Abstract
Oregano (Origanum vulgare L.) is a well-known traditional medicine and a cooking spice. Recent practice has also applied the essential oil from oregano (OEO) in poultry due to its great potential for an antibiotic alternative. Our objective was to evaluate the potential effects of OEO (with carvacrol and thymol as the main active ingredient) on preventing necrotic enteritis (NE) caused by Clostridium perfringens (Cp) in chickens. In the feeding trial, a total of 450 one-day-old commercial Arbor Acres broilers were randomly assigned in 5 experimental groups during a 26-day production period (d19 to d 26 was the Cp challenge stage), and each group consisted of 6 replicate pens (15 birds each pen). All treatments were: basal diet (control group); basal diet and Cp challenge (model group); Cp challenge and 10 mg/kg enramycin (positive control group); Cp challenge and 200 mg/kg OEO product (OEO low dosage group, OEOL); Cp challenge and 300 mg/kg OEO product (OEO high dosage group, OEOH). OEO feed supplement at both dosages had significant effects on increasing the body weight gain (BWG) and reversing the dropped feed intake (FI) induced by Cp challenge. Histopathological changes in the ileums of broiler chickens with NE induced by Cp were alleviated by OEO, which was mutually confirmed by the intestinal lesion scores. Dosage did not influence the protective effect of OEO on intestinal lesion scores. Furthermore, OEO was found to have limited effects on tight junction-related gene expressions (Occludin and ZO-1). The broilers of the OEOL and OEOH groups significantly decreased the expression of TNF-α mRNA in the ileum and only the OEOH group was found to inhibit the IFN-γ expression of IFN- induced by Cp challenge. Finally, despite the fact that in vitro antibacterial effects by OEO were observed, considering its high minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) value, we inferred that the protective effects by OEO against Cp challenge were not attributable to its direct antibacterial effects. We proposed OEO as a promising substitute for antibiotics against NE induced by Cp during poultry production.
1. Introduction
Poultry production is of great importance for animal husbandry, which is facing new challenges and needs to find more solutions to remain sustainable. Necrotic enteritis (NE) is a common but serious poultry disease which is a great threat worldwide [1]. Although Clostridium perfringens (C. perfringens, Cp) is a common commensal bacterium of the chicken intestine, the overgrowth of Cp leads to acute clinical symptoms, mainly intestinal disorders such as severe necrosis and inflammation, damaged intestinal mucosa, and significantly decreased digestion and absorption of nutrients which greatly affect chicken growth performance. It is estimated that, worldwide, Cp causes NE that costs the poultry industry ~two billion US dollars annually [2]. Traditionally, antibiotics showed great effectiveness in the control of NE [3], however, the use of antibiotics for feed in EU and many other countries has been banned since 2006. Furthermore, it started to be strictly restricted in many other countries including USA and China [4,5,6]. Prophylactic use of antibiotics and antimicrobial growth promoters (AGPs) in animal nutrition brings many debates, including threats to health and negative environmental impacts, therefore novel approaches to control NE in the replacement of antibiotics are urgently needed [7]. Among the different alternative substitutes for antibiotics, the usage of essential oils (EO) has been shown to have its effectiveness and potential for pre- and post-harvest antimicrobial strategies [8].
EOs are prepared using different fragrance extraction techniques from parts of plants, including leaves, roots, barks, stems, flowers, and seeds [9,10,11]. Strictly, they are not like edible oils, but usually have poor solubility in water, as are oils. EOs are complex mixture of hundreds of volatile compounds which have been reported with many biological benefits, such as anti-microbial, anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidant activities and many others [12]. Moreover, EOs been also have widely applied as effective reagent for the treatment of various diseases both in human medicine and animal husbandry [8]. Several trials have successfully shown the positive impacts of EOs against Cp induced NE during poultry production alone or in combination (blend) forms, such as Rosmarinus officinalis L. (rosemary), Thymus vulgaris L. (thyme) Pimpinella anisum L. (anise) and Origanum vulgare L.(oregano) [13].
Oregano is a well-known traditional medicine and a cooking spice. It also works as a useful poultry feed supplement for boosting the immunity and increasing birds’ growth performance [14]. Due to its rich in aromatic compounds, we hypothesize that EOs from oregano (OEO) might be useful for preventing NE for chickens. The aim of this study was to investigate the potential effects of OEO, which was chemically characterized with its main bioactive ingredient, on preventing NE caused by Cp in broilers chickens.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemical Analysis on the Oregano Essential Oil (OEO)
Thymol and carvacrol standard were purchased from Yuanye Bio-Technology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China) with compound purities at ~98%. The pure OEO was obtained from by Kemin (Zhuhai, China) Technologies Co., Ltd., Zhuhai, China. Thymol and carvacrol in the pure OEO were analyzed using a HPLC with an Agilent ZORBAX SB-C18 (4.6 × 100 mm, 3.5 μm particle size) analytical column using an isocratic elution with a binary mobile phase (acetonitrile and water, 33:67, v/v) was used. During assay, an aliquot of 10 μL of diluted mixed standard or samples of pure OEO was injected in duplicate into the analytical column at 30 °C at a flow rate of 1 mL/min. Thymol and carvacrol were detected at 276 nm and quantitatively determined using an external calibration method [15].
2.2. Animal Trial Experimental Design
The experiments were ethically approved by the China Agricultural University Laboratory Animal Welfare and Animal Experimental Ethic committee (AW22121202-1-1). A total number of 450 one-day-old commercial Arbor Acres broilers were randomly assigned in 5 experimental groups, and each group consisted of 6 replicate pens (15 birds each pen). All treatments were as follows: basal diet; basal diet + Cp challenge; Cp challenge + 10 mg/kg enramycin; Cp challenge + 200 mg/kg OEO; Cp challenge + 300 mg/kg OEO. The OEO product, also known as OrsentialTM used in the animal trial was a commercial product obtained from by Kemin (China) Technologies Co., Ltd., Zhuhai, China, which contained 5% pure Origanum vulgare L. Essential Oil (OEO) as active components and defatted rice bran and silica as carriers. Broilers were raised in a controlled environment and allowed ad libitum access to water and feed. Repetitions of different treatments were equally distributed among the cages as much as possible to reduce variations at the cage level. The entire experiment was divided into two phases: the non-Cp challenge phase (d0–18) and the Cp challenge phase (d19–26) using one basal diet formulation. All diets were designed following the instructions of NRC (1994) and the Chinese chicken feeding standard (NY/T-33–2004) (Table 1). The Cp challenge was performed on the basis of our previous study [16]. A field strain of Cp type A (CVCC2030) was cultured on tryptone-sulfite-cycloserine agar, and a single colony was then inoculated into cooked meat medium and subsequently cultured in an incubator at 37 °C for 8 h. In the infected groups, chickens were orally inoculated with 1 mL bacterial solution containing 108 CFU/mL Cp once a day from Day 19 to Day 25. Chickens in the basal diet group were subjected to the same gavage procedure described above but with sterilized medium. Body weight of chickens was measured by replicate on day 0, day18, and on the last day (day 26). Feed intake (FI), body weight gain (BWG) and the feed conversion ratio (FCR) were calculated. Mortality was recorded during the whole experiment.

Table 1.
Basal diet composition (as-fed basis).
2.3. The Histology Analysis
Upper ileum sections were obtained from all sacrificed birds (one bird was chosen randomly from each biological replicate) after removing the digesta and washing using PBS. Then the ileum samples were fixed using 4% paraformaldehyde for hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining following standard protocols [17]. Histological images were observed and taken under a light microscope with an attached image capture system (Nikon Eclipse Ci, Tokyo, Japan).
2.4. Intestinal Lesion Score Evaluations
Intestinal scoring was evaluated on the basis provided from previous study [18]. On the last day of the trial, one bird from the pen was chosen randomly and scarified for lesion scoring by cervical dislocation. After cutting opened the intestines, NE lesions were measured based on the description and observations on the intestine. 0 = normal intestinal appearance; 0.5 = severely congested serosa and mesentery engorged with blood; 1 = thin walled and friable intestines with small red petechiae; 2 = focal necrosis, grey appearance and small amounts of gas production; 3 = sizable patches of necrosis, gas-filled intestine and small flecks of blood; and 4 = severe extensive necrosis, marked hemorrhage, large amounts of gas in the intestine [19].
2.5. Total RNA Extraction and Reverse Transcription
Ileal tissues from one randomly chosen 26-day-old bird per replicate were collected for total RNA extraction using Trizol method (Invitrogen; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc., Waltham, MA, USA). The reverse transcription was conducted using a PrimeScript RT Reagent Kit (Takara Biotechnology Inc., Dalian, China). Real-time PCR reactions were performed using SYBR®Premix Ex TaqTM (Tli RNaseH Plus, TaKaRa, Dalian, China) under the 7500c Real-time PCR Detection System (Applied Biosystems, Carlsbad, CA, USA). The primers were designed to flank introns with the Primer 5 software (Premier Biosoft, Palo Alto, CA, USA). The primer sets are listed in the Supplemental Table S1. All measurements were carried out in triplicate, with calculations on the average values. The data were calculated using 2−ΔΔCT method, normalized to the expression of the housekeeping gene (β-actin), and expressed as a fold change compared to the control group [20].
2.6. In Vitro Anti-Bacterial Effects by the OEO
The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of the OEO against C. perfringens (CVCC2030) was determined via a conventional broth dilution method as described in our previous study [2]. The minimal bactericidal concentration (MBC) was defined as the lowest concentration of EO with which no viable bacteria were detected. All assays were performed in triplicate. For the bacterial morphology observations, Cp cells (~2 × 107 CFU/mL) were incubated with OEO at MIC or MBC or an equal volume of vehicle (methanol) at 37 °C for 6 h. After centrifugation at 1000 × g for 10 min, bacterial cells were prepared for scanning electron microscopy analysis with a Hitachi S-4800 scanning electron microscope following the manufacturer’s instruction.
2.7. Statistical Analyses
Quantitative data are presented as the arithmetic mean ± standard deviation (SD) for each treatment group. The data including growth performance, lesion score, gene expressions of both intestinal tight junction and pro-inflammation cytokine collected for quantitative parameters were analyzed using analysis of variance technique (ANOVA) under a completely randomized design. Significant differences among the treatments were measured by using Duncan’s multiple comparison. Variability in the data was expressed as the standard error of means, and a significant difference was declared when p < 0.05. All statistical tests were performed using SPSS version 17.0 (SPSS, Inc., Chicago, IL, USA).
3. Results & Discussion
3.1. Active Compounds Characterization of Carvacrol and Thymol from OEO
Origanum vulgare L. has been traditionally used for medicinal purposes but also widely applied in as food additive, veterinary medicine, pesticide and feed supplement [21]. The present study used pure oregano essential oil (OEO) was obtained from its mother plant processed using steam distillation after separation of the aqueous phase, which is in strict accordance with the requirement by the International Organization for Standardization. Furthermore, according to European Commission Regulation No 1334/20083, OEO can be applied as a feed additive in all animal feed, without extra evaluations [22,23]. Previous studies reported the major active components of oregano essential oil (OEO) from Origanum vulgare L. were carvacrol and thymol [21]. We therefore determinates these two active compounds in the pure OEO. We separated and quantified carvacrol and thymol in the pure OEO by HPLC by comparison with the retention times of authentic standards (Figure 1). The quantities of carvacrol and thymol in the pure OEO was 445 mg/g and 221 mg/g, respectively. Therefore, carvacrol and thymol concentrations in the experimental diet were 4.45 mg/kg and 2.21 mg/kg (low dosage experimental group) and 6.68 mg/kg and 3.32 mg/kg (high dosage experimental group), respectively. This composition and inclusion levels of OEO provided us a better understanding on the inclusion level of the phytogenic additives we used.
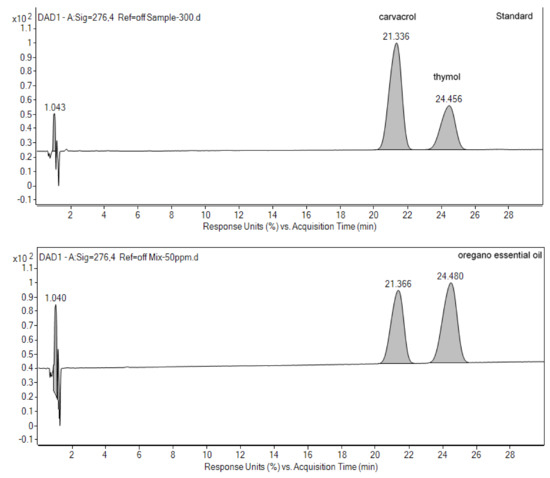
Figure 1.
High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) chromatograms of carvacrol and thymol in the pure oregano essential oil (OEO). Detection wavelength was at 276 nm. Mixed authentic standards (up) and pure OEO sample (down) were shown. Retention times (min) of carvacrol and peaks of OEO were shown.
3.2. OEO Imporved the Growth Performance in Cp Challenged Chickens
Despite many trials using the OEO in poultry production, its effects on growth performance were still controversial. Some of previous studies suggested that there were no significant impacts on chickens’ growth performance [24,25]. However, more studies noticed that OEO was found to improve growth performance, such as increasing the average daily gain (ADG), final body weight (BW) [26] and decreasing the feed conversion ratio (FCR) [27]. In this study, dietary supplementation of 200 and 300 mg/kg OEO (in with containing 5% pure OEO and 95% silicon dioxide as caking inhibitor) had no significant influence the growth performance of the broilers during d 0 to 18 (Table 2). During the Cp challenge stage (d19–d26), OEO feed supplement at both low (200 mg/kg) and high dosage (300 mg/kg) groups had significant effects on increasing the body weight gain (BWG) and reversing the dropped feed intake (FI) induced by Cp challenge (Table 2). We chose the dosages of OEO based on colleagues and our previous studies. Botsoglou et al. [28] showed that inclusion of 50 and 100 mg/kg OEO in the feed did not improve either feed conversion ratio or growth performances. A similar effect was reported by Hassanin et al. [29] when 0.005 and 0.01% was added in broilers feed. On the other hand, the study of Vlaicu and colleagues found that 0.01% OEO significantly improved broilers’ performances [30]. Nevertheless, Alagawany et al. concluded a study in which 500 mg/kg diet of OEO is the appropriate level of inclusion in broiler diets for best performance and health; higher doses could have negative effect on performances due to some toxic effects [14]. Based on these inconsistent data relating the growth performance, we hypothesize that potential effects of OEO on growth performance were closely related to the dosage chosen, or by some factors like oil extraction process, different growing geographical regions of the plants, storage conditions and so on. Therefore, supplementation of OEO in our study showed to be effective on improving growth performance in Cp challenged chickens [14,31].

Table 2.
The effect of supplementation oregano (Origanum vulgare L.) essential oil on growth performance in Cp-challenged broilers 1.
3.3. Feed Supplement with OEO Ileal Histopathological Changes in Broilers Challenged by C. perfringens
NE is a reemerging threaten to poultry production in the modern animal husbandry which requires us to reduce, replace and refine the usage of antibiotics and certain antimicrobial feed supplements [31]. Probiotics, prebiotics, plant extract as well as the active molecules from plant origins have shown great potential in mitigating NE in poultry [32]. For example, several species of genus Bacillus, Lactobacillus, have been shown with anti-Cp activity [33]. They usually supported the reduction of C. perfringens in the intestines positively by altering the intestinal microbial population and have improved the growth performance. Compared with these probiotics, plant extracts offer an alternative approach to put the underutilized some very cheap raw materials for good usages. Plant and plant-derived products, like garlic (Allium sativum), grape (Vitis vinifera), green tea (Camellia sinensis) as well as many others were found to positively affect growth performance and improve intestinal health alone or in combination with other compounds [34,35]. In addition to the growth-promoting effects, OEO may also be related to the decrease ileus inflammation during the Cp infection to the broilers. We further tested the potential impacts of OEO feed supplement on histopathological changes in ileums of broiler chickens challenged by Cp. As shown in Figure 2, chickens from the control group had no intestinal lesions. In contrast, upper ileum tissues were found with typical subclinical necrotic enteritis characteristics and severe intestinal inflammation in the model group. Feed supplement with OEO reduced the negative impacts caused by Cp with ameliorated ileitis, which is consistent with the previous findings in which they applied an essential oil, which contained 25% thymol and 25% carvacrol as active components [36].
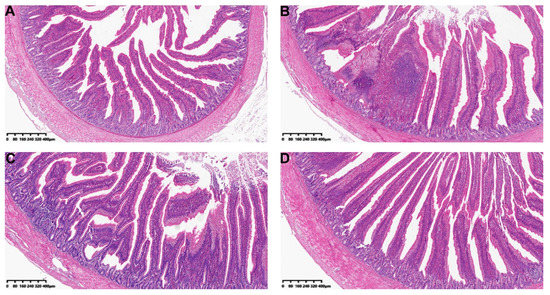
Figure 2.
Effects of OEO feed supplement on histopathological changes in ileums of broiler chickens with necrotic enteritis induced by C. perfringens. Ileum sections from the broiler chickens were proceeded based on H&E staining. Typical ileum images from (A) control group; (B) Cp induced necrotic enteritis group; (C) Cp birds fed with low dosage OEO group (200 mg/kg) and (D) Cp birds fed with high dosage OEO group (300 mg/kg).
3.4. Feed Supplement with OEO Improved the Gut Health of Broilers Challenged by C. perfringens
We next measured the effects of several key genes encoding inflammation responses and intestinal barrier permeability on the broiler jejunum challenged by Cp. As shown in Figure 3A, no intestinal lesions were observed in the unchallenged birds. In the challenged birds, intestinal lesion scores were significantly increased to 1.67 ± 0.52 (p ≤ 0.001), while dietary addition of enramycin (0.25 ± 0.27) also depressed the intestinal lesion (p = 0.004). The intestinal lesion scores in OEO Low dosage Group and OEO High dosage Group were 0.67 ± 0.26 and 0.50 ± 0.32, which were significantly lower than Cp -challenged Model group (p = 0.027 and 0.011). Interestingly, the dosage did not influence the protective effect of OEO on intestinal lesion scores. NE birds infected by Cp are shown with increased gut barrier permeability and losses of intestinal barrier functions [37], which not only greatly affects nutrient absorption, but also increases the possibility to be infected with other pathogens, like Campylobacter jejuni, Salmonella enterica or Eimeria maxima [38]. Regarding the intestinal barrier function-related gene expressions, Cp challenges lead to decreased Occludin expressions, but no significant effects on ZO-1 gene expressions. In addition, OEO fed to the broilers significantly dropped the expression of TNF-α mRNA in the ileum and only high dosage of OEO was found to inhibit the IFN-γ expression. Consistent with the previous findings, we inferred that OEO inhibited the inflammatory signaling pathways [37,38,39], therefore reasonable pathophysiological mechanisms and potential therapeutic strategies could be further developed in vitro for Cp induced chicken intestinal epithelial cell stresses.
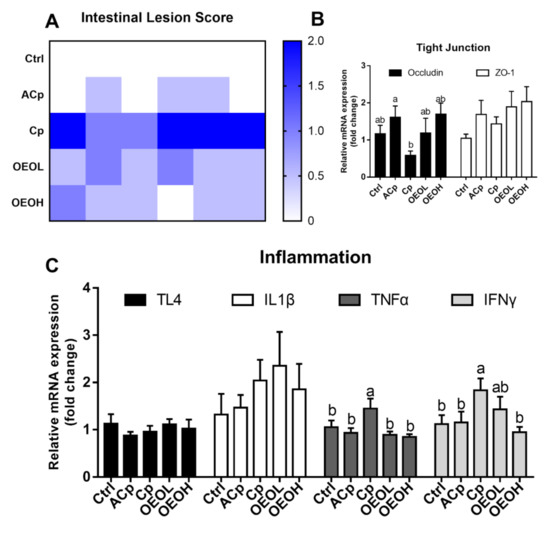
Figure 3.
Effects of OEO feed supplement on gut health parameters in broiler chickens with necrotic enteritis induced by C. perfringens. (A) Heat map showed the lesion score of the chickens. High histological scores are shown in blue and low histological scores in white. (B) Tight junctions related gene expressions in the ileum. (C) Inflammation related gene expressions in the ileum. Means with no common letters differed significantly (p < 0.05). (p ≤ 0.05). Treatment information: Ctrl Group, basal diet; A Cp Group, Cp challenge +10 mg/kg enramycin; Cp Group, basal diet and Cp challenge; OEOL Group, Cp challenge +200 mg/kg of OEO; OEOH Group, Cp challenge +300 mg/kg of OEO.
3.5. In Vitro Antibacterial Activity of OEO against C. perfringens
We next tested the in vitro antibacterial activity of the pure OEO against Cp. The MIC and MBC of the pure OEO against Cp were 375 μg/mL and 750 μg/mL, respectively, which were measured based on broth dilution method. As shown in Figure 4, surface morphology of Cp following exposure with OEO was visualized by SEM. PBS and methanol (vehicle) treated bacteria showed a regular intact rod shape and with an intact smooth surface, whereas propolis treatment at MIC concentration showed a relative longer, with rougher surface. Meanwhile, OEO treatment at MBC concentration to the Cp showed an extensively rough and collapsed surface. A number of previous studies investigated the antibacterial activity of OEO against different foodborne pathogens, including the Cp [40]. Our previous report obtained MICs of thymol and carvacrol at 187.5 and 375 μg/mL [36]. Nevertheless, the in vitro antibacterial effects of the OEO we applied is stronger than previous studies obtained. The possible interference of thymol and carvacrol on the Cp growth cannot be ruled out. Collectively, these data clearly showed OEO had potent in vitro antibacterial activity against Clostridium perfringens. As we calculated that the carvacrol and thymol concentrations in the experimental diet were 4.45 mg/kg and 2.21 mg/kg (low dosage experimental group) and 6.68 mg/kg and 3.32 mg/kg (high dosage experimental group), such dosages are far less to reach the direct optimal antibacterial concentrations. We therefore inferred that the protective effects by OEO against Cp challenge were not attributable to its direct antibacterial effects.
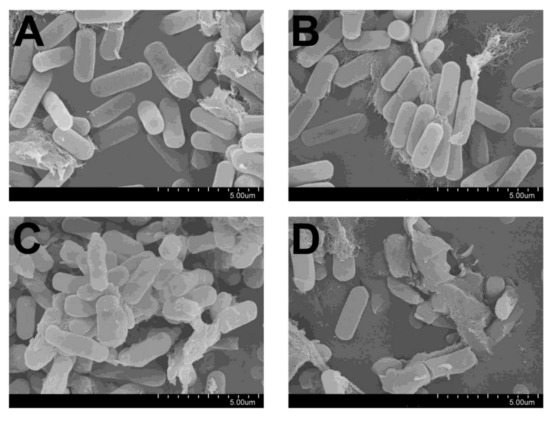
Figure 4.
Scanning electron microscopy analysis on the C. perfringens following treatment of OEO. C. perfringens (~2 × 107 cfu/mL) were incubated with PBS (A), vehicle (methanol, (B)) or OEO concentrations at MIC (375ug/mL, (C)) and MBC (750 ug/mL, (D)) at 37 °C for 6 h under anaerobic conditions. The bacterial surface morphology was observed with a Hitachi S-4800 SEM.
4. Conclusions
This study clearly shows that OEO containing carvacrol and thymol as the key ingredient in the feed supplement improved the subclinical NE induced by C. perfringens in broiler chickens by regulating host inflammatory responses and increasing intestinal barrier function. Although OEO was shown with in vitro anti-bacterial effects against C. perfringens, the calculated MIC will not be sufficient for its action in vivo, therefore further in-depth studies are still warranted to evaluate the OEO effects on the its pathophysiological mechanisms. This study also proposed OEO as a promising substitute for antibiotics against NE or other inflammatory-related intestinal diseases during poultry production.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/agriculture12010018/s1, Table S1: Primers sequences used for the real-time PCR.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.J. and D.L.; methodology, D.L.; software, G.H.; validation, Z.L. and D.L.; formal analysis, X.J. and D.L.; investigation, Z.L. and D.L.; resources, X.J. and D.L.; data curation, X.J. and D.L.; writing—original draft preparation, X.J.; writing—review and editing, Y.H. and D.L.; funding acquisition, Y.H. and D.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by Shandong Provincial Key R&D Program (2019JZZY020602) and the 2115 Talent Development Program of China Agricultural University.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the China Agricultural University Laboratory Animal Welfare and Animal Experimental Ethic committee (AW22121202-1-1) on 1 April 2020.
Data Availability Statement
Data supporting reported results can be requested from the corresponding author via email.
Conflicts of Interest
Z.L. was an executive director of Kemin Industries (China) Co., Ltd. and provided the experimental material for this study. The remaining authors have no conflicts of interest to declare. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript.
References
- El-Hack, M.E.A.; El-Saadony, M.T.; Elbestawy, A.R.; El-Shall, N.A.; Saad, A.M.; Salem, H.M.; El-Tahan, A.M.; Khafaga, A.F.; Taha, A.E.; Abu, S.F.; et al. Necrotic enteritis in broiler chickens: Disease characteristics and prevention using organic antibiotic alternatives–a comprehensive review. Poult. Sci. 2021, 101590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, E.; Gan, L.; Li, Z.; Wang, W.; Liu, D.; Guo, Y. In vitro antibacterial activity of thymol and carvacrol and their effects on broiler chickens challenged with Clostridium perfringens. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2015, 6, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, Q.; Liu, D.; Guo, S.; Chen, Y.; Guo, Y. Effects of dietary essential oil and enzyme supplementation on growth performance and gut health of broilers challenged by Clostridium perfringens. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2015, 207, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Xu, S.; Tang, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhang, L. Use of antimicrobials in food animals and impact of transmission of antimicrobial resistance on humans. Biosaf. Health 2021, 3, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casewell, M.; Friis, C.; Marco, E.; McMullin, P.; Phillips, I. The European ban on growth-promoting antibiotics and emerging consequences for human and animal health. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2003, 52, 159–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abudabos, A.M.; Alyemni, A.H.; Dafalla, Y.M.; Khan, R. The effect of phytogenic feed additives to substitute in-feed antibiotics on growth traits and blood biochemical parameters in broiler chicks challenged with Salmonella typhimurium. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 24151–24157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, M.; Vogl, C.R.; Amorena, M.; Hamburger, M.; Walkenhorst, M. Treatment of organic livestock with medicinal plants: A systematic review of european ethnoveterinary research. Complement. Med. Res. 2014, 21, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Micciche, A.; Rothrock, M.J.J.; Yang, Y.; Ricke, S.C. Essential oils as an intervention strategy to reduce campylobacter in poultry production: A review. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, S.; Sahoo, S.; Tripathy, K.; Singh, Y.D.; Sarma, M.K.; Babu, P.J.; Singh, M.C. Essential oils and their pharmacotherapeutics applications in human diseases. Adv. Tradit. Med. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attia, Y.A.; Hamed, R.S.; Bovera, F.; Al-Harthi, M.A.; Abd El-Hamid, E.; Esposito, L.; Shahba, H.A. Milk thistle seeds and rosemary leaves as rabbit growth promoters. Anim. Sci. Pap. Rep. 2019, 37, 277–295. [Google Scholar]
- Attia, Y.; Al-Hamid, A.A.; Ibrahim, M.; Al-Harthi, M.; Bovera, F.; Elnaggar, A. Productive performance, biochemical and hematological traits of broiler chickens supplemented with propolis, bee pollen, and mannan oligosaccharides continuously or intermittently. Livest. Sci. 2014, 164, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calo, J.R.; Crandall, P.G.; O’Bryan, C.A.; Ricke, S.C. Essential oils as antimicrobials in food systems—A review. Food Control 2015, 54, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radaelli, M.; da Silva, B.P.; Weidlich, L.; Hoehne, L.; Flach, A.; Da Costa, L.A.M.A.; Ethur, E.M. Antimicrobial activities of six essential oils commonly used as condiments in Brazil against Clostridium perfringens. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2016, 47, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alagawany, M.; El-Hack, M.A.; Farag, M.R.; Shaheen, H.M.; Abdel-Latif, M.A.; Noreldin, A.E.; Patra, A.K. The usefulness of oregano and its derivatives in poultry nutrition. World’s Poult. Sci. J. 2018, 74, 463–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekarchi, M.; Khanavi, M.; Adib, N.; Amri, M.; Hajimehdipoor, H. A validated high performance liquid chromatography method for the analysis of thymol and carvacrol in Thymus vulgaris L. volatile oil. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2010, 6, 154–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Luo, Z.; Liu, D. Supplemental bacillus subtilis PB6 improves growth performance and gut health in broilers challenged with Clostridium perfringens. J. Immunol. Res. 2021, 2021, 2549541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wan, Z.; Ou, A.; Liang, X.; Guo, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, L.; Xue, X. Monofloral honey from a medical plant, Prunella Vulgaris, protected against dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis via modulating gut microbial populations in rats. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 3828–3838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xuan, H.; Ou, A.; Hao, S.; Shi, J.; Jin, X. Galangin protects against symptoms of dextran sodium sulfate-induced acute colitis by activating autophagy and modulating the gut microbiota. Nutrients 2020, 12, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dahiya, J.P.; Hoehler, D.; Wilkie, D.C.; Van Kessel, A.G.; Drew, M.D. Dietary glycine concentration affects intestinal Clostridium perfringens and lactobacilli populations in broiler chickens1. Poult. Sci. 2005, 84, 1875–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Jin, X.L.; Li, Q.Q.; Sawaya, A.C.H.F.; Le Leu, R.K.; Conlon, M.A.; Wu, L.M.; Hu, F.L. Propolis from Different Geographic Origins Decreases Intestinal Inflammation and Bacteroides spp. Populations in a Model of DSS-Induced Colitis. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2018, 62, 1800080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezzani, R.; Vitalini, S.; Iriti, M. Bioactivities of Origanum vulgare L.: An update. Phytochem. Rev. 2017, 16, 1253–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Vito, M.; Cacaci, M.; Barbanti, L.; Martini, C.; Sanguinetti, M.; Benvenuti, S.; Tosi, G.; Fiorentini, L.; Scozzoli, M.; Bugli, F.; et al. Origanum vulgare essential oil vs. a commercial mixture of essential oils: In vitro effectiveness on Salmonella spp. from poultry and swine intensive livestock. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EFSA Panel on Biological Hazards (EFSA BIOHAZ Panel); Koutsoumanis, K.; Allende, A.; Alvarez-Ordóñez, A.; Bolton, D.; Bover-Cid, S.; Chemaly, M.; de Cesare, A.; Herman, L.; Hilbert, F.; et al. Salmonella control in poultry flocks and its public health impact. EFSA J. 2019, 17, e05596. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bampidis, V.; Christodoulou, V.; Florou-Paneri, P.; Christaki, E.; Spais, A.; Chatzopoulou, P. Effect of dietary dried oregano leaves supplementation on performance and carcass characteristics of growing lambs. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2005, 121, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerisuelo, A.; Marín, C.; Sánchez-Vizcaíno, F.; Gomez, E.; de la Fuente, J.M.; Durán, R.; Fernández, C. The impact of a specific blend of essential oil components and sodium butyrate in feed on growth performance and Salmonella counts in experimentally challenged broilers. Poult. Sci. 2014, 93, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Q.; Li, J.; Li, Z.; Duan, Z.; Wu, Y. Effects of dietary supplementation with oregano essential oil on growth performance, carcass traits and jejunal morphology in broiler chickens. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2016, 214, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Peng, Q.; Liu, Y.; Ma, Q.; Guo, Y.; Xue, Z.; Zhao, L. Effects of oregano essential oil as an antibiotic growth promoter alternative on growth performance, antioxidant status, and intestinal health of broilers. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 101163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botsoglou, N.A.; Florou-Paneri, P.; Christaki, E.; Fletouris, D.J.; Spais, A.B. Effect of dietary oregano essential oil on performance of chickens and on iron-induced lipid oxidation of breast, thigh and abdominal fat tissues. Br. Poult. Sci. 2002, 43, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanin, O.A.A. Positive impact of oregano essential oil on growth performance, humoral immune responses and chicken interferon alpha signaling pathway in broilers. Adv. Anim. Vet. Sci. 2015, 4, 57–65. [Google Scholar]
- Vlaicu, P.A.; Panaite, T.D.; Turcu, R.P.; Tabuc, C. Dietary origanum vulgare supplements for broilers. Rom. Biotechnol. Lett. 2020, 25, 1922–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, K.K.; Songer, J.G. Virulence of clostridium perfringens in an experimental model of poultry necrotic enteritis. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 142, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, K.; Rahman, S.; Hussain, I.; Abbas, R.; Khaliq, T.; Arif, J. Non-antibiotic strategies for the control of necrotic enteritis in poultry. World’s Poult. Sci. J. 2014, 70, 865–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalique, A.; Zeng, D.; Shoaib, M.; Wang, H.; Qing, X.; Rajput, D.S.; Pan, K.; Ni, X. Probiotics mitigating subclinical necrotic enteritis (SNE) as potential alternatives to antibiotics in poultry. AMB Express 2020, 10, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, A.; Sharma, N.K.; Kheravii, S.K.; Keerqin, C.; Ionescu, C.; Blanchard, A.; Wu, S.-B. Potential of a mixture of eugenol and garlic tincture to improve performance and intestinal health in broilers under necrotic enteritis challenge. Anim. Nutr. 2022, 8, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Sanchez, S.; D’Souza, D.; Biswas, D.; Hanning, I. Botanical alternatives to antibiotics for use in organic poultry production. Poult. Sci. 2015, 94, 1419–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, E.; Wang, W.; Gan, L.; Liping, G.; Guo, S.; Guo, Y. Effects of thymol and carvacrol supplementation on intestinal integrity and immune responses of broiler chickens challenged with Clostridium perfringens. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2016, 7, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, B.; Li, H.; Wu, Y.; Zhen, W.; Wang, Z.; Xia, Z.; Guo, Y. Effect of microencapsulated sodium butyrate dietary supplementation on growth performance and intestinal barrier function of broiler chickens infected with necrotic enteritis. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2017, 232, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, V.H.; Kan, L.; Huang, J.; Geng, Y.; Zhen, W.; Guo, Y.; Abbas, W.; Wang, Z. Dietary encapsulated essential oils and organic acids mixture improves gut health in broiler chickens challenged with necrotic enteritis. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2020, 11, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Awad, W.A.; Hess, C.; Hess, M. Enteric pathogens and their toxin-induced disruption of the intestinal barrier through alteration of tight junctions in chickens. Toxins 2017, 9, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gavaric, N.; Mozina, S.S.; Kladar, N.; Bozin, B. Chemical profile, antioxidant and antibacterial activity of thyme and oregano essential oils, thymol and carvacrol and their possible synergism. J. Essent. Oil Bear. Plants 2015, 18, 1013–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).