Organic Fertilizer and Deep Tillage Synergistically Regulate Soil Physicochemical Properties and Aggregate-Associated Distribution of Carbon and Nitrogen in Dryland Foxtail Millet Fields
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site Description
2.2. Field Experimental Design
2.3. Measurements and Methods
2.3.1. Soil pH and pH Buffering Capacity
2.3.2. Soil Three-Phase Composition
2.3.3. Soil Aggregate Stability
2.3.4. Soil Organic Carbon
2.3.5. Soil Total Nitrogen
2.4. Data Processing Methods
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Organic Fertilizer Application and Deep Tillage on Soil pH and pH Buffering Capacity
3.2. Effects on Soil Bulk Density, Total Porosity, and Three-Phase Composition
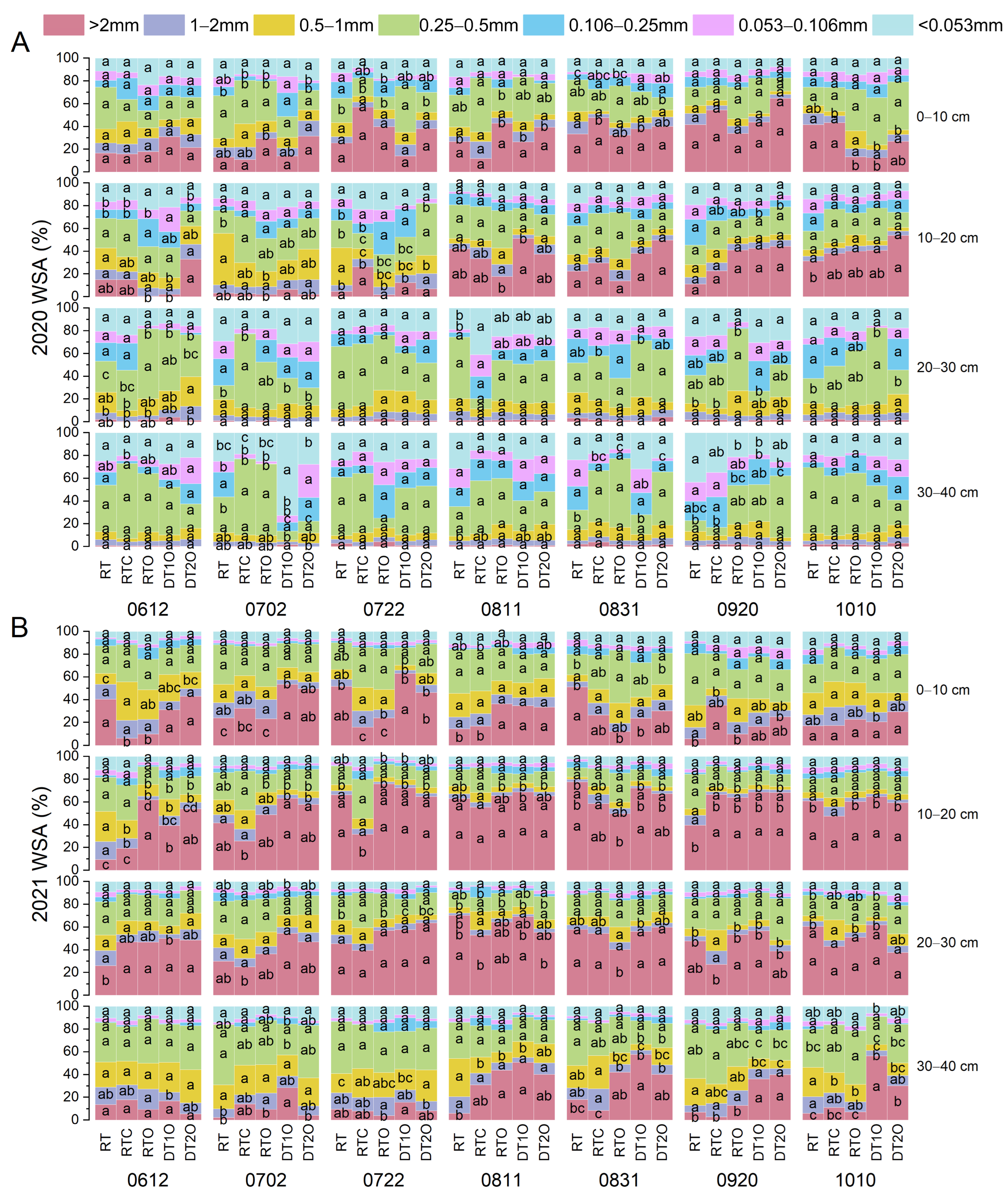
3.3. Effects on Soil Aggregate Stability
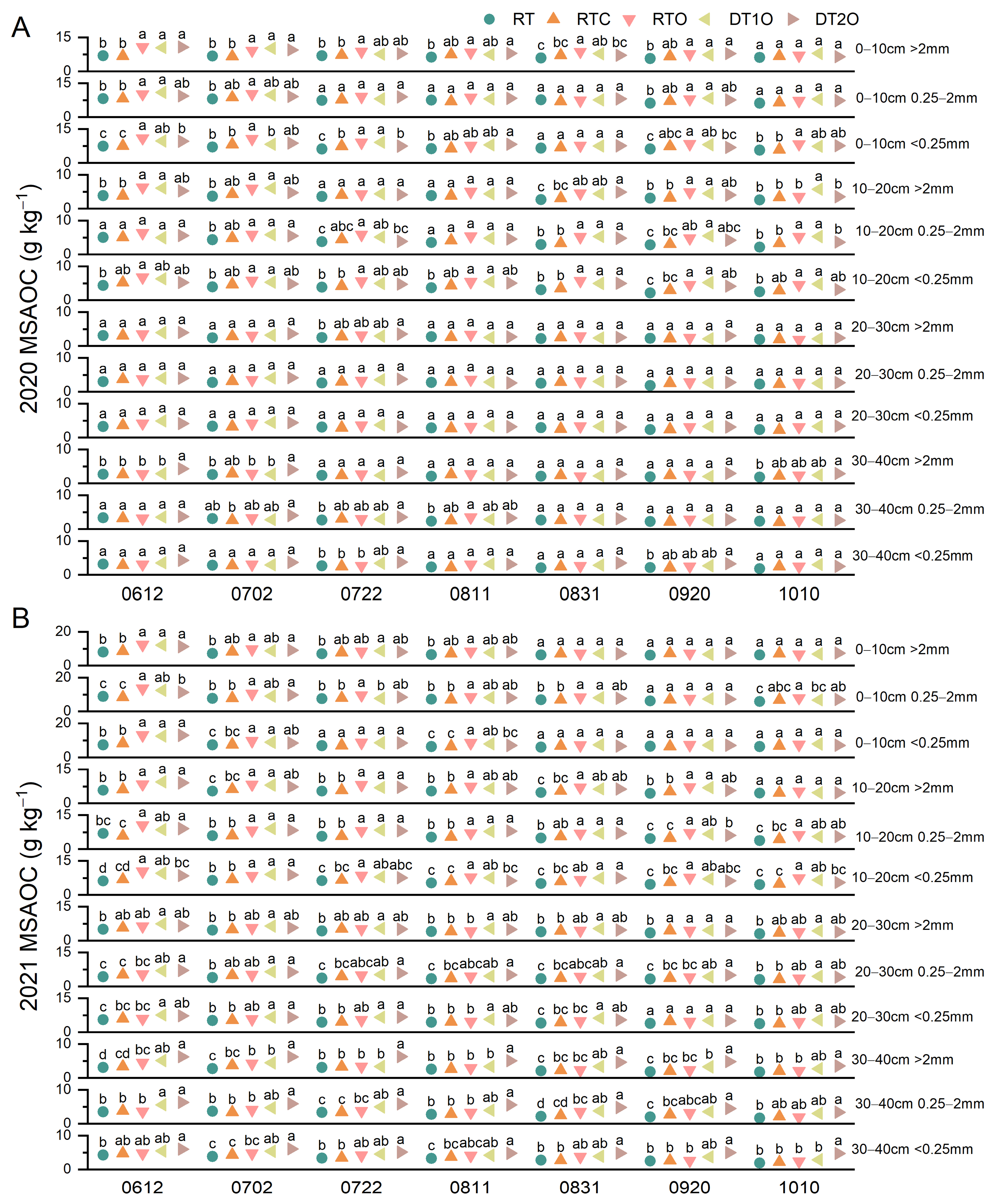
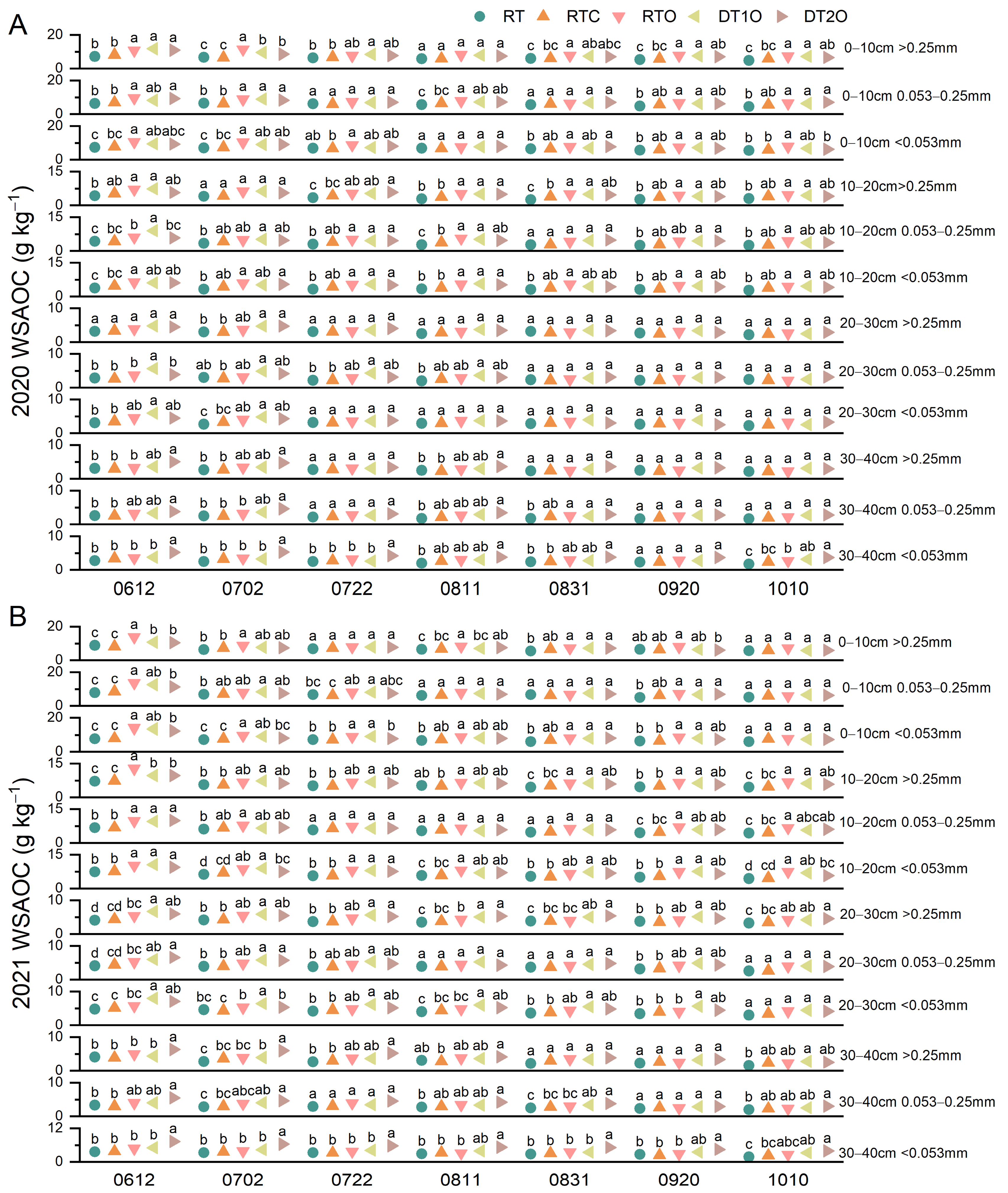
3.4. Effects on Aggregate-Associated Organic Carbon
3.5. Effects on Aggregate-Associated Total Nitrogen
4. Discussion
4.1. Deep Tillage Facilitates Organic Fertilizer Downward Migration and Co-Regulates Spatial Distribution of Soil pH and Buffering System
4.2. Organic Fertilizer Combines with Deep Tillage to Decrease Bulk Density and Optimize Soil Three-Phase Composition
4.3. Organic Fertilizer and Deep Tillage Synergistically Enhance Macroaggregate Content and Stability
4.4. Deep Tillage Promotes Organic Fertilizer-Induced Carbon Accumulation in Subsoil Aggregates
4.5. Deep Tillage Combined with Organic Fertilizer Enhances Nitrogen Retention
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RT | Rotary tillage without fertilization |
| RTC | Rotary tillage with compound fertilizer |
| RTO | Rotary tillage with organic fertilizer |
| DT1O | Deep tillage with organic fertilizer at 20–30 cm |
| DT2O | Deep tillage with organic fertilizer at 30–40 cm |
| pHBC | pH buffering capacity |
| Mv | Volumetric water content |
| A | Air-filled porosity |
| Sv | Solid volume fraction |
| BD | Bulk density |
| P | Total porosity |
| MSA | Mechanically stable aggregates |
| WSA | Water-stable aggregate |
| MWD | Mean weight diameter |
| GMD | Geometric mean diameter |
| MSAOC | Mechanically stable aggregate organic carbon |
| WSAOC | Water-stable aggregate organic carbon |
| MSATN | Mechanically stable aggregate total nitrogen |
| WSATN | Water-stable aggregate total nitrogen |
References
- Peng, R.H.; Zhang, B.H. Foxtail millet: A new model for c4 plants. Trends Plant Sci. 2021, 26, 199–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthamilarasan, M.; Prasad, M. Advances in setaria genomics for genetic improvement of cereals and bioenergy grasses. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2015, 128, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, L.; Newsome, S.D.; Chen, F.H.; Wang, H.; Guilderson, T.P.; Bettinger, R.L. Agricultural origins and the isotopic identity of domestication in northern China. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 5523–5528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.P.; Xia, L.H.; Sun, Y.T.; Gao, S. Soil nutrients and enzyme activities based on millet continuous cropping obstacles. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, J.Y.; Li, X.; Zhou, D.; Gao, Y.; Gao, X.L.; Wang, P.K.; Gao, J.F.; Yang, P.; Feng, B.L. Effects of foxtail millet continuous cropping on soil enzyme activities and nutrients. Agric. Res. Arid. Areas 2016, 34, 123–126+152. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, F.C.; Feng, X.L. Review, current status, and development direction of hybrid utilization of millet in China. China Seed Ind. 2013, 3, 11–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.B.; Gong, X.C.; Qiao, Y.M.; Zhao, Z.H.; Yin, N. A study on dry matter accumulation and light characteristics of hybrid foxtail millet. Crops 2014, 1, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, R.Y.; Liu, Z.D.; Li, Y.; Jiang, T.M.; Xu, M.G.; Li, J.Y.; Xu, R.K. Mechanisms for increasing soil resistance to acidification by long-term manure application. Soil Till. Res. 2019, 185, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Luo, M.; Zhang, T.G.; Yan, S.H.; Wang, C.; Feng, H.; Zhang, T.B.; Kisekka, I. Organic substitution improves soil structure and water and nitrogen status to promote sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) growth in an arid saline area. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 283, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, P.S.; Li, J.K.; Chen, P.; Wei, D.D.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Jia, Z.J.; He, C.; Ullah, J.; Wang, Q.; Ruan, Y.Z. Mitigating soil degradation in continuous cropping banana fields through long-term organic fertilization: Insights from soil acidification, ammonia oxidation, and microbial communities. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 213, 118385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.M.; Chi, F.Q.; Su, Q.R.; Kuang, E.J.; Zhang, L.; Jin, L.; Guo, W.Y.; Xue, J.S. Effect of different organic material turnover on soil structure and maize photosynthetic rate. J. Agric. Resour. Environ. 2014, 31, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheoran, H.S.; Kakar, R.; Kumar, N.; Seema. Impact of organic and conventional farming practices on soil quality: A global review. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2019, 17, 951–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.N.; Wright, D.L.; Hussain, S.; Koutroubas, S.D.; Seepaul, R.; George, S.; Ali, S.; Naveed, M.; Khan, M.; Altaf, M.T.; et al. Organic fertilizer sources improve the yield and quality attributes of maize (Zea mays L.) hybrids by improving soil properties and nutrient uptake under drought stress. J. King Saud. Univ. Sci. 2023, 35, 102570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, T.T.; Wang, J.K.; Li, S.Y.; Yu, S.; Zhu, P. Effects of manure application on organic carbon in aggregates of black soil. J. Appl. Ecol. 2008, 19, 369–373. [Google Scholar]
- Hei, Z.W.; Geisen, S.; Shao, J.Y.; Yang, Y.; Liu, F.T.; Hu, S.R.; Zhang, H.Y.; Kammenga, J.; Chen, Y.L. Increases in macroaggregate fractions following organic fertilizer application decrease microbial-driven CO2 release. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2024, 202, 105530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brar, B.S.; Singh, K.; Dheri, G.S.; Balwinder, K. Carbon sequestration and soil carbon pools in a rice–wheat cropping system: Effect of long-term use of inorganic fertilizers and organic manure. Soil Tillage Res. 2013, 128, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Bao, Y.W.; Li, B.W.; Wang, R.X.; Sun, C.; Ma, D.H.; Chen, L.; Zou, H.T.; Zhang, J.B. Effects of fertilization applications on soil aggregate organic carbon content and assessment of their influencing factors: A meta-analysis. CATENA 2024, 242, 108135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.Y.; Hou, M.M.; Zhou, Y.T.; Wang, R.J.; Zhang, S.L.; Yang, X.Y.; Sun, B.H. Carbon sequestration and mineralization of aggregate-associated carbon in an intensively cultivated anthrosol in north China as affected by long term fertilization. Geoderma 2017, 296, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Zhu, H.; Shutes, B.; Rousseau, A.N.; Feng, W.D.; Hou, S.N.; Ou, Y.; Yan, B.X. Soil aggregate-driven changes in nutrient redistribution and microbial communities after 10-year organic fertilization. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 348, 119306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Dai, Q.; Yin, L.C.; Gu, Z.Y. Effects of following-up fertilization reforming on distribution and turnover of aggregate-associated organic carbon in paddy soils. Soils 2017, 49, 969–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.L.; Jia, Z.X.; Jiao, X.Y.; Wang, J.L.; Huang, X.F. Long-term manure applications to increase carbon sequestration and macroaggregate-stabilized carbon. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2022, 174, 108827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DămătÎrcă, C.; Moretti, B.; Bertora, C.; Ferrarini, A.; Lerda, C.; Mania, I.; Celi, L.; Gorra, R.; Zavattaro, L. Residue incorporation and organic fertilisation improve carbon and nitrogen turnover and stabilisation in maize monocropping. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2023, 342, 108255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.P.; Zheng, S.X.; Nie, J.; Liao, Y.L.; Xie, J. Effects of long-term winter planted green manure on distribution and storage of organic carbon and nitrogen in water-stable aggregates of reddish paddy soil under a double-rice cropping system. J. Integr. Agric. 2014, 13, 1772–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.D.; Duan, W.D.; Guo, H.L.; Zong, J.Q.; Chen, J.B.; Wang, J.J. High-nitrogen organic fertilizer promotes the growth of bermudagrass (Cynodon dactylon), zoysiagrass (Zoysia japonica) and paspalum grass (Paspalum vaginatum) by enhancing nitrogen use efficiency associated with bacillus-stimulated bacterial community. Sci. Hortic. 2024, 329, 113027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.J.; Ros, G.H.; Xu, M.G.; Cai, Z.J.; Sun, N.; Duan, Y.H.; De Vries, W. Long-term impacts of mineral and organic fertilizer inputs on nitrogen use efficiency for different cropping systems and site conditions in southern China. Eur. J. Agron. 2023, 146, 126797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.J.; Liu, H.G.; Wang, T.G.; Gong, P.; Li, P.F.; Li, L.; Bai, Z.T. Deep vertical rotary tillage depths improved soil conditions and cotton yield for saline farmland in south Xinjiang. Eur. J. Agron. 2024, 156, 127166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Han, X.Z.; Wang, X.H.; Guo, Z.X.; Lu, X.C.; Yan, J.; Zou, W.X. Application of manure and straw by deep plough rapidly improves fertility and productivity of brown sandy soil. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2023, 29, 232–241. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.Y.; Tong, H.T.; Han, Y.L.; Li, P.P.; Chen, W.J.; Bi, Q.S. Effects of deep tillage andfertilization on wheat yield and physicochemical properties of lime concretion black soil. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 2022, 53, 1431–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.Y.; Bao, L.F.; Pu, Y.Y.; Shi, Z.F.; Yang, G.W.; Ni, M.; Yin, X.S.; Yang, P.W. Effects of deep tillage and fertilization on soil property and tobacco yield. Southwest China J. Agric. Sci. 2023, 36, 2026–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.H.; Richard, D. Study on the sensitivity of soil chemical properties, enzyme activities and yield to agricultural measures. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2021, 27, 2105–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; An, C.J.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Z. Can deep tillage enhance carbon sequestration in soils? A meta-analysis towards ghg mitigation and sustainable agricultural management. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 133, 110293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, F.; Don, A.; Hennings, I.; Schmittmann, O.; Seidel, S.J. The effect of deep tillage on crop yield–what do we really know? Soil Tillage Res. 2017, 174, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamouti, M.Y.; Navabzadeh, M. Investigation of plowing depth effect on some soil physical properties. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2007, 10, 4510–4514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Li, X.L.; Gao, J.L.; Hu, S.P.; Yu, X.F.; Wang, Z.G.; Su, Z.J.; Xie, M. Effects of various cultivation approaches on the three-phase ratio of soil and root system structure of maize. Agric. Res. Arid. Areas 2015, 33, 1–7+29. [Google Scholar]
- Kumari, M.; Chakraborty, D.; Gathala, M.K.; Pathak, H.; Dwivedi, B.S.; Tomar, R.K.; Garg, R.N.; Singh, R.; Ladha, J.K. Soil aggregation and associated organic carbon fractions as affected by tillage in a rice–wheat rotation in north India. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2011, 75, 560–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.J.; Hao, Q.J.; Yuan, X. Effect of tillage systems on the fractal features of soil micro-aggregate structure in a purple paddy soil. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2012, 28, 97–102. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, R.W.; Liu, Y.J.; Chen, T.; Zheng, Z.Y.; Peng, G.J.; Zou, Y.D.; Tang, C.G.; Shan, X.H.; Zhou, Q.M.; Li, J. Responses of soil aggregates, organic carbon, and crop yield to short-term intermittent deep tillage in southern China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 298, 126767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, D.; Chen, J.; Jin, M.; Li, H.; Luo, Y.; Li, W.; Chang, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z. Changes in soil micro- and macro-aggregate associated carbon storage following straw incorporation. CATENA 2020, 190, 104555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.L.; Wang, B.S.; Li, S.P.; Wu, H.J.; Wu, X.P.; Liang, G.P.; Gong, D.Z.; Zhang, X.M.; Cai, D.X.; DegrÉ, A. Soil wet aggregate distribution and pore size distribution under different tillage systems after 16 years in the loess plateau of China. CATENA 2019, 173, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlcÁntara, V.; Don, A.; Well, R.; Nieder, R. Deep ploughing increases agricultural soil organic matter stocks. Glob. Change Biol. 2016, 22, 2939–2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.W.; Chen, L.; Zhang, C.Z.; Ma, D.H.; Zhou, G.X.; Ning, Q.; Zhang, J.B. Combining rotary and deep tillage increases crop yields by improving the soil physical structure and accumulating organic carbon of subsoil. Soil Tillage Res. 2024, 244, 106252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basic, F.; Kisic, I.; Mesic, M.; Nestroy, O.; Butorac, A. Tillage and crop management effects on soil erosion in central Croatia. Soil Tillage Res. 2004, 78, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.B.; Liu, W.R.; Zheng, J.Y.; Luo, Y.; Li, R.P.; Wang, H.; Qi, H. Effect of long-term tillage on soil aggregates and aggregate-associated carbon in black soil of northeast China. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0199523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.L.; Li, Y.Y.; Zhang, D.D.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Q.X.; Dong, E.W.; Wang, J.S.; Jiao, X.Y. Long-term organic fertilization combined with deep ploughing enhances carbon sequestration in a rainfed sorghum-maize rotation system. Geoderma 2024, 442, 116778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, H.; Zhang, L.C.; Feng, X.B.; Wang, J.J.; Deng, X.P.; Li, J.Y.; Ma, E.D.; Tong, W.J. Effects of different tillage methods on soil nutrient storage capacity, spatial distribution of water and nitrogen and root morphology of flue-cured tobacco in mountainous tobacco fields. Soil Fertil. Sci. China 2021, 104–111. [Google Scholar]
- Behnke, G.D.; Kim, N.; Zabaloy, M.C.; Riggins, C.W.; Rodriguez-Zas, S.; Villamil, M.B. Soil microbial indicators within rotations and tillage systems. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.Q.; Li, S.H.; Guo, L.G.; Cao, C.G.; Li, C.F.; Zhai, Z.B.; Zhou, J.Y.; Mei, Y.M.; Ke, H.J. Advantages of nitrogen fertilizer deep placement in greenhouse gas emissions and net ecosystem economic benefits from no-tillage paddy fields. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 263, 121322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, R.; Arora, V.K. Deep tillage and residue mulch effects on productivity and water and nitrogen economy of spring maize in north-west India. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 213, 724–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abidela Hussein, M.; Muche, H.; Schmitter, P.; Nakawuka, P.; Tilahun, S.A.; Langan, S.; Barron, J.; Steenhuis, T.S. Deep tillage improves degraded soils in the (sub) humid ethiopian highlands. Land 2019, 8, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.X. Effects of Combined Regulation of Biocharand Tillage on Habitat Health and Cropgrowth in Seasonal Frozen Soil Area. Ph.D. Thesis, Northeast Agricultural University, Harbin, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.J.; Hu, X.; Ma, J.H.; Guo, Y.X.; Zong, J.J.; Yang, X.Q. Effects of tillage and fertility on soil nitrogen balance and greenhouse gas emissions of wheat-maize rotation system in central Henan province, China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2021, 32, 1753–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, R. Restoring soil quality to mitigate soil degradation. Sustainability 2015, 7, 5875–5895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kladivko, E.J. Tillage systems and soil ecology. Soil Tillage Res. 2001, 61, 61–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.A. Analysis of Soil Physicochemical Properties and Environmental Effects After 37 Years of Organic Fertilizer Application. Master’s Thesis, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.; Peng, X.X.; Huang, Q.R.; Zhang, W.J. Soil aggregation and organic carbon fractions affected by long-term fertilization in a red soil of subtropical China. Geoderma 2010, 154, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.M.; Hu, G.L.; Pan, G.X. New method for evaluating buffering capacity and equilibrium ph of paddy soil with simulation parameter. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2004, 23, 569–573. [Google Scholar]
- Soil Science Experiment. Available online: https://www.icourse163.org/course/NJAU-1206694856 (accessed on 6 May 2020).
- Nelson, D.W.; Sommers, L.E. Total carbon, organic carbon, and organic matter. In Methods of Soil Analysis; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1982; pp. 539–579. [Google Scholar]
- Sáez-Plaza, P.; Navas, M.J.; Wybraniec, S.; Michałowski, T.; Asuero, A.G. An overview of the kjeldahl method of nitrogen determination. Part II. Sample preparation, working scale, instrumental finish, and quality control. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2013, 43, 224–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.X.; Xu, J.L.; Liu, X.J.; Zhang, D.; Li, L.W.; Li, W.; Sheng, L.X. Effects of long-term application of organic fertilizer on improving organic matter content and retarding acidity in red soil from China. Soil Till. Res. 2019, 195, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.F.; Shu, A.P.; Liu, J.A.; Shi, W.C.; Li, M.C.; Zhang, W.X.; Li, Z.Z.; Liu, G.R.; Yuan, F.S.; Zhang, S.X.; et al. Effects of long-term fertilization with different substitution ratios of organic fertilizer on paddy soil. Pedosphere 2022, 32, 637–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.H.; Wang, H.; Ma, X.F.; Wang, Q.L.; Wang, Z.J. The effect of increasing application of bio-organic fertilizer on maize yield and soil physicochemical properties in saline-alkali land. Mod. Agric. 2022, 9, 21–23. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, M.X.; Wang, H.J.; Tu, X.Y.; Ma, J.L.; Zhu, X.G.; Bai, X.; Guan, H.L.; Xu, W.M. Effects of the application of organic fertilizer on the alkaline soil properties and crop growth. J. Yunnan Norm. Univ. 2022, 42, 50–57+63. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.T.; Gao, J.; Zhang, Q.; Li, J.H.; Jin, D.S.; Xu, M.G. Differences and reasons for the effects of organic fertilizer on the ph of acidic and alkaline soils in China. Chin. J. Appl. Environ. Biol. 2024, 30, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.R.; Cai, Z.J.; Wang, B.R.; Zhang, L.; Wen, S.L.; Zhu, J.Q.; Xu, M.G. Swine manure as part of the total n source improves red soil resistanceto acidification. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2022, 28, 2052–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.C.; Wang, J.D.; Shen, M.X.; Shen, Q.R.; Xu, X.J.; Ning, Y.W. Effects of long-term fertilization on soil acidification in Taihu lake region, China. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2010, 47, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Huang, Z.B. Effect of humic acid on soil restoration. Humic Acid. 2014, 4, 30–34+65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diacono, M.; Montemurro, F. Long-term effects of organic amendments on soil fertility. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2010, 30, 401–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.Z.; Yao, W.J.; Yang, S.; Xu, C.; Ma, H.B.; Wu, J.Y.; Wang, J.D.; Ai, Y.C.; Zhang, Y.C. The influence of organic material input on soil physical structure in the Yellow River old channel area. Jiangsu Agric. Sci. 2022, 50, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasool, R.; Kukal, S.S.; Hira, G.S. Soil organic carbon and physical properties as affected by long-term application of fym and inorganic fertilizers in maize–wheat system. Soil Tillage Res. 2008, 101, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meena, K.B.; Alam, M.S.; Singh, H.; Bhat, M.A.; Singh, A.K.; Mishra, A.K.; Thomas, T. Influence of farmyard manure and fertilizers on soil properties and yield and nutrient uptake of wheat. Int. J. Chem. Stud. 2018, 6, 386–390. [Google Scholar]
- Faisal, M.; Imran, K.; Umair, A.; Tanvir, S.; Sabir, H.; Muhammed, S.; Muhammad, A.; Sami, U. Effects of organic and inorganic manures on maize and their residual impact on soil physico-chemical properties. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2017, 17, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.N.; Shi, Y.; Yu, Z.W. Subsoiling improves soil physical and microbial properties, and increases yield of winter wheat in the Huang-Huai-Hai plain of China. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 187, 182–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.Y.; Liu, X.; Yan, L.Y.; Huang, X.F.; Wang, J.L. The addition of organic fertilizer can reduce the dependence of dryland yield on rainfall-based on a 32-year long-term study. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 915, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.B.; Yan, S.H.; Ouyang, X.F.; Hu, Y.J.; Song, X.L.; Wu, S.F.; Feng, H.; Siddique, K.H.M. Enhancing soil water, carbon, and nitrogen by partially substituting chemical fertilizer with organic fertilizer integrated with a rainwater collection system in rainfed orchards. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 435, 140443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.J.; Tan, W.J.; Han, J.R.; Li, F.M.; Zhang, F. Distribution pattern of rainwater in soil under vertical deep rotary tillage in dryland farmland. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 273, 107891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, R.M.; Li, R.; Han, Q.F.; Jia, Z.K.; Liang, L.Y.; Wang, X.J.; Ma, X.L. Effects of different organic manure with fertilization on soil aggregates in dry farmland. J. Northwest Agric. For. Univ. 2011, 39, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.Y.; Zhu, B.J.; Yin, R.; Wang, M.W.; Jiang, Y.J.; Zhang, C.Z.; Li, D.M.; Chen, X.Y.; Kardol, P.; Liu, M.Q. Organic fertilization promotes crop productivity through changes in soil aggregation. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2022, 165, 108533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.P.; Nan, S.Z.; Yang, X.G.; Qin, Y.; Ma, T.; Li, X.L.; Yu, Y.; Bodner, G. Macroaggregation is promoted more effectively by organic than inorganic fertilizers in farmland ecosystems of China—A meta-analysis. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 221, 105394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, H.Y.; Li, Z.Y.; Liu, D.; Li, Y.F.; Lu, L.; Wang, X.D.; Zhang, A.F.; Wang, Y.L. Effects of manure application rates on the soil carbon fractions and aggregate stability. Environ. Sci. 2019, 40, 4691–4699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.L.; Li, L.N.; Xie, L.H.; Sun, Y.X.; Zou, Y.; Dai, Q.; Yin, L.C. Effect of increased or decreased application of organicmanure on aggregates stability and soil cement in red paddy soil. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2021, 58, 978–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.C.; Zhang, J.B.; Fan, J.; Yang, X.Y.; Yi, Y.L.; Han, X.R.; Wang, D.Z.; Zhu, P.; Peng, X.H. Does animal manure application improve soil aggregation? Insights from nine long-term fertilization experiments. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 660, 1029–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.K. Effects of Different Tillage Models on Soil Physicochemical Properties and Winter Wheat Yield. Master’s Thesis, Shandong Agricultural University, Taian, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, X. Effects of Nitrogen Amounts Under Tillages on the Physical and Chemical Properties of Paddy Soil and the Nitrogen Use Efficiency. Master’s Thesis, Henan Agricultural University, Zhengzhou, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, B.W.; Liang, S.P.; Zhang, D.; Lyu, S.Q.; Xu, H.N. Effect of tillage and fertilization on particle size distribution and water stabilityof black soil aggregate. J. Northeast. Agric. Univ. 2019, 50, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.Q.; Li, R.; Jia, Z.K.; Han, Q.F.; Wang, W.; Yang, B.P. Effects of rotational tillage practices on soil properties, winter wheat yields and water-use efficiency in semi-arid areas of north-west China. Field Crops Res. 2012, 129, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Q.; Hou, R.X.; Gong, Y.S.; Li, H.W.; Fan, M.S.; Kuzyakov, Y. Effects of 11 years of conservation tillage on soil organic matter fractions in wheat monoculture in loess plateau of China. Soil Tillage Res. 2009, 106, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.T.; Zhang, Y.L.; Bei, S.K.; Li, X.L.; Reinsch, S.; Zhang, H.Y.; Zhang, J.L. Contrasting impacts of manure and inorganic fertilizer applications for nine years on soil organic carbon and its labile fractions in bulk soil and soil aggregates. CATENA 2020, 194, 104739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regelink, I.C.; Stoof, C.R.; Rousseva, S.; Weng, L.; Lair, G.J.; Kram, P.; Nikolaidis, N.P.; Kercheva, M.; Banwart, S.; Comans, R.N.J. Linkages between aggregate formation, porosity and soil chemical properties. Geoderma 2015, 247, 24–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.D.; Fu, C.X.; Zhu, H.Y.; Zhang, Q.; Ma, S.G.; Yao, Q.M. Spatial variation and stability of soil aggregates based on different deep turning years. Southwest China J. Agric. Sci. 2022, 35, 2843–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, K.; White, P.J.; Whalley, W.R.; Shen, J.B.; Shi, L. Shaping an optimal soil by root–soil interaction. Trends Plant Sci. 2017, 22, 823–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KÄtterer, T.; Bolinder, M.A.; AndrÉn, O.; Kirchmann, H.; Menichetti, L. Roots contribute more to refractory soil organic matter than above-ground crop residues, as revealed by a long-term field experiment. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2011, 141, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bissonnais, Y.; Prieto, I.; Roumet, C.; Nespoulous, J.; Metayer, J.; Huon, S.; Villatoro, M.; Stokes, A. Soil aggregate stability in mediterranean and tropical agro-ecosystems: Effect of plant roots and soil characteristics. Plant Soil 2018, 424, 303–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Y.; Li, X.L.; Yu, J.F.; Yixi, Z.M.; Song, X.; Ma, P.P.; Duan, C.W.; Xu, W.Y. Effects of different applications of organic fertilizer in degraded alpine meadow on soil aggregates and organic carbon in the source zone of Yellow River. Acta Agrestia Sin. 2022, 30, 1613–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.F. Effects of Organic Fertilizer Application on Soil Physical Properties and Aggregate Organic Carbon in Potato Field. Master’s Thesis, Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, Hohhot, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Freibauer, A.; Rounsevell, M.D.A.; Smith, P.; Verhagen, J. Carbon sequestration in the agricultural soils of Europe. Geoderma 2004, 122, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, R.Y.; Jin, T.T.; LÜ, Y.H.; Liu, G.H.; Fu, B.J. Soil carbon and nitrogen changes following afforestation of marginal cropland across a precipitation gradient in loess plateau of China. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e85426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.M.; Zhang, D.Q.; Liang, G.H.; Qiu, Q.Y.; Liu, J.X.; Zhou, G.Y.; Liu, S.Z.; Chu, G.W.; Yan, J.H. Effects of precipitation on soil organic carbon fractions in three subtropical forests in southern China. J. Plant Ecol. 2016, 9, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal Ferro, N.; Piccoli, I.; Berti, A.; Polese, R.; Morari, F. Organic carbon storage potential in deep agricultural soil layers: Evidence from long-term experiments in northeast Italy. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 300, 106967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumpel, C.; KÖgel-Knabner, I. Deep soil organic matter—A key but poorly understood component of terrestrial c cycle. Plant Soil 2011, 338, 143–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.F.; Xu, L.; Zhang, S.F.; Liang, M.J.; Qi, S.; Ding, Z.X.; Jiang, W. Responses of aggregate distribution and carbon and nitrogen contents in lime concretion black soil under wheat-corn double cropping system to different tillage modes. Shandong Agric. Sci. 2020, 52, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, B.Y.; Zhao, Y.L.; Guo, H.B.; Mu, X.Y.; Xue, Z.W.; Li, C.H. Effects of deep tillage and straw returning on different texture soils aggregate composition and stability. J. Henan Agric. Sci. 2015, 44, 65–70+107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berhe, A.A. Decomposition of organic substrates at eroding vs. Depositional landform positions. Plant Soil 2012, 350, 261–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Don, A.; BÖhme, I.H.; Dohrmann, A.B.; Poeplau, C.; Tebbe, C.C. Microbial community composition affects soil organic carbon turnover in mineral soils. Biol. Fertility Soils 2017, 53, 445–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiedung, M.; Tregurtha, C.S.; Beare, M.H.; Thomas, S.M.; Don, A. Deep soil flipping increases carbon stocks of New Zealand grasslands. Global Change Biol. 2019, 25, 2296–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Button, E.S.; Pett-Ridge, J.; Murphy, D.V.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Chadwick, D.R.; Jones, D.L. Deep-c storage: Biological, chemical and physical strategies to enhance carbon stocks in agricultural subsoils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2022, 170, 108697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Y. Research of Effects of Topsoil Control and Application of Organic Fertilizer on Topsoil-Canopy System of Winter wheat. Master’s Thesis, Henan Normal University, Xinxiang, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, H.T. Effects of Tillage and Fertilization on Physical and Chemical Properties of Shajiang Black Soil and Microbial Feedback. Master’s Thesis, Henan Agricultural University, Zhengzhou, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Harden, J.W.; Sharpe, J.M.; Parton, W.J.; Ojima, D.S.; Fries, T.L.; Huntington, T.G.; Dabney, S.M. Dynamic replacement and loss of soil carbon on eroding cropland. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 1999, 13, 885–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JobbÁgy, E.G.; Jackson, R.B. The vertical distribution of soil organic carbon and its relation to climate and vegetation. Ecol. Appl. 2000, 10, 423–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.H.; Gao, S.F.; Lu, C.Y.; Li, X.Y.; Li, F.; Wang, T.Y. Effects of different tillage and fertilization management practices on soil organic carbon and aggregates under the rice–wheat rotation system. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 212, 105071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.H.; Zhang, C.Z.; Zhang, J.B.; Liu, C.H.; Wu, Q.C. Effects of substituting manure for fertilizer on aggregation and aggregate associated carbon and nitrogen in a vertisol. Agron. J. 2019, 111, 368–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.D.; Li, H.P.; Gao, W.J.; Zhang, J.; Xu, M.G.; Hao, X.J. Effects of manures on carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus content and bacterial community in reclaimed soil aggregates. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2023, 29, 2193–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xin, X.L.; Zhu, A.N.; Yang, W.L.; Hou, Y.; Zou, W.X.; Xu, L.Y. Characteristics of the fraction of organic nitrogen in fluvo-aquic soil aggregates under long-term application of chemical fertilizer and organic manure. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2018, 55, 1494–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.S.; Jiang, X.F.; Zhu, T.; Lin, X.B.; He, S.L.; Wang, B.Q.; Wu, Y.; Lei, L.W.; Sun, Y.M. Effect of total substitution of organic fertilizer for chemical fertilizer in tea garden on distribution characteristics of inorganic nitrogen in soil mechanically stable aggregates. Acta Agric. Boreali-Sin. 2023, 38, 141–151. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Q.Y.; Wu, L.J.; Dong, F.; Yan, S.D.; Li, F.; Jia, Y.Q.; Zhang, J.C.; Zhang, R.F.; Huang, X. Subsoil tillage enhances wheat productivity, soil organic carbon and available nutrient status in dryland fields. J. Integr. Agric. 2024, 23, 251–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.H. Effect of Tillage and Nitrogen Application on Soil Properties and Yield of Wheat and Jade Double Cropping System. Master’s Thesis, Henan Institute of Science and Technology, Xinxiang, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Han, R. Study of Different Tillage Measures and Fertilizer Application on Soil Quality in System of Double Cropping. Master’s Thesis, Henan Normal University, Xinxiang, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, Y. The Effect of Organic Fertilizer Amount on the Concentration of C, N, Cu and Zn in Different Size Water-Stable Aggregates of Purple Soil. Master’s Thesis, Sichuan Normal University, Chengdu, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]






| Treatment | Practices |
|---|---|
| RT | Rotary tiller operation at 15–20 cm depth without fertilizer application |
| RTC | Rotary tiller operation at 15–20 cm depth with basal application of 600 kg/ha compound fertilizer |
| RTO | Rotary tiller operation at 15–20 cm depth with basal application of 30,000 kg/ha organic fertilizer |
| DT1O | Moldboard plowing followed by harrowing at 20–30 cm depth with basal application of 30,000 kg/ha organic fertilizer |
| DT2O | Moldboard plowing followed by harrowing at 30–40 cm depth with basal application of 30,000 kg/ha organic fertilizer |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Huo, T.; Xu, J.; Xia, F.; Hou, L.; Wang, C.; Yang, W.; Feng, M. Organic Fertilizer and Deep Tillage Synergistically Regulate Soil Physicochemical Properties and Aggregate-Associated Distribution of Carbon and Nitrogen in Dryland Foxtail Millet Fields. Agriculture 2025, 15, 2419. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15232419
Wang Z, Wang Z, Huo T, Xu J, Xia F, Hou L, Wang C, Yang W, Feng M. Organic Fertilizer and Deep Tillage Synergistically Regulate Soil Physicochemical Properties and Aggregate-Associated Distribution of Carbon and Nitrogen in Dryland Foxtail Millet Fields. Agriculture. 2025; 15(23):2419. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15232419
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zhihong, Zhigang Wang, Tingyue Huo, Jing Xu, Fan Xia, Lei Hou, Chao Wang, Wude Yang, and Meichen Feng. 2025. "Organic Fertilizer and Deep Tillage Synergistically Regulate Soil Physicochemical Properties and Aggregate-Associated Distribution of Carbon and Nitrogen in Dryland Foxtail Millet Fields" Agriculture 15, no. 23: 2419. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15232419
APA StyleWang, Z., Wang, Z., Huo, T., Xu, J., Xia, F., Hou, L., Wang, C., Yang, W., & Feng, M. (2025). Organic Fertilizer and Deep Tillage Synergistically Regulate Soil Physicochemical Properties and Aggregate-Associated Distribution of Carbon and Nitrogen in Dryland Foxtail Millet Fields. Agriculture, 15(23), 2419. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15232419





