Featured Application
This study supports the integration of the milling cutter drill into partially guided surgical protocol to optimize implant placement precision.
Abstract
Partially guided implant surgery has emerged as a technique that enhances the precision of implant placement while maintaining surgical flexibility. This in vitro experimental study evaluated the influence of the milling cutter drill on the angular and linear deviations of implant placement in synthetic polyurethane bone models using a partially guided surgical protocol. Additionally, the effects of bone density and implant macrogeometry were assessed. A total of 120 Straumann® implants (BL, BLT, and BLX) were placed in polyurethane blocks simulating four bone densities (D1–D4). Implant positions were virtually planned with coDiagnostiX® (version 10.9) software and executed with or without the use of the milling cutter drill. Deviations between planned and final implant positions were measured at the neck and apex using the software’s “Treatment Evaluation” tool. The use of the milling cutter drill significantly reduced angular deviation (p = 0.007), while linear deviations showed no statistically significant differences. Bone density and implant macrogeometry did not significantly affect angular deviation but influenced linear and 3D deviations. Given that angular deviation may compromise prosthetic fit and biomechanical function, the observed reduction is of potential clinical relevance. These findings indicate that the milling cutter drill enhances angular accuracy in partially guided implant surgery and may improve outcomes in anatomically challenging cases. However, the results should be interpreted within the limitations of this in vitro model, including the absence of soft tissue simulation, intraoral constraints, and inter-operator variability.
1. Introduction
Recent technological developments have led to significant advances in the creation of new materials and methods, and Dentistry has not been immune to these changes [1,2,3]. The integration of cutting-edge tools and new techniques has become a key to modern clinical practice. Consequently, the concept of Digital Dentistry (DD) is increasing in relevance in clinical and academic contexts, reflecting its growing impact on oral healthcare [1,2].
Digital Dentistry involves a wide range of applications in daily clinical practice, including data acquisition, patient communication, diagnosis, treatment planning, and follow-up. Advances in computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) have led to the development of high-definition 3D scanners, faster and more accurate planning software, and innovative additive and subtractive manufacturing techniques [1,2,3,4]. The digital workflow typically involves image acquisition (from CBCT, intraoral scanners, and facial scanners), data processing using CAD software, and the fabrication of physical components through CAM systems such as 3D printing or milling [3,4,5]. Each step introduces potential sources of error, highlighting the need to evaluate their cumulative effect on clinical outcomes [3,6,7].
In implantology, digital workflows have revolutionized treatment planning and execution. CBCT and intraoral scanning technologies allow an accurate analysis of anatomical structures and the virtual planning of prosthetically guided surgeries [3,6]. This has led to more predictable treatments with reduced clinical time and improved patient satisfaction. Digital workflow in prosthodontics has also enhanced restoration precision and reduced the need for postoperative adjustments [5,7]. Despite these benefits, challenges such as costs, learning curves, and the risk of deviations between planned and final implant positions remain [5,8,9,10,11,12].
Computer-Assisted Implant Surgery (CAIS), particularly static CAIS (s-CAIS), allows virtual planning and the fabrication of surgical guides. These guides direct the position, angulation, and depth of implant placement, improving surgical accuracy and reducing intraoperative complications. Among s-CAIS techniques, partially guided surgery (PGS) offers an alternative between guidance and manual control, maintaining clinical flexibility [13,14,15].
One specific instrument that can be used in partially guided surgery is the milling cutter drill (Straumann®, Institut Straumann AG, Basel, Switzerland) designed to flatten the alveolar crest and provide a more stable surface for subsequent drilling steps [16,17,18]. This flattening is especially relevant in irregular or sloped cortical bone, as it helps minimize drill slippage and reduce angular deviations during implant placement. Although the potential of the milling cutter drill to improve implant accuracy is acknowledged, evidence supporting its benefit remains limited and underexplored in the literature, particularly in partially guided protocols [6,19].
Given the increasing reliance on digital technologies and the continuous evolution of surgical protocols and implant designs, further research is essential to assess the biomechanical performance, predictability, and clinical efficacy of these tools. Therefore, the main aim of this study was to evaluate the impact of the milling cutter drill on the accuracy of bone level implants placement within a partially guided surgical protocol. A secondary objective was to assess how bone density and implant macrogeometry influence implant placement accuracy. This study contributes to the growing of evidence supporting digital implantology and aims to optimize outcomes through improved surgical planning and execution.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample
A power analysis determined that a sample size of 120 implants (Straumann®, Institut Straumann AG, Basel, Switzerland) was robust enough to achieve over 80% statistical power in the purposed analysis (at a significance level of 0.05). These implants were distributed across three experimental groups according to their macrogeometries: 40 BL (Bone Level), 40 BLT (Bone Level Tapered), and 40 BLX (Bone Level X) implants. These implant types were selected based on widespread clinical use, enabling the evaluation of how implant design may influence placement accuracy in guided protocols.
2.2. Surgical Protocol
In this laboratorial study, four artificial bone models (Bonemodels®, Castellón, Spain) were used, simulating four distinct bone densities according to the classification proposed by Lekholm and Zarb [20] (Figure 1). Although this classification was originally developed for human bone, previous studies have used polyurethane blocks with similar mechanical properties to represent D1–D4 bone types, allowing reproducible comparisons in in vitro settings [20,21].

Figure 1.
Artificial bone models with four distinct bone densities (D1–D4), shown from the inferior perspective.
Each bone model was sectioned into two halves to comply with the field of view (FOV) constraints of the CBCT scanner (NewTom Go, NewTom|Cefla S.C., Imola, Italy), resulting in eight mini bone blocks, each comprising two density zones (D1/D2 and D3/D4) (Figure 2).

Figure 2.
Mini bone block (each block containing two different bone densities).
Each mini block was identified with an alphanumeric code (e.g., A1 and A2 corresponding to the two halves of the first block). All mini blocks were scanned using CBCT and intraoral scanning (KaVo LS 3, Nobel Biocare USA, LLC, Yorba Linda, CA, USA) to enable digital implant planning and the subsequent design of the surgical guides.
The coDiagnostiX® software (Dental Wings GmbH, Chemnitz, Germany) was used for virtual planning of implant positioning and for the design of the surgical guides (Figure 3).
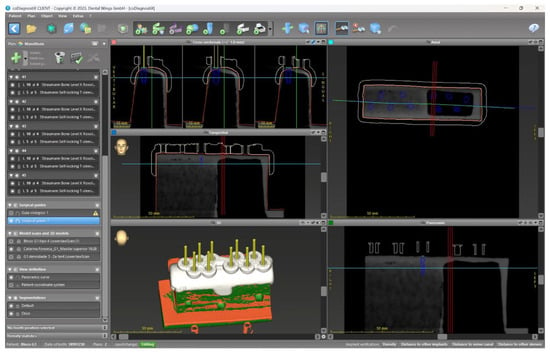
Figure 3.
CoDiagnostiX® software.
Each guide was labeled with the identifier of the corresponding mini block. The guides were fabricated using a 3D printer (Phrozen Sonic Mini 8K, Phrozen Technology, Hsinchu City, Taiwan) with ABS-like resin (Creamy White, Phrozen Tech Co., Ltd., Xiangshan Dist., Hsinchu City, Taiwan). After printing, all guides underwent post-processing, including washing and polymerization. Titanium sleeves (Straumann®, Institut Straumann AG, Basel, Switzerland) with a 5/5 mm diameter were manually inserted into the guides.
Implant placement was performed using guided surgery kits specific to each implant type, supplied by Straumann®, in combination with the iChiropro surgical motor (Bien-Air, Bienne, Switzerland).
A total of 120 implants were inserted into the mini bone blocks following two distinct surgical protocols:
Partially guided surgery using the milling cutter drill (n = 60);
Partially guided surgery without the milling cutter drill (n = 60).
The implant placement was performed by the same experienced dentist, who had formal training in implantology and digital dentistry and was fully familiar with the guided surgery protocols and kits employed. Using a single operator ensured consistency across procedures, although it limited the generalizability of results due to the absence of inter-operator variability.
The drilling and placement protocols were conducted in accordance with the manufacturer’s guidelines, tailored to the specific implant design and simulated bone density.
Following implant placement, a final digital impression was obtained using appropriate scan bodies from Straumann®. For BL and BLT implants, CARES® RC Mono Scan bodies (Ø4.1 mm, height 10 mm, PEEK/TAN) were used, and for BLX implants, CARES® RB/WB Mono Scan bodies (Ø3.8 mm, height 10 mm, PEEK/TAN) were employed. Scanning was performed using the Trios v.4 intraoral scanner (3Shape®, Copenhagen, Denmark), for the purpose of evaluating deviations between planned and final implant positions.
Deviations between the preoperative virtual planning and the postoperative implant position were assessed using the “Treatment Evaluation” tool in the coDiagnostiX® software (Institut Straumann AG, Switzerland). To ensure precise overlay of the pre and postoperative scans, three small dots of dental composite resin were applied to each bone block as fiducial markers. These markers facilitated the identification of anatomical landmarks during the digital alignment process, ensuring optimal overlay precision (Figure 4).
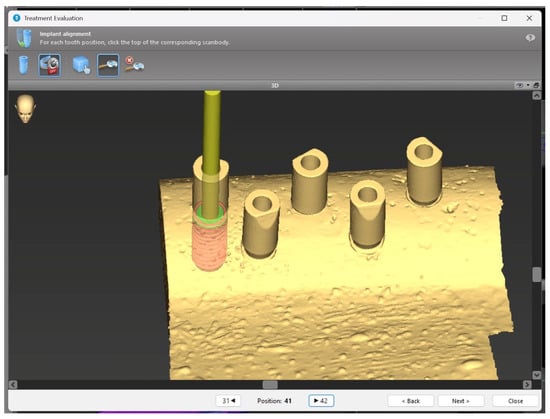
Figure 4.
Three-dimensional image of the macromodel bone with scan bodies.
The parameters analyzed included angular deviation (degrees); tridimensional deviations (mm) at the implant neck in the mesio-distal, bucco-lingual, and apico-coronal directions; and tridimensional deviations (mm) at the implant apex in the same three axes (Figure 5).
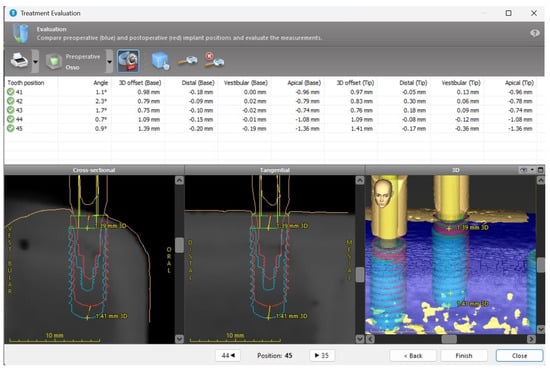
Figure 5.
Measurements using the “Treatment Evaluation” tool from the coDiagnostiX® software.
2.3. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using IBM SPSS Statistics software, version 24. A two-tailed significance level of p < 0.05 was adopted.
Continuous variables were expressed as median and interquartile range (IQR), due to non-normal data distribution as confirmed by the Kolmogorov–Smirnov test. Categorical variables were presented as absolute (n) and relative (%) frequencies. Comparisons of linear and angular deviations across implant types, bone densities, and the use of the milling cutter drill were conducted using the non-parametric Kruskal–Wallis and Mann–Whitney U tests.
3. Results
This study analyzed the placement of 120 implants of three distinct types (BL, BLT, and BLX) in four different bone densities, using a partially guided surgical protocol with and without the use of the milling cutter drill (Table 1).

Table 1.
Number of implants placed according to each variable tested.
The analysis of the impact of the milling cutter drill (Table 2) showed that its use led to a statistically significant reduction in the angular deviation (p = 0.007), decreasing from 3.40° to 2.45°. However, no statistically significant differences were observed between the groups with and without the milling cutter drill regarding 3D deviations or individual linear deviations (p > 0.05).

Table 2.
Influence of the use of the milling cutter drill on implant deviation parameters.
The comparison between bone densities (Table 3) revealed statistically significant differences for several parameters. The 3D deviation at the implant neck differed significantly across groups (p = 0.027), being highest in D1 bone (0.99 mm) and lowest in D3 bone (0.40 mm). The mesio-distal deviation at the neck also showed significant variation (p = 0.036), with higher values in D1 bone (0.12 mm). The bucco-lingual deviation at the neck was the most statistically significant variable (p < 0.001), being more pronounced in D1 bone (0.58 mm) and least in D3 bone (0.06 mm). The apico-coronal deviation at the apex also reached statistical significance (p = 0.005), with the highest deviation in D1 bone (0.84 mm) and the lowest in D3 bone (0.46 mm). In contrast, the angular deviation and the other deviations at the apex did not show statistically significant differences.

Table 3.
Influence of bone density on implant deviation parameters.
Regarding the comparison between implant types (Table 4), the 3D deviation at the neck was significantly higher in the BLX group (0.91 mm) than in the other groups (p < 0.001). The bucco-lingual deviation at the neck was also greater in BLX implants (0.25 mm) compared to the others (p = 0.020), as was the apico-coronal deviation at the neck (0.70 mm; p = 0.032). The bucco-lingual deviation at the apex showed a statistically significant difference as well (p = 0.045), with higher values recorded for the BLT implant group (0.49 mm). No statistically significant differences were observed among implant types for angular deviation or the remaining apical parameters.

Table 4.
Influence of implant type on implant deviation parameters.
4. Discussion
4.1. Influence of the Milling Cutter Drill
The results obtained in this study demonstrate that the use of the milling cutter drill led to a statistically significant difference in angular deviation, which was lower in the group where the drill was used.
The use of the milling cutter drill in the partially guided protocol demonstrated a measurable effect, confirming its influence on the angular deviation parameter. The differences found in this study support the hypothesis that, even in guided surgery, bone density and implant macrogeometry can affect the positioning of the implant in relation to the planned trajectory [16,18].
The milling cutter drill facilitates implant placement by enabling cortical flattening, which may explain the greater predictability of the final position [17]. By reducing surface irregularities at the alveolar crest, the drill likely enhances drill stability during initial osteotomy steps, decreasing angular deviation—a parameter particularly relevant in anterior and multi-unit prosthetic planning. However, it did not significantly reduce the other deviation values (3D and linear), although the angular improvement alone may already be clinically relevant [9,10,11,12,22].
4.2. Influence of Bone Density
Regarding bone density, the results showed statistically significant differences in 3D deviation at the implant neck and in all linear deviations at the same level, except for mesio-distal deviation at the apex.
These results indicate that higher density bone (particularly type D1) was associated with greater deviation in implant placement, especially at the cervical level. This may be explained by the greater resistance of cortical bone to drilling, which tends to deflect the drill in partially guided systems [20,23]. These findings are consistent with previous studies that suggest greater difficulties in guided surgery in dense bone [21,24].
In contrast, lower-density bones, such as D3, presented lower deviation values, indicating that the flexibility of trabecular bone allows better guidance of drills and implants along the planned trajectory [25]. Clinically, this implies that in high-density bone, additional control (such as extended guidance or countersinking tools) may be advisable to mitigate deviation.
4.3. Influence of Implant Type
In the present study, the BLX implant showed greater 3D deviation at the cervical level, as well as higher bucco-lingual and apico-coronal deviations when compared to the other two implant types.
These results may be related to the fact that BLX implants use a different guided surgery kit, and their tapered geometry, combined with a different connection (RB instead of RC), may have influenced the results. This system also differs in aspects such as drill diameter progression, depth control design, and sleeve tolerance, which may reduce drilling stability. Additionally, the BLX implant presents more aggressive cutting threads, which, while intended to enhance primary stability, may also increase the risk of deviation during insertion, especially in dense bone. These combined factors could help explain the greater deviations observed in the BLX implants [25,26].
It is important to highlight that the BL and BLT implants share the same guided surgery kit, and that BLT implants, despite their tapered geometry, presented lower deviation values than the BLX. Therefore, it is not possible to attribute these differences exclusively to implant geometry [27].
4.4. Limitations and Considerations
Although this study was performed in artificial bone models under controlled conditions, there are limitations in extrapolating the results directly to clinical practice.
All surgeries were performed by a single clinician with training in guided surgery, which may have minimized variability due to operator experience. However, this also limits generalizability, and future studies should include multiple operators and simulate in vivo conditions to assess the generalizability of these results.
Moreover, the milling cutter drill evaluated in this study was specifically designed by the manufacturer to be compatible with its surgical kits. Therefore, its effectiveness may vary across different implant systems and may also depend on the clinician’s surgical technique.
Additionally, the absence of soft tissues, intraoral access constraints, and patient-related variables (e.g., saliva, movement, and limited visibility) may have contributed to lower deviation values than those typically observed clinically.
The angular improvement observed, although modest numerically, may hold clinical relevance, especially in prosthetically demanding cases. Therefore, the findings should be interpreted considering the working hypothesis and previous studies on cortical bone flattening and guided accuracy tools.
Further clinical studies are required to confirm whether the observed reduction in angular deviation leads to improved implant longevity and prosthetic outcomes. Moreover, evaluating the performance of milling cutter drills from other manufacturers, or across different surgical protocols, would broaden the applicability of these results.
5. Conclusions
Within the limitations of this in vitro experimental study, the results suggest that the use of the milling cutter drill in a partially guided surgical protocol significantly improves angular accuracy in implant placement. Although it did not lead to statistically significant differences in 3D or linear deviations, the observed reduction in angular deviation may hold clinical relevance, particularly in cases requiring high prosthetic precision.
Bone density also played a significant role in the accuracy of implant positioning. Higher deviations were observed in denser bone types, such as D1, especially at the cervical level, which may be attributed to the greater resistance of cortical bone during the drilling sequence. In contrast, lower-density bone types allowed for more accurate placement, potentially due to reduced resistance and better adaptation to the guided trajectory.
Regarding implant macrogeometry, BLX implants presented higher deviation values compared to BL and BLT implants. This outcome may be associated with differences in surgical protocol, guided kit components, and implant design, particularly the tapered shape and connection type specific to BLX. However, as BL and BLT implants—despite their structural differences—shared the same guided system and exhibited lower deviations, it is not possible to attribute the discrepancies solely to implant geometry.
These findings highlight the multifactorial nature of implant placement accuracy in guided surgery, influenced by surgical instruments, bone quality, and implant design. Further clinical and in vivo studies are required to validate these results in vivo and to evaluate the long-term impact of placement deviations on functional and esthetic treatment outcomes.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.F. and C.M.F.; methodology, C.M.F. and A.C.; software, A.R.F. and A.C.; validation P.F., A.C. and C.M.F.; formal analysis, P.F., A.C. and C.M.F.; investigation, A.R.F.; resources, A.C. and P.F.; data curation, A.R.F. and C.M.F.; writing—original draft preparation, A.R.F. and C.M.F.; writing—review and editing, P.F. and A.C.; visualization, C.M.F.; supervision, P.F. and C.M.F.; project administration, P.F. and A.C.; funding acquisition, P.F. and A.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work is financially supported by National Funds through FCT–Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia, I.P., under the projects UIDB/04279/2023 and UIDP/04279/2023.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request.
Acknowledgments
Institut Straumann AG, Basel, Switzerland.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| 3D | Three-dimensional |
| BL | Bone Level (implant type) |
| BL | Bucco-lingual (in measurement context) |
| BLT | Bone Level Tapered (implant type) |
| BLX | Bone Level X (implant type) |
| CAIS | Computer-Assisted Implant Surgery |
| CAM | Computer-Aided Manufacturing |
| CAD | Computer-Aided Design |
| CBCT | Cone Beam Computed Tomography |
| DD | Digital Dentistry |
| FOV | Field of View |
| PEEK | Polyether ether ketone |
| PGS | Partially Guided Surgery |
| s-CAIS | Static Computer-Assisted Implant Surgery |
| SPSS | Statistical Package for the Social Sciences |
References
- Gawali, N.; Shah, P.P.; Gowdar, I.M.; Bhavsar, K.A.; Giri, D.; Laddha, R. The Evolution of Digital Dentistry: A Comprehensive Review. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2024, 16 (Suppl. S3), S1920–S1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joda, T.; Bornstein, M.M.; Jung, R.E.; Ferrari, M.; Waltimo, T.; Zitzmann, N.U. Recent Trends and Future Direction of Dental Research in the Digital Era. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva Salomão, G.V.; Chun, E.P.; Panegaci, R.D.S.; Santos, F.T. Analysis of Digital Workflow in Implantology. Case Rep. Dent. 2021, 2021, 6655908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Della Bona, A.; Cantelli, V.; Britto, V.T.; Collares, K.F.; Stansbury, J.W. 3D Printing Restorative Materials Using a Stereolithographic Technique: A Systematic Review. Dent. Mater. 2021, 37, 336–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelnabi, M.H.; Swelem, A.A. 3D-Printed Complete Dentures: A Review of Clinical and Patient-Based Outcomes. Cureus 2024, 16, e69698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangano, F.G.; Hauschild, U.; Veronesi, G.; Imburgia, M.; Mangano, C.; Admakin, O. Trueness and Precision of 5 Intraoral Scanners in the Impressions of Single and Multiple Implants: A Comparative In Vitro Study. BMC Oral Health 2019, 19, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, R.; Salmon, B.; Codari, M.; Hassan, B.; Bornstein, M.M. Cone Beam Computed Tomography in Implant Dentistry: Recommendations for Clinical Use. BMC Oral Health 2018, 18, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernauer, S.A.; Zitzmann, N.U.; Joda, T. The Complete Digital Workflow in Fixed Prosthodontics Updated: A Systematic Review. Healthcare 2023, 11, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Assche, N.; Quirynen, M.; Jacobs, R.; van Steenberghe, D. Accuracy of implant placement based on pre-surgical planning of three-dimensional cone-beam images: A pilot study. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2007, 34, 816–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Haese, J.; Van De Velde, T.; Komiyama, A.; Hultin, M.; De Bruyn, H. Accuracy and complications using computer-designed stereolithographic surgical guides for oral rehabilitation by means of dental implants: A review of the literature. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2012, 14, 321–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valente, F.; Schiroli, G.; Sbrenna, A. Accuracy of computer-aided oral implant surgery: A clinical and radiographic study. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2009, 24, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cassetta, M.; Stefanelli, L.V.; Giansanti, M.; Di Mambro, A.; Calasso, S. Accuracy of computer-guided implant placement: A prospective clinical study. J. Periodontal Implant Sci. 2013, 43, 68–76. [Google Scholar]
- Flügge, T.; Kramer, J.; Nelson, K.; Nahles, S.; Kernen, F. Digital Implantology—A Review of Virtual Planning Software for Guided Implant Surgery. Part II: Prosthetic Set-Up and Virtual Implant Planning. BMC Oral Health 2022, 22, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pimkhaokham, A.; Jiaranuchart, S.; Kaboosaya, B.; Arunjaroensuk, S.; Subbalekha, K.; Mattheos, N. Can Computer-Assisted Implant Surgery Improve Clinical Outcomes and Reduce the Frequency and Intensity of Complications in Implant Dentistry? A Critical Review. Periodontology 2000 2022, 90, 197–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putra, R.H.; Yoda, N.; Astuti, E.R.; Sasaki, K. The Accuracy of Implant Placement with Computer-Guided Surgery in Partially Edentulous Patients and Possible Influencing Factors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2022, 66, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.H.; Park, J.H.; Jeong, S.M.; Lee, J.H. Effect of Flat-End Drills on Implant Placement Accuracy in Guided Surgery: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2021, 32, 345–352. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, C. The Role of Drill Geometry in Implant Osteotomy Precision: An In Vitro Study on Flat versus Tapered Tips. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2023, 38, 55–63. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, C.A.; Mendes, R.; Rocha, L.; Rodrigues, F.; Silva, M.; Santos, P.; Gomes, T.; Cunha e Silva, B.; Lima, H.; Barbosa, J.; et al. Effectiveness of Flat Drills in Guided Implant Surgery: A Prospective Multicenter Study. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2023, 25, 102–109. [Google Scholar]
- Saran, R.; Ginjupalli, K.; George, S.D.; Chidangil, S.; Unnikrishnan, V.K. LASER as a Tool for Surface Modification of Dental Biomaterials: A Review. Heliyon 2023, 9, e17457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekholm, U.; Zarb, G.A. Patient Selection and Preparation. In Tissue-Integrated Prostheses: Osseointegration in Clinical Dentistry; Brånemark, P.I., Zarb, G.A., Albrektsson, T., Eds.; Quintessence Publishing Co., Ltd.: Chicago, IL, USA, 1985; pp. 199–209. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, M.; Calasans-Maia, J.A.; Rocha, L.A.; Mattos, C.M.; Granjeiro, J.M. The Effect of Bone Density on the Primary Stability of Dental Implants: A Critical Review. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2022, 110, 1031–1037. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.J.; Cho, Y.D.; Hwang, C.J. Enhancing Surgical Accuracy with Flat Milling Cutters in Irregular Bone Crests: A Clinical Study. J. Periodontal Implant Sci. 2024, 54, 15–23. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, M.; Iwasaki, C.; Takechi, M.; Yoshida, K.; Nakamura, T.; Tanaka, H.; Saito, A.; Ono, Y.; Suzuki, N.; Ueda, S.; et al. Influence of Bone Quality on Implant Stability in Immediate Loading Cases. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2023, 67, 73–80. [Google Scholar]
- González-García, R.; Monje, A.; Delgado-Ruiz, R. Preoperative Bone Quality Assessment Using CBCT and Its Correlation with Implant Stability. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2023, 38, 289–296. [Google Scholar]
- Lopes, P.; Neves, M.; Oliveira, H.; Santos, R.; Almeida, S.; Costa, L.; Fernandes, B.; Rodrigues, A.; Melo, C.; Castro, M.; et al. Evaluation of Implant Stability in Different Bone Types Using BL, BLT, and BLX Systems. Clin. Oral Investig. 2022, 26, 6705–6712. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, K.; Stenberg, T.; Sennerby, L. Influence of Implant Design on Primary Stability: A Randomized Clinical Trial. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2023, 50, 181–189. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, G.; Martins, A.; Dias, R. Implant Design and Bone Preservation: Finding the Balance for Clinical Success. Eur. J. Dent. 2023, 17, 512–520. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).