Ti | Beta-Phase Titanium Alloy |
| HAp | Hydroxyapatite (crystallographic notation, often interchangeable with HA) |
| Mg | Magnesium |
| ARB | Angiotensin II Receptor Blocker |
| EDC | 1-Ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide (crosslinking agent) |
References
- Badji, C.; Allal, A.; Dupin, J.-C.; Léonardi, F. Impact of Sterilization on the Adhesion Properties of a Polyamide 11 Coating on Textured Metal Substrates. Coatings 2024, 14, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avcu, E.; Abakay, E.; Yıldıran Avcu, Y.; Çalım, E.; Gökalp, İ.; Iakovakis, E.; Koç, F.G.; Yamanoglu, R.; Akıncı, A.; Guney, M. Corrosion Behavior of Shot-Peened Ti6Al4V Alloy Produced via Pressure-Assisted Sintering. Coatings 2023, 13, 2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, D. The Surface Modification of ZrO2 Film by Zr/Nb Ion Implantation and First-Principles Calculation. Coatings 2023, 13, 1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avcu, Y.Y.; Iakovakis, E.; Guney, M.; Çalım, E.; Özkılınç, A.; Abakay, E.; Sönmez, F.; Koç, F.G.; Yamanoğlu, R.; Cengiz, A.; et al. Surface and Tribological Properties of Powder Metallurgical Cp-Ti Titanium Alloy Modified by Shot Peening. Coatings 2023, 13, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avcu, E.; Guney, M.; Yıldıran Avcu, Y.; Sulak, M.; Uzuner, H.; İlçe Bahadır, M.; Abakay, E.; Armağan, M.; Yamanoğlu, R.; Elibol, C.; et al. Comparative Effects of Fine and Conventional Shot Peening on Surface Morphology, Topography, Wettability, and Antibacterial Activity of Biomedical Ti6Al4V Alloy. Coatings 2025, 15, 1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yang, F.; Sun, W.; Cui, N.; Xu, T. Enhancing Passivation Behaviors and Wear Resistance of Biomedical Ti-15Mo Alloy via {332} Twinning Pre-Tension and Aging. Coatings 2024, 14, 1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukaviciute, L.; Karciauskaite, J.; Grigoraviciute, I.; Vasiliauskiene, D.; Sokol, D.; Kareiva, A. Calcium Hydroxyapatite Coatings: Low-Temperature Synthesis and Investigation of Antibacterial Properties. Coatings 2023, 13, 1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidari Laybidi, F.; Bahrami, A.; Abbasi, M.S.; Rajabinezhad, M.; Heidari Beni, B.; Karampoor, M.R.; Mousavi Anijdan, S.H. Electrophoretic Deposition of ZnO-Containing Bioactive Glass Coatings on AISI 316L Stainless Steel for Biomedical Applications. Coatings 2023, 13, 1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chebodaeva, V.; Sedelnikova, M.; Khimich, M.; Bakina, O.; Tolmachev, A.; Miller, A.; Golohvast, K.; Zakharenko, A.; Egorkin, V.; Vyaliy, I.; et al. Antibacterial Calcium Phosphate Coatings with Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles. Coatings 2023, 13, 1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishnu, J.; Voss, A.; Hoffmann, V.; Alberta, L.A.; Akman, A.; Shankar, B.; Gebert, A.; Calin, M. Designing Gallium-Containing Hydroxyapatite Coatings on Low Modulus Beta Ti-45Nb Alloy. Coatings 2023, 13, 1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Liang, X.; Yuan, Y.; Jian, F.; Tang, H. Preparation of Superhydrophobic Hydroxyapatite Coating on AZ31 Mg Alloy by Combining Micro-Arc Oxidation and Liquid-Phase Deposition. Coatings 2025, 15, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Wang, Y.; Ma, J.; Ma, X. Corrosion Resistance and In Vitro Biological Properties of TiO2 on MAO-Coated AZ31 Magnesium Alloy via ALD. Coatings 2024, 14, 1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhassulan, A.; Rakhadilov, B.; Baizhan, D.; Kengesbekov, A.; Kakimzhanov, D.; Musataeva, N. Influence of TiO2 Nanoparticle Concentration on Micro-Arc Oxidized Calcium–Phosphate Coatings: Corrosion Resistance and Biological Response. Coatings 2025, 15, 1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Cui, J.; Yang, J.; Yan, H.; Zhu, X.; Shao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, J. Effect of Carrier Materials for Active Silver in Antibacterial Powder Coatings. Coatings 2024, 14, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walton, T.R. Effect of Electrodeposited Gold Coatings on Micro-Gaps, Surface Profile and Bacterial Leakage of Cast UCLA Abutments Attached to External Hexagon Dental Implants. Coatings 2023, 13, 1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panaitescu, T.G.; Niculescu, A.-G.; Grumezescu, V.; Costăchescu, B.; Bircă, A.C.; Balaure, P.C.; Oprea, O.C.; Voinea, I.C.; Stan, M.S.; Holban, A.M.; et al. Nanostructured Coatings for Spinal Fixation Screws: A Dual-Function Approach Against Biofilm Formation and Implant Failure. Coatings 2025, 15, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Rodríguez, K.A.A.; de González, W.Y.E.; Castañeda Monroy, V.; Murphy, S.; Martínez-Castañón, G.-A.; Bach, H.; Niño-Martínez, N. Silver Nanoparticles–Chitosan Nanocomposites as Protective Coatings for Dental Remineralization Treatment: An In Vitro Study. Coatings 2025, 15, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, A.V.P.; Figueiredo, V.M.G.d.; Ferreira, L.L.; Silva, A.d.M.; Oliani, M.G.; Queiroz, J.R.C.d.; Sobrinho, A.S.d.S.; Nogueira Junior, L.; Prado, R.F.d. Impact of Diamond-like Carbon Films on Reverse Torque: Superior Performance in Implant Abutments with Internal Conical Connections. Coatings 2024, 14, 1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ielpo, A.P.M.; de Matos, J.D.M.; Noritomi, P.Y.; da Rocha Scalzer Lopes, G.; Queiroz, D.A.; Borges, A.L.S.; Nascimento, R.D. Biomechanical Behavior of Different Miniplate Designs for Skeletal Anchorage in the Anterior Open Bite Treatment. Coatings 2022, 12, 1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, Y.G.; Magini, E.B.; Farias, I.V.; Della Pasqua Neto, J.; Fongaro, G.; Reginatto, F.H.; Silva, I.T.; Cruz, A.C.C. Potential of Cranberry to Stimulate Osteogenesis: An In Vitro Study. Coatings 2024, 14, 1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulinari-Santos, G.; Santos, J.S.d.; de Souza Batista, F.R.; Pitol-Palin, L.; Silva, A.C.E.d.; Botacin, P.R.; Antoniali, C.; Okamoto, R. Evaluation of Bone–Implant Interface: Effects of Angiotensin II Receptor Blockade in Hypertensive Rats. Coatings 2025, 15, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Liu, Y.; Xu, Z.; Yin, H. Ultrasound-Assisted Acellular Spinal Cord Scaffold for Spinal Cord Injury Treatment. Coatings 2024, 14, 1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Xin, H.; Li, X.; Kong, Y.; Zhu, S.; Zhou, Y.; Fan, Y.; Xia, J. Natural Selection on Hydroxyapatite Fiber Orientations for Resisting Damage of Enamel. Coatings 2024, 14, 1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avcu, E.; Avcu, Y.Y.; Armağan, M.; Abakay, E.; Yousif, B.F.; Guney, M. Editorial: Tribological behavior of biomaterials. Front. Mater. 2025, 12, 1549972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abakay, E.; Armağan, M.; Yıldıran Avcu, Y.; Guney, M.; Yousif, B.F.; Avcu, E. Advances in improving tribological performance of titanium alloys and titanium matrix composites for biomedical applications: A critical review. Front. Mater. 2024, 11, 1452288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildiran Avcu, Y.; Yetik, O.; Guney, M.; Iakovakis, E.; Sinmazcelik, T.; Avcu, E. Surface, Subsurface and Tribological Properties of Ti6Al4V Alloy Shot Peened under Different Parameters. Materials 2020, 13, 4363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, S.; Zhu, J.; Jing, Y.; He, S.; Cheng, L.; Shi, Z. A Comprehensive Review of Surface Modification Techniques for Enhancing the Biocompatibility of 3D-Printed Titanium Implants. Coatings 2023, 13, 1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishwakarma, V.; Kaliaraj, G.; Amirtharaj Mosas, K. Multifunctional Coatings on Implant Materials—A Systematic Review of the Current Scenario. Coatings 2022, 13, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishwakarma, V.; Kaliaraj, G.; Kirubaharan, A. Advanced Alloys and Coatings for Bioimplants. Coatings 2022, 12, 1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavuzyegit, B.; Karali, K.; Avcu, E.; De Mori, A.; Quizon, D.; Hacıosmanoğlu, M.; Hekimoğlu, A.P.; Smith, N.; Usov, S.; Shashkov, P.; et al. Corrosion and mechanical performance of novel electrochemical oxidation coatings on AZ31 magnesium alloys for biomedical applications. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2025, 507, 132151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavuzyegit, B.; Karali, K.; Davis, S.; Morrison, B.; Karabal, S.; Balandiz, K.; Smith, N.; Usov, S.; Shashkov, P.; Bonithon, R.; et al. High-resolution DIC analysis of in situ strain and crack propagation in coated AZ31 magnesium alloys under mechanical loading. J. Mater. Sci. 2025, 60, 14708–14730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).