Abstract
Xylella fastidiosa (Xf) is a quarantine pathogen heavily affecting economically important crops worldwide. Different sequence types (STs) belonging to Xf subspecies are present in various areas of Spain, including the Balearic Islands, and cause the almond leaf scorch disease (ALSD) in Prunus spp. The increased demand for rapid tests for early detection of the pathogen should enforce strict containment measures. Molecular detection through isothermal amplification reactions enables simplified instrumentation and the use of raw nucleic acid extracts. Colorimetric loop-mediated isothermal amplification (cLAMP) was applied to rapidly detect Xf in naturally infected almonds on Mallorca Island (Spain), using a quick crude sap extraction without DNA purification. Following tissue homogenization, an alkaline treatment for target DNA extraction was conducted before the cLAMP test. The cLAMP assay was able to detect up to 100 CFU/mL of the Xf bacterial suspension diluted in healthy almond sap. The same crude extracts used in the cLAMP test were also tested by qPCR. An overall positive agreement of about 47% was observed between the results of the two techniques, while a decrease in cLAMP sensitivity was evident as the bacterial titer declined in infected plants over Cq > 26–27. This study shows the potential of the cLAMP application as a rapid and low-cost point-of-care diagnostic method for the timely monitoring of Xf directly in the field.
1. Introduction
The plant-pathogenic Xylella fastidiosa (Xf; Lysobacteraceae family [1]) is a Gram-negative, aflagellate, xylem-limited Gammaproteobacterium, is native of the Americas, and is plant-to-plant transmitted by xylem sap-feeding insects. It currently affects almost 700 plant species belonging to 88 families [2] and causes serious diseases in crops of high economic importance, including, as follows: grapevine (Pierce’s disease, PD); citrus (citrus variegated chlorosis, CVC); almond (almond leaf scorch disease, ALSD); and olive (olive quick decline syndrome, OQDS).
Bacterial cell aggregates, attached to the xylem vessels along with tyloses and gums produced by the plant as an attempt to entrap the pathogen, cause vessel occlusion and a deficit of the sap carriage [3]. This results in the impairment of the water flux and generates visible symptoms like leaf scorching, twig desiccation, and gradual plant dieback. In almonds, ALSD [4] appears as a marginal scorching of leaves that begins as early as June and continues to develop during summer, when temperatures and water demand increase [5]. A peculiar golden-yellow band develops between the brown necrotic edge and the inner green tissues of the leaf. The whole canopy of the tree becomes seriously affected, showing a typical golden-brown appearance (known as ‘golden death’; [6]). Infected trees bloom and leaf out later than healthy trees, are stunted, less productive, and have reduced terminal growth [7,8].
The first Xf outbreak in the Balearic Islands dates to October 2016, when cherry trees (Prunus avium L.) and Polygala myrtifolia L. plants were found to be infected by Xf subsp. fastidiosa strain ST1 [9,10]. After this first record, subsequent surveys revealed that the bacterium was widespread on other islands in the archipelago. Indeed, through the years, the Balearic Islands Official Plant Health Laboratory (LOSVIB) also detected new sequence types (STs) belonging to the subspecies multiplex (Xfm; ST7 and 81; [11]) and pauca [Xfp, ST80 [12]) in symptomatic almond trees scattered across the islands [13]; lately, ST53 has been detected in olive trees in Mallorca (https://www.europapress.es/illes-balears/noticia-baleares-presenta-nuevo-plan-contencion-xylela-detectar-subespecie-mallorca20240201135337.html; accessed on 15 June 2024). Currently, about 80% of almond trees in Mallorca are compromised [14] since the containment strategies established by the Balearic Islands government were ineffective and failed to reduce disease spread [15]. This has caused a significant alteration to the rural landscape of the whole island and has reduced almond production by 20–40%, depending on the cultivar [16].
The management of Xf infections mostly relies on the prompt eradication of infected sources and control of the vector insect population. In this strategy, early detection of the bacterium is of paramount importance to limit its spread. Hence, an efficient containment requires point-of-care (PoC) tests with a short turnaround time, a low cost, and high accessibility. Molecular detection, mainly based on real-time quantitative PCR performed on purified DNA, is considered the gold standard because of its specific and sensitive identification of the bacterium at low titers and also in symptomless trees. While this assay is the most-used reference diagnostic procedure for Xf detection and is officially recognized by European phytosanitary authorities [17], its long duration, significant reagent costs, and the need for equipment, transport to laboratory facilities, and trained personnel can be hindering factors, particularly in a resource-limited environment and for in-field detection.
The loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP [18]) technique, already established for an extensive variety of pathogens [19,20], is extremely efficient and highly specific. Due to the auto-cycling strand displacement DNA synthesis and the tendency of the Bst polymerase enzyme to synthesize new DNA more quickly than conventional PCR at a constant temperature, reactions can be performed outdoors using only a portable, battery-operated heat block or any other device able to maintain a single temperature for the relatively short time needed. The stability and abundance of the produced amplicons make optical readout options, such as color changes or turbidimetric measurements, possible. Therefore, LAMP is an attractive alternative tool in resource-limited areas and in situations where time plays a crucial role in controlling the disease spread [21].
The present work describes an open-field colorimetric LAMP (cLAMP) application for Xf detection on trees in naturally Xf-infected almond orchards in Mallorca, employing only a stabilized reaction mix, unpurified buffered plant extracts as templates, and a simple portable microtube incubator. In addition, to evaluate the sensitivity and reliability of the method, the cLAMP results were compared with those obtained in laboratories using real-time quantitative PCR (qPCR assay) with the same crude extracts. This study aimed to demonstrate that the bulk detection of a reasonable percentage of infection in woody plants, like almond trees, up to the border of a pathogen titer where trees do not show yet any symptoms, could enable the cLAMP workflow as a preliminary screening tool in Xf-infected almond orchards for the timely support of management and eradication strategies.
2. Materials and Methods
In the framework of the European Union Horizon 2020 BIOVEXO project, during the summer of 2023, when the temperature ranged between 29 and 34 °C, a field survey was conducted in two orchards located on Mallorca Island, where Xfm (harboring the genotypes ST7 and ST81 [11,22]) was detected. Figure 1A–C shows the most representative symptoms induced by Xf on almond trees.
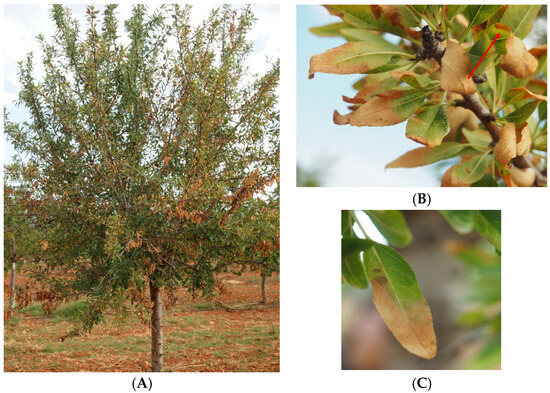
Figure 1.
(A) Infected almond tree in Mallorca orchard with ‘golden death’ symptoms; (B) scorch symptoms on almonds with the typical yellow band, marked with a red arrow; and (C) on the leaf tissue between the green and dead areas.
During the field survey in Mallorca (Balearic Islands) in July 2023, a total of 53 almond trees were randomly sampled from the two orchards having different planting ages and plantation plots (Table 1). All the samples used in the experiment consisted of chips from semi-lignified shoots. In detail, five young shoots per tree were collected from the basal branches, sometimes close to ALS symptoms when these were evident, but not yet senescent or desiccated. Plant material was stored in plastic bags and put in a refrigerated box with melting ice until processing.

Table 1.
List of collected almond samples analyzed by dual molecular assays. Comparative analysis of cLAMP and qPCR (Cq) results for the detection of Xf in the almond samples used in the study. The Cq values reported are the average obtained by the two laboratories. Cq value > 33 is considered negative. N/A: no absorbance. Successful amplification in cLAMP is indicated with “+”, whereas “−” indicates a negative result.
Small slices (0.2 cm thickness) of cortical tissues (up to 250 mg in total) were cut with a razor blade, disinfected after chopping each sample with diluted commercial bleach (ca. 1% active chlorine), and placed inside a mesh plastic bag (Agdia, Elkhart, IN, USA) in the presence of 1.5 mL sodium chloride–Tris–EDTA extraction buffer (STE 1x), containing also 2% DIECA (diethyldithiocarbamate), 1% PVP-40k (polyvinylpyrrolidone), and Triton 0.1%. Bags were manually crumbled with a hammer to facilitate the breaking of plant tissues and the release of bacterial cells in the extraction buffer [23]. The spilled liquid was recovered in a 1.5 mL centrifuge tube and stored on ice. One hundred µL of the decanted suspension was retrieved in a new labelled tube, avoiding the plant debris at the bottom. This crude sap aliquot was denatured by a 2 min incubation with an equal volume of 0.4 M NaOH, then subsequently neutralized by mixing for a short time with the same volume of HCl 0.2 M. The neutralized suspension was further diluted to 1:10 in distilled water and finally subjected to the cLAMP assay according to Ref. [24]. Crude sap from healthy almond tissues recovered from greenhouse-grown seedlings, previously tested by qPCR as being Xf-free, and nuclease-free water served as negative internal and no-template controls (NIC and NTC), respectively, for each cLAMP round. A standard 30 min incubation was performed at 65 °C in a portable BIOPIX DNA Technology battery-powered heat block [25]. Moreover, to compare the field-performed cLAMP test, the presence of Xf was then assessed by testing, in duplicate, the same almond crude extracts by qPCR in two different laboratories (IPSP-CNR, Bari and AIT, Vienna) involved with the project, following the TaqMan protocol described by Harper et al., 2010 [26]. One µL of the alkaline-denatured, neutralized and 1:10 water-diluted sap was added to the cLAMP and qPCR reactions. The primer sequences used in both tests that targeted the rimM gene, highly conserved among all Xf subspecies’ genomes and widely validated for Xf detection [17], are reported in Supplementary Table S1. To evaluate the limit of detection (LoD; i.e., the lowest copy number reliably detected of the Xf genome) of the cLAMP assay for the amplification of the Xf target DNA in almond crude extracts, 6-days-grown bacterial cells of Xfm strain ESVL ST6 on PD3 agar plates [27,28] were employed. The cell suspension was 10-fold serially diluted up to 10 CFU/mL (starting from an OD600 value = 0.5, equivalent to 4 × 108 CFU/mL; [29]) in healthy crude almond sap and then subjected to alkaline and neutralization treatments before the test, as specified above. NIC and NTC were also included. The formation of amplicon DNA was assessed by observing the color shift from pink (negative) to yellow (positive) after 30 min of incubation at 65 °C, due to the presence of phenol red, a pH indicator present in the master mix. The cLAMP assay was performed with a final volume of 25 μL, including, as follows: 12.5 μL Bst 2.0 WarmStart® DNA Polymerase 2x Master Mix (New England Biolabs, Ipswich, MA, USA); 2.5 μL LAMP primer mix (0.2, 1.6 and 0.4 μM of F3/B3, FIP/BIP and LF/LB primers, respectively); 1 μL of neutralized and diluted crude DNA extract and double-distilled water to a final volume; and 25 μL of mineral oil, added to each tube to cover the LAMP mix to avoid possible evaporation and contaminations. The consistency of the reaction for some tubes was also evaluated using 1.2% agarose gel electrophoresis run in Tris–acetate–EDTA (TAE 1x) buffer and stained with GelRed. The performance criteria, such as the diagnostic sensitivity (proportion of infected samples testing positive compared with the number of positive results from an alternative test, considered to be the gold standard) and specificity (calculated as the ratio of samples testing negative compared with the results from the alternative test) of the assay, were calculated according to Ref. [30]. A statistical comparison of correspondence between the results of positive and negative samples in both tests was performed by Fisher’s exact test on a contingency table. For all the tested samples (positive and negative) in cLAMP and qPCR, respectively, receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC) analyses were calculated by plotting the true positive rate (sensitivity) and the false positive rate (1-specificity) with a 95% confidence interval (CI). The area-under-the-curve (AUC) values were also calculated to evaluate the performance of both assays.
3. Results
A rough extraction of nucleic acids was adopted by using a simple, homemade buffer. The preliminary homogenization step in STE extraction buffer, before the NaOH-based denaturation, differently from what was reported in [24] for the olive tissues, was introduced to strongly reduce the quick polyphenols oxidation occurring in almond sap, when directly extracted by a hefty alkaline buffer. The sensitivity of the cLAMP assay showed that the LoD of the assay was 100 CFU/mL (Figure 2A, reaction tube 5), as was previously demonstrated in crude olive sap for Xfp ST53 using the same amplification conditions [24]. The qPCR detection limit on the same crude extracts was 10 CFU/mL, thus demonstrating a sensitivity that was an order of magnitude higher than that of the cLAMP assay. The cLAMP results were verified by observation of the amplification products in agarose gel electrophoresis, where a 180 bp-band was more evident and a ladder of larger-sized faint bands were visible in cases of positive amplification (Figure 2B, lanes 1 to 5).
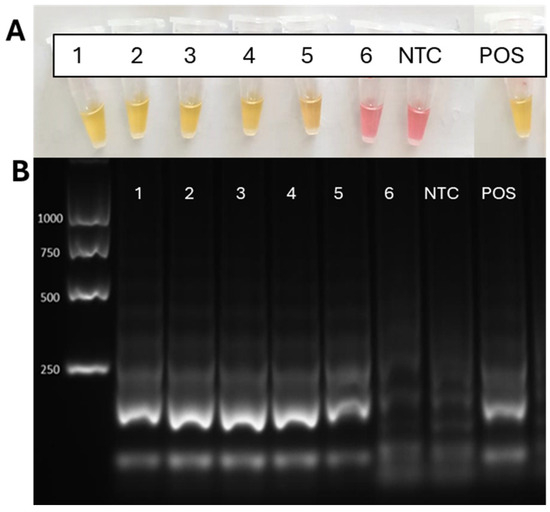
Figure 2.
(A) cLAMP reactions from healthy almond sap spiked with 10-fold serial dilutions of Xfm ESVL cells, from 106 to 10 CFU/mL (1–6; NTC: no template control; Pos: positive control); and (B) amplified products of each dilution analyzed by gel electrophoresis.
Concerning specificity, the primer sequences used in this experiment were derived from a single-copy gene in the Xf genome and are well-known to be highly specific for all the Xf subspecies only [17]. The same amplification procedures did not show any cross-reactions with some tested non-target bacteria such as different Xanthomonas spp. or other common, non-correlated, epiphytic, and endophytic bacteria [24].
The crude sap extracted from field-grown almond samples was tested by either cLAMP or qPCR assays. Results obtained from the tested trees for both methods are presented in Table 1. The trees were classified according to their Cq value generated in qPCR. The average Cq produced by the analysis of the two laboratories, CNR-IPSP and AIT, was considered. As reported in Table 2, 41 out of 53 samples tested positive in qPCR (77.35%); the remaining 12 tested negative (22.64%). Notably, in both laboratories, a real-time qPCR result is considered negative or undetermined when Cq is > 33, as these are borderline values close to the detection limit of the technique, due to the uneven and erratic distribution of the bacterium in host tissues [31]. Overall, the presence of the bacterium was properly determined by cLAMP in 19 out of 41 samples that tested positive using qPCR (i.e., 46.34% along with all the ‘true positive’ Cq values up to 33). For the samples showing negative results in qPCR, the cLAMP assay, correctly, did not exhibit any amplification signal in 11 out of 12 samples, except for sample no. 51, which behaved as a false positive sample. Therefore, the diagnostic specificity corresponds to 92.30%. The cLAMP AUC value (0.5938), illustrating the diagnostic ability and connection between diagnostic sensitivity and specificity, properly confirmed this concept with respect to the qPCR AUC number equal to 0.8750 (Supplementary Figure S1).

Table 2.
Comparative performance of cLAMP vs. qPCR assay for the detection of Xf in almond alkaline crude extracts. Positive samples in cLAMP are indicated for each average Cq group obtained from qPCR assay. Percentage of diagnostic sensitivity and specificity generated by cLAMP assay are also reported.
4. Discussion
As in other Xf epidemic areas, the rapid, accurate, and cost-effective detection of the bacterium is required for timely eradication and containment measures that prevent further spread of the disease in geographical areas still free from the pathogen, especially in small territories, such as the Balearic Islands, with a broad genetic diversity of Xf subspecies that affect a wide host range. The LAMP assay is an innovative, cost-effective, and user-friendly method for plant pathogen detection [32]. While several reports apply optical readers for fluorescent [33,34,35] or even colorimetric LAMP results detection [36,37], in the work herein described, it has been demonstrated that, without requiring prior DNA purification or thermal denaturation of the extracts, and by naked-eye observation only, a rapid test for Xf detection can be established for almond trees. The range of positively detected concentrations borders on what it is possible to detect in symptomless plants by the most sensitive qPCR.
Similar to the performance of the same assay applied to the olive matrix [24], some incongruity cases between cLAMP vs. qPCR results were observed at lower target concentrations (Cq ≥ 27) and could be ascribed to the different analytical sensitivities of the two methods, as well as to the stochastic target copy distribution in very low concentrated solutions [38,39].
The cLAMP diagnostic specificity on the truly negative samples was greater than 90%, with only one false positive result, which makes the assay reliable. In the cLAMP experiment using crude extracts both in olive and almond matrices, the tiny amount of tissues from a tree pooled in a sample and the very small volume of extract added to the reaction should account, mainly in a symptomless condition, for the highly erratic distribution of the pathogen, which produces a false-negative more frequently than a false-positive test. It is quite common that sampling from different quadrants or heights of a tree results in different pathogen concentrations [40,41]. It should also be noted that when samples from an ’undetermined’ qPCR status were analyzed in digital droplet PCR for the presence of Xf, the samples were infected by an absolutely low copy number of genome copies [31]. The average values of pathogen titers obtained by qPCR were used in our research as a standard reference to set a reliability range and not as an absolute demarcation.
A large-scale application of cLAMP certainly could suffer from the relatively low diagnostic sensitivity when compared to the standard qPCR. However, its strength and innovative impact reside in its being a fully field-operative practice that is almost instrument-free and could be used in a new or presumptive infection focus in perennial host orchards.
This new method of application, which offers the opportunity to positively test around 45% of symptomless infected trees in an orchard, can be added to the tools currently used for Xf diagnosis. Moreover, it will improve pathogen identification without the need to move plant material from the contaminated territory to centralized laboratories, thus limiting the risk of pathogen dissemination in areas that are pest-free.
Overall, the test can be completed in less than 45 min, including crude nucleic acid extract preparation and amplification; it requires very few manipulations and costs less than three euros per reaction. In comparison, qPCR requires 3–4 h, from the DNA extraction up to the final response in a fully equipped laboratory, employing sophisticated and expensive instruments. An additional application can be envisaged in nurseries as a quick and cheap self-control tool along the propagation pipelines of susceptible host plant material. Furthermore, integrating the LAMP assay with an optical imaging reader could increase the applicability and technology-readiness level of the method, avoiding the subjectivity of data interpretation by the operator.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/app15020739/s1, Table S1: List of primers used for qPCR and cLAMP assays [26]. Figure S1: Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curve for cLAMP and qPCR.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization A.M., P.S. and A.S.S.; Planning of experimental design, A.M., P.S., S.C., M.M. and J.M.G.-M.; methodology, A.M., A.F.-P. and P.S.; qPCR assay and validation, A.S.S., N.C., S.C. and M.P.; setting up of cLAMP reactions A.M., P.S. and A.F.-P.; writing—draft preparation, A.S.S. and A.M.; writing—review and editing, A.M., A.S.S., P.S., A.F.-P., S.C. and J.M.G.-M.; funding management and project administration, M.M., S.C. and P.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was conducted through a joint action of the EU’s Horizon 2020 Projects No. 887281. ‘Biovexo; Biocontrol of Xylella and its vector in olive trees for integrated pest management’ (GA n. 887281), ‘FREE@POC; Towards an instrument-FREE future of molecular diagnostics at the Point-Of-Care’ (GA n. 862840) and also partially supported by ‘BEXYL’ (Beyond Xylella, Integrated Management Strategies for Mitigating Xylella fastidiosa impact in Europe; grant number 101060593).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Acknowledgments
Kind acknowledgements are due to Pilar Puig (Aimerit SL) and Maria Antonia Tugores (Productors Mallorquins de Fruits Secs SAT) for having hosted the almond surveys in Mallorca.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Wells, J.M.; Raju, B.C.; Hung, H.-Y.; Weisburg, W.G.; Mandelco-Paul, L.; Brenner, D.J. Xylella fastidiosa Gen. Nov., Sp. Nov: Gram-Negative, Xylem-Limited, Fastidious Plant Bacteria Related to Xanthomonas spp. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1987, 37, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalieri, V.; Fasanelli, E.; Gibin, D.; Gutierrez Linares, A.; La Notte, P.; Pasinato, L.; Delbianco, A. Update of the Xylella spp. Host Plant Database—Systematic Literature Search up to 31 December 2023. EFSA J. 2024, 22, e8898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, B.L.; Purcell, A.H. Acquisition and Retention of Xylella fastidiosa by an Efficient Vector, Graphocephala atropunctata. Phytopathology 1995, 85, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, R.P.P.; Purcell, A.H. Transmission of Xylella fastidiosa to Grapevines by Homalodisca coagulata (Hemiptera: Cicadellidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2003, 96, 264–271. Available online: https://academic.oup.com/jee/article/96/2/264/2217700 (accessed on 29 September 2024). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teviotdale, B.L.; Connell, J.H. UC Agriculture & Natural Resources Almond Leaf Scorch; University of California: Parlier, CA, USA, 2003; ANR Pubblication. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanborn, R.R.; Mircetich, S.M.; Nyland, G.; Moller, W.J. “Golden Death” a new leaf scorch threat to almond growers. Calif. Agric. 1974, 28, 4–5. [Google Scholar]
- Sisterson, M.S.; Chen, J.; Viveros, M.A.; Civerolo, E.L.; Ledbetter, C.; Groves, R.L. Effects of Almond Leaf Scorch Disease on Almond Yield: Implications for Management. Plant Dis. 2008, 92, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Sisterson, M.S.; Ledbetter, C.A.; Chen, J.; Higbee, B.S.; Groves, R.L.; Daane, K.M. Management of Almond Leaf Scorch Disease: Long-Term Data on Yield, Tree Vitality, and Disease Progress. Plant Dis. 2012, 96, 1037–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Olmo, D.; Nieto, A.; Adrover, F.; Urbano, A.; Beidas, O.; Juan, A.; Marco-Noales, E.; López, M.M.; Navarro, I.; Monterde, A.; et al. First Detection of Xylella fastidiosa Infecting Cherry (Prunus avium) and Polygala myrtifolia Plants, in Mallorca Island, Spain. Plant Dis. 2017, 101, 1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landa, B.B.; Velasco-Amo, M.P.; Marco-Noales, E.; Olmo, D.; López, M.M.; Navarro, I.; Monterde, A.; Barbé, S.; Montes-Borrego, M.; Román-Écija, M.; et al. Draft Genome Sequence of Xylella fastidiosa subsp. Fastidiosa Strain IVIA5235, Isolated from Prunus Avium in Mallorca Island, Spain. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2018, 7, e01222-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moralejo, E.; Gomila, M.; Montesinos, M.; Borràs, D.; Pascual, A.; Nieto, A.; Adrover, F.; Gost, P.A.; Seguí, G.; Busquets, A.; et al. Phylogenetic Inference Enables Reconstruction of a Long-Overlooked Outbreak of Almond Leaf Scorch Disease (Xylella fastidiosa) in Europe. Commun. Biol. 2020, 3, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmo, D.; Nieto, A.; Borràs, D.; Montesinos, M.; Adrover, F.; Pascual, A.; Gost, P.A.; Quetglas, B.; Urbano, A.; de Dios García, J.; et al. Landscape Epidemiology of Xylella fastidiosa in the Balearic Islands. Agronomy 2021, 11, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baró, A.; Montesinos, L.; Badosa, E.; Montesinos, E. Aggressiveness of Spanish Isolates of Xylella fastidiosa to Almond Plants of Different Cultivars Under Greenhouse Conditions. Phytopathology 2021, 111, 1994–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giménez-Romero, À.; Moralejo, E.; Matías, M.A. A Compartmental Model for Xylella fastidiosa Diseases with Explicit Vector Seasonal Dynamics. Phytopathology 2023, 113, 1686–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quetglas, B.; Olmo, D.; Nieto, A.; Borràs, D.; Adrover, F.; Pedrosa, A.; Montesinos, M.; de Dios García, J.; López, M.; Juan, A.; et al. Evaluation of Control Strategies for Xylella fastidiosa in the Balearic Islands. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krugner, R.; Ledbetter, C.A. Rootstock Effects on Almond Leaf Scorch Disease Incidence and Severity. Plant Dis. 2016, 100, 1617–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- PM 7/24 (5) Xylella fastidiosa. EPPO Bull. 2023, 53, 205–276. [CrossRef]
- Notomi, T.; Okayama, H.; Masubuchi, H.; Yonekawa, T.; Watanabe, K.; Amino, N.; Hase, T. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, e63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Boer, S.H.; López, M.M. New Grower-Friendly Methods for Plant Pathogen Monitoring. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2012, 50, 197–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donoso, A.; Valenzuela, S. In-Field Molecular Diagnosis of Plant Pathogens: Recent Trends and Future Perspectives. Plant Pathol. 2018, 67, 1451–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldi, P.; La Porta, N. Molecular Approaches for Low-Cost Point-of-Care Pathogen Detection in Agriculture and Forestry. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 570862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greco, D.; Aprile, A.; De Bellis, L.; Luvisi, A. Diseases Caused by Xylella fastidiosa in Prunus Genus: An Overview of the Research on an Increasingly Widespread Pathogen. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 712452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaad, N.W.; Opgenorth, D.; Gaush, P. Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction for One-Hour On-Site Diagnosis of Pierce’s Disease of Grape in Early Season Asymptomatic Vines. Phytopathology 2002, 92, 721–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amoia, S.S.; Loconsole, G.; Ligorio, A.; Pantazis, A.K.; Papadakis, G.; Gizeli, E.; Minafra, A. A Colorimetric LAMP Detection of Xylella fastidiosa in Crude Alkaline Sap of Olive Trees in Apulia as a Field-Based Tool for Disease Containment. Agriculture 2023, 13, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadakis, G.; Pantazis, A.K.; Fikas, N.; Chatziioannidou, S.; Tsiakalou, V.; Michaelidou, K.; Pogka, V.; Megariti, M.; Vardaki, M.; Giarentis, K.; et al. Portable Real-Time Colorimetric LAMP-Device for Rapid Quantitative Detection of Nucleic Acids in Crude Samples. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, S.J.; Ward, L.I.; Clover, G.R.G. Development of LAMP and Real-Time PCR Methods for the Rapid Detection of Xylella fastidiosa for Quarantine and Field Applications. Phytopathology 2010, 100, 1282–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giampetruzzi, A.; Velasco-Amo, M.P.; Marco-Noales, E.; Montes-Borrego, M.; Román-Écija, M.; Navarro, I.; Monterde, A.; Barbé, S.; Almeida, R.P.P.; Saldarelli, P.; et al. Draft Genome Resources of Two Strains (“ESVL” and “IVIA5901”) of Xylella fastidiosa Associated with Almond Leaf Scorch Disease in Alicante, Spain. Phytopathology 2019, 109, 219–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marco-Noales, E.; Barbe, S.; Monterde, A.; Navarro-Herrero, I.; Ferrer, A.; Dalmau, V.; Aure, C.M.; Domingo-Calap, M.L.; Landa, B.B.; Rosello, M. Evidence That Xylella fastidiosa Is the Causal Agent of Almond Leaf Scorch Disease in Alicante, Mainland Spain (Iberian Peninsula). Plant Dis. 2021, 105, 3349–3352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Attoma, G.; Morelli, M.; Saldarelli, P.; Saponari, M.; Giampetruzzi, A.; Boscia, D.; Savino, V.N.; De La Fuente, L.; Cobine, P.A. Ionomic Differences between Susceptible and Resistant Olive Cultivars Infected by Xylella fastidiosa in the Outbreak Area of Salento, Italy. Pathogens 2019, 8, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- PM 7/76 (5) Use of EPPO Diagnostic Standards. EPPO Bull. 2018, 48, 373–377. [CrossRef]
- Amoia, S.S.; Minafra, A.; Ligorio, A.; Cavalieri, V.; Boscia, D.; Saponari, M.; Loconsole, G. Detection of Xylella fastidiosa in Host Plants and Insect Vectors by Droplet Digital PCR. Agriculture 2023, 13, 716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.W. Principles and Applications of Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification to Point-of-Care Tests. Biosensors 2022, 12, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aglietti, C.; Luchi, N.; Pepori, A.L.; Bartolini, P.; Pecori, F.; Raio, A.; Capretti, P.; Santini, A. Real-Time Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification: An Early-Warning Tool for Quarantine Plant Pathogen Detection. AMB Express 2019, 9, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luchi, N.; Migliorini, D.; Pecori, F.; Santini, A. Real-Time Portable LAMP Assay for a Rapid Detection of Xylella fastidiosa In-Field. In Plant-Pathogen Interactions; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 51–60. [Google Scholar]
- Yaseen, T.; Drago, S.; Valentini, F.; Elbeaino, T.; Stampone, G.; Digiaro, M.; D’Onghia, A.M. On-Site Detection of Xylella fastidiosa in Host Plants and in “Spy Insects” Using the Real-Time Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Method. Phytopathol. Mediterr. 2015, 54, 488–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Park, Y.; Kim, G. Development of Diagnostic Technology of Xylella fastidiosa Using Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification and PCR Methods. Res. Plant Dis. 2021, 27, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waliullah, S.; Di Genova, D.; Oliver, J.E.; Ali, M.E. Development of a CAPS Marker and a LAMP Assay for Rapid Detection of Xylella fastidiosa Subsp. Multiplex and Differentiation from X. fastidiosa Subsp. Fastidiosa on BlueBerry. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kogovšek, P.; Hodgetts, J.; Hall, J.; Prezelj, N.; Nikolić, P.; Mehle, N.; Lenarčič, R.; Rotter, A.; Dickinson, M.; Boonham, N.; et al. LAMP Assay and Rapid Sample Preparation Method for On-Site Detection of Flavescence Dorée Phytoplasma in Grapevine. Plant Pathol. 2015, 64, 286–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogovšek, P.; Mehle, N.; Pugelj, A.; Jakomin, T.; Schroers, H.J.; Ravnikar, M.; Dermastia, M. Rapid Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Assays for Grapevine Yellows Phytoplasmas on Crude Leaf-Vein Homogenate Has the Same Performance as QPCR. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2017, 148, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saponari, M.; Giampetruzzi, A.; Loconsole, G.; Boscia, D.; Saldarelli, P. Xylella fastidiosa in Olive in Apulia: Where We Stand. Phytopathology 2019, 109, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loconsole, G.; Zicca, S.; Manco, L.; El Hatib, O.; Altamura, G.; Potere, O.; Elicio, V.; Valentini, F.; Boscia, D.; Saponari, M. Diagnostic Procedures to Detect Xylella fastidiosa in Nursery Stocks and Consignments of Plants for Planting. Agriculture 2021, 11, 922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).