Abstract
Sprayed fiber-reinforced concrete is used in construction for the execution and repair of reinforced concrete elements. It is believed that the addition of steel fibers is most effective, due to their parameters and low costs. Some researchers, however, suggest that the addition of steel fibers can contribute to the initiation of corrosion of the main reinforcement. In consideration of the differences of opinion on the corrosion resistance of sprayed fiber-reinforced concrete, it has become necessary to analyze this issue. The article presents comparative studies of corrosion assessments of the main reinforcement in specimens made of ordinary concrete and concrete with steel fibers. The tests were performed using a semi non-destructive galvanostatic pulse method, which allows location of the areas of corrosion and estimation of the reinforcement corrosion activity. In order to initiate the corrosion processes the specimens were subjected to freezing cycles in NaCl solution. In addition, the shrinkage and compressive strength of specimens were measured, and the observation of specimen structure under a scanning microscope was performed. It was found that galvanostatic pulse method allowed estimation of the reinforcement corrosion progress. The corrosion of the main reinforcement in steel fiber reinforced concrete specimens was less advanced than in the specimens without fibers.
1. Introduction
Sprayed concrete (shotcrete) [1,2,3] is frequently used as a filling material, a protective and finishing material for repairs of civil engineering structures and industrial structures (mainly in concrete cover and to protect steel against corrosion), or in the reconstruction of damaged historic buildings, particularly in the case of limited or difficult access [3,4,5,6,7]. Repairs with sprayed concrete can be performed by casting the concrete mix onto thin-wired steel meshes placed on the surfaces of the repaired elements (this usually requires casting two layers of shotcrete), or by using fiber-reinforced concrete (FRC), i.e., concrete with dispersed reinforcement in the form of various fibers, which eliminates the need for meshes [2,3,8,9]. Using fiber-reinforced concrete is usually more efficient and economical (the material consumption is lower, as is the loss of material) than the conventional method based on steel meshes and shotcrete. Furthermore, concrete with dispersed reinforcement is a “quasi-plastic” and “quasi-uniform” material, with better adhesion, stress–strain behavior and tightness, and higher early strength [6,10,11,12,13,14,15]. Randomly dispersed fibers in the concrete mix reduce the concentration of stress, and thus, the cracking [6,13]. For this reason, FRC has found application as sprayed concrete in repairs of structures which are particularly exposed to aggressive environments, e.g., bridges, tunnels, overpasses, parking lots, thin-walled elements (reservoirs and basins), weirs, retaining walls, elements under dynamic loads, concrete surfaces, or industrial flooring [14,16,17]. The high early strength of FRC is especially useful in the repairs of structures which are in use, since it allows work to be performed without disusing them [3,6,14]. For dispersed reinforcement, various types of fibers can be used, such as steel, synthetic (polypropylene, polyester, polyacrylonitrile), glass, carbon, basalt, or even organic. A summary of the basic parameters for selected types of fibers is provided in Table 1 [18].

Table 1.
Parameters of various fibers used for concrete reinforcement [18].
The addition of fibers does not affect the method of application and curing of the concrete mix. The only difficulty might be the reduced workability of the concrete mix if steel fibers are used. In such cases, workability can be improved by adding appropriate plasticizers and super plasticizers, and using fine-fraction aggregates with the particle diameter not exceeding 1/2 of the fiber length for hooked-end steel fibers, or 1/3 of the length of smooth fibers [3,6,8,9,14]. Usually, a 8/16 mm aggregate is used. The water/cement ratio should not be higher than 0.45.
Steel fibers are among the most frequently used for concrete reinforcement, owing their popularity to both efficiency and relatively low cost. Steel fibers for concrete reinforcement are supplied in various shapes and sizes (Figure 1). The fiber content in a concrete mix usually ranges from 0.25–2% vol. per 1 m3, although some authors have provided a broader range up to 3.0% [10,13,18]. Adding less than 0.25% of reinforcement is insufficient (studies indicate that it will not improve the concrete parameters), while adding more than 2.0% of fibers considerably reduces the workability of the concrete mix (even if super plasticizers are used). The authors’ own research indicates that adding 1.5% of fibers is enough to significantly affect the workability of the mix; due to the formation of so-called “nests,” i.e., bundles of fibers, the mix loses uniformity and the concrete parameters are worse than those of a mix with a 1.0% fiber content [19]. Adding steel fibers improves tensile strength, fatigue resistance, impact strength, fracture resistance, and abrasion resistance [10,11,12,15,20]. Concrete with added fibers is more cohesive, as the fibers “clamp” the concrete matrix and prevent the formation of large pores in the concrete mix, and also reduce the formation and spreading of shrinkage cracks [6,13] during the setting and hardening of the concrete (Figure 2). The fibers also improve the freeze–thaw durability of the concrete [19]. Unlike synthetic fibers, which prevent cracks only in fresh concrete, steel fibers also reduce the cracking resulting from the drying of hardened concrete, as well as cracks caused by mechanical loads [10,11,12,13,15]. Since steel fibers “seal” the concrete cover [7,17], they might also indirectly inhibit the corrosion of the primary reinforcement in reinforced concrete structures, thus improving the rebar’s durability.
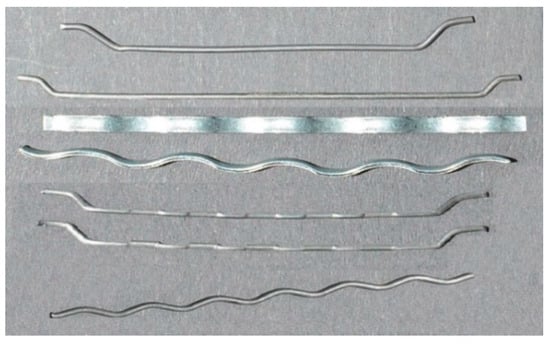
Figure 1.
Examples of steel fibers used for concrete reinforcement [own study].

Figure 2.
Size and distribution of cracks in reinforced concrete elements subjected to tension: (a) plain concrete; (b) fiber–reinforced concrete (FRC) [own study on the basis of Reference ([13], p. 266, figure 9.10)].
In highly developed countries, most construction works with shotcrete use concrete with dispersed reinforcement, usually in the form of steel fibers (so-called SFRC), due to its good parameters and relatively low price [4,5,8,9]. However, in many other countries, Poland included, this composite is not particularly popular, which is difficult to comprehend. Perhaps, as pointed out by some authors [6,18], one of the reasons is the concern that the micro-reinforcement fibers do not have adequate corrosion resistance and might trigger corrosion of the primary reinforcement.
The main objective of this research was to assess the impact of randomly dispersed steel fibers in concrete on the corrosion development of the main reinforcement by means of the electrochemical galvanostatic pulse method under environmental conditions conducive to the development of steel corrosion.
2. Corrosion Henomena
In reinforced concrete structures, corrosion of the reinforcement is the key factor directly affecting their durability [21,22]. Rebars typically corrode because the physical and chemical processes occurring in the environment of the structure reduce the protection of the reinforcement provided by the concrete cover. This is usually caused by gradual carbonation of concrete, the impact of chlorides, or other factors which, by compromising the concrete cover, indirectly cause the corrosion of the reinforcement [22,23,24,25].
Corrosion caused by concrete carbonation in the concrete cover usually results from the impact of the carbon dioxide in the air, as well as changes of the ambient temperature and humidity [26,27]. In reinforced concrete structures, the concrete (if sufficiently waterproofed and made with appropriate and properly mixed ingredients) provides basic and also the most efficient protection of the reinforcement [monograph]. The protective role of concrete is related to its alkalinity (pH ≈ 12.5–13.5) which results in passivation on the interface between the concrete and the steel (i.e., formation of a micro-layer with very low ionic conductivity), which practically prevents corrosion of the rebars. Unfortunately, prolonged negative impacts of the physical and chemical factors of the external environment, as well as potential mechanical damage, gradually deteriorate the protective capabilities of the concrete cover. Carbonation gradually reduces the pH value of concrete, with the neutralized areas of concrete spreading inwards and eventually reaching the passive film (Figure 3). If the pH value of concrete drops below ~11.8, the passive film is destroyed, directly triggering electrochemical corrosion of the reinforcement. Carbonation usually affects larger, surface layers of concrete. The level of carbonation of concrete can be determined directly on the structure using simple diagnostic methods (e.g., phenolphthalein test, thymolphthalein test, or Rainbow test) or by more complex laboratory analysis (X-ray diffraction (XRD), differential thermal analysis (DTA), scanning microscopy or IR spectroscopy).
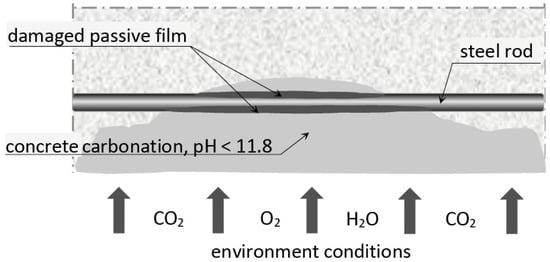
Figure 3.
Reinforcement corrosion caused by carbonation of the concrete cover [own study].
The second frequent cause of corrosion of the primary reinforcement bars in reinforced concrete structures is so-called chloride corrosion [23,28], which takes a markedly different form than carbonation. Chloride corrosion is a pitting spot corrosion which can burst the concrete cover from the inside without any visible changes on the surface of the concrete element (Figure 4). This type of corrosion affects structures located at seasides which either have direct contact with seawater, or are exposed to the so-called sea fog, and also all types of civil engineering structures (mostly roads) that in winter are de-iced with agents containing sodium chloride (NaCl) [24,29]. The spread of chloride corrosion is often mediated by frost, as the water freezing in the concrete pores generates stress, which leads to cracking of the concrete, thus opening the way for chloride ions which diffuse into the concrete cover and damage the passive film which protects the reinforcement. Electrochemical reactions result in corrosion cells forming on the surface of the reinforcement, and the corrosion process advances rapidly. Structures on which chloride corrosion is identified usually require renovation.
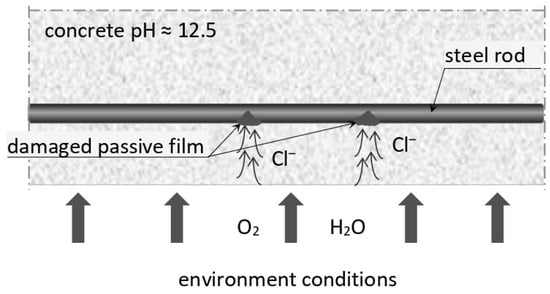
Figure 4.
Reinforcement corrosion caused by the penetration of chloride ions [own study].
Reinforcement corrosion can also be indirectly caused by all types of concrete damage arising from other types of corrosion (deterioration due to sulfate attack, corrosion caused by leaching of concrete), or by mechanical damage arising from the operation of the structure and leading to cracking and delamination of the concrete cover [22].
As previously mentioned, shotcreting is usually applied in construction and renovation works on industrial or civil engineering structures which are exposed to higher risk of corrosion, and for which the structural integrity requirements are much higher than in residential or public buildings [6,30]. For this type of work, using fiber-reinforced concrete (in particular SFRC), i.e., a composite with higher waterproofing and freeze–thaw durability parameters, appears reasonable.
However, some authors suggest that concrete with dispersed steel reinforcement is, in fact, not resistant to corrosion [6,18], while others [7,13,14] claim that steel fibers are not prone to corrosion, as they are too short for corrosion cells to be able to form on their surface. Furthermore, the fibers are not in contact with each other and are made of more resistant steel. Even if corrosion occurs in isolated cases, the volume of the corroded fiber is too small to burst the concrete; in fact, a corroded fiber can even improve its anchoring strength with the matrix [7,13,14]. Furthermore, shotcrete can be additionally protected by coating with epoxy resins, cement slurry with added bitumen, or asphalt solutions in toluene [3].
In consideration of the differences of opinion on the corrosion resistance of sprayed FRC with dispersed steel reinforcement described above, it has become necessary to analyze this issue both in laboratory conditions and in situ.
3. Diagnostic Methods for Assessing the Degree of Reinforcement Corrosion
Shotcrete tests are usually related to mechanical parameters, such as compressive strength determined on specimens cut from the test slab, bending strength tested on specimen bars, shrinkage measured after minimum 90 days, adhesion to concrete, as well as freeze–thaw durability, water absorption, and waterproofing of concrete. The tests are conducted in accordance with the applicable standards [31,32,33,34,35,36,37].
The tests mentioned above do not include corrosion diagnostics of the primary reinforcement. However, from a structural integrity standpoint, assessment of the degree of corrosion of the reinforcement, and forecast of the advancement of corrosion, is crucial. It is particularly important for industrial and civil engineering structures, which are usually operated in more aggressive environments and are frequently built with the use of shotcreting.
The available methods of reinforcement corrosion diagnostics for structures in use include electrochemical tests [38,39,40,41,42]. One such method is the semi-nondestructive method of measuring polarization resistance with the use of a galvanostatic pulse [43]. This method is based on the electrochemical corrosion of concrete reinforcement. Concrete has a porous structure, with the pores filled with alkaline liquid (a type of electrolyte through which ions can flow), while the steel rebar serves as the electrode placed in the electrolyte (conducting electrons). With the use of appropriate equipment (e.g., GP-5000 GalvaPulseTM), this makes it possible to measure some electrical parameters that allow indirect estimation of the reinforcement corrosion progress in concrete. The electrical parameters are: reinforcement stationary potential (Est), measured on the concrete surface; concrete cover resistivity (Θ); and the corrosion current density (icor). Measurements of the reinforcement stationary potential and the concrete cover resistivity are the basic measurements, which allow only for areas where conditions for corrosion are more favorable to be pointed out. These measurements are not very accurate. More reliable are so-called advanced measurements, consisting of additional corrosion current density measurements, so we can estimate the reinforcement corrosion activity and forecast its rate. In order to take the measurement, it is necessary to connect the diagnosed reinforcement with the measurement kit, which includes, among others, a gauge (minicomputer) and a reference electrode. Figure 5 shows a diagram of the connection of the GP-5000 GalvaPulseTM and the diagnosed rebar. The generated electric impulse then polarizes the reinforcement and the relevant electric parameters are measured, i.e., the stationary potential of the reinforcement, the resistivity of the concrete cover, and the corrosion current density. The obtained values are referenced to the threshold values (Table 2) to determine the areas with a higher probability of corrosion, and to estimate the corrosive activity of the diagnosed reinforcement and forecast the corrosion rate. It should be noted that other corrosion measuring devices have different reference scales, and the results cannot be directly compared.
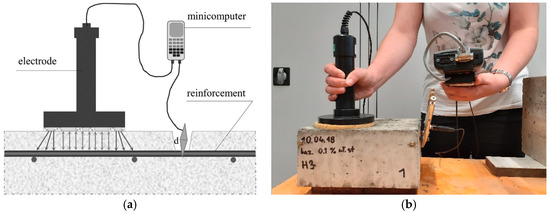
Figure 5.
Diagram of connection of GP-5000 GalvaPulseTM with diagnosed reinforcement: (a) sketch [own study on the basis of Reference [43]]; (b) measurement on a specimen.

Table 2.
Criteria for assessing the reinforcement corrosion risk level [40,43].
The paper presents the results of the studies conducted with the use of the method described above (partially discussed in Reference [19]) which made it possible to determine the differences in the corrosion rates of the primary reinforcement in plain concrete and fiber-reinforced concrete with randomly dispersed steel fibers. In order to simulate the impact of an corrosive environment and trigger the corrosion process on the reinforcement, the specimens were exposed to freezing cycles in 3% NaCl solution, which initiated the so-called chloride corrosion. Furthermore, the differences in shrinkage and compressive strength of the two analyzed types of concrete were determined, and the fiber-reinforced concrete macrostructure was identified with the use of scanning microscopy with EDS (Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy) analysis.
4. Laboratory Tests
4.1. Test Specimens and Methodology
For the test, 12 slab specimens were prepared to estimate the probability of corrosion and corrosion activity of the reinforcement (A), 12 rectangular specimens to determine the shrinkage (B), and 6 cube specimens to determine compressive strength (C). In each group, half of the specimens were made of plain concrete (PC), and the other half were made of fiber-reinforced concrete with randomly dispersed steel micro-reinforcement fibers (SFRC). All specimens were collected according to standard [44] from the same concrete mix; 1 m3 of the mix contained the following ingredients: CEM I cement—384 kg; sand—680 kg; gravel 2/8—600 kg; gravel 8/16—650 kg; water—160 L, and plasticizer (0.6%). The water/cement ratio was 0.43. In the SFRC specimens, the concrete mix was reinforced with steel BauMix 60/1 fibers making up 1% vol. of the mixture; the parameters of the fibers were as follows: fiber length lw = 60 mm; fiber diameter ∅ = 1.0 mm; shape—hooked-end (Figure 6). This type of fibers was chosen due to their widespread use. In addition, longer fibers seemed more exposed to corrosion. The content of fibers in the mixture (1%) was chosen for its efficiency as well as the workability of the mixture and its use as a spraying concrete.
Figure 6.
Fibers used for test specimens.
The specimens for the estimation of corrosion (A specimens, including A1-PC specimens and A2-SFRC specimens) had a surface area of 210 × 228 mm and a thickness of 100 mm. In each specimen, two parallel ribbed Φ8 mm BST 500 steel rods were cast (Figure 7). The rods had equal 70 mm clearance from the edge of the specimen. There were no transverse rods. The concrete cover thickness was 25 mm.
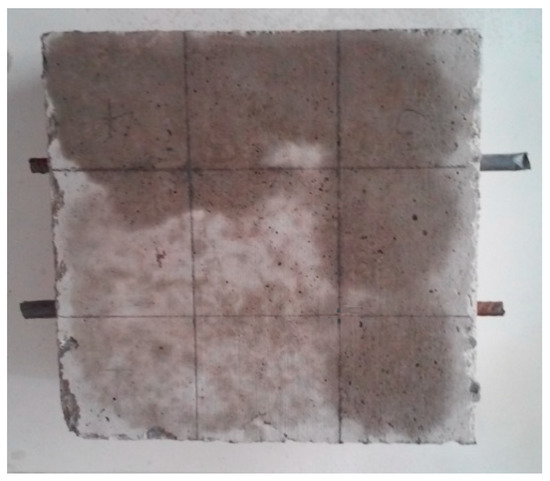

Figure 7.
Photograph of an example of test specimen A.
The measurements of the estimation of corrosion probability on the specimens surface, and the corrosion activity of the reinforcement, were performed on A specimens in two stages: stage I—preliminary measurements (reference measurements) taken after casting the specimens; stage II—measurements after 120 freeze–thaw cycles of specimens in 3% NaCl solution (the specimens were immersed in the NaCl solution so that the chloride ions could penetrate into the concrete cover in the direction of reinforcement, which was supposed to simulate the processes taking place in reality). The measurements were taken with the use of a galvanostatic pulse and the GP-5000 GalvaPulseTM measurement kit. The measurements of all relevant parameters, i.e., the reinforcement stationary potential (Est) and the concrete cover resistivity (Θ) to estimate the probability of corrosion on the analyzed surface, and the corrosion current density (icor) to determine the corrosion activity of the rod, were taken for each rod in each specimen at two measurement points spaced evenly in 70 mm intervals along the axis of the rod.
The dimensions of rectangular specimens for determining shrinkage (B specimens, including B1-PC specimens and B2-SFRC specimens) were 100 × 100 × 300 mm. The measurements were taken with the use of a demountable strain gauge (DEMEC) supplied by W.H. Mayes & Son; the gauge base was 100 mm, the accuracy was 0.002 mm; the strain gauge constant was 1.6 × 10−5. As per Reference [1], the measurements were taken after 90 days from casting.
The dimensions of the cube specimens for determining the compressive strength (C specimens, including C1-PC specimens and C2-SFRC specimens) were 150 × 150 × 150 mm. The test was conducted 28 days after casting, in accordance with standard [44], on a Zwick/Roell SP-Z6000 testing machine with a maximum compressive force of 6000 kN. The specimens were placed under continuous load until destruction with the load rate of 0.5 MPa/s.
A randomly selected SFRC specimen of the concrete cover, after testing the reinforcement corrosion (A1), was then analyzed with the use of scanning microscopy with EDS analysis. The microscopic analysis was performed with a Quenta 250 FEG scanning electron microscope (supplied by FEI Company). The surface area observed under SEM was approximately 1 m2. The applied magnifications ranged from 500× to 15,000×.
4.2. Results and Analysis of the Tests
The specimens tested for the probability of surface corrosion and the corrosion activity of the reinforcement provided a large number of results, since measurements were taken for three parameters (icor, Est, Θ) on four measurement points for each of the 12 specimens (two for each rod) in two stages (before and after freeze–thaw cycles). For the purpose of analyzing the results for each rod, a single representative measurement point was selected in which the corrosion current density (i.e., the most reliable parameter) was the highest after stage II measurements had been completed.
The obtained results were referenced to the threshold criterion values provided in Table 2.
The measurements of the corrosion current density taken on the first stage of tests for all rods of A1 and A2 specimens showed that the corrosion current density value did not exceed icor = 2 μA/cm2 for any of the measurement points (Table 3, Figure 8), which, according to the criteria adopted herein (Table 2) indicated a “negligible corrosion activity.” Comparative analysis of the results obtained on the second stage of the tests (after 120 freeze–thaw cycles in 3% NaCl solution) showed that in both A1 and A2 specimens, the density of the corrosion current increased, whereby in A1 specimens the density exceeded 5 μA/cm2 (icor = 5.5–9.9 μA/cm2) on all analyzed points, indicating “moderate corrosion activity,” whereas in A2 specimens the density did not exceed icor = 5 μA/cm2 on five measurement points, and for the remaining seven points, it fell within the range of icor = 5.4–6.9 μA/cm2, i.e., lower than in A1 specimens.

Table 3.
Summary of measurement results from the two stages of tests for each tested rod on the selected measurement point.
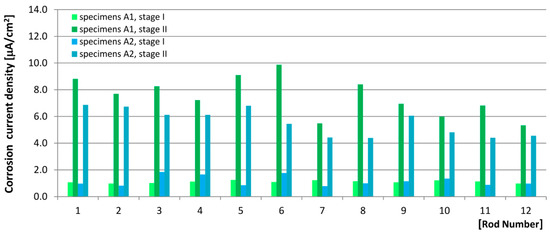
Figure 8.
Results of the corrosion current density measurements.
The measurements of the reinforcement stationary potential were taken together with the corrosion current density and were consistent with them. In the analyzed measurement points, the increase of the corrosion current density was accompanied by a reduction of the stationary potential. On the first stage of tests, on all measurement points of A1 and A2 specimens, the stationary potential values exceeded −200 mV (Figure 3) which, according to the specified criterion (Table 2) indicated a 5% probability of corrosion. The measurements of stage II in all specimens showed that the stationary potential of the reinforcement dropped, changing from Est < −297 mV to Est > −367 mV for A1 specimens, and from Est < −253 mV to Est > −338 mV for A2specimens. Comparative analysis of results for A1 and A2 specimens (Table 3, Figure 9) showed that in A1 specimens, the reinforcement stationary potential indicated a slightly increased corrosion rate than in A2 specimens.
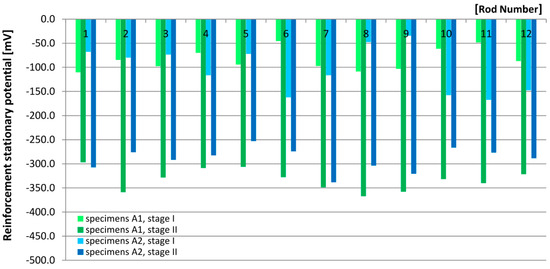
Figure 9.
Results the measurements of the reinforcement stationary potential.
The values obtained from the measurements of the concrete cover resistivity on all measurement points of all analyzed specimens, on both stage I and stage II of the tests, were Θ < 10 kΩ⋅cm (Figure 10), which would indicate “high probability of corrosion.” However, in this particular case, the measured values were unreliable due to the fact that the specimens were still fresh, and the hardening process had most likely not ended by the time of the test [19,25,29].
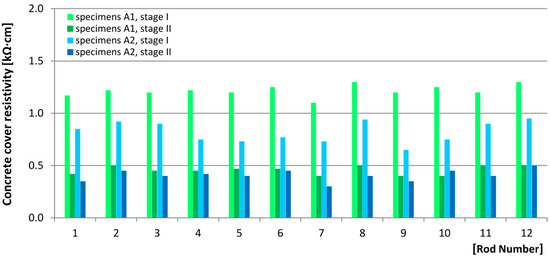
Figure 10.
Results of the measurements of the concrete cover resistivity.
The mean values of shrinkage strain determined from surface measurements of all B1 and B2 specimens are provided in Figure 11.
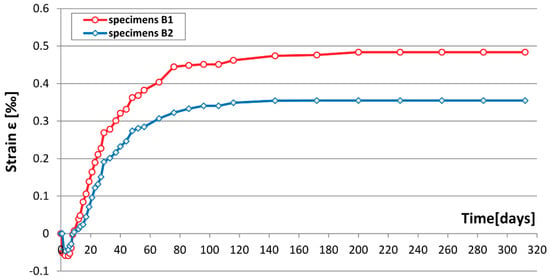
Figure 11.
Changes of average shrinkage strain over time.
In B2 specimens (with addition of steel fibers), total shrinkage stabilized earlier than in B1specimens. According to standard [1], a shrinkage measurement taken after 90 days is reliable for assessing shrinkage strains in sprayed concrete. The average strain values determined in that period clearly showed a significantly lower shrinkage in B2 specimens with the addition of randomly dispersed micro-reinforcement steel fibers, reaching ε = 0.35‰, whereas for B1 specimens, the shrinkage was ε = 0.48‰. The addition of 1% of steel fibers to concrete reduced total shrinkage in the analyzed specimens by over 26%.
C specimens were used for testing the compressive strength of concrete according to Reference [45] and calculating the mean strength, the standard deviation, and the coefficient of variation. The specimen compression charts are provided in Figure 12, and the obtained values are summarized in Table 4.
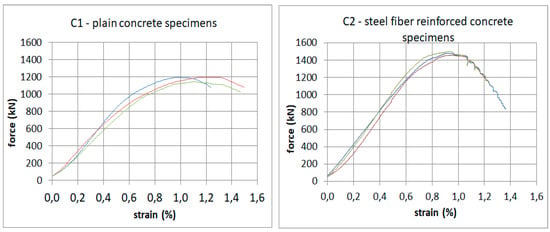
Figure 12.
Charts of compressive strength tests of the specimens.

Table 4.
Results of compressive strength tests of concrete for C1 and C2 specimens.
The obtained values indicate that the addition of 1% of steel fibers improved the compressive strength of the specimens by around 25%. Furthermore, C2 specimens had an approximately 45% lower coefficient of variation, which indicated higher uniformity of those specimens as compared to C1 specimens.
Figure 13 shows a scanning microscope image of the concrete sample cut from the concrete cover of an A2 specimen, with the visible fiber section (Figure 13a), as well as the charts from EDS analysis performed for the concrete covering the fiber (Figure 13b) and the fiber itself (Figure 13c). The sample was taken from a depth of about 20–25 mm, near the reinforcing bar. The results of the analysis showed no corrosion products in the structure of the concrete around the fiber, which may suggest that chloride ions had not penetrated into this place. At the same time, the microstructural image shows the absence of cracks, thus confirming good waterproofing of the concrete. Of course, on the surface of the specimens, corrosion products appeared around several of the fiber fragments found there. However, the fiber diameter in relation to the surrounding concrete was so small that the corrosion products formed on the surface did not pose a threat to the main reinforcement.
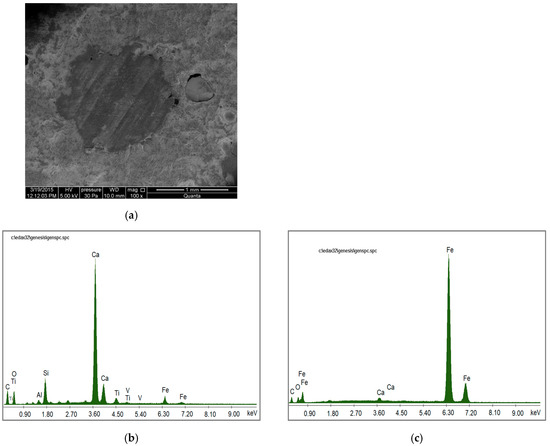
Figure 13.
Microstructure of the steel fiber-reinforced concrete (SFRC) specimen with EDS analysis: (a) the scanning microscope image of the concrete sample with the visible fiber section; (b) EDS analysis of the concrete; (c) EDS analysis of the fiber.
5. Conclusions
As shown by reduced shrinkage and slower corrosion rate of the primary reinforcement, the specimens with a 1% addition of steel fibers were characterized by higher durability than the specimens without fibers.
5.1. Conclusion No. 1
The tests conducted using the method of measuring polarization resistance with the use of galvanostatic pulse made it possible to estimate the corrosion rate of the primary reinforcement triggered by the impact of NaCl during the freeze–thaw cycles in specimens both without fibers and with the addition of 1% of steel micro-reinforcement fibers:
- —
- the measurement of the corrosion current density indicated that adding 1% of steel fibers to concrete reduces the corrosion rate of primary reinforcement bars by 33% on average; the reduction of the corrosion rate likely arises from “tightening” of the concrete cover of the analyzed specimens;
- —
- the measurements of the reinforcement stationary potential completed the corrosion current density measurements and further confirmed the positive impact of 1% of steel fibers on reducing the corrosion rate of the primary reinforcement in the analyzed specimens;
- —
- the measurement of the concrete cover resistivity, due to the need to significantly humidify the concrete for the test, was not reliable for the estimation of the corrosion rate in the analyzed specimens.
5.2. Conclusion No. 2
The addition of 1% of steel micro-reinforcement fibers to concrete reduced shrinkage and provided earlier stabilization of shrinkage strain.
5.3. Conclusion No. 3
The addition of 1% of steel micro-reinforcement fibers to concrete improved the compressive strength of tested specimens by 25% and significantly improved the uniformity of the concrete.
5.4. Conclusion No. 4
Scanning microscopy of the FRC specimen confirmed that the steel fibers in concrete were resistant to corrosion—in the sample taken from the concrete cover at a depth of about 20–25 mm, no elements were found in amounts that would indicate the presence of corrosion products of fibers.
It should be noted that the presented tests concerned specimens with only one type of fibers in an amount of 1% vol. of the mixture. It is likely that the use of other types of fibers and/or different amounts of fibers may affect the results to a greater or lesser extent. This issue is worth further research.
Author Contributions
Idea, P.G.K. and W.R.; Methodology and Tests, W.R.; Data Interpretation W.R.; Writing-Original Draft Preparation, W.R.; Editing, W.R. and P.G.K.; Writing-Review, W.R.; Funding Acquisition, P.G.K. and W.R.
Funding
This research was funded by grant number 02.0.06.00/2.01.01.01. 0007; MNSP. BKWB. 16.001 “Analysis of limit states, durability and diagnostics of structures and methods and tools for quality assurance in concstruction” [Kielce University of Technology, Kielce, Poland].
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- PN-EN 14487-1:2007 Sprayed Concrete–Part 1: Definitions Requirements and Compliance; Polish Committee for Standardization: Warsaw, Poland, 2007.
- PN-EN 14487-2:2007 Sprayed Concrete–Part 2: Execution; Polish Committee for Standardization: Warsaw, Poland, 2007.
- Słowek, G.; Majchrzak, W. Shotcrete in repairs of concrete structures. In Proceedings of the XXV International Conference on Structural Failures, Międzyzdroje, Poland, 24–27 May 2011; pp. 1175–1182. (In Polish). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Niu, D.; Wang, Y.; Wang, B. Durability performance of brine-exposed shotcrete in saltlake environment. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 188, 520–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galan, I.; Baldermann, A.; Kusterle, W.; Dietzel, M.; Mittermayr, F. Durability of shotcrete for underground support- Review and update. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 202, 465–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zych, T. Modern Shotcrete–the Ability to Shape Structural Elements and Architectural Forms; Technical Transactions. Architecture; Krakow University of Technology Publisher: Krakow, Poland, 2010; Volume 107/8-A, pp. 371–386. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Jasiczak, J.; Mikołajczak, P. Technology of Concrete Modified with Admixtures and Additives: Overview of Domestic and Foreign Trends; Poznan University of Technology Publisher: Poznań, Poland, 1997. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Yan, X.; Liu, L.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y. Experimental Study on Basic Mechanical Properties of Steel Fiber-Reinforced Siliceous Wet Shotcrete. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 4, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W. Design and specification of fiber reinforced shotcrete for underground supports. In Book Series: Proceedings and Monographs in Engineering Water and Earth Sciences, Proceedings of the North American Tunneling Conference 2006, Chicago, IL, USA, 10–15 June 2006; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006; pp. 331–335. [Google Scholar]
- Brandt, A.M. Fibre reinforced cement-based (FRC) composites after over 40 years of development in building and civil engineering. Compos. Struct. 2008, 86, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.K.; Barr, B.I.G. Strength and fracture properties of industrially prepared steel fibre reinforced concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2003, 25, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.S.; Hwang, S. Mechanical properties of high-strength steel fiber-reinforced concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2004, 18, 669–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, A.M. Cement Based Composites: Materials Mechanical Properties and Performance; Taylor & Francis: Abingdon, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Jamroży, Z. Fiber reinforced concrete for underground constructions. Min. Geoengin. 2003, 27, 331–335. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Skarżyński, L.; Suchorzewski, J. Mechanical and fracture properties of concrete reinforced with recycled and industrial steel fibers using Digital Image Correlation technique and X-ray micro computed tomography. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 183, 283–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glinicki, M.A. Testing of macro-fibres reinforced concrete for industrial floors. Cem. Wapno Beton 2008, 13, 184–195. [Google Scholar]
- Alsharie, H. Applications and Prospects of Fiber Reinforced Concrete in Industrial Floors. Open J. Civ. Eng. 2015, 5, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Karwowska, J.; Łapko, A. The usability of using modern fiber reinforced composites in building constructions. Civ. Environ. Eng. 2011, 2, 41–46. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Raczkiewicz, W. Effect of concrete addition of selected micro-fibers on the reinforcing bars corrosion in the reinforced concrete specimens. Adv. Mater. Sci. 2016, 16, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zych, T. Study on water permeability, frost damage and de-icing salt scaling of hybrid fibre reinforced concretes. In Proceedings of the 11th International Symposium on Brittle Matrix Composites (BMC), Warsaw, Poland, 28–30 September 2015; pp. 239–250. [Google Scholar]
- CEN. PN-EN 1992-1-1:2008 Eurocode 2: Design of Concrete Structures; General Rules and Rules for Buildings; CEN: Brussels, Belgium, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, H.; Jin, N. Degradation mechanisms of concrete subjected to combined environmental and mechanical actions: A review and perspective. Comput. Concr. 2019, 23, 107–119. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Ch.; Li, Q.; Wu, L. Chloride ion concentration distribution characteristics within concrete covering-layer considering the reinforcement bar presence. Ocean Eng. 2019, 173, 608–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajkova, K.; Smilauer, V.; Jendele, L.; Cervenka, J. Prediction of reinforcement corrosion due to chloride ingress and its effects on serviceability. Eng. Struct. 2018, 174, 768–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzmil, W.; Raczkiewicz, W. Evaluation of the effect of cement type on the carbonation of concrete and the corrosion of reinforcement in reinforced concrete samples. Cem. Wapno Beton 2017, 22, 311–319. [Google Scholar]
- Otieno, M.; Ikotun, J.; Ballim, Y. Experimental investigations on the influence of cover depth and concrete quality on time to cover cracking due to carbonation-induced corrosion of steel in RC structures in an urban, inland environment. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 198, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benitez, P.; Rodrigues, F.; Talukdar, S.; Sergio, G.; Humberto, V.; Enrico, S. Analysis of correlation between real degradation data and a carbonation model for concrete structures. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2019, 95, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montemor, M.F.; Simoes, A.M.; Ferreira, M.G.S. Chloride-induced corrosion on reinforcing steel: From the fundamentals to the monitoring techniques. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2003, 25, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raczkiewicz, W. Influence of the air-entraining agent in the concrete coating on the reinforcement corrosion process in case of simultaneous action of chlorides and frost. Adv. Mater. Sci. 2018, 18, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Niu, D.; He, H. Frost durability and stress-strain relationship of lining shotcrete in cold environment. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 198, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PN-EN 14488-1: 2008 Testing Sprayed Concrete—Part 1: Sampling Fresh and Hardened Concrete; Polish Committee for Standardization: Warsaw, Poland, 2008.
- PN-EN 14488-2: 2007 Testing Sprayed Concrete—Part 2: Compressive Strength of Young Sprayed Concrete; Polish Committee for Standardization: Warsaw, Poland, 2007.
- PN-EN 14488-3: 2008 Testing Sprayed Concrete—Part 3: Flexural Strengths (First Peak, Ultimate and Residual) of Fibre Reinforced Beam Specimens; Polish Committee for Standardization: Warsaw, Poland, 2008.
- PN-EN 14488-4:2008 Testing Sprayed Concrete—Part 4: Bond Strength of Cores by Direct Tension; Polish Committee for Standardization: Warsaw, Poland, 2008.
- PN-EN 14488-5:2008 Testing Sprayed Concrete—Part 5: Determination of Energy Absorption Capacity of Fibre Reinforced Slab Specimens; Polish Committee for Standardization: Warsaw, Poland, 2008.
- PN-EN 14488-6:2008 Testing Sprayed Concrete—Part 6: Thickness of Concrete on a Substrate; Polish Committee for Standardization: Warsaw, Poland, 2008.
- PN-EN 14488-7:2008 Testing Sprayed Concrete—Part 7: Fibre Content of Fibre Reinforced Concrete; Polish Committee for Standardization: Warsaw, Poland, 2008.
- Szweda, Z.; Jaśniok, T.; Jaśniok, M. Evaluation of the effectiveness of electrochemical chloride extraction from concrete on the basis of testing reinforcement polarization and chloride concentration. Corros. Prot. 2018, 61, 3–9. [Google Scholar]
- Jaśniok, M.; Jaśniok, T. Measurements on corrosion rate of reinforcing steel under various environmental conditions, using an insulator to delimit the polarized area. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Analytical Models and New Concepts in Concrete and Masonry Structures (AMCM), Gliwice, Poland, 5–7 June 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Raczkiewicz, W.; Wójcicki, A. Evaluation of effectiveness of concrete coat as a steel bars protection in the structure-galvanostatic pulse method. In Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on Metallurgy and Materials, Brno, Czech Republic, 24–26 May 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Brodnan, M.; Kotes, P.; Bahleda, F.; Šebök, M.; Kučera, M.; Kubissa, W. Using non-destructive methods for measurement of reinforcement corrosion in practice. Corros. Prot. 2017, 60, 55–58. [Google Scholar]
- Brodnan, M.; Kotes, P.; Vanerek, J.; Drochytka, R. Corrosion determination of reinforcement using the electrical resistance method. Mater. Tehnol. 2017, 51, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GalvaPulse. Available online: http://www.germann.org/TestSystems/GalvaPulse/GalvaPulse.pdf (accessed on 20 March 2014).
- PN-EN 206-1: 2003 Concrete—Part 1: Specification Performanc Production and Conformity; Polish Committee for Standardization: Warsaw, Poland, 2003.
- PN-EN 12390-3:2002 Testing Hardened Concrete—Part 3: Compressive Strength of Test Specimens; Polish Committee for Standardization: Warsaw, Poland, 2003.
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).