Gaming Against Frailty: Effects of Virtual Reality-Based Training on Postural Control, Mobility, and Fear of Falling Among Frail Older Adults
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Approval and Consent to Participate
2.2. Participants and Study Setting
2.3. Eligibility Criteria
2.4. Data Collection
2.5. Outcome Measures
- BBS: a clinical measure of static and dynamic balance;
- TUG test: a performance-based measure of functional mobility;
- ABC: a self-report measure of balance confidence during daily tasks;
- FES-I: a self-report measure of fear of falling.
2.6. CoP Data Acquisition and Procedures
2.7. Intervention
2.8. Sample Size Calculation
2.9. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Primary Outcomes
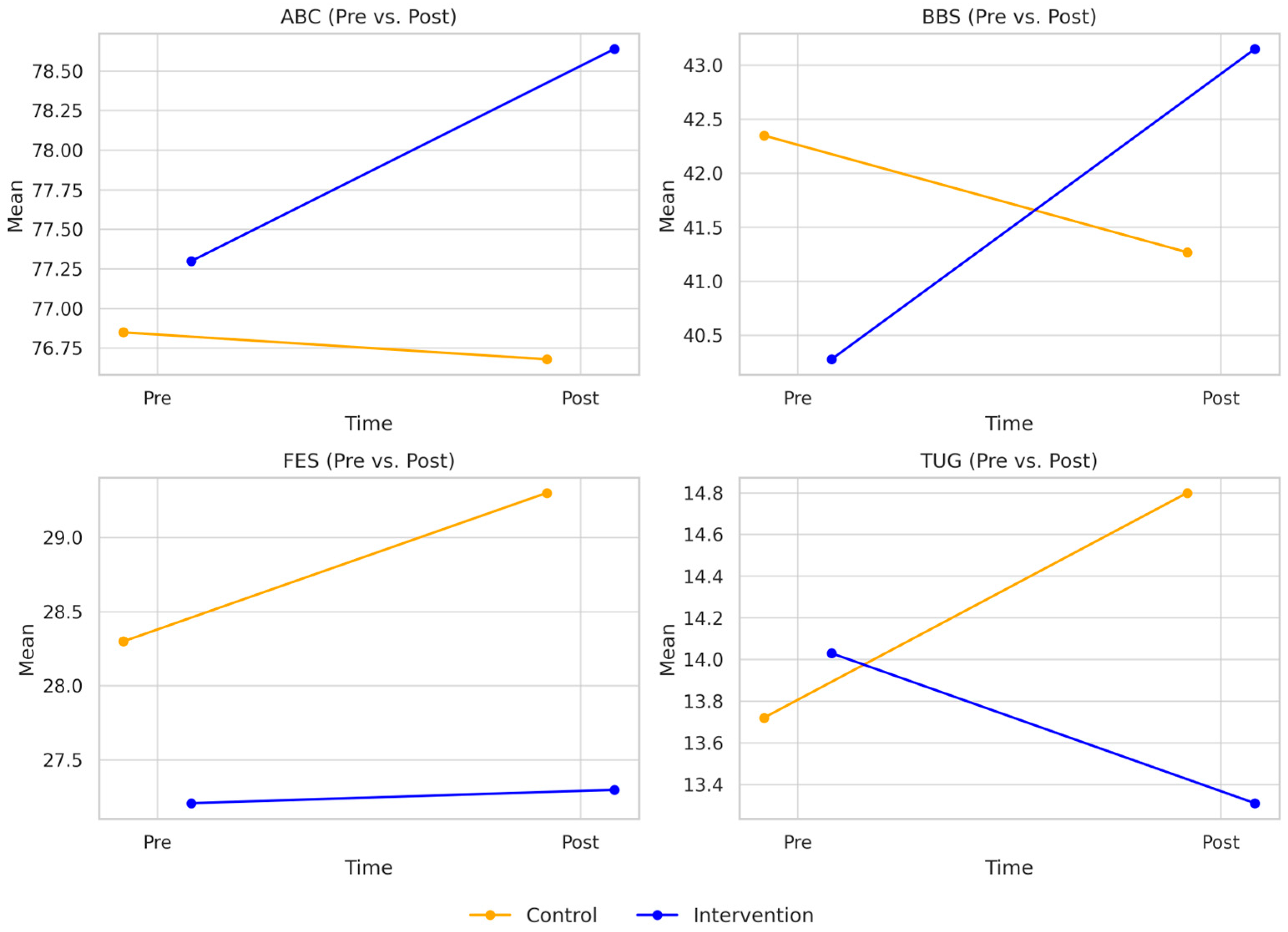
3.2. Secondary Outcomes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CoP | Center of Pressure |
| TUG | Timed Up and Go test |
| BBS | Berg Balance Scale |
| ABC | Activities-specific Balance Confidence Scale |
| FES-I | Falls Efficacy Scale—International |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| ANCOVA | Analysis of Covariance |
References
- Kaskirbayeva, D.; West, R.; Jaafari, H.; King, N.; Howdon, D.; Shuweihdi, F.; Clegg, A.; Nikolova, S. Progression of frailty as measured by a cumulative deficit index: A systematic review. Ageing Res. Rev. 2023, 84, 101789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.H.; Rockwood, K. Frailty in older adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 391, 538–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dlima, S.D.; Hall, A.; Aminu, A.Q.; Akpan, A.; Todd, C.; Vardy, E.R.L.C. Frailty: A global health challenge in need of local action. BMJ Glob. Health 2024, 9, e015173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, S.L.; Lee, J.; Emmence, L.; Bickerstaff, E.; Rayers, G.; Davidson, E.; Richardson, J.; Anderson, H.; Walker, R.; Dotchin, C. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the prevalence of frailty and pre-frailty amongst older hospital inpatients in low-and middle-income countries. Age Ageing 2025, 54, afae279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Money, A.; MacKenzie, A.; Parchment, A.; Norman, G.; Harris, D.; Ahmed, S.; McGarrigle, L.; Hawley-Hague, H.; Todd, C. Evidence on non-pharmacological interventions for preventing or reversing physical frailty in community-dwelling older adults aged over 50 years: Overview of systematic reviews. BMC Geriatr. 2025, 25, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, H.S.; Choi, Y.; Lim, J.Y.; Kim, K.; Choi, Y.H.; Lee, D.H.; Bae, S.J. The clinical frailty scale improves risk prediction in older emergency department patients: A comparison with qSOFA, NEWS2, and REMS. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 12584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fried, L.P.; Tangen, C.M.; Walston, J.; Newman, A.B.; Hirsch, C.; Gottdiener, J.; Seeman, T.; Tracy, R.; Kop, W.J.; Burke, G. Frailty in older adults: Evidence for a phenotype. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2001, 56, M146–M157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, M.; Wan, Y.-H.; Liang, Y.-D.; Shi, J.; Yang, Z.-K.; Wang, T.; Ji, C.; He, W.; Sun, N.; Guo, D. Comparison of the long-term prognostic value of different frailty instruments in older inpatients: A 5-year prospective cohort study. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2025, 30, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Duan, X.; Shen, S.; Wang, J. Independent and combined associations of depression and cognitive impairment with frailty in oldest-old adults. BMC Psychol. 2024, 12, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, P.; Nygaard, H.; Schultz, M.; Dela, F.; Aagaard, P.; Ryg, J.; Suetta, C. Frailty is associated with a history of falls among mobility-limited older adults—Cross-sectional multivariate analysis from the BIOFRAIL study. Eur. Geriatr. Med. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angulo, J.; El Assar, M.; Álvarez-Bustos, A.; Rodríguez-Mañas, L. Physical activity and exercise: Strategies to manage frailty. Redox Biol. 2020, 35, 101513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilgour, A.H.M.; Rutherford, M.; Higson, J.; Meredith, S.J.; McNiff, J.; Mitchell, S.; Wijayendran, A.; Lim, S.E.R.; Shenkin, S.D. Barriers and motivators to undertaking physical activity in adults over 70—A systematic review of the quantitative literature. Age Ageing 2024, 53, afae080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meredith, S.J.; Cox, N.J.; Ibrahim, K.; Higson, J.; McNiff, J.; Mitchell, S.; Rutherford, M.; Wijayendran, A.; Shenkin, S.D.; Kilgour, A.H.; et al. Factors that influence older adults’ participation in physical activity: A systematic review of qualitative studies. Age Ageing 2023, 52, afad145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wu, L.; Feng, H.; Ning, H.; Wu, S.; Hu, M.; Jiang, D.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, X. Comparison of exergames versus conventional exercises on the health benefits of older adults: Systematic review with meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. JMIR Serious Games 2023, 11, e42374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuan, S.-H.; Chang, L.-H.; Sun, S.-F.; Li, C.-H.; Chen, G.-B.; Tsai, Y.-J. Assessing the clinical effectiveness of an exergame-based exercise training program using ring fit adventure to prevent and postpone frailty and sarcopenia among older adults in rural long-term care facilities: Randomized controlled trial. J. Med. Internet Res. 2024, 26, e59468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallou-Guyot, M.; Mandigout, S.; Marie, R.; Robin, L.; Daviet, J.-C.; Perrochon, A. Feasibility and potential cognitive impact of a cognitive-motor dual-task training program using a custom exergame in older adults: A pilot study. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2023, 15, 1046676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Temprado, J.-J.; Torre, M.M. Are conventional combined training interventions and exergames two facets of the same coin to improve brain and cognition in healthy older adults? Data-based viewpoint. JMIR Serious Games 2022, 10, e38192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muheim, J.; Hotz, I.; Kübler, F.; Herren, S.; Sollereder, S.; Kruszewski, K.; Martin Niedecken, A.L.; Schättin, A.; Behrendt, F.; Böckler, S. ExerG–an exergame-based training device for the rehabilitation of older adults: A functional model usability study. BMC Geriatr. 2024, 24, 1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, W.L.S.; Chan, C.W.L.; Lam, F.M.H.; Chan, H.H.W.; Chan, K.C.K.; Chan, J.S.K.; Chan, O.L.W.; Cheung, D.S.K. Feasibility, safety, and effects of a Nintendo Ring Fit AdventureTM balance and strengthening exercise program in community-dwelling older adults with a history of falls: A feasibility randomized controlled trial. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2024, 24, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahat, G.; Ilhan, B.; Erdogan, T.; Catikkas, N.M.; Karan, M.A.; Drey, M.; Morley, J.E. Simpler modified Fried frailty scale as a practical tool to evaluate physical frailty: Methodological report for its cross-cultural adaptation and validation. Exp. Gerontol. 2022, 166, 111887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podsiadlo, D.; Richardson, S. The timed “Up & Go”: A test of basic functional mobility for frail elderly persons. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 1991, 39, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, K.Y.; Tan, K.B.; Tong, R.; Barrenetxea, J.; Koh, W.-P.; Chen, C. Relationship between handgrip strength and timed up-and-go test on hospitalization costs in older adults: A population-based study. BMC Public Health 2025, 25, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, L.; Patel, T.; Costa, A.; Bryce, E.; Hillier, L.M.; Slonim, K.; Hunter, S.W.; Heckman, G.; Molnar, F. Screening for frailty in primary care: Accuracy of gait speed and hand-grip strength. Can. Fam. Physician 2017, 63, e51–e57. [Google Scholar]
- Scoppa, F.; Capra, R.; Gallamini, M.; Shiffer, R. Clinical stabilometry standardization. Basic definitions, acquisition interval, sampling frequency. Gait Posture 2013, 37, 290–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maki, B.E.; Holliday, P.J.; Topper, A.K. A prospective study of postural balance and risk of falling in an ambulatory and independent elderly population. J. Gerontol. 1994, 49, M72–M84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zieliński, G. Effect size guidelines for individual and group differences in physiotherapy. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2025; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Sung, P.S. Normalized stability time analysis within the boundaries between adults with and without fear of falling. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2024, 36, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, P.-Y.; Su, B.-L.; You, Y.-L.; Yen, C.-W.; Wang, S.-T.; Guo, L.-Y. Measuring the reliability of postural sway measurements for a static standing task: The effect of age. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 850707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Almagro, D.; Achalandabaso-Ochoa, A.; Ibáñez-Vera, A.J.; Góngora-Rodríguez, J.; Rodríguez-Huguet, M. Effectiveness of virtual reality therapy on balance and gait in the elderly: A systematic review. Healthcare 2024, 12, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sápi, M.; Fehér-Kiss, A.; Csernák, K.; Domján, A.; Pintér, S. The effects of exergaming on sensory reweighting and mediolateral stability of women aged over 60: Usability study. JMIR Serious Games 2021, 9, e27884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandolfi, M.; Geroin, C.; Dimitrova, E.; Boldrini, P.; Waldner, A.; Bonadiman, S.; Picelli, A.; Regazzo, S.; Stirbu, E.; Primon, D. Virtual reality telerehabilitation for postural instability in Parkinson’s disease: A multicenter, single-blind, randomized, controlled trial. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 7962826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvajal-Parodi, C.; Mendoza, C.; Alvarez, C.; Soto-Martínez, A.; Ulloa-Díaz, D.; Jorquera-Aguilera, C.; Guede-Rojas, F. Effectiveness of exergames on functional physical performance in older adults with knee/hip osteoarthritis: A randomized controlled trial. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 2968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ting, H.X.T.; Ho, J.; Ong, P.H.; Young, W.R.; Soh, S.L.H. Convergent and predictive validity of the activities-specific balance confidence scales and balance recovery confidence scale, with regard to the falls efficacy scale-international: A cross-sectional study. Front. Aging 2025, 6, 1330612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powell, L.E.; Myers, A.M. The activities-specific balance confidence (ABC) scale. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 1995, 50, M28–M34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campo-Prieto, P.; Cancela-Carral, J.M.; Alsina-Rey, B.; Rodríguez-Fuentes, G. Immersive virtual reality as a novel physical therapy approach for nonagenarians: Usability and effects on balance outcomes of a game-based exercise program. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, O.; Arnold, N.; Thompson, L.A. Investigating the effects of virtual reality-based training on balance ability and balance confidence in older individuals. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 4581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, L.Y.W.; Tse, J.H.Y.; Chan, W.L.S.; Cheung, D.S.K. Effects of exergaming on frailty: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Nurs. 2025, 34, 1913–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Martinez, J.; Ramos-Espinoza, F.; Muñoz-Vásquez, C.; Guzman-Muñoz, E.; Herrera-Valenzuela, T.; Branco, B.H.M.; Castillo-Cerda, M.; Valdés-Badilla, P. Effects of active exergames on physical performance in older people: An overview of systematic reviews and meta-analysis. Front. Public Health 2024, 12, 1250299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, M.F.; de Avelar, I.S.; Silva, M.S.; Soares, V.; Lobo da Costa, P.H. Effects of four days hiking on postural control. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123214–e0123219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hufschmidt, A.; Dichgans, J.; Mauritz, K.H.; Hufschmidt, M. Some methods and parameters of body sway quantification and their neurological applications. Arch. Psychiatr. Nervenkr. 1980, 228, 135–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Clair, K.; Riach, C. Postural stability measures: What to measure and for how long. Clin. Biomech. 1996, 11, 176–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, M.; Freitas, S.M.S.F. Revision of posturography based on force plate for balance evaluation. Braz. J. Phys. Ther. 2010, 14, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.; Ferdjallah, M.; Harris, G.F. Fast differential analysis of center of pressure data in normal children and children with cerebral palsy. In Proceedings of the 25th Southern Biomedical Engineering Conference, Miami, FL, USA, 15–17 May 2009; McGoron, A.J., Li, C.Z., Lin, W.C., Eds. IFMBE Proc. 2009, 24, 341–342. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, L.F.; Simpson, D.M.; Nadal, J. Calculation of area of stabilometric signals using principal component analysis. Physiol. Meas. 1996, 17, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto, T.E.; Myklebust, J.B.; Hoffmann, R.G.; Lovett, E.G.; Myklebust, B.M. Measures of postural steadiness: Differences between healthy young and elderly adults. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1996, 43, 956–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Březina, T. Mechatronics 2017—Preface. Adv. Intell. Syst. Comput. 2018, 644. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, H.; Xiong, S. Center-of-pressure based postural sway measures: Reliability and ability to distinguish between age, fear of falling and fall history. Appl. Ergon. 2015, 47, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stel, V.S.; Smit, J.H.; Pluijm, S.M.F.; Lips, P. Balance and mobility performance as treatable risk factors for recurrent falling in older persons. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2003, 56, 659–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamburella, F.; Scivoletto, G.; Iosa, M.; Molinari, M. Reliability, validity, and effectiveness of center of pressure parameters in assessing stabilometric platform in subjects with incomplete spinal cord injury: A serial cross-sectional study. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2014, 11, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topper, A.K.; Maki, B.E.; Holliday, P.J. Are activity-based assessments of balance and gait in the elderly predictive of risk of falling and/or type of fall? J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 1993, 41, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanenburg, J.; de Bruin, E.D.; Favero, K.; Uebelhart, D.; Mulder, T. The reliability of postural balance measures in single and dual tasking in elderly fallers and non-fallers. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2008, 9, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moghadam, M.; Ashayeri, H.; Salavati, M.; Akhbari, B.; Ebrahimi, I.; Taghipour, M.; Mazaheri, M.; Negahban, H. Reliability of center of pressure measures of postural stability in healthy older adults: Effects of postural task difficulty and cognitive load. Gait Posture 2011, 33, 651–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raymakers, J.A.; Samson, M.M.; Verhaar, H.J.J. The assessment of body sway and the choice of the stability parameter(s). Gait Posture 2005, 21, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, P.O. Phase plane analysis of stability in quiet standing. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 1995, 32, 227–235. [Google Scholar]

| Activity | Description | Category |
|---|---|---|
| Warrior II | A slow, controlled yoga posture reinforcing balance and hip strength. Safe and effective in improving anticipatory balance. | Balance |
| Wide Squat | A squat-based resistance exercise targeting lower limb and core strength. | Strength |
| Overhead Bend | A stability-focused activity that activates balance responses. | Balance |
| Knee Lift | A gentle knee-raising exercise that targets hip flexor strength and enhances functional mobility. | Strength/Mobility |
| Variable | Intervention (n = 28) | Control (n = 23) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 70.68 ± 4.03 | 74.52 ± 5.06 | 0.006 |
| Sex (Male, %) | 53.6% | 52.2% | 0.9 |
| Height (cm) | 172.50 ± 4.86 | 166.30 ± 4.40 | <0.001 |
| Weight (kg) | 80.46 ± 9.75 | 70.35 ± 8.54 | 0.002 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 27.39 ± 3.31 | 24.89 ± 2.18 | 0.008 |
| Grip Strength (kg) | 24.79 ± 2.85 | 25.08 ± 2.68 | 0.709 |
| Fried score | 3.36 ± 0.73 | 3.57 ± 0.59 | 0.335 |
| Number of falls | 3.32 ± 1.59 | 2.65 ± 1.03 | 0.088 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alhasan, H.S.; Alshehri, M.A. Gaming Against Frailty: Effects of Virtual Reality-Based Training on Postural Control, Mobility, and Fear of Falling Among Frail Older Adults. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 5531. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14155531
Alhasan HS, Alshehri MA. Gaming Against Frailty: Effects of Virtual Reality-Based Training on Postural Control, Mobility, and Fear of Falling Among Frail Older Adults. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(15):5531. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14155531
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlhasan, Hammad S., and Mansour Abdullah Alshehri. 2025. "Gaming Against Frailty: Effects of Virtual Reality-Based Training on Postural Control, Mobility, and Fear of Falling Among Frail Older Adults" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 15: 5531. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14155531
APA StyleAlhasan, H. S., & Alshehri, M. A. (2025). Gaming Against Frailty: Effects of Virtual Reality-Based Training on Postural Control, Mobility, and Fear of Falling Among Frail Older Adults. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(15), 5531. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14155531






