Higher-Order Sliding-Mode Velocity Observer-Based Exponential Stabilization of the Second-Order Chained-Form System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Motivating Example and Control Example
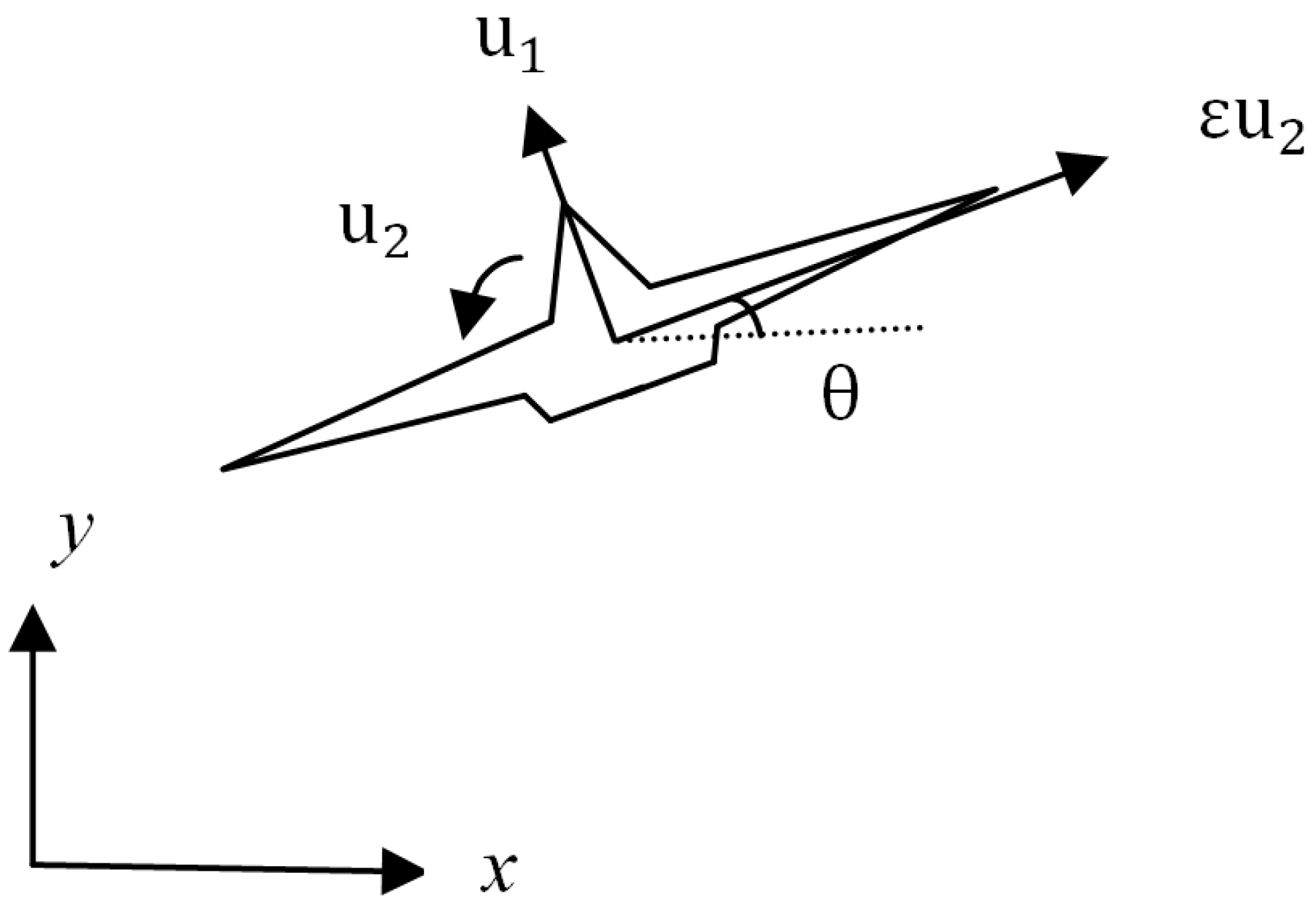
2.1. The Motivating Example
2.2. Control Design
3. Time-Varying Stabilization Control and Higher-Order Sliding-Mode Velocity Observer
3.1. Time-Varying Control
3.2. Higher-Order Sliding-Mode Velocity Observer
4. Extension to Stabilization of VTOL Aircraft
4.1. Dynamic Model of VTOL and Control Design
4.2. Time-Varying Control
4.3. Differentiator Design for and
5. Numerical Simulation
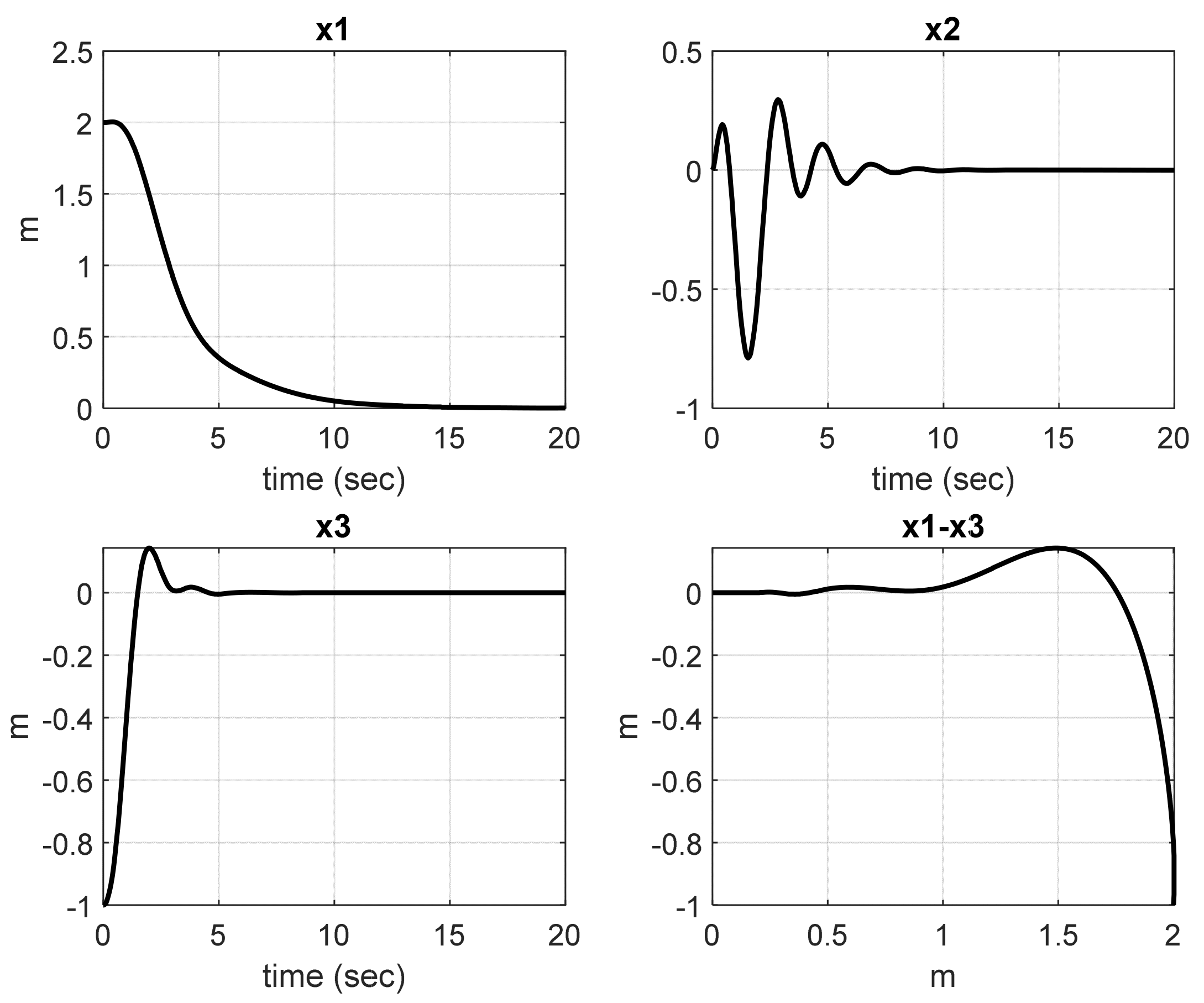
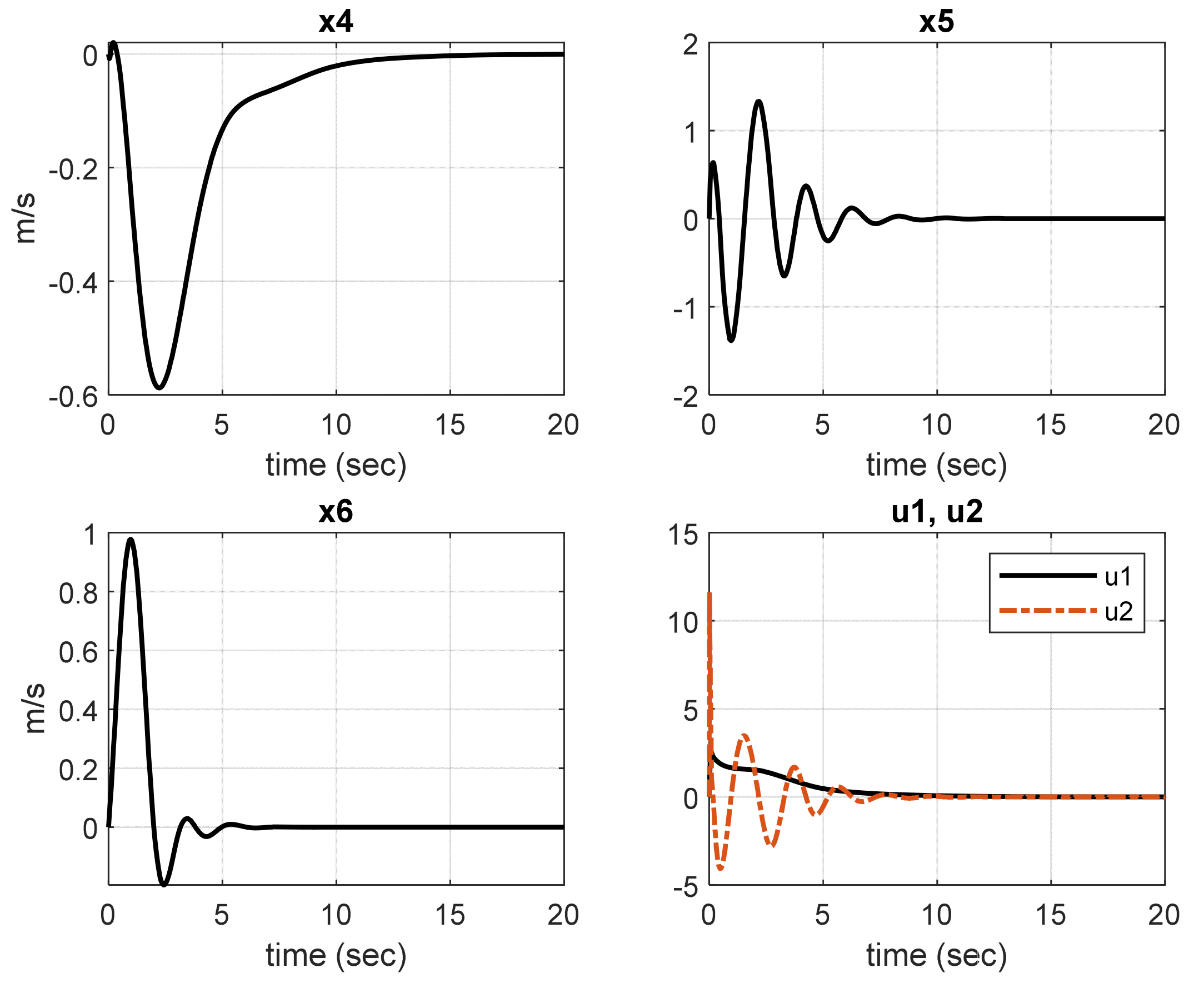
5.1. Hovercraft
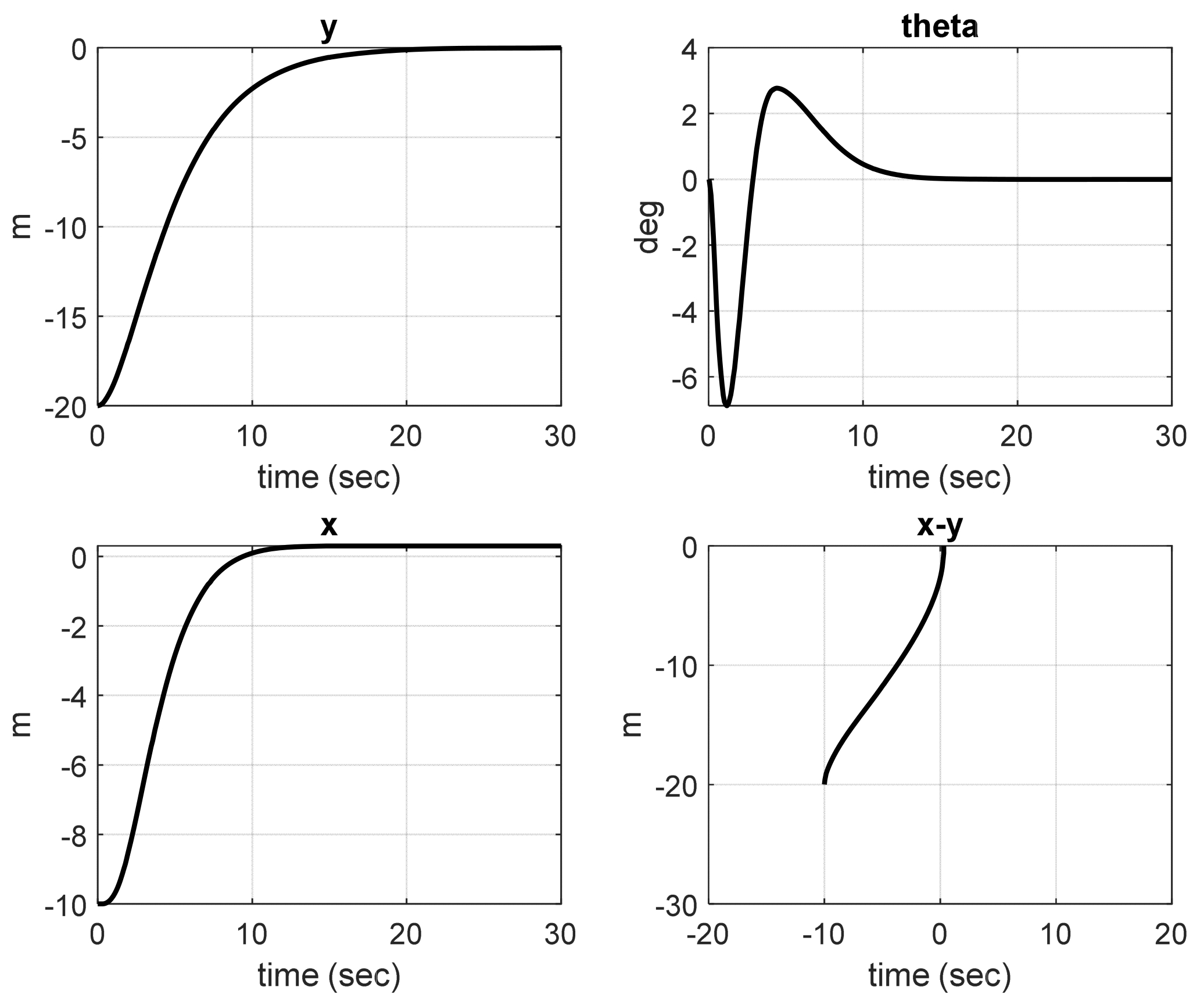
5.2. VTOL Aircraft
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Spong, M.W. Underactuated mechanical systems. In Control Problems in Robotics and Automation; Siciliano, B., Valavanis, K.P., Eds.; Springer: London, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Olfati-Saber, R. Nonlinear Control of Underactuated Mechanical Systems with Application to Robotics and Aerospace Vehicles. Ph.D. Thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, Cambridge, MA, USA, February 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Aneke, N.P.I. Control of Underactuated Mechanical Systems. Ph.D. Thesis, Technische Universiteit Eindhoven, Eindhoven, The Netherlands, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Fantoni, I.; Lozano, R. Non-linear Control for Underactuated Mechanical Systems; Springer: London, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Choukchou-Braham, A.; Braham, C.B.; Djemai, M.; Busawon, K. Analysis and Control of Underactuated Mechanical Systems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Rehanoglu, M.; Cho, S.; McClamroch, N.H. Discontinuous feedback control of a special class of underactuated mechanical systems. Int. J. Robust. Nonlinear Control 2000, 10, 265–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Özgüner, Ü. Sliding mode control of a class of underactuated systems. Automatica 2008, 44, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olfati-Saber, R. Normal forms for underactuated mechanical systems with symmetry. IEEE Trans. Automat. Contr. 2002, 47, 305–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olfati-Saber, R. Global configuration stabilization for the VTOL aircraft with strong input coupling. IEEE Trans. Automat. Contr. 2002, 47, 1949–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teel, A.R. Using saturation to stabilize a class of single-input partially linear composite systems. In Proceedings of the IFAC NOLCOS’92 Symposium, Bordeaux, France, 24–26 June 1992; pp. 369–374. [Google Scholar]
- Pettersen, K.Y.; Nijmeijer, H.; Gravdahl, J.T. Global uniform asymptotic stabilization of an underactuated surface vessel: Experimental results. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2004, 12, 891–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.-C.; Jiang, Z.-P. New cascade approach for global k-exponential tracking of underactuated ships. IEEE Trans. Automat. Contr. 2004, 49, 2297–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Guo, Y. Global time-varying stabilization of underactuated surface vessel. IEEE Trans. Automat. Contr. 2005, 50, 859–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Li, T.; Zhao, J.; Kang, Z. Finite-time discontinuous control of underactuated surface vessels: From underactuated to nonholonomic configuration. J. Franklin Inst. 2025, 362, 108034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yu, H. A survey of underactuated mechanical systems. IET Control Theory Appl. 2013, 7, 921–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolmanovsky, I.; McClamroch, N.H. Developments in nonholonomic control problems. IEEE Control Syst. Mag. 1995, 15, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Bloch, A. Nonholonomic Mechanics and Control; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, B.; Zhang, K.-K.; Jiang, H. Prescribed-time control of perturbed nonholonomic systems by time-varying feedback. Automatica 2023, 155, 111125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.L.; Yu, B. Stabilization of a class of second-order nonholonomic systems. In Proceedings of the American Control Conference, Anchorage, AK, USA, 8–10 May 2002; pp. 4365–4370. [Google Scholar]
- He, G.; Zhang, C.; Sun, W.; Geng, Z. Stabilizing the second-order nonholonomic systems with chained form by finite-time stabilizing controllers. Robotica 2016, 34, 2344–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, R.; Sastry, S. Nonholonomic motion planning: Steering using sinusoids. IEEE Trans. Automat. Contr. 1993, 38, 700–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Qu, Z. Smooth time-varying pure feedback control for chained nonholonomic systems with exponential convergent rate. IET Control Theory Appl. 2010, 4, 1235–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yan, W.; Shi, Y. A receding horizon stabilization approach to constrained nonholonomic systems in power form. Syst. Control Lett. 2017, 99, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuyev, A. Exponential stabilization of nonholonomic systems by means of oscillating controls. SIAM J. Control Optim. 2016, 54, 1678–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, J.G.; Nuño, E.; Aldana, C.I. Global consensus-based formation control of perturbed nonholonomic mobile robots with time varying delays. J. Franklin Inst. 2024, 361, 557–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizarraga, D.A.; Aneke, N.P.I.; Nijmeijer, H. Robust point stabilization of underactuated mechanical systems via the extended chained form. SIAM J. Control Optim. 2004, 42, 2172–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tian, Y.-P.; Li, S. Exponential stabilization of nonholonomic dynamic systems by smooth time-varying control. Automatica 2002, 38, 1139–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, T.; Kobayashi, K.; Watanabe, T. Design of a desirable trajectory and convergent control for 3-DOF manipulator with a nonholonomic constraint. J. Robot. Soc. Jpn. 2000, 18, 584–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Slotine, J.J.E.; Li, W. Applied Nonlinear Control; Prentice Hall: Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Levant, A. Higher-order sliding modes, differentiation and output-feedback control. Int. J. Control 2003, 76, 924–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridman, L.; Moreno, J.; Iriarte, R. (Eds.) Sliding Modes After the First Decade of the 21st Century: State of the Art; Lecture Notes in Control and Information Sciences 412; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Cremean, L.; Dunbar, W.B.; Van Gogh, D.; Hickey, J.; Klavins, E.; Meltzer, J.; Murray, R.M. The Caltech multi-vehicle wireless testbed. In Proceedings of the 41st IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 10–13 December 2002; pp. 86–88. [Google Scholar]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yih, C.-C.; Chin, P.-C. Higher-Order Sliding-Mode Velocity Observer-Based Exponential Stabilization of the Second-Order Chained-Form System. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 11001. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152011001
Yih C-C, Chin P-C. Higher-Order Sliding-Mode Velocity Observer-Based Exponential Stabilization of the Second-Order Chained-Form System. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(20):11001. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152011001
Chicago/Turabian StyleYih, Chih-Chen, and Pei-Chieh Chin. 2025. "Higher-Order Sliding-Mode Velocity Observer-Based Exponential Stabilization of the Second-Order Chained-Form System" Applied Sciences 15, no. 20: 11001. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152011001
APA StyleYih, C.-C., & Chin, P.-C. (2025). Higher-Order Sliding-Mode Velocity Observer-Based Exponential Stabilization of the Second-Order Chained-Form System. Applied Sciences, 15(20), 11001. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152011001





