Effect of Hydrothermal Aging on Mechanical and Microstructural Properties of Zirconia Ceramics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preperation of the Specimens
2.2. Sintering Procedure
2.3. Hydrothermal Aging
2.4. Three-Point Flexural Test
2.5. Vickers Hardness Test
2.6. Surface Roughness Analysis
2.7. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD)
2.8. Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM)
2.9. SEM and Energy-Dispersive X-Ray Spectroscopy (EDS)
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Three-Point Flexural Test
3.2. Vickers Hardness Test
3.3. Surface Roughness Analysis
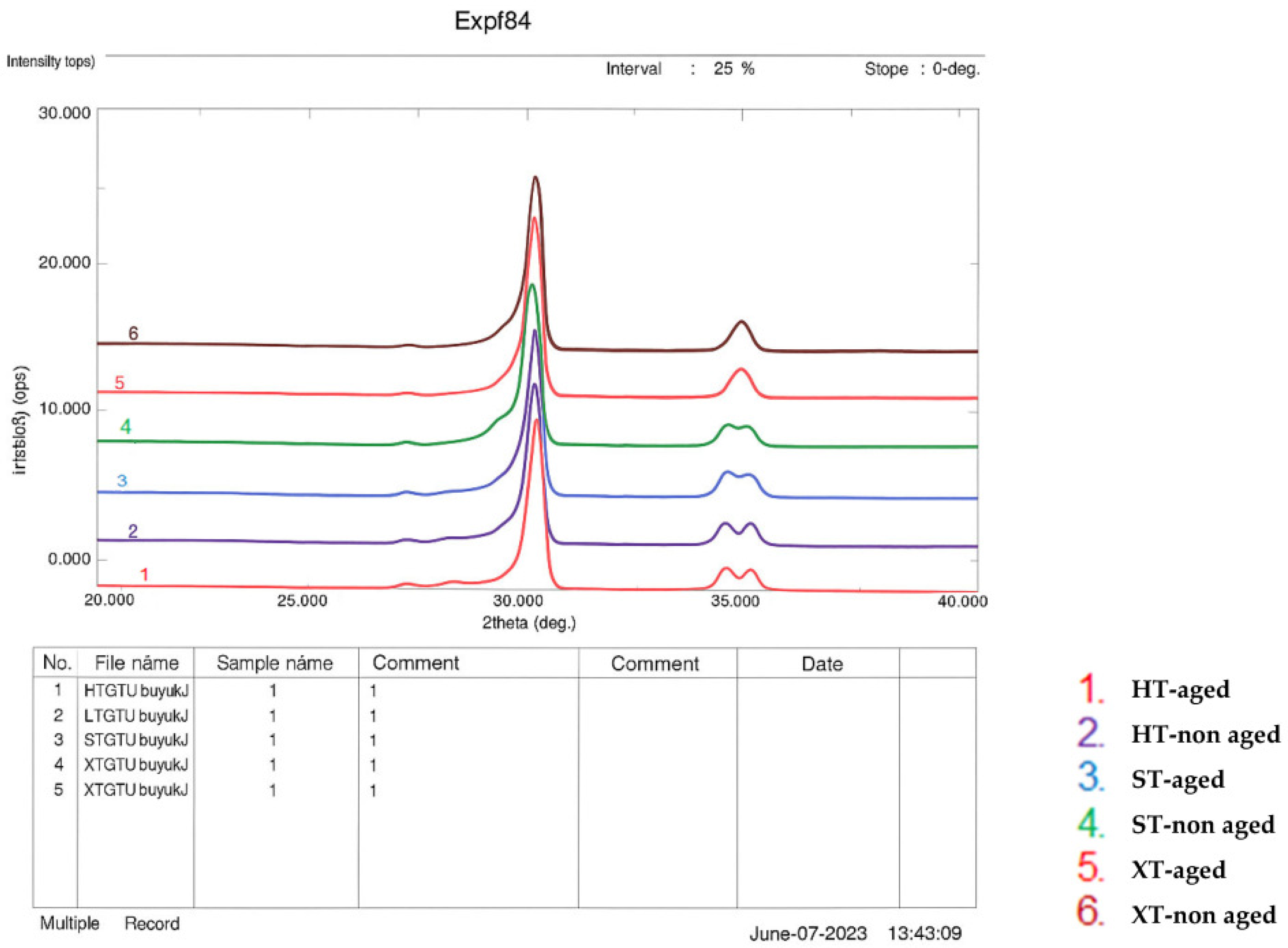
3.4. XRD
3.5. AFM
3.6. SEM/EDS
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- Different material formulations affected the mechanical behavior, surface roughness and microstructural properties of monolithic zirconia ceramics.
- The highest flexural strength values were observed in 3 Y-TZP, while the lowest was observed in 5 Y-TZP. The use of 3 Y-TZP may be recommended in the presence of high chewing forces such as posterior restorations or bruxism.
- Non-aged 3 Y-TZP and 5 Y-TZP showed highest and similar Vickers hardness values while aged 3 Y-TZP showed the lowest. According to these results, it can be concluded that the Vickers hardness of 3 Y-TZP is most affected by hydrothermal aging.
- Hydrothermal aging displayed effects on the Vickers hardness, phase transformations, and elemental compositions of monolithic zirconia ceramics.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Çelik, M.; Bural, C.; Bayrakdar, G. Application of zirconia in dentistry. J. Dent. Fac. Atatürk Univ. 2015, 8, 106–116. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.H.; Lee, S.J.; Park, J.S.; Ryu, J.J. Fracture load of monolithic CAD/CAM lithium disilicate ceramic crowns and veneered zirconia crowns as a posterior implant restoration. Implant. Dent. 2013, 22, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durkan, R.; Deste, G. Fixed dental rehabilitation using monolithic zirconia ceramic: A clinical case report. J. Dent. Fac. Atatürk Univ. 2018, 28, 385–390. [Google Scholar]
- Bayindir, F.; Koseoglu, M. The effect of restoration thickness and resin cement shade on the color and translucency of a high-translucency monolithic zirconia. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2020, 123, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candido, L.M.; Miotto, L.N.; Fais, L.M.G.; Cesar, P.F.; Pinelli, L.A.P. Mechanical and surface properties of monolithic zirconia. Oper. Dent. 2018, 43, E119–E128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hisbergues, M.; Vendeville, S.; Vendeville, P. Review zirconia: Established facts and perspectives for a biomaterial in dental implantology. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2009, 88, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bultan, Ö.; Öngül, D.; Türkoğlu, P. Fabrication techniques and microstructure classifications of zirconia. J. Dent. Fac. Istanbul. Univ. 2010, 44, 197–204. [Google Scholar]
- Lümkemann, N.; Stawarczyk, B. Impact of hydrothermal aging on the light transmittance and flexural strength of colored yttria-stabilized zirconia materials of different formulations. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2021, 125, 518–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansen, J.U.; Lümkemann, N.; Letz, I.; Pfefferle, R.; Sener, B.; Stawarczyk, B. Impact of high-speed sintering on translucency, phase content, grain sizes, and flexural strength of 3Y-TZP and 4Y-TZP zirconia materials. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2019, 122, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deniz, D.; Aktaş, G. Current zirconia generations: Clinical tricks. Acta Odontol. Turc. 2023, 40, 96–102. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, L.; Kaizer, M.R.; Zhao, M.; Guo, B.; Song, Y.F.; Zhang, Y. Graded ultra-translucent zirconia (5Y-PSZ) for strength and functionalities. J. Dent. Res. 2018, 97, 1222–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güth, J.-F.; Stawarczyk, B.; Edelhoff, D.; Liebermann, A. Zirconia and its novel compositions: What do clinicians need to know? Quintessence Int. 2019, 50, 512–520. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alammar, A.; Blatz, M.B. The resin bond to high-translucent zirconia—A systematic review. J. Esthet. Restor. Dent. 2022, 34, 117–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, K.; Güth, J.F.; Erdelt, K.; Stimmelmayr, M.; Kappert, H.; Beuer, F. Light transmittance by a multi-coloured zirconia material. Dent. Mater. J. 2015, 34, 310–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swab, J.J. Low temperature degradation of Y-TZP materials. J. Mater. Sci. 1991, 26, 6706–6714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, P.J.; Lee, J.H.; Ha, S.R.; Seo, D.G.; Ahn, J.S.; Choi, Y.S. Changes in the properties of different zones in multilayered translucent zirconia used in monolithic restorations during aging process. J. Funct. Biomater. 2025, 16, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mota, Y.A.; Cotes, C.; Carvalho, R.F.; Machado, J.P.B.; Leite, F.P.P.; Souza, R.O.A.; Özcan, M. Monoclinic phase transformation and mechanical durability of zirconia ceramic after fatigue and autoclave aging. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2017, 105, 1972–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-K.; Kim, S.-H. Effect of hydrothermal aging on the optical properties of precolored dental monolithic zirconia ceramics. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2019, 121, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Xie, H.; Wu, X.; Yang, J.; Liao, M.; Chen, C. Evaluation of the effect of low-temperature degradation on the translucency and mechanical properties of ultra-transparent 5Y-TZP ceramics. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, W.; Garbrielsson, K.; Borhani, A.; Carlborg, M.; Molin Thorén, M. The effects of artificial aging on high translucent zirconia. Biomater. Investig. Dent. 2019, 6, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VITA Zahnfabrik. VITA YZ Solutions—Guidelines for Processing Zirconia Materials. Available online: https://www.dismat.com/upload/dokuman/6112019-VITA-10446-10446E-YZ-SOLUTIONS-VA-EN-V01-en-13330.pdf (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- ISO 13356:2015; Implants for Surgery—Ceramic Materials Based on Yttria-Stabilized Tetragonal Zirconia (Y-TZP). International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015. Available online: https://www.iso.org/obp/ui/en/#iso:std:iso:13356:ed-3:v1:en (accessed on 22 October 2025).
- Hawsawi, R.A.; Miller, C.A.; Moorehead, R.D.; Stokes, C.W. Evaluation of reproducibility of the chemical solubility of dental ceramics using ISO 6872:2015. J. Prosth. Dent. 2020, 124, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO 6507-1; Metallic Materials—Vickers Hardness Test. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018.
- Bütikofer, L.; Stawarczyk, B.; Roos, M. Two regression methods for estimation of a two-parameter Weibull distribution for reliability of dental materials. Dent. Mater. 2015, 31, e33–e50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silmeoglu Yagli, O.; Talay Cevlik, E.; Kurklu Arpacay, D. The impact of aging and thickness on flexural strength of various zirconia ceramics. BMC Oral Health 2024, 24, 967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, S.R.; Choi, Y.S. Effect of hydrothermal aging on dental multilayered zirconia for monolithic restorations: An in vitro study. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 17057–17068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almirabi, R.S.; Alzahrani, K.M. Effect of the intaglio surface treatment and thickness of different types of yttria-stabilized tetragonal zirconia polycrystalline materials on the flexural strength: In-Vitro Study. Materials 2024, 17, 5256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshali, R.Z.; Awad, M.A.; Assiri, A.A.; Aljahdali, S.A.; Babeer, W.A.; Bukhary, D.M.; Altassan, M.M.; Al-Turki, L.E. The Effect of glazing and repeated firing on color, translucency, and flexural strength of different types of zirconia: An In Vitro Study. Ceramics 2025, 8, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, E.M.; Longhini, D.; Antonio, S.G.; Adabo, G.L. The effects of mechanical and hydrothermal aging on microstructure and biaxial flexural strength of an anterior and a posterior monolithic zirconia. J. Dent. 2017, 63, 63–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfahed, B.; Alayad, A. The effect of sintering temperature on Vickers microhardness and flexural strength of translucent multi-layered zirconia dental materials. Coatings 2023, 13, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerman, E.; Lümkemann, N.; Eichberger, M.; Zoller, C.; Nothelfer, S.; Kienle, A.; Stawarczyk, B. Evaluation of translucency, Marten’s hardness, biaxial flexural strength and fracture toughness of 3Y-TZP, 4Y-TZP and 5Y-TZP materials. Dent. Mater. 2021, 37, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayinger, F.; Ender, A.; Strickstrock, M.; Elsayed, A.; Nassary Zadeh, P.; Zimmermann, M.; Stawarczyk, B. Impact of the sintering parameters on the grain size, crystal phases, translucency, biaxial flexural strength and fracture load of zirconia materials. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2024, 155, 106580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyung, K.Y.; Park, J.M.; Heo, S.J.; Koak, J.Y.; Kim, S.K.; Ahn, J.S.; Yi, Y. Comparative analysis of flexural strength of 3D printed and milled 4Y-TZP and 3Y-TZP zirconia. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2024, 131, e1–e529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Choi, Y.S. Changes in properties of monolithic and conventional zirconia during aging process. Mech. Mater. 2019, 138, 103159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelch, M.; Schulz, J.; Edelhoff, D.; Sener, B.; Stawarczyk, B. Impact of different pretreatments and aging procedures on the flexural strength and phase structure of zirconia ceramics. Dent. Mater. 2019, 35, 1439–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kongkiatkamon, S.; Peampring, C. Effect of speed sintering on low temperature degradation and biaxial flexural strength of 5Y-TZP zirconia. Molecules 2022, 27, 5272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jerman, E.; Wiedenmann, F.; Eichberger, M.; Reichert, A.; Stawarczyk, B. Effect of high-speed sintering on the flexural strength of hydrothermal and thermo-mechanically aged zirconia materials. Dent. Mater. 2020, 36, 1144–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almansour, H.M.; Alqahtani, F. The effect of in vitro aging and fatigue on the flexural strength of monolithic high-translucency zirconia restorations. J. Contemp. Dent. Pract. 2018, 19, 867–873. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.Y.; Agingu, C.; Yang, H.; Cheng, H.; Yu, H. Effects of hydrothermal treatment on the phase transformation, surface roughness, and mechanical properties of monolithic translucent zirconia. Oper. Dent. 2022, 47, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arcila, L.V.C.; de Carvalho Ramos, N.; Campos, T.M.B.; Dapieve, K.S.; Valandro, L.F.; de Melo, R.M.; Bottino, M.A. Mechanical behavior and microstructural characterization of different zirconia polycrystals in different thicknesses. J. Adv. Prosthodont. 2021, 13, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grambow, J.; Wille, S.; Kern, M. Impact of changes in sintering temperatures on characteristics of 4YSZ and 5YSZ. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2021, 120, 104586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toma, F.R.; Bîrdeanu, M.I.; Uțu, I.D.; Vasiliu, R.D.; Moleriu, L.C.; Porojan, L. Surface characteristics of high translucent multilayered dental zirconia related to aging. Materials 2022, 15, 3606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohr, N.; Schönenberger, A.J.; Fischer, J. Influence of surface treatment and accelerated ageing on biaxial flexural strength and hardness of zirconia. Materials 2023, 16, 910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhotan, A.; Yilmaz, B.; Weber, A.; Babaier, R.; Bourauel, C.; Fouda, A.M. Effect of artificial aging on fracture toughness and hardness of 3D-printed and milled 3Y-TZP zirconia. J. Prosthodont. 2024, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peampring, C.; Kengtanyakich, S. Surface roughness and translucency of various translucent zirconia ceramics after hydrothermal aging. Eur. J. Dent. 2022, 16, 761–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, R.D.; Pereira, G.K.R.; Bottino, M.A.; de Melo, R.M.; Valandro, L.F. Effect of ceramic thickness, grinding, and aging on the mechanical behavior of a polycrystalline zirconia. Braz. Oral Res. 2017, 31, e82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benalcázar-Jalkh, E.B.; Campos, T.M.B.; dos Santos, C.; Alves, L.M.M.; Carvalho, L.F.; Bergamo, E.T.P.; Tebcherani, S.M.; Witek, L.; Coelho, P.G.; Thim, G.P.; et al. Novel bilayered zirconia systems using recycled 3Y-TZP for dental applications. Dent. Mater. 2025, 41, 402–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gremillard, L.; Chevalier, J.; Deville, S.; Epicier, T.; Fantozzi, G. Modeling the aging kinetics of zirconia ceramics. J. Europ. Ceram. Soc. 2004, 24, 3483–3489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziębowicz, A.; Oßwald, B.; Kern, F.; Schwan, W. Effect of simulated mastication on structural stability of prosthetic zirconia material after thermocycling aging. Materials 2023, 16, 1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Material | Manufacturer | Material Composition | Material Groups |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vita-YZ-HT (3Y-TZP) | Vita Zahnfabrik, Bad Säckingen, Germany | 90–95% ZrO2, 4–6% Y2O3, 1.5–2.5% HfO2, 0–0.3% Al2O3, 0–0.5% Er2O3, 0–0.3% Fe2O3 | HT |
| Vita-YZ-ST (4Y-TZP) | Vita Zahnfabrik, Bad Säckingen, Germany | 88–93% ZrO2, 6–8% Y2O3, 1.5–2.5% HfO2, 0–0.3% Al2O3, 0–0.5% Er2O2, 0–0.3% Fe2O3 | ST |
| Vita-YZ-XT (5Y-TZP) | Vita Zahnfabrik, Bad Säckingen, Germany | 86–91% ZrO2, 8–10% Y2O3, 1.5–2.5% HfO2, 0–0.3% Al2O3, 0–0.5% Er2O3, 0–0.3% Fe2O3 | XT |
| Groups | Flexural Strength (MPa) Mean ± SD | Vickers Hardness (GPa) Mean ± SD | Ra (µm) Mean ± SD |
|---|---|---|---|
| HT-non-aged | 1192.1 ± 143.9 A | 1169.6 ± 46.8 B | 0.43 ± 0.14 A |
| HT-aged | 1112.8 ± 201.1 A | 1104.5 ± 44.2 A | 0.43 ± 0.17 A |
| ST-non-aged | 945.5 ± 398 A,B | 1129 ± 93.7 A | 0.52 ± 0.12 A |
| ST-aged | 850 ± 115.4 B | 1283.4 ± 145.5 C | 0.44 ± 0.14 A |
| XT-non-aged | 434.4 ± 100.6 C | 1170.2 ± 34.3 B | 0.7 ± 0.21 B |
| XT-aged | 401.5 ± 65.8 C | 1257.4 ± 153.3 C | 0.63 ± 0.19 B |
| Groups | Weibull Modulus (m) | 95% Cl |
|---|---|---|
| HT-non-aged | 9.5 A | (7.5; 11.4) |
| HT-aged | 6.3 B | (4.4; 8.3) |
| ST-non-aged | 2.7 C | (0.78; 4.7) |
| ST-aged | 8.3 D | (6.4; 10.3) |
| XT-non-aged | 4.6 E | (2.7; 6.6) |
| XT-aged | 7.8 F | (5.9; 9.8) |
| Groups | Monoclinic Phase Ratio (%) |
|---|---|
| HT-non-aged | 2.13% |
| HT-aged | 6.67% |
| ST-non-aged | 1.47% |
| ST-aged | 6.38% |
| XT-non-aged | 0 |
| XT-aged | 0 |
| Groups | C | O | Hf | Y | Zr |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HT-non-aged | 13.95 | 11.62 | 2.28 | 6.64 | 65.5 |
| HT-aged | 12.76 | 12.47 | 2.34 | 8.75 | 63.68 |
| ST-non-aged | 13.93 | 10.76 | 2.29 | 9.68 | 63.14 |
| ST-aged | 11.38 | 12.24 | 3.27 | 9.65 | 63.47 |
| XT-non-aged | 15.21 | 11.51 | 2.9 | 9.85 | 60.53 |
| XT-aged | 10.59 | 10.68 | 2.84 | 11.89 | 63.99 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sayla Çelik, Ç.; Çakırbay Tanış, M. Effect of Hydrothermal Aging on Mechanical and Microstructural Properties of Zirconia Ceramics. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 1669. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15211669
Sayla Çelik Ç, Çakırbay Tanış M. Effect of Hydrothermal Aging on Mechanical and Microstructural Properties of Zirconia Ceramics. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(21):1669. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15211669
Chicago/Turabian StyleSayla Çelik, Çağlayan, and Merve Çakırbay Tanış. 2025. "Effect of Hydrothermal Aging on Mechanical and Microstructural Properties of Zirconia Ceramics" Nanomaterials 15, no. 21: 1669. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15211669
APA StyleSayla Çelik, Ç., & Çakırbay Tanış, M. (2025). Effect of Hydrothermal Aging on Mechanical and Microstructural Properties of Zirconia Ceramics. Nanomaterials, 15(21), 1669. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15211669





