Abstract
This research evaluated the influence of lactic acid bacteria and cellulase, individually or in combination, on the quality of mixed amaranth and sweet potato vine silages. The experiment included four groups: control group with no additives addition (CG), added cellulase group (AS1), added lactic acid bacteria group (AS2) and combined supplementation group (AS3), with five replicates per group. The ensiling period lasted for 60 days. Parameters of silage, including chemical components, fermentation profile, aerobic stability, and in vitro nutrient digestibility, were determined. The results revealed that the quality of amaranth and sweet potato vine mixed silage was improved to a certain degree after addition of two additives individually. Combining these additives observably increased (p < 0.05) the lactic acid and crude protein contents and decreased the pH, ratio of ammonia nitrogen to total nitrogen and neutral detergent fiber content of mixed silage. Compared with the CG and AS1 groups, the number of lactic acid bacteria in the AS3 group increased significantly (p < 0.05), while aerobic bacteria and mold counts showed the opposite tendency. Also, the in vitro dry matter, crude protein and neutral detergent fiber digestibility of the AS3 group were higher (p < 0.05) than those of the CG group. Combined inoculation observably reduced (p < 0.05) the ammonia nitrogen concentration and increased (p < 0.05) the propionic and butyric acid concentrations of mixed silage under in vitro incubation. In summary, the inoculation of lactic acid bacteria and cellulase can enhance the fermentation profile and nutritional values of mixed silage made from amaranth and sweet potato vine, and the best improvement effects are obtained by the combined utilization of the two additives.
1. Introduction
Roughage serves as the foundation for ruminant livestock farming, which can not only supply the crude protein and carbohydrates required to maintain production performance but also promote microbial fermentation to enhance rumen function [1]. Silage making, as a crucial preservation method, can improve the utilization efficiency of various types of roughage (especially low-quality forage) and alleviate seasonal feed shortages [2]. However, in regions where maize cultivation is restricted, the application of maize silage faces challenges. Moreover, compared with some silages made from grass, maize silage exhibits relatively reduced contents of crude protein (CP), minerals and vitamins as well as a lower rumen degradation rate [3]. With the increasing intensification of ruminant livestock farming, the demand for high-quality roughage continues to rise. However, resource shortages and the competition for grain between human beings and animals have constrained the sustainable development of the industry. Therefore, it is of great importance to fully utilize unconventional feed resources that are characterized by low cost, high yield and rich nutritional value.
In arid and semi-arid regions, forage shortage during the dry season limits ruminant production, as conventional silage crops such as maize require abundant water and compete with food crops for arable land. Developing alternative feed resources is therefore crucial for sustainable livestock systems. Amaranth, a drought- and salt-tolerant crop with high yield, can grow well on marginal lands, while sweet potato vine, a widely available agro-industrial by-product, remains underutilized. Producing mixed silage from these two materials can enhance nutrient balance, improve fermentation quality and promote the efficient use of local agricultural residues.
In recent years, the use of unconventional forage grass as feedstuff resources in sheep and cattle farming has attracted more and more attention in feed science research [4]. Amaranth (Amaranthus hypochondriacus), as a dicotyledonous plant with phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase and rubisco enzyme, has an efficient C4 photosynthetic pathway. Accordingly, amaranth can be cultivated in regions with scarce water, high temperatures and saline–alkali and nutrient-deficient soils [5].
As a type of feedstuff, amaranth offers high productivity and abundant nutrients. Based on the investigation of our research group, the fresh amaranth whole plant output reaped at the heading period is approximately 130 tons per hectare, and the dry matter (DM) yield can reach up to 20 tons per hectare [6]. On the other hand, amaranth boasts a high CP content (from 10% to 18% at different growth stages, DM basis) and favorable amino acid profiles, with lysine and sulfur-containing amino acids accounting for 4.4% of the total amino acid profile, when compared to those in maize [7,8]. Due to the advantages mentioned earlier, amaranth has been utilized as a component in the diet of livestock and poultry. In the production of dairy cows and broilers, supplementation of amaranth forage in the diet to replace soybean meal or alfalfa did not show adverse effects on productivity of animals but improved antioxidant capacity, which was conducive to saving feed resources and reducing feeding cost [9,10].
However, the direct utilization of amaranth as forage faces limitations, as the high moisture content (>80%) predisposes it to rapid spoilage, and anti-nutritional factors (e.g., oxalates and nitrates) may impair animal health [7]. Silage processing of amaranth may address these constraints through microbial fermentation, which not only preserves nutrients but also reduces anti-nutritional components.
Moisture and water-soluble carbohydrate (WSC) concentrations in raw materials are vital indicators that affect the fermentation characteristics of silage [2]. According to our previous study, the full-blossom to heading period of amaranth was the appropriate growth phase for ensiling [6]. However, the nutritional value of amaranth direct ensiling is rather low because of unsuitable moisture and WSC contents. In some countries, agricultural by-products, such as sweet potato vine, are abundant in quantity, and the DM and WSC contents of these by-products are high. Also, agricultural by-products contain a great deal of crude fiber, and the utilization efficiency is relatively low when directly provided to animals [11]. In the current study, amaranth and sweet potato vine were used as raw materials for ensiling to enhance the quality of amaranth silage and utilization rate of agricultural by-products. Although adding sweet potato vine to fresh amaranth can increase the DM content, due to the fact that sweet potato vine is abundant in crude fiber and has a low number of epiphytic microorganisms, it will dilute the content of fermentation substrate and lactic acid bacteria count. Supplementation of additives is an effective strategy to improve the fermentation characteristics and feeding value of silage.
Inoculation of lactic acid bacteria in silage can suppress the activity of unwanted microorganisms by utilizing substrates to create an acidic environment [12]. In high-fiber ensiling materials, cellulase supplementation can promote the fermentation process and improve silage quality by decomposing fiber to supply more fermentation substrate [13]. Apart from fermentation characteristics and nutritional composition, the utilization efficiency of nutrients in the rumen is an important parameter when analyzing ensiling quality. The nutrient digestibility and rumen fermentation parameters can be effectively evaluated by using the in vitro ruminal incubation method, which is commonly utilized in studying the nutritional value of roughage [14]. Thus, the purpose of the current experiment was to study the ensiling characteristics, nutritional value and in vitro ruminal fermentation and nutrient digestibility of mixed silage composed of amaranth and sweet potato vine with or without the supplementation of lactic acid bacteria and cellulase. We hypothesized that the combined inoculation of lactic acid bacteria and cellulase would synergistically enhance the fermentation characteristics and in vitro digestibility of the mixed silage. The objective was to assess the impacts of these additives, individually and in combination, on fermentation profile, nutritional components, aerobic stability and in vitro digestibility of the mixed silage.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials Preparation
At the heading period, whole plants of amaranth were manually harvested to 5 cm stubble heights by using a reaping hook. The sweet potato vine was collected after the harvest of sweet potato and then naturally sun-dried. Before ensiling, the harvested amaranth and sweet potato vine were cut into short pieces with a length ranging from 1.5 to 2 cm through a feed grinder. The chemical components of the sweet potato vine and amaranth are described in Table 1. In the present experiment, the mixing ratio of sweet potato vine to amaranth was set at 23%: 77% based on the principle of maintaining an approximately 65% moisture content in the raw ensiling materials [15]. In addition, commercial cellulase (6000 U/g; Dongheng Huadao Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Nanning, China) and lactic acid bacteria (Lactiplantibacillus plantarum ≥ 1.4 × CFU/g and Lactobacillus buchneri ≥ 6.0 × CFU/g; Yihao Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Weifang, China) were utilized as additives for improving silage quality.

Table 1.
Chemical components of sweet potato vine and amaranth.
2.2. Experimental Design
The processed amaranth and sweet potato vine were blended thoroughly to create four treatments: without silage additive addition (CG), cellulase test group (AS1, added level was 10.8 U of cellulase per kg of fresh ensiling materials), lactic acid bacteria test group (AS2, added level was Lactiplantibacillus plantarum ≥ 7 × CFU and Lactobacillus buchneri ≥ 3 × CFU per kg of fresh ensiling materials) and combined silage additives test group (AS3, the volume of the addition was same as that added separately). The additive doses were based on the producers’ recommendations. In the current experiment, cellulase and lactic acid bacteria were uniformly mixed with sterilized distilled water at ratios of 18 mg to 250 mL and 50 mg to 250 mL, respectively. Next, the mixtures were uniformly sprayed onto the ensiling materials (25 mL/kg) through a sterile sprayer. Meanwhile, distilled water was administered in the CG silage. Then, the sweet potato vine and amaranth materials were transferred into a clean 2 L fermentation container. After compaction of ensiling materials layer by layer, each container included approximately 2.2 kg of mixed materials (1.1 kg/L). The container was sealed with plastic wrap and covered with lids for the ensiling process at room temperature in the laboratory for 60 days, which was sufficient for the fermentation process to stabilize according to a previous study [16]. In total, 20 containers were prepared (4 groups with 5 replicates for each group). The containers were opened after 60 days of ensiling to obtain matured silages, which were used for analyzing fermentation characteristics, chemical compositions, aerobic stability and in vitro digestibility.
2.3. Analysis of Fermentation Indicators and Chemical Compositions in Mixed Silage
A total of 20 g of matured silage samples and 180 mL of distilled water were placed in a 250 mL conical flask (Huizeqin Digital Technology Co., Ltd., Guangzhou, China). After sealing with parafilm, the flask was placed into a freezer at 4 °C for extraction over a period of 24 h. Subsequently, 4 layers of gauze and quantitative filter paper were utilized to filter the extracted solution. After measurement of the pH value with a digital pH meter, the filtrate was carried out for centrifugation at the condition of 4 °C and 25,131× g for 10 min to obtain the supernatant. Next, the content of total nitrogen was analyzed by using a nitrogen analyzer (HD-KN60, Horde Electronic Technology Co., Ltd., Weifang, China), and the ammoniacal nitrogen (NH3-N) concentration was determined with reference to the method of phenol-sodium hypochlorite [17]. In addition, the content of lactic, acetic, butyric and propionic acids was quantified using high-performance liquid chromatography (EClassical 3200, Elite (Dalian, China) Analytical Instruments Co., Ltd., Dalian, China) following the operating steps of Wang et al. [18]. The fresh samples of mixed silage after fermentation were placed into a 65 °C oven for drying until a constant weight (48 h). Afterward, the air-dried samples were crushed by a feed crusher (Xulang Machinery Equipment Co., Ltd., Guangzhou, China) and sieved using a 1.0 mm mesh. The silage samples were utilized for measurement of DM (method 934.01), CP (method 984.13) and organic matter (OM, method 942.05) based on the AOAC methods [19]. In addition, the content of acid detergent fiber (ADF) and neutral detergent fiber (NDF) in the mixed silage was analyzed using a fiber analyzer (ANKOM A2000i, ANKOM Technology, New York, NY, USA) following the standard analytical procedures for fiber determination [20]. During the analysis of NDF, anhydrous sodium sulfite was added as a reducing agent to eliminate starch interference, and the results were corrected for residual ash. The WSC concentration of the samples was determined according to the sulfuric acid–anthrone colorimetric procedure [21].
2.4. Measurement of Microbial Number and Aerobic Stability in Mixed Silage
For analysis of microbial count, a total of 20 g of mixed silage was blended with 180 mL of sterile distilled water and then placed on an orbital shaker (JCSZ-300, Juchuang Environmental Protection Group Co., Ltd., Qingdao, China) and shaken at 180 rpm for 30 min to achieve uniformity and facilitate the release of microorganisms into the distilled water. Three successive dilutions (from 10−3 to 10−6) were performed. Subsequently, 100 μL aliquots of the diluted solutions, each in triplicate, were inoculated onto specific culture media for various microorganisms, and the microbial composition was enumerated using the plate count method. The culture plates for counting lactic acid bacteria were placed in an anaerobic chamber and then incubated at 37 °C for 48 h in a common incubator. The culture plates for coliform bacteria and aerobic bacteria were incubated under aerobic conditions in the same common incubator. Meanwhile, the culture plates for yeasts were incubated in a separate common incubator at 32 °C for 48 h [22].
A total of 250 g of matured silage samples from each container was placed into correspondingly sterilized 1 L beakers and left at room temperature (22 ± 1.2 °C) for 5 d. Meanwhile, real-time temperature loggers (TP2000, Mike Sensor Technology Co., Ltd., Hangzhou, China) were inserted into the beakers and used to detect the changes in silage temperature. Aerobic stability was regarded as the time before the temperature of the amaranth and sweet potato vine mixture silage surpassed room temperature by 2 °C [23]. The evaluation period was limited to 5 d because the onset of aerobic deterioration is mainly driven by yeasts that rapidly oxidize lactic acid and WSC once oxygen penetrates the silage mass, releasing heat and causing a temperature rise within approximately 48 to 96 h. Thus, the initial heating event, which represents the standard endpoint for aerobic stability, can be captured within this window, while longer exposures may lead to surface drying and secondary mold growth unrelated to the primary heating stage [16]. After 5 d of aerobic exposure, the mixed silage samples were collected to analyze the microbial counts with the procedures mentioned earlier.
2.5. In Vitro Fermentation, Nutrient Digestibility and Fermentation Characteristic of Mixed Silage
The rumen fluid samples were obtained from 4 healthy male Hu sheep (BW = 31.88 ± 1.18 kg) by utilizing ruminal fistulas before morning feeding. All sheep were fed an identical diet twice each day at 09:00 and 18:00, respectively, permitting approximately 10% orts with free access to drink clean water, and the sheep were reared in a sheepfold (10 m × 8 m). Feed ingredients and nutritional levels of the diet are described in Table 2. In the diet, the mineral element and vitamin levels of premix were provided by feed enterprise, and the ether extract (EE, method 954.02) and CP were analyzed following the AOAC procedures [19]. The analytical methods of NDF and ADF were mentioned earlier, and the contents of Ca and P in the diet were determined by permanganate titration and spectrophotometry, respectively, according to the national standards (GB/T 6436-2018 and GB/T 6437-2018) [24,25]. Before collecting ruminal fluid samples, the sheep had received the experimental diet for one month. The collected ruminal fluid samples from sheep were filtered using 4 layers of gauze. Immediately, the ruminal fluids were preserved in prewarmed thermoses (39 °C), which were full of carbon dioxide for the subsequent trial, and then transported to the laboratory. The processing time from collection to the start of in vitro incubation was strictly limited to less than 30 min to preserve microbial viability.
Ruminal fluid samples were blended with artificial buffer solution, which was prepared according to the procedures described by a previous study [26], at a volume ratio of 1 to 2 to obtain the mixed culture solution. Two grams of dried mixed silage from each replicate was sealed in filter bags (F57, 4 cm × 6 cm, aperture 25 µm, Ode New Filter Co., Ltd., Xinxiang, China) and placed in anaerobic fermentation flasks (Mancang Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing, China). Meanwhile, 200 mL of mixed culture solution was added in these flasks. In addition, a blank group without addition of mixed silage samples was used to correct the gas production of the inoculum. The substrate-to-medium ratio (1:100) was adopted according to the in vitro fermentation protocol described by Bai et al. [27], ensuring sufficient microbial activity and buffering capacity during incubation. Then, these flasks were sealed and incubated under the condition of 39 °C for 72 h with continuous carbon dioxide flushing. The total volume of each fermentation flask was 500 mL. Gas production (GP) was collected at intervals (2, 4, 8, 12, 24, 48, and 72 h) with 5 replicates for each group using a gas recording system (MC-ABSF-II, Mancang Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing, China). The system was calibrated prior to the experiment by injecting known volumes of air, and all reported gas volumes were standardized to standard temperature and pressure. The production of cumulative GP was used to analyze the kinetic parameter of in vitro GP based on a model described by Øskov and McDonald [28]. The computational process was carried out in the SAS statistical software (version 9.4) with the equation below:
GPt = A + B (1 − e−Ct)
“GPt” represents the cumulative GP at different times (mL/g); “A” is the GP of the rapid fermentation fraction (mL/g); “B” is the GP of the slow fermentation fraction (mL/g); “C” is the rate of GP (%/h) and “t” represents the fermentation time (h).
After 72 h of incubation, the pH of the rumen fluid samples in the fermentation flasks was measured. The incubation fluids were collected by filtration with gauze, and then supernatant samples were obtained by centrifugation of the incubation fluids under the condition of 25,131× g for 10 min, which was used for subsequent analysis. The in vitro ruminal concentrations of NH3-N and microbial protein (MCP) [29] were determined and quantified using the methods of phenol-sodium hypochlorite [17] and Lowry’s assay [29], respectively. The concentrations of individual volatile fatty acids (VFAs), including acetic, propionic and butyric acids, were determined using gas chromatography (GC-2010, Shimadzu Corporation, Kyoto, Japan) [18,25]. After 72 h of fermentation, the bags were immediately rinsed under cold running water to halt microbial activity. Then, the bags were washed in a commercial washing machine with multiple cold-water cycles until the effluent ran clear. Subsequently, the bags were dried in a forced-air oven at 65 °C for 48 h to determine dry matter disappearance. In addition, residues of the filter bags were washed and dried for measurement of DM, CP, NDF, ADF and OM, which were used to calculate the corresponding in vitro nutrient digestibility, including in vitro dry matter digestibility (IVDMD), in vitro crude protein digestibility (IVCPD), in vitro neutral detergent fiber digestibility (IVNDFD), in vitro acid detergent fiber digestibility (IVADFD) and in vitro organic matter digestibility (IVOMD), through the loss of nutritional components [22].

Table 2.
Ingredient compositions and nutritional levels of diet used in this experiment (DM basis).
Table 2.
Ingredient compositions and nutritional levels of diet used in this experiment (DM basis).
| Ingredients (%) | Nutritional Levels (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Alfalfa hay | 9.58 | CP | 14.61 |
| Sweet potato vine | 25.42 | EE | 2.87 |
| Maize | 33.75 | NDF | 33.20 |
| Wheat bran | 6.26 | ADF | 20.07 |
| Soybean meal | 6.78 | Ca | 0.91 |
| Rapeseed meal | 4.82 | P | 0.48 |
| Cottonseed meal | 5.64 | ME b, MJ/kg | 9.52 |
| NaCl | 0.52 | ||
| Limestone | 0.99 | ||
| CaHPO4 | 0.34 | ||
| NaHCO3 | 0.90 | ||
| Premix a | 5.00 |
DM, dry matter; CP, crude protein; EE, ether extract; NDF, neutral detergent fiber; ADF, acid detergent fiber; ME, metabolic energy. a Premix used in this study supplied the following per kg of experimental diet: 75 mg of Fe, 60 mg of Zn, 90 mg of Mn, 11 mg of Cu, 0.42 mg of I, 0.36 mg of Se, 0.18 mg of Co, 10,000 IU of vitamin A, 3000 IU of vitamin D3, 184 IU of vitamin E. b ME is a calculated value according to the standard (NY/T816-2021) [30], whereas remaining nutritional levels were measured in the laboratory.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
Prior to the analysis, a normality test was conducted on all the data, and the data were found to conform to a normal distribution. Variables of all data, including chemical components, fermentation parameters, microbial counts, aerobic stability and in vitro digestibility, were analyzed by the one-way ANOVA methods of the SPSS statistical software (version 24.0) on the basis of each replicate serving as an experimental unit. Tukey’s test was performed to assess the differences in different groups. The results are shown with mean values and standard error of means. Statistical significance was accepted at a threshold of p < 0.05, while p-values between 0.05 and 0.10 were interpreted as indicating a trend.
3. Results
3.1. Fermentation Indicators of Amaranth and Sweet Potato Vine Mixed Silage
Compared with the CG group, supplementation of lactic acid bacteria significantly reduced (p < 0.05) the pH and propionic acid content of the mixture silage, and the silage supplemented with cellulase significantly decreased (p < 0.05) the ratio of NH3-N to total nitrogen (Table 3). Also, additive supplementation obviously reduced (p < 0.05) the concentration of acetic acid in the mixed silage. Butyric acid was not detected in the AS3 group. Compared with the CG and AS1 groups, the lactic acid content as well as the lactic acid-to-acetic acid ratio of the AS2 and AS3 groups were observably elevated (p < 0.05).

Table 3.
Fermentation profile of mixed silages of amaranth and sweet potato vine with microbial and enzymatic additives.
3.2. Chemical Components of Amaranth and Sweet Potato Vine Mixed Silage
The content of WSC and OM was not obviously different (p > 0.05) among all silages (Table 4). However, the DM content of the mixture silage inoculated with lactic acid bacteria was observably increased as compared with the AS1 treatment (p < 0.05). The CP content of the AS3 silage was higher (p < 0.05) than that of the CG and AS2 silages. Supplementation of cellulase significantly decreased (p < 0.05) the NDF and ADF contents of the mixed silage composed of amaranth and sweet potato vine.

Table 4.
Chemical composition of mixed silages of amaranth and sweet potato vine with microbial and enzymatic additives.
3.3. Microbial Counts of Amaranth and Sweet Potato Vine Mixed Silage
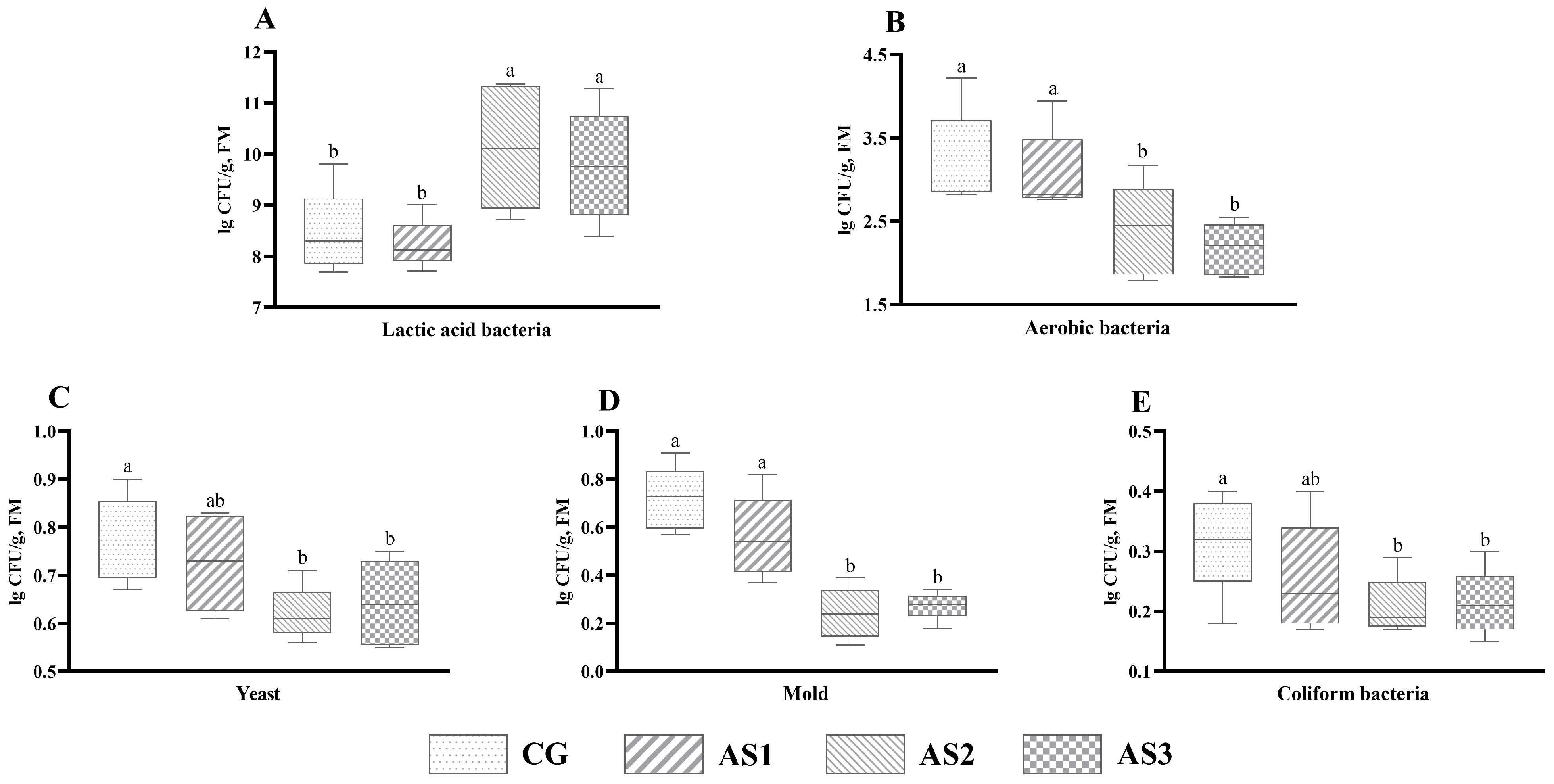
Obviously, compared with the CG and AS1 silages, the number of lactic acid bacteria (Figure 1A) in the AS2 and AS3 silages was significantly increased (p < 0.05), whereas the aerobic bacteria (Figure 1B) and mold (Figure 1D) counts were markedly decreased (p < 0.05). In addition, the yeast (Figure 1C) and coliform bacteria (Figure 1E) counts in the AS2 and AS3 silages were lower (p < 0.05) than those of the CG silage.
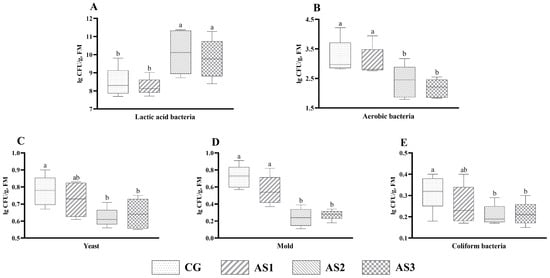
Figure 1.
The influence of additives on microbial counts of mixed silage prepared with amaranth and sweet potato vine. (A) Lactic acid bacteria; (B) aerobic bacteria; (C) yeast; (D) mold; (E) coliform bacteria. FM, fresh matter; CG, control without additives; AS1, cellulase treatment group; AS2, lactic acid bacteria treatment group; AS3, combined silage additives treatment group. Each group had 5 replicates. The line in the column represents the median. In addition, the line above the column represents the maximum, and the line below the column represents the minimum value. Different small letters above the columns indicate significant differences (p < 0.05).
3.4. Aerobic Stability of Amaranth and Sweet Potato Vine Mixed Silage
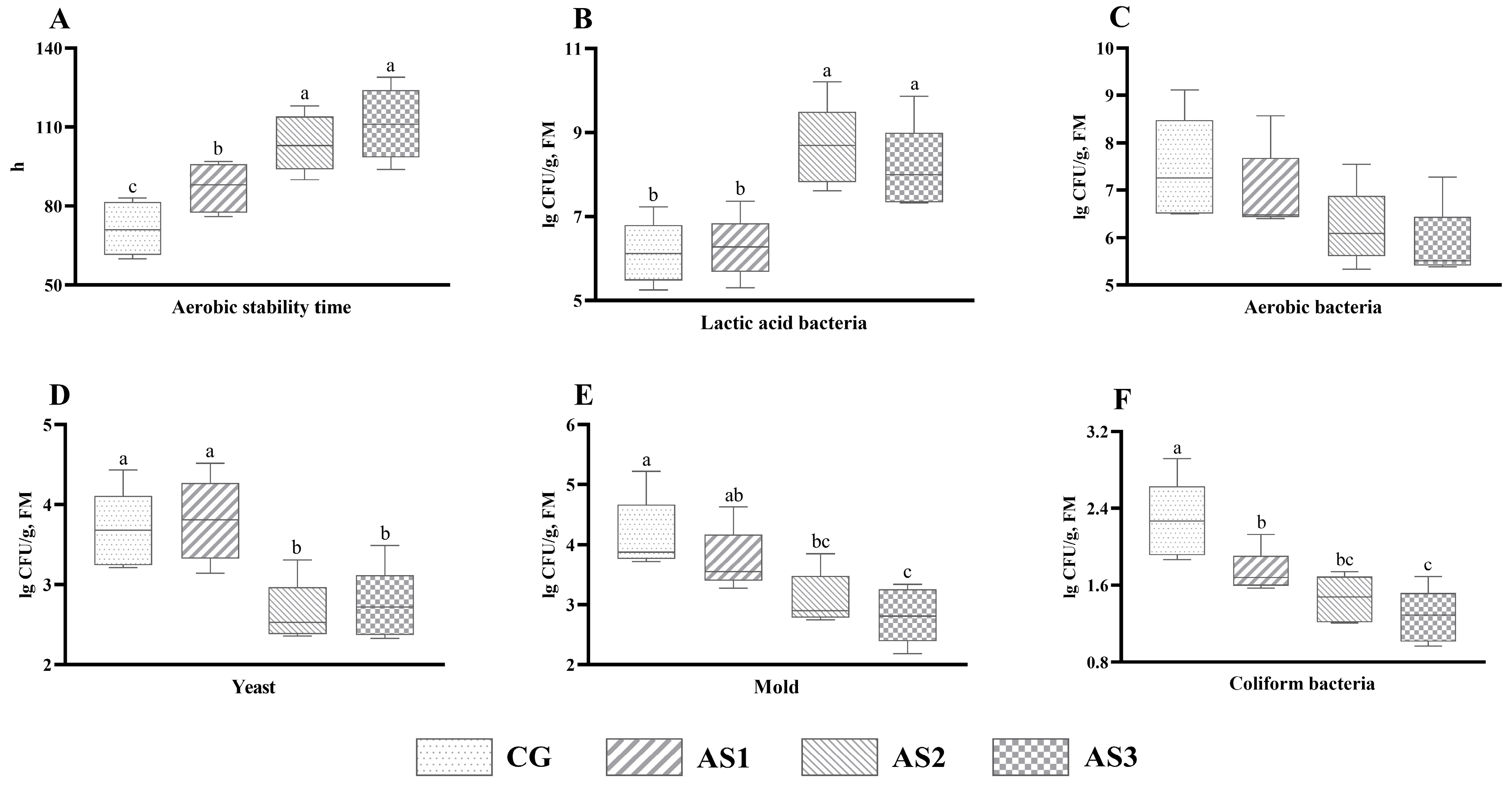
Silage additive inoculation showed a significant improvement (p < 0.05) in aerobic stability time (p < 0.05) (Figure 2A). Compared with the CG and AS1 silages, the count of lactic acid bacteria (Figure 2B) in the mixed silage of the AS2 and AS3 silages was obviously elevated (p < 0.05), whereas the yeast count (Figure 2D) displayed the opposite tendency. The number of aerobic bacteria (Figure 2C) in the AS3 silage tended to be reduced (0.05 < p < 0.10) by 21.48% as compared with the CG silage. In addition, the count of mold (Figure 2E) in the AS2 and AS3 groups was lower (p < 0.05) than the CG group. Likewise, combined inoculation of additives obviously reduced (p < 0.05) the number of coliform bacteria (Figure 2F) in the silage as compared with the CG and AS1 groups.
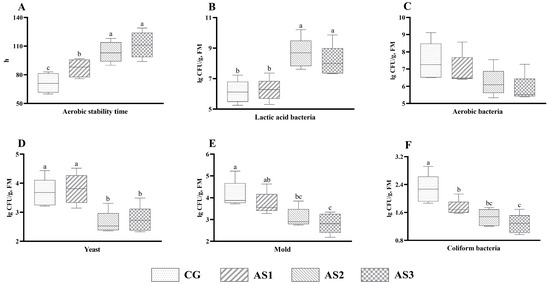
Figure 2.
The influence of additives on microbial population after silo opening and the aerobic stability of mixed silage prepared with amaranth and sweet potato vine. (A) Aerobic stability time; (B) lactic acid bacteria; (C) aerobic bacteria; (D) yeast; (E) mold; (F) coliform bacteria. FM, fresh matter; CG, control without additives; AS1, cellulase treatment group; AS2, lactic acid bacteria treatment group; AS3, combined silage additives treatment group. Each group had 5 replicates. The line in the column represents the median. In addition, the line above the column represents the maximum, and the line below the column represents the minimum value. Different small letters above the columns indicate significant differences (p < 0.05).
3.5. In Vitro Nutrient Digestibility of Amaranth and Sweet Potato Vine Mixed Silage
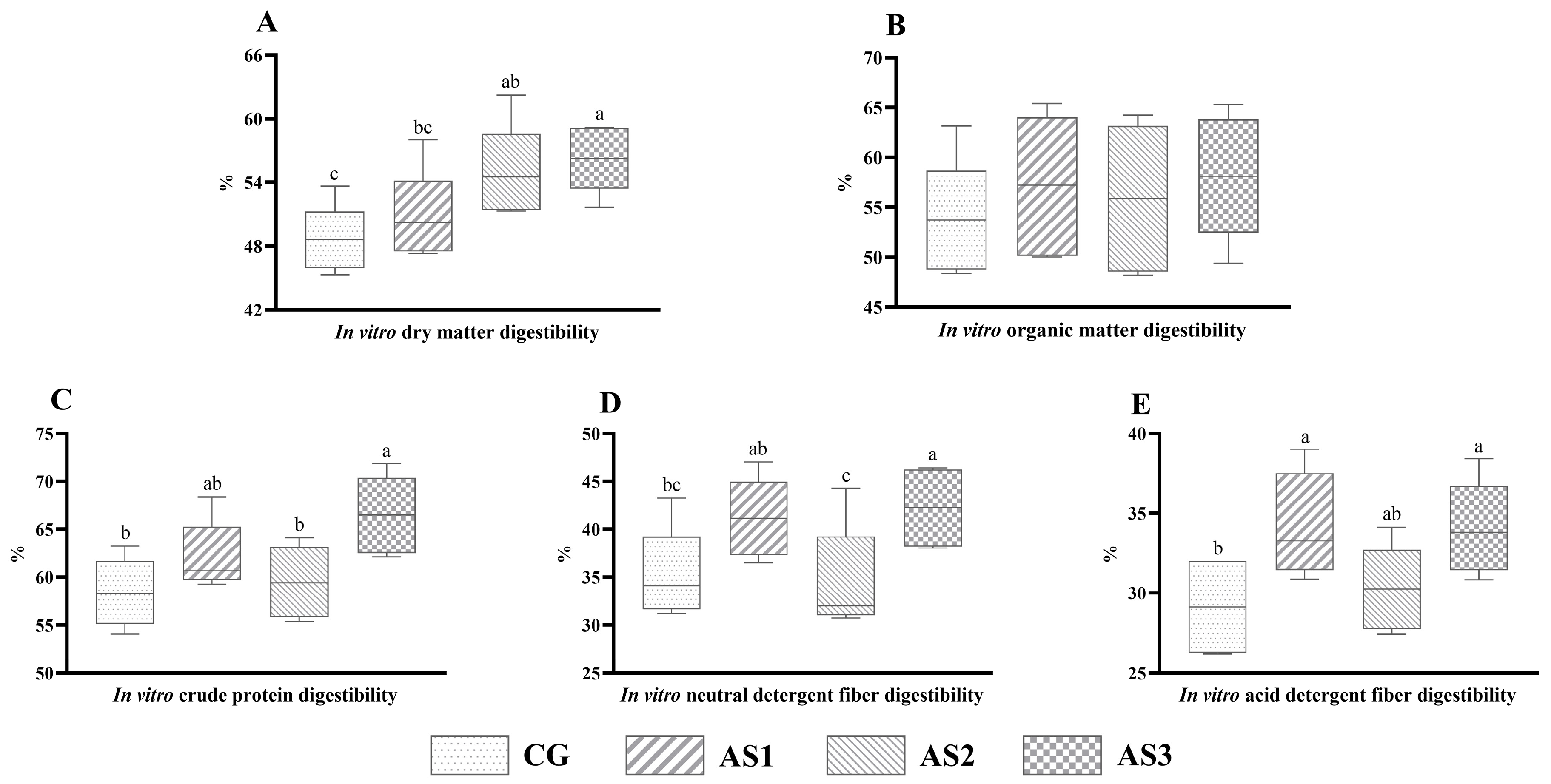
No obvious difference (p > 0.05) in IVOMD (Figure 3B) was observed among all mixed silages. Nevertheless, the IVDMD (Figure 3A) of the AS3 silage was higher (p < 0.05) than that of the CG and AS1 silages. Compared with the CG and AS2 silages, the IVCPD (Figure 3C) of the AS3 silage was increased (p < 0.05) by 13.81% and 11.74%, respectively. The IVNDFD (Figure 3D) of the mixed silage in the AS3 group exhibited an observable increase (p < 0.05) as compared with the CG and AS2 groups. Moreover, inoculation of cellulase significantly enhanced (p < 0.05) the IVADFD (Figure 3E) of the silage.
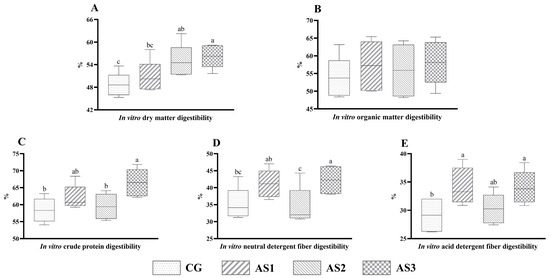
Figure 3.
The influence of additives on in vitro dry matter (A), organic matter (B), crude protein (C), neutral detergent fiber (D) and acid detergent fiber (E) digestibility of mixed silage prepared with amaranth and sweet potato vine. CG, control without additives; AS1, cellulase treatment group; AS2, lactic acid bacteria treatment group; AS3, combined silage additives treatment group. Each group had 5 replicates. The line in the column represents the median. In addition, the line above the column represents the maximum, and the line below the column represents the minimum value. Different small letters above the columns indicate significant differences (p < 0.05).
3.6. In Vitro Gas Production and Ruminal Fermentation Characteristics of Amaranth and Sweet Potato Vine Mixed Silage
The in vitro GP at 2 h was not different (p > 0.05) among all the mixed silages (Table 5). However, at 4 h, the GP of the AS3 group was higher (p < 0.05) than the CG group. Compared with the CG silage, the GP of the mixed silage at 8, 12 and 48 h was significantly increased (p < 0.05) after lactic acid bacteria intervention. Additionally, the GP of the AS2 and AS3 groups tended to be higher (0.05 < p < 0.10) than that of the CG group at 24 h. At 72 h, the in vitro GP of the AS3 silage was slightly increased (0.05 < p < 0.10) by 10.51% when compared to the CG silage.

Table 5.
The influence of additives on in vitro gas production of mixed silage prepared with amaranth and sweet potato vine (mL/g dry matter).
Compared with the CG and AS1 groups, the GP of the fast fermentation fraction in the AS3 group was significantly increased (p < 0.05) (Table 6). Also, additive supplementation showed an obvious improvement (p < 0.05) in the GP of the slow fermentation fraction and potential GP of the mixed silage.

Table 6.
The influence of additives on in vitro gas production parameters of mixed silage prepared with amaranth and sweet potato vine (dry matter).
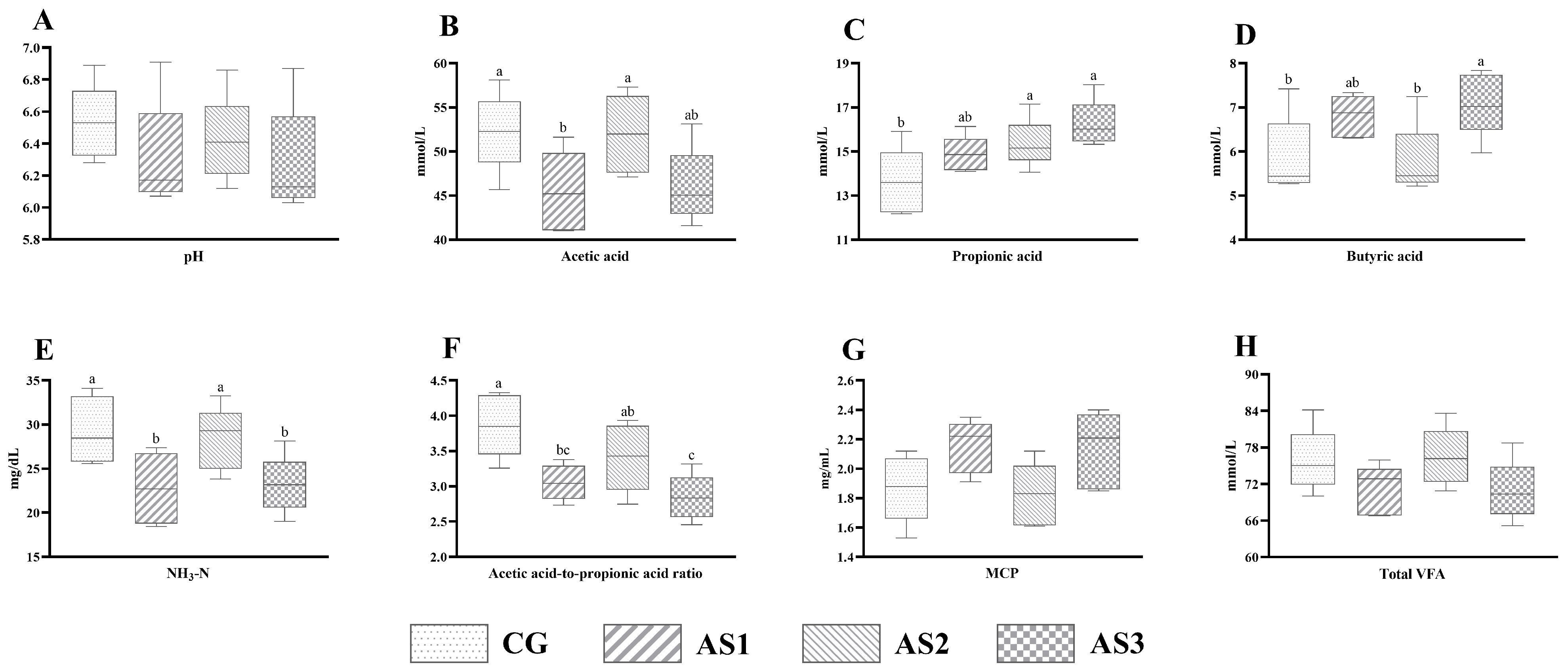
No obvious difference (p > 0.05) in in vitro rumen pH (Figure 4A) and total VFA (Figure 4H) concentration was found among all the mixed silages. The ruminal acetic acid (Figure 4B) content of the CG and AS2 groups was higher (p < 0.05) than the AS1 group. Lactic acid bacteria inoculation observably increased (p < 0.05) the propionic acid (Figure 4C) content. Also, the butyric acid (Figure 4D) concentration of the AS3 group was higher (p < 0.05) than that of the CG and AS2 groups. Compared with the CG silage, the NH3-N (Figure 4E) content and ratio of acetic acid to propionic acid (Figure 4F) of the AS1 and AS3 silages were obviously decreased (p < 0.05). Moreover, the in vitro ruminal MCP (Figure 4G) concentration of the AS1 and AS3 groups tended to be higher (0.05 < p < 0.10) than the AS2 group.
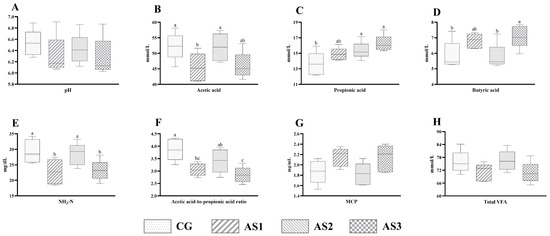
Figure 4.
The influence of additives on in vitro ruminal fermentation characteristics of mixed silage prepared with amaranth and sweet potato vine. (A) pH; (B) acetic acid; (C) propionic acid; (D) butyric acid; (E) NH3-N, ammonia nitrogen; (F) acetic acid-to-propionic acid ratio; (G) MCP, microbial protein; (H) total VFA, total volatile fatty acids; CG, control without additives; AS1, cellulase treatment group; AS2, lactic acid bacteria treatment group; AS3, combined silage additives treatment group. Each group had 5 replicates. The line in the column represents the median. In addition, the line above the column represents the maximum, and the line below the column represents the minimum value. Different small letters above the columns indicate significant differences (p < 0.05).
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Additives on the Chemical Components of Mixed Silage
A pH value below 4.2 is widely recognized as a key index of well-preserved silage [2]. In the current research, with the exception of the CG group, the pH in the additives groups remained under this threshold, implying that the amaranth and sweet potato vine mixed silage were well stored after additive treatment.
Compared with the CG group, the lactic acid bacteria-treated silages exhibited significantly lower pH values. Specifically, the AS3 group showed the lowest pH, approximately 9.7% lower than the CG group, accompanied by a 36% increase in lactic acid content. This improvement is likely attributable to the enhanced fermentative activity of lactic acid bacteria, while cellulase complemented this effect by releasing WSC from plant fibers, thus providing additional substrates for bacterial growth and amplifying acid production through a synergistic mechanism. Similar findings have been reported in oat silage, where the combination of lactic acid bacteria and cellulase reduced pH and increased lactic acid content [31]. Beyond lactic acid production, lactic acid bacteria can also compete with acetic-acid-producing bacteria for WSC substrates and secrete antimicrobial compounds that selectively inhibit their growth [32]. As a result, the lactic-to-acetic acid ratio in the AS3 group increased by approximately 1.8-fold, reflecting enhanced fermentation quality [16].
In our study, the ratio of lactic to acetic acid increased markedly in the AS2 and AS3 groups. The accumulation of propionic and butyric acids is associated with energy losses during fermentation, since the conversion of lactic acid to butyric acid reduces DM content [33], as verified by the DM result. Moreover, increased butyric acid levels in silage have been linked to an increased risk of subclinical ketosis in dairy cows, raising production costs and impairing animal performance [34]. In the AS3 silage, the absence of butyric acid and the 68% reduction in propionic acid provided strong evidence that spoilage microorganisms were effectively suppressed. These findings underscore the synergistic role of the two additives in shaping a fermentation environment that is unfavorable to undesirable microbes.
The concentration of NH3-N, expressed as a percentage of total nitrogen (% of total N), is another key indicator of silage quality, reflecting the degree of protein degradation during ensiling. Compared with CG group, the ratio of NH3-N to total nitrogen was reduced by 27% in the AS3 group, indicating inhibited proteolysis and improved nitrogen retention [35]. In this study, the cellulase inoculation significantly reduced this ratio, with the lowest value recorded in combination treatment of additives, which suggested that improved nitrogen preservation was closely related to the ability of additives to limit the proliferation of proteolytic microorganisms.
Silage pH plays a decisive role in suppressing protein breakdown. Here, the AS3 group showed the lowest pH value. Proteolysis is likely inhibited under acidic conditions in two distinct ways. The activity of protease-producing microorganisms such as Bacillus and Escherichia coli is diminished [36], and plant-derived proteases are suppressed, thereby restricting endogenous enzymatic protein hydrolysis [15]. Furthermore, lactic acid bacteria and cellulase may act synergistically to promote nitrification, in which NH3-N is converted into nitrate nitrogen [37], potentially contributing to the lower NH3-N–to-total nitrogen ratio observed in our experiment. Nonetheless, the precise mechanisms underlying nitrogen preservation with additive treatments remain insufficiently understood and warrant further investigation.
4.2. Effects of Additives on the Fermentation Parameters of Mixed Silage
The chemical component of silage, particularly DM, CP, NDF and ADF, serves as a fundamental criterion for evaluating nutritional values in ruminant feed and directly influences nutrient intake and utilization efficiency in animals [15]. In the present study, compared with the CG and AS1 groups, the DM content was increased in the AS2 and AS3 treatments. This positive effect may be attributed to the ability of lactic acid bacteria to improve silage fermentation and OM preservation, which has been associated with reduced effluent losses in a previous study [38]. Silage effluent typically contains approximately 8% of the total DM content, representing a major pathway of nutrient loss during ensiling. Although effluent production is largely governed by the initial DM content, plant moisture and compaction level rather than by the direct metabolic activity of lactic acid bacteria, the rapid acidification induced by these bacteria accelerates the establishment of anaerobic conditions, suppresses proteolytic and spoilage microorganisms and consequently decreases the solubilization of nutrients into effluent. Therefore, lactic acid bacteria indirectly contribute to lower effluent outflow by stabilizing fermentation and reducing nutrient leaching from the silages. Nevertheless, the underlying mechanisms responsible for this effect require further investigation.
During silage fermentation, proteases produced by spoilage microorganisms such as Bacillus can degrade CP into NH3-N, whereas an acidic environment suppresses their activity [39]. Cellulase hydrolyzes structural polysaccharides to release substrates for lactic acid fermentation, thereby promoting lactic acid production, lowering silage pH, reducing the activity of plant-derived proteases and ultimately inhibiting CP degradation [40]. In addition, homolactic fermentation by strains such as Lactiplantibacillus plantarum can alleviate protein breakdown caused by insufficient lactic acid production, thus effectively reducing nutrient losses during ensiling [41]. Our results confirmed that the combined application of microbial and enzymatic additives significantly enhanced the CP content of mixed silage. Similarly, Zhao et al. reported comparable results in mixed silage prepared from soybean residue and maize stover [42].
WSCs constitute the primary substrates for lactic acid fermentation and are intimately linked to fiber degradation. During ensiling, the proliferation and acid production of lactic acid bacteria rely on a steady supply of WSCs, most of which are ultimately converted into lactic acid [43]. Consequently, WSC concentrations in mixed silage typically decline over time. For high-fiber forages such as amaranth and sweet potato vines, cellulase plays a particularly important role. By hydrolyzing cellulose and hemicellulose, it releases WSCs that lactic acid bacteria can utilize, thereby ensuring sufficient fermentable substrates [40].
This enzymatic process also directly the reduced NDF and ADF contents, and the contents of NDF and ADF in the AS3 treatment were 9.5% and 11.6% lower than those in the CG group, respectively. These results corroborate the findings of Zhao et al. [44], who reported similar reductions in fiber fractions when cellulase was applied to mixed silage of wet brewer’s grains and maize stalk. A comprehensive evaluation of the chemical composition indicated that the AS3 silage achieved the most favorable profile, with higher DM and CP contents and lower NDF and ADF levels. This outcome likely stems from a synergistic mechanism: cellulase degrades fiber to release WSCs, supplying fermentable substrates for lactic acid bacteria, while lactic acid bacteria sustain an acidic environment that enhances cellulase activity and inhibits spoilage organisms.
4.3. Effects of Additives on the Microbial Population of Mixed Silage
The dynamic fluctuations in microbial populations directly shape the metabolic trajectory of silage fermentation, with lactic acid bacteria and controlled growth of harmful microorganisms jointly determining silage quality [39]. In the present study, the lactic acid bacteria count increased significantly in the AS2 and AS3 treatments compared with the CG treatment, while the numbers of yeasts, molds and aerobic bacteria were markedly decreased. The mechanisms underlying lactic acid bacteria enrichment differed between treatments: in the AS2 silage, the rapid establishment of lactic acid bacteria dominance was achieved through direct inoculation of exogenous strains, whereas in the AS3 silage, cellulase-mediated fiber degradation released WSCs, which provided substrates for indigenous and external bacteria proliferation, thereby promoting their growth through a distinct pathway. The proliferation and acid production of lactic acid bacteria further contributed to the development of an acidic environment that inhibited the metabolic activity of harmful microorganisms. Similarly, a previous study found that the combined utilization of lactic acid bacteria and cellulase effectively reduced the number of molds, yeasts and coliforms in mixed silages of whole-plant maize and peanut vines [35], which was in agreement with our findings.
Notably, in the CG and AS1 groups, the relatively low count of lactic acid bacteria allowed undesirable microorganisms to proliferate more actively, and trace amounts of butyric acid were detected. This observation concurs with Zhao et al. [45], who suggested that butyric acid can be produced via the metabolism of harmful microbes. The presence of butyric acid not only indicates a potential risk of silage spoilage but may also reduce dry matter preservation and negatively affect ruminant health [34]. These findings underscore the importance of maintaining a favorable balance between lactic acid bacteria and undesirable microorganisms during the ensiling process.
4.4. Effects of Additives on the Aerobic Stability of Mixed Silage
Exposure of silage to air stimulates the activity of aerobic microorganisms, which accelerates nutrient depletion and heat generation, thereby raising pH and exacerbating nutrient losses [23]. Our experiment showed that supplementation of additives significantly extended the aerobic stability of silage, with the AS3 silage exhibiting the longest stability period, indicating that additive treatments can effectively improve aerobic stability. Yeasts are regarded as the key initiators of aerobic spoilage, and the count is closely associated with the onset of heating in silage [46]. The improvement in aerobic stability observed with lactic acid bacteria inoculation may therefore be explained by their increased acetic acid formation, which inhibits yeast and mold activities through its antifungal activity [47]. In contrast, excessive lactic acid may serve as a substrate for aerobic microorganisms, accelerating spoilage. Lactobacillus buchneri enhances stability by converting lactic acid into acetic acid via heterofermentative metabolism and producing additional antifungal metabolites, such as propionic acid and ethyl esters, which further preserve silage after exposure to air [48]. In addition to yeasts, the counts of mold and aerobic bacteria were comparable between the CG and AS1 groups, which highlighted the limitations of applying a single additive. Although cellulase in the AS1 group supplied sufficient fermentable substrates, the absence of exogenous lactic acid bacteria restricted lactic acid production and prevented the establishment of an acidic environment that was capable of inhibiting undesirable microorganisms [44].
Compared with the CG silage, the aerobic bacteria count in the AS3 silage was significantly reduced by 21.48%, suggesting that the synergistic effects of substrate supply and microbial regulation constitute an effective strategy for enhancing the inhibition of undesirable microorganisms after aerobic exposure. In dairy production, coliforms are of particular concern because their proliferation increases the risk of endometritis. In this study, although coliform counts increased after aerobic exposure across treatments, their levels in the additives groups remained significantly lower than in the CG silage. This finding implies that, in practical farming, even when minor spoilage occurs after silage opening, additive-treated silages are better able to suppress pathogenic bacteria, thereby directly improving feeding safety and providing greater health protection for dairy cows.
4.5. Effects of Additives on the In Vitro Digestibility of Mixed Silage
In vitro nutrient digestibility provides a direct measure of the efficiency with which ruminants obtain nutrients from silage and is strongly influenced by its chemical composition and fermentation quality [49]. In this study, the silages receiving both lactic acid bacteria and cellulase demonstrated significantly higher IVDMD and IVCPD than the CG silage, suggesting that the dual-additive approach not only promoted nutrient digestibility but also confirmed the synergistic benefits of combining cellulase with lactic acid bacteria. Mechanistically, the improvement can be attributed to additives creating an acidic environment that restricts the activity of spoilage microorganisms and minimizes nutrient losses [15]. Similar findings have been reported in Leymus chinensis silage, where the combined use of lactic acid bacteria and cellulase markedly improved IVDMD and IVCPD [50]. Given that crude fiber content is a key determinant of IVNDFD and IVADFD, our results further indicated that adding cellulase to amaranth and sweet potato vine mixed silage significantly increased IVNDFD and IVADFD, likely by disrupting fiber chemical bonds and weakening cell wall integrity, thereby facilitating microbial adhesion in the rumen and subsequent degradation [51]. Collectively, these results demonstrated that the combined application of the two additives produced the most pronounced improvements in in vitro digestibility.
4.6. Effects of Additives on the In Vitro Gas Production and Rumen Fermentation of Mixed Silage
In vitro GP is a widely used parameter to analyze the intensity of rumen microbial fermentation and efficiency of energy conversion. Total GP reflects the overall fermentative potential, whereas the rate of GP indicates the efficiency of fermentation onset [52]. In this study, the dual-additive treatment increased both GP and potential GP between 4 and 72 h compared with the CG silage. These improvements can be explained by two complementary mechanisms. On the one hand, cellulase depolymerized NDF and ADF by cleaving glycosidic bonds within the fiber matrix, thereby releasing soluble substrates and expanding the pool of fermentable material available to rumen microorganisms, which enriched substrate supply and promoted microbial growth and metabolic activity [53], a conclusion supported by the chemical composition data. On the other hand, lactic-acid-generated silage fermentation decreased the pH of the in vitro ruminal environment, reducing the activity of spoilage organisms while favoring the proliferation of enzyme-producing microbes. This, in turn, accelerated the conversion of substrates into gas and VFAs [54].
A suitably acidic pH further enhanced microbial metabolism and substrate utilization, thereby increasing GP. Given that 70~80% of metabolizable energy in ruminants is derived from VFAs, these findings suggested that dual-additive silage can provide rapidly available energy during the critical early phase of rumen fermentation, which is helpful for reducing energy losses and particularly benefiting high-producing dairy systems with high energy demands. In contrast, low-quality roughages often shift fermentation toward an acetate-dominant pathway, which elevates methane output and reduces feed energy efficiency [55]. The cellulase and lactic acid bacteria combination mitigates these limitations and enhances the energy utilization efficiency of amaranth and sweet potato vine mixed silage.
In vitro rumen fermentation parameters provide critical insights into the nutritive value of silage by reflecting microbial activity, energy generation and nitrogen metabolism [49]. In our experiment, inoculation with lactic acid bacteria significantly increased the propionic acid concentration, while the AS3 silage exhibited a notably higher butyric acid level than both the CG and AS2 silage. Given that glucose is an important energy source for ruminants, derived largely from hepatic gluconeogenesis with propionate as a key precursor [56], the marked increase in propionic acid content in the AS3 group suggested that the mixed silage produced more metabolites readily converted into usable energy. Furthermore, cellulase supplementation markedly reduced the acetic-to-propionic acid ratio of mixed silage, reflecting a shift toward a propionate-dominant fermentation profile. As this metabolic orientation reduces energy loss through methane formation, it is expected to improve dietary energy efficiency and, in turn, enhance growth and production performance in ruminants [57].
We further observed that the NH3-N concentration was significantly lower in the AS1 and AS3 silages compared with the CG and AS2 silages. Interestingly, the AS3 treatment also exhibited a slightly higher MCP content than the AS2 group. The concurrent decline in NH3-N together with the rise in MCP demonstrated that nitrogen in the AS3 silage was more efficiently assimilated by ruminal microbes, thereby confirming a marked enhancement in microbial nitrogen conversion efficiency. This finding suggested that cellulase supplied abundant carbon skeletons and energy sources to ruminal microbes by degrading fiber, while lactic acid bacteria optimized the fermentation milieu by reducing rumen pH and inhibiting methanogenesis, thus reducing energy dissipation. Acting in concert, these processes substantially improved the energy supply and microenvironment required for the growth of nitrogen-utilizing bacteria [58].
More notably, the MCP content increased significantly, which was in agreement with the earlier IVCPD measurement. As a nitrogen source that can be directly absorbed and utilized by ruminants, an elevated MCP concentration translates into improved crude protein digestion and absorption efficiency [57]. The redirection of nitrogen from NH3-N to MCP, together with the improvement in IVCPD, clearly revealed the intrinsic links among these indicators and provided strong evidence that the additives markedly optimized rumen nitrogen metabolism. It is worth emphasizing that the rumen microbiota functions as the central conduit integrating these changes. Evidence from related study on the synergistic action of microbial and enzymatic additives in regulating the fermentation of woody plant silages likewise supported our interpretation that the advantage of AS3 reflected a targeted optimization of microbial metabolism [59]. Nonetheless, as the present experiment was conducted in vitro, further in vivo feeding studies are required to validate how amaranth and sweet potato vine mixed silage supplemented with lactic acid bacteria and cellulase influences rumen microbial ecology and production performance across different growth stages of ruminants, thereby providing a more comprehensive foundation for large-scale application.
5. Conclusions
The results of this research demonstrate that the addition of cellulase (10.8 U per kg of fresh ensiling materials) or lactic acid bacteria (Lactiplantibacillus plantarum ≥ 7 × CFU and Lactobacillus buchneri ≥ 3 × CFU per kg of fresh ensiling materials) has positive effects on the improvement in the quality of mixed silage composed of amaranth and sweet potato vine. The combined utilization of these two additives increased the lactic acid, DM and CP contents and decreased the NDF and ADF contents and yeast and mold counts as well as enhancing the aerobic stability of mixed silage. Furthermore, this combination enhanced its nutritive value, as reflected by the superior in vitro digestibility and ruminal fermentation parameters. Future studies should focus on elucidating the underlying synergistic mechanisms between these additives and validating these findings in large-scale feeding trials to assess their practical efficacy in livestock production systems.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.F., M.S. and J.M.; methodology, L.F. and M.S.; software, W.X. and B.W.; validation, W.X. and B.W.; formal analysis, S.W.; investigation, L.F., M.S., S.W., W.X., B.W. and Y.F.; resources, W.Z. and J.M.; data curation, L.F., M.S. and J.M.; writing—original draft preparation, L.F. and M.S.; writing—review and editing, L.F., M.S., S.W., W.X., B.W., Y.F., W.Z. and J.M.; visualization, L.F., M.S. and Y.F.; supervision, W.Z.; project administration, W.Z. and J.M.; funding acquisition, J.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Program for Scientific Research Start-up funds of Guangdong Ocean University, grant number 060302052318, Guangdong Feed Industry Technology System, grant number 2024CXTD14 and the third batch of “Tianchi Talents” Introduction Program for Young Doctoral Candidates in Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The sheep care and management carried out in this experiment were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Guangdong Ocean University (Zhanjiang, Guangdong, China; approval code: SYXK-2024-052).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Sasu, P.; Attoh-Kotoku, V.; Akorli, D.E.; Adjei-Mensah, B.; Tankouano, R.A.; Kwaku, M. Nutritional evaluation of the leaves of Oxytenanthera abyssinica, Bambusa balcooa, Moringa oleifera, Terminalia catappa, Blighia sapida, and Mangifera indica as non-conventional green roughages for ruminants. J. Agric. Food Res. 2023, 11, 100466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Zhao, M.; Sun, P.; Zhu, L.; Yan, X.; Hao, J.; Si, Q.; Wang, Z.; Jia, Y.; Wang, M.; et al. Effects of different additives on fermentation characteristics, nutrient composition and microbial communities of Leymus chinensis silage. BMC Microbiol. 2025, 25, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seven, P.T.; Yıldırım, E.N.; Seven, I.; Kaya, C.A.; Mutlu, S.I. An evaluation of the effectiveness of sumac and molasses as additives for alfalfa silage: Influence on nutrient composition, in vitro degradability and fermentation quality. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2024, 108, 1096–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.R.; Garcia, S.C.; Islam, M.A.; Bashar, M.K.; Roy, A.; Roy, B.K.; Sarker, N.R.; Clark, C.E.F. Ruminant production from Napier grass (Pennisetum purpureum Schum): A review. Animals 2024, 14, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulvento, C.; Sellami, M.H.; Lavini, A. Yield and quality of Amaranthus hypochondriacus grain amaranth under drought and salinity at various phenological stages in southern Italy. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2022, 102, 5022–5033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Sun, G.; Shah, A.M.; Fan, X.; Li, S.; Yu, X. Effects of different growth stages of amaranth silage on the rumen degradation of dairy cows. Animals 2019, 9, 793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oteri, M.; Gresta, F.; Costale, A.; Lo Presti, V.; Meineri, G.; Chiofalo, B. Amaranthus hypochondriacus L. as a sustainable source of nutrients and bioactive compounds for animal feeding. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotfi, S.; Rouzbehan, Y.; Fazaeli, H.; Feyzbakhsh, M.T.; Rezaei, J. The nutritional value and yields of amaranth (Amaranthus hypochondriacus) cultivar silages compared to silage from corn (Zea mays) harvested at the milk stage grown in a hot-humid climate. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2022, 289, 115336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhou, S.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yang, K.; Chen, W.; Zhao, S. Effects of different proportions of Amaranthus hypochondriacus stem and leaf powder inclusions on growth performance, carcass traits, and blood biochemical parameters of broilers. Animals 2023, 13, 2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Fan, X.; Sun, G.; Yin, F.; Zhou, G.; Zhao, Z.; Gan, S. Replacing alfalfa hay with amaranth hay: Effects on production performance, rumen fermentation, nutrient digestibility and antioxidant ability in dairy cow. Anim. Biosci. 2024, 37, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tadesse, A.; Titze, N.; Rodehutscord, M.; Melesse, A. Effect of substituting concentrate mix with sweet potato vines on growth performances and carcass components of yearling rams and its potential in mitigating methane production. Vet. Med. Int. 2025, 2025, 1054348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Ni, K.; Yang, F. Effects of lactic acid bacteria and cellulase additives on the fermentation quality, antioxidant activity, and metabolic profile of oat silage. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2024, 11, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, A.; Zhu, L.; Guo, W.; Guo, X.; Zhu, B.; Yang, M. Effect of additive cellulase on fermentation quality of whole-plant corn silage ensiling by a Bacillus inoculant and dynamic microbial community analysis. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1330538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazar, M.; Tian, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, S.; Khan, N.A.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, W.; Xu, N.; Liu, B.; Ding, C. Effect of biological lignin depolymerization on rice straw enzymatic hydrolysis, anerobic fermentation characteristics and in vitro ruminal digestibility. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 305, 141664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Guerra, N.A.; Gonzalez-Ronquillo, M.; Anderson, R.C.; Hume, M.E.; Ruiz-Albarrán, M.; Bautista-Martínez, Y.; Zúñiga-Serrano, A.; Nájera-Pedraza, O.G.; Salinas-Chavira, J. Improvements in fermentation and nutritive quality of elephant grass [Cenchrus purpureus (Schumach.) Morrone] silages: A review. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2024, 56, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, D.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, J.; Dong, Z.; Li, J.; Shao, T. Synergistic effects of exogenous lactobacillus plantarum and fibrolytic enzymes on fermentation quality, fiber degradation, and in vitro digestibility of napiergrass (Pennisetum purpureum) silage. Agronomy 2025, 15, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broderick, G.A.; Kang, J.H. Automated simultaneous determination of ammonia and total amino acids in ruminal fluid and in vitro media. J. Dairy Sci. 1980, 63, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, J.; Dong, Z.; Li, J.; Nazar, M.; Shao, T. Assessment of inoculating various epiphytic microbiota on fermentative profile and microbial community dynamics in sterile Italian ryegrass. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 129, 509–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AOAC. Association of Official Analytical Chemists Official Methods of Analysis; AOAC: Washington, DC, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Van Soest, P.J.; Robertson, J.B.; Lewis, B.A. Methods for dietary fiber, neutral detergent fiber, and nonstarch polysaccharides in relation to animal nutrition. J. Dairy Sci. 1991, 74, 3583–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, R.P. A method for the extraction of plant samples and the determination of total soluble carbohydrates. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1958, 9, 714–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Na, N.; Li, X.; Li, Z.; Wang, C.; Wu, X.; Xiao, Y.; Yin, G.; Liu, S.; Liu, Z. Impact of packing density on the bacterial community, fermentation, and in vitro digestibility of whole-crop barley silage. Agriculture 2021, 11, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okoye, C.O.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Gao, L.; Li, X.; Jiang, J. Fermentation profile, aerobic stability, and microbial community dynamics of corn straw ensiled with Lactobacillus buchneri PC-C1 and Lactobacillus plantarum PC1-1. Microbiol. Res. 2023, 270, 127329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 6436-2018; Determination of Calcium in Feeds. China Standards Press: Beijing, China, 2018.
- GB/T 6437-2018; Determination of Phosphorus in Feeds—Spectrophotometry. China Standards Press: Beijing, China, 2018.
- Menke, K.H.; Steingass, H. Estimation of the energetic feed value obtained from chemical analysis and in vitro gas production using rumen fluid. Anim. Res. Dev. 1988, 28, 7–55. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, J.; Li, Y.; Li, T.; Zhang, W.; Fan, M.; Zhang, K.; Qian, H.; Zhang, H.; Qi, X.; Wang, L. Comparison of different soluble dietary fibers during the in vitro fermentation process. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 61, 7446–7457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Øskov, E.R.; McDonald, I. The estimation of protein degradability in the rumen from incubation measurements weighed according to rate of passage. J. Agric. Sci. 1979, 92, 499–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makkar, H.P.S.; Sharma, O.P.; Dawra, R.K.; Negi, S.S. Simple determination of microbial protein in rumen liquor. J. Dairy Sci. 1982, 65, 2170–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NY/T 816-2021; Nutrient Requirements of Meat-Type Sheep and Goats. China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2021.
- Xu, J.; Zhang, K.; Lin, Y.; Li, M.; Wang, X.; Yu, Q.; Sun, H.; Cheng, Q.; Xie, Y.; Wang, C.; et al. Effect of cellulase and lactic acid bacteria on the fermentation quality, carbohydrate conversion, and microbial community of ensiling oat with different moisture contents. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1013258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauhan, N.; Kumari, N.; Mishra, D.B. Dynamic changes in microbial succession and fermentation profiles of sugarcane tops silage treated with exogenous enzymes and lactic acid bacteria following various duration of ensiling. Sugar Tech 2023, 25, 592–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kung, L.; Shaver, R.D.; Grant, R.J.; Schmidt, R.J. Silage review: Interpretation of chemical, microbial, and organoleptic components of silages. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 4020–4033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente, F.; Rodríguez, M.L.; Martínez-Fernández, A.; Soldado, A.; Argamentería, A.; Peláez, M.; de la Roza-Delgado, B. Subclinical ketosis on dairy cows in transition period in farms with contrasting butyric acid contents in silages. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 279614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, R.; Wang, C.; Dong, W.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, X. Effects of cellulase and Lactobacillus plantarum on fermentation quality, chemical composition, and microbial community of mixed silage of whole-plant corn and peanut vines. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2022, 194, 2465–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Tian, J.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Yu, Z. Effects of mixing red clover with alfalfa at different ratios on dynamics of proteolysis and protease activities during ensiling. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 8954–8964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queiroz, O.C.M.; Ogunade, I.M.; Weinberg, Z.; Adesogan, A.T. Silage review: Foodborne pathogens in silage and their mitigation by silage additives. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 4132–4142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, S.; Wang, Y. Lactobacillus plantarum inoculants delay spoilage of high moisture alfalfa silages by regulating bacterial community composition. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, T.; Yun, Y.; Yu, Z. Propionic Acid and sodium benzoate affected biogenic amine formation, microbial community, and quality of oat silage. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 750920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, C.; Liu, N.; Diao, X.; He, L.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, W. Effects of cellulase and xylanase on fermentation characteristics, chemical composition and bacterial community of the mixed silage of king grass and rice straw. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.; Li, S.; Chen, X.; Sun, Z.; Sun, Y.; Zhen, Y.; Qin, G.; Wang, T.; Demelash, N.; Zhang, X. Effects of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum inoculation on the quality and bacterial community of whole-crop corn silage at different harvest stages. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2022, 9, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Wang, L.; Ma, G.; Jiang, X.; Yang, J.; Lv, J.; Zhang, Y. Cellulase interacts with lactic acid bacteria to affect fermentation quality, microbial community, and ruminal degradability in mixed silage of soybean residue and corn stover. Animals 2021, 11, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, S.; Jia, Y.; Ge, G.; Du, S. Revealing the underlying potential mechanisms of lactic acid bacteria-mediated anaerobic fermentation of native grass by microbiome and metagenomic. J. Agric. Food Res. 2025, 23, 102283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Wu, H.; Li, Y.; Li, L.; He, J.; Yang, X.; Xie, X. Fermentation characteristics and microbial community composition of wet brewer’s grains and corn stover mixed silage prepared with cellulase and lactic acid bacteria supplementation. Anim. Biosci. 2024, 37, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Wang, Z.; Du, S.; Sun, L.; Bao, J.; Hao, J.; Ge, G. Lactobacillus plantarum and propionic acid improve the fermentation quality of high-moisture amaranth silage by altering the microbial community composition. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1066641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kung Jr, L.; Schmidt, R.J.; Ebling, T.E.; Hu, W. The effect of Lactobacillus buchneri 40788 on the fermentation and aerobic stability of ground and whole high-moisture corn. J. Dairy Sci. 2007, 90, 2309–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Guo, G.; Yuan, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Shao, T. Effects of applying molasses, lactic acid bacteria and propionic acid on fermentation quality, aerobic stability and in vitro gas production of total mixed ration silage prepared with oat-common vetch intercrop on the Tibetan Plateau. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 1678–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Shen, Y.; Ma, H. Silibinin reduces in vitro methane production by regulating the rumen microbiome and metabolites. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1225643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, T.; Dong, D.; Wang, J.; Yin, X.; Zong, C.; Jia, Y.; Shao, T. Effects of wet brewers grains on fermentation quality and in vitro ruminal digestibility of mixed silage prepared with corn stalk, sweet potato peel and dried apple pomace in southeast China. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2022, 107, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Yu, Y.; Yu, Z.; Shao, T.; Na, R.; Zhao, M. Effects of lactic acid bacteria inoculants and cellulase on fermentation quality and in vitro digestibility of Leymus chinensis silage. Grassl. Sci. 2014, 60, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, B.; Qiu, R.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Bao, J.; Sun, L.; Liu, T.; Ge, G.; Jia, Y. Effects of cellulase and lactic acid bacteria on ensiling performance and bacterial community of Caragana korshinskii silage. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, J.; Zhang, G.; Xiao, M.; Dong, C.; Zhang, R.; Du, L.; Zheng, Y.; Wei, M.; Wei, M.; Wu, B. Effects of cellulase and Lactiplantibacillus plantarum on the fermentation quality, microbial diversity, gene function prediction, and in vitro rumen fermentation parameters of Caragana korshinskii silage. Front. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 2, 1108043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, T.; Tahir, M.; Wang, T.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, S.; Teng, K.; Fu, Z.; Yun, F.; Wang, S. Lactobacillus cocktail and cellulase synergistically improve the fiber transformation rate in Sesbania cannabina and sweet sorghum mixed silage. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2024, 11, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Chen, H.; Liu, Y.; Hong, Q.; Yang, B.; Wang, J. Lactic acid bacteria strains selected from fermented total mixed rations improve ensiling and in vitro rumen fermentation characteristics of corn stover silage. Anim. Biosci. 2022, 35, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, J.; Ungerfeld, E.; Muñoz, C.; DiLorenzo, N. Feeding strategies to mitigate enteric methane emission from ruminants in grassland systems. Animals 2022, 12, 1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.T.; Girma, D.D.; Bionaz, M.; Ma, L.; Bu, D.P. Hepatic transcriptomic adaptation from prepartum to postpartum in dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 1053–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Wang, C.; Wang, Z.; Cao, G.; Hu, R.; Wang, X.; Zou, H.; Kang, K.; Peng, Q.; Xue, B.; et al. Active dry yeast supplementation improves the growth performance, rumen fermentation, and immune response of weaned beef calves. Anim. Nutr. 2021, 7, 1352–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maake, T.W.; Aiyegoro, O.A.; Adeleke, M.A. Effects of Lactobacillus rhamnosus and Enterococcus faecalis Supplementation as Direct-Fed Microbials on Rumen Microbiota of Boer and Speckled Goat Breeds. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Z.; Yamasaki, S.; Oya, T.; Cai, Y. Cellulase-lactic acid bacteria synergy action regulates silage fermentation of woody plant. Biotechnol. Biofuels Bioprod. 2023, 16, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).