Stress Distribution Around Roadway of Kunyang No. 2 Phosphate Mine: Analytical Study and Field Verification
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Calculation Principles for Analytical Solutions of Excavation-Induced Stress
2.1. Complex Variable Function Theory
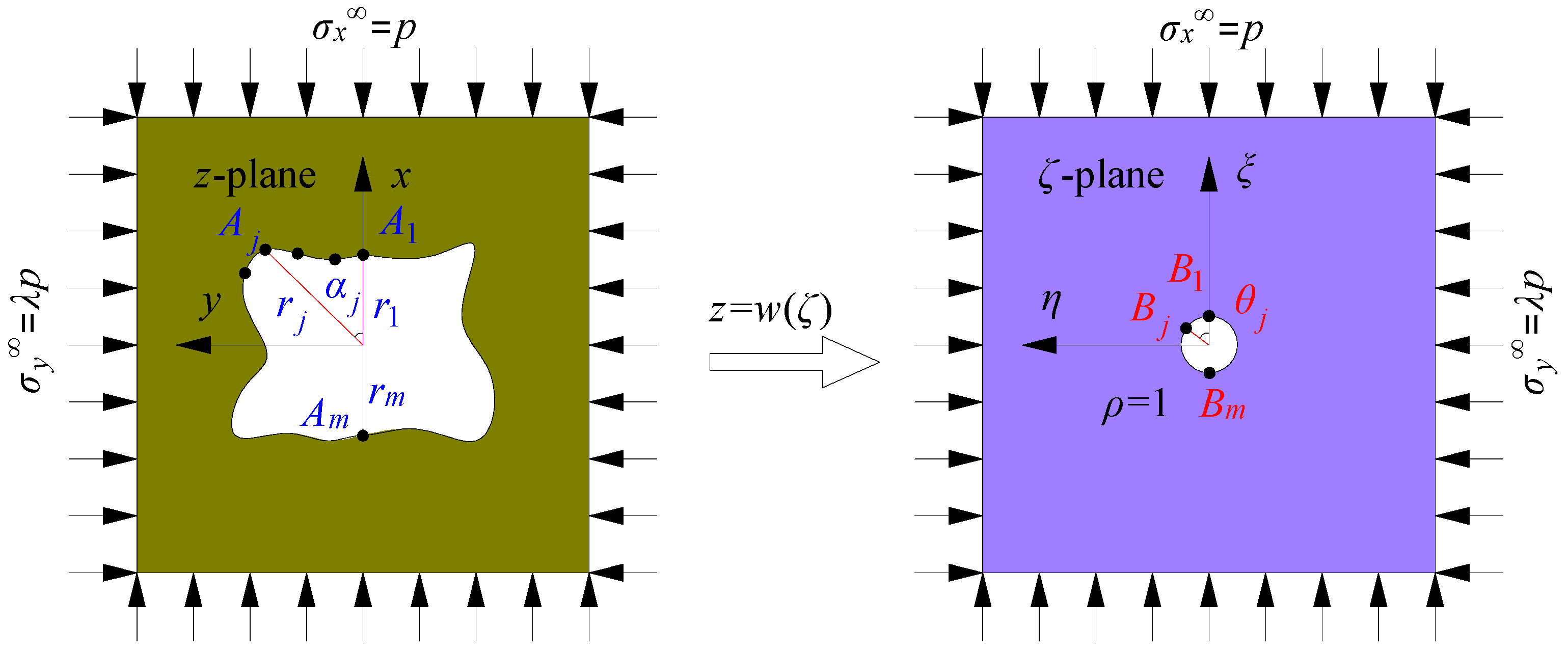
2.2. Conformal Transformation for Complex-Shaped Hole
2.3. Determination of Mapping Function
3. Stress Distribution Around Roadway in Kunyang No. 2 Phosphate Mine
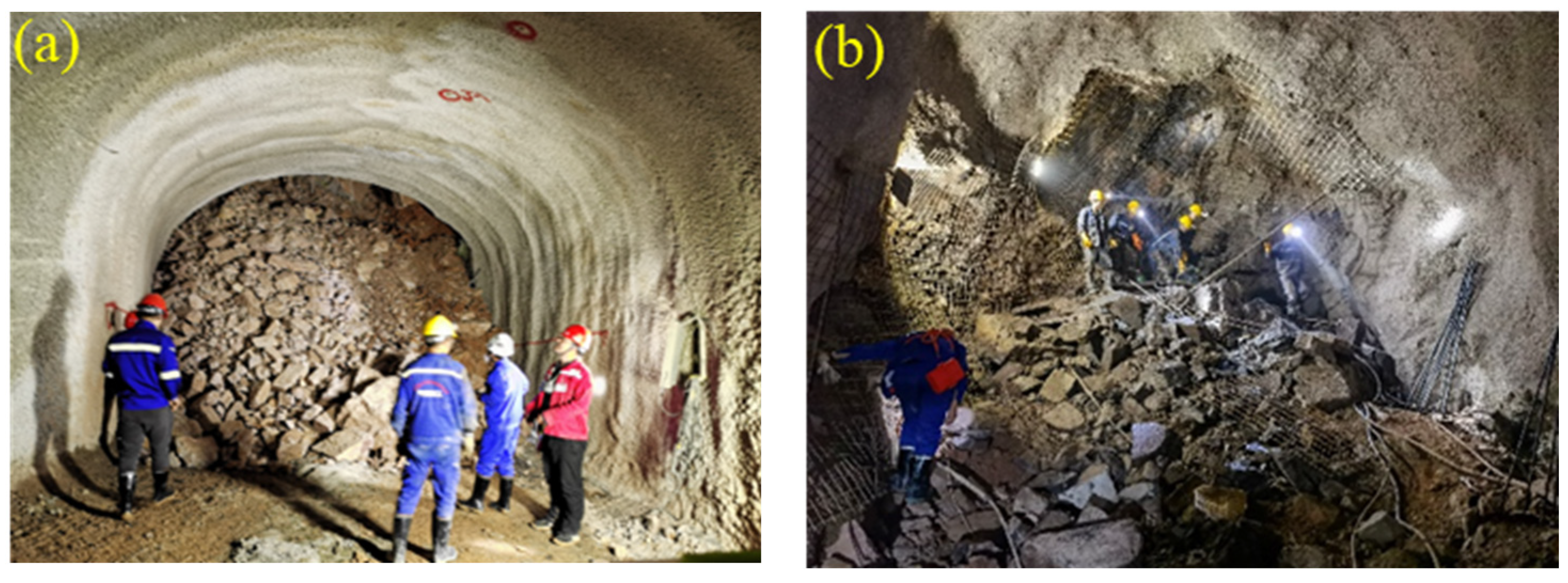
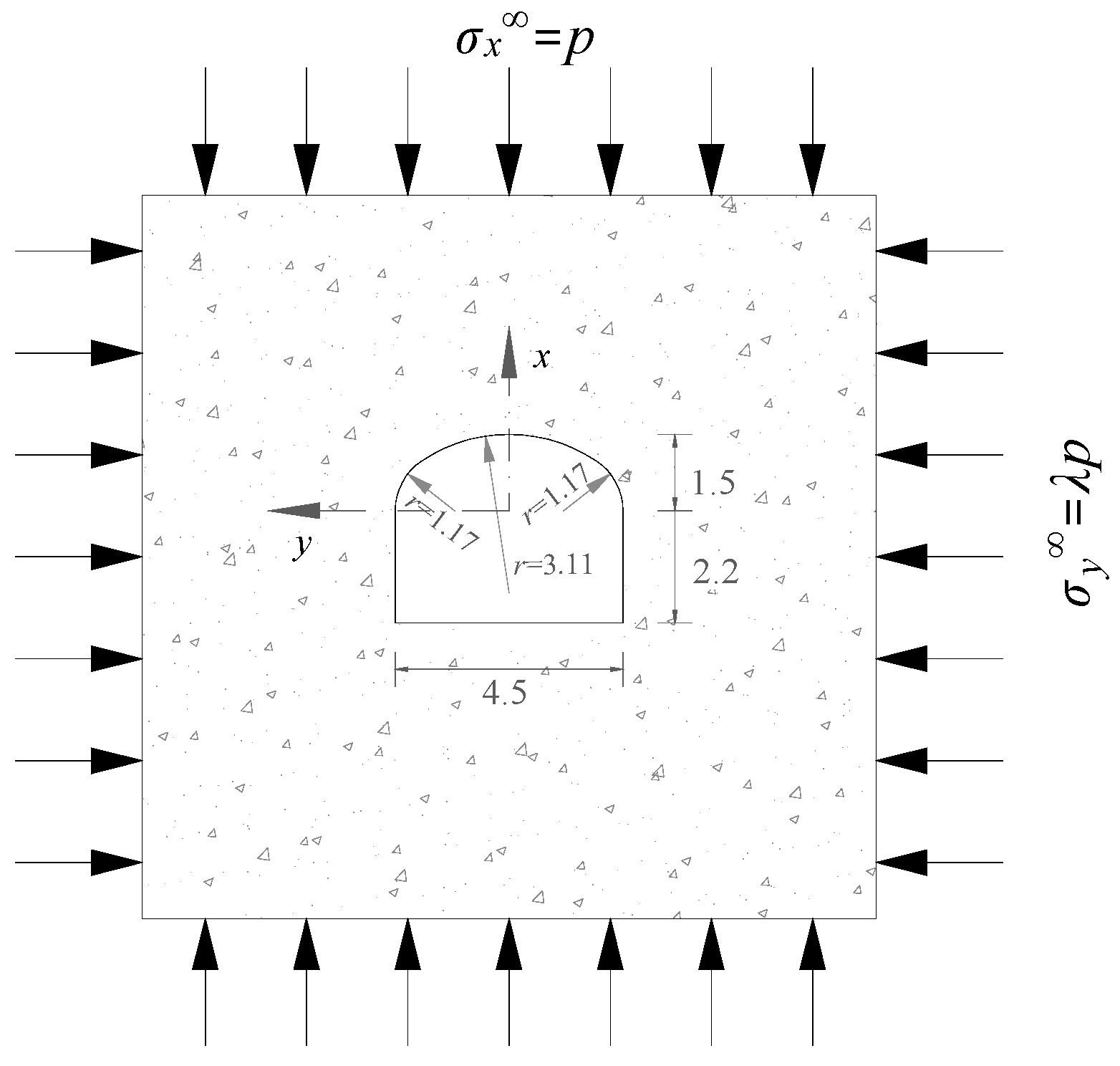
3.1. Project Overview
3.2. Mapping Function and Mapping Accuracy
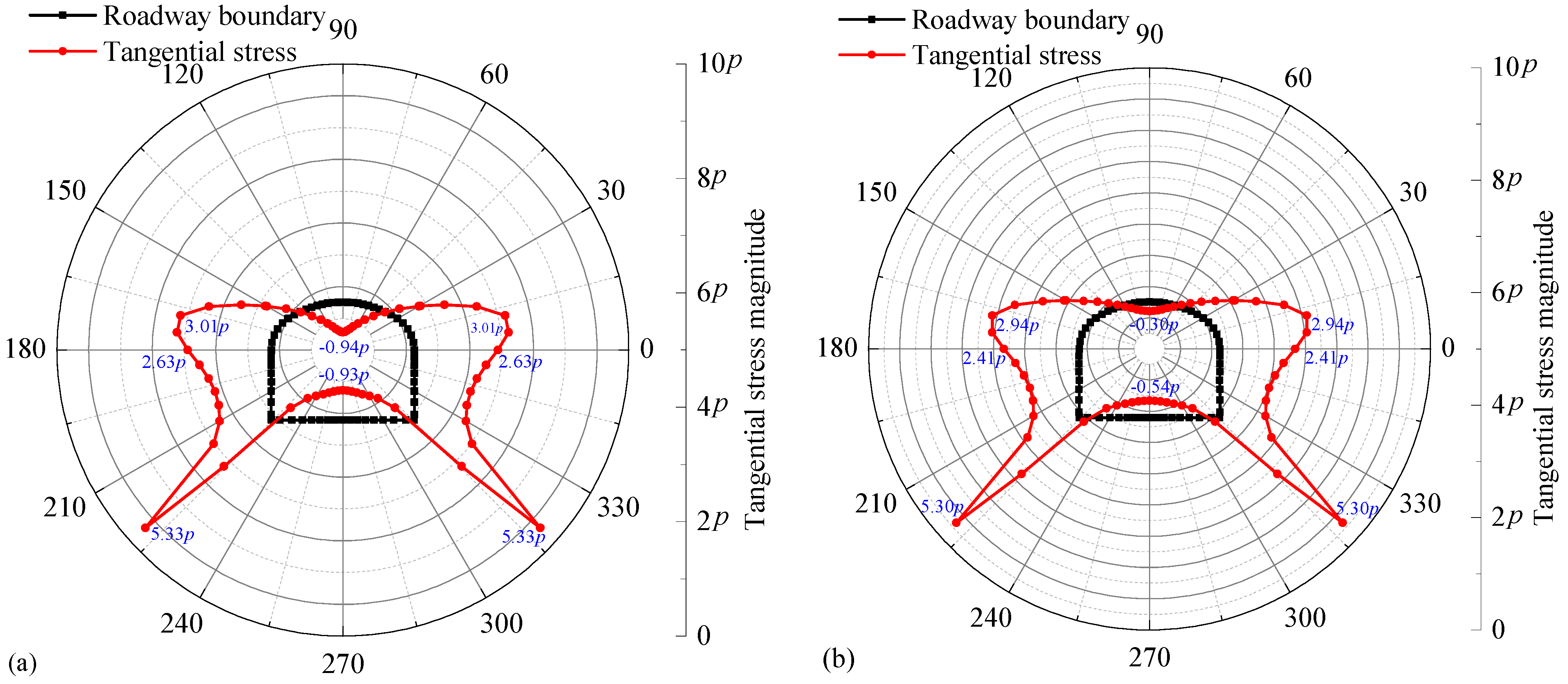
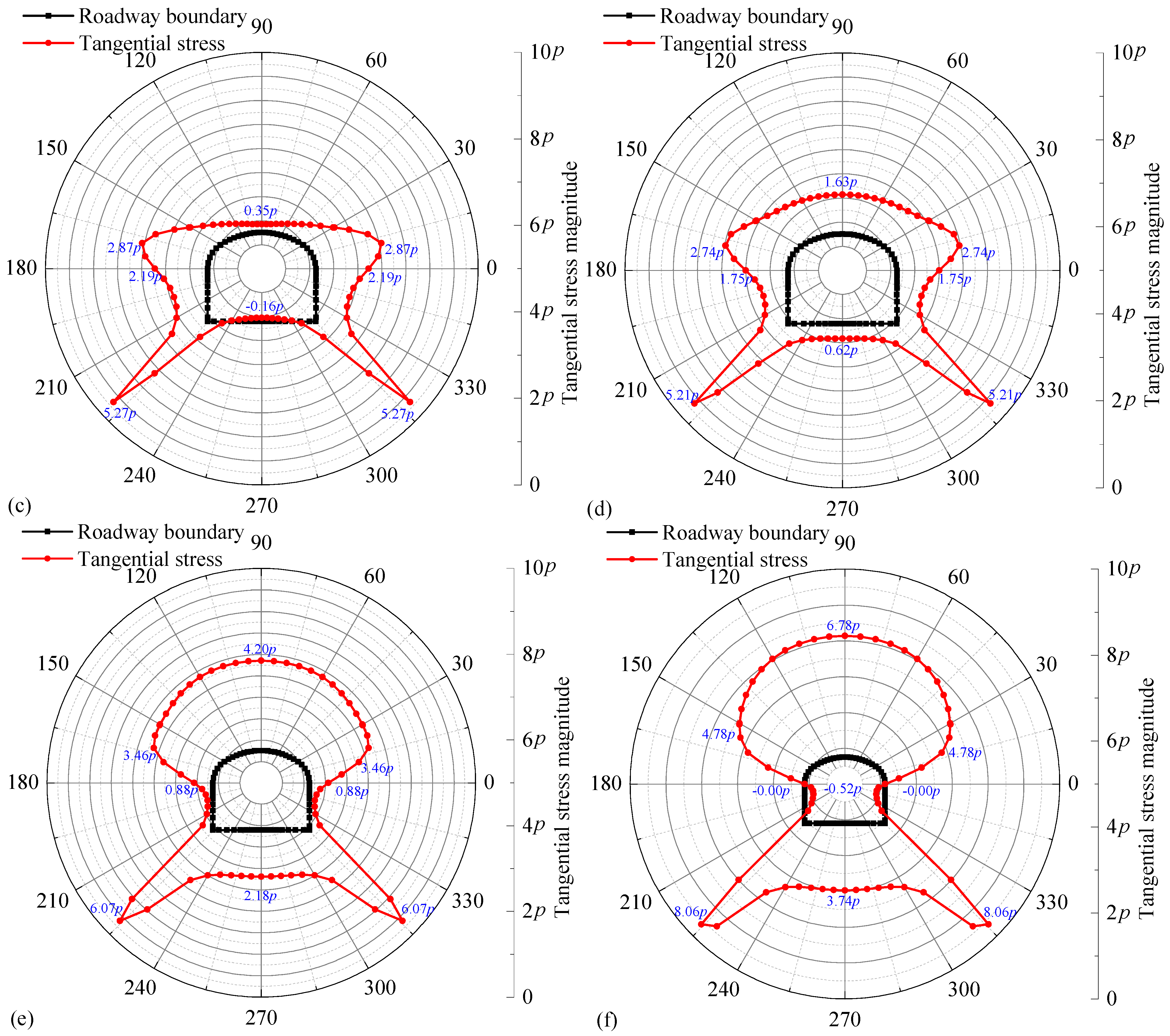
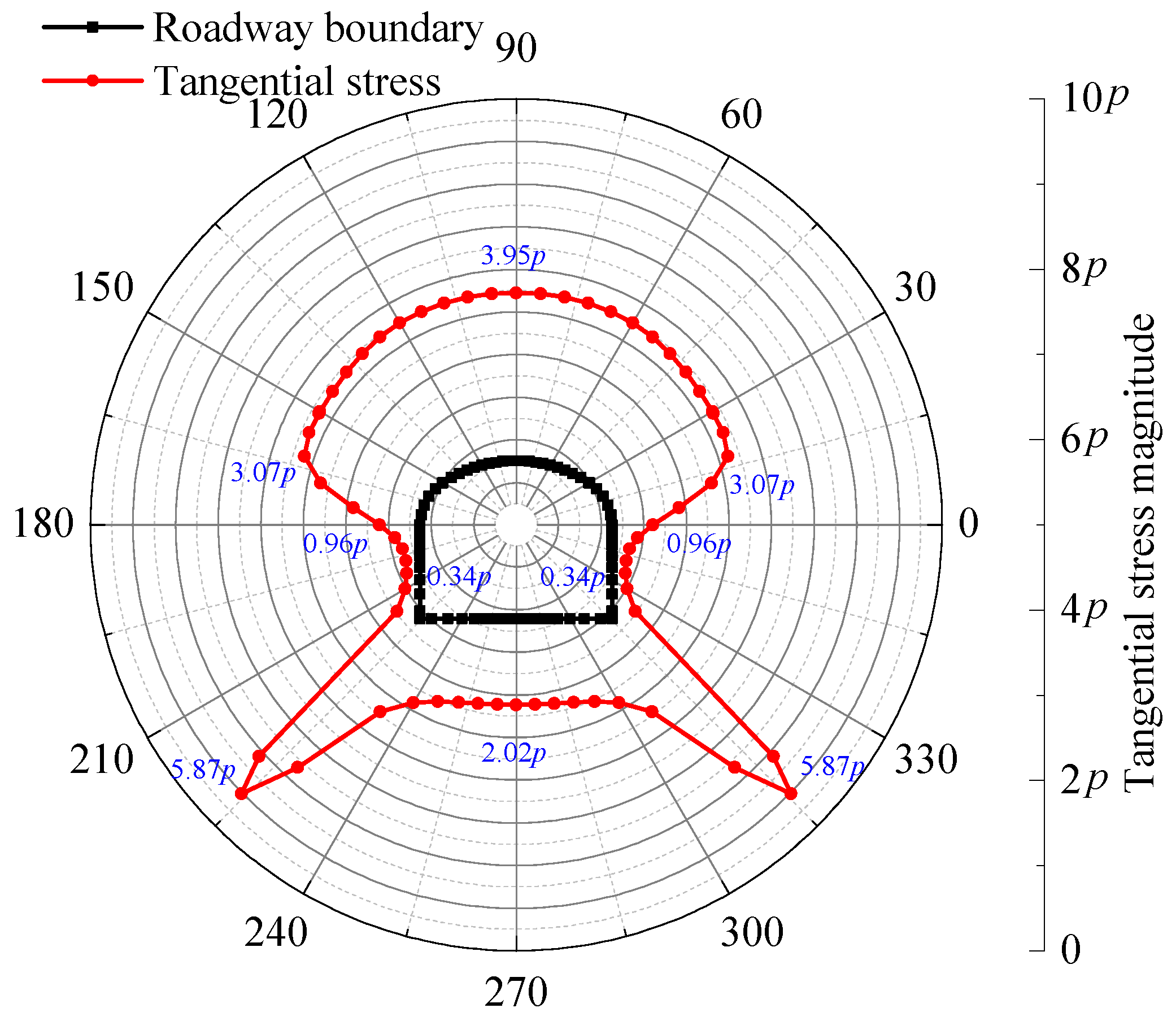
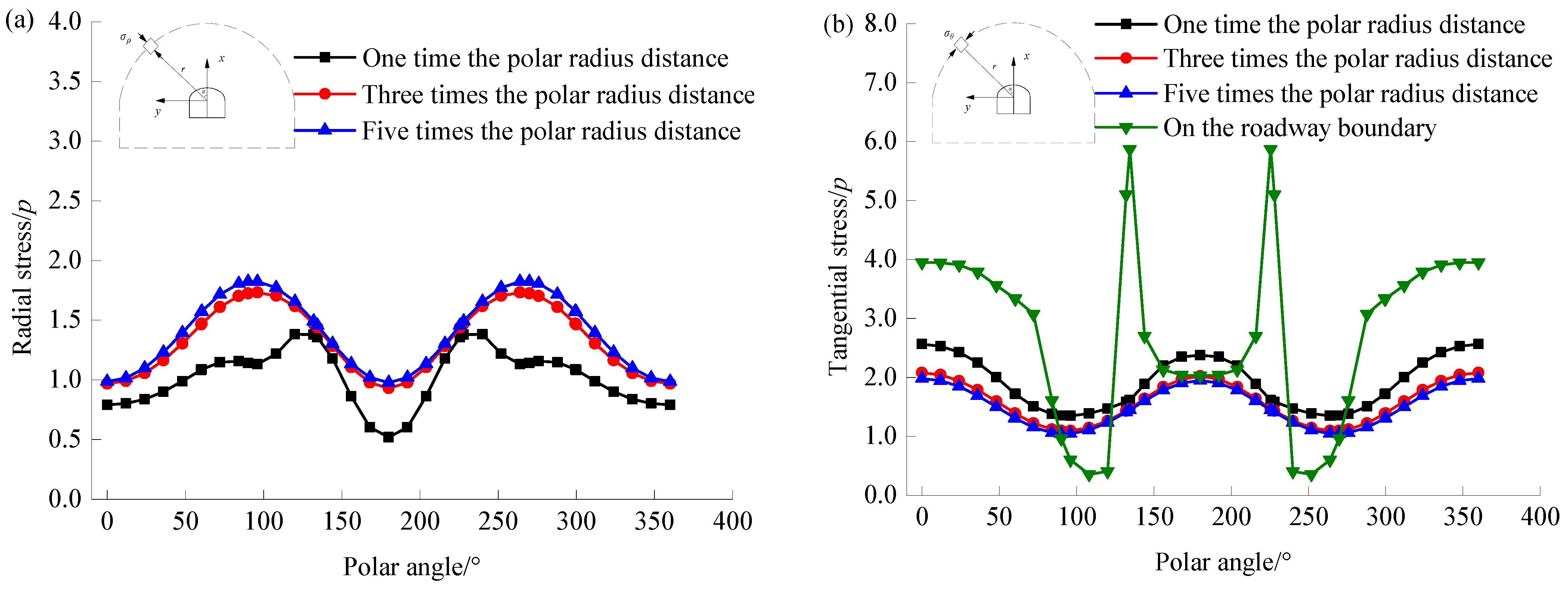
3.3. Stress Distribution Around the Roadway
4. On-Site Measurement of Surrounding Rock Stress Around Roadway
4.1. Measurement Principle of Surrounding Rock Stress
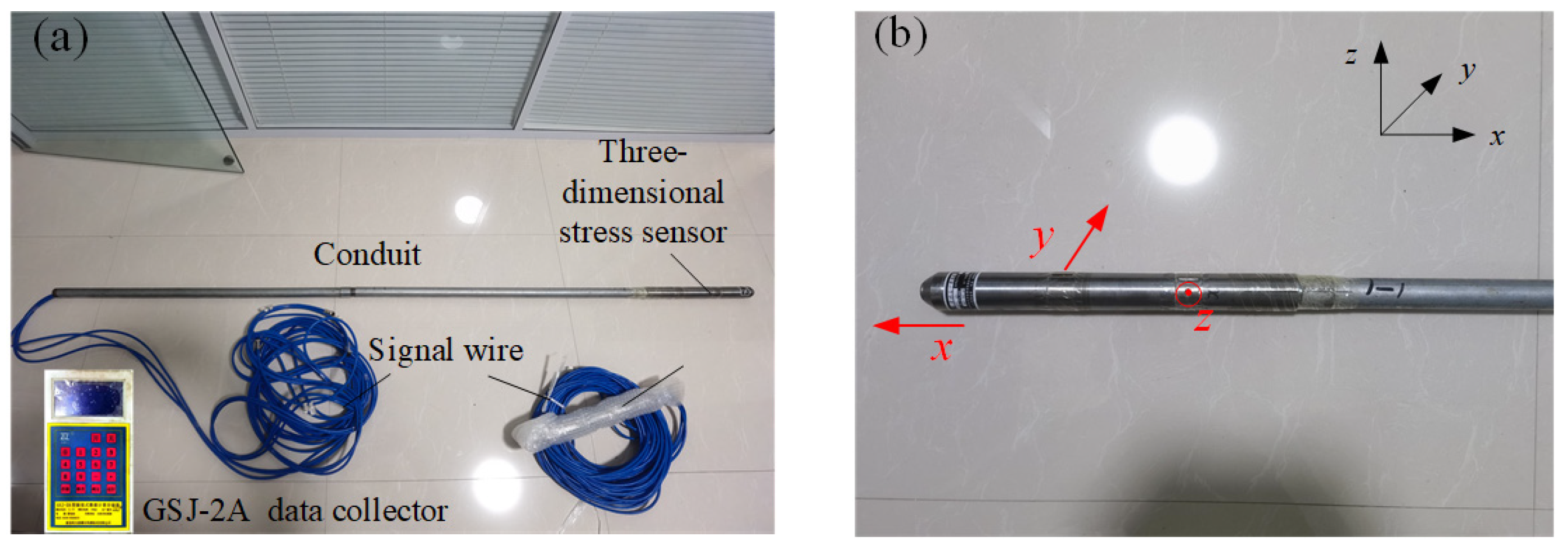
4.2. Measurement Scheme of Surrounding Rock Stress
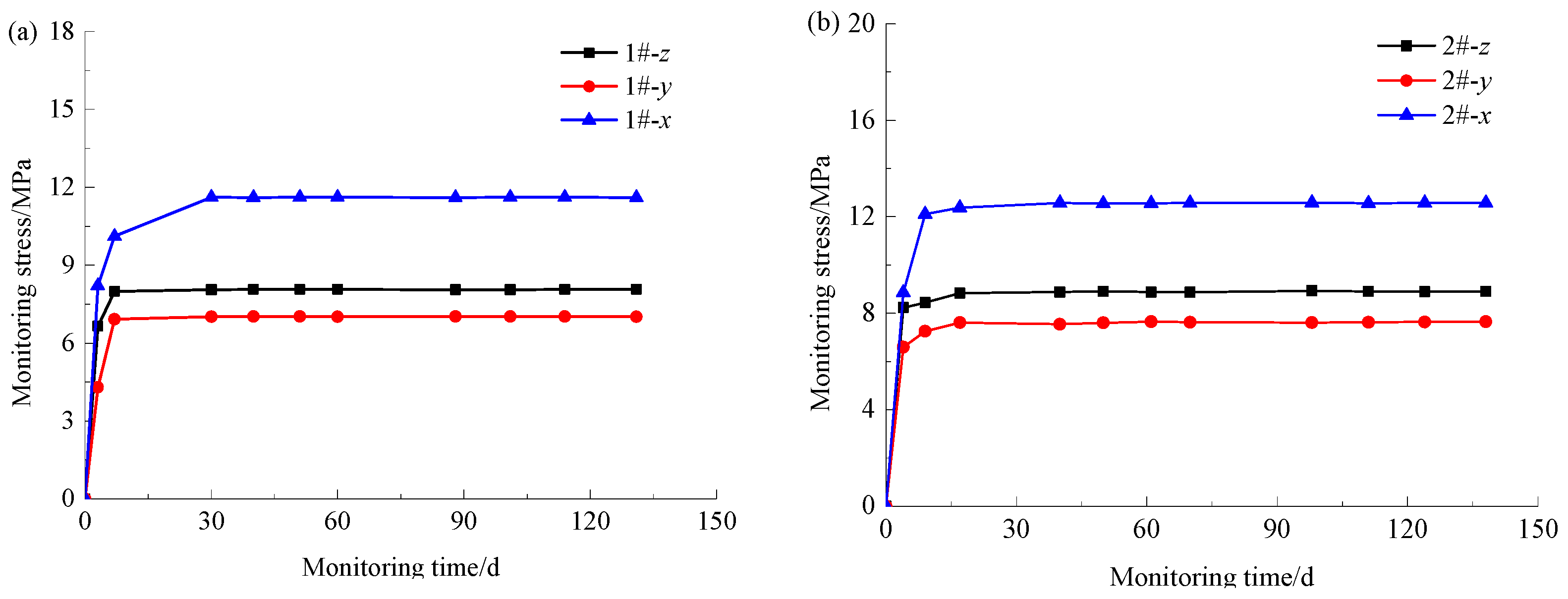
4.3. Measurement Results and Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- U. S. Geological Survey. Mineral Commodity Summaries 2025; Version 1.2; U. S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2025; pp. 134–135.
- Van Poolen, H.K. A Photoelastic Investigation of the Relationship Between Stresses Around Mine Openings and Resulting Failures. Ph.D. Thesis, Colorado School of Mines, Golden, CO, USA, 1955. [Google Scholar]
- Hoek, E. Rock Fracture Under Static Stress Conditions. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Cape Town, Cape Town, South Africa, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, M.; Han, L.; Meng, Q.; Ma, C.; Zong, Y.; Mao, P. Physical model experiment of surrounding rock failure mechanism for the roadway under deviatoric pressure form mining disturbance. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2020, 24, 1103–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Li, D.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, C.; Liang, L. Physical model test on the deformation behavior of an underground tunnel under blasting disturbance. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2021, 54, 91–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Han, L.; Xiao, Y.; Li, H.; Wen, S.; Zhang, J. Numerical simulation study of the failure evolution process and failure mode of surrounding rock in deep soft rock roadways. Int. J. Min. Sci. Eng. 2016, 26, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Stead, D.; Kang, H. Numerical simulation of squeezing failure in a coal mine roadway due to mining-induced stresses. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2015, 48, 1635–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, F.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, K. Physical model test and numerical simulation on the failure mechanism of the roadway in layered soft rocks. Int. J. Min. Sci. Eng. 2021, 31, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakhno, I.; Sakhno, S.; Skyrda, A.; Popova, O. Numerical modeling of controlling a floor heave of coal mine roadways with a method of reinforcing in wet soft rock. Geofluids 2022, 2022, 3855799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakhno, I.; Sakhno, S. Numerical studies of floor heave control in deep mining roadways with soft rocks by the rock bolts reinforcement technology. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2023, 2023, 2756105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, M.; Zhao, H.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Du, K. Failure characteristics and stress distribution of pre-stressed rock specimen with circular cavity subjected to dynamic loading. Tunn. Undergr. Sp. Tech. 2018, 81, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Z.; Li, C.; Xu, W.; Li, H. Measurements of in situ stress and mining-induced stress in Beiminghe iron mine of China. J. Cent. South Univ. 2009, 16, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Qiu, L.; Wang, E.; Song, D.; Liu, Z.; Shen, R.; Lv, G.; Xu, Z. Measurement of the stress field of a tunnel through its rock EMR. J. Geophys. Eng. 2017, 14, 949–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Wang, Y.; Kou, M.; Liang, C. Applications of microseismic monitoring technique in coal mines: A state-of-the-art review. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Du, L.; Fan, D.; Wang, A.; Shi, T.; Dai, L. Detection of stress distribution in surrounding rock of coal seam roadway based on charge induction principle. Electronics 2024, 13, 3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirsch, E. Die Theorie der elastizität und die bedürfnisse der festigkeitslehre. Zeit. Ver. Deut. Ing. 1898, 42, 797–807. [Google Scholar]
- Inglis, C. Stresses in a plate due to the presence of cracks and sharp corners. Proc. Inst. Nav. Arch. 1913, 55, 219–230. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Zhao, G.; Liang, W. Mechanical properties and fracture characteristics of pre-holed rocks subjected to uniaxial loading: A comparative analysis of five hole shapes. Theor. Appl. Fract. Mec. 2020, 105, 102433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhao, G.; Ma, S. Failure behavior of horseshoe-shaped tunnel in hard rock under high stress: Phenomenon and mechanisms. T. Nonferr. Metal Soc. 2022, 32, 639–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Fan, A.; Ma, D.; Spearing, A.; Zheng, Z. Fracturing process and initiation mechanism of hard rock tunnels with different shapes: Particle flow modeling and analytical study. Comp. Part. Mech. 2023, 10, 1859–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, R.; Krantz, S. Function Theory of One Complex Variable, 3rd ed.; American Mathematical Society: Providence, RI, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Muskhelishvili, N. Some Basic Problems of the Mathematical Theory of Elasticity; Noordhoff International Publishing: Groningen, The Netherlands, 1953. [Google Scholar]




| Column | Lithology | Thickness/m | Geological Description | Basic Physical and Mechanical Property Parameters of Main Rocks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 | Silty shale | 27.70~46.33 | Gray black–black, arenaceous texture and thin, sheet-like structures. The core is intact, columnar in shape, and locally fragmented into fragments. | ρ = 2718.80 kg/m3, v = 3716.70 m/s, σc = 113.09 MPa, σt = 6.27 MPa, E = 12.52 GPa, C = 18.29 MPa, φ = 42.52°, μ = 0.25 |
| Roof dolomite | 0~2.80 | Light gray-gray, fine crystalline texture, medium layered structure. The core is relatively fragmented and appears as blocks or fragments. | ρ = 2768.79 kg/m3, v = 5018.50 m/s, σc = 120.10 MPa, σt = 6.94 MPa, E = 20.66 GPa, C = 25.20 MPa, φ = 41.70°, μ = 0.24 | |
| Upper phosphate rock | 2.54~13.37 | Light gray and blue gray in color, clastic texture, and thin layer strip structure. The core is relatively fragmented and blocky, with upper areas being relatively intact and columnar. | ρ = 2776.96 kg/m3, v = 5532.80 m/s, σc = 123.33 MPa, σt = 6.55 MPa, E = 18.61 GPa, C = 19.25 MPa, φ = 45.11, μ = 0.24 | |
| Clay interlayer | 0~3.80 | Gray and dark gray mudstone interlayer, with broken rock cores in fragmented form. | ρ = 2444.62 kg/m3, σc = 11.25 MPa, C = 1.82 MPa, φ = 36.50° | |
| Lower phosphate rock | 0.32~10.51 | Light gray and blue gray in color, clastic texture, and thin layer strip structure. The core is relatively fragmented and blocky, with some areas being relatively intact and columnar. | ρ = 2790.50 kg/m3, v = 5527.80 m/s, σc = 99.58 MPa, σt = 9.23 MPa, E = 14.21 GPa, C = 20.35 MPa, φ = 46.81, μ = 0.33 | |
| Floor dolomite | About 150 | Light gray to gray in color, fine-grained texture, and medium-bedded structure. The core is relatively intact and short columnar in shape, with some areas broken and in the form of fragments. | ρ = 2778.96 kg/m3, v = 5271.10 m/s, σc = 123.91 MPa, σt = 8.06 MPa, E = 17.93 GPa, C = 25.24 MPa, φ = 44.90, μ = 0.27 |
| Number of Ck Terms | Number of Iterations | Objective Function Value | C0 | C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 | C6 | C7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 85 | 0.9561 | −0.2476 | −0.1314 | 0.0495 | — | — | — | — | — |
| 4 | 156 | 0.1552 | −0.2367 | −0.0994 | 0.0792 | −0.0788 | — | — | — | — |
| 5 | 233 | 0.0686 | −0.2471 | −0.1077 | 0.0753 | −0.0824 | 0.0235 | — | — | — |
| 6 | 278 | 0.0209 | −0.2456 | −0.1034 | 0.068 | −0.0962 | 0.0265 | 0.0139 | — | — |
| 7 | 584 | 0.0067 | −0.2458 | −0.1038 | 0.0725 | −0.0964 | 0.0289 | 0.0169 | −0.0103 | — |
| 8 | 479 | 0.0606 | −0.24 | −0.109 | 0.0523 | −0.1004 | 0.0366 | 0.0257 | 0.0014 | −0.0049 |
| Item | 1#-z | 1#-y | 1#-x | 2#-z | 2#-y | 2#-x |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M value | 1.73639 × 10−5 | 1.26855 × 10−5 | 5.21616 × 10−5 | 5.03488 × 10−6 | −1.5931 × 10−6 | −2.11127 × 10−5 |
| N value | 0.0025889 | 0.0151946 | −0.106807 | 0.0689548 | 0.0672041 | 0.0046013 |
| Time/d | 1#-z | 1#-y | 1#-x | Time/d | 2#-z | 2#-y | 2#-x |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 2016.07 | 2012.55 | 2055.51 | 0 | 2063.37 | 2072.13 | 2062.65 |
| 3 | 1922.49 | 1946.91 | 1976.12 | 4 | 1971.24 | 1982.63 | 1963.77 |
| 7 | 1902.87 | 1905.93 | 1956.84 | 9 | 1968.86 | 1973.60 | 1926.32 |
| 30 | 1901.95 | 1904.46 | 1941.29 | 17 | 1964.34 | 1968.70 | 1923.25 |
| 40 | 1901.85 | 1904.42 | 1941.32 | 40 | 1963.82 | 1969.67 | 1920.88 |
| 51 | 1901.90 | 1904.27 | 1941.25 | 50 | 1963.58 | 1968.91 | 1921.25 |
| 60 | 1901.87 | 1904.55 | 1941.29 | 61 | 1963.84 | 1968.32 | 1921.13 |
| 88 | 1901.95 | 1904.31 | 1941.31 | 70 | 1964.03 | 1968.57 | 1920.87 |
| 101 | 1901.96 | 1904.41 | 1941.26 | 98 | 1963.27 | 1968.69 | 1920.79 |
| 114 | 1901.83 | 1904.43 | 1941.29 | 111 | 1963.62 | 1968.54 | 1921.05 |
| 131 | 1901.82 | 1904.46 | 1941.32 | 124 | 1963.66 | 1968.49 | 1920.88 |
| 138 | 1963.56 | 1968.33 | 1920.89 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Hou, K.; Wang, M.; Wu, H. Stress Distribution Around Roadway of Kunyang No. 2 Phosphate Mine: Analytical Study and Field Verification. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 11002. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152011002
Wang Z, Hou K, Wang M, Wu H. Stress Distribution Around Roadway of Kunyang No. 2 Phosphate Mine: Analytical Study and Field Verification. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(20):11002. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152011002
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zongyong, Kepeng Hou, Menglai Wang, and Hao Wu. 2025. "Stress Distribution Around Roadway of Kunyang No. 2 Phosphate Mine: Analytical Study and Field Verification" Applied Sciences 15, no. 20: 11002. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152011002
APA StyleWang, Z., Hou, K., Wang, M., & Wu, H. (2025). Stress Distribution Around Roadway of Kunyang No. 2 Phosphate Mine: Analytical Study and Field Verification. Applied Sciences, 15(20), 11002. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152011002






