Abstract
As digital infrastructures become increasingly dynamic and complex, traditional static access control mechanisms are no longer sufficient to counter advanced and persistent cyber threats. In response, Zero Trust Architecture () emphasizes continuous verification and context-aware access decisions. To realize these principles in practice, this study introduces a Trust Score ()-based access control model as a systematic alternative to legacy, rule-driven approaches that lack adaptability in real-time environments. The proposed model quantifies the trustworthiness of users or devices based on four core factors—User Behavior (B), Network Environment (N), Device Status (D), and Threat History (T)—each derived from measurable operational attributes. These factors were carefully structured to reflect real-world Zero Trust environments, and a total of 20 detailed sub-metrics were developed to support their evaluation. This design enables accurate and granular trust assessment using live operational data, allowing for fine-tuned access control decisions aligned with Zero Trust principles. A comprehensive sensitivity analysis was conducted to evaluate the relative impact of each factor under different weight configurations and operational conditions. The results revealed that B and N are most influential in real-time evaluation scenarios, while B and T play a decisive role in triggering adaptive policy responses. This analysis provides a practical basis for designing and optimizing context-aware access control strategies. Empirical evaluations using the UNSW-NB15 dataset confirmed the model’s computational efficiency and scalability. Compared to legacy access control approaches, the model achieved significantly lower latency and higher throughput with minimal memory usage, validating its suitability for deployment in real-time, resource-constrained Zero Trust environments.
1. Introduction
The traditional perimeter-based security model operates by establishing clear boundaries between internal and external networks and trusting the internal network. This model is based on the traditional view of security, where internal users are trusted and only external access is considered a potential threat. However, with cloud computing, increased use of mobile devices, the proliferation of remote work environments, and the sophistication of cyber threats, the limitations of this perimeter-based security model are becoming clear [,]. Insider threats, account takeover attacks, ransomware, and more exploit vulnerabilities in the traditional model of trusting internal networks, accelerating the shift to a zero trust security model.
Zero Trust Architecture () is based on the principle of “Never Trust, Always Verify” and performs thorough verification of all access requests before granting trust []. It is an approach that removes the distinction between inside and outside the network and continuously evaluates the trustworthiness of users and devices to enhance security. To effectively implement , real-time threat assessment and dynamic authentication enforcement are essential [].
In a Zero Trust environment, access control is a key element of security, performing the critical function of evaluating and determining who, where, and how to access. Traditional static access control approaches such as role-based access control (), attribute-based access control (), and risk-based authentication () are limited by their inability to reflect rapidly changing security threats and user behavior in real time [,]. To overcome these limitations, this research proposes dynamic authentication enforcement through trust score evaluation.
Trust Score comprehensively evaluates various factors such as user and device status, network environment, and past threat history to dynamically adjust access rights in real time. This enables continuous authentication by continuously monitoring user activity and changes in the environment, rather than simply authenticating at a point in time. By implementing flexible security policies that enforce or restrict access privileges based on context, organizations can quickly respond to changing security threats [,].
In this paper, we derive the main factors for calculating the Trust Score and propose a method for calculating the Trust Score based on them. In particular, we propose a mathematical model for calculating the Trust Score by systematically analyzing factors such as user behavior, network environment, device status, and past threat history. We also analyze the impact on the Trust Score due to changes in weight values through simulation and theoretical analysis for various scenarios, and propose customized weight setting information considering security factors specific to each industry.
The results of this study will provide practical guidance for organizations that want to adopt Zero Trust Architecture. In particular, it is expected to contribute to improving security through real-time threat detection and dynamic authentication enforcement, while optimizing operational efficiency and user experience.
Section 2 analyzes the differences between the existing access control method and the trust score-based access control method in the Zero Trust Architecture environment, and introduces the research background and related research that support the need for this research. Then, in Section 3, we derive the details of the major factors for calculating the Trust Score value, and introduce the mathematical modeling of the Trust Score model and the calculation examples for each major scenario. In Section 4, we verify the effectiveness of the model through simulation and theoretical analysis, and in Section 5, we assess the computational performance and scalability of the proposed Trust Score model and compare it with legacy models, demonstrating its suitability for real-time deployment Finally, Section 6 concludes with conclusions and future research directions to discuss the potential for further development of trust score-based access control and its applicability to various industries.
2. Background and Related Work
2.1. Traditional Access Control
2.1.1. Role-Based Access Control ()
Role-Based Access Control () is a method of granting access based on a user’s role. Users are managed to access specific resources based on their defined roles within the organization. While provides simplicity of management and policy consistency, it is inflexible to dynamic security needs due to static permission settings [].
Singh et al. [] propose a framework to leverage in Internet of Things () networks to improve the security and efficiency of data processing. Since it grants authorization based on predefined roles, it lacks dynamic response by failing to reflect the real-time state changes of devices or networks.
Butt et al. [] present an mechanism that monitors user behavior in an electronic health () cloud environment and assigns roles based on trust values. Although this study applies a trust-based model, it remains limited in reflecting fine-grained changes in user states in real time due to its role-centric nature, and lacks continuous validation.
Marquis [] investigates how effective systems are in mitigating insider threats in different organizational environments. The study proposes dynamic extensions to , but still fails to overcome the static nature of authorization management, which makes real-time threat response difficult.
Mpamugo et al. [] explore the integration of with the OAuth 2.0 protocol in mobile applications to manage network access and enhance security. Mobile networks are characterized by rapid environmental changes, which has not been reflected in the dynamic changes in the mobile environment and is vulnerable to anomalous login attempts or location-based anomaly detection.
Carvalho Junior et al. [] highlight the implementation characteristics, concerns, and limitations of in health information systems; specifically, they address security trends and limitations related to emergency access, authorization delegation, and cross-domain access control. In healthcare environments, emergency situations require rapid authorization changes, but RBAC’s static authorization structure does not support this quickly enough.
2.1.2. Attribute-Based Access Control ()
Attribute-Based Access Control () is an approach to determining access rights based on attributes of users, resources, and environments. allows for policy flexibility and fine-grained access control, but complex policy management is considered a drawback [].
Servos et al. [] provided a comprehensive review of the concept and recent research trends in , highlighting issues such as delegation, management, auditing, and scalability. However, relies on predefined attribute values, which makes it difficult to reflect changes in attribute values immediately and limits real-time threat detection and response.
Singh et al. [] reviewed models in cloud computing environments and attempted to overcome the limitations of existing models by proposing attribute and user revocation mechanisms. Although they proposed user and attribute revocation mechanisms, the problem remains that attribute changes are not immediately reflected in security policies.
Fernandez et al. [] proposed a category-based model to streamline attribute management in systems and simplify the definition and management of access control policies. While category-based models increase management efficiency through attribute grouping, they have limitations in reflecting continuous changes in the environment in real time.
Panende et al. [] evaluated the security and efficiency of access control models by comparing and in Digital Evidence Storage (). While attribute-based enables fine-grained control, conflicts between attributes complicate management, and complexity exists in updating and managing policies.
Xu et al. [] proposed an Attribute-Based Access Control () mechanism that considers both privacy and efficiency. EPABAC focuses on granting access rights based on attributes, but it has limited ability to reflect real-time changing user behavior or network environment.
2.1.3. Risk-Based Authentication ()
Risk-Based Authentication () dynamically adjusts authentication strength by assessing the risk level of the user and environment in real time. balances user convenience and security, but risk assessment accuracy is a key challenge [].
Makowski et al. [] re-evaluated the systems of major online services through black-box testing, revealing differences based on account creation and rare activations, highlighting their complexity and limitations, and suggesting future research directions.
Büttner et al. [] analyzed how mechanisms are applied during account recovery in a major online service and presented a maturity model for . Security vulnerabilities can exist in the account recovery process.
Unsel et al. [] explored how to incorporate risk-based access control into the authentication process in OpenStack. Their approach assesses risk at the point of login and requires additional authentication, but does not perform continuous authentication after login and has limited capabilities for real-time detection and immediate access blocking.
Wiefling et al. [,] evaluated the security and usability of systems in large-scale online services and proposed improvements through machine learning-based optimization. They operate based on predefined risk assessment criteria but lack the ability to adjust weights or thresholds in real time based on changing circumstances, which is a challenge.
2.2. Zero Trust Security Models
2.2.1. Zero Trust Architecture
Key elements of Zero Trust security include strict access controls, least privilege access, micro-segmentation, and continuous monitoring and validation. Collectively, these elements significantly improve network security by minimizing the attack surface and preventing lateral movement within the network [].
NIST 800-207 [] defines Zero Trust Architecture as a framework consisting of the elements necessary for security policy decisions and enforcement. Figure 1 below illustrates the logical components of a Zero Trust Architecture and their interactions. This conceptual diagram illustrates the interaction of the Policy Decision Point () and Policy Enforcement Point (), which are the core elements of the Zero Trust Architecture.
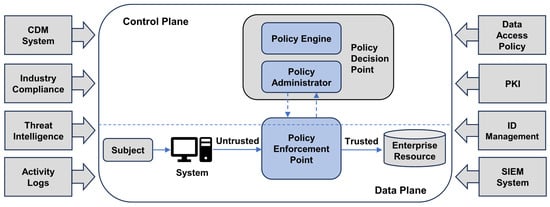
Figure 1.
Zero Trust Architecture logical concepts as defined by NIST 800-207.
The Policy Decision Point () functions as a key component for evaluating access requests and making security decisions based on predefined policies and real-time contextual information. PDPs collect data from a variety of sources, including user identity, device state, network environment, and behavioral patterns. This information is analyzed to determine whether an access request should be granted, denied, or require additional authentication, and the forwards the results to a Policy Enforcement Point () for enforcement. This continuous assessment enables you to maintain a flexible and adaptive security posture against internal and external threats.
Policy Enforcement Points () are responsible for enforcing access control decisions made by the . are deployed at the network perimeter or within specific applications, intercepting access requests and forwarding them to the PDP for evaluation. Upon receiving the PDP’s decision, the takes appropriate actions, such as allowing, denying, or requiring additional authentication for the request. Additionally, continuously monitor active sessions and can request real-time re-evaluation from the if anomalous behavior is detected. Such continuous monitoring enables immediate security responses even after initial access is granted.
The interaction between and forms the backbone of Zero Trust Architecture, embodying the principle that all access requests must be thoroughly validated and continuously monitored.
2.2.2. Zero Trust Use Cases
Zero Trust Architecture () is being widely adopted to enhance security across a variety of industries. As cyber threats escalate globally and cloud transformation and remote work environments become more common, the adoption of Zero Trust Architectures to overcome the limitations of traditional perimeter-based security is accelerating, especially after the U.S. government issued an executive order (EO 14028) mandating federal agencies to transition to Zero Trust. These global trends are driving technology standardization discussions and intensifying competition to develop ZTA-based security solutions and services across various industries.
A prominent example of a successful application of in this context is Google’s BeyondCorp [,,]. BeyondCorp breaks away from the traditional perimeter-based security model and enhances security by thoroughly validating all requests without distinguishing between inside and outside the network. This model dynamically grants access rights based on contextual information such as user identity, device status, location, and time, enabling employees to work securely from anywhere in the world. With the introduction of BeyondCorp, Google has dramatically improved its ability to respond to internal threats and external attacks and is considered a prime example of how the Zero Trust model can work effectively in a large-enterprise environment.
Another example of Zero Trust in action is Microsoft’s implementation of Azure Active Directory and its Zero Trust Security Framework []. Microsoft has adopted Zero Trust principles to enhance security across its cloud environment; the platform authenticates users and devices in real time and dynamically adjusts access privileges by continuously assessing risk levels.
Government agencies such as the U.S. Department of Defense (DoD) are also adopting the Zero Trust model to protect sensitive information []. These examples demonstrate that Zero Trust Architecture is revolutionizing the security landscape for organizations and is becoming a core component of modern security strategies.
2.3. Trust Score-Based Access Control
To effectively implement , a mechanism that goes beyond simply verifying access requests and can evaluate threats in real time and dynamically strengthen authentication is necessary. In this process, the concept of Trust Score is essential [].
Traditional access control approaches (, , ) manage access rights of users and resources based on static policies. However, these approaches face limitations in a Zero Trust environment due to the following reasons:
- Limitations of static policies: In an environment where a user’s environment or circumstances can change in real time, fixed access rights are insufficient to detect or respond to new threats.
- Lack of real-time threat assessment: Traditional access control performs authentication only at the point of access, so it cannot reflect changes in user behavior or environmental factors.
- Complex network environments: The adoption of cloud, mobile, and IoT devices has blurred network boundaries, making traditional access control models difficult to apply.
Trust Score is a trust algorithm-based access control approach that quantifies a user’s level of trust and dynamically adjusts access privileges in real time []. It provides the continuous verification and context-aware capabilities that are essential in a Zero Trust environment.
- Real-time data analysis: The Trust Score is updated in real time based on a comprehensive assessment of user behavior, network environment, device health, past threat history, and more.
- Dynamic access authorization: Access permissions are dynamically adjusted based on the Trust Score, requiring additional authentication or restricting access when trust levels are low.
- Flexible policy management: Because Trust Score is weighted, it can be flexibly adjusted to fit your organization’s environment.
The introduction of Trust Score quantifies a user’s trustworthiness, requiring them to align with access control policies and achieve a Trust Score that meets a specified threshold before accessing resources []. This has become a key element of access control in the implementation of Zero Trust architectures.
Table 1 analyzes the differences between traditional and Trust Score-based approaches, highlighting the security, scalability, and real-time detectability of Trust Score-based access control. Trust Score is also an effective way to maintain least privileged access based on continuous validation and real-time threat assessment, and provides high flexibility to apply customized access policies to different security requirements.

Table 1.
Comparative analysis of traditional access control and Trust Score-based Zero Trust.
3. Trust Score Modeling and Access Control Framework in Zero Trust Architecture
3.1. Trust Score Factors and Evaluation Criteria
Trust Score is a key mechanism for implementing dynamic access control in Zero Trust Architecture (), which evaluates various security factors in real time through a weight-based formula to produce a trust score []. The need for Trust Score stems from the fact that traditional static access control models (, , ) have limitations in real-time threat response and continuous authentication, as discussed theoretically in Section 2. To overcome these limitations, Trust Score uses continuous data collection and real-time analytics to dynamically assess a user’s trustworthiness and make decisions to allow access, require additional authentication such as Multi-Factor Authentication (), which requires two or more verification factors, or block access. Furthermore, Trust Score enhances security resilience by enabling adaptive policy enforcement that immediately responds to changing risk scenarios, minimizing the attack surface and effectively mitigating potential breaches.
To calculate the Trust Score, detailed items and evaluation criteria were derived for the four key factors. The following describes the main aspects of each factor.
- User Behavior (): Collect and evaluate data such as users’ login patterns, unusual access attempts, login time and location, etc. This factor, summarized in Table 2, is important for detecting insider threats and preventing account takeover.
 Table 2. User Behavior (B) Factor Details.
Table 2. User Behavior (B) Factor Details. - Network Environment (): Assesses the trustworthiness of the network by looking at the IP reputation of users, VPN usage, network traffic analysis, and more. The detailed items are shown in Table 3, which is essential for detecting external attacks and network-based threats.
 Table 3. Network Environment (N) Factor Details.
Table 3. Network Environment (N) Factor Details. - Device status (): Determine the security status of a device by assessing whether it is security patched, antivirus status, and whether the device is authenticated. The evaluation criteria are described in Table 4, which is especially important in BYOD environments or remote work environments.
 Table 4. Device Status (D) Factor Details.
Table 4. Device Status (D) Factor Details. - Threat History (): Analyzes a user’s history of previous security incidents, policy violations, etc., to assess their long-term trustworthiness. The detailed factors are presented in Table 5, and this is useful for proactively blocking repeat threat behavior.
 Table 5. Threat History (T) Factor Details.
Table 5. Threat History (T) Factor Details.
These factors are collected, analyzed, and weighted in real time to calculate a Trust Score, which is dynamically recalculated to trigger additional authentication or block access upon detecting anomalous behavior, providing a significant advantage over static models.
3.2. Mathematical Modeling and Computation of Trust Score
Trust Score () is calculated through a weighted average formula that reflects the evaluation scores and weights of various security factors. The model quantifies factors of user behavior (B), network environment (N), device state (D), and threat history (T) to enable dynamic access control.
3.2.1. Trust Score Calculation Formula
The Trust Score is calculated by the following formula:
- : weight of factor i();
- : evaluation score of factor i (range: 0 to 100);
- n: total number of evaluation factors (in this study, ).
Specifically, this study includes the following factors:
- : weights of each factor (their sum equals 1);
- : evaluation scores for user behavior, network environment, device status, and historical threat records, respectively.
3.2.2. Weight Assignment Rationale
The assignment of the weights (B = 0.4, N = 0.3, D = 0.2, T = 0.1) was grounded in three complementary perspectives.
First, existing research on dynamic trust evaluation emphasizes that user behavior and network context are the most critical and dynamic indicators for access control decisions in Zero Trust environments. Wang et al. [] proposed a Zero Trust-based dynamic access control model that integrates user behavior and network context with reinforcement learning, demonstrating their significant contribution to trust computation.
Second, empirical evidence from the UNSW-NB15 dataset further supports this prioritization. Feature importance analysis indicates that behavior-related attributes (e.g., login failures, access anomalies) and network-related attributes (e.g., protocol states, source/destination bytes) contribute more substantially to detection accuracy compared with device state or historical threat attributes. Kasongo and Sun [] confirmed that flow and content features are the most decisive in intrusion detection performance, aligning with the higher weight assignment for B and N.
Third, industry practice and security incident reports highlight the central role of human behavior and network vectors in real-world breaches. The 2023 Verizon DBIR [] reported that over 70% of security incidents involved the human element, including misuse of credentials, social engineering, or anomalous user activities. This reinforces the decision to assign higher weights to B and N, as they capture the most dynamic and risk-sensitive factors in trust assessment.
Taken together, theoretical reasoning, empirical validation, and industry evidence justify assigning relatively higher weights to user behavior (B = 0.4) and network context (N = 0.3), while device state (D = 0.2) and threat history (T = 0.1) were given lower weights due to their limited discriminative power in real-time trust evaluation.
These example scores were derived based on the predefined evaluation criteria presented in Section 3.1 and were intended only to illustrate how the Trust Score formula operates under different conditions.
3.2.3. Formula Calculation Examples
This section provides simplified examples of Trust Score () computation, using the four core factors (), their sub-factor scores (0–100), and the weighted formula in Section 3.2.1 (default weights: wB = 0.4, wN = 0.3, wD = 0.2, wT = 0.1). Final values are compared against thresholds (≥80 allow, 60–79 require additional authentication, <60 block).
(1) Case 1: Low-risk scenario
A user connects from a familiar environment with normal behavior. The remains high, and direct access is granted.
- Situation: A normal pattern of access in a secure environment (e.g., internal network).
- Scoring:
- –
- B = 90 points (Rationale: Overall good, with minor changes in some items);
- –
- N = 85 points (Rationale: Overall good);
- –
- D = 85 points (Rationale: Managed devices, good condition);
- –
- T = 80 points (Rationale: no history of severity).
- Calculation: = (0.4 × 90) + (0.3 × 85) + (0.2 × 85) + (0.1 × 80) = 86.5 points.
- Result: 86.5 points (above 80) → Decision to allow access.
(2) Case 2: Medium-risk scenario
Access originates from an external network using a personal device, though behavior is otherwise normal. The falls into the intermediate range, requiring Multi-Factor Authentication.
- Situation: Behavior is good, but use of external public networks (N) and BYOD devices (D).
- Scoring:
- –
- B = 80 points (Rationale: Relatively good);
- –
- N = 50 points (Rationale: Public network use reduces trust);
- –
- D = 65 points (Rationale: Moderate security with BYOD devices);
- –
- T = 80 points (Rationale: Good historical record).
- Calculation: = (0.4 × 80) + (0.3 × 50) + (0.2 × 65) + (0.1 × 80) = 68.0 points.
- Result: 68.0 points (60–79 points) → Decide it requires additional authentication (MFA).
(3) Case 3: High-risk scenario
Suspicious behavior is combined with an untrusted network, non-compliant device, and poor history. The TS drops below 60, leading to access denial.
- Multiple risk events including abnormal times/login attempts (B), suspicious IPs (N), and vulnerable devices (D).
- Scoring:
- –
- B = 35 points (Rationale: Highly suspicious behavior);
- –
- N = 25 points (Rationale: Network environment is highly risky);
- –
- D = 40 points (Rationale: Device security is very weak);
- –
- T = 30 points (Rationale: Poor past history).
- Calculation: = (0.4 × 35) + (0.3 × 25) + (0.2 × 40) + (0.1 × 30) = 32.5 points.
- Result: 32.5 points (less than 60 points) → Decision to block access.
3.3. Access Control Process Using Trust Score in
The real-time enforcement of Trust Score is a key mechanism for implementing continuous security assessment and dynamic access control within a Zero Trust Architecture (). Unlike traditional access control approaches, Trust Score provides the ability to quickly respond to security threats through real-time data collection and dynamic weight adjustments. This chapter describes how Trust Score interacts with Policy Decision Points () and Policy Enforcement Points () to control access privileges, and how it integrates with existing security policies.
In a environment, Trust Score-based access control is accomplished through the following step-by-step process, as shown in Figure 2.
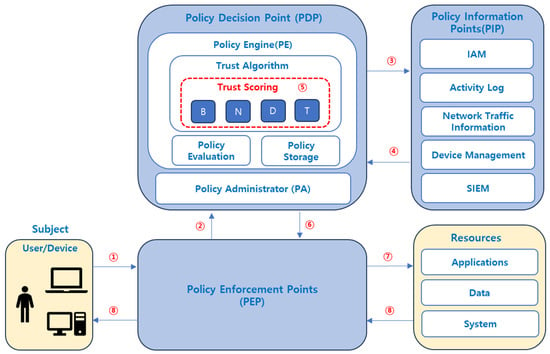
Figure 2.
Trust Score access control process in a ZTA environment.
- Access request: A user attempts to access a system or application.
- Request Intercept: The PEP intercepts an access request and forwards it to the PDP.
- Data collection requests: The PDP requests information from PIP-related systems to collect key element information (user behavior, network environment, device status, past threat history, etc.).
- Real-time information response: Each PIP system responds to the PDP in real time with the status of each key element related to the user.
- Calculate Trust Score: The PDP calculates a weighted Trust Score based on the collected data.
- Security decision: The PDP makes a decision to allow access, require additional authentication, or block access based on the calculated Trust Score.
- Execute the decision: The PEP executes the PDP’s decision, and the PEP connects a session to grant access to the resource as requested by the Subject.
- Send resource information: The resource responds to the user’s request and terminates the session if there is no response for a period of time.
This flow is a mechanism that practically implements Zero Trust Architecture. In addition, through continuous monitoring, the is continuously re-evaluated while the session is maintained, and immediate response is taken when anomalies are detected.
Trust Score flexibly integrates with existing security policies to enhance security. Existing security mechanisms such as Multi-Factor Authentication (), network isolation, and data encryption can be combined with Trust Score-based access control to dynamically adjust policies based on context. For example, you can improve the user experience by skipping additional authentication when the Trust Score is above a certain threshold, or automatically require or enforce network isolation when it’s below the threshold. This dynamic policy enforcement optimizes the user experience by minimizing unnecessary authentication steps while maintaining security levels.
You can also set weights and adjust thresholds to optimize policies to meet your organization’s security needs. For example, you can increase the network environment (N) weight for connections from certain regions or network environments to strengthen your response to external threats.
3.4. Benefits of Trust Score-Based Access Control
Trust Score-based access control effectively supports the core principles of Zero Trust Architecture—Continuous Verification and Least Privilege Access—and offers several advantages that overcome the limitations of traditional access control.
- Enhanced real-time threat detection and response: Trust Score continuously assesses the health of users and devices based on real-time data. This enables immediate detection of new threats and dynamic adjustment of access permissions as they arise.
- Enhanced dynamic authentication: Trust Score automatically adjusts authentication strength based on the user’s trust level. Legitimate users get seamless access without unnecessary additional authentication, while suspicious users are asked for additional authentication (e.g., two-factor authentication, biometrics, etc.).
- Flexible security policy management: Trust Score-based systems can set customized security policies by adjusting the weights to meet enterprise needs. This ensures the flexibility of security policies for different industries (finance, healthcare, cloud, etc.).
- Improve operational efficiency: Automated Trust Score assessment and access control minimizes administrator intervention, reducing operational costs and reducing the complexity of security management.
- Improve user experience: Minimize unnecessary authentication processes for legitimate users to maintain business efficiency and increase user satisfaction.
4. Trust Score Sensitivity Analysis and Policy Simulation
4.1. Simulation Environment Setup
To verify the validity and practical effectiveness of the proposed model, we constructed a simulation environment that mirrors the operational dynamics of real enterprise networks. The purpose was to evaluate how the model responds to varying conditions in user behavior, network status, device health, and historical threat patterns.
- Virtual Environment Configuration
A testbed was designed to simulate realistic access scenarios for users and devices. This environment includes diverse conditions—ranging from benign to potentially malicious behaviors—to analyze the model’s adaptability in different Zero Trust contexts.
- Data collection
During each simulation run, the Trust Score values were recorded for all four evaluation factors. Real-time data, such as behavioral logs, network events, device posture, and known threat records, were generated and used to calculate the for each simulated case.
- Weight and Threshold Configuration
To reflect importance, default weights were assigned to the four factors as follows:
User Behavior () = 0.4, Network Environment () = 0.3, Device Status () = 0.2, Threat History () = 0.1.
These weights emphasize the role of B and N in enabling real-time risk detection and access decisions, while assigning supportive but lower influence to more static or historical indicators like D and T.
Access control thresholds were defined as follows:
- −
- Allow access if ≥ 80.
- −
- Require multi-factor authentication (MFA) if is between 60 and 79.
- −
- Block access if < 60.
- Simulation Method:
- Setting Variables by Factor:
- We set the input values for , and T to 30, 50, 70, and 90, respectively.
- We assigned weight values for the four factors using the default configuration of 0.4 (B), 0.3 (N), 0.2 (D), and 0.1 (T).
- To assess factor impact, we varied the value of one factor at a time while keeping the others fixed and observed the resulting changes.
- Simulation Tools:
- We ran large-scale simulations using data analysis tools such as Python.
- We evaluated the responsiveness and sensitivity of Trust Score based on data from various scenarios.
This simulation configuration provided a foundation for analyzing the responsiveness, sensitivity, and policy applicability of the Trust Score model in Zero Trust environments.
4.2. Sensitivity Analysis of Trust Score by Factor Value Changes
Based on the data collected through simulation, we further analyzed the change pattern of Trust Score in more detail. We compared the response of Trust Score to changes in the value of each factor to derive specific insights for optimizing security policies.
In Table 6 and Figure 3, we fixed the weights (B = 0.4, N = 0.3, D = 0.2, T = 0.1) to analyze the impact of changing the values of each factor, and numerically analyzed the impact of each factor on the Trust Score value and how sensitive it is to changing the values of each factor to 90/70/50/30.

Table 6.
Calculated Trust Score by changing the value of each factor (weights B = 0.4, N = 0.3, D = 0.2, T = 0.1).
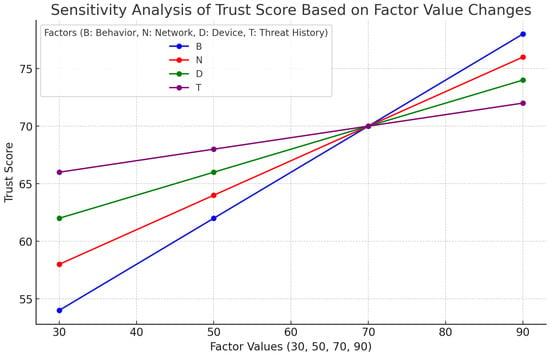
Figure 3.
Sensitivity analysis of Trust Score to changes in factor values.
The results of the impact and sensitivity analysis of the Trust Score value according to the change of each factor value through simulation are as follows:
- Prioritization of User Behavior ()
- –
- User Behavior, set to a weight of 0.4, shows the largest change in Trust Score value (24 points) and is found to have the largest impact and the most sensitivity to changes in factor values. The higher the B value, the greater the increase in , which provides important insights in insider threat or account takeover scenarios.
- –
- Detailed analysis: A increase of 20 in the User Behavior score is associated with an average 8-point increase in . User behavior is a key factor for anomaly detection, as unusual access patterns or changes in usage behavior sensitively change the Trust Score.
- Importance of Network Environment ()
- –
- With a weight of 0.3, the network environment has a large variation in Trust Score value (18 points) and has the second-largest impact on Trust Score after user behavior. decreases rapidly in untrusted network environments, which suggests increased security in remote work environments
- –
- Detailed analysis: increased by an average of 6 points when the network environment score increased by 20. This is a useful indicator for detecting external attacks or evaluating the stability of remote access environments, and shows that network environments are volatile and subject to change, which has a constant impact on Trust Score.
- The impact of device health () and past threat history ()
- –
- With weights of 0.2 and 0.1, respectively, device state ( variance of 12 points) and past threat history ( variance of 6 points) have a relatively small impact on Trust Score. However, when utilized in conjunction, these two factors contribute to balancing security policies.
- –
- Detailed analysis: A 20-point increase in Device Health Score increased by 4 points, and a 20-point increase in Past Threat History Score increased by 2 points. Device Health Score measures device integrity and security health, and plays an important role in maintaining a trusted environment, while Past Threat History has little impact on the current Trust Score, because in a Zero Trust Architecture environment, the focus is on current health rather than past history.
This in-depth analysis confirms that user behavior (B) and network environment (N) are the key factors in Trust Score-based access control, especially in terms of enhanced monitoring for real-time insider threat detection.
4.3. Sensitivity Analysis of Trust Score by Factor Weight Changes
In this section, we quantitatively analyze how the four factors (B: Behavior, N: Network, D: Device, and T: Threat History) that make up the Trust Score () in the Zero Trust policy model respond to changes in the when the factor values are fixed and only the weight of each factor is varied. We derive the sensitivity of each factor and quantitatively evaluate its impact on policy triggers.
The experiment consists of simulations to measure the impact of changing the weight of each factor within the Trust Score () calculation model on . The key objective of the experimental design is to determine how sensitive is to adjusting the weight of each factor independently. This allows us to identify highly sensitive factors and provide quantitative suggestions on which factors to focus on in policy design.
- Setting fixed factor values:
- –
- B (Behavior) = 85: Login time/location/behavior falls into the normal category.
- –
- N (Network) = 75: Access to corporate internal network, no VPN bypass.
- –
- D (Device) = 65: Frequently used device, but some security warnings present.
- –
- T (Threat History) = 55: Some minor threat history exists.
- Conditions for changing weights:
- –
- For each factor (), we vary the weights to 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, and 0.8.
- –
- For the other three factors, the remaining weights are distributed equally 1:1:1, so that the total sums to 1.
The experimental environment in Table 7 and Figure 4 was designed to determine which factor weight adjustments have the greatest impact on reaching the policy trigger boundary, based on the “average state of a real user or device”. Specifically, simulation results were calculated and plotted to quantitatively show the sensitivity of values to crossing policy bands (Allow ≥ 80, MFA 60–79, Block < 60).

Table 7.
TS simulation results based on flexible weight adjustment.
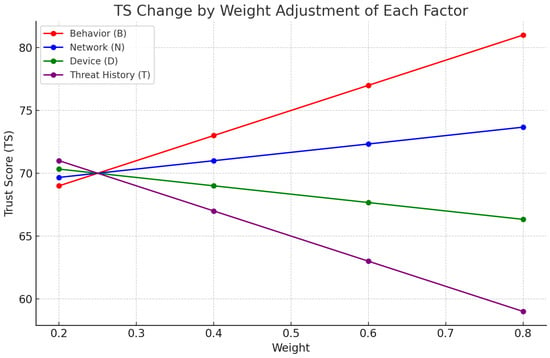
Figure 4.
TS change by weight adjustment of each factor.
The results of the simulation analysis of values by changing the weight value of each factor are shown below.
In Table 8, a change of 12 or more means that changing the weight of a particular factor alone can result in a change that crosses the policy threshold (e.g., Allow ≥ 80, Block < 60). For example, increasing the weight of B from 0.2 to 0.8 would increase from 69.00 to 81.00, which shows that the policy band can be shifted from to Allow simply because the user has a high behavior-based trust.

Table 8.
Sensitivity analysis summary.
Conversely, if we increase the weight of the T factor, plummets from 71.00 to 59.00, indicating that assigning high importance to users with a history of past threats can trigger a trigger to block access.
A change of more than 10 indicates that this factor is a highly sensitive variable for security policy decisions, and weighting is a key factor in ensuring policy agility and flexibility. Based on this sensitivity, policy designers can dynamically tune Trust Score to meet real-time security needs or service level agreements (SLAs).
Through the simulation results, we quantitatively analyzed the sensitivity of each factor’s weight change to the Trust Score (). The B and T factors have the highest sensitivity, suggesting that adjusting the weights of these factors in the policy trigger range (Allow ≥ 80, MFA 60–79, Block < 60) has a decisive impact on the policy transition.
- The B factor has a sharp increase in as its weight increases, contributing to the rapid induction of a permissive policy for legitimate users.
- The T factor is a threat history-based factor, with a sharp decrease in as its weight increases, enabling policy to quickly block or require additional authentication.
4.4. Summary of Simulation Results
The simulations in this study served three purposes: (1) to identify sensitive elements that can act as policy triggers; (2) to verify numerical thresholds for policy decisions (≥80 allow, 60–79 MFA, <60 block); (3) to suggest design directions for Trust Score–based policies suited to different industry contexts.
As summarized in Table 9, the experiments consistently showed that user behavior (B) and threat history (T) are the most sensitive factors, often shifting the Trust Score across decision thresholds, while network (N) and device (D) exert more moderate influence. This indicates that prioritizing B and T in policy design ensures timely detection of abnormal access, while N and D provide contextual balance.

Table 9.
Simulation result summary.
Taken together, these findings highlight that the most effective policy design centers on the B factor, with flexible adjustments to N or T as needed. This approach provides a practical basis for achieving real-time responsiveness, high sensitivity, and industry-specific applicability in the TS-based Zero Trust model.
5. Empirical Evaluation of Performance and Scalability
5.1. Experimental Setup
To empirically evaluate the scalability and computational burden of the proposed Trust Score () model, all experiments were conducted in a controlled desktop computing environment. The implementation and testing were carried out using a Python-based script, which is publicly available in the code repository [], designed to process large-scale tabular data extracted from the UNSW-NB15 dataset.
The system specifications for the performance evaluation are as follows:
- CPU: Intel(R) Core(TM) Ultra 7 155H 3.80 GHz.
- Memory: 32 GB DDR4 RAM (3200 MHz).
- Storage: 1 TB NVMe SSD (PCIe 4.0).
- Operating System: Windows 11 (64-bit).
- Python Environment: Python 3.13.
- Libraries: pandas, numpy, psutil, memory_profiler, concurrent.futures.
The Trust Score computation logic was implemented using Python’s data processing stack (pandas and numpy). Performance monitoring during batch processing was conducted using the psutil and memory_profiler libraries to track CPU utilization, memory usage, and processing time.
The dataset was loaded in CSV format and segmented into test batches of 10 K, 100 K, and 1 million rows. The values were computed per row using a weighted linear formula involving four components (), derived from preprocessed features in the UNSW-NB15 dataset. In addition to UNSW-NB15, we further incorporated the CICIDS2017 dataset (Wednesday subset), which contains both benign and multiple DoS/DDoS attack traffic, to validate the generalizability of the proposed model across different environments. For CICIDS2017, a similar preprocessing pipeline was applied, and the results are compared in Section 5.2.
To evaluate the scalability, experiments were conducted with varying data sizes while measuring execution time and throughput. For assessing computational burden, CPU usage, memory consumption, and processing latency were monitored throughout the experiment.
5.2. Cross-Dataset Performance Evaluation (UNSW-NB15 vs. CICIDS2017)
To verify the generalizability of the proposed Trust Score () model, we conducted additional experiments using not only the UNSW-NB15 dataset but also the CICIDS2017 dataset. While UNSW-NB15 includes a wide variety of network-based attack categories such as exploits, fuzzers, and denial-of-service (DoS), the CICIDS2017 dataset (Wednesday subset) contains both benign traffic and multiple DoS/DDoS scenarios that simulate large-scale flooding attacks. This combination allowed us to evaluate the model across heterogeneous network environments.
Table 10 presents the classification performance of the proposed model on the two datasets. On UNSW-NB15, the model achieved an accuracy of approximately 95.9% and an F1-score of 0.97, demonstrating strong performance under diverse attack types. On CICIDS2017, the results were nearly perfect, with accuracy, recall, and F1-score values close to 1.0. The exceptionally high performance on CICIDS2017 can be attributed to the distinct traffic patterns of DoS attacks, which make the separation between benign and malicious flows relatively straightforward.

Table 10.
Performance evaluation of the proposed TS model on UNSW-NB15 and CICIDS2017 datasets.
These findings highlight that the model maintains consistently high performance across different datasets and attack scenarios. The results confirm the robustness and general applicability of the proposed approach beyond a single dataset. However, it should also be noted that further evaluation with IoT- and cloud-oriented datasets (e.g., Bot-IoT, TON_IoT) is required to validate the model in broader real-world contexts, which will be considered in future research directions.
5.3. Performance Analysis Under Fixed Data Volume
To evaluate the computational efficiency of the proposed model under a fixed data volume, an empirical experiment was conducted using the UNSW-NB15 dataset. The dataset includes 175,000 traffic flow records labeled with normal and attack categories. Each record was processed to calculate a value based on the model’s four core elements: user behavior (B), network environment (N), device status (D), and threat history (T).
The computation was implemented in Python and executed on a standard workstation. The evaluation metrics included total processing time, per-row computation time, memory usage, and throughput measured in Trust Score computations per second ().
Each of the four components was derived from specific features within the UNSW-NB15 dataset. Table 11 below presents the mapping between each factor—user behavior (B), network environment (N), device status (D), and threat history (T)—and the corresponding dataset features used in the calculation.

Table 11.
Mapping of Trust Score factors to UNSW-NB15 dataset features.
The final value is calculated using a weighted sum:
The results in Table 12 show that the computation is extremely lightweight. The average processing time per row was only 0.0138 ms, and the total memory footprint remained under 8 MB, even when handling a dataset of substantial size. The model sustained a throughput of over 72,000 trust evaluations per second, which strongly supports its use in real-time decision-making systems within Zero Trust environments.

Table 12.
Experimental result.
5.4. Scalability Testing Under Varying Dataset
To assess the scalability of the proposed Trust Score () model under varying dataset sizes, a series of experiments was conducted with increasing volumes: 10,000, 50,000, 100,000, and 1,000,000 records. The objective of this analysis is to validate whether the model can maintain stable performance as the number of evaluation instances grows. This scalability is a crucial requirement for real-time deployment in Zero Trust environments. As shown in Table 13 below, the results demonstrate the model’s ability to sustain consistent computational performance across varying data scales.

Table 13.
Trust Score calculation performance at different data scales.
Since the original UNSW-NB15 dataset contains approximately 175,000 rows, the 1 million record case was generated by duplicating the available dataset to simulate large-scale environments without altering its feature distribution.
The results demonstrate a linear scalability pattern:
- The average computation time per row remains nearly constant across all dataset sizes, indicating that the model’s processing time increases proportionally with input volume rather than exponentially.
- Memory usage also increases gradually in proportion to the data size, showing no abrupt resource spikes even at one million records.
- Most importantly, the model achieves a throughput of over 70,000 Trust Score computations per second () in all scenarios, including the largest-scale test, which suggests that the model maintains performance even under high load.
This computational profile ensures that the model can be integrated into systems where real-time decisions are required at scale—such as user authentication gateways, micro-segmentation controllers, and security operations center () platforms—without introducing significant latency or resource overhead.
The experiments confirm that the proposed model is computationally lightweight, resource-efficient, and scalable, making it well-suited for deployment in practical Zero Trust environments that must process large volumes of contextual data continuously.
5.5. Comparative Benchmark with Legacy Access Control Models
To further validate the computational efficiency of the proposed Trust Score ()-based access control model, a comparative experiment was conducted against widely adopted legacy access control approaches. Specifically, the evaluation included Role-Based Access Control (), Attribute-Based Access Control (), and Risk-Based Access Control (). Unlike theoretical simulations, this benchmark was performed using the actual UNSW-NB15 dataset, which contains access-level network traffic data derived from real-world scenarios. All models were evaluated on the same dataset under identical hardware conditions. Prior validation confirmed that the model maintains consistent latency regardless of data volume, ensuring the fairness and generalizability of this comparison
Each model was operationalized with a Python-based evaluation logic:
- : Static role mapping and predefined permissions.
- : Attribute-rule matching using multiple features (e.g., protocol, flags).
- : Dynamic risk assessment based on context and event frequency.
- (Ours): Weighted arithmetic computation based on four normalized features ().
To ensure fairness, these implementations were executed under identical dataset size and hardware conditions. No system-level optimizations (e.g., caching or indexing) were applied, as the goal was to measure the intrinsic computational cost of each model in a uniform setting. For transparency and reproducibility, the complete implementation, including the comparative benchmarking scripts, is available in our GitHub repository []. The experiments were implemented using Python 3.10+, TensorFlow 2.12.0, and Scikit-learn 1.3.1.
As shown in Table 14, the proposed model significantly outperformed all legacy models in both latency and throughput. It achieved an average processing time of 0.0137 ms per record—approximately 3 to 4 times faster than the other approaches—and processed over 70,000 trust evaluations per second. These improvements are attributed to the model’s lightweight computational structure, which applies basic normalization and weighted summation over a minimal number of numeric inputs. It is noteworthy that the latency result in this benchmark closely aligns with the computational burden analysis conducted earlier (0.0138 ms/record, Section 5.3), confirming the consistency of the model’s performance across different evaluation scenarios. Overall, the model not only enables more adaptive and context-aware access decisions, but also imposes minimal computational overhead—making it well-suited for real-time Zero Trust deployment environments such as endpoint agents, network gateways, and security operations platforms.

Table 14.
Access Control model performance comparison.
Taken together, these results not only confirm the superior efficiency of the proposed Trust Score model compared to legacy access control approaches, but also demonstrate its stability across different evaluation settings. These findings provide a solid foundation for the broader discussion and future research directions presented in Section 6.
6. Conclusions and Future Research Directions
6.1. Contribution
This study makes three main contributions.
First, it defines four critical trust factors—user behavior (B), network environment (N), device status (D), and threat history (T)—and specifies 20 operational sub-metrics to compute the Trust Score. This structured framework provides the first concrete basis for aligning theoretical trust modeling with real-time decision-making requirements in Zero Trust environments.
Second, through simulation-based sensitivity analysis, we identified how each factor affects Trust Score outcomes. The results show that B and N are most sensitive for capturing dynamic user and network risks, while B and T are decisive in shifting policy triggers between allow, , and block decisions. These findings offer practical guidance for assigning weights and thresholds in adaptive access policies.
Third, empirical evaluation demonstrated that the model is lightweight and highly scalable. It achieved low latency (0.0138 ms/record) and high throughput (>70,000 TPS), even when tested with one million records. Comparative benchmarking further confirmed its superiority over legacy models such as , , and in both computational efficiency and deployment readiness. Collectively, these contributions bridge theory with operational practice and provide actionable insights for Zero Trust policy architects and implementers.
6.2. Future Research Directions
While this study presents a Trust Score-based Zero Trust policy model, further research is needed to enhance its scalability, universality, and robustness. We suggest the following directions:
(1) Dynamic Weight Optimization with AI/ML
Incorporating machine learning techniques (e.g., supervised or reinforcement learning) to adjust weights in real time will enable adaptive responses to evolving threats and user contexts.
(2) Federated Trust Score Learning
To ensure data privacy across organizations, applying federated learning can allow collaborative model training without sharing raw data, thereby supporting secure cross-domain deployments.
(3) Exploring Non-Linear Trust Score Models
While the current Trust Score model adopts a linear weighted approach for simplicity and real-time operability, it may not fully capture complex interactions among factors. For example, simultaneous risks in user behavior and network environment could escalate nonlinearly rather than additively. Future work will explore non-linear functions (e.g., logistic, exponential) and AI-based methods (e.g., neural networks, ensemble learning) to better reflect such compounding effects while maintaining interpretability.
(4) Cross-Dataset Validation for Universality
Although this study evaluated the model with UNSW-NB15 and CICIDS2017 datasets, further validation using IoT- and cloud-oriented datasets such as Bot-IoT and TON_IoT is necessary. These additional experiments will strengthen the universality and robustness of the proposed approach, ensuring applicability to emerging network environments
(5) Integration with Physical- and Link-Layer Security
Future work will also consider integrating with physical- and link-layer security mechanisms (e.g., encryption, secure tunneling, PHY security). This cross-layer integration will allow the model to correlate access-layer trust with anomalies observed at lower layers. In doing so, it can enhance resilience against undetected physical-layer attacks.
6.3. Conclusions
This paper presented a novel Trust Score-based access control model tailored for Zero Trust Architecture. Unlike traditional approaches that rely on static rules or predefined roles, the proposed model leverages real-time contextual information and multi-dimensional trust evaluation to deliver adaptive and fine-grained access decisions. Its structural simplicity—using a weighted sum of four normalized factors—ensures practical deployability without adding excessive complexity.
Empirical validation confirmed its feasibility for real-world environments. The model consistently maintained low latency and stable throughput even at large data volumes, and it outperformed conventional access control methods () in computational efficiency. These results demonstrate that the model can serve as a viable foundation for real-time Zero Trust deployment in performance-constrained infrastructures such as endpoints and gateways.
Ultimately, this research contributes a concrete step toward operationalizing Zero Trust principles. By integrating structured factor modeling, sensitivity analysis, and empirical evaluation, the proposed framework offers organizations a scalable and efficient means to enhance security resilience while maintaining flexibility and responsiveness in access control policies.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.J. and D.Y.; methodology, E.J.; software, D.Y.; validation, E.J.; formal analysis, E.J.; investigation, E.J.; data curation, D.Y.; writing—original draft preparation, E.J.; writing—review and editing, E.J. and D.Y.; visualization, E.J.; project administration, E.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Ghasemshirazi, S.; Shirvani, G.; Alipour, M.A. Zero Trust: Applications, Challenges, and Opportunities. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2309.03582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.; Lee, S.; Shieh, S.W. Strategy for Implementing of Zero Trust Architecture. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 2023, 72, 1234–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kindervag, J. No More Chewy Centers: Introducing the Zero Trust Model of Information Security; Forrester Research: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2010; Available online: https://www.forrester.com/report/No-More-Chewy-Centers-The-Zero-Trust-Model-Of-Information-Security/RES56682 (accessed on 6 August 2025).
- Kim, H.; Kim, Y.; Kim, S. A Study on the Security Requirements Analysis to Build a Zero Trust-based Remote Work Environment. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2401.03675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kahtani, M.; Sandhu, R. A Hybrid Access Control Model With Dynamic COI for Secure Localization of Satellite and IoT-Based Vehicles. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 24196–24208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angiulli, M.; Furfaro, F.; Lax, G.; Sacca, D. Toward an Ideal Access Control Strategy for Industry 4.0 Manufacturing Systems. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 114037–114050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Song, J.; Cheng, H. Attribute and User Trust Score-Based Zero Trust Access Control Model in IoV. Electronics 2023, 12, 4825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradatsch, L.; Miroshkin, O.; Trkulja, N.; Kargl, F. Zero Trust Score-Based Network-Level Access Control in Enterprise Networks. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 22nd International Conference on Trust, Security and Privacy in Computing and Communications (TrustCom), Changsha, China, 20–22 November 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2024; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, D.R.; Coyne, E.J.; Weil, T.R. Adding Attributes to Role-Based Access Control. Computer 2010, 43, 79–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Rani, S.; Kumar, V. Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) Enabled Secure and Efficient Data Processing Framework for IoT Networks. Int. J. Commun. Netw. Inf. Secur. 2024, 16, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, A.U.R.; Mahmood, T.; Saba, T.; Bahaj, S.O.; Alamri, F.S.; Iqbal, M.W. An Optimized Role-Based Access Control Using Trust Mechanism in E-Health Cloud Environment. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 138813–138826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquis, Y.A. From Theory to Practice: Implementing Effective Role-Based Access Control Strategies to Mitigate Insider Risks in Diverse Organizational Contexts. J. Eng. Res. Rep. 2024, 26, 138–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mpamugo, E.; Ansa, G. Enhancing Network Security in Mobile Applications with Role-Based Access Control. J. Inf. Secur. Innov. 2024, 6, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Carvalho Junior, M.A.; Bandiera-Paiva, P. Health Information System Role-Based Access Control: Current Trends and Issues. J. Healthc. Eng. 2018, 2018, 6510249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, V.C.; Ferraiolo, D.; Kuhn, D.R.; Schnitzer, A.; Sandlin, K.; Miller, R.; Scarfone, K. Guide to Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC) Definition and Considerations; NIST Special Publication 800-162; National Institute of Standards and Technology: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Servos, D.; Osborn, S.L. Current Research and Open Problems in Attribute-Based Access Control. In Proceedings of the 2016 ACM International Workshop on Attribute-Based Access Control, New Orleans, LA, USA, 11 March 2016; Bertino, E., Ed.; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Thada, V.; Sabri, M.S. Review of Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC) Models for Cloud Computing. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computing, Power and Communication Technologies (ComPE), Katra, India, 4–6 September 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; p. 9752139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, M.; Thuraisingham, B. A Category-Based Model for ABAC. In Proceedings of the Third ACM Workshop on Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC’18), Incheon, Republic of Korea, 4 June 2018; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 32–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panende, M.F.; Riadi, I.; Prayudi, Y. Comparison of Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC) Model and Rule-Based Access (RBAC) to Digital Evidence Storage (DES). Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2018, 9, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zeng, Q.; Wang, G.; Zhang, C.; Ren, J.; Zhang, Y. An Efficient Privacy-Enhanced Attribute-Based Access Control Mechanism. Concurr. Comput. Pract. Exp. 2019, 31, e5556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiefling, S.; Dürmuth, M.; Lo Iacono, L. Verify It’s You: How Users Perceive Risk-Based Authentication. IEEE Secur. Priv. 2021, 19, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makowski, J.-P.; Pöhn, D. Evaluation of Real-World Risk-Based Authentication at Online Services Revisited: Complexity Wins. In Proceedings of the 2023 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, Copenhagen, Denmark, 26–30 November 2023; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 3125–3137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Büttner, A.; Pedersen, A.T.; Wiefling, S.; Gruschka, N.; Lo Iacono, L. Is It Really You Who Forgot the Password? When Account Recovery Meets Risk-Based Authentication. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on Information Security and Cryptology, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 13–15 December 2024; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 345–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unsel, V.; Wiefling, S.; Gruschka, N.; Lo Iacono, L. Risk-Based Authentication for OpenStack: A Fully Functional Implementation and Guiding Example. In Proceedings of the 2023 ACM Conference on Cloud Computing Security Workshop, Copenhagen, Denmark, 26 November 2023; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiefling, S.; Jørgensen, P.R.; Thunem, S.; Lo Iacono, L. Pump Up Password Security! Evaluating and Enhancing Risk-Based Authentication on a Real-World Large-Scale Online Service. ACM Trans. Priv. Secur. 2022, 25, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiefling, S.; Dürmuth, M.; Lo Iacono, L. More Than Just Good Passwords? A Study on Usability and Security of Risk-Based Authentication. In Proceedings of the 2020 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, Orlando, FL, USA, 9–13 November 2020; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 1837–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, S.; Borchert, O.; Mitchell, S.; Connelly, S. Zero Trust Architecture; National Institute of Standards and Technology: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2020; NIST Special Publication 800-207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, R.; Beyer, B. BeyondCorp: A New Approach to Enterprise Security. Login 2014, 39, 6–11. Available online: https://research.google/pubs/beyondcorp-a-new-approach-to-enterprise-security/ (accessed on 23 August 2025).
- Osborn, B.; Allievi, A.; Beyer, B.; More, A.; Ward, R. BeyondCorp: Design to Deployment at Google. Login 2016, 41, 28–34. Available online: https://research.google/pubs/beyondcorp-design-to-deployment-at-google/ (accessed on 23 August 2025).
- Spear, B.; Beyer, B.; Cittadini, L.; Saltonstall, M. BeyondCorp: The Access Proxy. Login 2016, 41, 28–33. Available online: https://research.google/pubs/beyondcorp-the-access-proxy/ (accessed on 23 August 2025).
- Beraud, P.; Grasset, J.-Y.; Jumelet, A. Implementing a Zero Trust Approach with Azure Active Directory; Microsoft France: Paris, France, 2019; Available online: https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=58366 (accessed on 23 August 2025).
- Department of Defense. DoD Zero Trust Strategy; Department of Defense: Washington, DC, USA, 2022. Available online: https://dodcio.defense.gov/Portals/0/Documents/Library/DoD-ZTStrategy.pdf (accessed on 23 August 2025).
- George, A.T.; Neve, H.R.; Muraleedharan, N. A Trust Score Calculation Approach for Zero Trust Access System. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 20th India Council International Conference (INDICON), Ahmedabad, India, 15–17 December 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 392–397. Available online: https://www.proceedings.com/content/073/073473webtoc.pdf (accessed on 23 August 2025).
- Park, U.H.; Hong, J.H.; Kim, A.; Son, K.H. Endpoint Device Risk-Scoring Algorithm Proposal for Zero Trust. Electronics 2023, 12, 1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Li, C.; Zhang, K.; Tu, B. Zero-Trust Based Dynamic Access Control for Cloud Computing. Cybersecurity 2025, 8, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasongo, S.M.; Sun, Y. Performance Analysis of Intrusion Detection Systems Using a Feature Selection Method on the UNSW-NB15 Dataset. J. Big Data 2020, 7, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verizon. 2023 Data Breach Investigations Report (DBIR); Verizon Enterprise: New York, NY, USA, 2023; Available online: https://www.verizon.com/business/resources/T87b/reports/2023-dbir-executive-summary.pdf (accessed on 23 August 2025).
- Jeong, E.; Yang, D. Trust Score-Based Modeling—Experimental Code Repository. Available online: https://github.com/Yang9un/Trust-Score-Based-Modeling (accessed on 23 August 2025).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).