Abstract
Conventional spectrophotometric methods used for determining total phenolic content and antioxidant activity are typically time-consuming, labor-intensive, and require large amounts of reagents. In the context of sustainable development and green chemistry, minimizing the use of hazardous substances and reducing reagent consumption have become key priorities. The implementation of microplate-based methods offers significant advantages, including reduced reagent volumes and shorter analysis times compared with traditional methods. Therefore, the aim of this study was to validate the Folin–Ciocalteu and DPPH microplate methods and compare their performance with conventional protocols. The limits of detection (LOD) for the microplate methods were lower than those for the conventional approaches, being approximately 0.7 µg/mL and 4.1 µg/mL for TPC, and 0.015 µg/mL and 0.081 µg/mL for DPPH, respectively. The relative standard deviation (RSD) of repeatability and reproducibility for both microplate methods was ≤6%. The accuracy ranged from 95.0% to 97.7% for TPC and from 95.3% to 98.7% for DPPH. Overall, the results confirm that the microplate and conventional methods are statistically equivalent at the 95% confidence level, demonstrating that microplate assays represent a reliable and environmentally friendly alternative for assessing total phenolic content and antioxidant activity.
1. Introduction
Honey is widely regarded as the most valuable natural sweetener. In addition to the main ingredients such as sugars and water, honey contains protein substances, organic and amino acids, vitamins, phenolic compounds and minerals [1,2]. Honey’s antioxidant properties are primarily attributed to the presence of flavonoids, phenolic acids, ascorbic acid, enzymes, and carotenoids [3]. The composition on honey can vary significantly depending on the botanical and geographical origin of the nectar. Furthermore, environmental factors such as climate and plant species influence the profile and concentration of phenolic compounds, which are key indicators of honey quality [4].
Determining the total phenolic content of honey can be difficult due to the structural diversity of these compounds. The feature they have in common, which is used in quantitative determination, is their ability to undergo redox reactions [5,6]. The Folin–Ciocalteu method is based on an electron transfer mechanism in which the Folin–Ciocalteu reagent acts as an oxidant, and the antioxidant compounds act as electron donors [7]. The exact composition of this reagent is unknown, but researchers believe that it consists of a mixture of phosphomolybdate and phosphotungstic acids [6]. In an alkaline environment, phenolic compounds reduce molybdenum (VI) ions to molybdenum (V), leading to the oxidation of polyphenols and the formation of a blue-coloured complex [5,6]. The intensity of this colour is directly proportional to the reducing activity of the phenolic compounds [7]. The absorbance of the reaction mixture is typically measured in the 740–765 nm range, depending on the alkalinity of the solution and its phenolic content [5]. Despite its simplicity and usefulness, the Folin–Ciocalteu method has some limitations, including low specificity and the potential for the F-C reagent to react with other reducing agents, which can lead to an overestimation of the total phenolic content [7,8].
As a natural product, honey is rich in antioxidants that scavenge free radicals, such as peroxides, hydrogen peroxide and lipid peroxyl radicals [9]. The most common method of assessing honey’s antioxidant activity is the DPPH (2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl) method. This method is based on the ability of antioxidants to donate hydrogen atoms to the DPPH radical, which contains an unpaired electron on the nitrogen atom [10,11]. The DPPH radical is classified as a stable radical and is characterised by its deep purple colour [12]. When DPPH reacts with a hydrogen-donating antioxidant, it is reduced to the non-radical form (DPPH2), accompanied by a colour change from purple to yellow [13]. The degree of discolouration, measured at approximately 520 nm, is stoichiometrically related to the number of electrons captured by the radical [10]. The DPPH method is widely recognised as a rapid, simple and effective way of assessing the ability of compounds to scavenge free radicals, as well as the antioxidant activity of food products [9]. The main advantage of this method is that the DPPH radical does not require prior generation, unlike other radical-based assays. However, it has been found that some antioxidants, especially those that react rapidly with peroxide radicals, may be less reactive or even inert towards DPPH [14].
In food quality research, the development of modern analytical methods plays a significant role, as they not only ensure accuracy and precision, but are also more efficient in terms of time and laboratory material consumption. The microwell method has become the subject of intense research due to its advantages compared to traditional spectrophotometric methods. The microplate method is fast, sensitive, and accurate, and it also allows for simultaneous testing of many samples with minimal use of samples and reagents [15,16]. This is especially important in food analysis, where valuable and time-consuming samples require precise testing while minimizing material loss. This technology also enables a reduction in analysis time, which results in faster obtaining of results and increased efficiency of laboratory work [17]. Using the microplate method not only minimizes the risk of sample contamination, but also reduces the amount of laboratory waste, which is important from an ecological and economic perspective. Effective use of this technology supports the development of innovative research methodologies in the field of food, while ensuring high reliability and reproducibility of results. Using the microplate method not only minimizes the risk of sample contamination, but also reduces the amount of laboratory waste, which is important from an ecological and economic perspective. Effective use of this technology supports the development of innovative research methodologies in the field of food, while ensuring high reliability and reproducibility of results. Therefore, the aim of the work was to validate the Folin–Ciocalteu microplate method and the DPPH method and to compare them with conventional methods.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Commercial honey samples were purchased from various local markets and retailers. The flower origins and corresponding codes were as follows: acacia (Robinia pseudoacacia)—A, phacelia (Phacelia tanacetifolia Benth.)—P, honeydew—H, and buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum)—B. Samples were stored at room temperature in the dark until further analysis. All analyses were performed in six replicates.
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Extraction Procedure
Phenolic compounds were extracted from honey samples using methanol as the solvent. The final concentration of the extract was 0.1 g of honey per ml. The mixtures were shaken at 120 rpm and room temperature for 24 h to ensure complete extraction. After incubation, the extracts were filtered and stored in the refrigerator (4 °C) until further analysis.
2.2.2. Conventional Total Phenolic Content (TPC)
The total phenolic content (TPC) of the honey samples was determined using the Folin–Ciocalteu colorimetric assay [18]. Briefly, 0.5 mL of extract was mixed with 2.5 mL of 0.2 N Folin–Ciocalteu reagent. After 5 min, 2.0 mL of sodium carbonate solution (75 g/L) was added, and the mixture was incubated in the dark at room temperature for 2 h. The absorbance was measured at 760 nm using a UV–visible spectrophotometer (Shimadzu UV mini-1240, Kyoto, Japan).
A calibration curve was constructed using gallic acid monohydrate as a standard, with concentrations ranging from 0 to 300 mg/L. The TPC values were expressed as milligrams of gallic acid equivalents (mg GAE) per 100 g of honey.
2.2.3. 96-Well Plate Total Phenolic Method
The total phenolic content (TPC) of the honey samples was determined using the Folin–Ciocalteu colorimetric method [19], with minor modifications based on previous procedures [20,21]. In brief, 20 µL of the extract was mixed with 100 µL of 1:10 diluted Folin–Ciocalteu reagent and 75 µL of a 75 g/L sodium carbonate solution in the wells of a 96-well microplate. After incubating the mixture in the dark at room temperature for 2 h, the absorbance was measured at 740 nm using a microplate reader (SPECTROstar NANO, BMG LABTECH, Ortenberg, Germany).
A calibration curve was constructed using gallic acid monohydrate as a standard (10–200 mg/L). The TPC values were expressed as milligrams of gallic acid equivalents (mg GAE) per 100 g of honey.
2.2.4. DPPH Conventional Method
The antioxidant activity of the honey samples was evaluated using the conventional 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) radical scavenging assay, following the procedure described by Herald et al. [22], with slight modifications. 2.94 mL of a DPPH solution in methanol (60 µmol/L) was mixed with 60 µL of the honey extract. The mixture was incubated in the dark for 60 min at room temperature, and the absorbance was then measured at 515 nm using a UV–visible spectrophotometer (Shimadzu UV mini-1240, Kyoto, Japan).
The percentage of DPPH radical scavenging activity (% DPPH quenched) was calculated using the following equation:
where is the absorbance at 515 nm of the reaction mixture containing 60 µL of extract and 2.94 mL of DPPH solution, is the absorbance of 3.00 mL of methanol, and is the absorbance of 60 µL of methanol mixed with 2.94 mL of DPPH solution.
2.2.5. DPPH Microplate Method
The radical scavenging activity of the honey samples against 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) was evaluated according to the procedure described by Herald et al. [22], with minor modifications. 180 µL of DPPH solution (150 µmol/L in methanol) was added to the wells of a 96-well microplate, except for the blank wells, followed by the addition of 20 µL of sample or control solution. The mixtures were gently shaken for 60 s and allowed to react in the dark for 40 min at room temperature. The absorbance was subsequently measured at 517 nm using a microplate reader (SPECTROstar NANO, BMG LABTECH, Ortenberg, Germany).
The percentage of DPPH radical scavenging activity (% DPPH quenched) was calculated using the following Equation (1), where is the absorbance at 517 nm of a mixture containing 20 µL of extract and 180 µL of DPPH solution; is the absorbance at 517 nm of 200 µL of methanol; and is the absorbance at 517 nm of a mixture containing 20 µL of methanol and 180 µL of DPPH solution.
2.2.6. Methodology Validation
The methods used in the work have been validated based on the International Council for Harmonisation (ICH). Linearity, specificity, limit of detection, limit of quantification, accuracy and precision were investigated.
Linearity
The linearity of the methods was assessed by testing various concentrations of working standards: gallic acid in the TPC methods and Trolox in the DPPH methods. Six different concentrations were obtained by diluting prepared standard solutions containing 0.2 mg GAE/100 mL or 12.5 mg Trolox/100 mL. The concentration ranges were established based on a review of literature, previous laboratory studies, and preliminary research conducted by our group. These were then subjected to the relevant processes, and the results obtained allowed calibration curves to be plotted. Statistical analysis was performed using the least squares method. Linearity was predicted by estimating the regression coefficient (r2).
Specificity
Method specificity is defined as the ability to identify a specific analyte in the presence of other compounds, including impurities, degradation products and matrix compounds. This study assessed the specificity of the methods used by conducting analyses on solutions containing gallic acid, fructose, glucose and mixtures of these compounds.
Limit of Detection (LOD) and Limit of Quantification (LOQ)
The limits of detection and quantification are useful parameters for assessing the purity of the methods used. The LOD and LOQ of all methods were determined based on a linearity study using the linear regression model defined in the ICH guidelines. Both parameters were calculated using the following equations:
were σ is the standard deviation of the response and S is the slope of the calibration curve.
Accuracy
The accuracy of the methods employed in this study was assessed by analysing honey samples and honey samples enriched with a known amount of gallic acid. Accuracy, measured as the percentage of gallic acid detected in the enriched honey samples, was expressed as a percentage.
Precision
The precision of the methods employed in this study was evaluated by assessing both repeatability (within a day) and intermediate precision (over a two-month period). The repeatability of the process was verified by analysing honey solutions six times on the same day and under the same experimental conditions. Intermediate precision was subsequently assessed by means of similar analyses performed two months later in the same laboratory. All data obtained were expressed as relative standard deviation (RSD, %).
Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using Statistica 13 software (StatSoft, Tulsa, OK, USA). All data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation. The homogeneity of variance between the conventional and microplate methods was assessed using the F-Snedecor test at a significance level of α = 0.05. If homogeneity of variance was confirmed, comparisons of mean values were made using t-Student’s test for independent sample (α = 0.05). Additionally, Tukey’s post hoc test was used to group methods and verity the existences were considered statistically significant at p < 0.05.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Linearity
Calibration graphs were prepared to test the linearity of the methods are presented in Figure 1. In the case of the F-C methods, the curves were determined in the system of gallic acid concentration and absorbance. The conventional method examined eight concentration levels, ranging from 0.4 to 15 μg/100 mL. This range accounted for 75% of the expected results. In contrast, the microplate method examined seven concentration levels ranging from 0.08 to 3 μg/100 mL, covering nearly 85% of the expected analytical results. Satisfactory linearity was demonstrated in both cases within the analysed concentration ranges, with regression coefficients of R2 = 0.998 for the conventional method and R2 = 0.9987 for the microplate method. Other researchers using the conventional Folin–Ciocalteu method obtained regression coefficients of 0.9988 [4] and 0.996 [5]. For the microplate method, regression coefficients ranging from 0.9950 to 0.9990 were obtained [15,16].
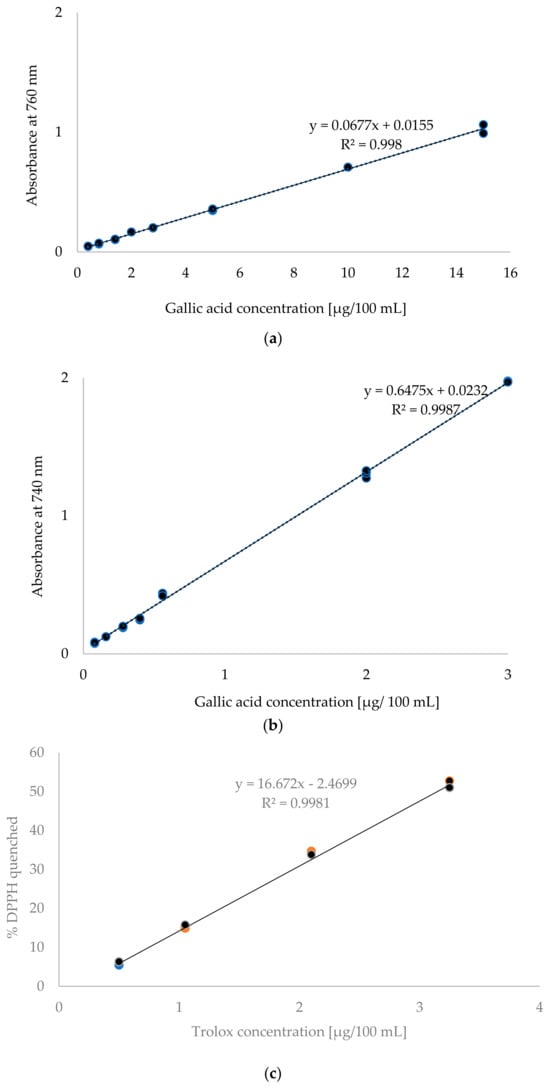
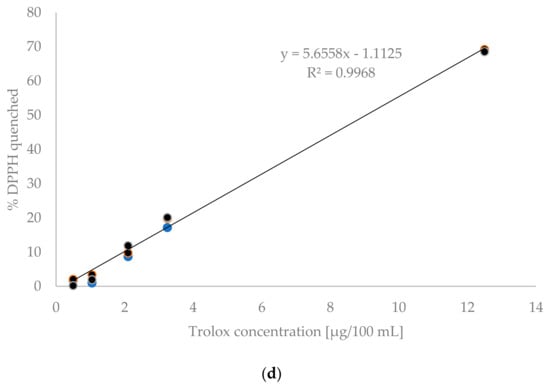
Figure 1.
Standard curves for: (a) conventional TPC method, (b) microplate TPC method, (c) conventional DPPH method, (d) microplate DPPH method.
In the DPPH methods the relationship between the Trolox concentration and the content of quenched DPPH was presented. Figure 1c shows the standard curve determined using the conventional method. Four standard solution concentrations ranging from 0.5 to 3.25 μg/100 mL were tested. Figure 1d shows the standard curve determined for the microplate method. In this case, five concentration levels ranging from 0.5 to 12.5 μg/100 mL were analysed. In both cases, the concentration range covered nearly 80% of the expected analytical values. Linearity was confirmed within the tested ranges for both the conventional and microplate methods, as evidenced by the obtained regression coefficients R2, which were 0.9981 and 0.9968 for the conventional and microplate methods, respectively. Herald et al. [22] obtained a coefficient of R2 = 0.9975 for the conventional DPPH method and R2 = 0.9997 for the microplate method. Meanwhile, Bobo-Garcia et al. [23] obtained an R2 value of 0.9999 for the microplate method.
3.2. Specificity
To determine the selectivity of the tested methods (TPC and DPPH), the influence of various interfering compounds on the assay results was examined. In the case of honey, the main interfering compounds are glucose and fructose, constituting approximately 70–80% of the honey’s dry weight. During the analysis, the methods were deemed selective because glucose and fructose are insoluble in methanol, which was used as the extraction solvent. To confirm selectivity, the possible influence of other honey components (proteins, amino acids, and enzymes) was also analyzed. However, in this case, the use of methanol as the extraction solvent also ruled out the possibility of these compounds affecting the analytical signal. Lawag et al. [8] conducted research into modifications to the Folin–Ciocalteu method. They used water as the solvent and analysed the effects of fructose, glucose, galactose, lactose, maltodextrin, maltose, mannose, sucrose and xylose. They found that fructose, sucrose and galactose had a minimal impact on the final results, which could be further reduced by lowering the pH to 7.9.
3.3. Limit of Detection and Limit of Quantification
The obtained LOD and LOQ values are presented in Table 1. For the microplate TPC method, LOD values of 0.7 μg/mL were obtained, whereas for the conventional method, this parameter was 4.1 μg/mL. These values are comparable to those reported by other authors, who obtained LOD values for the microplate method ranging from 0.74 μg/mL to 2.55 μg/mL [5,8,15,23]. The limit of quantification for the microplate TPC method was 7 μg/mL, whereas for the conventional method it was 41 μg/mL. Similar values were obtained by other researchers [5,8].

Table 1.
Limit of detection (LOD) and limit of quantification (LOQ).
For the DPPH microplate method, LOD values of 0.015 μg/mL were obtained, while in the conventional method this parameter was 0.081 μg/mL. The LOQ values for the microplate and conventional DPPH methods were 1.5 μg/mL and 8.1 μg/mL, respectively.
3.4. Accuracy
The results of the accuracy test are presented in Table 2. For the microplate and conventional TPC methods, the average recovery percentages were 95.3% and 96.8%, respectively. For the microplate and conventional DPPH methods, the average recovery percentages were 95.3% and 98.7%, respectively. These results confirm that both methods are accurate in determining TPC and DPPH in honey. The accuracy values obtained are comparable to reported by other researchers [5,8,15,24].

Table 2.
Accuracy and Precision.
3.5. Precision
The precision of the method, as expressed by the coefficient of variation, is presented in Table 2. This parameter is divided into repeatability and reproducibility. All values obtained were less than 6%, indicating good precision all methods. Similar precision values were also obtained by other researchers [5,8,16,17,25]. The precision of the validated methods was assessed using the Snedecor F-test. The test compared the variance of the results obtained using the validated methods. It was found that the variances of all groups were homogeneous. It was also found that the standard deviations for the series of measurements obtained using the compared methods did not differ statistically significantly.
3.6. Other Parameters
When it comes to analytical method validation, it’s important to evaluate how sensitive the procedure is to minor variations in experimental conditions, such as pH, temperature, or reaction time. Changes to these parameters can affect the stability of chemical reagents and the reliability of the results obtained. In the Folin–Ciocalteu method, the stability of the colored complex formed during the reaction depends on the pH of the reaction medium. According to the literature, deviations from the optimal pH range can lead to changes in color intensity and, consequently, an inaccurate estimation of total phenolic content [8]. In our studies, we maintained the pH according to the recommendations of the validation study, and additional pilot studies showed that small deviations of ±0.2 pH units did not significantly affect the final result. Similarly, in DPPH antioxidant activity assays, temperature is a significant factor, as it can accelerate or slow down the radical reduction reaction. Preliminary studies conducted in our laboratory confirmed that the reaction is stable and reproducible in the 20–25 °C range, whereas at higher temperatures, faster decolorization is observed, which can lead to lower absorbance values within the established incubation time. Therefore, all analyses were conducted under controlled room temperature conditions (22 ± 1 °C). Reaction time is also a critical parameter in both methods. If the time is too short, reactions may be incomplete, while if it is too long, the colour complex may degrade or the reagents may oxidise. In our studies, we monitored the progress of the reaction and determined the optimal incubation times to be 2 h for the Folin–Ciocalteu assay and 40 or 60 min for the DPPH test.
3.7. Determination of TPC and DPPH in Honeys
The total polyphenol content of the tested honeys was determined using two methods: the microplate method and the conventional method. The results are presented in Figure 2. Buckwheat honey had the highest polyphenol content, while acacia honey had the lowest.
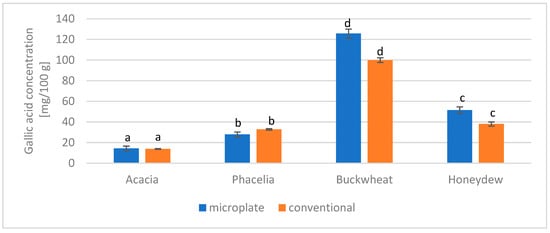
Figure 2.
Comparison of the microplate and conventional methods for determining the total phenol content in honey. The same letters (a–d) indicate no statistically significant differences at the 95% level (p ≤ 0.05).
The antioxidant activity of the tested honeys was determined using two methods, microplate and conventional. The results obtained are presented in Figure 3. Buckwheat honey exhibited the highest activity, while acacia honey exhibited the lowest.
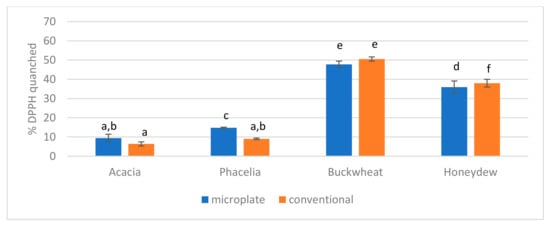
Figure 3.
Comparison of the microplate and conventional DPPH methods in honey. The same letters (a–f) indicate no statistically significant differences at the 95% level (p ≤ 0.05).
These results are comparable to those in the literature [26,27]; however, it should be noted that various modifications to the validated methods are employed, including the wavelength at which absorbance is measured the incubation time of the samples, and the volume and dilution of the reagents and extracts used for testing [28,29,30,31,32].
3.8. Comparison in Terms of Sustainability, Costs and Operational Time
Conventional methods require relatively large volumes of reagents (2.5–3 mL per test), resulting in high reagent consumption and increased waste. Microplate methods, on the other hand, limit reagent consumption to a small amount (20–200 μL), reducing chemical waste by more than tenfold. This approach aligns with green chemistry principles, reducing the environmental impact of the procedure. Using smaller volumes of reagents in microplate methods reduces the cost of analysis, as the Folin–Ciocalteu reagent, sodium carbonate, DPPH reagent and necessary solvents are expensive in large quantities. Furthermore, microplates enable a large number of measurements to be performed in parallel, thereby reducing the cost per analysis.
Conventional methods require sample preparation in cuvettes, individual incubations and spectrophotometric measurements for each sample, which significantly increases analysis time. In contrast, microplate methods use a microplate reader to measure multiple samples simultaneously, reducing analysis time by several times.
Microplate methods offer several advantages over conventional methods, including lower reagent and waste consumption, lower unit costs and shorter analysis times, as well as the potential for automation. Clearly, this comparison indicates that microplate methods are a more sustainable and effective alternative to classical spectrophotometric methods.
4. Conclusions
The linearity, the limits of quantification and the detection of the TPC and DPPH microplate methods were all acceptable. The repeatability and reproducibility of these methods, as expressed by the coefficient of variation, were both below 6%, and accuracy range of 95.3–96.8%. A comparison of the microplate and conventional methods showed that the TPC and DPPH microplate methods are as reproducible, accurate and precise as the conventional methods. Using microplate methods saves time and resources, making them suitable for routine honey analysis.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.M.; methodology, E.M.; software, E.M.; validation, E.M. and B.D.; formal analysis, E.M. and B.D.; investigation, E.M.; resources, E.M.; data curation, E.M.; writing—original draft preparation, E.M. and B.D.; writing—review and editing, E.M.; visualization, E.M.; supervision, E.M.; project administration, E.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data supporting reported results are restored at Warsaw University of Life Sciences.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Ahmed, S.; Sulaiman, S.A.; Baig, A.A.; Ibrahim, M.; Liaqat, S.; Fatima, S.; Jabeen, S.; Shamin, N.; Othman, N.N. Honey as a potential natural antioxidant medicine: An insight into its molecular mechanism of action. Oxidative Med. Cellural Longev. 2018, 2018, 8367846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatun, M.A.; Yoshimura, J.; Yoshida, M.; Suzuki, Y.; Huque, R.; Kelly, S.D.; Munshi, M.K. Isotopic characteristics (δ13C, δ15N, and δ18O) of honey from Bangladesh retail markets: Investigating sugar manipulation, botanical and geographical authentication. Food Chem. 2024, 435, 137612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mărgăoan, R.; Topal, E.; Balkanska, R.; Yücel, B.; Oravecz, T.; Cornea-Cipcigan, M.; Vodnar, D.C. Monofloral honeys as a potential source of natural antioxidants, minerals and medicine. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wabaidur, S.M.; Obbed, M.S.; Alothman, Z.A.; Alfaris, N.A.; Badjah-Hadj-Ahmed, A.Y.; Siddiqui, M.R.; Altamimi, J.Z.; Aldayel, T.S. Total phenolic acids and flavonoids contents determination in Yemeni honey of various floral sources: Folin-Ciocalteu and spectrophotometric approach. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 40, 647–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blainski, A.; Lopes, G.C.; Palazzo de Mello, J.C. Application and analysis of the Folin Ciocalteu method for the determination of the total phenolic content from Limonium brasiliense L. Molecules 2013, 18, 6852–6865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platzer, M.; Kiese, S.; Herfellner, T.; Schweiggert-Weisz, U.; Eisner, P. How does the phenol structure influence the results of the Folin-Ciocalteu assay? Antioxidants 2021, 10, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, M.; Dominguez-López, I.; Lamuela-Raventós, R.M. The chemistry behind the Folin-Ciocalteu method for the estimation of (poly)phenol content in food: Total phenolic intake in a mediterranean dietary pattern. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 17543–17553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawag, I.L.; Nolden, E.S.; Schaper, A.A.M.; Lim, L.Y.; Locher, C. A modified Folin-Ciocalteu assay for the determination of total phenolics content in honey. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munteanu, I.G.; Apetrei, C. Analytical methods used in determining antioxidant activity: A review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 22, 3380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moniruzzaman, M.; Khalil, M.I.; Sulaiman, S.A.; Gan, S.H. Advances in the analytical methods for determining the antioxidant properties of honey: A review. Afr. J. Tradit. Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 9, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kedare, S.B.; Singh, R.P. Genesis and development of DPPH method of antioxidant assay. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 48, 412–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulcin, I.; Alwasei, S.H. DPPH radical scavenging assay. Processes 2023, 11, 2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misha, K.; Ojha, H.; Chaudhury, N.K. Estimation of antiradical properties of antioxidants using DPPH assay: A critical review and results. Food Chem. 2012, 130, 1036–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Moore, J.; Yu, L. High-throughput relative DPPH radical scavenging capacity assay. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 7429–7436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Zhang, J.J.; Liu, C.Y.; Bai, W.S.; Cheng, N. A modified Folin-Ciocalteu method for the microdetermination of total phenolic content in honey. Int. Food Res. J. 2020, 27, 576–584. [Google Scholar]
- Pueyo, I.U.; Calvo, M.I. Assay conditions and validation of a new UV spectrophotometric method using microplates for the determination of polyphenol content. Fitoterapia 2009, 80, 465–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musci, M.; Yao, S. Optimization and validation of Folin-Ciocalteu method for determination of total polyphenol content of Pu-erh tea. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 68, 913–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Suarez, J.M.; Tulipani, S.; Díaz, D.; Estevez, Y.; Romandini, S.; Giampieri, F.; Damiani, E.; Astolfi, P.; Bompadre, S.; Battino, M. Antioxidant and antimicrobial capacity of several monofloral Cuban honeys and their correlation with color, polyphenol content and other chemical compounds. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 2490–2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singleton, V.L.; Rossi, J.A. Colorimetry of total phenolics with phosphomolybdic-phosphotungstic acid reagents. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 1965, 16, 144–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, L.; Gnoyke, S.; Popken, A.M.; Böhm, V. Antioxidant capacity and related parameters of different fruit formulations. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 43, 992–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Duais, M.; Müller, L.; Böhm, V.; Jetschke, G. Antioxidant capacity and total phenolics of Cyphostermma digitatum before and after processing: Use of different assays. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2009, 228, 813–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herald, T.J.; Gadgil, P.; Tilley, M. High-throughput micro plate assays for screening flavonoid content and DPPH-scavenging activity in sorghum bran and flour. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2012, 92, 2326–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobo-García, G.; Davidov-Pardo, G.; Arroqui, C.; Vírseda, P.; Marín-Arroyo, M.R.; Navarro, M. Intra-laboratory validation of microplate methods for total phenolic content and antioxidant activity on polyphenolic extracts, and comparison with conventional spectrophotometric methods. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2015, 95, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paula, V.B.; Sousa-Dias, M.L.; Seixas, N.L.; Combarros-Fuertes, P.; Estevinho, L.M.; Dias, L.G. Phenolic Class Analysis in Honey: Comparison of Classical and Single UV Spectrum Methodologies. Processes 2024, 12, 2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, J.G.; Dods, K.; Hammer, K.A. Development and validation of a new microplate assay that utilises optical density to quantify the antibacterial activity of honeys including Jarrah, Marri and Manuka. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0243246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Liu, R.; Lu, Q.; Hao, P.; Xu, P.; Xu, A.; Zhang, J.; Tan, J. Biochemical properties, antibacterial and cellular antioxidant activities of buckwheat honey in comparison to manuka honey. Food Chem. 2018, 252, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gośliński, M.; Nowak, D.; Kłębukowska, L. Antioxidant properties and antimicrobial activity of manuka honey versus Polish honeys. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 1269–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Farsi, M.; Al-Amri, A.; Al-Hadhrami, A.; Al-Belushi, S. Color, flavonoids, phenolics and antioxidant of Omani honey. Heliyon 2018, 4, e00874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauliuc, D.; Dranca, F.; Oroian, M. Antioxidant activity, total phenolic content, individual phenolics and physicochemical parameters suitability for Romanian honey authentication. Foods 2020, 9, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puścion-Jakubik, A.; Karpińska, E.; Moskwa, J.; Socha, K. Content of phenolic acids as a marker of Polish honey varieties and relationship with selected honey-quality-influencing variables. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawag, I.L.; Islam, M.K.; Sostaric, T.; Lim, L.Y.; Hammer, K.; Locher, C. Antioxidant activity and phenolic compound identification and quantification in Western Australian honeys. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergara-Barberán, M.; Lerma-García, M.J.; Simó-Alfonso, E.F.; García-Álvarez-Coque, M.C. Use of polyphenolic fingerprints established by comprehensive two-dimensional liquid chromatography for the classification of honeys according to their floral origin. J. Chromatogr. A 2023, 1705, 464138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).