Abstract
Golden pompano (Trachinotus ovatus) has become an economically important fish in China in the past decade. However, Cryptocaryon irritans, a parasitic ciliate, causes considerable economic losses in the mariculture of T. ovatus. To characterize the pathogenesis of C. irritans in T. ovatus, the pathological properties, immune-related enzyme activity and expression of the NEMO gene was analysed. The results from the histological sections showed that there was considerable metamorphosis and hyperplasia in the parasitized sites (skin) with leukocyte aggregation and mucous cell increases after C. irritans infection. Moreover, the activities of four enzymes, that is, alkaline phosphatase (AKP), acid phosphatase (ACP), superoxide dismutase (SOD) and lysozyme (LZM), were significantly increased in different tissues after C. irritans infection. Furthermore, the ORF of T. ovatus NF-kappa-B essential modulator (ToNEMO) measures 1650 bp, encoding 548 amino acids. The ToNEMO transcripts were universally expressed in all examined tissues, with higher levels being observed in the immune-relevant and central nervous tissues. The mRNA levels of ToNEMO after C. irritans infection were significantly increased in the gill, skin, liver, spleen and head kidney. These results suggested that ToNEMO might be involved in immune responses and helped to elucidate the physiological response after the C. irritans infection of fish.
1. Introduction
Cryptocaryon irritans is an obligate ciliated parasite of fish. There are four stages in its life cycle: trophozoite, cyst precursor, cyst and larva [1]. C. irritans can cause severely fatal “white spot disease” in tropical or subtropical marine fish [1,2]. In recent years, as the density of marine aquaculture has increased, “white spot disease” has frequently broken out in the marine aquaculture areas of the South China Sea, which seriously threatens marine aquaculture fishes, especially Trachinotus ovatus [3]. However, there are still few studies on the histology of T. ovatus infection with C. irritans and its immune mechanism.
Moreover, C. irritants mainly invades the superficial epithelium of host fish, including the skin, gills and eyes, and it damages the physiological functions of these organs with pathological features of white spots on the fins, skin or gills. Fish may rub against the wall of the pool, swim irregularly, float on the surface or sink to the bottom or show lethargy or shortness of breath as signs of distress. Symptoms include pinhead-sized white nodules on the gills and body, mucus hyperproduction, skin discoloration, corneal cloudiness, ragged fins and pale gills. C. irritans infection results in the serious mortality of fish due to asphyxiation, osmotic imbalance and/or secondary bacterial infections. In fish stocks, mortality may increase rapidly within a few days, depending on the parasite strains, fish species and the water temperature [1].
In previous histological studies of T. ovatus challenged by C. irritant, their surface was directly mechanically injured, and the better-defined systemic immune tissue was indirectly damaged, with degeneration and necrosis [4]. The migration and aggregation of leukocytes, including lymphocytes, eosinophils, macrophages and neutrophils, was observed in gills, and IL-8 was significantly upregulated in skin [3].
Tumour-necrosis-factor-receptor-associated factor (TRAF) is a kind of intracellular junction protein previously discovered using yeast two-hybrid technology and glutathione transferase fusion technology [5]. TRAF participates in signal transduction pathways of Toll-like receptors (TLRs) and other families and regulates nuclear factor κB (NF-κB), which are important signal transduction proteins in cells [5,6]. NEMO is one of the most important components of the IKK (IκB kinase) complex, a key protein in the NF-κB pathway [7,8]. TRAF ubiquitination activation was shown to lead to the activation of the IκB kinase complex and the phosphorylation of NEMO (NF-kappa-B Essential Modulator) [5], which caused the released NF-κB to be transferred to the nucleus and initiate transcription of the TNF, Pro-IL-1b, IkBz, ATF3, Zc3 h12a and TTP genes [6]. The NF-κB pathway is essential for the immune response and inflammatory response to pathogens [9]. NEMO plays an essential role in the activation of the IKK kinase in the NF-κB signalling pathway [10]. NEMO is highly conserved. Structure prediction shows that it has an α-helix with three coiled coil regions, a leucine zipper domain and a C-terminal zinc finger structure [11].
The specific immunity of fish is lower than that of mammals, while the non-specific immunity of fish plays a major role in the body’s immunity [12]. The antioxidant system of fish is the first line of defence in the innate immunity of fish. In addition to the intracellular activation of innate immune signalling pathways and the release of extracellular inflammatory factors, immune-related enzymes in the body are also important immune indicators when the body undergoes pathogen invasion. ACP plays a role in killing and digesting pathogens in immune responses. AKP is also a multi-functional enzyme involved in immune responses [13]. Superoxide dismutase (SOD) is the main antioxidant enzyme in the antioxidant system to remove excess active free radical ROS [14]. As a humoral immune factor, Lysozyme (LZM) activity can reflect the non-specific immune ability of fish to a certain extent [3,15].
Golden pompano is one of the most important farmed fish in the South China Sea [16]. Similar to other species, golden pompons are also affected by C. irritans. Although environmental studies have been reported [17,18,19,20], the infective characteristics and mechanisms of C. irritans in T. ovatus have not been adequately studied. In this study, the histopathology and gene expression of NEMO and immune-related enzyme activity were detected after C. irritans infection. The influence of the infection on the immune response of T. ovatus provides basic theoretical data and guidance for later studies of disease resistance breeding and blocking the effects of C. irritans on T. ovatus.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
All trials in this study were authorized by the Animal Care and Use Committee of South China Sea Fisheries Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Fishery Sciences (No. SCSFRI96-253) and were performed according to the regulations and guidelines formulated by this committee.
2.2. C. irritans Challenge and Sampling
Healthy T. ovatus (body weight = 98 ± 15 g) were purchased from Linshui Marine Fish Farm in Hainan Province, China. Before the experiment, the fish were put into a circulating marine pool at 28 ± 2 °C with 25‰ salinity and acclimated for two weeks with commercial feed (Hengxin, Zhanjiang, China, crude protein > 37%, crude fat > 7%). The C. irritans strain used in this study was originally isolated from infected T. ovatus and artificially propagated in the laboratory according to the methods described in previous research [21].
Fifty healthy fish were randomly selected as the control group. Then, one hundred and twenty healthy fish were challenged with C. irritans at a dose of 600 theronts/fish. After infection for 0 h, 3 h, 6 h, 12 h, 1 d, 2 d and 3 d, five tissue samples (skin, gill, liver, spleen and head kidney) were collected from six challenged fish to examine enzyme activities and gene expression. Blood, brain, muscle, heart, gonad, spleen, kidney, liver, skin, gill, and intestine was detected via qRT-PCR. Before dissection, the fish were anaesthetized using MS222 (0.1 g/L; Sigma, Alcobendas, Spain). In addition, the second branchial arch and skins were taken and stored in 4% paraformaldehyde for tissue section samples. The same tissues from uninfected fish were regarded as a negative control at each time point. All samples were immediately frozen in liquid nitrogen and then stored at −80 °C until use.
2.3. HE Staining of Tissue Sections
The tissue samples of the gills and skin stored in 4% paraformaldehyde were sent to Servicebio Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Wuhan, China) for paraffin embedding, tissue sectioning and HE staining. The HE-stained sections were observed under a microscope (ZEISS Axio Scope A1, Jena, Germany) and photographed.
2.4. Determination of Immunity-Related Enzyme Activities
The acid phosphatase (ACP), alkaline phosphatase (AKP), superoxide dismutase (SOD) and lysozyme (LZM) activities and total protein content (TP) were measured in five tissues from infected fish (skin, gill, liver, spleen and head kidney). ACP, AKP, SOD and LZM enzyme activity and total protein content were measured with assay kits according to the protocol supplied by the manufacturer of the kits. Colorimetry was used to determine ACP and AKP activity, and enzyme activity that produced 1 mg of phenol by 1 g of tissue protein at 37 °C in 15 min was defined as 1 U (U/g prot). To measure the SOD activity, 50 mL of supernatant was mixed with 1.3 mL of reaction solution containing. 75 mM nitroblue tetrazolium (NTB) and 20 mM riboflavin. The mixture was incubated at 37 for 40 min, and then, the appearance of NTB-diformazan was measured with a Mindray BS-420 automatic biochemical instrument (Shenzhen Mindray Biological Medical Electronics Co., Ltd., Shenzhen, China). The method of determining LZM activity has been described in a previous study [22].
2.5. Cloning of the NEMO Gene
The tissues were homogenized with a tissue homogenizer (JXFSTPRP-24, Shanghai Jingxin Industrial Development Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China) after adding magnetic beads. Total RNA (1 μg) was isolated from each tissue using the HiPure Universal RNA Kit (Magen, Guangzhou, China) and reverse transcribed into cDNA using the PrimeScriptTM RT Reagent Kit with gDNA Eraser (Perfect Real Time) (Takara, Japan). Moreover, the quantity and quality of the extracted RNA were detected using a NanoDrop 2000 spectrometer (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) and 1% agarose gels. The synthetic cDNA samples were stored at −20 °C until use. The NEMO predicted sequences were obtained from T. ovatus genomic data [23]. To determine the accuracy of the encoding sequence of NEMO, gene-specific primers were designed (Table 1) based on the proposed sequence.

Table 1.
Information regarding the NEMO primers used in this study.
2.6. Bioinformatic Analysis of the NEMO Gene
To learn about the bioinformatic features of the NEMO gene, the Compute pl/Mw online tool on ExPASy (https://web.expasy.org/compute_pi/ (accessed on 11 December 2019)) was used to predict the molecular weight and isoelectric point of the protein encoded by NEMO. Showorf, an online tool from EMBOSS (http://www.bioinformatics.nl/emboss-explorer/ (accessed on 11 December 2019)), showed the open reading frame and predicted amino acid sequence. Other species’ NEMO genes were searched for and downloaded using the NCBI database (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ (accessed on 11 December 2019)). The structure and domains of the NEMO gene of T. ovatus were predicted using the SMART online tool (http://smart.embl-heidelberg.de/ (accessed on 11 December 2019)). The amino acid sequences of the conserved domains of the NEMO gene of T. ovatus were analysed using the Clustal Omega online tool in EMBL (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/msa/clustalo/ (accessed on 11 December 2019)). The phylogenetic trees of NEMO were constructed using MEGA 7.0 software with the neighbour-joining (NJ) method.
2.7. Quantitative Real-Time PCR and Statistical Analysis
To determine the relative mRNA expression level of T. ovatus NEMO in normal tissues under normal conditions and after infection with C. irritans, qRT-PCR was used to analyse the expression pattern of NEMO in five infected tissues (skin, gill, liver, spleen and head kidney) from T. ovatus. Based on the NEMO cDNA sequences, specific primers for NEMO were designed with Primer 5.0 software, and the housekeeping gene EF-1α (elongation factor 1, alpha) was used as a reference in a previously reported study [24]. The qRT-PCR procedure was executed as previously described. To evaluate the relative expression of these genes, the 2–ΔΔCT method was used [25].
2.8. Statistical Analysis
The data are shown as the means ± SE (n = 3). The one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test was used in the present study at a significance level of p < 0.05. Statistical analyses were implemented using SPSS 20.0 (SPSS, Chicago, IL, USA).
3. Result
3.1. Histological Analysis
HE staining of the gill is shown in Figure 1. In the control group, the gill filaments and gill lamellae of healthy T. ovatus were completed and arranged in a comb shape, and the mitochondrial-rich cells, blood cells and epithelial cells were clearly identified. After challenge with C. irritans for 3–6 h, round or elliptical trophonts floated in the water and then attached to the gill lamellae of T. ovatus, with a size of 20.36 ± 5.00 μm. Vesiculate- and horseshoe-shaped nuclei could be observed. After challenge for 12 h–1 d, the C. irritans trophont developed into an elliptical solid protomont with a size of 84.24 ± 4.00 μm; the gill lamellae were swollen, curved and hyperplastic. MRC and other structures were not observed. After challenge for 2–3 d, tomonts developed and asexually reproduced as theronts. Part of the tomonts split, and theronts were released into the water. Hyperplasia and curves were observed in the gill filaments, and a large number of tissues swelled, split, shed cells and exhibited tissue necrosis.
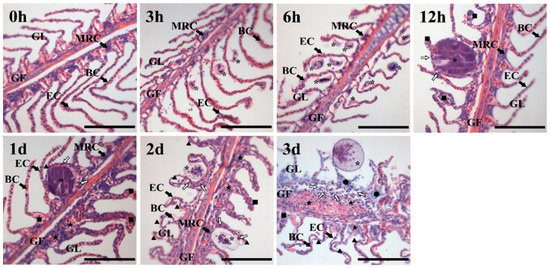
Figure 1.
HE staining of the gill tissue of T. ovatus infected by C. irritans. Abbreviations: GF: gill filaments; GL: gill lamellae; EC: epithelial cell; MRC: mitochondrial-rich cell; BC: blood cell; ▲: split; ■: swell; ★: hyperplasia; ●: necrosis. The white arrow shows white blood cells migrating and aggregating at the parasitic site. *: C.irritans (life cycle: 3–6 h: trophont; 12–24 h: protomont; 48 h: tomont; 72 h: theronts). Scale bar = 100 μm.
HE staining of the skin is shown in Figure 2. The structure of the epidermis and muscle layer of healthy T. ovatus was complete. After challenge for 3–6 h, there was no obvious change in the skin surface structure. After challenge for 12 h–2 d, the glandular parts of the epidermal layer thickened, and the mucous cells and secretion fluid increased. After challenge for 3 d, the skin tissue was destroyed, the epidermis layer was exposed, the cells fell off and tissue necrosis occurred.
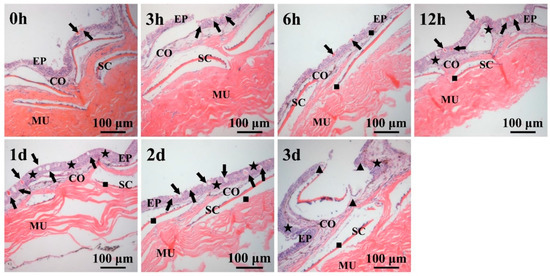
Figure 2.
HE staining of the skin tissue of T. ovatus infected by C. irritans. Abbreviations: EP: epidermis layer; CO: dermis layer; MU: muscle layer; ▲: break; ■: flat; ★: thickening; the black arrow shows the distribution of mucous cells in the gland of the epidermis layer. Scale bar = 100 μm.
3.2. Immune-Related Enzyme Activity Analysis
To investigate the antioxidant activity and non-specific immune response of T. ovatus after infection with C. irritans, the enzyme activity of ACP, AKP, SOD and LZM in the defence against parasite infection was determined at local infection sites (skin and gills) and system immune tissues (liver, spleen and head kidney) (Figure 3).
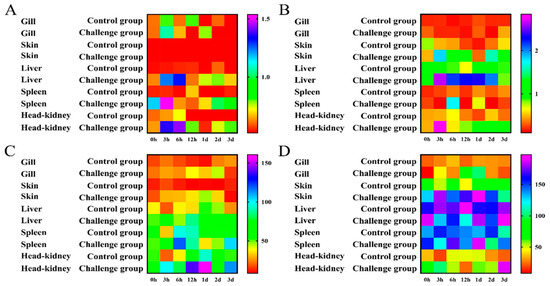
Figure 3.
Enzyme activities of ACP (A), AKP (B), SOD (C) and LZM (D) were detected in gill, skin, liver, spleen and head kidney after infection with C. irritans (0 h, 3 h, 6 h, 12 h, 1 d, 2 d and 3 d). The heatmap was constructed using Graphpad Prism 5.0 software.
The results of the ACP activity assay are shown in Figure 3A. In the gill, ACP was upregulated to a peak at 6 h, then decreased and had a second peak at 1 d. In the skin, ACP was upregulated to its maximum (3.14-fold relative to the control) from 3 h to 6 h and then downregulated. In the liver, ACP was upregulated to a maximum (2.39-fold relative to the control) from 3 h to 6 h and then it decreased to normal levels. In the liver, ACP was upregulated at 6 h and then downregulated. In the head kidney, ACP was upregulated to a peak (1.97-fold relative to the control) from 3 h to 6 h and then downregulated to normal levels. ACP had the smallest change in the gill and the largest change in the head kidney. The ACP activity in the skin was the lowest, with an average of 0.15 (U/gprot), and the ACP activity in the spleen was the highest, with an average of 0.93 (U/gprot).
The results of the AKP activity assay are shown in Figure 3B. In the gill, AKP showed no significant changes between the challenge group and the control group. In the skin, AKP was upregulated to a peak (3.80-fold relative to the control); then, it decreased and had a second peak (4.65-fold relative to the control) at 2 d. In the liver, AKP was upregulated at 3 h and 6 h, and it reached a peak (3.55-fold relative to the control) at 12 h and then was maintained to 2 d. In the spleen, AKP had a peak (4.96-fold relative to the control) at 6 h. In the head kidney, AKP reached a peak (6.01-fold relative to the control) at 3 h. AKP had the smallest change in the gill and the largest change in the head kidney. The activity of AKP in the gills was the lowest, with an average of 0.24 (U/gprot), and the activity of AKP in the liver was the highest, with an average of 1.94 (U/gprot).
The results regarding SOD activity are shown in Figure 3C. In the gill, SOD was upregulated to a peak (2.98-fold relative to the control) from 3 h to 1 d. In the skin, SOD was upregulated to a peak (4.70-fold relative to the control) from 3 h to 1 d. In the liver, SOD was upregulated at 3 h and 12 h and then maintained at a certain level. In the spleen, SOD was upregulated at 6 h and 12 h, and then it decreased, with a second peak at 3 d. In the head kidney, SOD was upregulated to a maximum from 3 h to 1 d and then downregulated. SOD displayed the smallest change in the spleen and the largest change in the skin. The activity of SOD in the spleen was the lowest, with an average of 1.06 U/mg prot, and the activity of SOD in the skin was the highest, with an average of 2.52 U/mg prot.
The results of the LZM activity assays are shown in Figure 3D. In the gill, LZM was upregulated to a maximum (3.27-fold relative to the control) from 3 h to 1 d. In the skin, LZM reached a peak at 3 h and was then maintained at a certain level. In the liver, no significant change was observed in the challenge group. In the spleen, LZM had a peak (1.41-fold relative to the control) on day 1. In the head kidney, LZM was upregulated at 6 h and had a peak (8.49-fold relative to the control) on day 3. LZM displayed the smallest change in the liver and the largest change in the skin. The activity of LZM in the gills was the lowest, with an average of 43.30 U/mL, and the activity of LZM in the liver was the highest, with an average of 160.13 U/mL.
3.3. NEMO Bioinformatic Analysis
The NEMO ORF of T. ovatus was 1650 bp in length and encoded 548 amino acids (GenBank accession number: MW076540) (Figure 4). The predicted molecular weight of NEMO was 62.68 kDa, and the predicted isoelectric point was 5.52. It included a 68 amino acid Pfam NEMO domain (28–95 aa); a 222 amino acid coiled coil domain (138–359 aa); a 95 amino acid Pfam CC2-LZ (coiled coil region–leucine zipper domain) (365–459 aa) and a 19 amino acid ZnF C2H2 (zinc finger domain) (526–545 aa).

Figure 4.
NEMO ORF sequence and predicted amino acid sequence analysis. NEMO domain is marked by light grey shadows. The low-complexity region is underlined. The CC2-LZ (coiled coil region–leucine zipper) domain is marked by dark grey shadows. The ZnF C2H2 (Zinc finger) domain is marked by a box. * stands for termination codon.
To study protein structure conservation, SMART was used to predict and align the NEMO protein structure of T. ovatus with other species (Figure 5A). Multiple alignment analysis of the NEMO amino acid sequence showed that NEMO has three conserved domains.
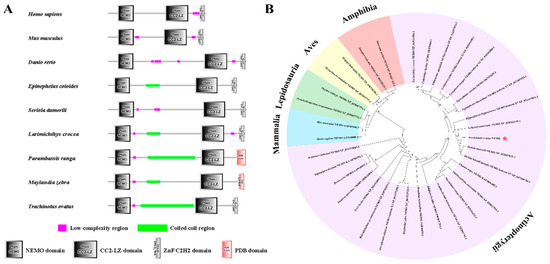
Figure 5.
Protein structure (A) and phylogenetic tree (B) of comparing ToNEMO with other NEMO vertebrates. SMART was used to predict and aligned NEMO protein structure of T. ovatus and other species. MEGA 7.0 with neighbour-joining (NJ) method was used to structure phylogenetic tree. T. ovatus is marked by green shading (A) and red asterisk (B). The accession numbers are listed in Table S1.
Multiple sequence alignment results revealed that the amino acid sequences of ToNEMO were highly conserved with the corresponding sequences of other species. To further study the homology of ToNEMO with other species, the amino acid sequence of ToNEMO was aligned with other species via MEGA 7.0 with the neighbour-joining (NJ) method (Figure 5B). In teleosts, ToNEMO had the highest homology with Seriola dumerili NEMO and Seriola lalandi dorsalis NEMO isoform X3 and the lowest homology with Acipenser ruthenus NEMO. Compared with Mammalia, Lepidosauria, Aves and Amphibia, ToNEMO had the highest homology with Mammalia and the lowest homology with Amphibia.
3.4. NEMO Gene Expression Pattern Analysis
To study the relative mRNA level in various tissues, the constitutive expression of NEMO in blood, brain, muscle, heart, gonad, spleen, kidney, liver, skin, gill and intestine was detected via qRT-PCR (Figure 6A). The NEMO gene was highly expressed in the blood, brain and muscle, while low expression was observed in the intestine, gill and skin (p < 0.05).
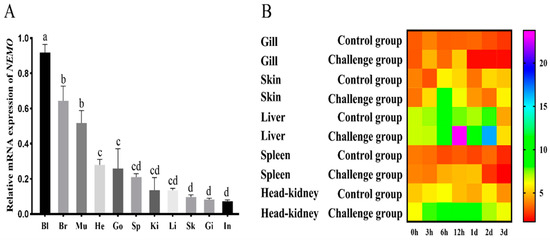
Figure 6.
ToNEMO transcriptions in various tissues. (A) qRT-PCR was used to test relative NEMO mRNA levels in healthy fish, containing blood (Bl), brain (Br), muscle (Mu), heart (He), gonad (Go), spleen (Sp), kidney (Ki), liver (Li), skin (Sk), gill (Gi) and intestine (In). Significant differences at p < 0.05 are labelled with different letters, and mean ± SEM of each mRNA quantity is shown for each tissue tested. (B) Temporal mRNA expression analyses of ToNEMO in different tissues (gill, skin, liver, spleen and head kidney) after PBS (control), C. irritans challenges (0 h, 3 h, 6 h, 12 h, 1 d, 2 d and 3 d). EF-1a is used as the internal control to calibrate the cDNA templates for all the samples. The heatmap was constructed using Graphpad Prism 5.0 software.
To further study the expression pattern of NEMO in the defence against parasite infection, the mRNA levels of NEMO were determined in local infection sites (skin and gills) and systemic immune tissues (liver, spleen and head kidney) after C. irritans challenge (Figure 6B). The relative expression level of NEMO in gills was upregulated from 3 h to 12 h, and a peak (1.55-fold relative to the control) was observed at 12 h, and then, it was generally downregulated. In the skin, NEMO was upregulated to a peak from 3 h to 6 h, and then, it returned to normal levels. In the liver, NEMO was upregulated to its maximum (3.12-fold relative to the control) from 3 h to 12 h, then downregulated on 1 d, and it had a second peak (2.06-fold relative to the control) at 2 d. In the spleen, NEMO was upregulated at 6 h, 12 h, and 1 d and then returned to normal levels. In the head kidney, NEMO was upregulated to a peak from 6 h to 12 h and then generally downregulated to normal levels. According to these results, the difference in the relative expression of the NEMO gene in the gills and spleen was the smallest, and the difference in the relative expression in the liver was the largest. The highest peak of NEMO was observed at 6 h and 12 h after challenge with C. irritans.
4. Discussion
In the present study, T. ovatus was infected by stimulating C. irritans. HE staining was used to observe the life history of C. irritans and the histopathological characteristics of the infected T. ovatus. The enzyme activity of ACP, AKP, SOD and LZM was detected via colorimetry to study the histological and immune stress response of T. ovatus after challenge with C. irritans. Moreover, qRT-PCR was used to detect the relative expression levels of NEMO in response to C. irritans infection.
The infection of T. ovatus by C. irritans will result in direct mechanical damage to the parasitized tissue, internal tissue haemorrhage and necrosis, as well as the migration and proliferation of a large number of immune cells and the upregulation of chemokines [4,26]. Histopathological results showed hyperplasia in the gill filaments, cell shedding and tissue necrosis. The gill lamellae were swollen, separated and split seriously, and a large number of white blood cells had migrated and gathered in the parasitized part. Mucous cells in the skin had thickened, and mucous cells and secreted fluid quantity increased significantly. The skin was destroyed, the dermis layer was exposed, and cell shedding and tissue necrosis were observed. The pathological tissue morphology was similar to that in a previous report [4,26].
Immuno-related enzymes, such as ACP, AKP, SOD and LZM, are important immune indicators for aquaculture animals when they undergo pathogen invasion. ACP plays a role in killing and digesting pathogens in immune responses [13]. AKP is also a multi-functional enzyme involved in immune responses [13]. Research has shown that the serum ACP activity of snails (Biomphalaria glabrata) will increase significantly in response to the pathogen infection [27]. Studies have shown that when infected by acute viral necrosis virus (AVNV), the blood AKP level of Chlmys frreri was higher than that of the control group [28]. Increases in ACP and AKP activities indicate that defence against foreign materials is enhanced in Apostichopus japonicus [29]. According to these results, AKP activity in the head kidney and ACP activity in the skin were changed the most after C. irritans challenge, suggesting that 6–12 h after infection, ACP and AKP may mainly participate in detoxification in these tissues.
Among antioxidant responses in fish, SOD production is a first line of defence against oxidative stress, converting superoxide anions to hydrogen peroxide and oxygen [30]. SOD showed significant upregulation in the immune tissues, suggesting that SOD may clear superoxide free radicals and enhance the antioxidant capacity of cells instead of directly acting on the pathogen at the site of C. irritans infection. LZM is also an important lysosomal enzyme that can lyse and digest pathogenic microorganisms [31]. The results of LZM showed significant upregulation in all five tissues. The upregulation of lysozymes on the skin may be due to the secretion of mucosal immune tissue as a barrier against the stimulation of cryptosporidium, and a high level of its expression in the immune system indicates the initiation of a non-specific immune response in the body.
Bioinformatic analysis showed that the NEMO domain, coiled coil region–leucine zipper domain and zinc finger domain were highly conserved in different species. It has been previously reported that orange-spotted grouper TLR2 and its downstream pathway genes were significantly upregulated after challenge with C. irritans [32]. The challenge of C. irritans may activate the innate immune inflammatory response through the TLR2 pathway [6]. MyD88 and TIRAP are recruited by TLR2 and form the IRAK-TRAF6 complex. TRAF ubiquitination leads to the formation of the IKK complex via NEMO, IKKα and IKKβ, which results in the phosphorylation of IκB. Next, NF-κB is transferred to the nucleus to activate the target genes and induce the transcription of TNF, Pro-IL-1b, IkBz, ATF3, Zc3 h12a, TTP, etc. [6]. The NEMO domain is an important structure for recognizing and binding IKKβ [33]. The coiled coil domain ensures the integrity of the NEMO structure. Conservation among different species suggests that T. ovatus NEMO may play the same role in innate immunity as other species [34].
The infection of T. ovatus by C. irritans activates the innate immune signalling pathway of TLR2, and its downstream factors are significantly upregulated in infected sites and systemic immune tissues [35,36]. NEMO is a necessary regulator of NF-κB and plays a crucial role in the innate immunity response to pathogens, including bacteria and viruses. NEMO receives upstream signals from the TLR family [6].
The NEMO gene was upregulated in the skin, liver, spleen, head and kidney after infection, which is similar to the results found for the TLR2 signalling pathway in orange-spotted groupers infected by C. irritans reported in a previous study [32]. After infection, NEMO in the gill, skin, spleen and head kidney reached a peak at 6–12 h after infection. Compared with TLR2, the time at which NEMO reached its peak was significantly delayed. qRT-PCR results suggested that the pathogen recognition reaction was initiated at 3–6 h, and the innate immune NEMO downstream pathway was upregulated to its peak at 6–12 h.
In conclusion, the histological sections showed that there was considerable meta-morphosis and hyperplasia in the parasitized sites (skin) with leukocyte aggregation and mucous cell increases after C. irritans infection. Moreover, the activities of four enzymes were significantly increased in different tissues after C. irritans infection. The ToNEMO transcripts were universally expressed in all of the examined tissues, with higher levels being observed in the immune-relevant and central nervous tissues. The mRNA levels of ToNEMO after C. irritans infection were significantly increased in the gill, skin, liver, spleen and head kidney. This study could help deepen the understanding of the poisoning mechanism of C. irritans to golden pompano at the molecular level. It could provide some basic data for the study of the healthy culture and physiological function regulation of golden pompano.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/jmse11020262/s1, Table S1: Information for NEMO amino acid sequence alignment and constructing phylogenetic tree.
Author Contributions
K.-C.Z., D.-C.Z. conceived and designed the experiments; K.-C.Z. performed the experiments; B.-S.L. and N.Z. contributed to sample collection; H.-Y.G. and W.-F.L. analysed the data and wrote the paper; B.L., J.-W.Y. and D.-C.Z. assisted with writing and proofreading. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (U20A2064), the Central Public-interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund CAFS (NO.2020TD29), the China Agriculture Research System (CARS-47) and the Guangdong Provincial Special Fund for Modern Agriculture Industry Technology Innovation Teams (2019KJ143).
Institutional Review Board Statement
All applicable international, national and institutional guidelines for the care were followed by the authors.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study. Written informed consent has been obtained from the patients to publish this paper.
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Colorni, A.; Burgrss, P. Cryptocaryon irritans Brown 1951, the cause of ‘white spot disease’ in marine fish: An update. Aquar. Sci. Conserv. 1997, 1, 217–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.H.; Jiang, B.; Li, Z.C.; Li, S.Y.; Li, A.X. Quantification of parasite abundance: A novel method to evaluate anti-Cryptocaryon irritans efficacy. Aquaculture 2020, 528, 735482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Y.; Wei, X.M.; Yang, J.L.; Zhang, R.R.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, J.M. The bacteriolytic mechanism of an invertebrate-type lysozyme from mollusk Octopus ocellatus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 93, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.Y.; Liang, W.W.; Chen, M.; Huang, T.; Li, L.P.; Lei, A.Y.; Wang, R.; Yang, X.M.; Luo, H.L.; Ouyang, X.H. Histopathology study on the Cryptocaryon irritans disease of Trachinotus ovatus. J. Fish Res. 2017, 39, 181–187. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Braue, J.; Murugesan, V.; Holland, S.; Patel, N.; Naik, E.; Leiding, J.; Yacoub, A.T.; Prieto-Granada, C.N.; Greene, J.N. NF-kappaB Essential Modulator Deficiency Leading to Disseminated Cutaneous Atypical Mycobacteria. Mediterr. J. Hematol. Infect. Dis. 2015, 7, e2015010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, O.; Akira, S. Pattern recognition receptors and inflammation. Cell 2010, 140, 805–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- May, M.J.; D`Acquisto, D.; Madge, L.A.; Glochner, J.; Pober, J.S.; Ghosh, S. Selective Inhibition of NF-κB Activation by a Peptide That Blocks the Interaction of NEMO with the IκB Kinase Complex. Science 2000, 289, 1550–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solt, L.A.; May, M.J. The IκB kinase complex: Master regulator of NF-κB signaling. Immunol. Res. 2008, 42, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayden, M.S.; Ghosh, S. NF-kappaB, the first quarter-century: Remarkable progress and outstanding questions. Genes Dev. 2012, 26, 203–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, M.S.; Ghosh, S. Signaling to NF-kappaB. Genes Dev. 2004, 18, 2195–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheidereit, C. IkappaB kinase complexes: Gateways to NF-kappaB activation and transcription. Oncogene 2006, 25, 6685–6705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, F.; Dan, X.M.; Sun, P.; Shi, Z.H.; Gao, Q.X.; Peng, S.M.; Li, A.X. Growth, feed intake and immune responses of orange-spotted grouper (Epinephelus coioides) exposed to low infectious doses of ectoparasite (Cryptocaryon irritans). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014, 36, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, X.H.; Wang, S.P.; Jiang, H.X.; Nie, G.X.; Li, X.J. Responses of acid/alkaline phosphatase, lysozyme, and catalase activities and lipid peroxidation to mercury exposure during the embryonic development of goldfish Carassius auratus. Aquat. Toxicol. 2012, 120, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, S.K.; Hur, Y.B. Toxic effects of waterborne nitrite exposure on antioxidant responses, acetylcholinesterase inhibition, and immune responses in olive flounders, Paralichthys olivaceus, reared in bio-floc and seawater. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 97, 581–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.N.; Zhang, J.L.; Liu, M.; Huang, M.X. Molecular cloning, expression and antibacterial activity of goose-type lysozyme gene in Microptenus salmoides. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 82, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Z.H.; Guo, W.L.; Lei, Y.; Wang, F.; Wang, S.F.; Sun, Y.; Hu, W.T.; Zhou, Y.C. Antiparasitic efficacy of honokiol against Cryptocaryon irritans in pompano, Trachinotus ovatus. Aquaculture 2019, 500, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, Y.; How, K.H.; Zenke, K.; Itoh, N.; Yoshinaga, T. Characterization of the proteases in the parasitic stage of Cryptocaryon irritans, and in vitro and in vivo effects of protease inhibitors on cryptocaryoniasis. Aquaculture 2019, 512, 734311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Zhu, K.C.; Guo, L.; Liu, B.S.; Guo, H.Y.; Zhang, N.; Yang, J.W.; Zhang, D.C. Molecular characterization of GRP94 and HSP90 alpha from Trachinotus ovatus, Linnaeus 1758 and their expression responses to various levels of stocking density stress and Cryptocaryon irritans infection. Aquaculture 2019, 529, 735601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; He, P.Y.; Zhu, K.C.; Guo, H.Y.; Liu, B.S.; Zhang, N.; Jiang, J.G.; Zhang, D.C. Functional identification of ToLAAO genes and polymorphism association analysis of Cryptocaryon irritans resistance in Trachinotus ovatus. Aquac. Res. 2021, 53, 208–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.C.; Liu, J.; Liu, B.S.; Guo, H.Y.; Zhang, N.; Guo, L.; Jiang, S.G.; Zhang, D.C. Functional characterization of four ToRac genes and their association with anti-parasite traits in Trachinotus ovatus (Linnaeus, 1758). Aquaculture 2022, 560, 738514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, X.M.; Li, A.X.; Lin, X.T.; Teng, N.; Zhu, X.Q. A standardized method to propagate Cryptocaryon irritans on a susceptible host pompano Trachinotus ovatus. Aquaculture 2006, 258, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, F.; Sun, P.; Tang, B.J.; Dan, X.M.; Li, A.X. Immunological, ionic and biochemical responses in blood serum of the marine fish Trachinotus ovatus to poly-infection by Cryptocaryon irritans. Exp. Parasitol. 2015, 154, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.C.; Guo, L.; Guo, H.Y.; Zhu, K.C.; Li, S.Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, N.; Liu, B.S.; Jiang, S.G.; Li, J.T. Chromosome-level genome assembly of golden pompano (Trachinotus ovatus) in the family Carangidae. Sci. Data 2019, 6, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, K.C.; Song, L.; Guo, H.Y.; Guo, L.; Zhang, N.; Liu, B.S.; Jiang, S.G.; Zhang, D.C. Elovl4a participates in LC-PUFA biosynthesis and is regulated by PPAR alpha beta in golden pompano Trachinotus ovatus (Linnaeus 1758). Sci. Rep.-Uk. 2019, 9, 4684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(T)(-Delta Delta C) method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.W.; Jiang, B.; Dan, X.M.; Li, A.X. Advances in the research on mucosal immune response of fish against Cryptocaryon irritans infection. J. Fish. China 2019, 43, 156–167. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, T.; Dougherty, W. Ultrastructural evidence for the destruction of Schistosoma mansoni sporocysts associated with elevated lysosomal enzyme levels in Biomphalaria glabrata. J. Parasitol. 1989, 75, 928–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, J.; Zhan, W.B.; Zhou, L. Endoenzymes associated with haemocyte types in the scallop (Chlamys farreri). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2002, 13, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, D.; Sun, L.; Ru, X.; Zhang, L.; Lin, C.; Liu, S.; Xin, X.; Yang, H. Impact of hypoxia stress on the physiological responses of sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus: Respiration, digestion, immunity and oxidative damage. Peer J. 2018, 6, e4651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Ge, X.; Zhu, J.; Xuan, F.; Jiang, X. Identification and mRNA expression of antioxidant enzyme genes associated with the oxidative stress response in the Wuchang bream (Megalobrama amblycephala Yih) in response to acute nitrite exposure. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2014, 159, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Ding, S.; He, M.; Liu, A.; Long, H.; Guo, W.; Cao, Z.; Xie, Z.; Zhou, Y. Construction and analysis of the immune effect of Vibrio harveyi subunit vaccine and DNA vaccine encoding TssJ antigen. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 98, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.W.; Dan, X.M.; Zhang, T.W.; Luo, X.C.; Li, A.X. Immune-related genes expression profile in orange-spotted grouper during exposure to Cryptocaryon irritans. Parasite Immunol. 2011, 33, 679–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rushe, M.; Silvian, L.; Bixler, S.; Chen, L.L.; Cheung, A.; Bowes, S.; Cuervo, H.; Berkowitz, S.; Zheng, T.; Guckian, K.; et al. Structure of a NEMO/IKK-associating domain reveals architecture of the interaction site. Structure 2008, 16, 798–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barczewski, A.H.; Ragusa, M.J.; Mierke, D.F.; Pellegrini, M. The IKK-binding domain of NEMO is an irregular coiled coil with a dynamic binding interface. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.W.; Luo, X.C.; Dan, X.M.; Huang, X.Z.; Qiao, W.; Zhong, Z.P.; Li, A.X. Orange-spotted grouper (Epinephelus coioides) TLR2, MyD88 and IL-1beta involved in anti-Cryptocaryon irritans response. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2011, 30, 1230–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, K.C.; Liu, B.S.; Zhang, N.; Guo, H.Y.; Guo, L.; Jiang, S.G.; Zhang, D.C. Interferon regulatory factor 2 plays a positive role in interferon gamma expression in golden pompano, Trachinotus ovatus (Linnaeus 1758). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 96, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).