Abstract
Fake news is false or misleading information that looks like real news and spreads through traditional and social media. It has a big impact on our social lives, especially in politics. In Pakistan, where Urdu is the main language, finding fake news in Urdu is difficult because there are not many effective systems for this. This study aims to solve this problem by creating a detailed process and training models using machine learning, deep learning, and large language models (LLMs). The research uses methods that look at the features of documents and classes to detect fake news in Urdu. Different models were tested, including machine learning models like Naïve Bayes and Support Vector Machine (SVM), as well as deep learning models like Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM), which used embedding techniques. The study also used advanced models like BERT and GPT to improve the detection process. These models were first evaluated on the Bend-the-Truth dataset, where CNN achieved an F1 score of 72%, Naïve Bayes scored 78%, and the BERT Transformer achieved the highest F1 score of 79% on Bend the Truth dataset. To further validate the approach, the models were tested on a more diverse dataset, Ax-to-Grind, where both SVM and LSTM achieved an F1 score of 89%, while BERT outperformed them with an F1 score of 93%.
1. Introduction
False or misleading information presented as news is known as fake news. This information is often used to harm an individual’s or organization’s reputation or generate profits through advertising [1,2]. The term ‘fake news’ was first used in the 1890s to describe sensational or false reports in newspapers. However, spreading false information has been happening throughout history [3,4].
Urdu belongs to the Indo-Aryan language group, the eighth most commonly spoken language globally, with more than 100 million speakers [5]. Urdu is a low-resource language due to a lack of benchmark datasets available, and important tools like tokenizers and stemmers that are either insufficient or lack appreciable size. Urdu language processing: a survey [6].
Urdu is Pakistan’s national language, also spoken in the Indian subcontinent. It is a beautiful and rich language with a long literary tradition. However, the recent advancement in the NLP for Western languages is mainly because of the machine learning combined with term frequency-inverse document frequency (TF-IDF), along with other features like ACC, ACC2, OR, GINI, and NDM [7]. Specifically, one of the major advancements in attaining high levels of accuracy has been the addition of embeddings to various deep learning strategies used in a series of NLP applications [8].
For instance, supervised machine learning techniques using TF-IDF, ACC, ACC2, OR, GINI, and NDM have been vital in fake news Identification [7]. These techniques are able to analyze the text documents while maintaining the characteristics of the language, as well as recognizing motifs in the given data [9].
Furthermore, embedding based deep learning models like Word2Vec have proved to be highly efficient in NL processing of different Western languages like Portuguese [10], Italian, Dutch, and Spanish [11,12]. However, this technique has been successful in identifying fake news in Western languages, but its applicability to identify fake news in Urdu text is yet to be explored. This research, therefore, seeks to address this gap by comparing the traditional machine learning features, techniques, and embedding features in machine learning and deep learning for fake news detection in Urdu text documents.
In light of this, it is particularly important that LLMs such as BERT and GPT-2 should be employed for fake news identification in the Urdu language. Although LLM has been widely incorporated in rich-resource languages, its incorporation in the Urdu language is still quite constrained. By utilizing the advanced capability of LLM, which has demonstrated superior performance in several NLP areas, such as language comprehension and synthesis [13], it is possible to enhance the speed and accuracy of fake news detection in Urdu text [13]. This approach can prove highly effective in moving the field forward and can fill the current research gap of employing modern analysis techniques on Urdu text.
The availability of information has posed challenges to testing data. For this reason, it is necessary to create a system to control the amount of inaccurate and misleading data on websites. Now, we can eliminate this deficiency by designing a computational model to observe fake news. It will be easy to build a system to detect Urdu fake news if datasets are available in a collected form.
Different classification methods have been used to detect Urdu fake news in the last decade. In recent research [5], the authors divided the methods of detecting fake news into three categories: style-based (by analyzing writing style), context-based (by analyzing news spread in social media), and knowledge-based (by relating to known facts). This article aims to analyze the Urdu text data by identifying the gap and analyzing the performance of supervised learning models. In all cases, the method requires a corpus of news, which is an additional challenge due to rare labeled fake news datasets in Urdu and few fake news datasets available in English [14].
The main contributions of this work are:
- To the best of our knowledge, it is the first time that the performance of the methods used for fake news identification has been compared for the Urdu language in conjunction with deep learning algorithms. In particular, we have performed more than 30 experiments using the existing two Urdu corpora, such as Bend the Truth and Ax-to-Grind. The TFIDF, ACC, ACC2, OR, GINI, and NDM features, with three traditional supervised learning techniques. The traditional techniques include Gaussian Naïve Bayes (GNB), Burnolie Naïve Bayes (BNB), and Support Vector Machine (SVM). Whereas, the deep learning techniques include Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM), and CNN, which uses Embedding, pre-trained Word2vec embedding, and One-Hot Encoding.
- In this study, the fine-tuning of the BERT and GPT2 LLMswas performed. Fine-tuning refers to the process of fine-tuning a model that has been trained on a large dataset and is then adjusted for a specific task. In this research, we used the BERT and GPT2 models and trained them on the Bend the Truth and Ax-to-Grind datasets for fake news identification in Urdu. This process helps the model to capture the language pattern in the Urdu language and various writing styles, and then helps in the process of fake news identification of the Urdu text.
- The performances of supervised learning models and neural network sequential models are compared.
The rest of the paper is composed as follows. Section 2 covers the state-of-the-art work on fake news detection. Section 3 describes the material and method. In Section 4 and Section 5, we examined and derived conclusions from the experimental outcomes of fake news. Subsequently, Section 6 and Section 7 describe the limitations and implications of the study. Section 8 presents general conclusions and points to the permissible steps of future work.
2. Related Work
Fake news has an important role in our lives. Fake news has a long history; it started around the beginning of the nineteenth century. European publishers publish fake news in newspapers, “Discovery of Life on the Moon” [9].
Several studies employed traditional machine learning techniques to detect fake news, as shown in Table 1. Farooq et al. [15] utilized TF-IDF and BoW with N-grams for feature extraction, combined with Random Forest, SVM, and stacking classifiers, achieving a 0.93 F1 score. Salahuddin and Wasim [16] used logistic regression with TF-IDF, obtaining a 0.72 F1 score. Ahmed [17] explored six classifiers, finding that TF-IDF with LSVM yielded the highest accuracy of 92%, while Decision Trees achieved 89%. MaazAmjad et al. [5] experimented with weighting schemes like TF-IDF and log entropy, finding AdaBoost and SVM effective for specific datasets, achieving scores of 0.87 F1 Fake and 0.94 F1 Real from ROC-AUC. Saikh [18] used hand-crafted linguistic features with SVM, obtaining accuracies of 74% and 76% for AMT and Celebrity datasets, respectively.
Deep learning methods have shown significant promise in addressing fake news detection challenges. Bhawal et al. [19] evaluated neural networks such as DNN, CNN, Bi-LSTM, and BERT, with BERT achieving the highest F1 score of 0.87. Maslej [20] applied Word2Vec embeddings with CNN and LSTM models, with CNN achieving a remarkable F1 score of 97.52%. Sequential models like RNNs, LSTMs, and GRUs were explored for their ability to capture sequential dependencies, as demonstrated by studies addressing long-term relationships and vanishing gradient issues [21,22].
Hybrid and multimodal techniques integrate diverse methods for enhanced performance. Kalra et al. [23] adopted a multimodal approach with transfer learning, showing superior results on textual data. Kelly Stahl et al. [24] combined Naïve Bayes and SVM for fact-checking, achieving better results than individual classifiers. Liu and Wu [25] proposed a propagation path classification (PPC) model combining RNN and CNN, with accuracies of 84.2%, 86.3%, and 92.1% for Twitter15, Twitter16, and Weibo datasets, respectively. Khilji et al. [26] used XLNet with fine-tuning but without feature weighting, achieving an F1 macro score of 0.84. Vogel et al. [27] worked on English and Spanish datasets, combining SVM and logistic regression with TF-IDF and N-gram features, achieving scores of 0.73 and 0.79, respectively.

Table 1.
Related Work for existing Urdu Fake News Classification.
Table 1.
Related Work for existing Urdu Fake News Classification.
| Ref. | Dataset | Algorithm | Description | Limitations of the Study | Authentic Source | Output |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [28] | Urdu four different Datasets | LLM, and Linear SVM | Linear SVM with TFIDF and LLM | Limited to LLM like GPT and LSVM with TFIDF and does not explore Embeddings | Yes | 87% Significant |
| [29] | Urdu Tweets | SVM, LR, DT, RF, NB, RNN, CNN | TFIDF with ML models | Limited to ML models and does not explore other models | yes | 91% Significant |
| [15] | Urdu | Stacked Logistic Regression, SVM and Random Forest | BoW with Ngram and Tf-IDF with Stacked LR, Random Forest, SVM | Limited to traditional Machine Learning techniques, did not apply deep learning and transfer learning approaches | Yes | 93% F1 with 5fold validation on Urdu data Significant |
| [16] | Urdu | Logistic Regression, SVM, and Multimodal | TF_IDF with LR, N-gram with SVM, and Transfer Learning with Multimodal | Achieved lower performance on Transfer Learning with Multimodal | Yes | 72% F1, 66%, and Accurate result on textual data Significant |
| [14] | Urdu News Articles | Multinomial Naïve Bayes, Bernoulli Naïve Bayes, support vector machines | TF-IDF, N-gram Features with Naïve Bayes and Support Vector Machine | Used only traditional Machine Learning Models and does not explore deep learning or transfer learning | Yes | 87% F1 fake and 90% F1 legit Significant |
| [5] | Urdu Machine Translated Dataset | Ada-Boost classifier | N-gram Features with Ada-Boost classifier | Limited to traditional classifier and does not explore other models | Yes | 84% F1 fake and 94% ROC-AUC Significant |
| [19] | Urdu | Logistic Regression, Random Forest, Naïve Bayes, DNN, CNN, Bi-LSTM, and Transfer Learning BERT Model | N-gram and TFIDF Features with Machine Learning Classifier | Focus mainly on BERT model and does not applied other models like GPT | Yes | 87% F1 achieved by BERT model Significant |
| [30] | Spanish Dataset | Random Forest Classifier | BOW, POS tags with Random Forest Classifier | Used only traditional Machine Learning Classifier | Yes | 76% Significant |
| [24] | English | Naïve Bayes, SVM and Semantic Analysis Classifier | Hybrid Algorithm of Naïve Bayes and SVM | Limited to only the ML model and does not apply Deep learning | No | Not Significant |
| [25] | English Weibo, twitter15 and twitter16 Dataset | Propagation path classification (PPC), CNN and RNN | PPC_RNN, PPC_CNN and PPC_CNN+RNN | Only works for short text from social media and does not generalize to long text from news articles | Yes | 92% Significant |
| [26] | Urdu Dataset | XLNet Model | XLNet Pre-trained Model with 6 Layers and 4 Attention Heads | Limited to XLNet model and does not explore other models | Yes | 83% Significant |
| [20] | English | CNN and LSTM | Word2Vec Word Embedding with CNN and LSTM | Used only Word2Vec with DL models and does not explore the BERT model | Yes | 97% Significant |
| [18] | English | SVM and BiGRU | ELMo Embedding Model with BiGRU | Performance is lower than the recent embedding modes like BERT | Yes | 76% Significant |
| [27] | Spanish and English | SVM and Logistic Regression | TF-IDF, N-gram Features with SVM and Logistic Regression | Limited to traditional Machine Learning models and does not explore neural networks or transformers | Yes | 79% Spanish 73% English Significant |
| [17] | English | SGD, DT, LR, and KNN | TF-IDF, N-gram Features with SGD, DT, LR, and KNN | Does not explore Neural Networks or transformers | Yes | 92% Significant |
By analyzing the literature, most of the studies related to fake news detection, especially in low-resource languages like Urdu, have selected traditional Machine learning algorithms, including Logistic Regression, Naïve Bayes, and SVMs (SVM). These works employed simple feature extraction techniques such as TF-IDF, N-grams, and Bag of Words (BoW), which are known to perform well in some scenarios but are not contextually sophisticated enough to grasp the rich linguistic features of Urdu. For example, the studies often experienced lower performance when using transfer learning models or deep learning models due to the limited dataset size and the lack of complex pre-processing. Despite achieving reasonable accuracy on some datasets, methods like Ada-Boost and stacking classifiers do not consider more enhanced and complex deep learning architectures like BERT, GPT-2, or other transformer models that have performed well in other languages.
This research intends to overcome the limitation of the previous study by applying a more effective and precise approach to fake news identification in the context of the Urdu language. We use not only the traditional machine learning techniques but also the deep learning methods, such as CNN and LSTM, which are better for capturing long-range dependencies in text. Additionally, we fine-tuned state-of-the-art models such as BERT and GPT-2 on the Bend the Truth and Ax-to-Grind datasets in the Urdu language, and the results demonstrated that a larger dataset like Ax-to-Grind leads to significantly better performance. These models are capable of understanding the context from both directions and capturing subtle patterns that traditional methods may overlook. Finally, by leveraging state-of-the-art feature extraction and pre-processing techniques, including word embeddings and one-hot encoding, we ensure that our models can more effectively handle the complexities of the Urdu language, thus addressing the limitations faced by previous studies.
3. Materials and Methods
The proposed framework of Urdu fake news detection is divided into five layers, as shown in Figure 1.
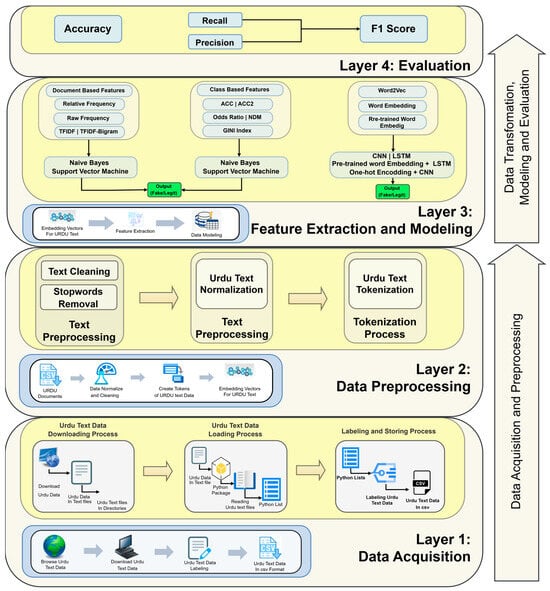
Figure 1.
Fake News Detection Architecture. Alt Text: The figure outlines a four-layer framework for fake news detection in Urdu text. Layer 1 (Data Acquisition) involves downloading, labeling, and storing Urdu text data in structured formats. Layer 2 (Data Preprocessing) focuses on cleaning, normalizing, and tokenizing text while generating embedding vectors. Layer 3 (Feature Extraction and Modeling) applies document-based, class-based, and embedding-based features using machine learning (Naïve Bayes, SVM) and deep learning models (CNN, LSTM) for classification. Finally, Layer 4 (Evaluation) assesses model performance using metrics like accuracy, precision, recall, and F1 score, ensuring reliable detection of fake news.
3.1. Layer 1: Data Acquisition
The data Bend the Truth used in this study were collected from the UrduFake2020 website, ref. [31] a major source for Urdu fake news classification. The dataset includes 900 news articles, labeled with 500 real news items and 400 fake ones. These articles cover five distinct topics: Business, Technology, Showbiz, Sports, and Health. The data, downloaded in text files, were extracted and analyzed with the help of the Python Glob package (https://docs.python.org/3/library/glob.html, accessed on 7 July 2025) as a tool to read and sort the text data in Python lists. These lists were labeled with target values corresponding to real or fake classifications.
The dataset is divided into two parts: 638 articles (350 real and 288 fake) were used for training, and 262 articles (150 real and 112 fake) were reserved for testing, as summarized in Table 2. The labeled data were saved in a CSV file for additional preprocessing and model learning.

Table 2.
Distribution of the Bend the Truth Dataset.
Each of the five categories in the dataset has a distribution of real and fake news articles. For example, Business & Sports contain fewer fake news articles than real articles, whereas Health, Showbiz, and Technologies contain an almost equal number of fake and real news articles, as illustrated in Table 3.

Table 3.
Total categories of the Bend the Truth Dataset.
Additionally, a word-level analysis was used to capture the vocabulary size of each category for both real and fake news articles. For instance, the Business category in the training set contains 4640 words for real news and 1939 for fake news, while the Technology category shows 4494 words for real and 4679 for fake news, as shown in Table 4. This comprehensive word distribution supports insights into the linguistic features present in the dataset.

Table 4.
Description of the words in the Bend the Truth dataset and vocabulary size.
Along with the analysis of the Ax-to-Grind Urdu Dataset [32], another diverse dataset was also analyzed in order to examine the vocabulary distribution by the categories of real and fake news, as discussed in Table 5.

Table 5.
Distribution of the Ax-to-Grind Urdu Dataset.
The Ax-to-Grind Urdu Dataset was specifically created with the aim of fake news detection in the Urdu language. The corpus consists of fifteen categories with 10,083 news articles, evenly divided into the TRUE 5030 and FAKE 5053 categories, which guarantee an equal classification environment. It also reveals a high variation in the linguistic feature of the two classes: TRUE articles include 173,267 words that contain 13,877 unique words, and their average sentence length is 34.45 words whereas FAKE articles are much more voluminous, 585,299 words, 27,037 unique words, and average sentence length is much longer 115.83 words as shown in Table 6. This demonstrates the stylistic and constructional differences in genuine and fake news, which could be a pivotal feature of allowing successful training of models and performance. On the whole, the collection comprises 758,566 words and 30,448 unique terms, which indicate its wealth and possibility of using it in various NLP tasks.

Table 6.
Description of the Ax-to-Grind Urdu Dataset.
3.2. Layer 2: Data Pre-Processing
The methodology consists of different steps in which our dataset was in the text (with a .txt extension) files. Before preprocessing the dataset, we converted text files into a CSV file and labeled them. The preprocessing includes text cleaning, where unnecessary elements such as punctuation, English alphabet, URLs, numbers, and currency symbols were removed. Stop words that have no significance in data (آئے, پر, یہ, تو, اور, etc.) were also removed. Tokenization played a major part in addressing this process, and the StanfordNLP library was utilized in splitting Urdu text into meaningful units. However, challenges in tokenization, shown in Table 7, such as improper splitting of words and merging of Urdu and English text, were encountered. The StanfordNLP library addressed these issues by providing better support for the complex structure of Urdu language tokenization [33].

Table 7.
Challenges in tokenization.
3.3. Layer 3: Feature Extraction and Modeling
In this layer, we have presented data transformation and training of models. The feature extraction techniques are as follows:
3.3.1. Feature Extraction
The feature extraction process involves converting raw data into numerical features that can be processed while maintaining the information contained in the original dataset. This process transforms raw data into a form that can be more easily analyzed and understood. These feature extraction techniques are document-based.
3.3.2. Term Frequency
Term Frequency (TF) is used to find how often the specific term is present in the document. It counts the number of occurrences in simple words. It also defines the significance of a particular word or expression in a document.
3.3.3. Term Frequency-Inverse Document Frequency (Tf-Idf)
Term Frequency-Inverse Document Frequency (TF-IDF) is a weighting metric that measures the value of a term used in the document. Term frequency is the frequency of terms in the document. Inverse document frequency is how important rare words are present and devalues common words in a document.
3.3.4. Relative Frequency
Relative frequency is provided maximum likelihood probability and divides the count of a word by the total number of words “N” in a dataset.
3.3.5. Raw Frequency
Raw frequency is the arithmetic count of the number of times an n-gram was encountered. Where wi = 1 if tf > 0 and wi = 0 if tf = 0, where tfi is defined as the number of times term i appears in document D.
These feature extraction techniques are class-based [7].
We discussed some basic terms used in these feature extraction techniques. These feature extraction techniques depend upon a binary class. True positive (tp) is the number of documents in the positive class that contain the term. True negative (tn) is the number of documents that are not in the positive class and do not contain the term. False positive (fp) is the number of documents in the negative class that contain the term. False negative (fn) is the number of documents that are not in the negative class and do not contain the term.
3.3.6. Accuracy (ACC)
ACC [7] used for feature ranking matrices, calculated using true and false positive. To subtract these terms mathematically:
3.3.7. Balanced Accuracy (ACC2)
ACC2 [7] uses the true positive and false positive rate of a term. ACC is simple accuracy for balanced accuracy; we take the absolute value of |tpr − fpr|.
3.3.8. Odds Ratio
Odds Ratio (OR) [7] depends on the probability of a term’s occurrence or the term’s absence in a document. This feature extraction technique only depends on the probability of the occurrence of terms.
3.3.9. Gini Index
Gini index [7] was originally used to estimate income distribution over a population. It is also used as a feature ranking metric, where it is used to estimate the distribution of an attribute over different classes.
3.3.10. Normalized Difference Measure
Normalized difference measure (NDM) is a new feature selection technique proposed in 2019 [7]. It is based on ACC2 |tpr − fpr|.
- An important term should have a high |tpr − fpr| value.
- One of the tpr or fpr values should be closer to zero.
- If two terms have equal |tpr − fpr| values, then the term
- having a lower min (tpr, fpr) value should be assigned a higher rank, where min is the function to find a minimum of the two values.
When tpr or fpr is zero, then the min will be zero.
If min (tpr, fpr) = 0, then replace with a smaller value like 0.01.
3.3.11. Word Embedding
We used word embedding for the vector representation of Urdu words. It is a way to represent words numerically, such that similar words have similar numerical representations. The method for creating word embeddings is known as Word2Vec. Usually, humans can understand the relationship between words, but it is difficult for a computer to understand them. Word embedding is used to understand the relationship between words and learns the relation between words based on the similarity of words.
3.4. Model Building
In this paper, two different methodologies have been used to evaluate Urdu news documents. We input Urdu text data and preprocess it to normalize it. After the text normalization, tokens of the text were created and applied to two methods: Machine learning and Deep learning. After computing features, we apply the machine learning algorithms Naïve Bayes and SVM. The second method is Deep Learning, in which we have used One-hot representation, Word embedding, and pre-trained word embedding as weights, then applied Deep Learning models, LSTM and CNN, as shown in Figure 2.
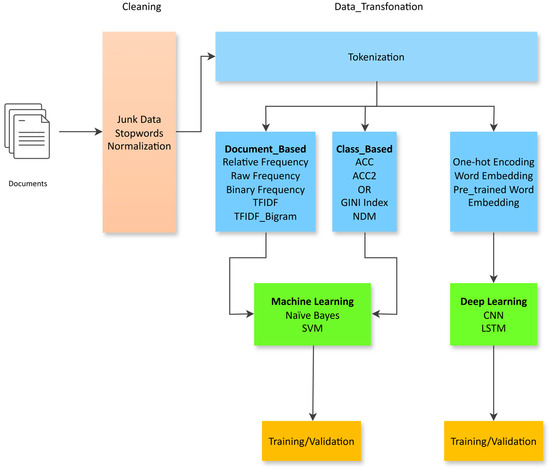
Figure 2.
Methodology of Automatic identification of Urdu fake news. Alt Text: This diagram illustrates the fake news detection workflow for Urdu text, beginning with cleaning steps such as removing junk data, stopwords, and normalizing the text. The cleaned data undergoes tokenization and is transformed into three feature types: document-based (e.g., TFIDF), class-based (e.g., ACC, GINI), and embedding-based (e.g., word embeddings). These features feed into either machine learning models (Naïve Bayes, SVM) or deep learning models (CNN, LSTM), followed by training and validation for classification performance.
3.5. Machine Learning
In this research, the objective of this research is to improve the accuracy of the Machine Learning algorithms for the detection of fake news in Urdu language documents with different feature extraction techniques i.e., TF-IDF, TFIDF-bigram, Relative frequency, Raw frequency, ACC, Balanced Accuracy, Normalized Difference Measure, Odds Ratio, and Gini Index that help in converting the textual data of the Urdu language into machine learning suitable binary numerical data. The effectiveness of these classifiers in predicting the fake news of Urdu text is discussed, along with the algorithms Naïve Bayes and Support Vector Classifier, which are evaluated in terms of their effectiveness in identifying fake news. Figure 3 illustrates the overall architecture of the machine learning.
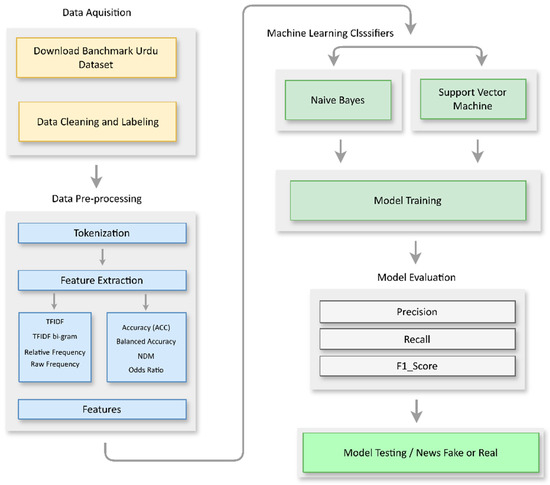
Figure 3.
Machine Learning Architecture. Alt Text: This flowchart outlines the process of detecting fake news in Urdu, starting with data acquisition from the Benchmark Urdu Dataset, followed by cleaning, labeling, and pre-processing. The text is tokenized, and features like TPDF, relative frequency, and raw frequency are extracted. Machine learning classifiers such as Naïve Bayes and SVM are trained and evaluated using metrics like accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score. Finally, the model is tested to classify news as fake or real.
3.5.1. Support Vector Machine (SVM)
A SVM is a supervised model mostly used for classification. In SVM, the predicted data is separated by a decision boundary called a hyperplane. In SVM, we compute the distance between positive and negative points. The sum of these distances is known as the margin plan. We have applied a support vector classifier with a StanfordNLP Urdu language-supported tokenizer to classify Urdu fake news. SVM kernel trick with the help of kernel function K(x, x′), where K can be linear, polynomial, RBF, or sigmoid maps the data from a lower dimension into a higher dimension [34]. This data then becomes linearly separable and thus more easily classified in this new, higher-dimensional space. The respective algorithm is given in Algorithm 1.
| Algorithm 1: Support Vector Machine |
| Given: The training dataset with features vectors , Where: • are the feature vectors of -th training sample. • are class labels. Steps Initialize Parameters: • Define a hyperplane in the transformed feature space using a Kernel function . Select a Kernel Function: • To select a kernel function and compute the similarity between samples and . Linear Kernel: Optimize the problem and Compute Decision Boundary: • To find the Lagrange multipliers for each training sample. • Calculate the weight vector and bias in the transformed feature space. Classify Test Samples: • For a given test sample X, predict its class based on sign . Output: Predict the test class for each test sample. |
3.5.2. Naïve Bayes
Naïve Bayes is a probabilistic learning technique based on the Bayesian theorem, and in Naïve Bayes, the assumption is that the features are independent of each other given the class. This assumption makes the computation of the posterior probability much simpler and makes the algorithm function even with large numbers of dimensions.
Naïve Bayes computes the posterior possibility of a class given certain input with reference to the possibilities of the features given those classes and a prior likelihood of the classes. The last step is to choose that class which has the highest probability of occurrence as given by the Bayesian theorem. Despite that, Naïve Bayes has a simple structure and a rather strong assumption of independent features; it works well on many actual cases, especially when it is used for text classification. The respective algorithm is shown in Algorithm 2.
| Algorithm 2: Naïve Bayes |
| Given: are class labels. For each class Procedure: • Calculate prior probabilities: • Compute the prior probability as the proportion of the training samples belonging to . • Estimate the likelihood for training feature given : • Calculate the likelihood which represents the probability of observing feature given class For each test sample : • Compute the posterior probability: • Compute the likelihood probability for test class using the prior probability and likelihood. • Predict the output class: Output: Predict the test class for each test sample. |
3.6. Deep Learning
In the domain of fake news identification in the Urdu language, deep learning approaches can be an effective way to identify distinct features. Specifically, this research employs two prominent deep learning architectures: LSTM and CNNs. These models, which are designed for high performance in pattern recognition and dependent variables in sequential data, provide possibilities for automatically acquiring useful features from the text. Hence, LSTMs are used to model dependencies and contextual information concerning each word in text, and CNNs’ sequential nature is believed to be suitable for Urdu text for the presentation of deep learn architect for Urdu fake news identification as depicted in Figure 4.
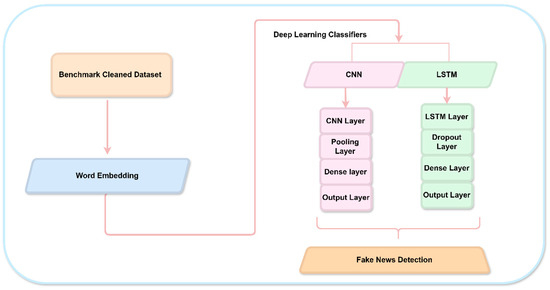
Figure 4.
Deep Learning Architecture. Alt Text: This flowchart describes a deep learning approach for Urdu fake news detection using word embeddings. The process starts with a benchmark cleaned dataset, followed by word embedding to convert text into numerical vectors. Deep learning classifiers like CNN and LSTM are used, with layers including convolution, pooling, dropout, dense, and output layers for feature extraction and classification. The final goal is fake news detection in Urdu.
3.6.1. Convolution Neural Network (CNN)
CNNs are a type of deep learning architecture that can learn from data without requiring manual feature extraction, automatically allowing the network to identify important features in the data. Our work initially performed a certain pre-processing on the Urdu text corpus for fake news detection, and the text was converted into a vector sequence. These text sequences with integer values were fed into the convolutional hidden layers. These layers consist of an ID convolutional layer with a dropout layer and then a pooling layer, connected to a fully connected Dance layer with a sigmoid layer to classify whether Urdu news is fake or legit.
In the proposed architecture, the pooling layer was used, and this pooling layer converts texts of various lengths into a fixed-length vector. The pooling layer can extract important information from the entire text. Other pooling layers, such as average pooling layers, were not utilized because only a few specific words and their combinations are essential for understanding the document’s meaning [35]. On the other hand, the max-pooling layer effectively identifies the document’s most significant latent semantic factors. The pooling layer takes the output of the recurrent structure as its input [20]. Finally, the sigmoid function is applied in this architecture, and the last part of this architecture is the output layer, similar to the traditional neural network. The respective algorithm is given in Algorithm 3.
| Algorithm 3: Convolution Neural Network |
| Given: Input data, such as sequential data. Procedure: Input Layer: • Accept the input data as a multi-dimensional array. Convolutional Layer: • Apply kernel to extract features from the input data by performing convolutional operations. • Use activation function to introduce nonlinearity Pooling and Fully Connected Layer: • Apply pooling layer to down sampling the features. • Flatten the features and pass as fully connected. Output Layer: • Use the activation function to produce class probabilities. Output: Predict the class labels. |
3.6.2. Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM)
The LSTM is a sequence classification model in which the input is contained in forward and backward directions. This model is used for long-range dependencies because it is contained in the memory cell. In this architecture, as depicted in Figure 5, the pre-processed Urdu text data for detecting fake news is fed into the embedding. An LSTM sequential neural network was applied to classify Urdu news. The embedding output was fed into LSTM hidden layers, consisting of a dropout layer with a value of 0.3. Finally, the output layer with a sigmoid activation function is used to detect Urdu fake news.
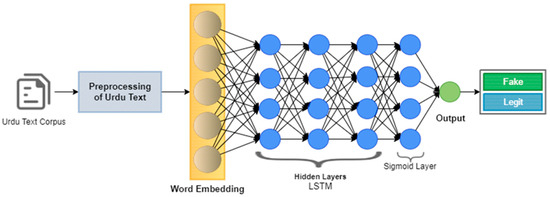
Figure 5.
Urdu Fake LSTM Architecture. Alt Text: This is the LSTM architecture proposed to detect fake and legitimate news.
LSTMs include memory cells and gates that allow the network to decide what information is important and what information is not within several time steps. The hidden state ht and cell state ct of an LSTM unit can be updated as follows:
where it, ft, and ot are the input, forget, and output gates, respectively and gt is the candidate cell state Wi, Wf, Wo, Wg are the weight matrices for the gates. bi, bf, bo, bg are the bias terms for the gates. [ht−1, xt] denotes the concatenation of the previous hidden state ht−1 and the current input xt.
3.7. Transformers
Transformers are a state-of-the-art architecture of the machine learning algorithm that was introduced in a groundbreaking paper in 2017 [36] that created a chain of events that would dramatically change the world of artificial intelligence. They transformed NLP tasks because their structure allows modelling sequences while using self-attention to capture long-range interactions. They have subsequently been the foundation of glorious pre-trained language models like BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers) and GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer) as shown in Figure 6.
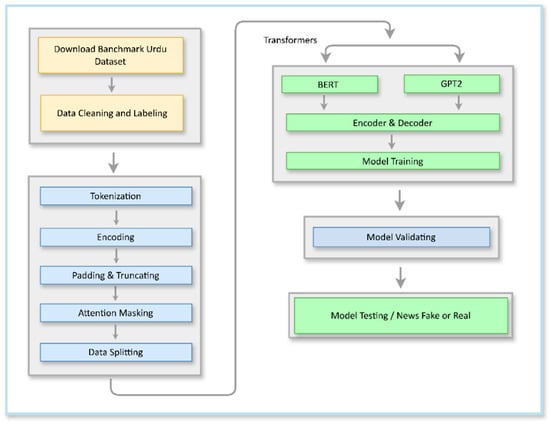
Figure 6.
Transformer Architecture. Alt Text: This is the Transformer architecture proposed to detect fake and legit news.
BERT and GPT2
BERT and GPT-2 are two leading models of NLP-BERT, which stands for Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers, and GPT-2 which stands for Generative Pre-trained Transformer 2. One such model is BERT, developed by Google [37]. It identifies the context of a word based on both its left and right context, thus making it very efficient in classification [38]. On the other hand, GPT-2 produced by OpenAI is a generative model that is proficient in generating coherent and contextually appropriate text by predicting the next word in the sequence, which, as such, is fit for tasks like text generation and translation [38]. Although both models have been fine-tuned for numerous uses, the casework involves fake news detection in Urdu. The Transformer algorithm is given in Algorithm 4, and Table 8 shows the hyperparameters for the pretrained model.
| Algorithm 4: Transformer |
| Given: Input sequence . Procedure: Input Embeddings and Positional Encoding: • Encoded the given input tokens to dense representations. • Positional encoding addition to learn sequential data. Encoder Layer: For encoder layer repeat the following steps: • Apply multi-head self-attention , where Q, K, V are query, key, and a value matrices computed from inputs embeddings. • Apply feed-forward-network , where W is weight of the network and b is bias. • Layer normalization and residual connections have to made after every block. Decoder Layer: • Similar to the encoder, but includes an additional cross-attention layer that attends to encoder outputs. Output Layer: • A softmax activation function is used in order to predict the next token or the next sequence of the output. Output: the last prediction for the sequence. |

Table 8.
Hyperparameters for Pre-trained Models: BERT and GPT2 Models.
3.8. Layer 4: Evaluation Metrics
We used these metrics for Urdu fake news evaluation, and the accuracy metric gives better results when both positive and negative classes have equal distribution. In our classification problem, the imbalanced class distribution exists. In this imbalanced distribution, the F1 score gives better results. That is the reason we used the F1 score metric for trained Urdu fake news model evaluation. It is important to check how well a machine learning model or algorithm works in a project. We used special ways to measure the model’s performance called evaluation metrics. It helped us understand how good the model is and what we can do to improve it. There are many different evaluation metrics available to test a model, as follows:
TP is the True Positive in which the model correctly predicts the class is positive, whereas TN is the True Negative in which the model correctly predicts the negative class. FP is the False Positive, in which the model incorrectly predicts the class is positive, while FN is the False Negative, in which the model incorrectly predicts the negative class.
In this section, where applicable, authors are required to disclose details of how generative artificial intelligence (GenAI) has been used in this paper (e.g., to generate text, data, or graphics, or to assist in study design, data collection, analysis, or interpretation). The use of GenAI for superficial text editing (e.g., grammar, spelling, punctuation, and formatting) does not need to be declared.
4. Experiments
In this research, two datasets were used: Bend the Truth and Ax-to-Grind. The Bend the Truth dataset consists of a total of 900 news articles, which were split into 638 articles for training and 262 articles for testing. In this experiment, we aimed to identify fake news in Urdu using both machine learning and deep learning models on this dataset. In our research work, we employed traditional machine learning models such as Naïve Bayes (Gaussian and Bernoulli variants) and SVM, and deep learning models comprising CNN and LSTM. Additionally, we fine-tuned transformer-based models, BERT and GPT-2, to enhance the results. The dataset became subject to preprocessing steps, including text cleaning, normalization, and tokenization using the StanfordNLP library, in order to deal with issues unique to Urdu tokenization. The methods applied for feature extraction included TF-IDF, raw frequency, relative frequency, ACC, ACC2, Gini index, OR, and NDM for machine learning models, and word embeddings (e.g., Word2Vec) for deep learning. Due to the imbalanced dataset, we used the F1 score as our principal metric when assessing each model, while accuracy, precision, and recall were also part of the evaluation. Our aim through this extensive method was to evaluate how effective various models and feature extraction techniques are in categorizing Urdu fake news.
In addition to the Bend the Truth dataset, the Ax-to-Grind Urdu Dataset, which comprises a total of 10,083 news articles, with 5030 true and 5053 fake labeled samples, was assessed in terms of its potential to be utilized to identify fake news, and the following experiments with transformer-based models and deep learning were conducted. Given the balanced nature of the dataset, it served as a strong foundation for evaluating the model’s performance without bias toward any specific class.
5. Results
This section presents the results of traditional Machine Learning, Deep Learning, and Transformers.
5.1. Traditional Machine Learning
The traditional machine learning models, such as Naïve Bayes and SVM, illustrated the best performance consistency. On the Bend the Truth dataset, Naïve Bayes, using Relative Frequency for feature transformation, achieved the highest F1 score of 78%, while SVM, with TF-IDF and Gini index features, reached an F1 score of 73% mentioned in Table 9. The models have performed well largely because of their simplicity and effectiveness working with smaller datasets. It is suitable for text classification because, like most probabilistic models, Naïve Bayes uses word frequencies and makes the conditional independence assumption. This enables it to work well with small amounts of data and pick out important patterns without needing a rich contextual understanding. On the other hand, SVM was outstanding for searching for the best decision functions as well as TF-IDF, which minimizes the effect of high-frequency but low-discriminating words. However, these models are naturally inadequate in their ability to represent rich, contextual relations between words and phrases. Despite this, their use of feature-based transformations such as TF-IDF and simple term frequencies makes them ideal for smaller and structured datasets.

Table 9.
Results of Traditional Machine Learning with Bend the Truth and Ax-to-Grind Datasets.
Furthermore, when evaluated on the Ax-to-Grind Urdu Dataset, the SVM model with TF-IDF bigram features achieved better performance, attained an accuracy of 0.89, a precision of 0.90, a recall of 0.87, and an F1 score of 0.89. This demonstrates that SVM, when combined with more n-gram features, can effectively capture important patterns even in larger and balanced datasets. However, despite their strengths, traditional machine learning models are naturally limited in representing rich contextual relationships between words and phrases. The feature-based transformations of similarity and word frequencies, like TF-IDF and term frequencies, performed well when working with structured and moderately large datasets used in this research.
5.2. Deep Learning Neural Network
The deep learning models, CNN and LSTM, underperformed on the Bend the Truth dataset compared to traditional machine learning models because of a small dataset. The CNN model incorporated with pre-trained Word2Vec has an F1-score of 72%; on the other hand, the LSTM with the same Word2Vec has 62% of the F1-score. CNNs are efficient at extracting local features because they use convolutional layers to find specific word features or the words that comprise fake news. Nevertheless, their use of a larger dataset to train deeper layers effectively meant poor performance when simpler word embeddings were used, and this resulted in a lower F1 score of 68% mentioned in Table 10. LSTM, which is known to be good at capturing long-distance dependencies in sequences, was severely affected by the limited amount of data. An LSTM requires a large amount of data to extract important patterns over time; inadequate training examples created underfitting, resulting in an F1 score of 57% using basic word embeddings. Deep learning models, by default, require substantial datasets in order to optimize their parameters and to learn complex representations.

Table 10.
Results of Deep Learning Neural Network with the Bend the Truth Dataset.
On the other hand, Table 11 presents the results of deep learning models, including CNN and LSTM, trained on the Ax-to-Grind Urdu Dataset with word embeddings. The CNN model recorded a 0.86 accuracy and a 0.87 precision and recall, giving a 0.86 F1 score. These findings show that CNN moderately succeeded in the extraction of local features and patterns on the Urdu text. In comparison, the LSTM model performed better than the CNN in all three metrics, with an accuracy of 0.91, a precision of 0.91, a recall of 0.88, and an F1 score of 0.89. The good performance of LSTM is attributed to the fact that it models the dependencies and contextual relationships in textual data, which is very significant in such morphologically rich languages as Urdu. The results imply that the use of a sequence-based architecture, like LSTM, is more appropriate in tasks of fake news detection in Urdu as compared to convolutional models.

Table 11.
Results of Deep Learning Neural Network with Ax-to-Grind Urdu Dataset.
5.3. Transformers (BERT and GPT-2)
In this study, we used two datasets, Bend the Truth and Ax-to-Grind, to evaluate the performance of Transformers models BERT and GPT-2. The following results refer to the models that were fine-tuned on the Bend the Truth dataset. Transformer models, especially BERT, performed better than both traditional machine learning models and deep learning models. The fine-tuned Urdu BERT model obtained an F1 score that was 79%, better than the 66% achieved by GPT-2 mentioned in Table 12. The capability of the BERT model to understand the context bi-directionally leads to its success, permitting it to extract important information and linguistic styles in the text, even with a small dataset. BERT’s architecture, based on self-attention mechanisms, allows it to focus on important words and their context within a sentence, making it highly effective for text classification tasks. The capability to capture relationships between words from both directions creates an important advantage for BERT compared to traditional and deep learning approaches, which tend to rely on simpler word features or sequential information.

Table 12.
Results of BERT and GPT2 Model with Bent the Truth Dataset.
On the other hand, the powerful generative model GPT-2 performs effectively less because this model is more text generation-oriented than classification Its architecture, being unidirectional, gives more concern to the prediction of the next word in the sequence compared with the prior words and limits it from comprehensively understanding relationships within the whole text in the classification task. For example, fine-tuning BERT on the task of text classification would train it much more accurately to fit the nuanced specifics of Urdu fake news detection, compared to GPT-2, where more data may be required for the optimization of its text classification task.
To further demonstrate the model’s performance on the Ax-to-Grind dataset. Table 13 shows the performance results of GPT-2 and BERT transformer-based models trained on the Ax-to-Grind Urdu Dataset on the fake news detection task. GPT-2 model displayed excellent performance, and its accuracy, precision, and recall were 0.93 and an F1 score of 0.93. These findings indicate the good performance of GPT-2 to acquire sophisticated context and semantic patterns in the Urdu language. Another model that achieved very good results is the multilingual BERT model with an accuracy of 0.95, a precision and recall of 0.94, and an F1 score of 0.93. The results indicate BERT achieved fairly high classification performance.

Table 13.
Results of BERT and GPT2 Model with Ax-to-Grind Urdu Dataset.
5.4. Comparative Analysis of Datasets and Model Performance
The performance of the models was found to vary considerably in a comparison of the results on the Bend the Truth dataset and the Ax-to-Grind Urdu Dataset. The Bend the Truth data consists of a mere 900 news articles, and the dataset is highly imbalanced in terms of different types of news. This will adversely affect the learning process of both traditional and deep learning models. The small amount of data limits the models in terms of generalization, and the imbalance makes the classifier biased towards the majority class and thus shows low recall and F1 scores, particularly for the minority class. The Ax-to-Grind dataset, in contrast, has 10,083 well-balanced articles that allow a much higher representation of the overall distribution of fake and real news in many categories. This balance and scale allow models to learn more annotated patterns and semantic differences in text, and have better performance and more accurate measures. In such a way, the higher performance on the Ax-to-Grind dataset could be explained, not only by the increase in size, but also by the balanced nature, which allows a model to train and be measured more effectively.
Table 14 provides a comparative analysis of our experimentation with our approach in terms of the Bend the Truth and Ax-to-Grind Urdu datasets against those cited in the literature. The fine-tuned BERT model on the Bend the Truth dataset obtained a significantly low F1 score and accuracy of 0.79 compared to the results provided by previous studies, F1-score 0.87, and Accuracy 0.90. Such a performance gap can be explained by the fact that the 900 articles and the imbalance of the dataset limit the learning process of deep and transformer-based models.

Table 14.
Comparison with the Existing Research with Urdu Benchmark Datasets.
On the other hand, the fine-tuning on a considerably larger and balanced dataset of Ax-to-Grind Urdu 10,083 articles on 15 domains resulted in a notable performance gain. Compared to the existing study, our fine-tuned BERT model outperformed with an F1 score of 0.936 and an accuracy of 0.957, which was better than the F1 and accuracy of 0.924 and 0.956 in the existing work. The significance of the current findings is evident in the importance of the scale, balance, and diversity of the dataset in the enhancement of the reliability and performance of fake news detection in the Urdu language.
6. Limitations of the Study
The limitation of this study lies in the size and diversity of the datasets used. While the inclusion of both the smaller Bend the Truth dataset and the larger, balanced Ax-to-Grind Urdu Dataset allowed for comparative evaluation, the performance of deep learning models, particularly LSTM and CNN, remained constrained due to data dependency and the complexity of sequential learning. Despite applying a range of NLP feature transformation techniques such as TF-IDF, Gini index, Odds Ratio, and word embeddings, deep learning models did not significantly outperform traditional machine learning or transformer-based models. This outcome highlights the data-hungry nature of deep learning and suggests that even richer feature representations or larger datasets may be required to fully exploit their potential.
The study is also limited to the following aspect, as it examines the detection of fake news using text only. Since fake news is usually disseminated with the use of a variety of different modalities (e.g., with the use of texts and pictures), such findings are one-dimensional in defining the issue. Also, the dataset being used was already annotated by other scholars, so the consistency of the labels was guaranteed, but it did not leave a chance to explore any other, more specific classification types.
Moreover, obtaining good and large-scale Urdu fake news data is still a wider challenge since there are limited labeled datasets and noise that could be brought in through web scraping. In further studies, the experiences of creating high-quality Urdu data sources, working with multi-modal information, applying the principles of transfer learning, and training in a specific domain should also be considered.
7. Implications of the Study
The study has dual implications: First, it highlights the importance of addressing the negative impact of false news on social and political spheres, especially in languages with limited detection systems. The research also contributes a useful framework for the Urdu language, demonstrating the viability of integrating machine learning and deep learning techniques to combat the spreading of false news. It can also help newsrooms flag irrelevant, misleading articles, help government agencies identify politically motivated disinformation, and enable tools to advance digital literacy through identifying false claims. The obtained F1 scores are indicative of the potential for practical implementation and further development of mechanisms for detecting false news in the Urdu language. The study may be helpful for journalists, knowledge workers, and information seekers who can evaluate the authenticity of the news to keep themselves updated about the current affairs of the world.
8. Conclusions and Future Work
In this study, we explored the use of machine learning, deep learning, and transformer-based models to detect fake news in the Urdu language using two different datasets: The Bend the Truth dataset and the Ax-to-Grind Urdu Dataset. Using both datasets, transformer-based models, particularly BERT and GPT-2, outperformed other approaches. The best performance was achieved on the Ax-to-Grind Dataset, where GPT-2 and BERT achieved an F1 score of 0.93. These high scores are attributed to the models’ ability to capture contextual meaning through self-attention mechanisms and their adaptability when fine-tuned on a large and balanced dataset.
On the other hand, the Bend the Truth dataset, Urdu BERT delivered the highest F1 score of 79%, demonstrating its robustness even on smaller datasets due to its bidirectional nature and strong contextual understanding. Traditional machine learning models like Naïve Bayes and SVM achieved F1-score 78% and F1-score 73% respectively, and also performed relatively well on the smaller dataset. However, these models lacked the capacity to understand deeper contextual relationships, which limited their performance against transformer-based models.
Deep learning models such as CNN and LSTM variants worked particularly well on the larger dataset, but on the smaller dataset, they performed moderately to poorly owing to their data-greedy efficiency. For example, LSTM achieved only 57% F1 with basic word embeddings, while CNN reached 72% F1 with pre-trained Word2Vec embeddings. Their performance improved on the Ax-to-Grind dataset; however, those results were still lower than those of BERT and GPT-2.
Moreover, the Ax-to-Grind Urdu Dataset proved to be highly effective for fake news detection in the Urdu language. Its balanced structure, larger size, and domain diversity enabled transformer and deep learning models to learn meaningful linguistic patterns. These findings affirm the importance of using well-structured and balanced datasets for advancing fake news detection in low-resource languages like Urdu and clearly demonstrate the superiority of transformer-based architectures in accurately identifying fake and real news content.
In the future, we aim to improve deep learning models’ performance by scaling the dataset with data augmentation or web scraping from trustworthy Urdu news sources. It will resolve the lack of data limitation, which hindered the applicability of models such as LSTM and CNN in this study. Furthermore, fine-tuning advanced transformer models, such as XLNet, would further enhance fake news detection as well as multimodal ideas combining both text and image data. In addition, we aim to test ensemble models, using traditional machine learning methods and transformers to exploit the strengths of the two approaches. One direction is to train language models in a multilingual fashion to create a framework that transfers findings from high-resource languages to Urdu. We then finally want to build a system to detect and flag fake news as it travels in real time, to curtail the spread of misinformation before it circulates as widely as it does today.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.M.A.G. and M.F.M.; Methodology, S.M.A.G. and M.F.M.; Supervision, M.S.F. and M.S.; Writing—Original Draft, S.M.A.G., M.S.F. and M.S.; Formal Analysis, M.F.M. and S.M.A.G. contributed equally as the first author. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Ethics Committee of the University of Management and Technology, Lahore (approval code: UMT/IEC/2024/042, date of approval: 8 November 2024).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on the website UrduFake2020 as discussed in Section 3.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| NLP | Natural Language Processing |
| BERT | Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers |
| GPT | Generative Pre-trained Transformer |
| CNN | Convolution Neural Network |
| LSTM | Long Short-Term Memory |
| GRU | Gated Recurrent Unit |
| RNN | Recurrent Neural Networks |
| MR | Machine Translation |
| TF-IDF | Term Frequency-Inverse Document Frequency |
| SGD | Stochastic Gradient Descent |
| DT | Decision Tree |
| LSVM | Linear Support Vector Machine |
| LR | Logistic Regression |
| SVM | Support Vector Machine |
| KNN | K-Nearest Neighbor |
| CSV | Comma-Separated Values |
References
- Hunt, E. What Is Fake News. Available online: https://www.theguardian.com/media/2016/dec/18/what-is-fake-news-pizzagate (accessed on 17 December 2016).
- Schlesinger, R. Fake News in Reality. Available online: https://www.usnews.com/opinion/thomas-jefferson-street/articles/2017-04-14/what-is-fake-news-maybe-not-what-you-think (accessed on 14 April 2017).
- Soll, J. The Long and Brutal Story of Fake News. 2016. Available online: https://www.politico.com/magazine/story/2016/12/fake-news-history-long-violent-214535/ (accessed on 20 April 2025).
- Webster, M. The Real Story of Fake News. Available online: https://www.merriam-webster.com/words-at-play/the-real-story-of-fake-news (accessed on 23 March 2017).
- Amjad, M.; Instituto, A.Z.; Adorno, H.G. ‘Bend the truth’: Benchmark dataset for fake news detection in Urdu language and its evaluation. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2020, 39, 2457–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daud, A.; Khan, W.; Che, D. Urdu language processing: A survey. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2017, 47, 279–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, K.; Babri, H.A. Feature selection based on a normalized difference measure for text classification. Inf. Process. Manag. 2017, 53, 473–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhou, W.; Jiang, C. A survey of word embeddings based on deep learning. Computing 2019, 102, 717–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondielli, A.; Marcelloni, F. A survey on fake news and rumour detection techniques. Inf. Sci. 2019, 497, 38–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omran, H.; Elafandy, R.T.; Arsalan, M.; Salama, K.N. Direct Mismatch Characterization of Femtofarad Capacitors. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2016, 63, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinoara, R.A.; Camacho-Collados, J.; Rossi, R.G.; Navigli, R.; Rezende, S.O. Knowledge-enhanced document embeddings for text classification. Knowl. Based Syst. 2019, 163, 955–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Díaz, J.A.; Cánovas-García, M.; Colomo-Palacios, R.; Valencia-García, R. Detecting misogyny in Spanish tweets. An Approach Based on Linguistics Features and Word Embeddings. 2020. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0167739X20301928 (accessed on 10 July 2024).
- Tanishka, G. The Power of BERT: Revolutionizing NLP. Nash Tech. Available online: https://blog.nashtechglobal.com/the-power-of-bert-revolutionizing-nlp/ (accessed on 10 July 2024).
- Amjad, M.; Sidorov, G.; Zhila, A. Data augmentation using machine translation for fake news detection in the Urdu language. In Proceedings of the LREC 2020—12th International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation, Marseille, France, 13–15 May 2020; pp. 2537–2542. [Google Scholar]
- Farooq, M.S.; Naseem, A.; Rustam, F.; Ashraf, I. Fake news detection in Urdu language using machine learning. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2023, 9, e1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salahuddin, R.; Wasim, M. Automatic identification of Urdu fake news using Logistic Regression Model. In Proceedings of the 2022 16th International Conference on Open Source Systems and Technologies (ICOSST), Lahore, Pakistan, 14–15 December 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, H.; Traore, I.; Saad, S. Intelligent, Secure, and Dependable Systems in Distributed and Cloud Environments. In Proceedings of the First International Conference on Intelligent, Secure, and Dependable Systems in Distributed and Cloud Environments, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 26–28 October 2017; Volume 10618, pp. 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saikh, T.; De, A.; Ekbal, A.; Bhattacharyya, P. A Deep Learning Approach for Automatic Detection of Fake News. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2005.04938. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/2005.04938 (accessed on 11 May 2020).
- Bhawal, S.; Roy, P.K. Fake News Detection in Urdu Language Using BERT. 2021. Available online: http://ceur-ws.org (accessed on 20 April 2025).
- Krešňáková, V.M.; Sarnovský, M.; Butka, P. Deep learning methods for Fake News detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE 19th International Symposium on Computational Intelligence and Informatics and 7th IEEE International Conference on Recent Achievements in Mechatronics, Automation, Computer Sciences and Robotics (CINTI-MACRo), Szeged, Hungary, 14–16 November 2019; pp. 143–148. [Google Scholar]
- Imran, I. CNN-RNN Deep Learning Networks for Pattern Recognition Problems. 2023. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/10111363 (accessed on 20 April 2025).
- Tyagi, A.A.A.K. Recurrent Neural Networks: Concepts and Applications. 2022. Available online: https://books.google.com.pk/books?hl=en&lr=&id=5phxEAAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PR2&dq=Tyagi,+A.+K.,+%26+Abraham,+A.+(Eds.).+(2022).+Recurrent+Neural+Networks:+Concepts+and+Applications.&ots=xPqhl8xZXG&sig=VQUixsNOjMN0kQo-Z8KHBK-yJy8&redir_esc=y#v=onepage&q=Tyagi%252 (accessed on 20 April 2025).
- Kalra, G.C.S.; Kumar, C.H.; Sharma, Y. Multimodal Fake News Detection on Fakeddit Dataset Using Transformer-Based Architectures. In Machine Learning, Image Processing, Network Security and Data Sciences; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahl, K. Fake News Detector in Online Social Media. Int. J. Eng. Adv. Technol. 2019, 9, 58–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, Y.B. Early Detection of Fake News on Social Media Through Propagation Path Classification with Recurrent and Convolutional Networks. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, LA, USA, 2–7 February 2018; pp. 354–361. [Google Scholar]
- Khilji, A.F.U.R.; Laskar, S.R.; Pakray, P.; Bandyopadhyay, S. Urdu fake news detection using generalized autoregressors. CEUR Workshop Proc. 2020, 2826, 452–457. [Google Scholar]
- Vogel, I.; Meghana, M. Fake News Spreader Detection on Twitter Using Character N-Grams Notebook for PAN at CLEF 2020. CEUR Workshop Proc. 2020, 2696, 22–25. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, M.Z.; Wang, Y.; Pfahringer, B.; Smith, T. Detection of Human and Machine-Authored Fake News in Urdu. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.19517. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/2410.19517 (accessed on 25 October 2024).
- Iqbal, Z.; Khan, F.M.; Khan, I.U.; Khan, I.U. Fake News Identification in Urdu Tweets Using Machine Learning Models. Asian Bull. Big Data Manag. 2024, 4, 52–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pablo, J.; Gomez-Adorno; Sidorov, G.; Escobar, J.J.M. Detection of fake news in a new corpus for the Spanish language. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2019, 36, 4868–4876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amjad, M. Fake News Detection in Udru Language. Available online: https://www.urdufake2020.cicling.org/ (accessed on 20 December 2020).
- Harris, S.; Liu, J.; Hadi, H.J.; Cao, Y. Ax-to-Grind Urdu: Benchmark Dataset for Urdu Fake News Detection. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/2403.14037 (accessed on 20 March 2024).
- Stanfordnlp Stanfordnlp. Available online: https://stanfordnlp.github.io/stanfordnlp/models.html (accessed on 5 October 2018).
- Sanchhaya Education Private Limited. Support Vector Machine (SVM) Algorithm; GeeksforGeeks: Noida, India, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Collobert, R.; Weston, J.; Bottou, L.; Karlen, M.; Kavukcuoglu, K.; Kuksa, P. Natural Language Processing (Almost) from Scratch. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2493–2537. [Google Scholar]
- Emanuilov, S. The Transformer Revolution; UnfoldAI Building ML System: Roma, Italy, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Sanchhaya Education Private Limited. BERT Model—NLP; GeeksforGeeks: Noida, India, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Harrag, F.; Debbah, M.; Darwish, K.; Abdelali, A. BERT Transformer Model for Detecting Arabic GPT2 Auto-Generated Tweets. Available online: https://www.wired.com/story/ai-generated-text-is-the-scariest-deepfake-of-all/ (accessed on 20 April 2025).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).