Abstract
Heavy metal ions pose a significant threat to the environment and human health due to their high toxicity and bioaccumulation. Traditional instrumentations, although sensitive, are often complex, costly, and unsuitable for on-site rapid detection of heavy metal ions. Lateral flow assay technology has emerged as a research hotspot due to its rapid, simple, and cost-effective advantages. This review summarizes the applications of lateral flow assay technology based on nucleic acid molecules and antigen–antibody interactions in heavy metal ion detection, focusing on recognition mechanisms such as DNA probes, nucleic acid enzymes, aptamers, and antigen–antibody binding, as well as signal amplification strategies on lateral flow testing strips. By incorporating these advanced technologies, the sensitivity and specificity of lateral flow assays have been significantly improved, enabling highly sensitive detection of various heavy metal ions, including Hg2+, Cd2+, Pb2+, and Cr3+. In the future, the development of lateral flow assay technology for detection of heavy metal ions will focus on multiplex detection, optimization of signal amplification strategies, integration with portable devices, and standardization and commercialization. With continuous technological advancements, lateral flow assay technology will play an increasingly important role in environmental monitoring, food safety, and public health.
1. Introduction
Heavy metal ions, characterized by their high density and toxicity, are widely present in natural environments and industrial processes [1]. Due to their non-degradability and bioaccumulation, heavy metal ions pose significant threats to both the environment and human health [2,3]. Heavy metal pollution primarily originates from industrial wastewater, mining activities, agricultural chemical use, and improper disposal of electronic waste [4,5]. These ions enter ecosystems through water, soil, and air, eventually accumulating in organisms through the food chain [6], thereby posing potential risks to human health.
For instance, lead (Pb) is a neurotoxin that causes delayed intellectual development in children and neurological damage in adults [7,8,9]. Cadmium (Cd) exhibits nephrotoxicity and carcinogenicity, leading to osteoporosis via long-term ingestion [10,11,12]. Mercury (Hg), especially methylmercury, crosses the blood–brain barrier, causing irreversible central nervous system damage [13,14]. Hexavalent chromium (Cr(VI)) is highly carcinogenic, linked to lung cancer and skin ulcers [15,16]. Excessive copper (Cu) induces liver damage, while silver (Ag+) impairs cellular functions and aquatic ecosystems [17,18]. Arsenic (As), uranium (U), and thallium (Tl) disrupt cellular structures, causing various diseases [19,20,21].
High-concentration heavy metal pollution incidents, such as mercury contamination in the Wanshan Special District of Guizhou (with mercury levels reaching 358.51 mg/kg) [22,23], and heavy metal contamination exceeding safety standards in the Dongjiang River Basin [24], have highlighted the severe threats to human health and ecosystems. These cases underscore the urgent need for better monitoring and remediation, including rapid detection methods like lateral flow assays, to protect human health and the environment. Therefore, the development of rapid and sensitive detection methods, such as lateral flow assays, is crucial for the timely intervention and management of such pollution incidents.
Given the toxicity and widespread presence of heavy metal ions, the development of efficient and sensitive detection methods is crucial for environmental monitoring, food safety, and public health. Traditional detection methods for heavy metal ions include atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS) [25,26], inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) [27,28], and high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) [29,30]. While these methods offer high sensitivity and accuracy, they typically require complex sample preparation, expensive instrumentation, and specialized technical expertise, making them unsuitable for on-site rapid detection. Consequently, the development of a rapid, simple, and cost-effective heavy metal ion detection technology has become a research focus.
In addition to traditional instrumental analysis, electrochemical methods (such as voltammetry [31,32,33], which detects heavy metal ions by measuring current changes from redox reactions on electrode surfaces, with a detection limit of 0.1 nM) and spectroscopic techniques (such as surface enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) spectroscopy, which quantifies ions through characteristic Raman signals generated by interactions between heavy metal ions and nanomaterials [34,35], achieving a detection limit as low as 1 pM) are also used for heavy metal ion detection. However, these technologies face significant limitations: voltammetry is susceptible to matrix interference and requires frequent electrode maintenance, while SERS relies on expensive spectrometers and professional data analysis, making it difficult to deploy on-site and unsuitable for real-time screening in sudden pollution incidents.
Lateral flow assay (LFA) is more suitable for on-site rapid detection due to its minimal operation (visual or smartphone reading within 10–30 min after sample addition), low cost (each test strip < $1), strong portability (no power supply or instruments required), and excellent resistance to matrix interference. By integrating nanomaterial labeling and signal amplification strategies, LFA can enhance sensitivity to the pM level and is compatible with various complex samples. In contrast, other technologies often rely on specialized instruments or complicated pretreatment, making them difficult to popularize in emergency monitoring and other on-site scenarios. Its core significance lies in enabling real-time on-site sampling and analysis of water, soil, and other samples during sudden heavy metal pollution incidents, providing immediate data support for pollution source control and early warning of population exposure risks-thereby filling the gap of traditional technologies in scenarios requiring ‘rapid response and on-site screening’.
In recent years, emerging rapid detection technologies for heavy metal ions have focused on integrating nanomaterials, microfluidics, and optoelectronic devices. For example, surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) combined with microfluidic chips enables ultrasensitive detection by amplifying characteristic spectral signals [35], while electrochemical sensors based on metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) achieve sub-nanomolar sensitivity through in situ redox reactions [36]. Fluorescent nanoprobes (e.g., quantum dots) have also been developed for real-time imaging of ions in biological samples [37], and smartphone-integrated detection systems are being designed to realize portable [38], high-throughput analysis. These technologies highlight trends toward miniaturization, high sensitivity, and intelligence in on-site rapid detection, though challenges remain in cost reduction and anti-interference capability for practical applications.
Lateral flow assay (LFA) technology is a rapid detection method known for its simplicity, low cost, and quick response, widely used in the detection of biomarkers, pathogens, and environmental pollutants [39,40,41,42,43]. A typical lateral flow test strip consists of a sample pad, conjugate pad, nitrocellulose membrane (NC membrane), and absorbent pad. When a sample solution is applied to the sample pad, the target analyte in the sample binds to the labeled conjugate on the conjugate pad, forming a complex. This complex then migrates along the NC membrane via capillary action, binding to the capture reagent immobilized on the membrane to form a visible test line [44]. The advantages of LFA technology lie in its independence from complex instrumentation and specialized technical personnel, making it suitable for on-site rapid detection [45,46,47].
In recent years, advancements in nanomaterials and biosensing technologies have significantly enhanced the application of LFA technology in heavy metal ion detection. Although plenty of work has been performed to develop rapid detection methods using LFA technology [48,49,50,51,52], there is no review specially focusing on the development of LFA-based heavy metal ion detection techniques. This review summarizes recent developments in heavy metal ion detection methods based on LFA technology. It focuses on the detection principles, detection limits, as well as signal readout methods and the types of detection samples for various heavy metal ions. By systematically analyzing existing research, this review aims to provide a reference for the future development of more efficient and sensitive heavy metal ion detection technologies.
2. Detection Strategies for Heavy Metal Ions Based on LFA Technology
This review systematically examines heavy metal ion detection methods utilizing LFA technology, with a focused exploration of four principal detection strategies and their recent advancements. From perspective of sensing principle, the LFA-based heavy metal detection methods mainly include four types: (1) DNA probe-based detection, (2) aptamer-assisted recognition, (3) nucleic acid enzyme-mediated analysis, and (4) antigen–antibody immunoassay techniques (Figure 1). In the following paragraphs, we will discuss the detailed sensing principles and applications for various meatal ions.
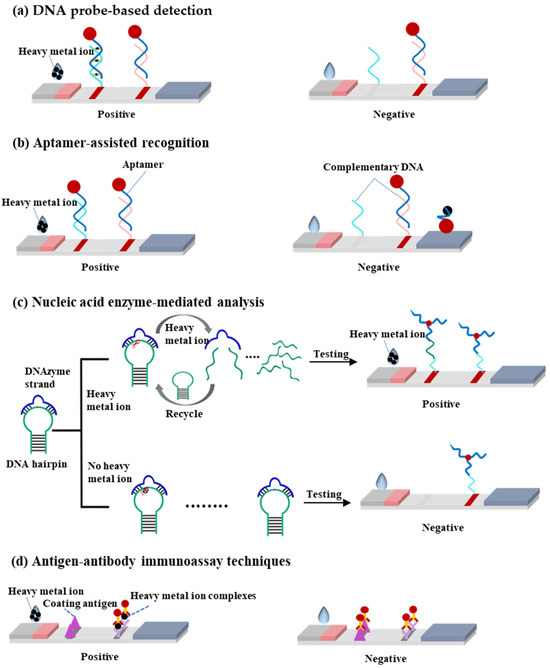
Figure 1.
(a) Schematic diagram of DNA probe-based detection principle. (b) Schematic diagram of aptamer-assisted recognition principle. (c) Schematic diagram of nucleic acid enzyme-mediated analysis principle. (d) Schematic diagram of antigen–antibody immunoassay technique principle.
2.1. DNA Probe-Based LFA Technology
The DNA probe-based lateral flow assay represents a rapid and portable detection technology for heavy metal ions, with its core principle relying on the specific recognition capability of DNA molecules toward target metal ions. The detection mechanism involves three key steps (Figure 1a):
- (i)
- Specific binding: DNA probes (e.g., T-rich sequences) form stable complexes or chemical bonds with target ions (e.g., Hg2+ through T-Hg2+-T coordination).
- (ii)
- Signal labeling: Gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) are labeled by a thiol terminated probing DNA sequence, which contains the recognition bases or groups for target metal ions.
- (iii)
- Visual readout: The labeled gold nanoparticle will be captured by the complementary DNA probes at the T line by forming stale double DNA structures, producing distinct red bands whose intensity correlates with target concentration.
For the DNA probe-based detection principle, it has advantages of simple probe design and high selectivity. To date, this strategy has been used for detection of various heavy metal ions, including Cu2+, Hg2+, Ag+, Pb2+, As3+, etc. By rational experimental design, these methods exhibit satisfactory sensitivity, and the detection limit can reach as low as nM levels. More importantly, these methods also are applicable to different real samples including environmental samples, food samples, and human fluids, demonstrating its applicability for on-site environmental monitoring and point-of-care testing applications. Details are provided in Table 1.

Table 1.
Detection of Heavy Metal Ions Using DNA Probe-Based LFA Technology.
Abrams et al. [53] utilized gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) as signal labels and employed azide-DNA and alkyne/biotin-DNA as recognition units. Through a click chemistry reaction, the linkage product was formed and conjugated with AuNPs to create a complex, enabling the visual detection of Cu2+ with a detection limit of 100 nM. Similarly, Wang et al. [54] employed AuNPs and modified single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) to detect Cu2+ via click chemistry, achieving detection limits of 5 nM (visual) and 4.2 nM (quantitative). This method is characterized by its simplicity, low cost, and high sensitivity, making it suitable for on-site diagnostics and environmental monitoring (e.g., detection of Cu2+ contamination in drinking water or industrial wastewater).
Zhu et al. [55] developed a lateral flow strip based on AuNPs and ssDNA probes for the rapid and ultrasensitive detection of Hg2+ in water. This method relies on the specific binding of T-rich ssDNA probes to Hg2+, forming T-Hg2+-T mismatch structures. AuNPs were used as signal labels, and signal amplification was achieved through enhanced probe hybridization, as illustrated in Figure 2. This approach enables simultaneous detection and signal amplification in a single step, with a visual detection limit of 25 pM and a quantitative detection limit of 7.5 pM. The method has been successfully applied to real samples such as tap water, tea water, and lake water, demonstrating its broad application potential.
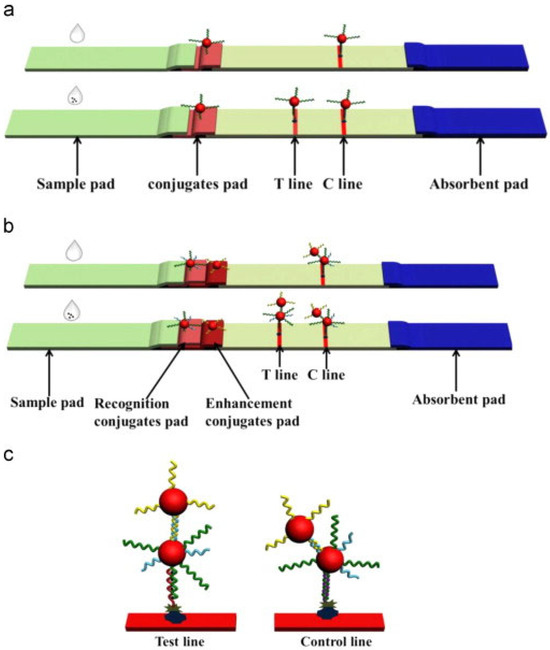
Figure 2.
(a) The sensing principle of the traditional lateral flow strip. (b) The sensing principle of the signal amplified lateral flow strip. (c) The test line and control line of the signal amplified lateral flow strip. Adapted with permission from [55].
Liu et al. [56], Guo et al. [57], Cheng et al. [58], and Yao et al. [59] developed various highly sensitive Hg2+ detection methods based on the T-Hg2+-T specific recognition mechanism, combined with AuNPs and DNA probes. These methods achieved Hg2+ detection through signal amplification techniques such as isothermal nucleic acid amplification and surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS), with detection limits ranging from 0.36 pM to 5 nM.
Wang et al. [60] utilized the T-Hg2+-T and C-Ag+-C structures for specific recognition and employed isothermal nucleic acid amplification for signal amplification to detect Hg2+ and Ag+ in water samples. The detection limits were 2.19 pM for Hg2+ and 5.41 pM for Ag+, as illustrated in Figure 3. This method exhibits high sensitivity and selectivity, making it suitable for on-site rapid detection.
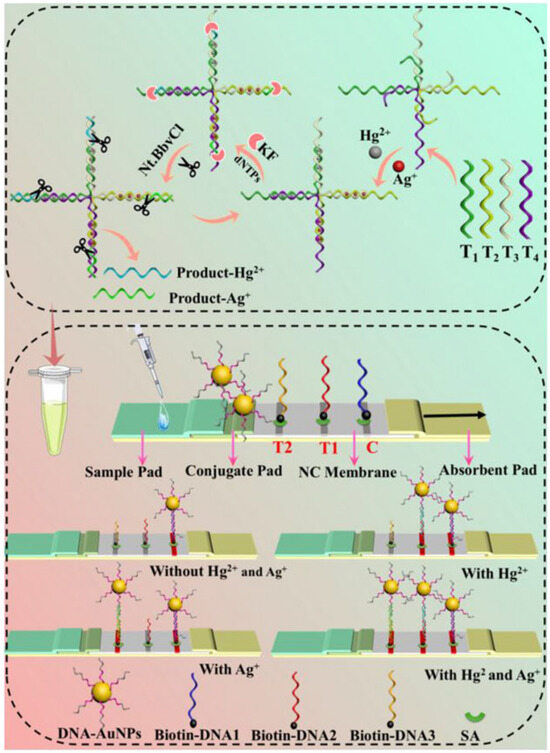
Figure 3.
Schematic diagram of LFA based on an isothermal amplification strategy for the detection of Hg2+ and Ag+. Adapted with permission from [60].
Ren et al. [61] employed AuNPs and G-quadruplex structures to detect Pb2+ in bottled drinking water. The method relies on lead ion-induced G-quadruplex formation and signal amplification through the release of anti-G4 single-stranded DNA. The detection limits were 20 nM (visual) and 7.32 nM (quantitative), as shown in Figure 4. Similarly, Wang et al. [62] developed a Pb2+ detection sensor based on the G-quadruplex structural switching mechanism, achieving a detection limit of 25 nM. This method combines the high specificity of G-quadruplex structures with the simplicity of lateral flow test strips, making it suitable for on-site rapid detection.
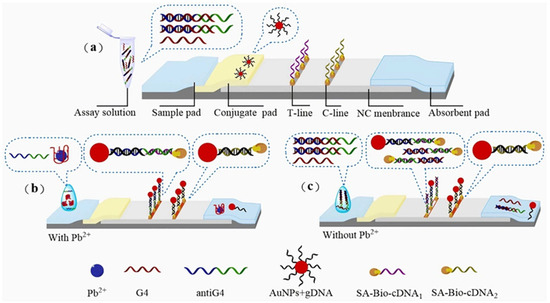
Figure 4.
Principle of test strip detection: (a) structural diagram; (b) with Pb2+; (c) without Pb2+. Adapted with permission from [61].
Zhang et al. [63] utilized a short single-stranded DNA (Apt-21) that binds to As(III) to form an As(III)-Apt-21 complex, serving as the recognition unit for As(III). Signal amplification was achieved through As(III)-induced aggregation of AuNPs, enabling the detection of As(III) in tap water and river water with a detection limit of 2.4 nM. This method combines the high specificity of short-chain DNA with the colorimetric properties of gold nanoparticles, making it suitable for on-site rapid detection.
This part of the research focuses on using DNA probes to detect heavy metal ions. The core principle is to form stable complexes through the specific binding of specific DNA sequences to target ions. Although the research cases vary, they all demonstrate the technology’s ability to detect multiple ions. This technology is generally easy to operate, low-cost, and highly sensitive, showing great potential in fields such as on-site diagnosis and environmental monitoring. However, this strategy can be only used for some special heavy metal ions such as Cu2+, Hg2+, Ag+, Pb2+, As3+, etc. In addition, the design and synthesis of some DNA probes with chemical modification are still complex, such as the modification of azide- and alkyne for the Cu2+ DNA probe.
Common challenges: Despite its advantages, this technology faces several limitations: (i) chemical modification of DNA probes (e.g., azide/alkyne for Cu2+ detection) increases synthesis complexity and cost; (ii) detection is primarily limited to specific ions (Hg2+, Pb2+) due to reliance on sequence-specific coordination; (iii) matrix interference from coexisting ions (e.g., Na+ in environmental water) may reduce binding specificity. These challenges highlight the need for universal probe design and anti-interference optimization.
2.2. Aptamer-Based LFA Technology
The aptamer-based lateral flow assay represents a cutting-edge biosensing platform that employs artificially selected nucleic acid aptamers for specific target detection. This innovative technology operates through three fundamental mechanistic steps:
- (i)
- Specific binding: Aptamers bind to target heavy metal ions (e.g., Hg2+, Cd2+) with high affinity through their unique three-dimensional structures, inducing significant conformational changes.
- (ii)
- Signal labeling: The spatial distribution or aggregation state of reporter molecules (e.g., gold nanoparticles, fluorescent dyes) conjugated to aptamers is altered by these conformational changes.
- (iii)
- Visual readout: Signal molecules accumulate at the test line (T-line), producing colored bands whose intensity correlates with target concentration, while the control line (C-line) validates assay performance.
The combination of molecular recognition precision and lateral flow simplicity positions this technology as a powerful tool for point-of-care testing and field-deployable analysis. Continuous improvements in aptamer selection and signal enhancement methodologies promise to further expand its application scope and detection capabilities. Details are provided in Table 2.

Table 2.
Detection of Heavy Metal Ions Using Aptamer-Based LFA Technology.
In the field of environmental monitoring, aptamer technology has demonstrated significant value for heavy metal ion detection, as detailed in Table 3. Specific examples include the following.

Table 3.
Detection of Heavy Metal Ions Using Nucleic Acid Enzyme-Based LFA Technology.
Jin et al. [64] utilized the fluorescence emission properties of upconversion nanoparticles (UCNPs) under near-infrared light excitation. By leveraging the specific binding of aptamers to target analytes, they achieved a highly sensitive and selective detection of Hg2+ with a detection limit of 25 nM. This detection platform completed the analysis of real water samples (e.g., tap water) within 30 min, demonstrating its broad application potential in environmental monitoring and food safety, as illustrated in Figure 5.
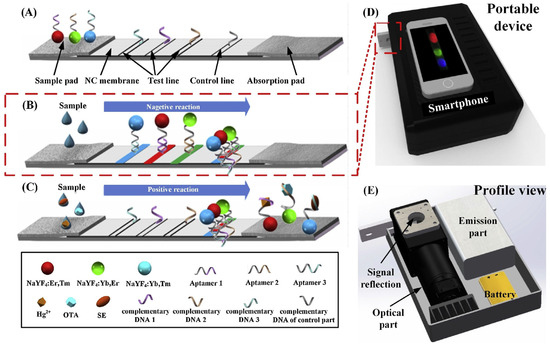
Figure 5.
Schematic illustration of LFAA for simultaneous multiple targets detection. (A) The structure of the developed LFAA. (B) In the absence of target, UCNP probes were separately hybridized with the corresponding complementary DNA. (C) In the presence of targets, the aptamers preferentially bonded to the corresponding targets and caused fewer aptamers to be hybridized with complementary DNA, thereby liberating UCNPs and resulting in fluorescence decrease. (D) A smartphone-based portable device is used to read the detection results. (E) The schematic of the smartphone-based portable device. Adapted with permission from [64].
Irfan et al. [65] and Wu et al. [66] developed lateral flow test strips based on aptamers and fluorescence technology for the detection of Cd2+ and Hg2+ in river water, achieving detection limits of 30 nM and 0.65 nM, respectively. Srinivasan et al. [67] utilized the specific binding of aptamers to Tl+ to enable rapid detection of thallium ions, as shown in Figure 6.
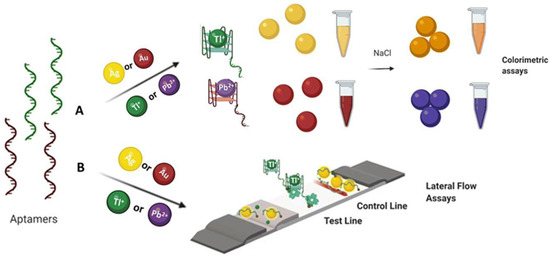
Figure 6.
Schematic illustration of (A) colorimetric and (B) lateral flow assay approaches for the detection of Tl(I) and Pb(II) ions. Adapted with permission from [67].
Berlina et al. [68] designed a lateral flow test strip based on phenylboronic acid and oligocytosine aptamers for the highly selective detection of Pb2+, with an instrumental detection limit of 0.24 nM and a visual detection limit of 4.8 nM, completing the detection within 5 min. In summary, aptamer-based LFA technology offers the advantages of simplicity, low cost, and high sensitivity.
The key to this technology is the high-affinity binding between aptamers and target heavy metal ions, achieving specific recognition. Research has been conducted on the detection of various ions such as Hg2+, Cd2+, Tl+, and Pb2+. Its advantages include simple operation, low cost, and high sensitivity, making it highly valuable in environmental monitoring. However, the aptamer screening process is complex and time-consuming, and the binding stability between aptamers and ions may be affected by other components in the sample, posing certain limitations in the detection of complex samples in practice.
Common challenges: The technology is constrained by (i) time-consuming aptamer screening (SELEX process requiring weeks to months); (ii) conformational instability of aptamers under varying salt/temperature conditions, leading to inconsistent detection signals; (iii) limited multiplexing capability for simultaneous ion analysis.
2.3. Nucleic Acid Enzyme-Based LFA Technology
The nucleic acid enzyme-based lateral flow assay is an advanced detection platform that leverages the specific catalytic activity of DNAzymes or MNAzymes for rapid heavy metal ion analysis. The detection mechanism operates through three precisely coordinated steps:
- (i)
- Specific binding: Target heavy metal ions (e.g., Pb2+) specifically activate nucleic acid enzymes (e.g., 8–17 DNAzyme), initiating cleavage of substrate DNA strands.
- (ii)
- Signal labeling: The cleavage reaction releases labeled fragments (e.g., fluorophore-conjugated or gold nanoparticle-tagged DNA segments).
- (iii)
- Visual readout: Released markers are captured at the T-line, generating visible signals (e.g., red bands) with intensity proportional to ion concentration.
This innovative approach combines the precision of nucleic acid enzymes with the simplicity of lateral flow technology, making it particularly valuable for environmental monitoring and field-deployable diagnostics where both accuracy and speed are essential. The system’s modular design also permits adaptation for various metal ion targets through appropriate enzyme selection. Details are provided in Table 3.
Kim et al. [69] developed a colorimetric detection method based on multicomponent nucleic acid enzymes (MNAzymes) and lateral flow test strips for the rapid detection of Hg2+ in tap water. This method utilizes MNAzymes containing T-T mismatches to specifically recognize Hg2+ and activate catalytic activity, leading to substrate cleavage. The cleaved substrate fails to produce a color signal on the test strip, while the uncleaved substrate generates a distinct red signal, enabling signal amplification. The detection limit of this method is 9.34 nM, as illustrated in Figure 7.
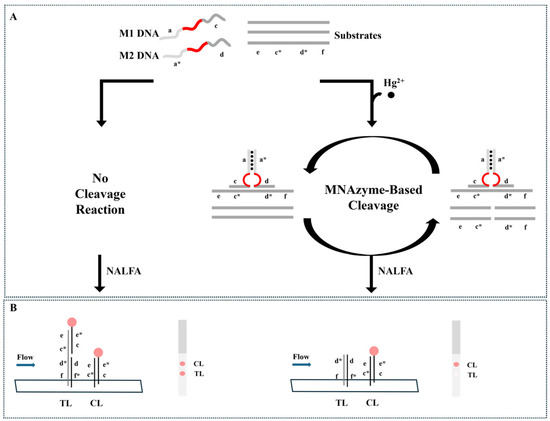
Figure 7.
Schematic illustration of the Hg2+ detection assay where (A) MNAzyme-based cleavage reaction occurs only in the presence of Hg2+ and (B) the reaction products are analyzed by the NALFA strip. Adapted with permission from [69].
Wang et al. [70] developed a lateral flow assay strip based on DNAzyme catalysis and stem-loop structure signal amplification. This innovative approach utilizes Cu2+ to activate DNAzyme, which cleaves the stem-loop DNA substrate to release ssDNA fragments. The liberated DNAzyme can subsequently bind to new stem-loop DNA molecules, enabling multiple turnover cycles where each DNAzyme molecule catalyzes the production of numerous ssDNA fragments. This amplification strategy achieves highly sensitive and specific detection of Cu2+ with a remarkable detection limit of 31.5 nM, as illustrated in Figure 8. The approach offers high selectivity and the advantage of not requiring complex instrumentation.
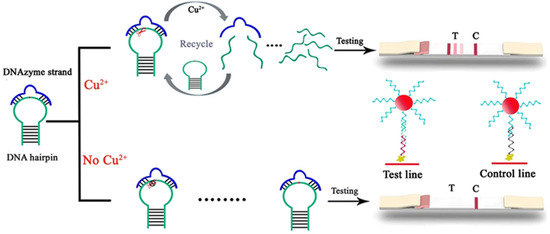
Figure 8.
Schematic representation of the catalytic and stem-loop signal amplification strategy-based Cu2+ lateral flow assay. Adapted with permission from [70].
Mazumdar et al. [71], Wang et al. [72], and Pei et al. [73] employed DNAzyme for the detection of Pb2+ in environmental samples, achieving detection limits of 5 μM, 20 nM, and 0.05 nM, respectively. Additionally, Fang et al. [74] employed DNAzyme to specifically recognize Cu2+ with a detection limit of 10 nM.
This technology detects heavy metal ions by amplifying the detection signal through enzyme-catalyzed reactions that produce colored or fluorescent products. Many studies have been carried out on various ions such as Hg2+, Cu2+, and Pb2+. Its advantages include high selectivity and the absence of the need for complex equipment, making it suitable for on-site rapid detection. However, it also has obvious disadvantages. The activity of the enzyme is easily affected by environmental factors such as temperature and pH, which may lead to unstable test results. Moreover, the storage conditions for enzymes are harsh, increasing the cost and difficulty of use.
Common challenges: Key limitations include (i) enzyme activity susceptibility to environmental factors (e.g., pH and temperature fluctuations); (ii) high cost and harsh storage requirements (4 °C or below) for nucleic acid enzymes; (iii) potential false positives from non-specific cleavage in complex matrices.
2.4. Antigen–Antibody-Based LFA Technology
The antibody–antigen-based lateral flow immunoassay represents a well-established immunochromatographic detection methodology, whose operational mechanism comprises three critical phases:
- (i)
- Specific binding: Immobilized antibodies (or antigens) on the test strip specifically bind to target analytes (e.g., metal ion–carrier protein complexes) in samples.
- (ii)
- Signal labeling: Gold-conjugated antibodies form immunocomplexes that migrate via capillary action.
- (iii)
- Visual readout: Immunocomplexes accumulate at the T-line, producing colored bands, while the C-line confirms assay validity.
Heavy metal ions, due to their small molecular weight and lack of immunogenicity, are classified as haptens and cannot directly stimulate antibody production in the immune system. Therefore, they must be chemically conjugated to carrier proteins (such as BSA, KLH, OVA, etc.) to form complete antigens [75], which can then be used to immunize animals for antibody production.
The combination of robust immunological specificity with simple visual readout has established this platform as a gold standard for rapid diagnostic applications across multiple sectors. Continuous improvements in bioreceptor engineering and detection modalities promise to further expand their utility and performance characteristics. Details are provided in Table 4.

Table 4.
Detection of Heavy Metal Ions Using Antigen–Antibody-Based LFA Technology.
For example, Ling et al. [76] used lateral flow test strips to detect Cd2+ in environmental water samples. By leveraging the specific binding of gold nanospheres (AuNS) and gold nanoflowers (AuNF)-labeled antibodies to target Cd2+, immune complexes were formed and captured at the test line, producing visible red bands. This enabled highly sensitive detection of Cd2+, with visual detection limits of 3.34 nM (AuNS) and 0.27 nM (AuNF), as illustrated in Figure 9. This method offers high selectivity and does not require complex instrumentation, making it suitable for on-site rapid detection.
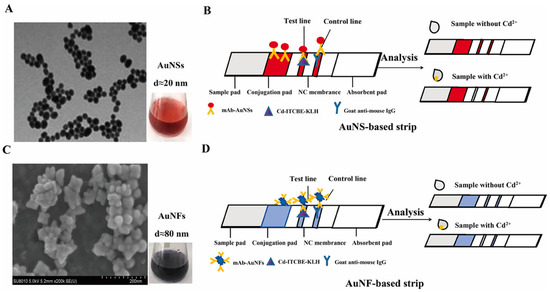
Figure 9.
Characterization and Detection Principle of Cd2+ Using AuNS and AuNF-Labeled Lateral Flow Test Strips. (A) Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) image and colloidal solution of AuNS. (B) Schematic diagram of the detection principle for Cd2+ using AuNS-based lateral flow test strips. (C) Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) image and colloidal solution of AuNF. (D) Schematic diagram of the detection principle for Cd2+ using AuNF-based lateral flow test strips. Adapted with permission from [76].
Huang et al. [77] developed a photothermal lateral flow immunoassay (LFIA) sensor using micro-fiber long-period grating (mLPG) and AuNPs for the detection of chromium ions (Cr3+) in water and serum samples. The sensor leverages the localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR) effect of AuNPs to generate photothermal signals. Combined with the thermo-optic conversion of a polymer encapsulation layer, the concentration information of the target analyte is converted into spectral changes in the mLPG. Through the signal amplification of the photothermal effect, the sensor achieved highly sensitive detection of Cr3+ with a detection limit of 4.21 nM, as illustrated in Figure 10.
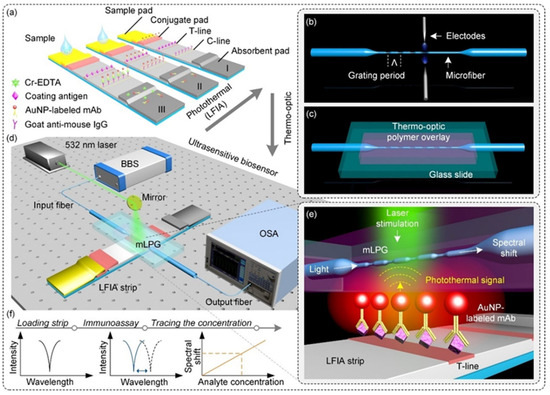
Figure 10.
(a) Illustration of the competitive lateral flow immunoassay. (b) Schematic of the microfiber long-period grating (mLPG) and its fabrication procedure using the electric arc discharge method. (c) Schematic of the encapsulated mLPG with a UV-curable polymer overlay supported by a glass slide. (d) Illustration of the experimental setup for the proposed biosensor. (e) Sensing mechanism of the signal transduction. (f) Spectral change during measurement with the proposed biosensor. Adapted with permission from [77].
In recent years, lateral flow immunoassay technology based on nanomaterials (e.g., gold and silver nanoparticles) and monoclonal antibodies has been widely applied for the detection of heavy metal ions such as Cr3+, UO22+, Hg2+, Cd2+, and Pb2+ [78,79,80,81,82,83,84,85,86]. By combining competitive or non-competitive immunoassays with signal amplification strategies (e.g., surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS), fluorescent microspheres), this technology has achieved high sensitivity (detection limits ranging from pM to μM levels), rapid response (3–4 min), and portable detection. These advancements make LFIA suitable for on-site rapid screening of heavy metal ions in complex matrices such as environmental water samples and food.
This technology detects heavy metal ions by forming immune complexes through the specific binding of antigens and antibodies. Research has been carried out on various ions such as Cd2+, Cr3+, U4+, Hg2+, and Pb2+.
Common challenges: This approach is hindered by (i) high production costs for monoclonal antibodies (typically $1000+/mg); (ii) weak immunogenicity of metal ions, requiring unstable conjugation with carrier proteins; (iii) cross-reactivity risks with similar metal-chelate complexes.
3. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Lateral flow assay technology has emerged as a transformative platform for rapid, on-site detection of heavy metal ions, addressing critical needs in environmental monitoring, food safety, and public health. This review summarized four principal LFA methodologies, each employing distinct recognition mechanisms and using different signal readout methods for various detection samples to achieve sensitive and specific detection of heavy metal ions.
The DNA probe-based approach capitalizes on the programmable binding between synthetic oligonucleotides and target ions, exemplified by T-Hg2+-T coordination and G-quadruplex formation with Pb2+. These systems achieve exceptional sensitivity (e.g., 0.0015 ppb for Hg2+) through gold nanoparticle labeling, though they face challenges in probe design complexity and matrix interference. The nucleic acid enzyme-based method utilizes the specific catalytic activation of nucleic acid enzymes (such as DNAzyme and MNAzyme) by targeting heavy metal ions (such as Pb2+ and Hg2+), cleaving the substrate DNA strand to release labeled fragments and generate detection signals (such as red bands), thus achieving high-sensitivity detection (for example, the detection limit of Pb2+ can reach 0.05 nM). However, the activity of the enzyme is easily affected by the environment and the storage conditions are harsh.
Aptamer-based platforms employ synthetic nucleic acid receptors that undergo conformational changes upon ion binding, enabling multiplexed detection of Hg2+, Cd2+, and Tl+ through innovative signal reporters. While offering superior adaptability, these systems require labor-intensive aptamer development. The well-established antigen–antibody format provides robust detection of metal-chelate complexes (e.g., Cd2+-EDTA) with commercial-ready test strips, though at higher antibody production costs.
Comparative analysis reveals technology-specific advantages: DNA probes deliver ultra-sensitive and cost-effective detection, nucleic acid enzymes enable isothermal amplification, aptamers permit customizable multiplexing, while immunoassays offer regulatory-friendly solutions. Emerging innovations in nanomaterial labels, smartphone-based quantification, and integrated multi-analyte strips are addressing current limitations in sensitivity, cost, and field applicability. Standardization of these advanced LFA systems will be crucial for widespread adoption in global monitoring programs, particularly for addressing acute heavy metal contamination events and ensuring food chain safety. The continuous evolution of LFA technologies promises to reshape environmental and health surveillance paradigms through decentralized, user-friendly metal ion detection, as shown in Table 5 specifically.

Table 5.
Performance and Advantages Comparison of Four Heavy Metal Ion Detection Strategies.
In the future, the development of lateral flow analysis technology will focus on the following directions, with clarified application scenarios and retained references:
- (i)
- Multiplex Detection
Scenario: Industrial wastewater treatment plants can utilize multiplex LFIA strips to simultaneously monitor Pb2+, Cd2+, and Hg2+, enabling real-time adjustment of purification processes. This addresses the complex metal contamination challenges observed in the Dongjiang River Basin.
- (ii)
- Signal Amplification Optimization
Scenario: During drinking water source emergencies, LFIA integrated with nanomaterial-based amplification can achieve ultrasensitive Hg2+ detection to prevent toxic substance infiltration. The electrochemical signal enhancement strategies discussed further optimize sensitivity for field applications.
- (iii)
- Integration with Portable Devices
Scenario: Fishery aquaculture monitoring can employ smartphone-integrated LFIA systems to quantify Cu2+ in pond water within 10 min, building on the portable detection frameworks developed for tap water analysis. IoT technology enables real-time data transmission to prevent metal accumulation in seafood.
- (iv)
- Standardization and Commercialization
Scenario: Grassroots public health centers can adopt standardized LFIA kits for rapid screening of heavy metal exposure in children, leveraging the cost-effective design suitable for poor regions.
- (v)
- SERS-Microdevice Integration
Recent advancements in SERS-based microdevices [34,78,87] show promise for LFA integration. As demonstrated by Lee et al. [88], a SERS-LFA hybrid device with microfluidic pretreatment achieves sub-pM Hg2+ detection in environmental samples, combining on-chip nucleic acid extraction with multiplexed SERS amplification. This integration reduces sample volume to 10 μL and analysis time to 20 min, enabling point-of-care testing for sudden heavy metal pollution incidents.
With continuous technological advancements, lateral flow analysis is expected to play an increasingly important role in heavy metal ion detection, addressing critical challenges in environmental protection, food safety, and public health.
Author Contributions
X.X., Z.Z. and J.Q. conceived the idea and designed the review. X.X. and X.H. were responsible for the literature collection, summarization of the review, and the writing of the paper. X.C., Q.Z., W.Y., R.Y., S.L. and H.H. were responsible for researching the literature. H.H., J.Q. and Z.Z. supervised the project. Z.Z. and J.Q. provided resources. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Key Deployment Project of the Centre for Ocean Mega-Research of Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences (COMS2020Q11, COMS2019J01), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (22006162, 51501071, 21976099, 21976105, 21804010), the Taishan Scholars Program (ts20190962, ts202103134), the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (ZR2024QD258), and the Special Fund for the Scholar Program of Yantai.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available upon request to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Koller, M.; Saleh, H.M. Introductory chapter: Introducing heavy metals. HMs 2018, 1, 3–11. [Google Scholar]
- Igwe, E.; Onoja, S.; Nwodo, P.; Baharane, V.; Diakite, S.; Saquee, F.; Ugwu, B.; Amechi, O.; Niambe, O.; Shaibu, O. Identification of sources of some priority heavy metallic pollutants caus-ing environmental degradation and it’s health implications. J. Ind. Pollut. Control 2023, 39, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Tiwari, S.M. Impact of heavy metal pollution on the biotic and abiotic components of the environment. South Asian J. Res. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 38–54. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Sun, Z.; Hu, Y.; Zeng, X.; Yu, Z.; Cheng, H. Comparison of soil heavy metal pollution caused by e-waste recycling activities and traditional industrial operations. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 9387–9398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briffa, J.; Sinagra, E.; Blundell, R. Heavy metal pollution in the environment and their toxicological effects on humans. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, R. Heavy metals in our ecosystem. In Heavy Metals in Plants; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2022; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Olufemi, A.C.; Mji, A.; Mukhola, M.S. Potential health risks of lead exposure from early life through later life: Implications for public health education. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 16006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collin, M.S.; Venkatraman, S.K.; Vijayakumar, N.; Kanimozhi, V.; Arbaaz, S.M.; Stacey, R.S.; Anusha, J.; Choudhary, R.; Lvov, V.; Tovar, G.I. Bioaccumulation of lead (Pb) and its effects on human: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2022, 7, 100094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, T.; Liu, Y.; Buchner, V.; Tchounwou, P.B. Neurotoxic effects and biomarkers of lead exposure: A review. Rev. Environ. Health 2009, 24, 15–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; He, C.; Shen, C.; Guo, J.; Mubeen, S.; Yuan, J.; Yang, Z. Toxicity of cadmium and its health risks from leafy vegetable consumption. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 1373–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Hassan, M.F.; Ali, W.; Zou, H.; Liu, Z.; Ma, Y. Effects of Cadmium Pollution on Human Health: A Narrative Review. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charkiewicz, A.E.; Omeljaniuk, W.J.; Nowak, K.; Garley, M.; Nikliński, J. Cadmium toxicity and health effects—A brief summary. Molecules 2023, 28, 6620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.-S.; Osman, A.I.; Hosny, M.; Elgarahy, A.M.; Eltaweil, A.S.; Rooney, D.W.; Chen, Z.; Rahim, N.S.; Sekar, M.; Gopinath, S.C. The toxicity of mercury and its chemical compounds: Molecular mechanisms and environmental and human health implications: A comprehensive review. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 5100–5126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carocci, A.; Rovito, N.; Sinicropi, M.S.; Genchi, G. Mercury toxicity and neurodegenerative effects. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2014, 229, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez, C.C.; Gómez, M.E.B.; Zavala, A.H. Hexavalent chromium: Regulation and health effects. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2021, 65, 126729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossini, H.; Shafie, B.; Niri, A.D.; Nazari, M.; Esfahlan, A.J.; Ahmadpour, M.; Nazmara, Z.; Ahmadimanesh, M.; Makhdoumi, P.; Mirzaei, N. A comprehensive review on human health effects of chromium: Insights on induced toxicity. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 70686–70705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, V.; Kaler, S.G. Role of copper in human neurological disorders. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 88, 855S–858S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crisponi, G.; Nurchi, V.M.; Fanni, D.; Gerosa, C.; Nemolato, S.; Faa, G. Copper-related diseases: From chemistry to molecular pathology. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2010, 254, 876–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faa, A.; Gerosa, C.; Fanni, D.; Floris, G.; Eyken, P.V.; Lachowicz, J.I.; Nurchi, V.M. Depleted uranium and human health. Curr. Med. Chem. 2018, 25, 49–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozturk, M.; Metin, M.; Altay, V.; Bhat, R.A.; Ejaz, M.; Gul, A.; Unal, B.T.; Hasanuzzaman, M.; Nibir, L.; Nahar, K. Arsenic and human health: Genotoxicity, epigenomic effects, and cancer signaling. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2022, 200, 988–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, A.J.; Viraraghavan, T. Thallium: A review of public health and environmental concerns. Environ. Int. 2005, 31, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Wu, X.; Tang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, J.; Zhang, J.; Liu, H. Distribution characteristics and risk of heavy metals and microbial community composition around the Wanshan mercury mine in Southwest China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 227, 112897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Xia, T.; Jia, X.; Wang, S. Heavy metal pollution and human health risk assessment at mercury smelting sites in Wanshan district of Guizhou Province, China. Rsc Adv. 2020, 10, 23066–23079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.; Hu, W.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Meng, Y.; Xiao, Q.; Guo, X.; Zhou, Y.; Bi, Y. Analysis of heavy metal contamination of agricultural soils and related effect on population health—A case study for East River Basin in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Lv, L.; Liu, Y.; Ji, M.; Zang, E.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, M.; Li, M. Applied analytical methods for detecting heavy metals in medicinal plants. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2023, 53, 339–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, L.A.; Bashir, A.; Qureashi, A.; Pandith, A.H. Detection and removal of heavy metal ions: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2019, 17, 1495–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Yang, Y.; Fu, K.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Z. Progress in ICP-MS analysis of minerals and heavy metals in traditional medicine. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 891273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voica, C.; Kovacs, M.H.; Dehelean, A.; Ristoiu, D.; Iordache, A. ICP-MS determinations of heavy metals in surface waters from Transylvania. Rom. J. Phys. 2012, 57, 1184–1193. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Q.; Yang, G.; Zhao, Y.; Yin, J. Determination of copper, nickel, cobalt, silver, lead, cadmium, and mercury ions in water by solid-phase extraction and the RP-HPLC with UV-Vis detection. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2003, 375, 831–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Guangyu, Y.; Lin, Q. Determination of heavy metal ions in Chinese herbal medicine by microwave digestion and RP-HPLC with UV-Vis detection. Microchim. Acta 2004, 144, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Liang, X.; Niyungeko, C.; Zhou, J.; Xu, J.; Tian, G. A review of the identification and detection of heavy metal ions in the environment by voltammetry. Talanta 2018, 178, 324–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Rahim, M.A.; Tang, J.; Allioux, F.M.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K. Post-transition metal electrodes for sensing heavy metal ions by stripping voltammetry. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2022, 7, 2100760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrill, A.J.; Reily, N.E.; Macpherson, J.V. Addressing the practicalities of anodic stripping voltammetry for heavy metal detection: A tutorial review. Analyst 2019, 144, 6834–6849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guselnikova, O.; Postnikov, P.; Erzina, M.; Kalachyova, Y.; Švorčík, V.; Lyutakov, O. Pretreatment-free selective and reproducible SERS-based detection of heavy metal ions on DTPA functionalized plasmonic platform. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 253, 830–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Chu, F.; Zhang, H.; Yuan, Y.; Huang, Y.; Liu, A.; Wang, S.; Li, W.; Li, S.; Wen, W. Rapid, one-step preparation of SERS substrate in microfluidic channel for detection of molecules and heavy metal ions. Spectrochim. Acta Part A: Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2019, 220, 117113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Feng, S.; Peng, Y.; Li, B.; Zhao, J.; Xu, H.; Meng, X.; Zhai, W.; Pang, H. Emerging insights into the application of metal-organic framework (MOF)-based materials for electrochemical heavy metal ion detection. Food Chem. 2024, 463, 141387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarur, F.; Macairan, J.-R.; Naccache, R. Ratiometric detection of heavy metal ions using fluorescent carbon dots. Environ. Sci. Nano 2019, 6, 1121–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, P.; Yadav, L.; Laddha, H.; Agarwal, M.; Gupta, R. Upsurgence of smartphone as an economical, portable, and consumer-friendly analytical device/interface platform for digital sensing of hazardous environmental ions. Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 2022, 36, e00177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, R.Y.T.; Jue, E.; Yip, A.T.; Berg, A.R.; Wang, S.J.; Kivnick, A.R.; Nguyen, P.T.; Kamei, D.T. Simultaneous concentration and detection of biomarkers on paper. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 3021–3028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.H.; Lee, S.K.; Oh, Y.K.; Bae, B.W.; Lee, S.D.; Kim, S.; Shin, Y.B.; Kim, M.G. A dual gold nanoparticle conjugate-based lateral flow assay (LFA) method for the analysis of troponin I. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 25, 1999–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posthuma-Trumpie, G.A.; Korf, J.; van Amerongen, A. Lateral flow (immuno) assay: Its strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats. A literature survey. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 393, 569–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohrman, B.A.; Richards-Kortum, R.R. A paper and plastic device for performing recombinase polymerase amplification of HIV DNA. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 3082–3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sajid, M.; Kawde, A.-N.; Daud, M. Designs, formats and applications of lateral flow assay: A literature review. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2015, 19, 689–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.C.; Chen, S.Q.; Guo, J.H.; Ma, X. Nanomaterial labels in lateral flow immunoassays for point-of-care-testing. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 60, 90–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panferov, V.G.; Zherdev, A.V.; Dzantiev, B.B. Post-Assay chemical enhancement for highly sensitive lateral flow immunoassays: A critical review. Biosensors 2023, 13, 866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najib, M.A.; Selvam, K.; Khalid, M.F.; Ozsoz, M.; Aziah, I. Quantum dot-based lateral flow immunoassay as point-of-care testing for infectious diseases: A narrative review of its principle and performance. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panferov, V.G.; Ivanov, N.A.; Mazzulli, T.; Brinc, D.; Kulasingam, V.; Krylov, S.N. Electrophoresis-assisted multilayer assembly of nanoparticles for sensitive lateral flow immunoassay. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202215548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loynachan, C.N.; Thomas, M.R.; Gray, E.R.; Richards, D.A.; Kim, J.; Miller, B.S.; Brookes, J.C.; Agarwal, S.; Chudasama, V.; McKendry, R.A.; et al. Platinum nanocatalyst amplification: Redefining the gold standard for lateral flow immunoassays with ultrabroad dynamic range. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.Q.; Liu, Y.Q.; Yang, L.; Tan, T.; He, J.; Chen, W.W.; Li, R.H.; Wang, W.G. Popcorn-like bimetallic palladium/platinum exhibiting enhanced peroxidase-like activity for signal enhancement in lateral flow immunoassay. Anal. Chim. Acta 2024, 1309, 342698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.D.; Wang, Y.T.; Zhang, Q.J.; Wang, C.; Du, Y.X.; Liang, D.B.; Shen, J.C.; Pan, X.; Sheng, E.Z.; Zhu, D. Hierarchical magneto-colorimetric labels for immediate lateral flow immunoassay of chlorothalonil residues. Talanta 2024, 280, 126743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angela, S.; Hsiao, W.W.W.; Fadhilah, G.; Le, T.N.; Chiang, W.H. Detection of avian influenza virus utilizing fluorescent nanodiamonds for lateral flow immunoassay enhanced by magnetic modulation. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2025, 169, 105945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, C.Y.; Zhao, L.J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, K.; Li, H.W.; Li, X.; Zi, M.; Zeng, J.B. Colorimetric and photothermal dual-mode lateral flow immunoassay based on Au-Fe3O4 multifunctional nanoparticles for detection of Salmonella typhimurium. Microchim. Acta 2023, 190, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Ge, C.; Wang, L.; Xing, X.; Zeng, L. A simple lateral flow biosensor for the rapid detection of copper (II) ions based on click chemistry. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 75722–75727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Xue, J.; Dong, J.; Cai, J.; Hua, X.; Wang, M.; Zhang, C.; Liu, F. Signal-amplified lateral flow test strip for visual detection of Cu2+. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Wang, Y.; Deng, Y.; Yao, L.; Adeloju, S.B.; Pan, D.; Xue, F.; Wu, Y.; Zheng, L.; Chen, W. Ultrasensitive detection of mercury with a novel one-step signal amplified lateral flow strip based on gold nanoparticle-labeled ssDNA recognition and enhancement probes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 61, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, L.; Chen, J.; Ge, C.; Fang, Z.; Wang, L.; Xing, X.; Zeng, L. An autonomous T-rich DNA machine based lateral flow biosensor for amplified visual detection of mercury ions. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 2024–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Kang, Y.; Liang, S.; Zhang, J. Detection of Hg (II) in adsorption experiment by a lateral flow biosensor based on streptavidin-biotinylated DNA probes modified gold nanoparticles and smartphone reader. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 266, 115389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, N.; Xu, Y.; Huang, K.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Z.; Luo, Y.; Xu, W. One-step competitive lateral flow biosensor running on an independent quantification system for smart phones based in-situ detection of trace Hg (II) in tap water. Food Chem. 2017, 214, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, L.; Chen, Y.; Wang, R.; Yan, C.; Xu, J.; Yao, B.; Cheng, J.; Chen, W. Rapid and sensitive detection of Hg2+ with a SERS-enhanced lateral flow strip. Analyst 2022, 147, 4337–4347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Tang, T.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, X. Simultaneous or separate detection of heavy metal ions Hg2+ and Ag+ based on lateral flow assays. Microchim. Acta 2025, 192, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Sun, J.; Ma, S.; Wang, D.; Qi, R.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, Q.; Qin, Z.; Jiang, L. A novel lateral flow assay for lead ion detection based on G-quadruplex. Biochem. Eng. J. 2025, 213, 109562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Ge, C.; Lv, K.; Zou, Q.; Liu, Q.; Liu, L.; Yang, Q.; Bao, S. A simple lateral flow biosensor for rapid detection of lead(II) ions based on G-quadruplex structure-switching. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 13718–13721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Liu, Y.; Ding, J.; Hayat, K.; Zhan, X.; Zhou, P.; Zhang, D. Label-free colorimetric assay for arsenic (III) determination based on a truncated short ssDNA and gold nanoparticles. Microchim. Acta 2021, 188, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, B.; Yang, Y.; He, R.; Park, Y.I.; Lee, A.; Bai, D.; Li, F.; Lu, T.J.; Xu, F.; Lin, M. Lateral flow aptamer assay integrated smartphone-based portable device for simultaneous detection of multiple targets using upconversion nanoparticles. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 276, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irfan, M.; Murtaza, G.; Fu, S.; Chen, A.; Qu, F.; Su, X. Molecular simulation-guided aptasensor design of robust and sensitive lateral flow strip for cadmium ion detection. Analyst 2023, 148, 1961–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Shen, H.; Hu, J.; Fu, Q.; Yao, C.; Yu, S.; Xiao, W.; Tang, Y. Aptamer-based fluorescence-quenching lateral flow strip for rapid detection of mercury (II) ion in water samples. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409, 5209–5216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, S.; Ranganathan, V.; McConnell, E.M.; Murari, B.M.; DeRosa, M.C. Aptamer-based colorimetric and lateral flow assay approaches for the detection of toxic metal ions, thallium (i) and lead (ii). RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 20040–20049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berlina, A.N.; Komova, N.S.; Zherdev, A.V.; Boris, B.D. Combination of phenylboronic acid and oligocytosine for selective and specific detection of lead(ii) by lateral flow test strip. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1155, 338318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Kim, Y.; Kim, S.; Lee, E.S.; Cha, B.S.; Park, K.S. MNAzyme-Assisted Nucleic Acid Lateral Flow Assay for Cost-Effective, On-Site Mercury Detection. Biosensors 2024, 14, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, C.; Liu, F. A lateral flow assay for copper (II) utilizing catalytic and stem-loop based signal amplification. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazumdar, D.; Lan, T.; Lu, Y. “Dipstick” colorimetric detection of metal ions based on immobilization of DNAzyme and gold nanoparticles onto a lateral flow device. In Biosensors and Biodetection; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 389–406. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, B.; Duan, J.; Hao, T.; Jiang, X.; Guo, Z.; Wang, S. A test strip for lead (II) based on gold nanoparticles multi-functionalized by DNAzyme and barcode DNA. J. Anal. Chem. 2015, 70, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, X. Nanogold-signalized lateral-flow strip for visual detection of lead ion based on cleavage of metal-ion-induced DNAzyme. Chem. Lett. 2014, 43, 1643–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Huang, J.; Lie, P.; Xiao, Z.; Ouyang, C.; Wu, Q.; Wu, Y.; Liu, G.; Zeng, L. Lateral flow nucleic acid biosensor for Cu2+ detection in aqueous solution with high sensitivity and selectivity. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 9043–9045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Liu, F. Antibody developments for metal ions and their applications. Food Agric. Immunol. 2020, 31, 1079–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, S.; Zhao, Q.; Iqbal, M.N.; Dong, M.; Li, X.; Lin, M.; Wang, R.; Lei, F.; He, C.; Wang, S. Development of immunoassay methods based on monoclonal antibody and its application in the determination of cadmium ion. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2021, 411, 124992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.; Fu, Q.; Sun, L.P.; Liu, P.; Wu, Z.; Li, K.; Xiao, R.; Yang, X.; Huang, Y.; Lin, W.; et al. Photothermal lateral flow immunoassay using microfiber long-period grating. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 344, 130283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Liu, H.; Lan, C.; Fu, Q.; Huang, C.; Luo, Z.; Jiang, T.; Tang, Y. Silver nanoparticle enhanced Raman scattering-based lateral flow immunoassays for ultra-sensitive detection of the heavy metal chromium. Nanotechnology 2014, 25, 495501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quesada-González, D.; Jairo, G.A.; Blake, R.C.; Blake, D.A.; Merkoçi, A. Uranium (VI) detection in groundwater using a gold nanoparticle/paper-based lateral flow device. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Xiang, J.-J.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, X.-L.; Fu, Q.-Q.; Zou, J.-H.; Lin, Y. Colloidal gold nanoparticle probe-based immunochromatographic assay for the rapid detection of chromium ions in water and serum samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 745, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Zhai, Y.-F.; Xiang, J.-J.; Wang, H.; Liu, B.; Guo, C.-W. Colloidal gold probe-based immunochromatographic assay for the rapid detection of lead ions in water samples. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 2074–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Zou, S.; Zhu, J.; Liu, L.; Kuang, H. Immunochromatographic paper sensor for ultrasensitive colorimetric detection of cadmium. Food Agric. Immunol. 2018, 29, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Wu, X.; Liu, L.; Zhu, J.; Xu, L.; Kuang, H. Development of a fluorescent immunoassay strip for the rapid quantitative detection of cadmium in rice. Food Agric. Immunol. 2020, 31, 501–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Jia, J.; Xu, N.; Zhu, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y. Comparative analysis of three immunochromatographic test strips for rapid detection of cadmium ion in Asparagus. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 58, 6598–6608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López_Marzo, A.M.; Pons, J.; Blake, D.A.; Merkoçi, A. High sensitive gold-nanoparticle based lateral flow Immunodevice for Cd2+ detection in drinking waters. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 47, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, Y.-S.; Meng, X.-Y.; Zhang, Y.-Y.; Yang, L.; Zhang, J.-H.; Wang, X.-R.; Lu, S.-Y.; Ren, H.-L.; Liu, Z.-S. Development of an immunochromatographic strip and its application in the simultaneous determination of Hg (II), Cd (II) and Pb (II). Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 183, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Wang, H.; Zhong, W.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Gao, X.; Yan, M.; Zhu, C. The development and application of SERS-based lateral flow immunochromatography in the field of food safety. Microchim. Acta 2025, 192, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Dang, H.; Moon, J.-I.; Kim, K.; Joung, Y.; Park, S.; Yu, Q.; Chen, J.; Lu, M.; Chen, L. SERS-based microdevices for use as in vitro diagnostic biosensors. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2024, 53, 5394–5427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).