An Ease-Off Based Tooth Contact Analysis Method for Measured Face Gear Flanks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Tooth Flanks Models of Face Gear Drives
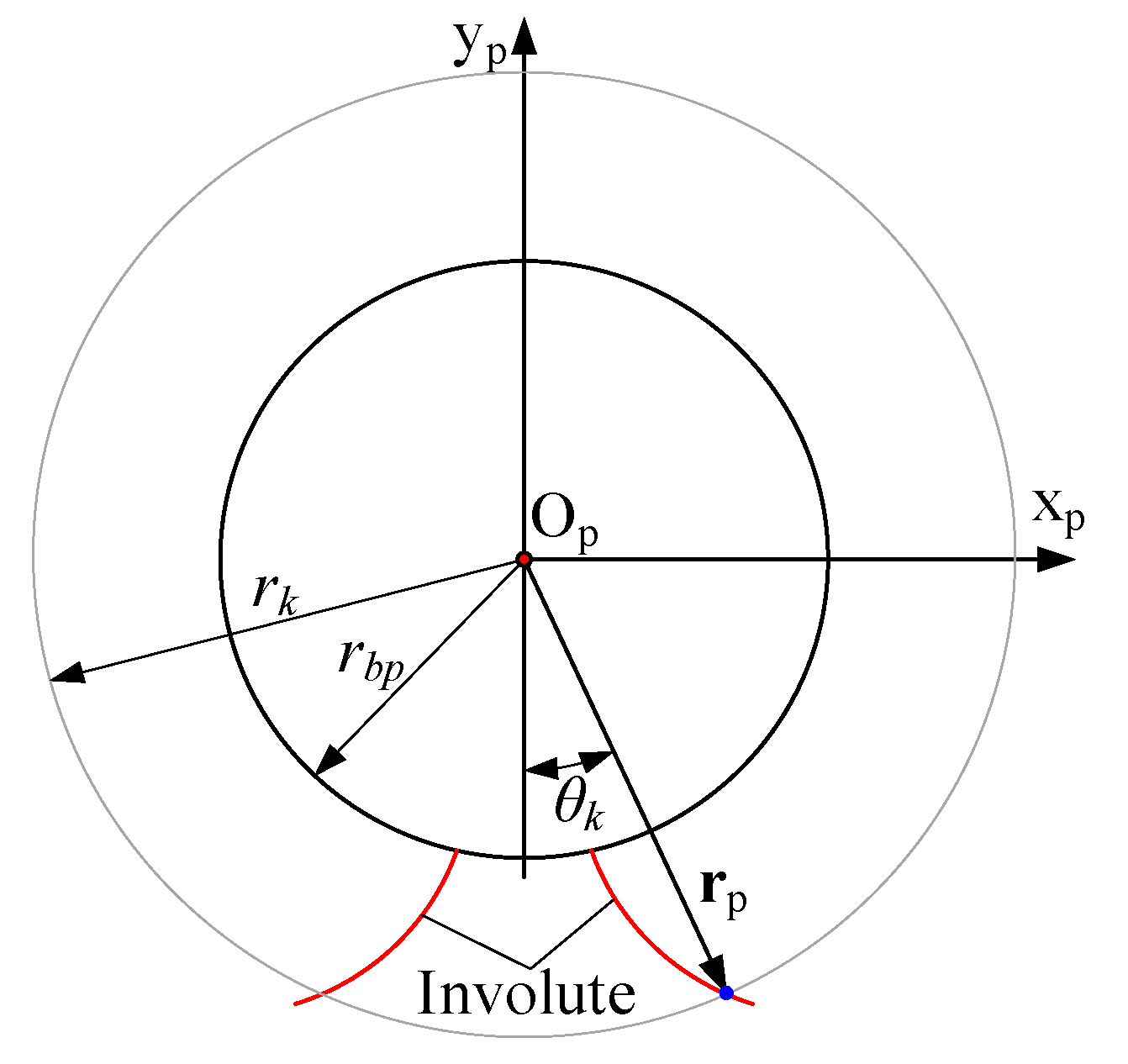
2.1. Tooth Flank of the Pinion
2.2. Tooth Flank of the Face Gear
3. Ease-Off Surface-Based TCA Framework
3.1. Conjugate Surface of the Pinion
3.2. Ease-Off Surface Construction
3.3. TCA Method Based on Ease-Off Surface
4. Measured Flank Processing and Error Integration
4.1. Flank Measurement Methodology
4.2. Error Surface Reconstruction and Integration
- Step 1: Surface Parameterization
- Step 2: Bicubic Spline Fitting
- Step 3: Prediction and Extrapolation
- Step 4: Error Analysis
5. Validation and Discussions
5.1. Numerical and Experimental Validation
5.1.1. Numerical Verification
5.1.2. Experimental Validation
5.2. Discussions
5.2.1. Method Advantages
- Simultaneously determine the edge contact and tooth surface contact states
- Computational stability in different application scenarios
- Computational efficiency
5.2.2. Limitations and Outlook
- The current method only considers the entire process of a single tooth from meshing-in to meshing-out, without taking into account the load distribution among multiple teeth and the influence of contact ratio. This consideration mainly relies on the calculation of the meshing stiffness of face gear teeth. In future work, we should address this gap.
- In future research, the proposed method can be further combined with on-machine measurement technology to develop closed-loop manufacturing correction using real-time TCA feedback.
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hao, J.; Song, C.; Liu, S.; Xue, C.; Wang, Z. A low sensitivity design method for spiral bevel gear tooth surface contact pattern considering comprehensive errors of manufacturing and assembling. Meccanica 2025, 60, 217–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litvin, F.; Fuentes, A.; Zani, C.; Pontiggia, M.; Handschuh, R. Face-gear drive with spur involute pinion: Geometry, generation by a worm, stress analysis. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2002, 191, 2785–2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, L.; Tang, J.; Chen, Z.C. CNC milling of face gears with a novel geometric analysis. Mech. Mach. Theory 2019, 139, 46–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanzi, C.; Pedrero, J.I. Application of modified geometry of face gear drive. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2005, 194, 3047–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litvin, F.L.; Fuentes, A.; Zanzi, C.; Pontiggia, M. Design, generation, and stress analysis of two versions of geometry of face-gear drives. Mech. Mach. Theory 2002, 37, 1179–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Fan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cao, X.; Cai, Z. A five-axis CNC machining method of orthogonal variable transmission ratio face gear. J. Adv. Mech. Des. Syst. Manuf. 2014, 8, JAMDSM0040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, X.; Wang, Y.; Du, S.; Huang, Y.; Su, G.; Liu, D.; Zang, L. An efficient generation grinding method for spur face gear along contact trace using disk CBN wheel. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 110, 1179–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Wang, X.; Zhao, N.; Fu, B.; Liu, L. Simulation analysis and experiment of instantaneous temperature field for grinding face gear with a grinding worm. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 120, 4989–5001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-z.; Chu, X.-m.; Zhao, W.-j.; Wang, Z.; Su, G.-y.; Huang, Y.-z. A precision generating hobbing method for face gear with assembly spherical hob. J. Cent. South Univ. 2019, 26, 2704–2716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Su, G.; Liu, D.; Huang, Y.; Xie, M.; Zhang, W. A hobbing method for spur face gears with bidirectional modification. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 119, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, K.-Q.; Wu, Y.-R.; Tran, V.-Q.; Tran, H.-Q. A flexible method to correct tooth surface deviation for CNC power skiving of face gears. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2024, 134, 3665–3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, S.; Wang, S.; Luo, B.; Liu, Z.; Cen, G.; Huang, Y. Machining principle and cutter design of face gear skiving. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B-J. Eng. Manuf. 2023, 237, 468–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litvin, F.L.; Fuentes, A. Gear Geometry and Applied Theory; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Litvin, F.L.; Fuentes, A.; Fan, Q.; Handschuh, R.F. Computerized design, simulation of meshing, and contact and stress analysis of face-milled formate generated spiral bevel gears. Mech. Mach. Theory 2002, 37, 441–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, S.; Luo, B.; Song, W.; Zhang, Y.; Cen, G.; Bao, H. Geometry design and tooth contact analysis of non-orthogonal asymmetric helical face gear drives. Mech. Mach. Theory 2022, 173, 104831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhou, Y.; Tang, J.; Tang, K.; Li, Z. Digital tooth contact analysis of face gear drives with an accurate measurement model of face gear tooth surface inspected by CMMs. Mech. Mach. Theory 2022, 167, 104498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Zhou, Y.; He, D.; Zheng, F.; Tang, K.; Tang, J. A novel two-variable optimization algorithm of TCA for the design of face gear drives. Mech. Mach. Theory 2022, 175, 104960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, S.; Sun, X.; Dong, Z.; Yang, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Meng, Q.; Zhao, Y. Meshing theory of point-contact conical-envelope cylindrical worm-face worm gear drive. Mech. Mach. Theory 2025, 205, 105870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, G.; Tao, Y.; Zhao, X.; He, X. Loaded tooth contact analysis for helical gears with surface waviness error. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2025, 224, 112045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.-Y.; Tsai, S.-J. A computerized method for loaded tooth contact analysis of high-contact-ratio spur gears with or without flank modification considering tip corner contact and shaft misalignment. Mech. Mach. Theory 2016, 97, 190–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, J. Meshing characteristics of a sphere-face gear pair with variable shaft angle. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2019, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Liu, Y.; Gong, J.; Wei, Y.; Zhao, G. A novel method for longitudinal modification and tooth contact analysis of non-circular cylindrical gears. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2022, 36, 6157–6170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheveleva, G.I.; Volkov, A.E.; Medvedev, V.I. Algorithms for analysis of meshing and contact of spiral bevel gears. Mech. Mach. Theory 2007, 42, 198–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, K.; Tang, J.; Tian, Z.; Song, B.; Li, H.; Ding, H. A novel accurate- efficient loaded contact analysis method for hypoid gears based on ease-off topography discretization and TE-interference assessment. Mech. Mach. Theory 2025, 209, 106012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banchoff, T.F.; Lovett, S. Differential Geometry of Curves and Surfaces, 3rd ed.; Chapman and Hall/CRC: New York, NY, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ANSI/AGMA 2009-B01; Bevel Gear Classification, Tolerances, and Measuring Methods. American Gear Manufacturers Association: Alexandria, VA, USA, 2009.
- Wang, N.; Li, X.; Wang, K.; Zeng, Q.; Shen, X. A novel axial modification and simulation analysis of involute spur gear. Stroj. Vestn.-J. Mech. Eng. 2017, 63, 736–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golebski, R.; Ivandic, Z. Analysis of modification of spur gear profile. Teh. Vjesn.-Tech. Gaz. 2018, 25, 643–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Name | Sign | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Module | m | 3.9 | mm |
| Pressure angle | α | 25 | ° |
| Teeth number of the shaper cutter | Ns | 22 | / |
| Teeth number of the face gear | Nf | 142 | / |
| Teeth number of the pinion | Np | 21 | / |
| Shaft angle | γ | 90 | ° |
| Inner radius of the face gear | Ri | 253.5 | mm |
| Outer radius of the face gear | Ro | 305 | mm |
| Tooth addendum | ha | 3.9 | mm |
| Tooth dedendum | hf | 4.875 | mm |
| Tooth width of the pinion | B | 55 | mm |
| Contact Path | Skived Face Gear |
|---|---|
| Traditional method |  |
| Proposed method |  |
| FEA method |  |
| Contact Path | Ground Face Gear |
|---|---|
| Traditional method |  |
| Proposed method |  |
| FEA method |  |
| Cases | ar | fd | apr | alr | fpd | fld |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | 0.0005 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 3 | 0.0005 | −2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 4 | 0.0005 | −2 | 0.0010 | 0.0005 | 1 | 0 |
| 5 | 0.0005 | −2 | 0.0010 | 0.0005 | 1 | 10 |
| 6 | 0 | 0 | 0.0010 | 0.0005 | −1 | −10 |
| Cases | Contact Path on the Face Gear Tooth Flanks |
|---|---|
| 1 |  |
| 2 |  |
| 3 |  |
| 4 |  |
| 5 |  |
| 6 |  |
| Methods | Time |
|---|---|
| Proposed method | 2.66 s |
| Traditional method | 1.98 s |
| FEA method | About 6 h |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Tang, J. An Ease-Off Based Tooth Contact Analysis Method for Measured Face Gear Flanks. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 9336. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179336
Tang Z, Zhou Y, Tang J. An Ease-Off Based Tooth Contact Analysis Method for Measured Face Gear Flanks. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(17):9336. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179336
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Zhongwei, Yuansheng Zhou, and Jinyuan Tang. 2025. "An Ease-Off Based Tooth Contact Analysis Method for Measured Face Gear Flanks" Applied Sciences 15, no. 17: 9336. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179336
APA StyleTang, Z., Zhou, Y., & Tang, J. (2025). An Ease-Off Based Tooth Contact Analysis Method for Measured Face Gear Flanks. Applied Sciences, 15(17), 9336. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179336







