Abstract
Work investigates the doping of molybdenum oxide (MoOx) with tungsten (W). The successful incorporation of W into the MoOx lattice was confirmed through X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS). Structural and optical analysis revealed the presence of oxygen vacancies within the W-MoOx film, which are known to facilitate resistive switching (RS) in memristive devices. Based on this, a flexible memristor with the structure PET/ITO/W-MoOx/polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA)/Al was fabricated. PMMA was strategically introduced between the W-MoOx layer and the aluminum electrode to modulate interfacial properties that influence RS behavior. The W-MoOx/PMMA-based memristor exhibited good resistive switching characteristics, with a memory window of approximately 12 and a retention time exceeding 2 × 104 s, demonstrating a non-volatile memory behavior. In the high-resistance state (HRS), the conduction mechanism under higher applied voltages follows a space-charge-limited current (SCLC) model, indicating that the RS process is primarily governed by charge trapping and de-trapping at the interface. Overall, the consistent and robust switching performance of the W-MoOx/PMMA heterostructure underlines its potential as a reliable functional layer for next-generation resistive random-access memory (ReRAM) devices.
1. Introduction
In modern life, the growing demand for data processing and storage has put great pressure on computing hardware. From smartphones to cloud-based systems, large amounts of data are generated and analyzed every day. This need calls for more powerful and efficient computing solutions. As a result, artificial intelligent devices have taken on an important role, especially in designing and optimizing neural network configurations [1,2,3]. These systems inspired by the human brain need a lot of processing power and storage to function effectively. Consequently, much effort has been made in developing high-density information storage technologies. Memristor-based resistive random-access memory (ReRAM) is a promising candidate for next-generation computing architectures, due to the ease of the device structure and monolithic integration, rapid switching speed, and low power consumption [4,5]. Resistive switching (RS) devices using various materials as functional or active layers have been reported, including metal oxides [6,7,8], transition metal dichalcogenides [9,10,11], organic semiconductors [12,13], and organic–inorganic halide perovskites [14,15,16].
Transition metal oxides (TMOs) are a class of materials widely used in memristors. Molybdenum oxide (MoO3) and tungsten oxide (WO3) are two TMOs that have received significant attention for their unique properties including wide optical bandgap, eco-friendly nature, and excellent electrical and thermal stability, which make them ideal materials for memristive devices [17,18]. Particularly, MoO3’s high stability under different conditions, along with its ability to store and release charge efficiently, makes it a reliable material for resistive switching applications [19]. MoO3 also demonstrates artificial synaptic properties, which are important for neuromorphic computing imitating synaptic behavior [20]. Moreover, WO3 exhibits good stability and a high capacity for charge storage, making it a strong candidate for memristors, especially in applications that need high endurance and reliability. More importantly, the electrical properties of both MoO3 and WO3 can be adjusted by modifying their stoichiometry, allowing greater control over the switching characteristics and performance of memristive devices [21,22]. Their resistive switching behavior is closely related to oxygen vacancies within the oxide. The distribution and density of these vacancies greatly influence the conductive mechanisms that drive the switching process. Therefore, controlling the oxygen content within the resistive switching layer is essential for achieving the desired performance in memristors.
Doping in metal oxide-based memristors is an efficient approach for improving the electrical performance and reliability of the devices. By adding dopants like aluminum (Al) [23], lithium (Li) [24], or nickel (Ni) [25] into the metal lattice, the oxygen vacancy concentration, electronic conductivity, and switching thresholds can be tuned. Moreover, Li doping boosts ionic mobility, allowing for faster switching and improved synaptic behavior in neuromorphic applications [26]. Doping of molybdenum oxide-based memristors has also been investigated. In particular, silver (Ag) [27] and copper (Cu) [28] doping of MoOx resulted in controlled oxygen vacancies, which led to better switching uniformity and endurance. These dopants tune the local electronic structure and defect concentration, influencing filament formation, charge trapping, and overall device stability. Consequently, doped MoOx memristors showed higher ON/OFF ratios, lower variability, and longer retention times.
In this work, the doping of molybdenum oxide (MoOx) with tungsten (W) is investigated, motivated by the complementary and favorable electronic properties of both MoO3 and WO3. The fabrication of a W-doped MoOx-based flexible memristor lies in the unique potential of tungsten doping to modulate the electronic structure and oxygen vacancy dynamics of MoOx, thereby influencing switching behavior. While memristors based on MoOx have been studied previously, W-doping remains relatively underexplored in flexible devices. Our work focuses on the trade-offs involved in developing flexible devices, where performance is often constrained by mechanical and thermal limitations. In our approach, the W-MoOx film is formed using hot-wire chemical vapor deposition, where the substrate remains at room temperature and no further annealing process is performed. Consequently, this study offers valuable experimental insights into the feasibility, stability, and resistive switching characteristics of W-doped MoOx devices implemented on flexible substrates. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) confirmed the presence of W in the MoOx lattice. The structural, optical, and electronic properties of the deposited W-MoOx were also investigated using various technique characterization methods including X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), ultraviolet–visible (UV-vis) spectroscopy, photoluminescence spectroscopy (PL), and ultraviolet photoelectron spectroscopy (UPS). It was found that oxygen vacancies existed in the developed W-MoOx film, which could facilitate the resistive switching (RS) of a memristor. Therefore, a flexible memristive device with the PET/ITO/W-MoOx/polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA)/Al structure was fabricated. The PMMA was inserted between the W-doped molybdenum oxide and the aluminum in order to control interfacial properties influencing the RS behavior of the device. The memristor based on the W-MoOx/PMMA heterostructure exhibits stable resistive switching with a memory window of approximately 12 and a retention time of 2 × 104 s, confirming its non-volatile behavior. In the high-resistance state (HRS) under high applied voltages, the conduction mechanism follows space-charge-limited current (SCLC), indicating that the resistive switching is primarily governed by an interface-driven mechanism involving charge trapping and de-trapping. The consistent switching performance highlights the effectiveness of the W-MoOx/PMMA heterostructure as a functional layer for reliable ReRAM applications.
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Film Preparation and Characterization
A tungsten (W)-doped molybdenum oxide (named hereafter as W-MoOx) thin film was deposited on various substrates including poly(ethylene terephthalate) (PET) coated with indium-tin oxide (ITO), glass, and silicon (Si) using a chemical vapor deposition (CVD) method. In particular, a hot-wire CVD system consisting of a stainless steel reactor, an aluminum base, and copper leads was used for the development of W-MoOx thin films. Between the two copper leads, two wires, one molybdenum and one tungsten, with a diameter of 0.5 mm were placed to form the W-doped molybdenum oxide. The deposition process started with the evacuation of the reactor chamber to a base pressure of 10 mTorr using a mechanical pump. W-MoOx films were obtained using forming gas, a mixture consisting of 90% nitrogen and 10% hydrogen. Films were deposited at a chamber pressure of 80 mTorr, with a molybdenum and a tungsten wire heated to 560 °C serving as the evaporation source. The gas flow rate was maintained at 100 ppm throughout the process. The deposition duration was 90 s, resulting in film thicknesses of approximately 100 nm.
Elemental composition identification was conducted using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) provided by Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Waltham, MA, USA. Particularly, a variable pressure FEI Quanta microscope (FEI Company, Hillsboro, OR, USA) equipped with an EDAX Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (EDS) detector (AMETEK, Inc., Berwyn, PA, USA) was used. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) was performed using a Mg Kα radiation source (photon energy: 1253.64 eV) to probe the elemental composition and chemical states at the sample surface. The spectra were acquired with a PHOIBOS 100 mm hemispherical analyzer (SPECS GmbH, Berlin, Germany), operated at a pass energy of 7 eV to achieve high energy resolution. All measurements were conducted under ultra-high vacuum conditions, with base pressures maintained below the 10−8 mbar range. For ultraviolet photoelectron spectroscopy (UPS), a He I (21.22 eV) discharge lamp was used as the excitation source to investigate the valence band structure and the work function of the sample. The same hemispherical analyzer was employed to collect the emitted photoelectrons. The structural analysis of the W-MoOx films was investigated using a Rigaku Smart Lab X-ray Diffractometer (Rigaku SmartLab, Neu-Isenburg, Germany) with Cu-Ka radiation. Θ/2Θ scans were performed, and the angular range for data collection was 2.0–80.0°, scanned in steps of 0.03° with a scan speed of 0.3 s/step. The surface nanomorphology of the W-doped molybdenum oxide films was studied with an NT-MDT AFM system (LaborScience SA, Athens, Greece) operating in tapping mode. Photoluminescence measurements were performed using a Shimadzu RF-6000 spectrofluorophotometer (Asteriadis, Thessaloniki, Greece). The thickness and the reflectance of the prepared W-MoOx films were measured using an FR-pRo UV/NIR-HR (SPS Polos, Putten, The Netherlands) operating in the 190–1100 nm spectral range, capable of measuring film thickness in the 1 nm–100 μm spectral range. The UV–visible absorbance and transmittance spectra of the W-doped molybdenum oxide were recorded with a Shimadzu UV-1900-i spectrometer (Asteriadis, Greece). Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy was performed using a Fourier Bruker Tensor 27 spectrometer (Bruker, Billerica, MA, USA) (at 4 cm−1 resolution, 64 scans) equipped with a DTGS detector. Cyclic voltammetry measurements were obtained using a VersaSTAT4 potentiostat using an Ag/AgCl electrode as a reference.
2.2. Memristive Device Fabrication and Characsterization
Memristors were fabricated following the structure PET/ITO/W-MoOx/poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA)/Al. First, the PET/ITO substrates, which were used as the bottom electrode of the memristor, were subjected to a cleaning routine, where the substrates were placed in an ultrasonic bath of deionized water, acetone, and isopropanol for 10 min each. Then, the substrates were dried by a flow of nitrogen and placed in the hot-wire CVD system. The W-doped MoOx oxide was deposited on the PET/ITO, forming a 100 nm thick film. Next, a PMMA layer (~80 nm) was spin-coated on the mixed oxide film from a methyl isobutyl ketone solution with a concentration of 1 mg mL−1. The device was completed with the thermal deposition of an aluminum layer, which served as the top electrode of the memristor.
The electrical measurements of the fabricated memristor were conducted using a VersaSTAT4 potentiostat. The bottom-ITO and the top-Al electrodes were connected to the ground and bias, respectively.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Deposition of W-Doped MoOx Thin Films
Tungsten (W)-doped molybdenum oxide films of 100 nm thickness were prepared using a hot-wire CVD reactor. Two wires, one of tungsten and another of molybdenum, were used for the deposition of the W-MoOx films. During the deposition, a reduced gas consisting of 90% nitrogen (N2) and 10% hydrogen (H2) was flown into the CVD reactor to form a sub-stoichiometric W-doped molybdenum oxide, as described in previous work [29,30]. The structural properties of the W-MoOx mixed oxide were firstly studied. Figure 1a shows the X-ray diffraction (XRD) pattern of the doped oxide film, where any diffraction peak appeared, leading to the conclusion that the W-MoOx film is amorphous. The elemental analysis of the developed oxide film was performed using energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS). Figure 1b shows the EDS image of the W-MoOx, while the quantitative elemental analysis is summarized in Table 1. The W-doping of molybdenum oxide was successfully achieved due to the substitution of Mo atoms with W atoms during the CVD procedure. The remarkable similarities between the molybdenum and tungsten ionic radii (0.059 nm and 0.06 nm for Mo and W, respectively), valence band, and electronegativity facilitated the incorporation of W into the MoOx lattice [31]. In our CVD system, the molybdenum (Mo) and tungsten (W) wires are co-located within the deposition chamber, which limits the ability to precisely control or vary the W-doping concentration during film growth. The final doping level is inherently determined by the fixed relative positioning and evaporation characteristics of the precursor materials, i.e., the two wires. Consequently, independent tuning of the W content is not feasible in the current setup. To address this constraint, the study focused on optimizing other process parameters, particularly film thickness, to ensure consistent and reliable device performance. Another approach to controlling the concentration of doping is by changing the environment of deposition. The deposition of MoO3-x in a nitrogen (N2) environment decreased the concentration of doping as shown in the EDS image in Figure S1 and Table S1. The devices investigated in this work incorporate a W atomic ratio of 9.72%, representing an optimized configuration identified through extensive preliminary experimentation. Although detailed data from the optimization studies (e.g., film thickness variations, environment of deposition) are not presented here, they guided the selection of this specific composition. The aim of this work is to study and demonstrate resistive switching behavior in flexible W-doped MoOx devices, for which the chosen doping level was found to be effective. The surface elementary composition of the W-doped molybdenum oxide was also investigated by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). Figure 1c presents the XPS Mo 3d peak, which appears as a doublet due to spin–orbit splitting. The peaks with binding energy (BE) at 236.7 eV and 233.6 eV correspond to the higher oxidation state (Mo6+) of Mo cations, while the peaks at 235.9 eV and 232.7 eV BE are assigned to the Mo5+, confirming the sub-stoichiometric nature of the molybdenum oxide sample [32,33]. Apart from the Mo6+ and Mo5+, the appearances of W6+ at 37.4 eV and 35.8 eV BE and of W5+ located at 38.0 eV and 35.2 eV BE are observed in the XPS spectrum of the sample (Figure 1d showing the W 4f XPS spectrum), indicating the deposition of a sub-stoichiometric W-doped molybdenum oxide film [34,35]. Moreover, the peak at 533 eV BE in the O 1s XPS spectrum of the sample is assigned to the hydroxyl groups incorporated in the W-MoOx lattice during the deposition using a reduced environment (90%/10% N2/H2). Figure 1f illustrates the development of amorphous W-doped MoOx, showing the substitution of Mo cations with W6+ and W5+ in the amorphous MoOx lattice. In addition, the reduced deposition environment and the low deposition pressure of ~80 mTorr reduced the evaporation rate of MoOx, which favors the W-doping process [36].
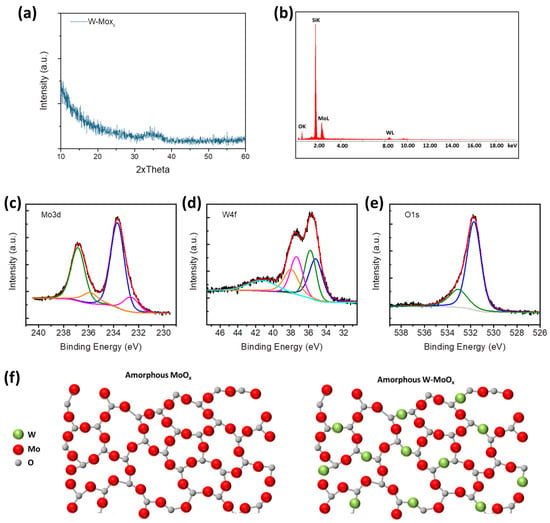
Figure 1.
(a) XRD patterns and (b) EDS image of W-doped MoOx film deposited on silicon substrate. XPS (c) Mo 3d, (d) W 4F, and (e) O 1s of W-MoOx film. (f) Schematic illustration of the substitution of Mo atoms with Mo atoms forming the W-MoOx film.

Table 1.
Quantitative analysis, weight, and atomic ratios in percentage for oxygen (O, K series), molybdenum (Mo, L series), and tungsten (W, L series) of W-doped MoOx sample.
The structure of the W-MoOx film was also investigated using FTIR spectroscopy. Figure 2a presents the FTIR transmittance spectrum of the W-doped oxide film. In the molybdenum oxide FTIR spectrum shown in Figure S2a (Supporting Information), a peak at about 713 cm−1 appears, which is related to the bending vibration of the Mo–O bond. Moreover, the peak at 984 cm−1 is assigned to the stretching mode of the Mo=O bond, while the weak peak at around 848 corresponds to the stretching vibration of the Mo–O bond. The new peaks appearing in the FTIR spectrum of the W-doped MoOx at about 975 cm−1 and 953 cm−1 could be a combination of the vibrations of Mo=O and W=O. The peak at 568 cm−1 is related to the stretching mode of the Mo–O bond. Another broad peak at 568 cm−1 also appears in the W-MoOx FTIR spectrum, which could be attributed to the shift of the W–O band (Figure S2b) to lower wavenumbers (from 625 cm−1 to 568 cm−1). Furthermore, the peak at around 1066 cm−1 is assigned to the bending mode Mo–OH and W–OH bonds formed during the deposition of the W-MoOx oxide in a reduced environment [37].
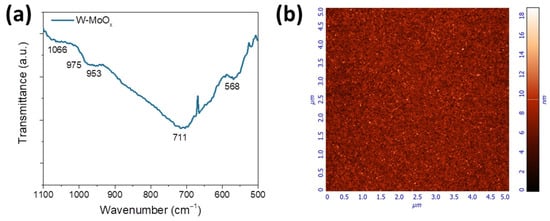
Figure 2.
(a) FTIR transmittance spectrum of W-MoOx thin film. (b) 5 × 5 μm2 AFM images of the surface of the same sample.
In order to investigate the nanomorphology of the W-doped MoOx film, atomic force microscopy (AFM) measurements were performed. Figure 2b shows the 5 × 5 μm2 AFM 2D height image. It is observed that the surface of the mixed oxide film is smooth, exhibiting a root mean square (RMS) roughness of 1.8 nm. Moreover, the W-MoOx surface consists of small grains in a range of 20–36 nm, as revealed by the grain analysis presented in Figure S3, which was performed in the 5 × 5 μm2 AFM image.
The optical properties of the developed W-MoOx sample were also studied using ultraviolet–visible (UV-Vis) spectroscopy. The prepared W-doped oxide film deposited on the glass substrate exhibited high transparency, over 73%, in the visible region, as shown in the transmittance spectrum in Figure 3a. The optical bandgap (Eg) of the W-MoOx film was also estimated using the absorption measurements presented in Figure S4. As revealed from the corresponding Tauc plot ((ahv)1/2 versus energy, where a is the absorption coefficient and hv is the photon energy) shown in Figure 3b, the W-MoOx sample exhibited an Eg of approximately 3.4 eV. Figure 3c shows the reflectance of the W-doped molybdenum oxide film, where the signal response in the UV region (200–400 nm) is assigned to the optical bandgap of the W-MoOx (3.4 eV). On the other hand, in the visible region, the W-doped oxide exhibited a broad absorption which could be related to the concentration of oxygen vacancies increasing the reflectivity of the film [38]. The oxygen vacancies in the W-MoOx are also evident in the photoluminescence (PL) spectrum of the film (Figure 3d). In particular, the broad peak in the visible region (~384 nm) could be assigned to d-d band transitions, while the weaker peak at around ~414 nm could be attributed to the existence of defect and oxygen vacancies of the mixed oxide. Note that the peak at 328 nm located close to the near band edge (NBE) emission is mainly due to the free exciton recombination. The existence and concentration of oxygen vacancies may facilitate the resistive switching mechanism in a memristor.
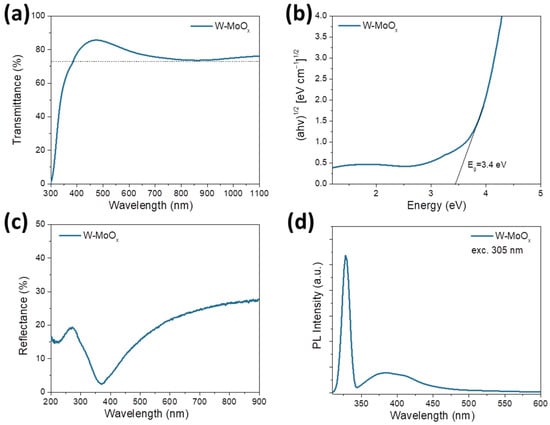
Figure 3.
(a) Transmittance spectrum, (b) Tauc plot, (c) reflectance spectrum, and (d) photoluminescence spectrum of W-doped MoOx deposited on glass substrate.
3.2. Computational Results
To confirm our experimental findings, we performed density functional theory (DFT) calculations for the perfect MoO3 structure and the defected-with-W structure. Our calculations were carried out using the Vienna Ab initio Simulation Package (VASP) [39,40,41]. We employed spin-polarized DFT with projector augment wave (PAW) pseudopotentials [39] for all species. The exchange-correlation effects were described by the regularized-restored strongly constrained and appropriately normed (r2SCAN) meta-GGA functional [42] with DFT-D3 dispersion corrections [43] to improve the accuracy of the lattice parameters, which were converged within 1.50% of the experimental values.
To ensure the accuracy of our results, we performed convergence tests for the determination of cut-off energy and k-point mesh. A plane-wave basis set with an energy cut-off of 750 eV was used in combination with a 4 × 4 × 2 k-point sampling grid. We chose these values after following the criteria of 1 meV/atom convergence of total energy for one electronic self-consistent field (SCF) iteration. The residual forces on all atoms were below 0.01 eV/Å. To minimize interactions between periodic image of defects, we used a large supercell of 128 atoms which had at least 10 Å in every direction. To find the correct ground state as well as the formation energy, we used the packages ShakeNBreak and Doped [44,45].
To predict the formation energy as a function of the fermi level, we followed the methodology that is described in previous work [46]. Through this approach, we can identify the stable charges of the defect as well as the charge transition levels. For a defect D at a charge state q, the formation energy is calculated from
where Etot [Dq] is the total energy of the defect D at charge q and EH is the energy of the defect-free supercell of MoO3. ni represents the number of atoms that are added or removed with chemical potentials μi. The chemical potentials are variables that depend on the experimental synthesis. In this work, μO is the total energy of a single atom in the O2 molecule, μMo is the energy of a single atom in the bulk Mo crystal, and μW is the energy of a W atom in the bulk W crystal.
The perfect crystalline MoO3 is a van der Waals structure that belongs to the space group Pnma. Each structural layer consists of two sublayers of distorted MoO6 octahedra which connect through edge sharing along the c-axis and corner sharing along the a-axis. In the stoichiometric form, MoO3 is a wide-bandgap material with an approximately 3.0 eV gap and a 4d0 electron configuration. The application of the r2SCAN functional for this material has never been reported before. Using this functional, we calculate all the optimized lattice parameters being within 1.50% error from the experimental value. Specifically, the experimental values that are reported for the Pbnm space group are 9 a = 3.96 Å, b = 13.85 Å, and c = 3.70 Å, while our r2SCAN+D3 values which are for Pnma space group are a = 3.68 Å, b = 3.90 Å, and c = 13.77 Å. These two groups have the exact same symmetry with the axis defined differently, so we expect to have the same properties [47].
Our calculated bandgap is at a value of 2.30 eV, which is underestimated compared to the experimental bandgap but is still improved compared to the Perdew–Burke–Ernzerhof (PBE) functional value of 1.95 eV [48]. As shown in previous studies, while meta-GGA tends to underestimate the bandgap, this does not affect the calculation and prediction of the stable charges or their optical transition properties and is a good alternative to the computationally expensive hybrid functionals [49,50,51].
To predict the stable charge states of the WMo in MoO3, we use the defect formation energy diagrams as described in the Methods above. For every case, we verify the spin multiplicity for each charge state to make sure that we predict the correct ground state for each charge state. Figure S5 shows the formation energy diagram for WMo, where it is seen that, as a defect, it is stable in neutral and −1 charge. Our calculations represent the O-rich conditions. We find a low formation energy for the neutral defect at 0.22 eV. This result indicates that W on the Mo site should be energetically accessible under these conditions.
After identifying the stable charges and the formation energies, we now discuss the electronic structure of the stable configurations. In Figure S6a,b, we show the density of states for the neutral and −1 charge, respectively, as well as the undoped MoO3 (Figure S6c). From our analysis, we found that, in both charges, no gap states are created, so we expect that the peaks that are presented in the PL plot should be transitions from the VBM to the CBM. Furthermore, we find that the bandgap is slightly decreased with the WMo incorporation. The Eg of MoOx with the same thickness was estimated for comparison reasons and is presented in Figure S6d.
3.3. Fabrication of Memristor Using W-MoOx/PMMA Heterostructure
In order to investigate the resistive switching behavior of the W-doped molybdenum oxide, a flexible memristor based on the structure PET/ITO/W-MoOx/PMMA/Al was fabricated. A PMMA layer of 50 nm thickness spin-coated on the W-doped molybdenum oxide was used as a interfacial layer between the W-MoOx and the Al. The prepared device, the schematic illustration of which is presented as an inset in Figure 4a, was electrically characterized to study its memristive performance. The resistive switching mechanism of the fabricated device is clearly evidenced by the hysteresis loop observed in the characteristic semilog current–voltage (I-V) curve shown in Figure 4a. The pristine state of the W-MoOx/PMMA device is the high-resistance state (HRS). The device transition from the HRS to the low-resistance state (LRS) resulting in the SET operation of the memristor is obtained by the application of positive voltage to the top Al electrode. This abrupt change in current occurred at around 0.8 V, which is the VSET of the device. When a negative voltage is applied, the memristor gradually returns from the LRS to the HRS, leading to the RESET operation of the device. The resistive switching voltage at the RESET operation was around 3.1 V (VRESET).
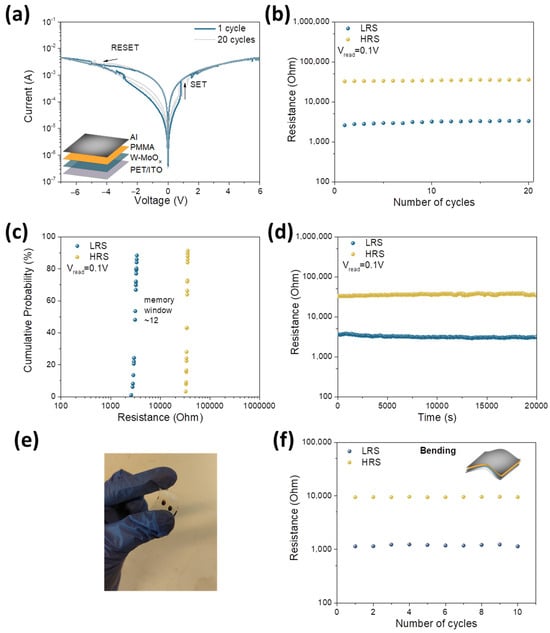
Figure 4.
(a) I-V switching curves of the memristor based on W-MoOx for 20 consecutive cycles of sweep voltages. The device structure is presented as an inset. (b) Endurance characteristics of the same memristor under 20 SET/RESET switching cycles. (c) Cumulative probability plots of HRS and LRS of the W-MoOx memristor. (d) Retention performance of the LRS and HRS of the same device after SET and RESET operation. The pulse SET and RESET voltages were 1.2 V and −4 V, respectively, while the Vread was 0.1 V. (e) Photograph of flexible W-MoOx/PMMA-based memristor. (f) Endurance characteristic of the same device upon mechanical stress.
An endurance test was also performed on the memristor based on the W-MoOx/PMMA heterostructure, recording the I-V characteristic curves over several cycles (Figure 4a). The memristor exhibited good endurance, maintaining the RS behavior for 20 cycles, as presented in Figure 4b. Moreover, the memory window of the device as estimated from the cumulative probability presented in Figure 4c was about 12, which is appropriate for ReRAM devices. A reference memristor without the PMMA layer was also fabricated for comparison reasons. Figure S7a,b show the I-V characteristic curves and the endurance of the device. It is observed that the memory window (~1.5) after 10 cycles is far smaller for bare W-MoOx film compared with that of the heterostructure, indicating that the RS behavior is strongly correlated to the incorporation of the PMMA in the device. Figure 4d shows the retention performance of the W-MoOx/PMMA-based memristor, where, in the case of SET and RESET operation, a pulse with amplitude +1.2 V and −4V, respectively, was applied to the device. In addition, the reading voltage was set at 0.1 V. It is observed that the fabricated memristor retained the data over 2 × 104 s, with no changes in the memory window between the LRS and HRS. The wide bandgap of the PMMA may limit the movement of trapped charge carriers after disconnecting the applied bias, helping to preserve the memristor’s state and leading to long retention times. The memristive behavior upon mechanical bending stress was also investigated. Figure 4e shows a photograph of our flexible memristor, and Figure 4f presents the endurance of the device in the bending state. The radius for the bending deformation was 5 mm. The LRS and HRS of the W-MoOx/PMMA memristor remained stable under mechanical stress, demonstrating the device’s potential for use in flexible memory applications.
In order to investigate the conductive mechanism of the W-MoOx/PMMA-based memristor, the I-V characteristic curves of the SET and RESET operation were plotted on a double logarithmic coordinate axis, as depicted in Figure 5a and Figure 5b, respectively. At low voltages, in both cases (SET and RESET), the slope of the I-V is around 1, suggesting that the ohmic transition mechanism dominates, while in the region of high voltages, the slope of the fitting I-V curves is >1, indicating that the RS mechanism obeys the space charge limited conduction (SCLC) model. In order to shed light on the SCLC mechanism, the trap density (Nt) was estimated using Mott–Gurney analysis (Equation (2)).
where VTFL refers to the trap-filled limit voltage, q is the elementary charge, Nt refers to the trap density, d is the film thickness, and εο and εr are the vacuum and relative permittivity, respectively. Based on Figure 5a,b, the trap density for the SET and RESET operation (assuming εr of ~3) [52] is ~1.66 × 1016 cm−3 and ~3.32 × 1016 cm−3, respectively. These values are in good agreement with previously reported trap densities [53] for oxide-based memristors, further validating the SCLC model in explaining the conduction mechanism of the W-doped MoOx devices.
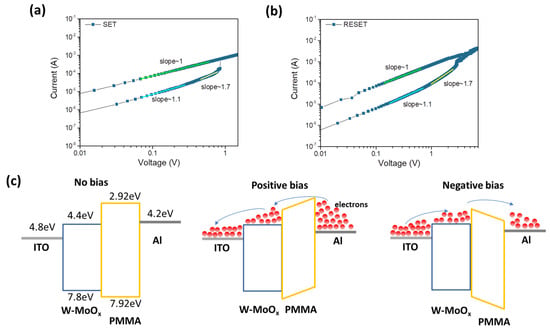
Figure 5.
I-V curve analysis for conductive mechanism of the W-MoOx/PMMA-based memristor during (a) SET and (b) RESET operation. (c) Schematic illustration of the conductive mechanism of the ITO/W-MoOx/PMMA/Al device without bias application (left), with positive bias (middle), and with negative bias (right).
Figure 5c illustrates the conductive mechanism of the ITO/W-MoOx/PMMA/Al memristor, where the left panel shows the energy level diagram of the memristor without bias. The energy levels presented in Note S1 of the W-doped MoOx and PMMA films were estimated by cyclic voltammetry measurements, shown in Figure S8a,b, respectively [54]. The valence band (VB) of the W-MoOx sample was also estimated using ultraviolet photoelectron spectroscopy. Figure 6a,b show the high-energy cut-off and Fermi level regions of W-MoOx’s UPS spectrum, respectively. The VB of the doped oxide is located 3 eV below the Fermi level and thus is estimated at −7.8 eV, in accordance with the cyclic voltammetry measurement, while the work function (WF) is 4.8 eV. When a positive voltage is applied to the top electrode (middle panel of Figure 5c), energy level bending occurs and the electrons reach the W-MoOx layer, passing through the PMMA film. The electrons fill the traps in the W-MoOx layer attributed to the oxygen vacancies of the W-doped molybdenum oxide film, as revealed by the reflectance and PL measurement, and when the filling is completed (at VSET), the conductive filament is formed. Therefore, the memristor switches from the HRS to LRS. On the other hand, when a negative voltage is applied to the Al, the electrons move reversely, leading to the depletion of the W-MoOx, the disruption of the conductive filament, and thus the LRS-to-HRS transition.
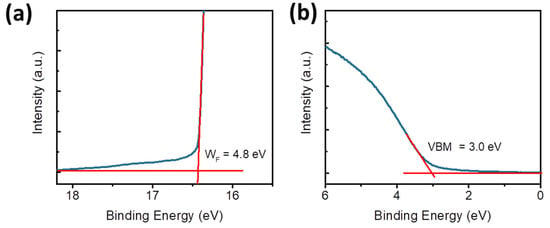
Figure 6.
(a) High-energy cut-offs and (b) Fermi level regions of W-MoOx’s UPS spectrum.
4. Conclusions
An inorganic/organic heterostructure consisting of W-doped molybdenum oxide and PMMA was used as functional layer in a flexible memristive device. The W-MoOx film was developed using a hot-wire CVD method using Mo and W wires as the precursor materials. EDS and XPS analysis confirmed the presence of W in the MoOx film, while the amorphous nature of the deposited W-MoOx was evident from XRD measurements. The memristor based on the W-MoOx/PMMA heterostructure exhibited good resistive switching behavior, with a memory window of about 12 and retention time of 2 × 104 s, indicative of the non-volatile behavior. In the case of HRS and at high applied voltages, the conductive mechanism obeys SCLC, suggesting that the memristor resistive switching behavior is an interface-dominated conductive mechanism attributed to the charge trapping and de-trapping effect. The good reproducibility of the memristor demonstrates the effectiveness of the W-MoOx/PMMA heterostructure as the functional layer in ReRAM devices.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/nano15221707/s1. Figure S1: EDS image of W-doped MoOx film deposited on silicon substrate in N2 environment; Figure S2: FTIR transmittance spectra of (a) molybdenum and (b) tungsten oxide thin films; Figure S3: Grain analysis of 5 × 5 μm2 AFM image of W-MoOx surface; Figure S4: Absorbance spectrum of the mixed W-MoOx film deposited on glass substrate; Figure S5: The formation energy versus the fermi level for the O-rich conditions using r2SCAN+D3 functional; Figure S6: The density of states plot for the (a) neutral and (b) −1 charge WMo0:MoO3 and (c) undoped MoO3; Figure S7: I-V characteristic curves of the PET/ITO/W-MoOx/Al memristor without the PMMA film; Figure S8: Cyclic voltammetry measurements of (a) W-MoOx and (b) PMMA films coated on ITO substrates; Note S1: Energy levels of W-MoOx and PMMA films as estimated by cyclic voltammetry measurements. The reference electrode was Ag/AgCl. Table S1: Quantitive analysis, weight and atomic ratios in percentage for oxygen (O, K series), molybdenum (Mo, L series), and tungsten (W, L series) of W-doped MoOx sample deposited in N2 environment.
Author Contributions
Investigation, G.K., P.-P.F., P.T., E.S., and A.S.; Methodology, P.T., K.A., E.S., and D.D.; Writing—Original Draft, G.K., P.-P.F., K.A., and A.S.; Writing—Review and Editing, A.S.; Resources, D.D.; Supervision, A.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article/Supplementary Materials. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge Marianna Argeiti for her valuable contribution to the characterization of the films and devices, carried out as part of her internship. Computing resources were provided by the University of Nottingham, through the EPSRC-funded HPC Midlands+ consortium [EP/T022108/1], for access to Sulis.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- El-Haji, M. Enhancing communication networks in the new era with artificial intelligence: Techniques, applications, and future directions. Network 2025, 5, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ielmini, D.; Wong, H.S.P. In-Memory Computing with Resistive Switching Devices. Nat. Electron. 2018, 1, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zidan, M.A.; Strachan, J.P.; Lu, W.D. The Future of Electronics Based on Memristive Systems. Nat. Electron. 2018, 1, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Kang, K.-M.; Kim, M.; Lee, H.-S.; Waser, R.; Wouter, D.; Dittmann, R.; Yang, J.J.; Park, H.-H. Mott-transition-based RRAM. Mater. Today 2019, 28, 63–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.H.; Song, Y.-W.; Ham, W.; Park, J.-M.; Kwon, J.-Y. A review on device requirements of resistive random access memory (RRAM)-based neuromorphic computing. APL Mater. 2023, 11, 090701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.; Ilyas, N.; Shamim, M.Z.M.; Khan, M.I.; Sohail, M.; Rahman, N.; Khan, A.A.; Khan, S.N.; Khan, A. Oxide-based resistive switching-based devices: Fabrication, influence parameters and applications. J. Mater. Chem. C 2021, 9, 15755–15788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshekh, H.; Wang, H.; Zhu, S.; Yang, C.; Wang, J. Nonvolatile resistive switching memory behavior of the TiOx-based memristor. Chem. Phys. 2024, 580, 112217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Huang, Y.; Wei, M.; Qiu, X. Ultralow voltage resistive switching characteristics of HfOx/NiOx stacks. J. Appl. Phys. 2025, 137, 075701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Wu, F.; Ouyang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Tian, H.; Dong, M. Oxygen incorporated MoS2 for rectification-mediated resistive switching and artificial neural network. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2213348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.C.; Li, J.; Chen, X.-D.; Kong, Y.; Wang, F.-D.; Zhang, G.-X.; Lu, T.-B.; Zhang, J. Low-voltage ultrafast nonvolatile memory via direct charge injection through a threshold resistive-switching layer. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, J.; Dong, P.; Jian, Z.; Zhao, T.; Miao, C.; Chang, H.; Chen, J.; Chen, Y.-F.; Chen, Y.-B.; Feng, H.; et al. Ultralow-power RRAM with high switching ratio based on the large van der Waals interstice radius of TMDs. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 20445–20456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahmani, M.K.; Khan, S.A.; Geum, D.-M.; Jeon, H.; Park, S.Y.; Yun, C.; Kang, M.H. Enhanced resistive switching behaviors of organic resistive random access memory devices by adding polyethyleneimine interlayer. Org. Electron. 2024, 132, 107089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Liu, H.; Kong, H.-Y.; Bian, X.-Y.; Yao, B.-W.; Li, Y.J.; Gu, C.; Ding, X.; Sun, L.; Han, B.-H. Resistive memristors using robust electropolymerized porous organic polymer films as switching materials. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 16511–16520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Xia, F.; Du, B.; Zhang, S.; Xu, L.; Su, Q.; Zhang, D.; Yang, J. 2D halide perovskites for high-performance resistive switching memory and artificial synapse applications. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, 2310263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, K.; Peng, M.; Yu, X.; Cai, X.; Chen, S.; Hu, H.; Chen, B.; Gao, X.; Dong, B.; Zou, D. High-performance perovskite memristor based on methyl ammonium lead halides. J. Mater. Chem. C 2016, 4, 1375–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, R.A.; Milozzi, A.; Tsarev, S.; Brönnimann, R.; Boehme, S.C.; Wu, E.; Shorubalko, I.; Kovalenko, M.V.; Ielmini, D. IonicElectronic Halide Perovskite Memdiodes Enabling Neuromorphic Computing with a Second-Order Complexity. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eade0072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatheema, J.; Shahid, T.; Mohammad, M.A.; Islam, A.; Malik, F.; Akinwande, D.; Rizwan, S. A comprehensive investigation of MoO3 based resistive random access memory. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 19337–19345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.; Yin, X.-B.; Yang, R.; Guo, X. Pt/WO3/FTO memristive devices with recoverable pseudo-electroforming for time-delay switches in neuromorphic computing. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 9338–9343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Sun, B.; Mao, S.; Yang, Y.; Liu, M.; Rao, Z.; Ke, C.; Zhao, Y. Improved resistive switching performance and mechanism analysis of MoO3 nanorods based memristors. Mater. Today Commun. 2023, 36, 106770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Shi, P.; Xing, R.; Xing, Y.; Ge, Y.; Wei, L.; Wang, D.; Zhao, L.; Yan, S.; Chen, Y. Quasi-two-dimensional α-molybdenum oxide thin film prepared by magnetron sputtering for neuromorphic computing. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 17706–17714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudrapal, K.; Bisws, M.; Jana, B.; Adyam, V.; Chaudhuri, A.R. Tuning resistive switching properties of WO3−x-memristors by oxygen vacancy engineering for neuromorphic and memory storage applications. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2023, 56, 205302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Wang, A.; Humayun, M.; Wang, C. Recent advances of oxygen vacancies in MoO3: Preparation and roles. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 498, 155246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Li, Y.; Ai, C.; Wen, D. Resistive switching characteristics of Li-doped ZnO thin films based on magnetron sputtering. Materials 2019, 12, 1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, T.; Du, Y.; Cao, A.; Sun, Y.; Zha, G.; Lei, H.; Zheng, X. The resistive switching characteristics of Ni-doped HfOx film and its application as a synapse. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 766, 918–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, D.; Dwivedi, A.K.; Verma, S.; Avasthi, D.K. Transition metal oxide based resistive random-access memory: An overview of materials and device performance enhancement techniques. J. Sci. Adv. Mater. Dev. 2024, 9, 100813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, S.; Jiang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Jiang, B.; Cheng, G.; Wu, F.; Cao, G.; Peng, Z.; Zhu, M.; et al. Brain-like synaptic memristor based on lithium-doped silicate for neuromorphic computing. Front. Phys. 2022, 17, 53508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharathi, M.; Balraj, B.; Sivakumar, C.; Wang, Z.; Shuai, J.; Ho, M.; Guo, D. Effect of Ag doping on bipolar switching operation in molybdenum trioxide (MoO3) nanostructures for non-volatile memory. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 862, 158035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.; Dong, R.; Lee, D.; Seong, D.; Choi, H.; Pyun, M.; Hwang, H. A materials approach to resistive switching memory oxides. J. Semicond. Technol. Sci. 2008, 8, 66–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soultati, A.; Aidinis, K.; Chroneos, A.; Vasilopoulou, M.; Davazoglou, D. Ambipolar surface conduction in oxygen sub-stoichiometric molybdenum oxide films. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 21166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasilopoulou, M.; Douvas, A.M.; Georgiadou, D.G.; Palilis, L.C.; Kennou, S.; Sygellou, L.; Soultati, A.; Kostis, I.; Papadimitropoulos, G.; Davazoglou, D.; et al. The influence of hydrogenation and oxygen vacancies on molybdenum oxides work function and gap states for application in organic optoelectronics. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 16178–16187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Tu, J.P.; Xia, X.H.; Qiao, Y.; Lu, Y. An all-solid-state electrochromic device based on NiO/WO3 complementary structure and solid hybrid polyelectrolyte. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2009, 93, 1840–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criinert, W.; Stakheev, A.Y.; Feldhaus, R.; Anders, K.; Shpiro, E.S.; Minachev, K.M. Analysis of molybdenum(3d) XPS spectra of supported molybdenum catalysts: An alternative approach. J. Phys. Chem. 1991, 95, 1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleisch, T.H.; Mains, G.J. An XPS study of the UV reduction and photochromism of MoO3 and WO3. J. Chem. Phys. 1982, 76, 780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinhardt, L.; Blum, M.; Bär, M.; Heske, C.; Cole, B.; Marsen, B.; Miller, E.L. Electronic Surface Level Positions of WO3 Thin Films for Photoelectrochemical Hydrogen Production. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 3078–3082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höchst, H.; Bringans, R.D. Electronic structure of evaporated and annealed tungsten oxide films studied with UPS. Appl. Surf. Sci. 1982, 11–12, 768–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.B.; Zhong, X.X.; Shao, R.W.; Chen, Y.A.; Cvelbar, U.; Ostrikov, K. Effects of tungsten doping on structure and amorphous photoluminescence of MoO3-x nanomaterials. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2020, 53, 415109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Layegh, M.; Ghodsi, F.E.; Hadipour, H. Experimental and theoretical study of Fe doping as a modifying factor in electrochemical behavior of mixed-phase molybdenum oxide thin films. Appl. Phys. A 2020, 126, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Jin, H.; Lu, H.; Fei, Y.; Zhu, X.; Yang, G. Movement of oxygen vacancies in oxide film during annealing observed by an optical reflectivity difference technique. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 102, 053107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kresse, G.; Furthmüller, J. Efficient iterative schemes for ab initio total-energy calculations using a plane-wave basis set. Phys. Rev. B 1996, 54, 11169–11186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kresse, G.; Furthmüller, J. Efficiency of ab-initio total energy calculations for metals and semiconductors using a plane-wave basis set. Comput. Mater. Sci. 1996, 6, 15–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kresse, G.; Joubert, D. From ultrasoft pseudopotentials to the projector augmented-wave method. Phys. Rev. B 1999, 59, 1758–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furness, J.W.; Kaplan, A.D.; Ning, J.; Perdew, J.P.; Sun, J. Accurate and Numerically Efficient r2SCAN Meta-Generalized Gradient Approximation. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2020, 11, 8208–8215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimme, S.; Antony, J.; Ehrlich, S.; Krieg, H. A consistent and accurate ab initio parametrization of density functional dispersion correction (DFT-D) for the 94 elements H-Pu. J. Chem. Phys. 2010, 132, 154104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosquera-Lois, I.; Kavanagh, S.R.; Walsh, A.; Scanlon, D.O. ShakeNBreak: Navigating the defect configurational landscape. J. Open Source Softw. 2022, 7, 4817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavanagh, S.R.; Squires, A.G.; Nicolson, A.; Mosquera-Lois, I.; Ganose, A.M.; Zhu, B.; Brlec, K.; Walsh, A.; Scanlon, D.O. doped: Python toolkit for robust and repeatable charged defect supercell calculations. J. Open Source Softw. 2024, 9, 6433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippatos, P.-P.; Chroneos, A.; Kelaidis, N. A first-principles investigation of halogen doped diamond and its application to quantum technologies. J. Appl. Phys. 2025, 138, 094401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carcia, P.F.; McCarron, E.M. Synthesis and properties of thin film polymorphs of molybdenum trioxide. Thin Solid Films 1987, 155, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Flor, G.; Aroyo, M.I.; Gimondi, I.; Ward, S.C.; Momma, K.; Hanson, R.M.; Suescun, L. Free tools for crystallographic symmetry handling and visualization. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2024, 57, 1618–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scanlon, D.O.; Watson, G.W.; Payne, D.J.; Atkinson, G.R.; Egdell, R.G.; Law, D.S.L. Theoretical and Experimental Study of the Electronic Structures of MoO3 and MoO2. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 4636–4645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, G.; Bulancea-Lindvall, O.; Davidsson, J.; Armiento, R.; Abrikosov, I.A. Theoretical characterization of NV-like defects in 4H-SiC using ADAQ with the SCAN and r2SCAN meta-GGA functionals. arXiv 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Liu, L.; Zhuang, H.L. Spin qubit based on the nitrogen-vacancy center analog in a diamond-like compound C3BN. J. Appl. Phys. 2021, 130, 225702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushima, T.; Jin, G.-H.; Murata, H. Marked improvement in electroluminescence characteristics of organic light-emitting diodes using an ultrathin hole-injection layer of molybdenum oxide. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 104, 054501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joung, D.; Chunder, A.; Khondaker, S.I. Space charge limited conduction with exponential trap distribution in reduced graphene oxide sheets. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 97, 093105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayesh, A.S. Electrical and optical characterization of PMMA doped with Y0.0025Si0.025Ba0.9725 (Ti(0.9)Sn0.1)O3 ceramic. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 2010, 28, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).