Abstract
Conducted against the background of a highway project in Zhuji, Zhejiang Province, this study investigates the deterioration behavior of tuffaceous sandstone under the combined action of acid rain and wet–dry cycles. Laboratory experiments were carried out to explore its mechanical properties and damage evolution mechanisms. Standard specimens prepared from field rock samples were subjected to wet–dry cycles using an acidic solution with pH ≈ 5.0. By integrating uniaxial compression, Brazilian splitting, ultrasonic wave monitoring, and acoustic emission techniques, a systematic analysis was carried out to evaluate the degradation of mechanical parameters, the evolution of wave velocity, and the underlying damage and failure mechanisms. The results indicate the following: (1) With the increase in the number of acidic dry–wet cycles, the compressive and tensile strengths of tuffaceous sandstone decrease significantly; the deterioration rate first decreases and then increases, with 150 cycles identified as the critical threshold for strength deterioration, beyond which the material enters a stage of rapid degradation. (2) The evolution of ultrasonic wave velocity shows a significant negative correlation with strength deterioration, and the attenuation rate of wave velocity exhibits a consistent trend with the number of cycles as that of strength deterioration. (3) Acoustic emission RA-AF analysis reveals that tensile cracks in tuffaceous sandstone gradually decrease while shear cracks slowly increase, with cracks primarily developing along the weakly cemented tuffaceous areas. (4) This study established fitting formulas for the deterioration of compressive and tensile strengths with the number of cycles, as well as a damage calculation formula based on changes in wave velocity. (5) This study provides practical support for mitigating natural disasters, such as slope instability, induced by this type of combined weathering.
1. Introduction
In acid rain-prone regions, acidic wet–dry cycles can accelerate the deterioration of rock mass properties and increase slope instability. With the advancement of highway engineering construction, the development and operation of expressway projects are increasingly challenged by diverse geological conditions and environmental factors. Particularly under extreme weather conditions and complex geological settings, such deterioration may severely lead to geological hazards—including landslides, rockfalls, and debris flows—during both construction and operational phases, jeopardizing the safety of expressway infrastructure and operations [1]. Currently, extensive research has been conducted on the effects of acidic wet–dry cycles on the mechanical properties of rock masses. Zhou et al. [2] found that the degree of rock damage is positively correlated with the acidity of the solution in dry–wet cycles. Furthermore, Song et al. [3] found that under the action of dry–wet cycles, the failure mechanism of sandstone is primarily attributed to moisture infiltration and expansion, leading to gradual destabilization of the internal structure, initiation of microcracks, and their progressive propagation. Sun et al. [4] revealed that dry–wet cycles in an acidic environment significantly reduce the compressive strength, toughness, and tensile strength of red sandstone. Pu et al. [5] observed that dry–wet cycles result in progressive degradation of the mechanical properties of sandstone, with particularly notable reductions in compressive strength and elastic modulus under wet conditions. Huang et al. [6] identified 10 cycles as a critical threshold for physico-mechanical indicators under acidic dry–wet cycling; beyond this point, changes in all metrics accelerated markedly. Wedekind [7] found that tuff weathers more rapidly under humid and warm climatic conditions, while sandstone exhibits more pronounced physical weathering in arid regions. Based on existing literature, Zhang et al. [8] analyzed and discussed rock deterioration mechanisms. Their findings indicate that clay content is also a critical factor influencing the extent of rock degradation under dry–wet cycles. Meanwhile, Chen et al. [9] conducted dry–wet cycle experiments and observed that as the number of cycles increases, the wave velocity and dry mass of unloaded specimens exhibit distinct stage-wise evolutionary characteristics. Gao et al. [10] proposed a new constitutive model and demonstrated that with an increasing number of freeze–thaw cycles, the compaction stage of the stress–strain curve elongates and nonlinear characteristics become more pronounced. Chen et al. [11] employed mechanical tests and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) to investigate variations and evolutionary mechanisms in the microstructure and strength of altered granite. Guo et al. [12] developed a quantitative description of the mechanical degradation of clay-bearing sandstone under dry–wet cycles, noting that the influence of each cycle on tensile strength diminishes progressively with increasing cycle number until eventually stabilizing. Ying et al. [13] employed an RSM-SY5(T) non-metallic ultrasonic detector to measure the P-wave and S-wave velocities under different numbers of dry–wet cycles. It was found that as the number of cycles increased, the crack propagation velocity increased, while the crack initiation time decreased. Khanlari and Abdilor [14] found that dry–wet cycles lead to an increase in rock porosity and a reduction in strength, with rocks exhibiting more pronounced brittleness and damage characteristics after multiple cycles. Hua et al. [15] reported that under a higher number of dry–wet cycles, the failure mode of sandstone transitions from brittle to ductile behavior. Azimian and Ajalloeian [16] experimentally established empirical relationships between P-wave velocity and various physical and mechanical properties of marl. Gong et al. [17] recorded stress–strain curves of rocks and incorporated energy-based calculations to examine energy storage and dissipation during loading and unloading processes. Hua et al. [18] found that both mode-I fracture toughness and tensile strength decrease with an increasing number of dry–wet cycles. Li et al. [19] observed that the water absorption rate of rock increases monotonically with the number of dry–wet cycles, while both strength and deformation properties deteriorate accordingly.
Moreover, the extent of degradation gradually diminishes as cycling continues. Through experimental investigation, Sun and Zhang [20] reported that the impact of dry–wet cycles on sandstone specimens immersed in saline solution is more pronounced than on those soaked in pure water. They identified 30 cycles as a critical threshold for changes in P-wave velocity, thermal conductivity, and tensile strength. By combining qualitative analysis and quantitative characterization, Qin et al. [21] revealed that the meso-structural evolution of rock under water invasion–loss cycles can be divided into four distinct stages: overall homogeneous densification, original pore expansion, pore flocculation, and pore–fracture development. Ma et al. [22] conducted UCS tests on sandstone subjected to different numbers of dry–wet cycles and measured ion content in the soaking solution. Their results indicated a gradual decrease in ion concentration with an increasing number of cycles. Cai et al. [23] experimentally observed that dry–wet cycles lead to a significant reduction in the mechanical properties of sandstone, including compressive strength and elastic limit, while simultaneously inducing internal cracking and micro-damage. Xie et al. [24] found that with an increasing number of dry–wet cycles and cyclic shear actions, fracture surfaces gradually become smoother, and the degradation rate of shear strength progressively slows. Through experimental data and microstructural analysis, Wen et al. [25] demonstrated that dry–wet cycles not only exacerbate physical damage in rocks but also promote directional crack propagation, ultimately resulting in complete rock failure. Zhang et al. [26] investigated the mechanical behavior of soft silty sandstone as rockfill material under varying environmental conditions, particularly focusing on its deformation characteristics and shear strength in response to dry–wet cycles and temperature fluctuations. Zhao et al. [27] reported that the porosity of mudstone samples increases significantly during cyclic dry–wet processes, with a notable linear relationship observed between the increment in porosity and the number of dry–wet cycles. Zhou et al. [28] found that the decline in dynamic compressive strength after cyclic wetting–drying treatment is primarily attributed to the growth and propagation of microcracks within the rock. As the number of wet–dry cycles increases, the mechanical properties of sandstone gradually deteriorate.
Acoustic Emission (AE) technology is a non-destructive testing method widely used in rock mechanics and related engineering fields. It enables quantitative assessment of rock damage and deterioration by monitoring the acoustic emission signals generated during the loading process. Zhang et al. [29] analyzed AE signals from sandstone samples subjected to dry–wet cycles and found that both the frequency and energy of AE events gradually increase with repeated cycling. Meng et al. [30] reported that higher loading rates lead to increased uniaxial compressive strength (UCS), elastic modulus, and total AE count in sandstone after dry–wet cycling. Backers et al. [31] found that AE activity increases with higher loading rates, whereas under low loading rates, stress corrosion microcracking may contribute to fracture propagation. Sagar et al. [32] employing a Gaussian mixture model (GMM) algorithm, revealed that the formation and propagation of shear and tensile cracks generate distinct AE patterns and energy release characteristics. Liu et al. [33] evaluated AE signals from coal under uniaxial compression and analyzed the spectral characteristics, energy distributions, and fractal features of AE waveforms at different stress levels. Li et al. [34] monitored AE signals during the loading of coal samples using AE techniques and introduced a fractal analysis method to investigate AE characteristics. Liu et al. [35] analyzed AE signals generated during rock failure and observed that in low-strain-rate tests, the Ratio of acoustic emission rise time to amplitude and Average frequency (RA–AF) distribution was predominantly concentrated along the horizontal axis. However, as the strain rate increased, the distribution gradually shifted toward the vertical axis. Using digital image correlation (DIC) technology, Dutler et al. [36] obtained full-field surface deformations associated with fracture propagation and identified the fracture process zone. Yun et al. [37] proposed a method for predicting crack initiation strength, damage strength, and failure strength in freeze–thaw (F–T) sandstone based on the nonlinear growth characteristics of cumulative AE event counts. In a related study, Liu et al. [38] found that variations in strain rate influence AE characteristics, particularly during the initial and critical stages of rock failure. By monitoring the frequency, energy distribution, and time-domain features of AE signals, Shi et al. [39] investigated the relationship between AE activity and fatigue crack propagation in sandstone. Xiao et al. [40] studied the failure mechanisms of thermally damaged sandstone under uniaxial compression and employed AE techniques to analyze crack evolution and material nonlinearity. Zhang et al. [41] reported that P-wave velocity increases with rising stress, but begins to decrease as the rock approaches critical failure stress. During unloading, the variation in P-wave velocity differed from that during loading, exhibiting distinct recovery characteristics. Silva et al. [42] discussed how non-destructive testing techniques can be used not only to detect the presence of defects, but also to accurately characterize their nature, size, shape, and location. Meanwhile, Li et al. [43] utilized ultrasonic velocity measurements to evaluate elastic properties and the evolution of wave velocity, concluding that P-wave velocity can serve as an effective indicator for measuring and predicting internal damage evolution in rock mass.
This study presents an in-depth investigation into the deterioration of tuffaceous sandstone under the coupled effects of acid rain and wet–dry cycles. Through a series of laboratory tests, including the acidic wet–dry cycling test, UT, UCS tests, Brazilian splitting test, and AE monitoring test, the mechanical properties and damage evolution of tuffaceous sandstone were systematically examined. Based on the experimental results, fitting formulas were established to describe the degradation of compressive and tensile strength with increasing number of cycles, along with a damage calculation model based on changes in wave velocity. This work addresses a research gap in the evolutionary characteristics of tuffaceous sandstone deterioration under coupled acidic wet–dry conditions, providing a theoretical basis for durability evaluation and the design of protective measures for highway slopes in Zhuji and similar acid rain-affected regions.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Background
The engineering slope is located in a denudational hilly area, which forms part of an open-pit quarry. The excavation profile is clearly visible, with moderately weathered bedrock exposed. The slope top is covered by a thin layer of residual slope deposit consisting of silty clay with gravel. The bedrock belongs to the tuffaceous sandstone of the Zhitang Formation from the Sinian system, characterized by developed joint fissures and a relatively fragmented rock mass.
The slope top is overlaid by residual slope deposits comprising gravel-containing silty clay. This layer is greyish-yellow in color, plastic, with medium dry strength and toughness, and contains a small amount of gravel. It is classified as ordinary soil (Category II). Below this layer is highly weathered tuffaceous sandstone, exhibiting greyish-yellow and purplish-red colors, sandy structure, and medium-thick layered formation with well-developed joints and fractures. It is categorized as soft rock (Category IV). Further below is the moderately weathered tuffaceous sandstone, which shows interbedded purplish-red and greyish-green layers, sandy structure, and medium-thick bedding with tuffaceous cementation. Locally, it contains intercalated weak layers of argillaceous siltstone. The rock mass is relatively fragmented, produces a clear ringing sound when struck by a hammer, and is classified as sub-hard rock (Category VI) [44]. The engineering location and original topography is shown in Figure 1.
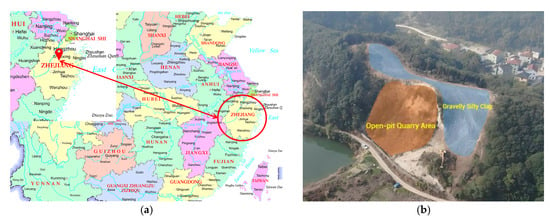
Figure 1.
Figure of engineering location and original topography, (a) The engineering location, (b) The original topography.
Zhejiang Zhuji exhibits a distinct monsoon-influenced climate characterized by abundant annual precipitation. Rainfall is particularly concentrated and frequent during the summer Meiyu season. The humid climatic conditions cause rocks in the Zhejiang region to exhibit specific characteristics under long-term dry–wet cycling, which significantly influences their physical properties and weathering processes.
Zhejiang Province exhibits a characteristic warm and humid monsoon climate with relatively abundant annual precipitation. Rainfall is particularly concentrated during the Meiyu season from June to July each year, often accompanied by acid rain events. The Zhejiang Meteorological Bureau monitored acid rain conditions between 2010 and 2021 through 13 acid rain observation stations across the region. Analysis of rainfall pH values revealed that the highest pH recorded during this decade was 5.29. Although monitoring results indicate a gradual reduction in the acidity of precipitation in Zhejiang, the frequency of acid rain occurrence remains relatively high. Under these conditions, rocks in the region undergo long-term dry–wet cycling. This cyclical process plays a significant role in rock weathering, disintegration, and alterations in physical properties. Prolonged dry–wet cycling accelerates the weathering process: repeated absorption and evaporation of moisture intensify chemical weathering processes such as mineral dissolution and oxidation, thereby weakening the rock structure and making it more susceptible to erosion and mechanical damage.
In summary, under the combined influence of acid rain and dry–wet cycles, slope rocks undergo accelerated deterioration and damage, thereby promoting slope instability and ultimately triggering natural disasters such as landslides, which can result in substantial property loss and human casualties.
2.2. Preparation of Rock Specimens
This study is based on a slope engineering project along an expressway in Zhuji City, Zhejiang Province. Sufficient rock samples were collected from the site. Considering the challenges associated with field sampling and the need for a large number of specimens, rock samples from various parts of the slope were retained without specific focus on bedding-parallel sections. The tuffaceous sandstone was cored into standard specimens with dimensions of 100 mm in height × 50 mm in diameter and 25 mm in height × 50 mm in diameter and 3 test specimens per group. Some of the processed tuffaceous sandstone specimens are shown in Figure 2.
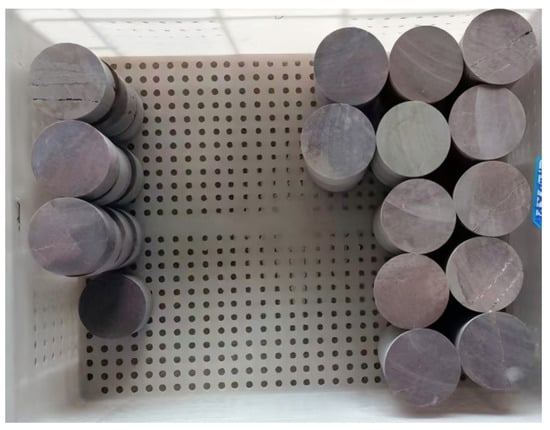
Figure 2.
Some Tuffaceous Sandstone Specimens for Testing.
To enhance the accuracy of the experiment, the wave velocity and density of each rock specimen were measured. Specimens with similar measured values of both parameters were selected for testing. The average density and average wave velocity of the finally selected samples were 2.74 g/cm3 and 3871 m·s−1, respectively.
2.3. Experimental Procedures and Equipment
As shown in Figure 3, the specimens were first subjected to acidic dry–wet cycles. During this process, UCS tests, AE testing, and ultrasonic wave measurements were conducted at monthly intervals. During the cycles, the moistened portion of the specimen was exposed to an acidic environment.
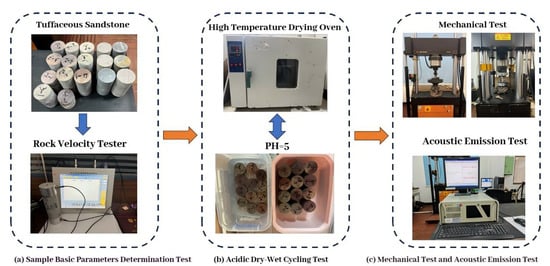
Figure 3.
Experimental procedures and Equipment.
The testing procedure primarily included acidic dry–wet cycle tests, ultrasonic tests, UCS tests, and Brazilian splitting tests. The specific steps are as follows:
- i.
- Acidic Dry–Wet Cycle Testing
For this experiment, the acidic solution was prepared using concentrated sulfuric acid and water. In accordance with the acid rain conditions in Zhejiang Province described above and based on the most unfavorable principle, the pH value of the solution was adjusted to approximately 5.0. The pH of the prepared solution was verified using pH test paper (i.e., litmus paper), as shown in Figure 4. The dry–wet cycle tests consisted of two steps: the first involved immersing the rock specimens in a custom-made immersion tank for 12 h, and the second step entailed drying the immersed specimens in an oven at 60 °C for 12 h. This procedure completed one acidic dry–wet cycle. A total of n = 0 (natural state), 30, 60, 90, 120, 150, and 180 dry–wet cycles were conducted in this experiment.

Figure 4.
Cycles Preparing the solution for acidic wet–dry cycles.
- ii.
- Ultrasonic Testing (UT)
The UT was conducted in both vertical and horizontal directions. Vertically, measurements were taken from the top and bottom surfaces of the standard specimens. Horizontally, measurement points were arranged on the specimens as illustrated in Figure 5a: three acoustic measurement surfaces were set at intervals of 25 cm, with four measurement points distributed on each surface, as shown in Figure 5b.
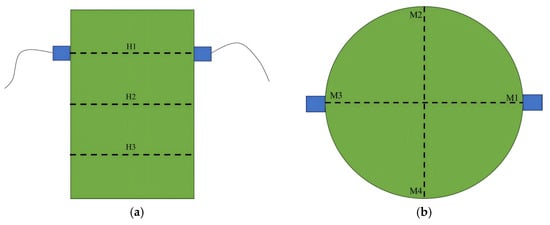
Figure 5.
Layout of measurement points for lateral sonic testing: (a) Plan view of test specimen layout; (b) Plan view of test specimen layout.
A thin layer of vaseline was applied to the transducer to ensure proper coupling with the specimen surface. The testing parameters were configured as follows: sampling rate was set to 0.1 μs, sample points to 1 k, signal attenuation to 2, and pulse width to 1 μs.
- iii.
- Uniaxial Compression Test and Brazilian Disc Test
Tuffaceous sandstone specimens subjected to different numbers of acidic dry–wet cycles were tested under uniaxial compression and Brazilian splitting to determine their compressive and tensile strengths. The tests were conducted using an electro-hydraulic servo universal testing machine (Its loading capacity is 2000 kN) at the Modern Analysis and Testing Center of Central South University. This system offers high precision and excellent stability, meeting all the requirements of the experiment.
- iv.
- Acoustic Emission (AE) Monitoring Test
The PCI-2 AE system, as shown in Figure 6, was employed in this experiment. It effectively monitors and analyzes rock fracture processes, evaluates mechanical properties, predicts critical failure points, and provides precise experimental data. The system plays a critical role in rock mechanics research, geological surveys, and performance assessment of rock materials in related engineering projects. Through the analysis of AE signals, the PCI-2 AE system enables researchers to gain deeper insights into rock fracture mechanisms, offering essential data support for studies and applications in relevant fields.
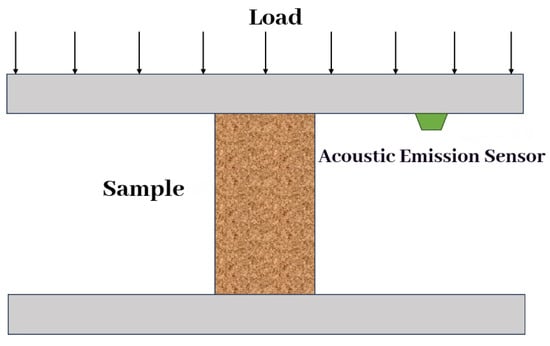
Figure 6.
Schematic diagram of the acoustic emission setup.
3. Deterioration Patterns of Mechanical Parameters in Tuffaceous Sandstone
3.1. Stress–Strain Curve Analysis
Figure 7 shows the stress–strain curves of tuffaceous sandstone under uniaxial compression and Brazilian splitting tests after different numbers of acidic dry–wet cycles. As can be seen from Figure 7a, the uniaxial test process of tuffaceous sandstone, from loading to failure, can be divided into four stages: the elastic stage, yield stage, plastic deformation stage, and failure stage.
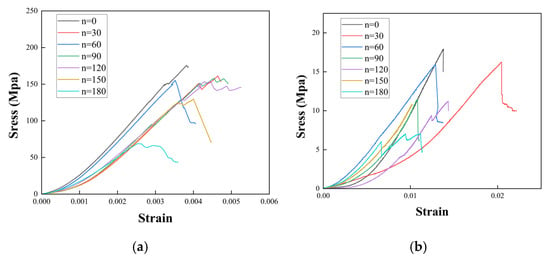
Figure 7.
Stress–Strain curves of tuffaceous sandstone subjected to various numbers of acidic wet–dry cycles (n). (a) Uniaxial compressive test; (b) Brazilian tensile split test.
- Elastic Stage
During the initial loading phase under compression, the rock exhibits elastic deformation, characterized by a linear relationship between stress and strain. In this stage, the stress–strain curve is linear and adheres to Hooke’s law. The rock primarily undergoes minor deformation without significant signs of failure.
- Yielding Stage
With further increase in stress, the rock specimen enters the yield stage, during which the stress–strain relationship begins to deviate from linearity, indicating the onset of plastic deformation. Microcracks initiate and gradually propagate within the rock, though macroscopic failure has not yet occurred. At this point, the strength of the rock starts to decline, manifested as a slowdown in the rate of stress increase.
- Plastic Flow Stage
Following the yield stage, the rock undergoes significant plastic deformation. The specimen exhibits increased deformation, while the stress may experience a slight decrease. This behavior results from the gradual propagation of internal cracks, leading to microscopic failure and the generation of additional microcracks. During this phase, the stress–strain curve often shows a plateau or a stress drop region, indicating that pronounced plastic deformation has occurred in the rock.
- Failure Stage
When the stress reaches the compressive strength of the rock, macroscopic failure occurs, characterized by rapid crack propagation that ultimately leads to disintegration or fragmentation of the specimen. Failure is typically caused by the coalescence and propagation of cracks within the rock. This process is accompanied by a sharp drop in stress, resulting in a sudden loss of the specimen’s load-bearing capacity.
As can be seen from Figure 7b, the Brazilian splitting test process of tuffaceous sandstone, from loading to failure, can be divided into four stages: the elastic stage, crack initiation stage, crack propagation stage, and rupture stage.
- Elastic Stage
At the initial stage of external force application, the stress–strain relationship of the rock exhibits a linear characteristic, representing the elastic deformation stage. During this phase, no cracks have yet formed, the deformation of the rock is minimal, and failure has not occurred.
- Crack Initiation Stage
With further increase in external load, microcracks begin to initiate inside the rock specimen, particularly in the central region where the tensile stress reaches its maximum, promoting crack formation. At this stage, crack growth remains limited, and most cracks have not yet penetrated through the entire specimen.
- Crack Propagation Stage
With the increase in stress, internal cracks progressively expand and coalesce, forming larger-scale damage zones, which manifest as pronounced deformation or embrittlement of the specimen. At this stage, the rate of crack propagation accelerates, leading to a gradual reduction in the tensile strength of the rock and the emergence of evident tensile cracking phenomena.
- Fracture Stage
When the tensile stress applied to the specimen reaches the tensile strength limit of the rock, macroscopic cracks within the specimen will propagate, ultimately resulting in its fracture.
3.2. Degradation of Tensile and Compressive Strength
Based on uniaxial compression and Brazilian splitting tests conducted on tuffaceous sandstone subjected to different numbers of acidic dry–wet cycles, the statistical data of its compressive and tensile strength were obtained as shown in Table 1, the errors in uniaxial compressive strength and tensile strength are shown in Figure 8.

Table 1.
Compressive and tensile strength of tuffaceous sandstone subjected to various numbers of acidic wet–dry cycles.
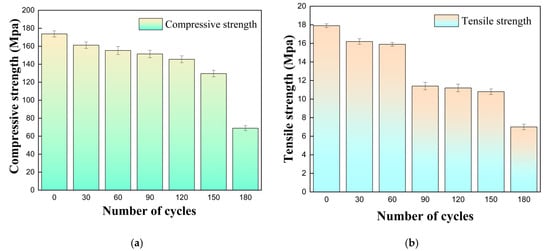
Figure 8.
Errors in uniaxial compressive and tensile strength measurements. (a) Uniaxial compressive strength; (b) Tensile strength.
To evaluate the effect of the number of wet–dry cycles on the degradation of tuffaceous sandstone, the following Equation (1) for calculating the degree of deterioration was employed:
In Equation (1), represents the degree of deterioration (%) of the tuffaceous sandstone specimen after n wet–dry cycles; denotes the initial mechanical parameter of the tuffaceous sandstone specimen; and refers to the mechanical parameter of the specimen after being subjected to n acidic wet–dry cycles.
The deterioration rate of tuffaceous sandstone between consecutive wet–dry cycles is calculated using the following Equation (2):
In Equation (2), denotes the deterioration rate (in %) of the tuffaceous sandstone specimen.
Using Equations (1) and (2), the compressive and tensile strength data from Table 1 were calculated to determine the deterioration degree and deterioration rate trends of the tuffaceous sandstone after being subjected to different numbers of acidic wet–dry cycles, as shown in Figure 9.
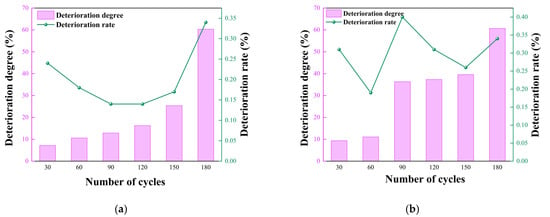
Figure 9.
Variation trends in deterioration degree and rate of tuffaceous sandstone under different numbers of acidic dry–wet cycles. (a) Deterioration of compressive strength; (b) deterioration of tensile strength.
As shown in Figure 9, with the increase in the number of wet–dry cycles, both the compressive and tensile strengths of the tuffaceous sandstone decreased significantly, while the deterioration rate exhibited an initial decrease followed by an upward trend. Under acidic wet–dry cycles, the deterioration rate of the tensile strength (Brazilian splitting strength) of tuffaceous sandstone is significantly higher than that of its uniaxial compressive strength. Notably, after 180 cycles under pH = 5 conditions, the deterioration of compressive and tensile strengths exceeded 50%, indicating a gradual and irreversible accumulation of degradation effects. Beyond 150 cycles, the deterioration rate accelerated markedly: the compressive strength deterioration rate increased from 0.17% to 0.34%, and the tensile strength deterioration rate rose from 0.26% to 0.34%. These results further demonstrate that the deterioration of tuffaceous sandstone under cyclic wet–dry conditions is a continuously accumulating process, with a pronounced acceleration occurring after 150 cycles.
3.3. Degradation Model for Mechanical Properties
Under the action of wet–dry cycles, micro-cracks within the tuffaceous sandstone expand rapidly, allowing acidic ions to penetrate more easily, resulting in a slight initial decline in mechanical properties. As corrosion accumulates, further deterioration of pores occurs, leading to a significant reduction in strength. Eventually, the decrease in reactive substances in the acidic solution causes the chemical reaction to stabilize, thereby attenuating the degradation effect. To quantitatively describe the influence of acidic wet–dry cycles on the mechanical parameters, it was assumed that both the compressive and tensile strengths vary continuously with the number of cycles. Experimental data were fitted accordingly, and the results are presented in Figure 10.
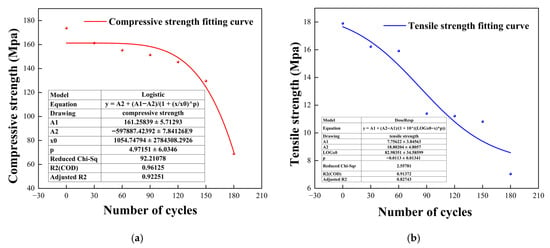
Figure 10.
Fitted curves for mechanical parameters of tuffaceous sandstone versus number of acidic wet–dry cycles. (a) Fitting curve for uniaxial compressive strength; (b) Fitting curve for uniaxial tensile strength.
The fitting curve equation for compressive strength is given as follows:
where represents the compressive strength (in MPa) of the rock after wet–dry cycles; denotes the number of wet–dry cycles; and ,, and are constants with values of 161.25839, −597,887.42392, 1054.74794, and 4.97151, respectively.
The fitting curve equation for tensile strength is given as follows:
where denotes the tensile strength (in MPa) of the rock after wet–dry cycles; represents the number of wet–dry cycles; and , , and are constants with values of 7.75622, 18.80204, 82.98351, and −0.0113, respectively.
As shown in Figure 9, under the condition of pH = 5, the mechanical parameters of tuffaceous sandstone exhibit a clear functional relationship with the number of wet–dry cycles. The deterioration models of both compressive and tensile strength are presented in the figure, and the R2 values of their fitting curves exceed 0.9, demonstrating good fitting performance and a practical reference value.
4. Analysis of Ultrasonic Wave Velocity Characteristics in Tuffaceous Sandstone
4.1. Principle and Procedure of Ultrasonic Testing
- Principle and method of ultrasonic testing
The testing principle of ultrasonic waves in concrete is primarily based on their propagation characteristics within the material. As one of the non-destructive testing methods, it is commonly used to assess the quality of concrete, detect internal defects, and estimate its strength. By utilizing how ultrasonic waves travel through concrete, this method obtains information about the internal structure of the material.
Ultrasonic waves are mechanical waves with frequencies beyond the audible range of the human ear, typically between 20 kHz and 1 MHz. When propagating through concrete, these waves are influenced by factors such as density, elasticity, moisture content, and internal defects of the material. By analyzing parameters such as wave propagation velocity, travel time, or waveform alterations, the physical properties and structural integrity of the concrete can be evaluated.
The primary methods employed in ultrasonic testing of concrete include the pulse transmission method and the echo (or reflection) method. In the pulse transmission method, an ultrasonic transducer emits a pulse that travels through the concrete and is captured by a receiver on the opposite side. By measuring the travel time of the pulse between transmission and reception, the wave propagation velocity can be determined. The echo method, on the other hand, involves emitting an ultrasonic wave that reflects off internal interfaces within the concrete (such as defects or boundaries). The reflected signal is then received by the same or a different transducer, providing information about the location and nature of the reflecting interface.
The propagation velocity of ultrasonic waves is correlated with the strength of concrete. Generally speaking, concrete with higher strength exhibits faster wave propagation due to its denser structure. In contrast, lower-strength concrete tends to have slower wave velocities, which can be attributed to the presence of more pores and microcracks. These internal defects absorb or scatter ultrasonic energy, resulting in signal attenuation and reduced speed. By measuring variations in wave velocity, it is possible to identify and locate defects within the concrete structure.
- Procedure of ultrasonic testing
During ultrasonic wave velocity testing, transverse measurements were conducted layer by layer along the acoustic testing surfaces H1, H2, and H3, as illustrated in Figure 5. Prior to testing, a couplant was applied to both the measurement points on the specimen surface and the transducer surfaces, and the center of the transducer was aligned precisely with each measurement point. For the first specimen, measurements were taken on plane H1 in two sets: between points M1 and M3, and between M2 and M4. The average value of these two sets was recorded as the result for H1. The same procedure was applied to the other planes. For vertical testing, each specimen was measured three times, and the average value was recorded as S1.
Starting from the initiation of the wet–dry cycle tests, ultrasonic wave velocity measurements were performed every 30 cycles. To ensure accuracy, specimens were cooled to room temperature after removal from the drying oven before conducting measurements.
4.2. Variation in Ultrasonic Wave Velocity
Following the calculation method described above, the measured ultrasonic wave velocities were processed, and their variation trends are plotted in Figure 11.
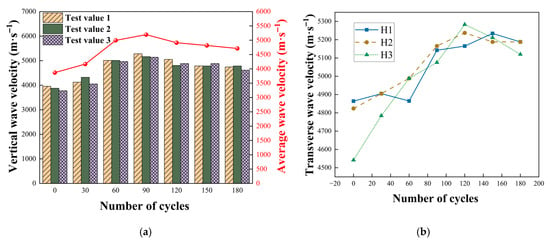
Figure 11.
Wave velocity variation in tuffaceous sandstone subjected to various numbers of acidic wet–dry cycles. (a) Axial wave velocity. (b) Radial wave velocity.
As shown in Figure 11, the average wave velocity of the specimens generally exhibited an initial increase followed by a subsequent decrease. For the vertical wave velocity, a rapid increase was observed during the early stages of wet–dry cycling, indicating reactions between the specimen and the acidic solution leading to rapid filling of internal pores. The vertical wave velocity peaked after 90 cycles, after which further deterioration in the later stages resulted in increased porosity and a corresponding decline in wave velocity. In terms of transverse wave velocity, greater variations were observed at the end planes, while the central plane showed relatively minor changes. This suggests that deterioration progressed from the ends toward the center of the specimen. The transverse wave velocities of all three planes reached their maximum values at 120 cycles, after which they decreased and eventually converged toward similar values. This indicates that the specimen was entirely eroded after 120 wet–dry cycles, resulting in a rapid loss of strength—a finding consistent with the changes observed in compressive and tensile strength mentioned earlier.
To analyze the change in wave velocity of the specimens during wet–dry cycling, the average variation in wave velocity, denoted as (in %), is defined and calculated using the following Equation (5):
where denotes the initial wave velocity (in ) of the specimen before wet–dry cycles, and represents the average wave velocity (in ) of the specimen after n wet–dry cycles.
Based on Equation (5), the measured wave velocity data were calculated to determine the variation rate of the average wave velocity of the specimens. The results are presented in Figure 12.
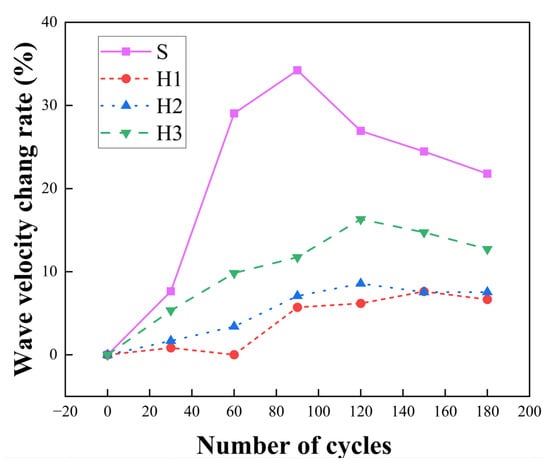
Figure 12.
Variation rates of wave velocity in lateral and longitudinal directions.
As shown in Figure 12, both the transverse and longitudinal wave velocity variation rates generally exhibited an initial increase followed by a subsequent decrease. For the longitudinal variation rate, a rapid increase of 26.94% was observed between 0 and 90 cycles, after which it gradually decreased and eventually stabilized. Regarding the transverse variation rate, the H1 increased to a maximum of 7.62% from 0 to 150 cycles, while the H2 and H3 reached their peak values at 120 cycles, with increases of 8.57% and 16.31%, respectively. Ultimately, all three planes showed a declining trend and stabilized over further cycles.
4.3. Predictive Strength Model for Tuffaceous Sandstone from Ultrasonic Wave Velocity
The ratio X of the transverse average wave velocity to the longitudinal average wave velocity, and the ratio Y of the UCS to the tensile strength of the rock specimen, were adopted to establish a relational expression. These two parameters were then coupled, simulations for strength calculation of tuffaceous sandstone were conducted utilizing Origin 2024 software, as illustrated in Figure 13.
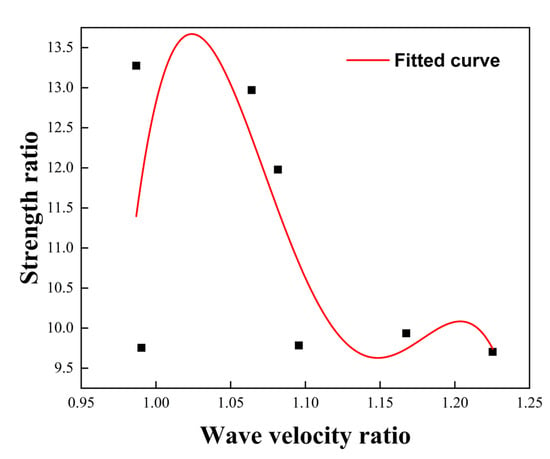
Figure 13.
Fitting curve of strength ratio versus wave velocity ratio.
The resulting fitting equation is expressed as follows:
where denotes the strength ratio; represents the wave velocity ratio; and , , , , and are constants with values of −42,414.3298, 151,869.59889, −203,356.32003, 120,734.39406, and −26,820.52641, respectively.
5. Damage and Failure Evolution Characteristics of Tuffaceous Sandstone Determined by Acoustic Emission
5.1. Evolution of Cumulative Acoustic Emission Ring-Down Count and Energy
Based on the experimental results and the variations in AE signals, the failure process of tuffaceous sandstone can be divided into three distinct stages: the initial active period, the stable growth period, and the steep-increase peak period. Figure 14 illustrates the relationship between stress, cumulative count, energy, and strain. Moreover, as shown in Figure 13, during uniaxial loading, the abrupt changes in the cumulative AE ring-down count and energy correspond closely with sudden stress variations. Notably, the AE energy signal increases rapidly at the point of specimen failure.
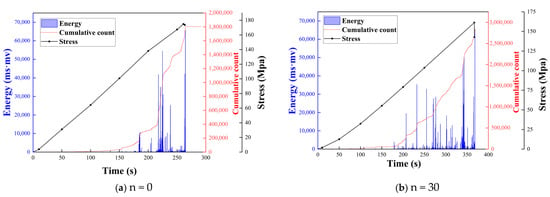
Figure 14.
Relationships among stress, cumulative AE counts, cumulative energy, and time for tuffaceous sandstone under different numbers of acidic wet–dry cycles. (a) n = 0; (b) n = 30; (c) n = 60; (d) n = 90; (e) n = 120; (f) n = 150; (g) n = 180.
During the initial active stage of rock failure, the AE energy signals remain at low values, and the slope of the cumulative ring-down count curve is very small. However, even as the number of wet–dry cycles increases, the slope exhibits no significant change, indicating that the erosion of tuffaceous sandstone by weakly acidic wet–dry cycles is a slow process. No noticeable crack propagation was observed even after 180 cycles.
As the axial stress increases, the cumulative count rises sharply around the 200-s mark. With an increasing number of wet–dry cycles, the deterioration of tuffaceous sandstone is progressively exacerbated, and crack development is accelerated. Accordingly, the growth rate of the cumulative AE count gradually intensifies. Furthermore, this critical point typically occurs approximately 100 s before the peak UCS is reached, making it a potential early-warning indicator for the failure of tuffaceous sandstone.
When the tuffaceous sandstone specimen approaches failure, as it nears its ultimate load-bearing capacity, a large number of internal microcracks develop and may interconnect to form fracture networks. The contact and friction between rock particles within the specimen significantly enhance the AE signals, thereby inducing a sudden surge in the AE energy signal.
5.2. Damage Evolution Characteristics Based on RA-AF and Acoustic Emission Source Location
RA-AF are key parameters for identifying types of rock cracks. Based on existing studies on sandstone, a critical value of K = 2 is adopted. Figure 15 presents the scatter plot of RA and AF distributions for tuffaceous sandstone in its natural state.
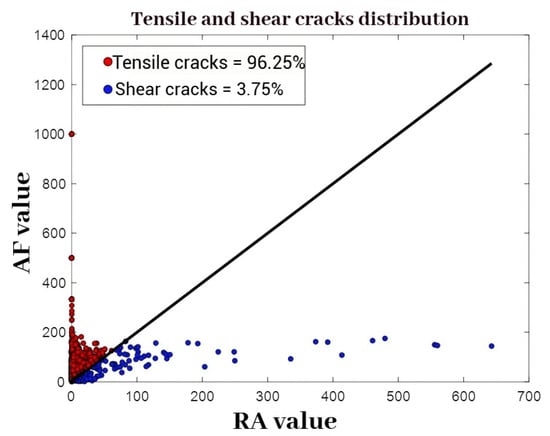
Figure 15.
The ratio of acoustic emission rise time to amplitude and average frequency value plot.
As can be seen from Figure 15, during the uniaxial compression failure process, 96.25% of the RA-AF AE signals cluster in the upper region where K > 2, indicating that the failure of the specimen is predominantly driven by tensile cracks. Meanwhile, the relatively low proportion of original pores and fractures results in a notably small share of signals corresponding to shear cracks.
Figure 16 presents the evolution trend of RA–AF-based crack distribution in tuffaceous sandstone under different numbers of wet–dry cycles. With an increasing number of cycles, tensile cracks gradually decrease while shear cracks increase slightly, although the changes are not pronounced. The most noticeable variation occurs after the first 30 wet–dry cycles, during which the proportion of tensile cracks during failure decreases by 5%. These results indicate that the damage and failure characteristics of tuffaceous sandstone are not significantly influenced by the acidic solution (pH = 5) or the number of wet–dry cycles. This finding further validates the conclusions drawn from the cumulative AE ring-down counts and energy evolution analysis.
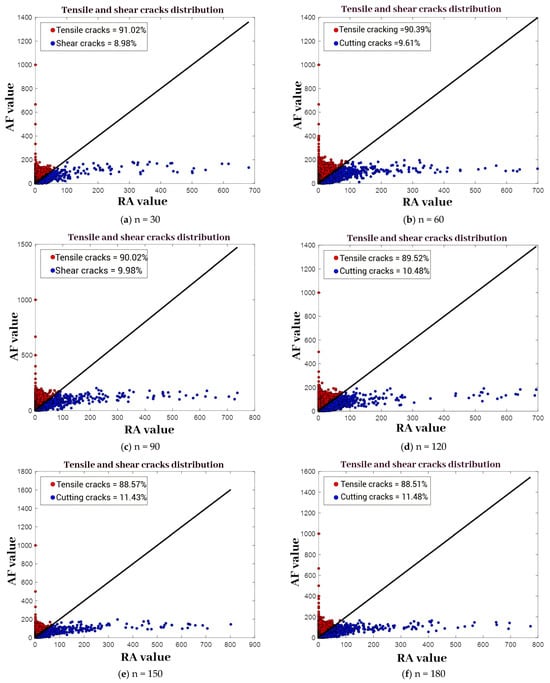
Figure 16.
RA-AF value plots of tuffaceous sandstone under different numbers of acidic wet–dry cycles. (a) n = 30; (b) n = 60; (c) n = 90; (d) n = 120; (e) n = 150; (f) n = 180.
6. Discussion
During both construction and operational phases of slopes, surface rocks are subjected to cyclic wet–dry actions caused by rainwater erosion and moisture evaporation, as well as long-term chemical corrosion from acidic substances in acid rain. These processes gradually weaken slope stability. Under the combined effects of acidic wet–dry cycles, the physico-mechanical properties of tuffaceous sandstone deteriorate, posing significant risks to slopes composed of this material and potentially endangering nearby communities. Therefore, investigating the degradation and damage behavior of tuffaceous sandstone under acidic wet–dry cycling is of great importance for enhancing slope reliability and formulating effective preventive measures.
Based on a case study of a slope in Zhuji, Zhejiang Province, this paper investigates the degradation of tuffaceous sandstone under cyclic wet–dry conditions. Experimental results indicate that the degradation degree of both compressive and tensile strength exhibits a positive correlation with the number of wet–dry cycles, while the degradation rate first decreases and then increases. After 150 cycles, a significant reduction in rock strength is observed, demonstrating that the acidic wet–dry cycles cause pronounced and irreversible deterioration in mechanical properties. The established degradation model effectively captures the variation in rock strength with increasing cycles.
The ultrasonic wave velocity of the rock shows an initial increase followed by a subsequent decrease throughout the acidic wet–dry cycling process. The rate of wave velocity change rises rapidly in the early stage and then gradually stabilizes, suggesting that the internal structure of the rock is partially filled at first and later deteriorates due to acidic erosion. Moreover, the cumulative ring-down count and energy evolution of AE signals demonstrate good consistency with the stress–strain curves, revealing notable precursor characteristics prior to failure. As the number of wet–dry cycles increases, the development of internal cracks progresses slowly. The AE signals further confirm that the acidic wet–dry cycles have limited influence on crack propagation within the rock.
However, several limitations remain in this study. The time allocation of the wet–dry cycles and the experimental conditions were overly idealized and did not fully reflect real-field situations. Furthermore, the tests were conducted only on typical tuffaceous sandstone from the Zhuji region. Since tuffaceous sandstones from different areas (e.g., regions with more intense volcanic activity) may vary in mineral composition, their degradation characteristics could differ accordingly. Comparative studies involving samples from multiple regions are thus necessary in the future.
Several aspects can be improved in subsequent research. First, based on collected rainfall data and slope conditions, a physical model could be established that incorporates actual natural wet–dry processes to investigate the degradation behavior of tuffaceous sandstone under such cycles. Second, the specific biological, chemical, and mechanical interactions between acidic solutions and the rock should be further explored. Third, more optimized theoretical models should be adopted or developed to better describe the wet–dry cycling process and predict the deterioration behavior of tuffaceous sandstone. Such efforts would bring the experiments closer to real-world conditions and lead to more accurate conclusions regarding the degradation characteristics of tuffaceous sandstone under acidic wet–dry cycles.
The findings of this study are applicable to the short-term (≤10 years, corresponding to approximately 180 cycles) stability assessment of slopes with geological and environmental conditions similar to those of Zhuji—specifically, weakly acidic rainfall and tuffaceous sandstone slopes. For slopes under strongly acidic (pH < 4.0) or dynamic hydraulic conditions, further validation based on subsequent dynamic coupling tests is required.
7. Conclusions
Through a series of tests, including acidic wet–dry cycles, uniaxial compression, Brazilian splitting, ultrasonic wave measurement, and AE monitoring, this study investigated the effects of different numbers of wet–dry cycles on the degradation characteristics of tuffaceous sandstone in an acidic environment. The deterioration patterns of mechanical parameters, wave velocity characteristics, and AE data were analyzed, leading to the following conclusions.
The degradation degree of both compressive and tensile strength of tuffaceous sandstone exhibits a positive correlation with the number of wet–dry cycles, while the degradation rate shows an initial decrease followed by a subsequent increase as the cycles progress. Meanwhile, the compressive and tensile strengths gradually decrease with an increasing number of cycles. A significant reduction in strength is observed after n = 150 cycles.
Based on the analysis of ultrasonic wave velocity, the process of acidic wet–dry cycling in tuffaceous sandstone can be divided into two distinct stages: (ⅰ) Initial Strengthening Stage: During the early cycles, both the compressive and tensile strength of the tuffaceous sandstone show a slight improvement, which may be attributed to adaptive changes in the pore structure or hardening effects of certain minerals. The acidic solution likely dissolves soluble minerals such as gypsum, releasing additional space within the structure and facilitating recrystallization, thereby reducing initial porosity. This results in an increase in ultrasonic wave velocity. (ⅱ) Subsequent Degradation Stage: As the number of acidic wet–dry cycles increases, continued acidic erosion and cyclic wetting–drying progressively intensify internal weathering, particularly affecting mineral composition and rock structure. In addition, repeated interaction with the acidic solution induces expansion, cracking, and increased porosity in the rock, ultimately leading to a decrease in ultrasonic wave velocity.
During the UCS of tuffaceous sandstone, the cumulative ring-down count and energy evolution of AE can be divided into three stages: the initial active period, the stable growth period, and the steep increase peak period, demonstrating relatively clear precursor characteristics before sudden failure. Under the coupled effects of acidic wet–dry cycles, internal fractures and cracks in the tuffaceous sandstone develop slowly. Correspondingly, the proportion of tensile crack signals based on RA-AF analysis shows a continuous yet very gradual decrease. This further indicates that acidic wet–dry cycling has a limited influence on the development of fractures in tuffaceous sandstone.
This study on the deterioration characteristics of tuffaceous sandstone under the coupled effects of acid rain and wet–dry cycles provides practical support for mitigating natural hazards induced by such combined weathering processes. By monitoring rainfall pH, cycle frequency, and groundwater depth, it is possible to predict the approach of the rock’s deterioration stage, enabling early initiation of slope and subgrade monitoring to prevent landslides and collapses. Combined with the “wave velocity–damage” formula, internal rock damage can be rapidly quantified, facilitating efficient safety risk screening in tunnel surrounding rock and slope support structures. Furthermore, the established “strength–cycle number” fitting model can inform engineering site selection and bearing capacity design, thereby reducing disasters such as roadbed settlement and slope instability.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.L., M.W., C.Y. and X.S.; methodology, D.L., M.W., C.Y. and X.S.; software, M.W. and C.Y.; validation, M.W., C.Y. and X.S.; formal analysis, D.L.; investigation, M.W. and C.Y.; resources, D.L.; data curation, M.W. and C.Y.; writing—original draft preparation, M.W. and C.Y.; writing—review and editing, D.L., M.W. and C.Y.; visualization, X.S.; supervision, D.L.; project administration, D.L.; funding acquisition, D.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Siva Subramanian, S.; Ishikawa, T.; Tokoro, T. Stability Assessment Approach for Soil Slopes in Seasonal Cold Regions. Eng. Geol. 2017, 221, 154–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Zhu, Z.; Zhu, A.; Zhou, L.; Fan, Y.; Lang, L. Deterioration of Mode II Fracture Toughness, Compressive Strength and Elastic Modulus of Concrete under the Environment of Acid Rain and Cyclic Wetting-Drying. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 228, 116809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Sun, L.; Cheng, S.; Liu, Z.; Tan, J.; Ning, F. Experimental Study on the Property Degradation and Failure Mechanism of Weakly Cemented Sandstone under Dry-Wet Cycles. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2022, 2022, 9431319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Du, B.; Cheng, Q. Experimental Study of the Dynamic Mechanical Behavior and Degradation Mechanism of Red Sandstone in Acid Dry-Wet Cycles. Geofluids 2023, 2023, 5541567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, H.; Yi, Q.; Jivkov, A.P.; Bian, Z.; Chen, W.; Wu, J. Effect of Dry-Wet Cycles on Dynamic Properties and Microstructures of Sandstone: Experiments and Modelling. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2024, 34, 655–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Pang, J.; Liu, G.; Chen, Y. Experimental Study on Physicomechanical Properties of Deep Sandstone by Coupling of Dry-Wet Cycles and Acidic Environment. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2020, 2020, 2760952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedekind, W. Weathering and Conservation of Monuments Constructed from Tuff and Sandstone in Different Environmental Conditions. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Göttingen, Göttingen, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Niu, Y.; Shang, X.; Ye, P.; Zhou, R.; Gao, F. Deterioration of Physical and Mechanical Properties of Rocks by Cyclic Drying and Wetting. Geofluids 2021, 2021, 6661107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Chen, X.; Gong, S.; Li, Z.; Su, Z. Experimental Study on Pore Structure Evolution of Unloaded Rock Mass during Excavation of Reservoir Slope under Dry-Wet Cycle. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 4716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Xiong, X.; Xu, C.; Zhou, K. Mechanical Property Deterioration Characteristics and a New Constitutive Model for Rocks Subjected to Freeze-Thaw Weathering Process. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2021, 140, 104642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; He, P.; Qin, Z. Damage to the Microstructure and Strength of Altered Granite under Wet–Dry Cycles. Symmetry 2018, 10, 716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, P.; Gu, J.; Su, Y.; Wang, J.; Ding, Z. Effect of Cyclic Wetting–Drying on Tensile Mechanical Behavior and Microstructure of Clay-Bearing Sandstone. Int. J. Coal Sci. Technol. 2021, 8, 956–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, P.; Zhu, Z.; Ren, L.; Deng, S.; Niu, C.; Wan, D.; Wang, F. Deterioration of Dynamic Fracture Characteristics, Tensile Strength and Elastic Modulus of Tight Sandstone under Dry-Wet Cycles. Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech. 2020, 109, 102698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanlari, G.; Abdilor, Y. Influence of Wet–Dry, Freeze–Thaw, and Heat–Cool Cycles on the Physical and Mechanical Properties of Upper Red Sandstones in Central Iran. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2015, 74, 1287–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, W.; Dong, S.; Li, Y.; Wang, Q. Effect of Cyclic Wetting and Drying on the Pure Mode II Fracture Toughness of Sandstone. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2016, 153, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azimian, A.; Ajalloeian, R. Empirical Correlation of Physical and Mechanical Properties of Marly Rocks with P Wave Velocity. Arab. J. Geosci. 2015, 8, 2069–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, F.; Yan, J.; Luo, S.; Li, X. Investigation on the Linear Energy Storage and Dissipation Laws of Rock Materials Under Uniaxial Compression. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2019, 52, 4237–4255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, W.; Dong, S.; Li, Y.; Xu, J.; Wang, Q. The Influence of Cyclic Wetting and Drying on the Fracture Toughness of Sandstone. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2015, 78, 331–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Peng, K.; Peng, J.; Hou, D. Experimental Investigation of Cyclic Wetting-Drying Effect on Mechanical Behavior of a Medium-Grained Sandstone. Eng. Geol. 2021, 293, 106335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Zhang, Y. Combined Effects of Salt, Cyclic Wetting and Drying Cycles on the Physical and Mechanical Properties of Sandstone. Eng. Geol. 2019, 248, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Fu, H.; Chen, X. A Study on Altered Granite Meso-Damage Mechanisms Due to Water Invasion-Water Loss Cycles. Environ. Earth Sci. 2019, 78, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Yao, H.; Xiong, J.; Zhu, D.; Lu, J. Experimental Study on the Deterioration Mechanism of Sandstone under the Condition of Wet-Dry Cycles. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2022, 26, 2685–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Zhou, Z.; Tan, L.; Zang, H.; Song, Z. Fracture Behavior and Damage Mechanisms of Sandstone Subjected to Wetting-Drying Cycles. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2020, 234, 107109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Z.; Peng, H.; Fu, X.; Ban, Y. Investigation of Morphological Features and Mechanical Behavior of Jointed Limestone Subjected to Wet-Dry Cycles and Cyclic Shear in Drawdown Areas of the Three Gorges Reservoir. Eng. Geol. 2025, 350, 107990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, T.; Wang, Y.; Tang, H.; Zhang, J.; Hu, M. Damage Evolution and Failure Mechanism of Red-Bed Rock under Drying–Wetting Cycles. Water 2023, 15, 2684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.Y.; Zhang, J.H.; Sun, G.L. Deformation and Shear Strength of Rockfill Materials Composed of Soft Siltstones Subjected to Stress, Cyclical Drying/Wetting and Temperature Variations. Eng. Geol. 2015, 190, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Ren, S.; Jiang, D.; Liu, R.; Wu, J.; Jiang, X. Influence of Wetting-Drying Cycles on the Pore Structure and Mechanical Properties of Mudstone from Simian Mountain. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 191, 923–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Cai, X.; Chen, L.; Cao, W.; Zhao, Y.; Xiong, C. Influence of Cyclic Wetting and Drying on Physical and Dynamic Compressive Properties of Sandstone. Eng. Geol. 2017, 220, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Lu, K.; Zhang, W.; Li, D.; Yang, G. Quantification and Acoustic Emission Characteristics of Sandstone Damage Evolution under Dry–Wet Cycles. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 48, 103996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Jing, H.; Yin, Q.; Gu, X. Investigation on Mechanical and AE Characteristics of Yellow Sandstone Undergoing Wetting-Drying Cycles. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2020, 24, 3267–3278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backers, T.; Stanchits, S.; Dresen, G. Tensile Fracture Propagation and Acoustic Emission Activity in Sandstone: The Effect of Loading Rate. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2005, 42, 1094–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagar, R.V.; Srivastava, J.; Singh, R.K. A Probabilistic Analysis of Acoustic Emission Events and Associated Energy Release during Formation of Shear and Tensile Cracks in Cementitious Materials under Uniaxial Compression. J. Build. Eng. 2018, 20, 647–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Li, X.; Li, Z.; Chen, P.; Yang, X.; Liu, Y. Energy Distribution and Fractal Characterization of Acoustic Emission (AE) during Coal Deformation and Fracturing. Measurement 2019, 136, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wang, E.; Kong, X.; Ali, M.; Wang, D. Mechanical Behaviors and Acoustic Emission Fractal Characteristics of Coal Specimens with a Pre-Existing Flaw of Various Inclinations under Uniaxial Compression. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2019, 116, 38–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, Z.; Li, X.; Gong, F.; Du, K. Experimental Study on the Effect of Strain Rate on Rock Acoustic Emission Characteristics. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2020, 133, 104420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutler, N.; Nejati, M.; Valley, B.; Amann, F.; Molinari, G. On the Link between Fracture Toughness, Tensile Strength, and Fracture Process Zone in Anisotropic Rocks. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2018, 201, 56–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, M.; Ren, J.; Zhang, L.; Chen, X. Fracture Process and Instability Precursor Determination of Freeze-Thaw Red Sandstone Based on Acoustic Emission Monitoring. Eksploat. Niezawodn. Maint. Reliab. 2024, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Fan, J.; Guo, J.; Kong, F. Effect of Strain Rate on Mechanical Properties and AE Characteristics of Hard Rock Under the Impact of Uniaxial Compression. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2022, 40, 4313–4326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Li, J.; Wang, J. Effect of Creep Load on Fatigue Behavior and Acoustic Emission Characteristics of Sandstone Containing Pre-Existing Crack during Fatigue Loading. Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech. 2022, 119, 103296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Zhang, D.; Li, S.; Lu, J.; Li, Y. Fracture Evolution and Nonlinear Characterization of Thermally Damaged Sandstone under Uniaxial Compression Based on Acoustic Emission Parameters. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2023, 82, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, R.; Gao, M.; Xie, J. The Ultrasonic P-Wave Velocity-Stress Relationship and Energy Evolution of Sandstone under Uniaxial Loading-Unloading Conditions. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 2021, 9921716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inês Silva, M.; Malitckii, E.; Santos, T.G.; Vilaça, P. Review of Conventional and Advanced Non-Destructive Testing Techniques for Detection and Characterization of Small-Scale Defects. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2023, 138, 101155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Si, G.; Oh, J.; Canbulat, I.; Xiang, Z.; Li, T. A Pre-Peak Elastoplastic Damage Model of Gosford Sandstone Based on Acoustic Emission and Ultrasonic Wave Measurement. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2022, 55, 4819–4838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omrani, H.; Hajipour, M.; Jamshidi, S.; Behnood, M. A New Method in Reservoir Rock Classification in Carbonate and Sandstone Formations. J. Geophys. Eng. 2023, 20, 883–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).