Abstract
Background: The aim of this multicenter retrospective study was to investigate the effectiveness and safety of the available JAK-inhibitors (JAKi) in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and interstitial lung disease (ILD). Methods: We retrospectively analyzed patients with classified RA and RA-ILD undergoing JAKi in 6 Italian tertiary centers from April 2018 to June 2022. We included patients with at least 6 months of active therapy and one high-resolution chest tomography (HRCT) carried out within 3 months of the start of JAKi treatment. The HRCT was then compared to the most recent one carried out within 3 months before the last available follow-up appointment. We also kept track of the pulmonary function tests. Results: We included 43 patients with RA-ILD and 23 males (53.48%) with a median age (interquartile range, IQR) of 68.87 (61.46–75.78) treated with JAKi. The median follow-up was 19.1 months (11.03–34.43). The forced vital capacity remained stable in 22/28 (78.57%) patients, improved in 3/28 (10.71%) and worsened in 3/28 (10.71%). The diffusing capacity of lung for carbon monoxide showed a similar trend, remaining stable in 18/25 (72%) patients, improving in 2/25 (8%) and worsening in 5/25 (20%). The HRCT remained stable in 37/43 (86.05) cases, worsened in 4/43 (9.30%) and improved in the last 2 (4.65%). Discussion: This study suggests that JAKi therapy might be a safe therapeutic option for patients with RA-ILD in a short-term follow-up.
1. Introduction
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease characterized by joint inflammation and destruction, with an incidence of 0.5–1% in the adult population of Western countries [1,2]. In addition to joint involvement, extra-articular manifestations of RA can affect several organs and systems [3].
Approximately 10% of the RA population develops a clinically significant ILD responsible for the decreased quality of life and progressive chronic disability. ILD is also connected to 10–20% of all mortality associated with the disease, with a mean survival of 5–8 years [3].
The treatment to adopt when ILD is detected in RA patients has always been a matter of debate. The management and treatment of RA-ILD is challenging because there is still little information available on this topic, and the main literature comes from observational studies. No clinical trials have been dedicated to this topic; however, its consideration is increasing in guidelines [4]. Current therapies for the treatment of RA are being extensively evaluated worldwide in order to determine their effect on the lung and on RA-ILD patients. The introduction of biotechnological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (bDMARDs) and, more recently, of Janus-kinases inhibitors (JAKi) has changed the course of RA, markedly improving the control of synovitis and consequently reducing joint destruction and physical disability [5]. We have also recently underlined the “protective” effect of abatacept [6] and tocilizumab [7], leading to a substantial stability of ILD, both assessed with high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) and with pulmonary function tests (PFT). Rituximab has also been suggested for treating patients with RA-ILD, but its high risk of infections, when compared to abatacept, undermines its viability in such a complex patient subset [8].
There are relatively limited data on the use of JAKi in patients with RA-associated ILD. A mouse model demonstrated that tofacitinib (TOF) reduced arthritis and ILD by enhancing the expansion of myeloid-derived suppressor cells. TOF remarkably suppressed the progression of ILD in mice compared to controls [9]. A single-centre retrospective study from Tardella et al. [8] also reported scarce or null fibrosis progression in HRCT assessment in patients with RA-ILD treated with JAKi.
In this study, we aimed to investigate the effectiveness and safety of the available JAKi in patients with RA-ILD in a multicenter retrospective cohort with a central DICOM review performed by an expert radiologist.
2. Material and Methods
We retrospectively analyzed patients with RA classified according to the current criteria [1] and RA-ILD undergoing JAKi in 6 Italian tertiary centers from April 2018 to June 2022.
The different patterns of interstitial lung involvement defined by chest HRCT were classified according to the standardized criteria of the American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society International Multidisciplinary Consensus Classification of the Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias [10]. Clinical and demographic characteristics were recorded, including RA and ILD disease duration, rheumatoid factor (RF) and anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody (ACPA) status.
We included patients with at least 6 months of active therapy and at least one HRCT carried out within 3 months before the start of the JAKi treatment. This HRCT, together with the most recent HRCT, carried out within 3 months from the last available follow-up, was sent to the central DICOM and was reviewed by an expert radiologist. In particular, we defined ILD as “worsened” if the fibrosing features were greater than 10% compared to previous HRCT. We defined “stable” as those with progression or reduction in fibrosis of less than 10% and “improved” as those with a more than 10% reduction in ILD.
We kept track of the ILD patterns and eventual acute exacerbations. We also recorded pulmonary function tests (PFTs) corrected for age, gender, and height, carried out in the 3 months before the JAKi treatment started and at the last available follow-up. The results of PFTs were expressed as percentages of the predicted value for each parameter and corrected for age, gender and height. Pulmonary function was considered abnormal if forced vital capacity (FVC) was <80% of predicted values. Single-breath Diffusing Capacity of Lung for Carbon Monoxide (DLCO-SB) and DLCO adjusted by the alveolar volume (DLCO-VA) were used to assess gas transfer. For FVC, we defined “stable” those with lung function improvement or deterioration of less than 20% and “improved” those with a more than 20% increase. Conversely, patients were defined as “worsened” if FVC deterioration was greater than 20%. For DLCO, an improvement or deterioration of 15% had to be observed to classify patients as improved or worsened, respectively.
Mann–Whitney U-test was used to test the difference between DLCO and FVC at either JAKi baseline or at the last available follow-up. Fisher’s exact test was used in contingency tables. Kaplan–Meier estimates were used to investigate the survival functions of the different JAKi. No imputation for missing data was carried out. This study received local ethical committee approval (Comitato Etico dell’Area Vasta Emilia Nord 109/2019/OSS/AOUMO). All living patients gave written informed consent.
3. Results
We included 43 patients with RA-ILD, 23 were male (53.48%) and the median age (Interquartile Range, IQR) was 68.87 (61.46–75.78); they were treated with JAKi.
For all patients, HRCT was available in the previous 3 months before the beginning and at the end of the therapy with JAKi, whereas FVC was available in 27/43 (62.79%) patients and DLCO in 30/43 (69.76%). Repeated FVC measures over time were available for 28 patients (65.11%), whereas DLCO was only available for 25 (58.13%).
Baricitinib (BAR) was prescribed in 28 out of 43 patients (65.12%) and TOF in 9/43 (20.93%), whereas either filgotinib (FIL) or upadacitinib (UPA) were prescribed in 3 patients (6.98%, respectively).
All patients were naïve to anti-fibrotic drugs and none of them received concomitant nintedanib during the observation period.
The baseline characteristics of RA-ILD patients included in the study are summarized in Table 1.

Table 1.
Patient characteristics at treatment baseline.
The median follow-up was 19.1 months (interquartile range (IQR) 11.03–34.43). Thirty-eight were positive for RF (88.37%) and all but eight for ACPA (81.40%). A usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP) pattern was described in 25/43 (58.14%) patients, whereas a non-specific interstitial pneumonia (NSIP) pattern was identified in five other patients (11.62%). Lymphocytic interstitial pneumonia (LIP) was present in 2/43 patients (4.65%). In one patient only, a combined pattern of pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema (CPFE) was recorded (2.33%). Ten out of forty-three patients had an indeterminate pattern (23.26%). All patients experienced therapies with synthetic or biologic DMARD before JAKi. Thirty-two out of forty-three (74.41%) patients had previously been treated with methotrexate (MTX), and three out of forty-three (6.97%) with leflunomide. With regard to biologic DMARDs, 19/43 (44.19%) patients experienced therapy with TNF inhibitors (TNFi), 12/43 (27.91%) with rituximab, 16/43 (38.10%) with abatacept and 13/43 (30.23%) with tocilizumab. All patients were JAKi-naïve. Only 16 out of 43 patients took JAKi with MTX combotherapy (38.10%); on the other hand, 26/43 (60.47%) patients were on glucocorticoids at JAKi baseline. The evolution of lung function and radiology is summarized in Figure 1.
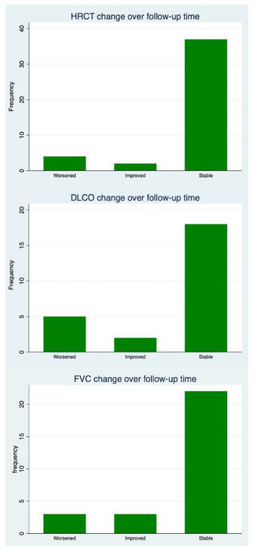
Figure 1.
Pulmonary function tests and high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) evolution. Upper Panel: ILD evolution at HRCT, Middle Panel: diffusing capacity of lung for carbon monoxide (DLCO). Lower Panel: forced vital capacity (FVC).
After a median follow-up of 19.1 months, FVC remained stable in 22/28 (78.57%) patients, and it improved in 3/28 (10.71%) and worsened in 3/28 (10.71%). At the end of the follow-up, the mean FVC did not change significantly from the JAKi treatment baseline (mean difference from baseline 3.39% ± 11.18, p = 0.12). DLCO showed a similar trend, remaining stable in 18/25 (72%) patients, improving in 2/25 (8%) and worsening in 5/25 (20%). A slight but statistically significant decrease was recorded at the end of the follow-up for DLCO (mean difference from baseline 3.44% ± 7.18, p = 0.02). HRCT remained stable in 37/43 (86.05%) cases, worsened in 4/43 (9.30%) and improved in the other 2 (4.65%). The worsened HRCT was recorded in two patients with UIP and two with NSIP, respectively. In contrast, the improved HRCT was observed in a patient with NSIP and one with an indeterminate pattern. Table 2 summarizes the HRCT evolution of RA-ILD in the different treatment groups. No difference in terms of expected frequency was found in the contingency table (p for Fisher’s exact test = 1.00)

Table 2.
HRCT evolution in different JAKi groups.
Similarly, no improvement or deterioration was seen in the HRCT and PFTs between those with MTX combotherapy and patients with JAKi monotherapy. Between the follow-up periods, JAKi were withdrawn in 21 out of 43 patients (48.84%): in 15 out of 21 (71.42%) patients this was due to a loss of effectiveness in terms of articular involvement, whereas in 3 out of 21 patients (14.28%) this was due to JAKi-unrelated adverse events.
Two withdrawals (one death) were recorded for acute exacerbations of ILD out of forty-three patients (9.52%), all in individuals on BAR. One patient’s treatment (on BAR) was discontinued due to a serious infection (4.76%). The causes of discontinuation and adverse events have also been reported in Table 3.

Table 3.
Causes of treatment discontinuation and adverse events.
The median follow-up time was different between non-selective and selective JAKi, reflecting the recent availability of UPA and FIL in Italy. Patients on BAR had a median follow-up of 20.7 months (IQR 13.41–34.16) and those on TOF of 22.13 months (IQR 9.96–36.53). On the other hand, those on UPA had a median follow-up of 15.13 months (IQR 10–15.13), whereas patients on FIL had a median follow-up of 7 months (IQR 6.1–8). Restricted mean survival time for BAR was 32.78 months (95%CI 26.32–39.24), 34.71 months (95%CI 19.38–50.03) for TOF, 7.57 months (98%CI 7.57–7.57) for FIL and 15.13 (95%CI 15.13–15.13) for UPA (underestimated because of the censoring of the largest observed analysis time). Figure 2 shows our cohort’s survival function and the Kaplan–Meier separate estimates for each JAKi. Figure 3 representatives HRCTs.
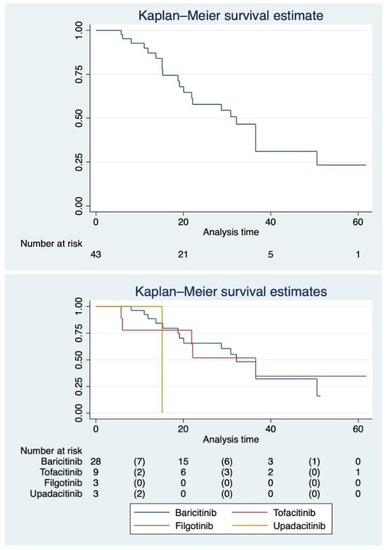
Figure 2.
Survival function of patients with RA-ILD on JAKi. Upper panel: survival function in the whole cohort with the at-risk panel. Lower panel: survival function stratified by different JAKi with at-risk panel.
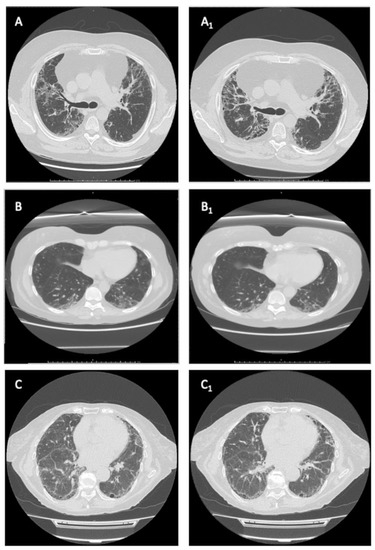
Figure 3.
Representative HRCTs. (A,A1) series: a “worsened” RA-ILD with UPI pattern in a patient treated with baricitinib. (B,B1) series: an “improved” RA-ILD with indeterminate pattern in a patient treated with baricitinib. (C,C1) series: a “stable” RA-ILD with UIP pattern in a patient treated with baricitinib.
4. Discussion
In our study, we evaluated the effectiveness and safety of JAKi in a retrospective cohort of patients affected with RA-ILD. The treatment of such patients is challenging due to the possible role of bDMARDs in the progression of the disease and the development of acute exacerbation.
Several authors described a possible effect of all TNFi in the new onset or exacerbation of RA-ILD [11,12,13]. Perez-Alvarez et al. and the British Society of Rheumatology have historically cautioned against prescribing TNFi to patients with RA-ILD for the supposed increased risk of exacerbation of ILD [13,14].
Conversely, there is increasing evidence that rituximab, tocilizumab and abatacept are associated with better patient survival; substantial PFTs stability; and little or no HRCT deterioration [6,7,15,16] in patients with RA-ILD.
Scarce data have been published on the clinical and radiological outcomes of RA-ILD patients on JAKi. Aside from anecdotal case reports [17], JAK inhibition had been considered relatively safe, since the pooled incidence of new-onset ILD, following tofacitinib treatment, was 0.18 per 100 patients/year in a pooled analysis of phases 1,2,3, 3a, 4 and long-term extension studies [18].
Recently, the impact of the first-generation JAKi on the short-term evolution of RA-ILD was evaluated in a small Italian cohort of 31 patients. In the cohort, 18 patients were on BAR, whereas 13 were on TOF. The extension of ILD was assessed with a computer-aided method able to estimate the percentage of fibrosis in the HRCT. At the 18 month follow-up, 5/31 (16.1%) patients showed a HRCT deterioration (i.e., ≥15% progression of fibrosis from baseline HRCT), 20/31 (64.5%) were considered stable (i.e., progression or reduction in fibrosis <15%) whereas 6/31 (19.4%) patients showed an HRCT improvement (i.e., ≥ 15% reduction in fibrosis) [8].
Mean FVC and DLCO remained stable at the 18-month follow-up of JAKi therapy.
Such data are somewhat concordant with results from our cohort, where most patients, about 90%, experienced no ILD progression at the follow-up HRCT. Additionally, our criteria was slightly stricter than the one in the above report. We considered a more conservative cut-off of 10% fibrosis progression to define an RA-ILD worsening.
Consistent with Tardella et al. [8], we also found that patients on JAKi had stable FVC during the observation period.
Moreover, although we observed stability or improvement of DLCO in more than two thirds of our cohort, the mean DLCO at the end of follow-up was significantly reduced. Nevertheless, one should consider that a mean decrease of about 3 percentage points over a median of 19.1 months of follow-up might not be clinically significant.
About a third of patients were treated with combination therapy, including MTX. Despite inconclusive results, recent data have suggested the safety of MTX in RA-ILD patients [19]. The American College of Rheumatology (ACR) [20] stated that clinicians (rheumatologists and pulmonologists) should prioritize any alternative option rather than accepting any additional risk of lung toxicity; therefore, the ACR conditionally recommends MTX over alternative DMARDs for the treatment of RA-ILD patients.
Less than half of our cohort discontinued JAKi by the end of the observation period. These data are somewhat consistent with the recent report by Kalyoncu et al. [21]. In this report, Kalyoncu et al. observed a retention rate of 42.6% over a median follow-up of 15 months (IQR 9–32) in a cohort of 46 patients with RA-ILD on TOF. The latter was not significantly different from the retention rate observed in patients on TOF without RA-ILD by the same authors (44.3%, median follow-up 11 (IQR 4–24 months)). In comparison, our cohort was different. It included patients with different JAKi, either selective or non-selective.
We found that discontinuation happened mainly due to the loss of effectiveness on articular involvement, and only one serious infection leading to BAR discontinuation was recorded. Finally, we observed 2 acute exacerbations of RA-ILD out of 43 patients (4.65%), 1 of which was lethal.
Acute exacerbations may occur, with a reported incidence of 5.77 patients/year in those with autoimmune ILD. A study by Manfredi et al. [22,23] observed 2 cases of acute exacerbations (10.52%) over a mean follow-up of 23.9 ± 10.9 months in a prospective cohort of 19 patients with RA-ILD. The two patients with acute exacerbation were on etanercept and methotrexate, respectively. That is to say, further studies are needed on prospective cohorts in order to investigate whether JAKi therapy might prevent acute exacerbations in patients with RA-ILD.
Our study has several limitations. First, we must acknowledge the low sample size and short follow-up time frame, especially for selective JAKi, such as FIL and UPA. Moreover, the retrospective design of the study did not allow us to record some meaningful data, such as the patients’ disease activity either at baseline or at the end of the observation period. Recently, an ORAL surveillance study [24] raised some concerns about the safety of JAKi, particularly in connection with the risk of lung cancer. On the other hand, ILD represents per se one of the most significant risk factors for lung cancer; therefore, patients with ILD should be carefully monitored for this complication. In the absence of a specific post hoc analysis on the ORAL surveillance study [24], any definitive conclusion can be made on the long-term risk of lung cancer in RA-ILD patients treated with JAKi. Since international scientific societies have not yet definitively expressed the possible use of MTX, this could have suggested a larger use of JAKi as monotherapy and influenced the choice of specific JAKi.
5. Conclusions
Our study suggest that JAKi therapy might be a safe therapeutic option for patients with RA-ILD, leading to a substantial stability of ILD at HRCT and possibly preventing PFTs deterioration, at least in a short-term follow-up.
Further research on a larger prospective cohort with long-term follow-up is needed to corroborate our results.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, V.V. and A.M.; methodology, V.V.; formal analysis, V.V.; data curation, A.C., S.G. (Stefano Gentileschi), F.A., S.G. (Serena Guiducci), M.L., L.L.C., E.P. and A.S.; writing—original draft preparation, V.V. and A.M.; writing—review and editing, F.I., M.S., C.T., C.S. and B.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted following the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Institutional Review Board (or Ethics Committee) of Comitato Etico dell’Area Vasta Emilia Nord 109/2019/OSS/AOUMO.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available upon request to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Aletaha, D.; Neogi, T.; Silman, A.J.; Funovits, J.; Felson, D.T.; Bingham, C.O.; Birnbaum, N.S.; Burmester, G.R.; Bykerk, V.P.; Cohen, M.D.; et al. 2010 Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: An American College of Rheumatology/European League against rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 2569–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venerito, V.; Angelini, O.; Fornaro, M.; Cacciapaglia, F.; Lopalco, G.; Iannone, F. A machine learning approach for predicting sustained remission in rheumatoid arthritis patients on biologic agents. J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2022, 28, e334–e339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfredi, A.; Cassone, G.; Luppi, F.; Atienza-Mateo, B.; Cavazza, A.; Sverzellati, N.; González-Gay, M.A.; Salvarani, C.; Sebastiani, M. Rheumatoid arthritis related interstitial lung disease. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2021, 17, 485–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holroyd, C.R.; Seth, R.; Bukhari, M.; Malaviya, A.; Holmes, C.; Curtis, E.; Chan, C.; Yusuf, M.A.; Litwic, A.; Smolen, S.; et al. The British society for rheumatology biologic DMARD safety guidelines in inflammatory arthritis. Rheumatology 2019, 58, e3–e42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venerito, V.; Lopalco, G.; Cacciapaglia, F.; Fornaro, M.; Iannone, F. A bayesian mixed treatment comparison of efficacy of biologics and small molecules in early rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2019, 38, 1309–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassone, G.; Manfredi, A.; Atzeni, F.; Venerito, V.; Vacchi, C.; Picerno, V.; Furini, F.; Erre, G.L.; Tomietto, P.; Fedele, A.L.; et al. Safety of abatacept in Italian patients with rheumatoid arthritis and interstitial lung disease: A multicenter retrospective study. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfredi, A.; Cassone, G.; Furini, F.; Gremese, E.; Venerito, V.; Atzeni, F.; Arrigoni, E.; Della Casa, G.; Cerri, S.; Govoni, M.; et al. Tocilizumab therapy in rheumatoid arthritis with interstitial lung disease: A multicentre retrospective study. Intern. Med. J. 2020, 50, 1085–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tardella, M.; Di Carlo, M.; Carotti, M.; Ceccarelli, L.; Giovagnoni, A.; Salaffi, F. A retrospective study of the efficacy of JAK inhibitors or abatacept on rheumatoid arthritis-interstitial lung disease. Inflame Pharmacol. 2022, 30, 705–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sendo, S.; Saegusa, J.; Yamada, H.; Nishimura, K.; Morinobu, A. Tofacitinib facilitates the expansion of myeloid-derived suppressor cells and ameliorates interstitial lung disease in SKG mice. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2019, 21, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travis, W.D.; Costabel, U.; Hansell, D.M.; King, T.E.; Lynch, D.A.; Nicholson, A.G.; Ryerson, C.J.; Ryu, J.H.; Selman, M.; Wells, A.U.; et al. An official American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society statement: Update of the International multidisciplinary classification of the idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care. Med. 2013, 188, 733–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laria, A.; Lurati, A.M.; Zizzo, G.; Zaccara, E.; Mazzocchi, D.; Re, K.A.; Marrazza, M.; Faggioli, P.; Mazzone, A. Interstitial lung disease in rheumatoid arthritis: A practical review. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 837133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, W.G.; Hyrich, K.L.; Watson, K.D.; Lunt, M.; BSRBR Control Centre Consortium; Symmons, D.P.M.; British Society for Rheumatology Biologics Register. Influence of anti-TNF therapy on mortality in patients with rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease: Results from the British society for rheumatology biologics register. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2010, 69, 1086–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Alvarez, R.; Perez-de-Lis, M.; Diaz-Lagares, C.; Pego-Reigosa, J.M.; Retamozo, S.; Bove, A.; Brito-Zeron, P.; Bosch, X.; Ramos-Casals, M. Interstitial lung disease induced or exacerbated by TNF-targeted therapies: Analysis of 122 cases. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 41, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledingham, J.; Deighton, C.; on behalf of the British Society for Rheumatology Standards, G. and AWG (SGAWG). Update on the British society for rheumatology guidelines for prescribing TNFα blockers in adults with rheumatoid arthritis (update of previous guidelines of April 2001). Rheumatology 2005, 44, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fui, A.; Bergantini, L.; Selvi, E.; Mazzei, M.A.; Bennett, D.; Pieroni, M.G.; Rottoli, P.; Bargagli, E. Rituximab therapy in interstitial lung disease associated with rheumatoid arthritis. Intern. Med. J. 2020, 50, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vadillo, C.; Nieto, M.A.; Romero-Bueno, F.; Leon, L.; Sanchez-Pernaute, O.; Rodriguez-Nieto, M.J.; Freites, D.; Jover, J.A.; Álvarez-Sala, J.L.; Abasolo, L. Efficacy of rituximab in slowing down progression of rheumatoid arthritis-related interstitial lung disease: Data from the NEREA registry. Rheumatology 2020, 59, 2099–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacchi, C.; Manfredi, A.; Cassone, G.; Cerri, S.; Della Casa, G.; Andrisani, D.; Salvarani, C.; Sebastiani, M. Tofacitinib for the treatment of severe interstitial lung disease related to rheumatoid arthritis. Case Rep. Med. 2021, 2021, 6652845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citera, G.; Mysler, E.; Madariaga, H.; Cardiel, M.H.; Castañeda, O.; Fischer, A.; Richette, P.; Chartrand, S.; Park, J.K.; Strengholt, S.; et al. Incidence rates of interstitial lung disease events in tofacitinib-treated rheumatoid arthritis patients: Post hoc analysis from 21 clinical trials. J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2021, 27, e482–e490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juge, P.A.; Lee, J.S.; Lau, J.; Kawano-Dourado, L.; Rojas Serrano, J.; Sebastiani, M.; Koduri, G.; Matteson, E.; Bonfiglioli, K.; Sawamura, M.; et al. Methotrexate and rheumatoid arthritis associated interstitial lung disease. Eur. Respir. J. 2021, 57, 2000337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraenkel, L.; Bathon, J.M.; England, B.R.; St Clair, E.W.; Arayssi, T.; Carandang, K.; Deane, K.D.; Genovese, M.; Huston, K.K.; Kerr, G.; et al. 2021 American College of Rheumatology guideline for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Care. Res. 2021, 73, 924–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyoncu, U.; Bilgin, E.; Erden, A.; Satış, H.; Tufan, A.; Tekgöz, E.; Ateş, A.; Coşkun, B.N.; Yağız, B.; Küçükşahin, O.; et al. Efficacy and safety of tofacitinib in rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease: TReasure real-life data. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2022, 40, 2071–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luppi, F.; Sebastiani, M.; Salvarani, C.; Bendstrup, E.; Manfredi, A. Acute exacerbation of interstitial lung disease associated with rheumatic disease. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2022, 18, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfredi, A.; Sebastiani, M.; Cerri, S.; Vacchi, C.; Tonelli, R.; Della Casa, G.; Cassone, G.; Spinella, A.; Fabrizio, P.; Luppi, F.; et al. Acute exacerbation of interstitial lung diseases secondary to systemic rheumatic diseases: A prospective study and review of the literature. J. Thorac. Dis. 2019, 11, 1621–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ytterberg, S.R.; Bhatt, D.L.; Mikuls, T.R.; Koch, G.G.; Fleischmann, R.; Rivas, J.L.; Germino, R.; Menon, S.; Sun, Y.; Wang, C.; et al. Cardiovascular and cancer risk with tofacitinib in rheumatoid arthritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 316–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).