Abstract
Background/Objectives: Hip fractures in older patients frequently lead to early readmissions, which negatively impact patient outcomes and significantly increase healthcare costs. Identifying and understanding risk factors for 30-day readmission following hip fracture surgery is essential for improving patient management and optimizing healthcare resource utilization. Methods: A systematic literature search was conducted using PubMed, EMBASE, and the Cochrane Library databases up to 30 December 2024. Studies investigating potential risk factors for 30-day readmission following hip fracture surgery were included. The risk factors were meta-analytically pooled, and odds ratios (ORs) were calculated using a random-effects model. Results: Twelve studies comprising 128,053 patients were included. Pooled analyses revealed significant associations between higher readmission rates and factors such as male sex (OR = 1.45; 95% CI, 1.27–1.65), hip arthroplasty surgery (OR = 1.36; 95% CI, 1.03–1.80), advanced age (OR, 1.22; 95% CI 1.00–1.49), high American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) Physical Status Classification System class (OR, 2.22; 95% CI, 1.28–3.85), and high Charlson comorbidity index (OR, 1.67; 95% CI, 1.36–2.05). Additionally, the most frequently reported comorbidities associated with higher readmission risks were diabetes mellitus and congestive heart failure, with ORs of 1.63 and 1.57, respectively. Conclusions: Male sex, advanced age, higher ASA scores, and greater preoperative comorbidity burdens significantly increase the risk of 30-day readmission following hip fracture surgery. Effective risk stratification and targeted perioperative management strategies addressing these identified factors may reduce early readmission rates and enhance postoperative patient outcomes.
1. Introduction
Hip fractures represent a major public health challenge among older adults, often resulting in significant morbidity, mortality, and substantial economic burden [1]. With global populations aging, the incidence of hip fractures continues to rise, and these injuries are frequently compounded by multiple comorbidities and frailty. Despite advancements in surgical techniques and perioperative care, early hospital readmissions remain alarmingly common. These readmissions serve as critical indicators of healthcare quality and patient outcomes. According to a study by Jencks et al., the cost to Medicare for unplanned readmissions in a single year was estimated to exceed USD 17 billion [2]. Similarly, the rate of early readmissions after hip fractures continues to rise, with a 41.2% increase in 28-day readmissions in the United Kingdom over the past 12 years [3].
Unplanned readmissions following hip fractures have been linked to adverse clinical outcomes, including increased mortality, impaired functional recovery, and escalated healthcare costs [4]. In light of these challenges, understanding the underlying risk factors for early readmission is essential for guiding improvements in patient management and healthcare resource allocation.
Previous studies have explored various predictors for 30-day readmission after hip fracture surgery. These predictors include patient demographics, preoperative health status, and perioperative management strategies [5,6]. Notably, factors, such as age, sex, comorbidities (e.g., diabetes, congestive heart failure), surgical technique, and postoperative complications, have frequently been examined in prior studies. However, their relative impact on readmission rates remains controversial. Although some studies report a strong association between specific factors—such as high American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) Physical Status Classification System scores or the presence of cardiovascular diseases—and early readmission, others have failed to replicate these findings. Variability in reported risk factors may result from differences in study design and sample size. Other contributing factors include varying healthcare system characteristics and differing definitions of readmission. Furthermore, regional variations in discharge planning, rehabilitation availability, and follow-up care may also contribute to these discrepancies.
Therefore, the objective of this systematic review and meta-analysis was to identify and quantitatively synthesize the significant risk factors associated with 30-day readmission following hip fracture surgery.
2. Materials and Methods
We conducted this study in accordance with the Revised Assessment of Multiple Systematic Reviews and the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses guidelines [7,8]. Although this research involved human participants, ethical approval was not required for this systematic review and meta-analysis as all analyses were based on previously published, publicly available data, and no new patient data or interventions were involved. This study adheres to the principles outlined in the Declaration of Helsinki.
2.1. Literature Search
A computerized search of MEDLINE (PubMed), Embase, and the Cochrane Library was conducted to identify studies analyzing risk factors for short-term readmission after hip fracture surgery. Using a predefined search strategy, we identified articles published up to 30 December 2024. The search terms included synonyms and related terms for hip fracture and readmission. The full search strategies and results for all databases are presented in Supplementary Materials S1. No language restrictions were applied to our literature search, and we placed no restrictions on the publication year. Following the initial electronic search, we manually screened relevant articles and their bibliographies.
2.2. Study Selection
Two board-certified orthopedic surgeons (K.-J.L. and C.-H.K.) independently selected the articles for full-text review based on the titles and abstracts of the studies. If the abstract provided insufficient data to decide, the entire article was reviewed. Paper inclusion was based on the Patient/Intervention/Comparator/Outcome/Study design (PICOS) criteria [9]: (1) “Patient” was set as patients who underwent hip fracture; (2) “Intervention” was set as hip fracture surgery; (3) 30-day readmission was set as the “Comparator”; and (4) “Outcomes” were investigated for all variables.
This systematic review and meta-analysis were performed in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines. We included only original articles, and the exclusion criteria were as follows: papers from which appropriate data could not be extracted despite contacting the author, and cases where study populations overlapped, in which we selected the publication with the largest population for the meta-analysis. The process of identifying and selecting studies is outlined in Figure 1.
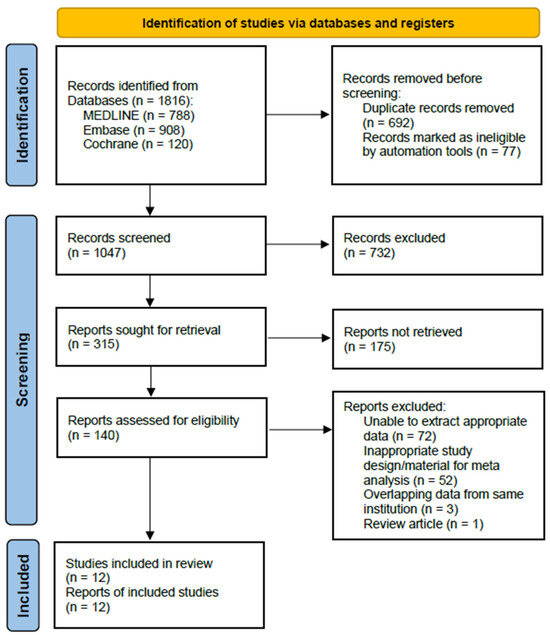
Figure 1.
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) 2020 flow diagram for identifying and selecting the studies included in this meta-analysis.
At each stage of article selection, the κ-value was calculated to determine inter-reviewer agreement regarding study selection. Agreement between reviewers was correlated a priori with κ-values as follows: κ = 1 corresponded to “perfect” agreement, 1.0 > κ ≥ 0.8 to “almost perfect” agreement, 0.8 > κ ≥ 0.6 to “substantial” agreement, 0.6 > κ ≥ 0.4 to “moderate” agreement, 0.4 > κ ≥ 0.2 to “fair” agreement, and κ < 0.2 to “slight” agreement. Disagreements at each stage were resolved by discussion between the two investigators to reach a consensus or by a discussion with a third investigator (J.W.K), who was a board-certified orthopedic faculty member, when a consensus could not be reached.
2.3. Data Extraction
For qualitative data synthesis, the following information and variables were extracted using a standardized form: (1) study design, (2) the country in which the investigation took place, (3) mean patient age, (4) sex, (5) type of hip surgery, (6) overall readmission rate, and (7) potential risk factors investigated.
The potential risk factors examined in each included study were ranked based on frequency, and the top five most frequently investigated variables were identified. Among all included papers, the top five risk factors were sex, type of surgery, older age, high ASA score, and high Charlson comorbidity index (CCI). A meta-analysis was conducted using these five key risk factors.
Additionally, we did not include underlying comorbidities in the top five most frequent potential risk factors mentioned earlier. This decision was made because the classification of comorbidities varied across individual studies and was highly heterogeneous. Instead, comorbidities were categorized separately, and a meta-analysis was conducted on the most frequently reported underlying comorbidities: diabetes mellitus (DM) and congestive heart failure (CHF).
2.4. Statistical Analysis
A meta-analysis was conducted to analyze the risk factors for 30-day readmission after hip fracture. Univariate odds ratios (ORs) and their 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated. We pooled all data using a random-effects model, as recommended in the medical field, to avoid overestimating the study results [10]. The fixed-effects model begins with the assumption that the true effect size is similar in all included studies; thus, we hypothesized that the random-effects model was generally a more plausible match for the current study. For analysis metrics with more than 10 included studies, publication bias was assessed following Cochrane’s recommendations [10]. All statistical analyses were performed using the “metafor” package in R (R Foundation for Statistical Computing, version 4.3.0).
3. Results
3.1. Article Identification
Details of the study identification and selection processes are summarized in Figure 1. The initial electronic literature search yielded 1816 articles. After removing 769 duplicates and ineligible articles using automated tools, 1047 articles remained and were screened. Of these, we excluded 732 articles after checking the title of reports, and then, 175 articles were excluded after reviewing the abstracts. Finally, after examining the content of the text, 128 articles were excluded because appropriate data for analysis could not be extracted, they had overlapping research subjects, or they were review articles. Thus, 12 studies were eligible for qualitative and quantitative data syntheses in the current meta-analysis. The κ-values between the two reviewers were 0.756 at the title review stage and 0.782 at the abstract review stage, indicating substantial agreement; this value was 1.000 at the full-text review stage, indicating perfect agreement.
3.2. Study Characteristics and Qualitative Synthesis
Of the 12 studies [5,6,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20], except for one randomized controlled trial [16], all the others had a retrospective study design. The majority of the studies (8 out of 12) were conducted in North America [6,11,12,13,14,17,18,19], followed by 3 studies from Europe [15,16,20] and 1 from Asia [5].
The mean age of the study participants ranged from 74.9 to 85.1 years, and in all studies, the proportion of female patients was higher. Information on the type of surgery was available for all but two studies [13,14], with most procedures being either hip arthroplasty or osteosynthesis. The average 30-day readmission rate ranged from 8.1% to 15.9%. Additional details on the investigated potential risk factors for readmission are presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
Information from 12 articles included for meta-analysis.
3.3. Risk-of-Bias Assessment
The methodological quality and risk of bias of the included studies were assessed using the MINORS tool [21] (Table 1). The mean MINORS score for methodological quality assessment was 18.58/24, and the scores ranged from 18 to 21 out of a possible 24 points, indicating moderate to high overall methodological quality among the selected studies. The most common methodological limitations identified included retrospective study designs, lack of prospective sample size calculations, and baseline differences in patient characteristics between readmitted and non-readmitted groups. Despite these limitations, the majority of studies exhibited clearly defined aims, comprehensive inclusion of consecutive patients, appropriate and relevant study endpoints, adequate follow-up periods, and robust statistical analyses. Therefore, the evidence synthesized from these studies was considered sufficiently reliable for the purposes of this meta-analysis.
3.4. Meta-Analysis
3.4.1. Top Five Reasons for 30-Day Readmission Following Hip Surgery
Among the 12 papers included [5,6,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20], past medical history was excluded due to inconsistent analysis. The top five reasons were determined based on the frequency with which the remaining indicators were analyzed. The most frequently identified risk factor was sexual difference (12 out of 12 papers), followed by the type of surgery—whether hip arthroplasty or osteosynthesis (8 out of 12 papers). Next, both older age and high ASA scores were analyzed in 6 out of the 12 papers, making them equally common, and high CCI score was investigated in 2 papers, ranking it as the fifth most studied factor.
For older age, the majority of papers (four out of six) calculated the OR by dividing participants into older age and control groups using 90 years as the cutoff, whereas the remaining two papers used 85 and 80 years, respectively. In all six papers, the ASA score was used to split subjects into groups based on a cutoff of ≥3 points, and the CCI score was similarly grouped using a cutoff of ≥4 points. Additional details are shown as a bar graph in Figure 2.
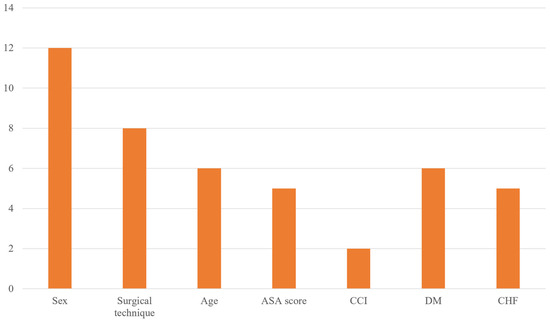
Figure 2.
Most frequently investigated potential risk factors for 30-day readmission after hip fracture surgery in included studies.
This figure demonstrates the odds ratios for significant demographic and perioperative predictors of emergency room visits using multivariate logistic regression analysis.
3.4.2. Sexual Differences
All of the 12 included studies [5,6,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20] evaluated sexual differences as a risk factor for 30-day readmission following hip fracture by reporting ORs. The pooled OR for the male sex was 1.45 (95% CI, 1.27–1.65), with significant heterogeneity of I2 = 84%. Additional details are shown in Figure 3. Also, no publication bias was observed upon visual assessment of the funnel plot (Figure 4) and Egger’s test (p = 0.792).
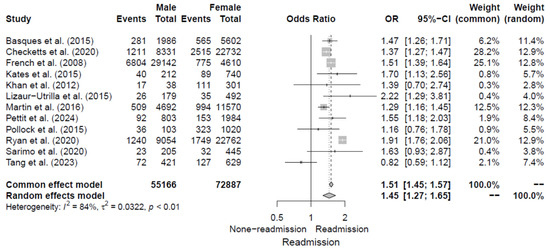
Figure 3.
Forest plot of odds ratios for male sex in relation to 30-da readmission risk following hip fracture [5,6,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20].
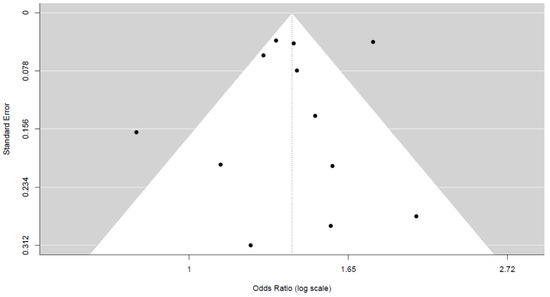
Figure 4.
Funnel plots and Egger’s test show that no significant publication bias was present in the studies assessing sexual differences.
3.4.3. Type of Surgery
Eight studies [5,6,15,16,17,18,19,20] analyzed whether the type of surgery was associated with the risk of 30-day readmission following hip fracture surgery and presented the corresponding ORs. The pooled OR for hip arthroplasty was 1.36 (95% CI, 1.03–1.80) compared to osteosynthesis, with significant heterogeneity of I2 = 84%. Additional details are shown in Figure 5.
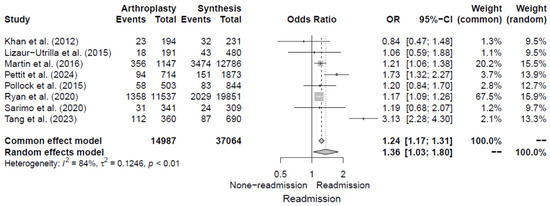
Figure 5.
Forest plot of odds ratios for type of surgery in relation to 30-day readmission risk following hip fracture [5,6,15,16,17,18,19,20].
3.4.4. Older Age
The six studies [5,11,12,13,14,20] evaluated older age as a risk factor for 30-day readmission following hip fracture by reporting ORs. Variations were observed in the definition of older age across the studies when categorizing the study population into binary groups. Among the six studies, four [11,12,14,20] set 90 years as the cut-off value, one [13] set 85 years, and one [5] set 80 years. The pooled OR for older age was 1.22 (95% CI, 1.00–1.49), with significant heterogeneity of I2 = 81%. Additional details are shown in Figure 6.
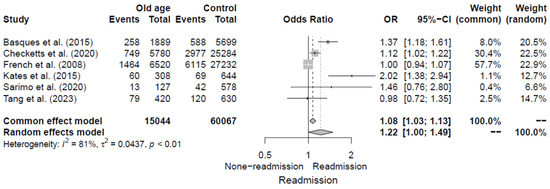
Figure 6.
Forest plot of odds ratios for older age in relation to 30-day readmission risk following hip fracture [5,11,12,13,14,20].
3.4.5. High ASA Score
The six studies [5,11,15,16,17,19] evaluated high ASA score (≥3 points) as a risk factor for 30-day readmission following hip fracture by reporting ORs. The pooled OR for high ASA scores was 2.22 (95% CI, 1.28–3.85), with significant heterogeneity of I2 = 98%. Additional details are shown in Figure 7.
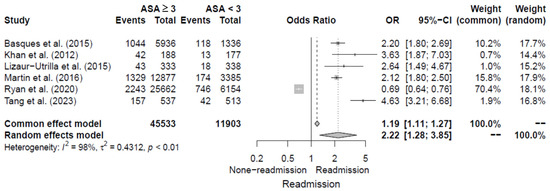
Figure 7.
Forest plot of odds ratios for high ASA score in relation to 30-day readmission risk following hip fracture [5,11,15,16,17,19].
3.4.6. High CCI Score
Two studies [12,14] evaluated high CCI score (≥4 points) as a risk factor for 30-day readmission following hip fracture by reporting ORs. The pooled OR for high CCI scores was 1.67 (95% CI, 1.36–2.05), with moderate heterogeneity of I2 = 37%. Additional details are shown in Figure 8.
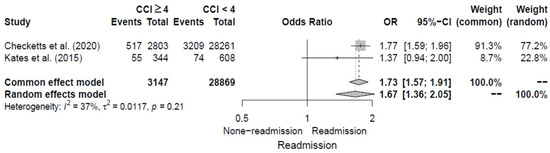
Figure 8.
Forest plot of odds ratios for high CCI score in relation to 30-day readmission risk following hip fracture [12,14].
3.4.7. Underlying Comorbidity: DM and CHF
Six studies analyzed DM as an underlying comorbidity and risk factor for 30-day readmission following hip fracture, whereas five studies analyzed CHF.
The pooled OR for patients with underlying DM, compared to the control group, was 1.63 (95% CI, 1.16–2.30; I2 = 84%), indicating a significantly higher 30-day readmission rate. Similarly, for patients with underlying CHF, the pooled OR was 1.57 (95% CI, 1.32–1.87; I2 = 86%), showing a significantly increased risk of 30-day readmission compared to the control group. Additional details are provided in Figure 9.
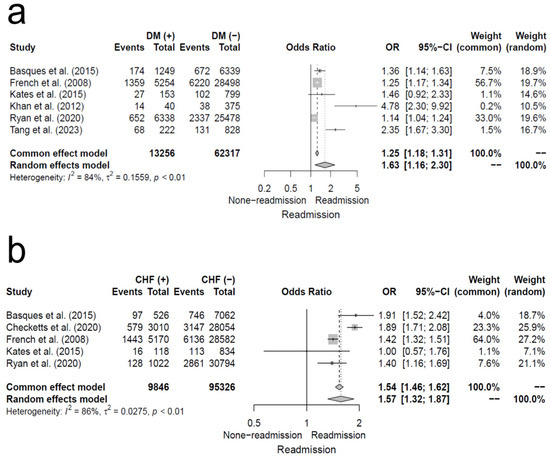
Figure 9.
Forest plot of odds ratios for (a) underlying patient with diabetes mellitus, and (b) underlying patient with congestive heart failure in relation to 30-day readmission risk following hip fracture [5,11,12,13,14,15,19].
4. Discussion
The findings of the current meta-analysis indicate that, among the top five risk factors for readmission within 30 days following a hip fracture, (1) males have a 1.45 times higher readmission rate than females; (2) undergoing hip arthroplasty is associated with a 1.36 times higher readmission rate compared to osteosynthesis; (3) advanced age is associated with a 1.22 times higher readmission rate compared to the control group; (4) a preoperative ASA score of 3 or higher is associated with a 2.22 times higher readmission rate; and (5) a preoperative CCI score of 4 or higher is associated with a 1.67 times higher readmission rate. Regarding underlying comorbidities, patients with DM had a 1.63 times higher likelihood of readmission compared to the control group, whereas patients with CHF had a 1.57 times higher likelihood of readmission.
It is well established in the field of orthopedic hip surgery that males have higher mortality and morbidity rates compared to females. According to a study conducted by Kim et al. on an Asian population [22], the one-year mortality rate after a hip fracture was 6% higher in males than in females. Additionally, a European study by Olalla et al. [23], utilizing national registry data, confirmed that male sex remained a significant risk factor for increased mortality following hip fracture surgery, even after adjusting for other variables. Given these previous findings, male sex is also, unsurprisingly, a risk factor for short-term readmission following hip surgery; this is likely because despite their smaller numbers, male patients tend to have a higher preoperative comorbidity burden compared to female patients.
Secondly, the type of surgery also influenced the likelihood of readmission, with hip arthroplasty being associated with a 1.36 times higher 30-day readmission rate than the control group. We speculate that this is due to the increased short-term risks of complications, such as dislocation and infection, following hip arthroplasty compared to other procedures. In fact, previous literature has identified prosthesis dislocation and postoperative infection following arthroplasty as the most common causes of short-term readmission after hip surgery [24,25]. Furthermore, a retrospective analysis of 4551 patients with hip fractures at our institution revealed that among patients readmitted within 30 days due to surgical complications excluding medical complications, dislocation following hip arthroplasty surgery was the most common surgical cause, occurring in 9.2% of cases in overall 30-day readmission. Therefore, greater attention to surgical technique is warranted when performing arthroplasty to minimize these complications.
Next, older age was identified as a significant factor increasing the likelihood of short-term readmission (pooled OR, 1.22). Although it was not included in this meta-analysis, as it did not meet our inclusion criteria, a large-cohort study analyzing 514,455 patients using UK National Health Service data previously reported that increasing age was strongly associated with 30-day readmission following hip arthroplasty [26]. Furthermore, a recent study by Yohe et al. [27] found that when total hip arthroplasty was performed in patients aged 80 years and older, the unplanned readmission rate was significantly higher compared to younger patients (OR, 2.4). Considering these findings, our study results are in line with previous research and can be regarded as reasonable and consistent outcomes from previous studies.
Although the findings are not limited to the field of orthopedic hip surgery, one study reported that the pre-injury ASA score is a predictor of 30-day readmission following major traumatic injury [28]. Moreover, this study suggested that the ASA score is an even better predictor of readmission compared to the CCI. Similarly, in the current study, although both a high preoperative ASA score and a high preoperative CCI were identified as significant risk factors for 30-day readmission, the pooled OR for an ASA score ≥ 3 was 2.22, whereas the pooled OR for a high CCI was 1.67, indicating that a high ASA score is a stronger predictor of short-term readmission following hip surgery.
The analysis of comorbidities was highly heterogeneous, making systematic evaluation challenging. Among the most frequently investigated comorbidities, DM and CHF were the most commonly studied, as data extraction was possible from at least three studies. These two conditions are well known as poor prognostic factors in orthopedic surgeries for older patients [29,30].
Ultimately, identifying both modifiable and non-modifiable predictors will help guide targeted interventions aimed at reducing readmission rates and improving overall patient outcomes in this population. Comorbidities, sex, age, and preoperative physical status scores (ASA or CCI) are non-modifiable risk factors. However, surgical techniques and procedural precision represent modifiable aspects that clinicians can optimize. Therefore, greater attention should be given to these controllable factors to minimize the risk of readmission.
This study had some limitations. First, due to its meta-analytical nature, the findings were inevitably influenced by the included studies. Most of these studies had retrospective designs, potentially limiting the generalizability of our results. Nonetheless, this meta-analysis is the first to systematically examine risk factors associated with 30-day readmission after hip fracture surgery, analyzing the largest available cohort, which underscores its clinical significance. Second, as mentioned earlier, preoperative comorbidity is a major factor contributing to readmission during the acute postoperative stage. However, high heterogeneity (I² > 80%) likely arises from variability in study populations, healthcare practices, differing definitions of readmission, and variations in surgical techniques across the included studies. Furthermore, potential limitations such as publication bias, variability in data standardization, and methodological heterogeneity among the included studies should be considered when interpreting our findings. These issues warrant careful consideration and should be addressed in future research.
5. Conclusions
Among all the included papers, the top five risk factors for 30-day readmission after hip surgery were male sex, hip arthroplasty surgery, older age, high ASA score, and high CCI. The most frequently investigated comorbidities identified as potential risk factors were DM and CHF.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/jcm14082779/s1, Search term related materials S1.
Author Contributions
Data curation, investigation, writing—original draft, review and editing, K.-J.L.; supervision, writing—review and editing, J.W.K.; conceptualization, formal analysis, resources, writing—original draft, review, and editing, C.-H.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by a grant from KyongBo Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. (Chungnam, Republic of Korea). The funding sources were not involved in the study design, data collection, analysis or interpretation of the data, writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to submit the manuscript for publication.
Institutional Review Board Statement
While this study involved human participants, neither ethical approval nor the acquisition of informed consent from participants was required because all data were based on previously published studies and were anonymously analyzed without any potential harm to the participants.
Informed Consent Statement
The manuscript does not contain clinical studies or patient data. For this type of study, formal consent is not required.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
| ORs | odds ratios |
| ASA | American Society of Anesthesiologists |
| PICOS | Patient/Intervention/Comparator/Outcome/Study design |
| CCI | Charlson comorbidity index |
| DM | diabetes mellitus |
| CHF | congestive heart failure |
| MINORS | methodological index for non-randomized studies |
| CIs | confidence intervals |
| RCS | retrospective cohort study |
| RCT | randomized controlled trial |
| N/A | not available |
| HA | hemi-arthroplasty |
| THA | total hip arthroplasty |
| IM | intra-medullary |
| BMI | body mass index |
| LOS | length of stay |
| ISS | injury severity score |
References
- Sing, C.W.; Lin, T.C.; Bartholomew, S.; Bell, J.S.; Bennett, C.; Beyene, K.; Bosco-Levy, P.; Bradbury, B.D.; Chan, A.H.Y.; Chandran, M.; et al. Global Epidemiology of Hip Fractures: Secular Trends in Incidence Rate, Post-Fracture Treatment, and All-Cause Mortality. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2023, 38, 1064–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jencks, S.F.; Williams, M.V.; Coleman, E.A. Rehospitalizations among Patients in the Medicare Fee-for-Service Program. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 1418–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.M.; Gibbons, C.E.R. Predictors of 30-day hospital readmission after hip fracture: A systematic review. Injury 2017, 48, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.-K.; Huang, H.-T.; Ho, M.-L.; Lin, H.-T.; Ho, P.-S.; Lee, T.-C. One-Year Readmission Risk and Mortality after Hip Fracture Surgery: A National Population-Based Study in Taiwan. Aging Dis. 2017, 8, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.Y.; Yao, W.; Wang, W.; Lv, Q.M.; Ding, W.B.; He, R.J. Development and validation of a nomogram for 30-day readmission after hip fracture surgery in geriatric patients. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2023, 27, 11517–11534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollock, F.H.; Bethea, A.; Samanta, D.; Modak, A.; Maurer, J.P.; Chumbe, J.T. Readmission Within 30 Days of Discharge After Hip Fracture Care. Orthopedics 2015, 38, e7–e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Shamseer, L.; Clarke, M.; Ghersi, D.; Liberati, A.; Petticrew, M.; Shekelle, P.; Stewart, L.A.; Group, P.-P. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 statement. Syst. Rev. 2015, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shea, B.J.; Grimshaw, J.M.; Wells, G.A.; Boers, M.; Andersson, N.; Hamel, C.; Porter, A.C.; Tugwell, P.; Moher, D.; Bouter, L.M. Development of AMSTAR: A measurement tool to assess the methodological quality of systematic reviews. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2007, 7, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; Group, P. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, F.L.; Oh, I.S.; Hayes, T.L. Fixed- versus random-effects models in meta-analysis: Model properties and an empirical comparison of differences in results. Br. J. Math. Stat. Psychol. 2009, 62, 97–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basques, B.A.; Bohl, D.D.; Golinvaux, N.S.; Leslie, M.P.; Baumgaertner, M.R.; Grauer, J.N. Postoperative length of stay and 30-day readmission after geriatric hip fracture: An analysis of 8434 patients. J. Orthop. Trauma 2015, 29, e115–e120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Checketts, J.X.; Dai, Q.; Zhu, L.; Miao, Z.; Shepherd, S.; Norris, B.L. Readmission Rates After Hip Fracture: Are There Prefracture Warning Signs for Patients Most at Risk of Readmission? J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2020, 28, 1017–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, D.D.; Bass, E.; Bradham, D.D.; Campbell, R.R.; Rubenstein, A.L.Z. Rehospitalization After Hip Fracture: Predictors and Prognosis from a National Veterans Study. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2007, 56, 705–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kates, S.L.; Behrend, C.; Mendelson, D.A.; Cram, P.; Friedman, S.M. Hospital readmission after hip fracture. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 2014, 135, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Hossain, F.S.; Dashti, Z.; Muthukumar, N. Causes and predictors of early re-admission after surgery for a fracture of the hip. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 2012, 94, 690–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizaur-Utrilla, A.; Serna-Berna, R.; Lopez-Prats, F.A.; Gil-Guillen, V. Early rehospitalization after hip fracture in elderly patients: Risk factors and prognosis. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 2015, 135, 1663–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, C.T.; Gao, Y.; Pugely, A.J. Incidence and Risk Factors for 30-Day Readmissions After Hip Fracture Surgery. Iowa Orthop. J. 2016, 36, 155–160. [Google Scholar]
- Pettit, C.J.; Herbosa, C.F.; Ganta, A.; Rivero, S.; Tejwani, N.; Leucht, P.; Konda, S.R.; Egol, K.A. Can We Predict 30-day Readmission Following Hip Fracture? J. Orthop. Trauma 2024, 39, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, G.; Nowak, L.; Melo, L.; Ward, S.; Atrey, A.; Schemitsch, E.H.; Nauth, A.; Khoshbin, A. Anemia at Presentation Predicts Acute Mortality and Need for Readmission Following Geriatric Hip Fracture. JBJS Open Access 2020, 5, e20.00048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarimo, S.; Pajulammi, H.; Jämsen, E. Process-related predictors of readmissions and mortality following hip fracture surgery: A population-based analysis. Eur. Geriatr. Med. 2020, 11, 613–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slim, K.; Nini, E.; Forestier, D.; Kwiatkowski, F.; Panis, Y.; Chipponi, J. Methodological index for non-randomized studies (minors): Development and validation of a new instrument. ANZ J. Surg. 2003, 73, 712–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.-S.; Lim, J.-Y.; Ha, Y.-C. Recent Epidemiology of Hip Fractures in South Korea. Hip Pelvis 2020, 32, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzon-Illescas, O.; Perez Fernandez, E.; Crespí Villarias, N.; Quirós Donate, F.J.; Peña, M.; Alonso-Blas, C.; García-Vadillo, A.; Mazzucchelli, R. Mortality after osteoporotic hip fracture: Incidence, trends, and associated factors. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2019, 14, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phruetthiphat, O.-a.; Otero, J.E.; Zampogna, B.; Vasta, S.; Gao, Y.; Callaghan, J.J. Predictors for readmission following primary total hip and total knee arthroplasty. J. Orthop. Surg. 2020, 28, 2309499020959160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Gao, C.; Wu, D.; Li, C.; Cheng, X.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Y. One-year unplanned readmission after total hip arthroplasty in patients with osteonecrosis of the femoral head: Rate, causes, and risk factors. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2023, 24, 845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.M.; Loeffler, M.D.; Aylin, P.; Bottle, A. Factors Associated with 30-Day Readmission after Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty: Analysis of 514 455 Procedures in the UK National Health Service. JAMA Surg. 2017, 152, e173949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yohe, N.; Weisberg, M.D.; Ciminero, M.; Mannino, A.; Erez, O.; Saleh, A. Complications and Readmissions After Total Hip Replacement in Octogenarians and Nonagenarians. Geriatr. Orthop. Surg. Rehabil. 2020, 11, 2151459320940959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, A.; Mai, T.; El-Haddad, J.; Lampron, J.; Yelle, J.-D.; Pagliarello, G.; Matar, M. Preinjury ASA score as an independent predictor of readmission after major traumatic injury. Trauma Surg. Acute Care Open 2017, 2, e000128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantrell, C.K.; DeBell, H.A.; Lehtonen, E.J.; Patel, H.A.; McKissack, H.M.; McGwin, G.; Shah, A.; Naranje, S. Risk factors for readmission within thirty days following revision total hip arthroplasty. J. Clin. Orthop. Trauma 2020, 11, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuera, C.A.; Elsharkawy, K.; Klika, A.K.; Brocone, M.; Barsoum, W.K. 2010 Mid-America Orthopaedic Association Physician in Training Award: Predictors of Early Adverse Outcomes after Knee and Hip Arthroplasty in Geriatric Patients. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2011, 469, 1391–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).