Mediterranean Diet and Agri-Food By-Products: A Possible Sustainable Approach for Breast Cancer Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
Agri-Food By-Products as a Potential Target for the Treatment of Breast Cancer
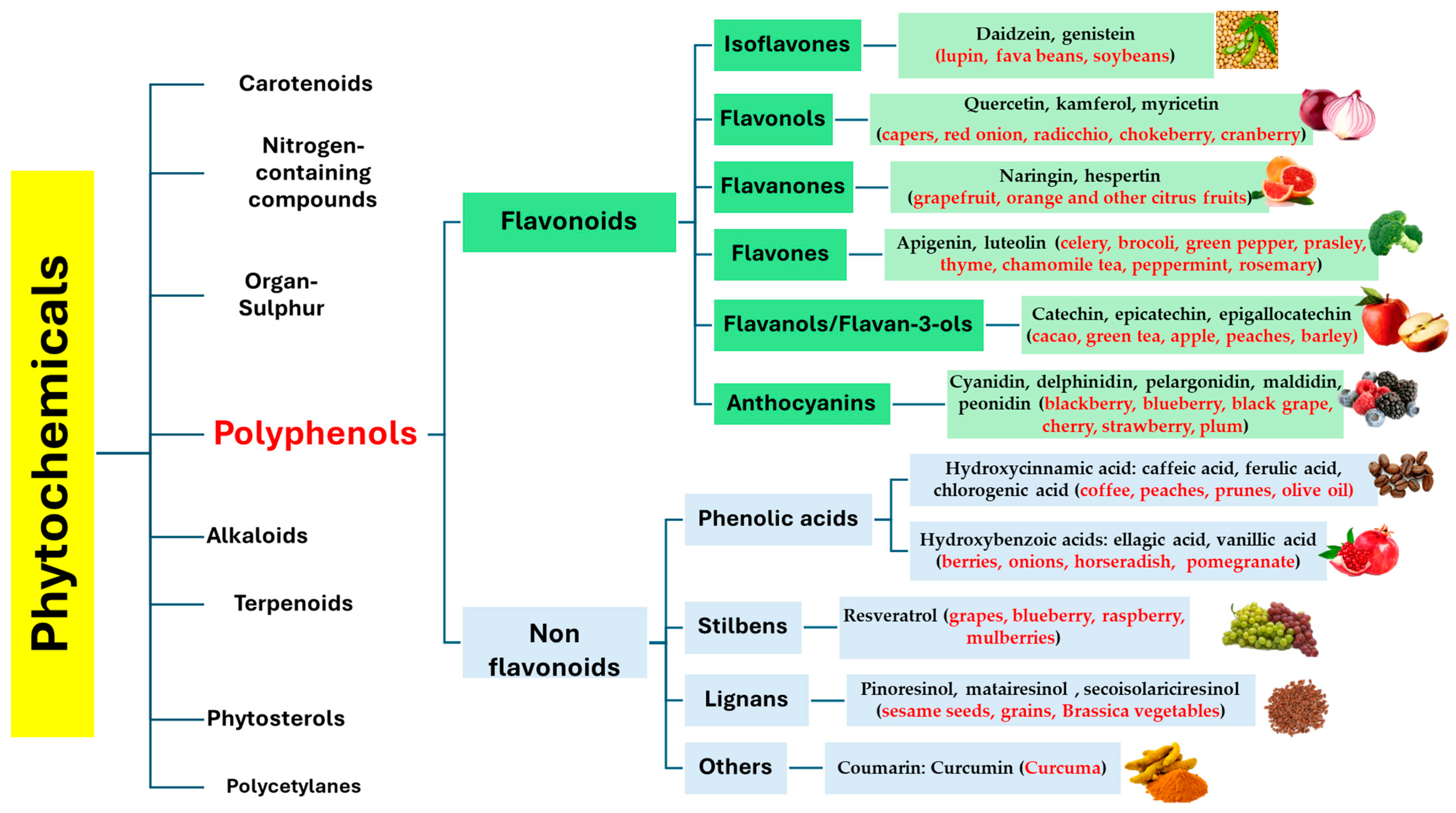
2. Phytochemicals: Naturally Occurring Compounds in the Human Diet
3. Polyphenols: The Most Abundant Phytochemicals in the Plant Kingdom
3.1. Polyphenols Classification
3.2. Oxidative Stress and Inflammation Processes
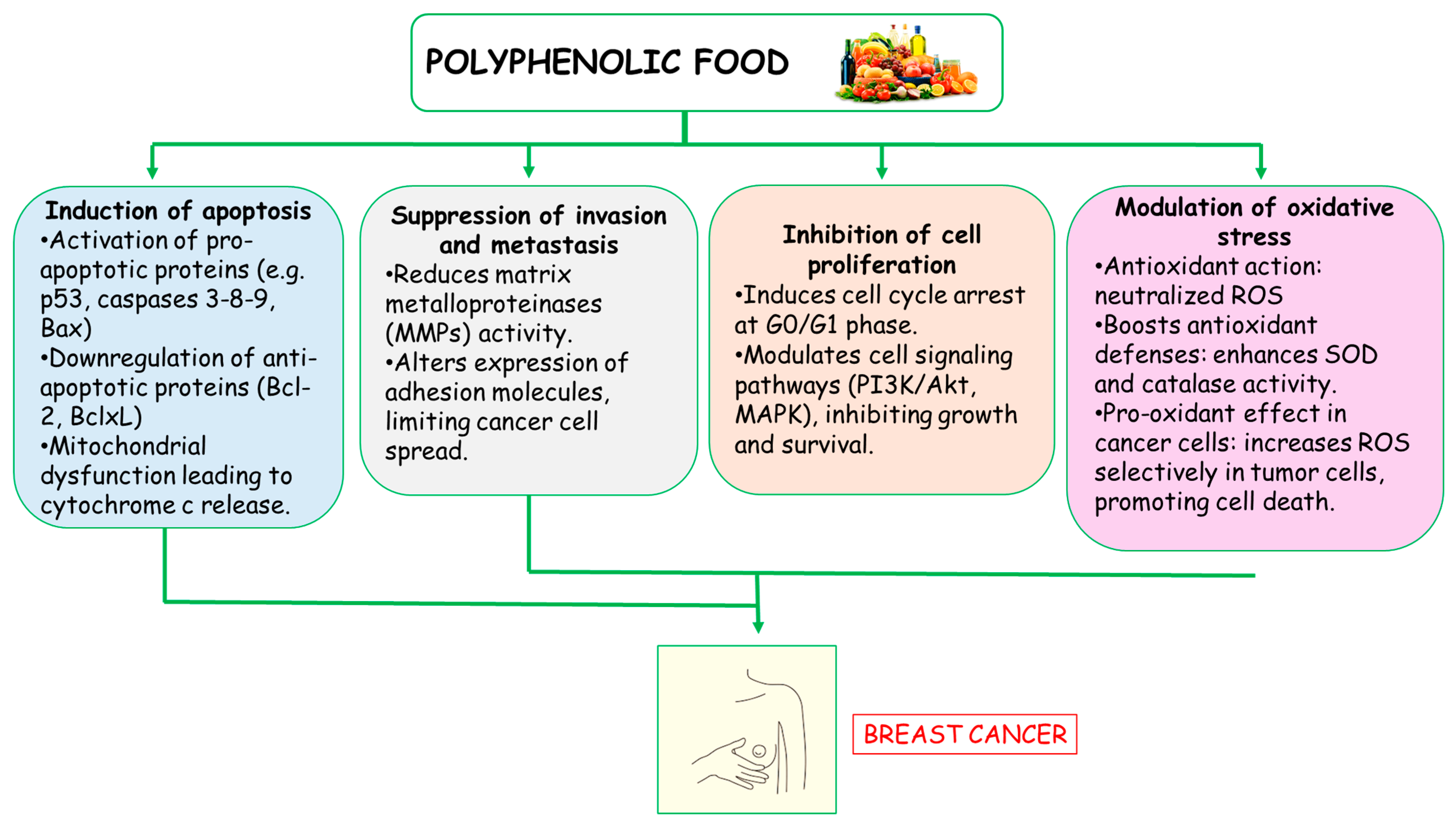
3.3. Anti-Breast Cancer Activity of Polyphenols
4. The Foods of the Mediterranean Diet: A Polyphenolic-Food Strategy Against Breast Cancer
4.1. Fruits
4.1.1. Punica granatum L.
4.1.2. Apples
4.1.3. Citrus Fruits
4.1.4. Walnuts
4.1.5. Berries
4.2. Extra Virgin Olive Oil
4.3. Flaxseeds
4.4. Red Wine
5. The Mediterranean Diet and Breast Cancer: A Protective Nutritional Approach
6. Conclusions on Sustainable Breast Cancer Therapy
- Reduces Food Waste: Repurposing food processing residues into functional nutraceuticals minimizes environmental impact.
- Cost-Effective Cancer Therapy: Agri-food by-products offer an affordable source of anticancer compounds, making them accessible to a broader population.
- Eco-Friendly and Renewable Resource: Unlike synthetic drugs, plant-based bioactive compounds are naturally available and biodegradable.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MedDiet | Mediterranean Diet |
| ROS | Reactive Oxygen Species |
| PPs | Polyphenols |
| TNBC | Triple-Negative Breast Cancer |
References
- Torre, L.A.; Bray, F.; Siegel, R.L.; Ferlay, J.; Lortet-Tieulent, J.; Jemal, A. Statistiche globali sul cancro. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2015, 65, 87–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferlay, J.; Ervik, M.; Lam, F.; Colombet, M.; Mery, L.; Piñeros, M.; Znaor, A.; Soerjomataram, I.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Observatory: Cancer Today; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Campeau, P.M.; Foulkes, W.D.; Tischkowitz, M.D. Hereditary breast cancer: New genetic developments, new therapeutic avenues. Hum. Genet. 2008, 124, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sisti, J.S.; Collins, L.C.; Beck, A.H.; Tamimi, R.M.; Rosner, B.A.; Eliassen, A.H. Reproductive risk factors in relation to molecular subtypes of breast cancer: Results from the nurses’ health studies. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 138, 2346–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiovitz, S.; Korde, L.A. Genetics of Breast Cancer: A Topic in Evolution. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, 1291–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, A.A.; Rolph, R.; Cutress, R.I.; Copson, E.R. A Review of Modifiable Risk Factors in Young Women for the Prevention of Breast Cancer. Breast Cancer (Dove. Med. Press) 2021, 13, 241–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.-C.; Do, C.; Andrulis, I.L.; John, E.M.; Daly, M.B.; Buys, S.S.; Chung, W.K.; Knight, J.A.; Bradbury, A.R.; Keegan, T.H.M.; et al. Breast Cancer Family History and Allele-Specific DNA Methylation in the Legacy Girls Study. Epigenetics 2018, 13, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loibl, S.; Poortmans, P.; Morrow, M.; Denkert, C.; Curigliano, G. Breast cancer. Lancet 2021, 397, 1750–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolan, E.; Lindeman, G.J.; Visvader, J.E. Deciphering breast cancer: From biology to the clinic. Cell 2023, 186, 1708–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chunarkar-Patil, P.; Kaleem, M.; Mishra, R.; Ray, S.; Ahmad, A.; Verma, D.; Bhayye, S.; Dubey, R.; Singh, H.N.; Kumar, S. Anticancer Drug Discovery Based on Natural Products: From Computational Approaches to Clinical Studies. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Zheng, L.W.; Ding, Y.; Chen, Y.F.; Cai, Y.W.; Wang, L.P.; Huang, L.; Liu, C.C.; Shao, Z.M.; Yu, K.D. Breast cancer: Pathogenesis and treatments. Sig. Transduct Target Ther. 2025, 10, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2017, 67, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jagsi, R. Early-stage breast cancer: Falling risks and emerging options. Lancet 2017, 390, 1010–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Echave, J.; Fraga-Corral, M.; Pereira, A.G.; Soria-Lopez, A.; Barral, M.; Chamorro, F.; Cao, H.; Xiao, J.; Simal-Gandara, J.; Prieto, M.A. Chapter 8—Valorization of food waste biomass and biomaterials from a circular economy approach. In Sustainable Development and Pathways for Food Ecosystems; Accorsi, R., Bhat, R., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2023; pp. 183–226. ISBN 9780323908856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Li, F.; Duan, Y.; Wen, C.; Wang, W.; Zhang, L.; Huang, R.; Yin, Y. Oxidative stress, nutritional antioxidants and beyond. Sci. China Life Sci. 2020, 63, 866–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinton, S.K.; Giovannucci, E.L.; Hursting, S.D. The World Cancer Research Fund/American Institute for Cancer Research Third Expert Report on Diet, Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Cancer: Impact and Future Directions. J. Nutr. 2020, 150, 663–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotepui, M. Diet and Risk of Breast Cancer. Contemp. Oncol. 2016, 20, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorrenti, V.; Burò, I.; Consoli, V.; Vanella, L. Recent Advances in Health Benefits of Bioactive Compounds from Food Wastes and By-Products: Biochemical Aspects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varghese, E.; Samuel, S.M.; Abotaleb, M.; Cheema, S.; Mamtani, R.; Busselberg, D. The “yin and yang” of natural compounds in anticancer therapy of triple-negative breast cancers. Cancers 2018, 10, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos-Buelga, C.; González-Paramás, A.M.; Oludemi, T.; Ayuda-Durán, B.; González-Manzano, S. Plant phenolics as functional food ingredients. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2019, 90, 183–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meccariello, R.; D’Angelo, S. Impact of Polyphenolic-Food on Longevity: An Elixir of Life. An Overview. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, K.; Aggarwal, B.B.; Singh, R.B.; Buttar, H.S.; Wilson, D.; De Meester, F. Food antioxidants and their anti-inflammatory properties: A potential role in cardiovascular diseases and cancer prevention. Diseases 2016, 4, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.H. Potential synergy of phytochemicals in cancer prevention mechanism of action. J. Nutr. 2004, 134, 3479–3485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scalbert, A.; Andres-Lacueva, C.; Arita, M.; Kroon, P.; Manach, C.; Urpi-Sarda, M.; Wishart, D. Databases on food phytochemicals and their health-promoting effects. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 4331–4348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, P.E.; Snyder, D.C. Phytochemicals and cancer risk: A review of the epidemiological evidence. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2012, 27, 599–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapira, N. The potential contribution of dietary factors to breast cancer prevention. Eur. J. Cancer Prev. 2017, 26, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, L.S.; Chen, S. Phytochemicals for breast cancer prevention by targeting aromatase. Front. Biosci. 2009, 14, 3846–3863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gökalp, F. Therapeutic effect of some natural active compounds for breast cancer. Med. Oncol. 2022, 39, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapinova, A.; Kubatka, P.; Golubnitschaja, O.; Kello, M.; Zubor, P.; Solar, P.; Pec, M. Dietary phytochemicals in breast cancer research: Anticancer effects and potential utility for effective chemoprevention. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2018, 23, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, J.J.; Xu, D.P.; Zhou, T.; Zhou, Y.; Li, S.; Li, H.B. Bioactivities and health benefits of wild fruits. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.S.; Wazed, M.A.; Asha, S.; Amin, M.R.; Shimul, I.M. Dietary Phytochemicals in Health and Disease: Mechanisms, Clinical Evidence, and Applications-A Comprehensive Review. Food Sci. Nutr. 2025, 13, e70101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinoush, B.; Shirdel, I.; Wink, M. Phytochemicals: Potential Lead Molecules for MDR Reversal. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moga, M.A.; Dimienescu, O.G.; Bălan, A.; Dima, L.; Toma, S.I.; Bîgiu, N.F.; Blidaru, A. Pharmacological and Therapeutic Properties of Punica granatum Phytochemicals: Possible Roles in Breast Cancer. Molecules 2021, 26, 1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vini, R.; Sreeja, S. Punica granatum and its therapeutic implications on breast carcinogenesis: A review. BioFactors 2015, 41, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, K.S.; Almalki, W.H.; Makeen, H.A.; Albratty, M.; Meraya, A.M.; Nagraik, R.; Sharma, A.; Kumar, D.; Chellappan, D.K.; Singh, S.K.; et al. Role of Medicinal plant-derived Nutraceuticals as a potential target for the treatment of breast cancer. J. Food Biochem. 2022, 46, e14387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colantuono, A.; Ferracane, R.; Vitaglione, P. Potential bioaccessibility and functionality of polyphenols and cynaropicrin from breads enriched with artichoke stem. Food Chem. 2018, 245, 838–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Angelo, S.; Cimmino, A.; Raimo, M.; Salvatore, A.; Zappia, V.; Galletti, P. Effect of reddening-ripening on the antioxidant activity of polyphenol extracts from cv. ‘Annurca’ apple fruits. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 9977-85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, R. Chemistry and biochemistry of dietary polyphenols. Nutrients 2010, 2, 1231–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boccellino, M.; D’Angelo, S. Anti-Obesity Effects of Polyphenol Intake: Current Status and Future Possibilities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abotaleb, M.; Samuel, S.M.; Varghese, E.; Varghese, S.; Kubatka, P.; Liskova, A.; Büsselberg, D. Flavonoids in Cancer and Apoptosis. Cancers 2018, 11, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Rio, D.; Rodriguez-Mateos, A.; Spencer, J.P.; Tognolini, M.; Borges, G.; Crozier, A. Dietary (poly)phenolics in human health: Structures, bioavailability, and evidence of protective effects against chronic diseases. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2013, 18, 1818–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraga, C.G.; Croft, K.D.; Kennedy, D.O.; Tomás-Barberán, F.A. The effects of polyphenols and other bioactives on human health. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 514–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, L.; Joksimovic, M.; D’Angelo, S. Effects of Punica granatum Fruit (a Super Food) Juice on Human Health. Curr. Res. Nutr. Food Sci. 2022, 18, 618–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscolo, A.; Mariateresa, O.; Giulio, T.; Mariateresa, R. Oxidative Stress: The Role of Antioxidant Phytochemicals in the Prevention and Treatment of Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofiullah, S.S.M.; Murugan, D.D.; Muid, S.A.; Seng, W.Y.; Kadir, S.Z.S.A.; Abas, R.; Ridzuan, N.R.A.; Zamakshshari, N.H.; Woon, C.K. Natural Bioactive Compounds Targeting NADPH Oxidase Pathway in Cardiovascular Diseases. Molecules 2023, 28, 1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marino, A.; Russo, D.; Leone, A. Natural Antioxidant Compounds as Potential Pharmaceutical Tools against Neurodegenerative Diseases. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 25974–25990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Angelo, S. Current Evidence on the Effect of Dietary Polyphenols Intake on Brain Health. Curr. Res. Nutr. Food Sci. 2020, 16, 1170–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Z. Therapeutic Effects of Natural Compounds against Diabetic Complications via Targeted Modulation of Ferroptosis. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1425955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Ma, J.; Li, Y. Natural Antioxidant Compounds as Potential Therapy for Diabetic Complications. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, L.; Joksimovic, M.; D’Angelo, S. Could Polyphenolic Food Intake Help in the Control of Type 2 Diabetes? A Narrative Review of the Last Evidence. Curr. Res. Nutr. Food Sci. 2022, 18, 785–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, P.; Janmeda, P.; Docea, A.O.; Yeskaliyeva, B.; Abdull Razis, A.F.; Modu, B.; Calina, D.; Sharifi-Rad, J. Oxidative stress, free radicals and antioxidants: Potential crosstalk in the pathophysiology of human diseases. Front. Chem. 2023, 11, 1158198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Angelo, S. Polyphenols: Potential Beneficial Effects of These Phytochemicals in Athletes. Curr. Sports Med. Rep. 2020, 19, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrone, P.; D’Angelo, S. Hormesis and health: Molecular mechanisms and the key role of polyphenols. Food Chem. Adv. 2025, 7, 101030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boccellino, M.; Quagliuolo, L.; D’Angelo, S. Annurca Apple Biophenols’ Effects in Combination with Cisplatin on A549 Cells. Curr. Res. Nutr. Food Sci. 2021, 17, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuoso, D.C.; D’Angelo, S.; Ferraro, R.; Caserta, S.; Guido, S.; Cammarota, M.; Porcelli, M.; Cacciapuoti, G. Annurca apple polyphenol extract promotes mesenchymal-to-epithelial transition and inhibits migration in triple-negative breast cancer cells through ROS/JNK signaling. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuoso, D.C.; Porcelli, M.; Cacciapuoti, G.; D’Angelo, S. Biological Activity of MelAnnurca Flesh Apple Biophenols. Curr. Res. Nutr. Food Sci. 2020, 16, 1149–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Angelo, S.; Martino, E.; Cacciapuoti, G. Effects of Annurca Apple (Malus pumila cv Annurca) Polyphenols on Breast Cancer Cells. Curr. Res. Nutr. Food Sci. 2019, 15, 745–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahfoufi, N.; Alsadi, N.; Jambi, M.; Matar, C. The Immunomodulatory and Anti-Inflammatory Role of Polyphenols. Nutrients. 2018, 10, 1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scalbert, A.; Manach, C.; Morand, C.; Rémésy, C.; Jiménez, L. Dietary Polyphenols and the Prevention of Diseases. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2005, 45, 287–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myhrstad, M.C.W.; Wolk, A. Antioxidants and phytochemicals—A scoping re-view for Nordic Nutrition Recommendations 2023. Food Nutr. Res. 2023, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Liu, T.; Lin, Q.; Gao, D.; Wang, C. Polyphenols in health and food processing: Antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant insights. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 143, 112–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Huang, C.; Lin, Z.; Zeng, Y. Research advances in the bioactiv-ity of plant polyphenols. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 57, 7515–7527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozzetti, L.; Ferrara, F.; Marotta, L.; Gemma, S.; Butini, S.; Benedusi, M.; Fusi, F.; Ahmed, A.; Pomponi, S.; Ferrari, S.; et al. Extra Virgin Olive Oil Extracts of Indigenous Southern Tuscany Cultivar Act as Anti-Inflammatory and Vasorelaxant Nutraceuti-cals. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambari, L.; Cellamare, A.; Grassi, F.; Grigolo, B.; Panciera, A.; Ruffilli, A.; Faldini, C.; Desando, G. Overview of Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Nociceptive Effects of Pol-yphenols to Halt Osteoarthritis: From Preclinical Studies to New Clinical Insights. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, G.; Kucheryavenko, O.; Wordsworth, J.; von Zglinicki, T. The senescent bystander effect is caused by ROS-activated NF-κB signalling. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2018, 170, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Angelo, S. Diet and Aging: The Role of Polyphenol-Rich Diets in Slow Down the Shortening of Telomeres: A Review. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pizzino, G.; Irrera, N.; Cucinotta, M.; Pallio, G.; Mannino, F.; Arcoraci, V.; Squadrito, F.; Altavilla, D.; Bitto, A. Oxidative Stress: Harms and Benefits for Human Health. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 8416763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tee, J.K.; Ong, C.N.; Bay, B.H.; Ho, H.K.; Leong, D.T. Oxidative Stress by Inorganic Nanoparticles. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2016, 8, 414–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharifi-Rad, M.; Anil Kumar, N.V.; Zucca, P.; Varoni, E.M.; Dini, L.; Panzarini, E.; Rajkovic, J.; Tsouh Fokou, P.V.; Azzini, E.; Peluso, I.; et al. Lifestyle, Oxidative Stress, and Antioxidants: Back and Forth in the Pathophysiology of Chronic Diseases. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Meo, S.; Reed, T.T.; Venditti, P.; Victor, V.M. Role of ROS and RNS Sources in Physiological and Pathological Conditions. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 1245049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phaniendra, A.; Jestadi, D.B.; Periyasamy, L. Free Radicals: Properties, Sources, Targets, and their Implication in Various Diseases. Indian J. Clin. Biochem. 2015, 30, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozcan, A.; Ogun, M. Biochemistry of Reactive Oxygen and Nitrogen Species. In Basic Principles and Clinical Significance of Oxidative Stress; Gowder, S.J.T., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2015; Chapter 3; pp. 37–58. [Google Scholar]
- Donia, T.; Khamis, A. Management of Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Cardiovascular Diseases: Mechanisms and Challenges. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 34121–34153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castanheira, F.V.S.; Kubes, P. Review Series Human Neutrophils Neutrophils and NETs in Modulating Acute and Chronic Inflammation. Blood 2019, 133, 2178–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannoodee, S.; Nasuruddin, D.N. Acute Inflammatory Response. Nature 1965, 206, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varela, M.L.; Mogildea, M.; Moreno, I.; Lopes, A. Acute Inflammation and Metabolism. Inflammation 2018, 41, 1115–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margraf, A.; Lowell, C.A.; Zarbock, A. Neutrophils in acute inflammation: Current concepts and translational implications. Blood 2022, 139, 2130–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloth, D.D.; Iacovelli, L.; Arbuckle, R.; McIntosh, A.C. The escalating role of epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors in cancer management: Clinical considerations for the health system pharmacist. Pharm. Ther. 2010, 35, 219. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.; Qi, B.; Yang, L.; Wang, X.; Huang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, Y.; Xiao, W. Phytoestrogens, novel dietary supplements for breast cancer. Biomed. Pharmacothe. 2023, 160, 114341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putra, O.D.; Hirano, M.; Tanaka, Y.; Kondo, R. Polyphenols and their roles in cancer therapy. Biomed. Pharmacothe. 2020, 129, 110469. [Google Scholar]
- Mileo, A.M.; Miccadei, S. Polyphenols as Modulator of Oxidative Stress in Cancer Disease: New Therapeutic Strategies. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2016, 2016, 6475624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuter, S.; Gupta, S.C.; Chaturvedi, M.M.; Aggarwal, B.B. Oxidative stress, inflammation, and cancer: How are they linked? Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2010, 49, 1603–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Danielski, R.; Santhiravel, S.; Shahidi, F. Unlocking the Nutraceutical Potential of Legumes and Their By-Products: Paving the Way for the Circular Economy in the Agri-Food Industry. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid Ra, E.B.; Ayman, E.E.; Rahman, H.; Abdelkarim, G.; Najda, A. Natural products against cancer angiogenesis. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 14513–14536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raman, R.P.; Joseph, L.; Kim, S.H.; Park, J.Y. Polyphenol-based cancer therapy: A review. Mol. Oncol. 2018, 12, 1022–1037. [Google Scholar]
- Rezadoost, H.; Kordrostami, M.; Hamzeh-Mivehroud, M. Polyphenols and their role in cancer prevention and treatment. Nat. Prod. Res. 2019, 33, 2501–2513. [Google Scholar]
- Losada-Echeberría, M.; Herranz-López, M.; Micol, V.; Barrajón-Catalán, E. Polyphenols as Promising Drugs against Main Breast Cancer Signatures. Antioxidants 2017, 6, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chimento, A.; De Luca, A.; D’Amico, M.; De Amicis, F.; Pezzi, V. The Involvement of Natural Polyphenols in Molecular Mechanisms Inducing Apoptosis in Tumor Cells: A Promising Adjuvant in Cancer Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keys, A. Mediterranean diet and public health: Personal reflections. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1995, 61, 1321S–1323S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willett, W.C.; Sacks, F.; Trichopoulou, A.; Drescher, G.; Ferro-Luzzi, A.; Helsing, E.; Trichopoulos, D. Mediterranean diet pyramid: A cultural model for healthy eating. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1995, 61 (Suppl. S6), 1402S–1406S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trichopoulou, A.; Naska, A.; Orfanos, P.; Trichopoulos, D. Mediterranean diet in relation to body mass index and waist-to-hip ratio: The Greek European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition Study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 82, 935–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofi, F.; Cesari, F.; Abbate, R.; Gensini, G.F.; Casini, A. Adherence to Mediterranean diet and health status: Meta-analysis. BMJ 2008, 337, a1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotsis, E.; Anagnostis, P.; Mariolis, A.; Vlachou, A.; Katsiki, N.; Karagiannis, A. Health benefits of the Mediterranean Diet: An update of research over the last 5 years. Angiology 2015, 66, 304–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobroslavska, P.; Silva, M.L.; Vicente, F.; Pereira, P. Mediterranean Dietary Pattern for Healthy and Active Aging: A Narrative Review of an Integrative and Sustainable Approach. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwingshackl, L.; Hoffmann, G. Adherence to Mediterranean diet and risk of cancer: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Cancer Med. 2015, 4, 1933–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trichopoulou, A.; Bamia, C.; Lagiou, P.; Trichopoulos, D. Conformity to traditional Mediterranean diet and breast cancer risk in the Greek EPIC (European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition) cohort. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 92, 620–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Li, S.; Meng, X.; Gan, R.Y.; Zhang, J.J.; Li, H.B. Dietary Natural Products for Prevention and Treatment of Breast Cancer. Nutrients 2017, 9, 728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, S.; Meng, X.; Gan, R.-Y.; Zhang, J.J.; Li, H.B. Natural Polyphenols for Prevention and Treatment of Cancer. Nutrients 2016, 8, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aune, D.; Chan, D.; Vieira, A.R.; Rosenblatt, D.; Vieira, R.; Greenwood, D.C.; Norat, T. Fruits, vegetables and breast cancer risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective studies. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2012, 134, 479–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aune, D.; Chan, D.S.M.; Greenwood, D.C.; Vieira, A.R.; Rosenblatt, D.A.N.; Vieira, R.; Norat, T. Dietary fiber and breast cancer risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective studies. Ann. Oncol. 2012, 23, 1394–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.J.; Gu, Y.T.; Zhang, S.J. Consumption of vegetables and fruits and breast cancer survival: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, C.; Qi, X.; Qianyong, Z.; Xiaoli, P.; Jundong, Z.; Mantian, M. Flavonoids, flavonoid subclasses and breast cancer risk: A meta-analysis of epidemiologic studies. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Angelo, S.; Rosa, R. The impact of supplementation with Pomegranate fruit (Punica Granatum L.) on sport performance. Sport Sci. 2020, 13 (Suppl. S1), 29–37. [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee, N.; Talcott, S.; Safe, S.; Mertens-Talcott, S.U. Cytotoxicity of pomegranate polyphenolics in breast cancer cells in vitro and vivo: Potential role of miRNA-27a and miRNA-155 in cell survival and inflammation. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2012, 136, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, T.L.; Strandberg, K.R.; Croley, C.R.; Fraser, S.E.; Nagulapalli Venkata, K.C.; Fimognari, C.; Sethi, G.; Bishayee, A. Pomegranate bioactive constituents target multiple oncogenic and oncosuppressive signaling for cancer prevention and intervention. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2021, 73, 265–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, N.D.; Mehta, R.; Yu, W.; Neeman, I.; Livney, T.; Amichay, A.; Poirier, D.; Nicholls, P.; Kirby, A.; Jiang, W.; et al. Chemopreventive and adjuvant therapeutic potential of pomegranate (Punica granatum) for human breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2002, 71, 203–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toi, M.; Bando, H.; Ramachandran, C.; Melnick, S.J.; Imai, A.; Fife, R.S.; Carr, R.E.; Oikawa, T.; Lansky, E.P. Preliminary studies on the anti-angiogenic potential of pomegranate fractions in vitro and in vivo. Angiogenesis 2003, 6, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirode, A.B.; Kovvuru, P.; Chittur, S.V.; Henning, S.M.; Heber, D.; Reliene, R. Antiproliferative effects of pomegranate extract in MCF-7 breast cancer cells are associated with reduced DNA repair gene expression and induction of double strand breaks. Mol. Carcinog. 2014, 53, 458–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, A.; Bishayee, A. Mechanism of breast cancer preventive action of pomegranate: Disruption of estrogen receptor and Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathways. Molecules 2015, 20, 22315–22328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantini, S.; Rusolo, F.; De Vito, V.; Moccia, S.; Picariello, G.; Capone, F.; Guerriero, E.; Castello, G.; Volpe, M.G. Potential anti-inflammatory effects of the hydrophilic fraction of pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) seed oil on breast cancer cell lines. Molecules 2014, 19, 8644–8660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dikmen, M.; Ozturk, N.; Ozturk, Y. The antioxidant potency of Punica granatum L. fruit peel reduces cell proliferation and induces apoptosis on breast cancer. J. Med. Food 2011, 14, 1638–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, L.S.; Zhang, Y.; Seeram, N.P.; Heber, D.; Chen, S. Pomegranate ellagitannin-derived compounds exhibit antiproliferative and antiaromatase activity in breast cancer cells in vitro. Cancer Prev. Res. 2010, 3, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, M.; Gupta, K.; Rasheed, Z.; Khan, K.A.; Haqqi, T.M. Bioavailable constituents/metabolites of pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) preferentially inhibit COX-2 activity ex vivo and IL-1β-induced PGE₂ production in human chondrocytes in vitro. J. Inflamm. 2008, 5, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturgeon, S.R.; Ronnenberg, A.G. Pomegranate and breast cancer: Possible mechanisms of prevention. Nutr. Rev. 2010, 68, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández, J.G.; Rodríguez, D.A.; Valenzuela, M.; Calderon, C.; Urzúa, U.; Munroe, D.; Rosas, C.; Lemus, D.; Díaz, N.; Wright, M.C.; et al. Survivin expression promotes VEGF-induced tumor angiogenesis via PI3K/Akt enhanced β-catenin/Tcf-Lef dependent transcription. Mol. Cancer 2014, 13, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, R.; Lansky, E.P. Breast cancer chemopreventive properties of pomegranate (Punica granatum) fruit extracts in a mouse mammary organ culture. Eur. J. Cancer Prev. 2004, 13, 345–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyson, D.A. A comprehensive review of apples and apple components and their relationship to human health. Adv. Nutr. 2011, 2, 408–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jedrychowski, W.; Maugeri, U.; Popiela, T.; Kulig, J.; Sochacka-Tatara, E.; Pac, A.; Sowa, A.; Musial, A. Case-control study on beneficial effect of regular consumption of apples on colorectal cancer risk in a population with relatively low intake of fruits and vegetables. Eur. J. Cancer Prev. 2010, 19, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaganathan, S.K.; Vellayappan, M.V.; Narasimhan, G.; Supriyanto, E.; Dewi, D.E.O.; Narayanan, A.L.T.; Balaji, A.; Subramanian, A.P.; Yusof, M. Chemopreventive effect of apple and berry fruits against colon cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 17029–17036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, S.H.; Chen, L.C.; Ho, Y.S. An apple a day to prevent cancer formation: Reducing cancer risk with flavonoids. J. Food Drug Anal. 2017, 25, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Angelo, S.; Martino, E.; Ilisso, C.P.; Bagarolo, M.L.; Porcelli, M.; Cacciapuoti, G. Pro-oxidant and pro-apoptotic activity of polyphenol extract from Annurca apple and its underlying mechanisms in human breast cancer cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2017, 51, 939–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.F.; Zhang, H.S.; Yang, X.B.; Zhu, Y.L.; Zhang, M. Evaluation of antioxidative and antitumor activities of extracted flavonoids from Pink Lady apples in human colon and breast cancer cell lines. Food Funct. 2015, 6, 3789–3798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavano, G.F.; De Santi, M.; Brandi, G.; Fanelli, M.; Bucchini, A.; Giamperi, L.; Giomaro, G. Inhibition of breast cancer cell proliferation and in vitro tumorigenesis by a new red apple cultivar. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H.; Liu, R.H. Effect of selected phytochemicals and apple extracts on NF-kappaB activation in human breast cancer MCF-7 cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 3167–3173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langgut, D. The Citrus Route Revealed: From Southeast Asia into the Mediterranean. Hort Sci. 2017, 52, 814–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roohbakhsh, A.; Parhiz, H.; Soltani, F.; Rezaee, R.; Iranshahi, M. Molecular mechanisms behind the biological effects of hesperidin and hesperetin for the prevention of cancer and cardiovascular diseases. Life Sci. 2015, 124, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morley, K.L.; Ferguson, P.J.; Koropatnick, J. Tangeretin and nobiletin induce G1 cell cycle arrest but not apoptosis in human breast and colon cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2007, 251, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripoli, E.; La Guardia, M.; Giammanco, S.; Di Majo, D.; Giammanco, M. Citrus flavonoids: Molecular structure, biological activity and nutritional properties: A review. Food Chem. 2007, 104, 466–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koolaji, N.; Shammugasamy, B.; Schindeler, A.; Dong, Q.; Dehghani, F.; Valtchev, P. Citrus Peel Flavonoids as Potential Cancer Prevention Agents. Curr. Dev. Nutr. 2020, 4, nzaa025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhary, A.; Jaswal, V.S.; Sharma, A. Naringenin induces apoptosis in breast cancer cells by targeting multiple signaling pathways. Oncol. Lett. 2012, 3, 1263–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adina, A.B.; Goenadi, F.A.; Handoko, F.F.; Nawangsari, D.A.; Hermawan, A.; Jenie, R.I.; Meiyanto, E. Combination of Ethanolic Extract of Citrus aurantifolia Peels with Doxorubicin Modulate Cell Cycle and Increase Apoptosis Induction on MCF-7 Cells. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 2014, 13, 919–926. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmadi, A.; Shadboorestan, A. Oxidative stress and cancer; the role of hesperidin, a citrus natural bioflavonoid, as a cancer chemoprotective agent. Nutr. Cancer 2016, 68, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motallebi, M.; Bhia, M.; Rajani, H.F.; Bhia, I.; Tabarraei, H.; Mohammadkhani, N.; Pereira-Silva, M.; Kasaii, M.S.; Nouri-Majd, S.; Mueller, A.L.; et al. Naringenin: A potential flavonoid phytochemical for cancer therapy. Life Sci. 2022, 305, 120752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaii, S.; Tomono, Y.; Katase, E.; Ogawa, K.; Yano, M. Antiproliferative activity of flavonoids on several cancer cell lines. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1999, 63, 896–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhai, Y.; Heng, X.; Che, F.Y.; Chen, W.; Sun, D.; Zhai, Q. Nobiletin inhibits MMP-9 expression and cell invasion by suppressing NF-κB activation in breast cancer cells. Toxicol. Lett. 2011, 200, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Li, Q.; Lv, L.L.; Chen, J.X.; Ying, H.F.; Ruan, M.; Zhu, W.H.; Xu, J.Y.; Zhang, C.Y.; Zhang, K.Y.; et al. Nobiletin inhibits breast cancer cell migration and invasion by suppressing the IL-6-induced ERK-STAT and JNK-c-JUN pathways. Phytomedicine 2023, 110, 154610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.Y.; Du, G.J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, C.L.; Lu, W.L.; Liang, W. Naringenin enhances the anti-tumor effect of doxorubicin through selectively inhibiting the activity of multidrug resistance-associated proteins but not P-glycoprotein. Pharm. Res. 2009, 26, 914–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, M.; Wei, W.; Zhang, J.; Wang, H.; Bai, Y.; Guo, D.-a. A Scientometric Study for a Critical Review on Promising Anticancer and Neuroprotective Compounds: Citrus Flavonoids. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ros, E. Health benefits of nut consumption. Nutrients 2010, 2, 652–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.S.; Bai, M.H.; Zhang, T.; Li, G.D.; Liu, M. Ellagic acid induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis through TGF-β/Smad3 signaling pathway in human breast cancer MCF-7 cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 46, 1730–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardman, W.E. Dietary walnuts inhibit the development of mammary gland tumors in the C3(1) TAg mouse. Nutri. Cancer 2014, 66, 538–548. [Google Scholar]
- Hardman, W.E.; Primerano, D.A.; Legenza, M.T.; Morgan, J.; Fan, J.; Denvir, J. Dietary walnuts altered gene expressions related to tumor growth, survival, and metastasis in breast cancer patients: A pilot clinical trial. Nutr. Res. 2019, 66, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateș, L.; Banc, R.; Zaharie, F.A.; Rusu, M.E.; Popa, D.S. Mechanistic Insights into the Biological Effects and Antioxidant Activity of Walnut (Juglans regia L.) Ellagitannins: A Systematic Review. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pap, N.; Fidelis, M.; Azevedo, L.; do Carmo, M.A.V.; Wang, D.; Mocan, A.; Pereira, E.P.R.; Xavier-Santos, D.; Sant’Ana, A.S.; Yang, B.; et al. Berry polyphenols and human health: Evidence of antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, microbiota modulation, and cell-protecting effects. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2021, 42, 167–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somasagara, R.R.; Hegde, M.; Chiruvella, K.K.; Musini, A.; Choudhary, B.; Raghavan, S.C. Extracts of strawberry fruits induce intrinsic pathway of apoptosis in breast cancer cells and inhibits tumor progression in mice. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, V.; Tang, J.; Oroudjev, E.; Lee, C.J.; Marasigan, C.; Wilson, L.; Ayoub, G. Cytotoxic effects of bilberry extract on MCF7-GFP-Tubulin breast cancer cells. J. Med. Food 2010, 13, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Liu, R.H. Cranberry phytochemical extracts induce cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2006, 241, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, L.S.; Phung, S.; Yee, N.; Seeram, N.P.; Li, L.; Chen, S. Blueberry phytochemicals inhibit growth and metastatic potential of MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells through modulation of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 3594–3605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seeram, N.P. Protective Role of Dietary Berries in Cancer. Antioxidants 2016, 5, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, M.J. Estrogen receptors: Role in breast cancer. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2006, 43, 325–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escrich, E.; Moral, R.; Solanas, M. Olive oil, an essential component of the Mediterranean diet, and breast cancer. Public Health Nutr. 2011, 14, 2323–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sealy, N.; Hankinson, S.E.; Houghton, S.C. Olive oil and risk of breast cancer: A systematic review and dose–response meta-analysis of observational studies. Br. J. Nutr. 2021, 125, 1148–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trichopoulou, A.; Katsouyanni, K.; Stuver, S.; Tzala, L.; Gnardellis, C.; Rimm, E.; Trichopoulos, D. Consumption of olive oil and specific food groups in relation to breast cancer risk in Greece. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1995, 87, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrone, P.; Spinelli, S.; Mantegna, G.; Notariale, R.; Straface, E.; Caruso, D.; Falliti, G.; Marino, A.; Manna, C.; Remigante, A.; et al. Mercury Chloride Affects Band 3 Protein-Mediated Anionic Transport in Red Blood Cells: Role of Oxidative Stress and Protective Effect of Olive Oil Polyphenols. Cells 2023, 12, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrone, P.; Notariale, R.; Lettieri, G.; Mele, L.; La Pietra, V.; Piscopo, M.; Manna, C. Protective Effects of Olive Oil Antioxidant Phenols on Mercury-Induced Phosphatidylserine Externalization in Erythrocyte Membrane: Insights into Scramblase and Flippase Activity. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2024, 227, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrone, P.; Ortega-Luna, R.; Manna, C.; Álvarez-Ribelles, Á.; Collado-Diaz, V. Increased Adhesiveness of Blood Cells Induced by Mercury Chloride: Protective Effect of Hydroxytyrosol. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrone, P.; D’Angelo, S. Original Article Extra Virgin Olive Oil as a Functional Food for Athletes: Recovery, Health, and Performance. J. Phys. Educ. Sport 2025, 25, 370–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayat, S.; Ebrahimi, S.N.; De Souza, N.J.; Hamburger, M. Olive polyphenols: A promising approach for breast cancer treatment. Cancer Lett. 2019, 448, 32–45. [Google Scholar]
- Han, S.Y.; Hou, H.M.; Zhang, Y.R.; Fang, Z.X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, H.; Jin, Q.; Wu, G.; et al. Oleuropein and its hydrolysate from extra virgin olive oil inhibit breast cancer cells proliferation interfering with the PI3K-AKT signal pathway. J. Funct. Foods 2003, 108, 105880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrone, P.; D’Angelo, S. Gut Microbiota Modulation Through Mediterranean Diet Foods: Implications for Human Health. Nutrients 2025, 17, 948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Talorete, T.P.; Yamada, P.; Isoda, H. Anti-proliferative and apoptotic effects of oleuropein and hydroxytyrosol on human breast cancer MCF-7 cells. Cytotechnology 2009, 59, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menendez, J.A.; Vazquez-Martin, A.; Colomer, R.; Brunet, J.; Carrasco-Pancorbo, A.; Garcia-Villalba, R.; Fernandez-Gutierrez, A.; Segura-Carretero, A. Olive oil’s bitter principal reverses acquired autoresistance to trastuzumab (Herceptin) in HER2-overexpressing breast cancer cells. BMC Cancer 2007, 7, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledo, E.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Donat-Vargas, C.; Buil-Cosiales, P.; Estruch, R.; Ros, E.; Corella, D.; Fitó, M.; Hu, F.B.; Arós, F.; et al. Mediterranean Diet and Invasive Breast Cancer Risk Among Women at High Cardiovascular Risk in the PREDIMED Trial: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Intern. Med. 2015, 175, 1752–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerber, M.; Richardson, S. Re: Consumption of olive oil and specific food groups in relation to breast cancer risk in Greece. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1995, 87, 1021–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goren, L.; Zhang, G.; Kaushik, S.; Breslin, P.A.S.; Du, Y.-C.N.; Foster, D.A. (-)-Oleocanthal and (-)-oleocanthal-rich olive oils induce lysosomal membrane permeabilization in cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeGendre, O.; Breslin, P.A.; Foster, D.A. (-)-Oleocanthal rapidly and selectively induces cancer cell death via lysosomal membrane permeabilization. Mol. Cell Oncol. 2015, 2, e1006077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markellos, C.; Ourailidou, M.E.; Gavriatopoulou, M.; Halvatsiotis, P.; Sergentanis, T.N.; Psaltopoulou, T. Olive oil intake and cancer risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0261649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, S.; Shah, M.A.; Sanches Silva, A. Flaxseed in Diet: A Comprehensive Look at Pros and Cons. Molecules 2025, 30, 1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Chen, J.; Thompson, L.U. The inhibitory effect of flaxseed on the growth and metastasis of estrogen receptor negative human breast cancer xenograftsis attributed to both its lignan and oil components. Inter. J. Cancer 2005, 116, 793–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Tan, K.P.; Ward, W.E.; Thompson, L.U. Exposure to flaxseed or its purified lignan during suckling inhibits chemically induced rat mammary tumorigenesis. Exp. Biol. Med. 2003, 228, 951–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.P.; Chen, J.; Ward, W.E.; Thompson, L.U. Mammary gland morphogenesis is enhanced by exposure to flaxseed or its major lignan during suckling in rats. Exp. Biol. Med. 2004, 229, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, N.E.; Beral, V.; Casabonne, D.; Kan, S.W.; Reeves, G.K.; Brown, A.; Green, J. Million Women Study Collaborators Moderate alcohol intake and cancer inci-dence in women. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2009, 101, 296–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, R.K.; Rhee, J.; Hoang, M.; Qureshi, A.A.; Cho, E. Consumption of Red Versus White Wine and Cancer Risk: A Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. Nutrients 2025, 17, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romieu, I.; Scoccianti, C.; Chajès, V.; de Batlle, J.; Biessy, C.; Dossus, L.; Baglietto, L.; Clavel-Chapelon, F.; Overvad, K.; Olsen, A.; et al. Alcohol intake and breast cancer in the European prospective investigation into cancer and nutrition. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2015, 137, 1921–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohi, I.; Rehm, J.; Saab, M.; Virmani, L.; Franklin, A.; Sánchez, G.; Jhumi, M.; Irshad, A.; Shah, H.; Correia, D.; et al. Alcoholic beverage consumption and female breast cancer risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 2024, 48, 2222–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, J.H.; Sethi, G.; Um, J.Y.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Arfuso, F.; Kumar, A.P.; Bishayee, A.; Ahn, K.S. The role of resveratrol in cancer therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elshaer, M.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.J.; Tang, X. Resveratrol: An overview of its anti-cancer mechanisms. Life Sci. 2018, 207, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huminiecki, L.; Horbańczuk, J. The functional genomic studies of resveratrol in respect to its anticancer effects. Biotechnol. Adv. 2018, 36, 1699–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poschner, S.; Maier-Salamon, A.; Thalhammer, T.; Jäger, W. Resveratrol and other dietary polyphenols are inhibitors of estrogen metabolism in human breast cancer cells. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2019, 190, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, K.P.; Pezzuto, J.M. Cancer chemopreventive activity of resveratrol. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2002, 957, 210–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fulda, S. Resveratrol and derivatives for the prevention and treatment of cancer. Drug Discov. Today 2010, 15, 757–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarlatti, F.; Sala, G.; Somenzi, G.; Signorelli, P.; Sacchi, N.; Ghidoni, R. Resveratrol induces growth inhibition and apoptosis in metastatic breast cancer cells via de novo ceramide signaling. FASEB J. 2003, 17, 2339–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina-Aguilar, R.; Pérez-Plasencia, C.; Marchat, L.A.; Gariglio, P.; García Mena, J.; Rodríguez Cuevas, S.; Ruíz-García, E.; Astudillo-de la Vega, H.; Hernández Juárez, J.; Flores-Pérez, A.; et al. Methylation Landscape of Human Breast Cancer Cells in Response to Dietary Compound Resveratrol. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubecka, K.; Kurzava, L.; Flower, K.; Buvala, H.; Zhang, H.; Teegarden, D.; Camarillo, I.; Suderman, M.; Kuang, S.; Andrisani, O.; et al. Stilbenoids remodel the DNA methylation patterns in breast cancer cells and inhibit oncogenic NOTCH signaling through epigenetic regulation of MAML2 transcriptional activity. Carcinog 2016, 37, 656–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Chang, H.; Peng, X.; Bai, Q.; Yi, L.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, J.; Mi, M. Resveratrol inhibits breast cancer stem-like cells and suppresses tumorigenesis. Mol. Carcinog. 2014, 53, 893–904. [Google Scholar]
- Suh, J.; Kim, D.H.; Surh, Y.J. Resveratrol suppresses migration, invasion and stemness of human breast cancer cells by interfering with tumor-stromal cross-talk. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2018, 643, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.; Serrero, G. Resveratrol, a natural product derived from grape, exhibits antiestrogenic activity and inhibits the growth of human breast cancer cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 1999, 179, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). Personal Habits and Indoor Combustions; IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans, Volume 100E; IARC: Lyon, France, 2012; ISBN 978-92-832-1322-2. Available online: https://publications.iarc.fr (accessed on 13 May 2025).
- Bagnardi, V.; Rota, M.; Botteri, E.; Tramacere, I.; Islami, F.; Fedirko, V.; Scotti, L.; Jenab, M.; Turati, F.; Pasquali, E.; et al. Alcohol consumption and site-specific cancer risk: A comprehensive dose–response meta-analysis. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 112, 580–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touvier, M.; Fezeu, L.; Ahluwalia, N.; Julia, C.; Charnaux, N.; Sutton, A.; Hercberg, S. Types of alcoholic beverages and breast cancer risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 135, 1921–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Cancer Research Fund International. Cancer Prevention Recommendations. Available online: https://www.wcrf.org/dietandcancer/cancer-prevention-recommendations (accessed on 12 April 2022).
- Le Marchand, L.; Hankin, J.H.; Wilkens, L.R.; Kolonel, L.N.; Lyu, L.C. Alcohol and breast cancer risk in an ethnically diverse population. Int. J. Cancer 2005, 113, 454–460. [Google Scholar]
- Fanfarillo, F.; Caronti, B.; Lucarelli, M.; Francati, S.; Tarani, L.; Ceccanti, M.; Piccioni, M.G.; Verdone, L.; Caserta, M.; Venditti, S.; et al. Alcohol Consumption and Breast and Ovarian Cancer Development: Molecular Pathways and Mechanisms. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2024, 46, 14438–14452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Augimeri, G.; Montalto, F.I.; Giordano, C.; Barone, I.; Lanzino, M.; Catalano, S.; Andò, S.; De Amicis, F.; Bonofiglio, D. Nutraceuticals in the Mediterranean Diet: Potential Avenues for Breast Cancer Treatment. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorca-Camara, V.; Bosque-Prous, M.; Bes-Rastrollo, M.; O’Callaghan-Gordo, C.; Bach-Faig, A. Environmental and Health Sustainability of the Mediterranean Diet: A Systematic Review. Adv. Nutr. 2024, 15, 100322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potentas, E.; Witkowska, A.M.; Zujko, M.E. Mediterranean diet for breast cancer prevention and treatment in postmenopausal women. Prz. Menopauzalny 2015, 14, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mourouti, N.; Kontogianni, M.D.; Papavagelis, C.; Panagiotakos, D.B. Diet and breast cancer: A systematic review. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2015, 66, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cathcart-Rake, E.J.; Ruddy, K.J.; Johnson, R.H. Modifiable risk factors for the development of breast cancer in young women. Cancer J. 2018, 24, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Cancer Research Fund/American Institute for Cancer Research (WCRF/AICR). Cancer Prevention Recommendations [Internet]. 2018. Available online: https://www.wcrf.org/diet-activity-and-cancer/cancer-prevention-recommendations/ (accessed on 13 May 2025).
- Schwedhelm, C.; Boeing, H.; Hoffmann, G.; Aleksandrova, K.; Schwingshackl, L. Effect of diet on mortality and cancer recurrence among cancer survivors: A systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. Nutr. Rev. 2016, 74, 737–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finicelli, M.; Di Salle, A.; Galderisi, U.; Peluso, G. The Mediterranean Diet: An Update of the Clinical Trials. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckland, G.; Travier, N.; Cottet, V.; González, C.A.; Luján-Barroso, L.; Agudo, A.; Trichopoulou, A.; Lagiou, P.; Trichopoulos, D.; Peeters, P.H.; et al. Adher-ence to the mediterranean diet and risk of breast cancer in the European prospective investigation into cancer and nutrition cohort study. Int. J. Cancer 2013, 132, 2918–2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwingshackl, L.; Hoffmann, G. Adherence to Mediterranean diet and risk of cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 135, 1884–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Brandt, P.A.; Schulpen, M. Mediterranean diet adherence and risk of postmenopausal breast cancer: Results of a cohort study and meta-analysis. Int. J. Cancer 2017, 140, 2220–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quartiroli, M.; Roncallo, C.; Pala, V.; Simeon, V.; Ricceri, F.; Venturelli, E.; Pattaro-ni, L.; Sieri, S.; Agnoli, C. Adherence to Diet Quality Indices and Breast Cancer Risk in the Italian ORDET Cohort. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porciello, G.; Montagnese, C.; Crispo, A.; Grimaldi, M.; Libra, M.; Vitale, S.; Palumbo, E.; Pica, R.; Calabrese, I.; Cubisino, S.; et al. Mediterranean diet and quality of life in women treated for breast cancer: A baseline analysis of DEDiCa multicentre trial. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0239803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, T.T.; Hu, F.B.; McCullough, M.L.; Newby, P.K.; Willett, W.C.; Holmes, M.D. Diet quality is associated with the risk of estrogen receptor-negative breast cancer in postmenopausal women. J. Nutr. 2006, 136, 466–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trichopoulou, A.; Costacou, T.; Bamia, C.; Trichopoulos, D. Adherence to a Mediterranean diet and survival in a Greek population. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 2599–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelló, A.; Pollán, M.; Buijsse, B.; Ruiz, A.; Casas, A.M.; Baena-Cañada, J.M.; Lope, V.; Antolín, S.; Ramos, M.; Muñoz, M.; et al. Spanish Mediterranean diet and other dietary patterns and breast cancer risk: Case-control EpiGEICAM study. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 111, 1454–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, M.; Liu, S.H.; Mitchell, C.; Fung, T.T. Associations between Diet Quality Scores and Risk of Postmenopausal Estrogen Receptor-Negative Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review. J. Nutr. 2018, 148, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.H.; Willett, W.C.; Fung, T.; Rosner, B.; Holmes, M.D. Diet quality indices and postmenopausal breast cancer survival. Nutr. Cancer 2011, 63, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwan, M.L.; Greenlee, H.; Lee, V.S.; Castillo, A.; Gunderson, E.P.; Habel, L.A.; Kushi, L.H.; Sweeney, C.; Tam, E.K.; Caan, B.J. Multivitamin use and breast cancer outcomes in women with early-stage breast cancer: The Life after Cancer Epidemiology study. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2011, 130, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izano, M.A.; Fung, T.T.; Chiuve, S.S.; Hu, F.B.; Holmes, M.D. Are diet quality scores after breast cancer diagnosis associated with improved breast cancer survival? Nutr. Cancer 2013, 65, 820–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vrieling, A.; Buck, K.; Seibold, P.; Heinz, J.; Obi, N.; Flesch-Janys, D.; Chang-Claude, J. Dietary patterns and survival in German postmenopausal breast cancer survivors. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 108, 188–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantzorou, M.; Tolia, M.; Poultsidi, A.; Vasios, G.K.; Papandreou, D.; Theocharis, S.; Kavantzas, N.; Troumbis, A.Y.; Giaginis, C. Adherence to Mediterranean Diet and Nutritional Status in Women with Breast Cancer: What Is Their Impact on Disease Progression and Recurrence-Free Patients’ Survival? Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 7482–7497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; de la Parra, J.; Elouafi, I.; German, B.; Jarvis, A.; Lal, V.; Lartey, A.; Longvah, T.; Malpica, C.; Vázquez-Manjarrez, N.; et al. Foodomics: A Data-Driven Approach to Revolutionize Nutrition and Sustainable Diets. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 874312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sáez-Almendros, S.; Obrador, B.; Bach-Faig, A.; Serra-Majem, L. Environmental footprints of Mediterranean versus Western dietary patterns: Beyond the health benefits of the Mediterranean diet. Environ. Health 2013, 12, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morazzoni, P.; Vanzani, P.; Santinello, S.; Gucciardi, A.; Zennaro, L.; Miotto, G.; Ursini, F. Grape Seeds Proanthocyanidins: Advanced Technological Preparation and Analytical Characterization. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Extra Virgin Olive Oil: A Powerful Antioxidant Source. Olive oil, particularly extra virgin olive oil (EVOO), is a fundamental part of the Mediterranean diet and plays a significant role in cancer prevention. It is rich in monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs) and polyphenols, such as hydroxytyrosol and oleocanthal, which have potent anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-proliferative properties. Studies suggest that these bioactive compounds help protect DNA from oxidative damage, reduce the expression of cancer-promoting genes, and inhibit tumor growth. Research has shown that women who consume high amounts of EVOO have a reduced risk of developing hormone receptor-positive breast cancer. |
| Fruits and Vegetables: A Source of Vitamins and Bioactive Compounds. The Mediterranean diet emphasizes a high intake of colorful fruits and vegetables, which provide essential vitamins, minerals, and phytochemicals such as flavonoids, carotenoids, and polyphenols. These compounds have strong antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, neutralizing free radicals that can cause DNA mutations, leading to cancer. Additionally, cruciferous vegetables like broccoli, cabbage, and kale have sulforaphane, which has been shown to inhibit cancer cell proliferation and promote apoptosis (programmed cell death) in breast cancer cells. |
| Whole Grains and Legumes: High in Fiber and Phytoestrogens. Whole grains (such as oats, quinoa, and whole wheat) and legumes (such as lentils, chickpeas, and beans) are excellent sources of fiber, which aids in digestion and plays a key role in regulating estrogen levels in the body. Excess estrogen is a risk factor for hormone-dependent breast cancers, and fiber helps bind estrogen in the gut, promoting its excretion and reducing its circulating levels. Moreover, legumes have phytoestrogens, plant-derived compounds that mimic estrogen but have protective effects against hormone-related cancers. |
| Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Anti-Inflammatory and Tumor-Suppressing Properties. The Mediterranean diet includes fatty fish, like salmon, sardines, and mackerel, which are rich in omega-3 fatty acids. These essential fatty acids have been shown to reduce chronic inflammation, inhibit cancer cell proliferation, and prevent angiogenesis (the formation of new blood vessels that supply tumors). A balanced intake of omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids is crucial, as an excess of omega-6 fatty acids (found in processed foods and vegetable oils) can promote inflammation and tumor growth. |
| Nuts and Seeds: A Source of Healthy Fats and Polyphenols. Almonds, walnuts, flaxseeds, and chia seeds are staple ingredients in the Mediterranean diet. They provide healthy fats, fiber, and polyphenols, which contribute to reducing inflammation and oxidative stress. Walnuts, for instance, have ellagic acid, which has been shown to suppress breast cancer cell growth, while flaxseeds are rich in lignans, a type of phytoestrogen that helps regulate estrogen metabolism. |
| Red Wine: Resveratrol and Its Anti-Cancer Potential. In moderation, red wine is consumed in the Mediterranean diet and is a natural source of resveratrol, a polyphenol with antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-cancer properties. Resveratrol has been found to induce apoptosis in breast cancer cells, inhibit their proliferation, and suppress tumor growth. However, it is important to note that excessive alcohol consumption is associated with an increased risk of breast cancer, so intake should be limited to small amounts (e.g., one glass per day for women). |
| Reduced Consumption of Processed and Red Meats. Unlike Western diets, which often include high amounts of red and processed meats, the Mediterranean diet prioritizes lean protein sources, such as fish and plant-based proteins. Processed and red meats have compounds like heterocyclic amines and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, which are formed during high-temperature cooking and have been linked to cancer development. Reducing consumption of these meats can lower exposure to these carcinogenic compounds. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Perrone, P.; De Rosa, C.; D’Angelo, S. Mediterranean Diet and Agri-Food By-Products: A Possible Sustainable Approach for Breast Cancer Treatment. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 789. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14070789
Perrone P, De Rosa C, D’Angelo S. Mediterranean Diet and Agri-Food By-Products: A Possible Sustainable Approach for Breast Cancer Treatment. Antioxidants. 2025; 14(7):789. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14070789
Chicago/Turabian StylePerrone, Pasquale, Chiara De Rosa, and Stefania D’Angelo. 2025. "Mediterranean Diet and Agri-Food By-Products: A Possible Sustainable Approach for Breast Cancer Treatment" Antioxidants 14, no. 7: 789. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14070789
APA StylePerrone, P., De Rosa, C., & D’Angelo, S. (2025). Mediterranean Diet and Agri-Food By-Products: A Possible Sustainable Approach for Breast Cancer Treatment. Antioxidants, 14(7), 789. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14070789







