Abstract
This study proposes a method for separating asphalt and aggregates in recycled asphalt pavement (RAP) materials using surfactants as solvents. This method utilizes surfactants to soften the asphalt by reducing its surface tension, separating the RAP clusters, and washing away the asphalt from the RAP. The wastewater is recycled during the emulsification–separation process without discharge. Factors affecting the separation effect of RAP, including the type of anionic surfactants, the surfactant concentration, the emulsion-to-RAP ratio, temperature, the rotation rate and time, and the RAP’s particle size, were investigated in depth, and the separation effect and its influence on the aggregate properties were evaluated. The experimental results indicate that when using the optimal process to mix and treat 13.2 mm and 9.5 mm RAP clusters, it is possible to achieve 100% separation of the coarse RAP above 4.75 mm, with a 64.58% reduction in the asphalt content. The angularity of the aggregate remained unchanged after separation. It was observed from scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images that the asphalt on the surface of the coarse aggregate had been eluted, and the morphology of the aggregate surface was completely exposed. This environmentally friendly separation method provides new possibilities for high-content RAP recycling in pavement engineering.
1. Introduction
With the acceleration of urbanization and infrastructure development, many RAP materials have accumulated [1,2,3]. These materials not only cover a lot of land but can also cause serious environmental pollution [4]. As the costs of pavement materials rise, research into RAP recycling technology is receiving increased attention [5]. Typically, 15–30% material cost reductions can be achieved, with RAP utilization rates between 5% and 15% [6,7]. Factors hindering the application of high-content RAP materials in recycled asphalt pavement include the phenomenon of its pseudo-granularity and the complexity of quality control in the construction process [8,9,10,11].
Promoting higher content percentages of RAP used in pavement engineering has drawn the attention of researchers [12,13]. However, one problem relating to the use of a higher RAP content is the agglomeration effect. The agglomeration of RAP aggregates is attributed to the viscoelastic effect of old asphalt, where the fine RAP aggregates agglomerate into coarse RAP aggregates, leading to the creation of RAP clusters. RAP clusters cannot be completely separated during asphalt pavement milling [14]. The RAP cluster phenomenon during the cold milling of asphalt pavements has been investigated, and the cold milling method was determined to inevitably cause RAP clusters [15]. Currently, the mix design of reclaimed hot mix asphalt mixtures (RHMAs) does not take into account the effect of RAP clusters [16,17]. Navaro et al. have argued that, even if a rejuvenator is added, RAP aggregates are difficult to disperse completely during the mixing process [18]. Pan et al. concluded that when the RAP content exceeded 30%, the actual and design grade difference would be enlarged due to the agglomeration effect of RAPs [19]. Therefore, the agglomeration effect is considered a phenomenon that negatively affects recycled asphalt mixtures [20].
Currently, there are two main categories of RAP aggregate separation methods: physical separation methods and chemical separation methods [7,21]. Xin et al. used a centrifugal device to crush, shear, and grind the coarse RAP in order to achieve a purely physical action [22]. Qu et al. chiefly used special wire brushes to impact, scrape, and grind the RAP material to separate the aged asphalt-rich mortar from the pseudo-size particles [23]. Feng et al. proposed a biological separation process for asphalt aggregate, using microorganisms to alter the adhesion between the asphalt and aggregate to achieve oil–rock separation [7]. To further verify that the biological separation process could effectively solve the phenomenon of RAP clusters, Xue et al. proposed a method for asphalt aggregate separation using bio-oil as a solvent; the results indicated that the separation of old asphalt and aggregate could effectively remove agglomerates and solve the pseudo-granularity problem in recycled mixtures [3]. However, none of these methods can be widely used. The mechanical stripping method uses friction and collision to peel asphalt from the aggregate surface [24]. It damages the edges and surface characteristics of the aggregate, and separating the asphalt and aggregates in RAP with small particle sizes is difficult [22]. The stripped asphalt still adheres to some mineral aggregates, and the aging interface persists [25]. The chemical separation method mainly uses solvents, such as trichloroethylene, carbon tetrachloride, gasoline, diesel, kerosene, etc., to extract the asphalt [26]. Although it can effectively ensure the integrity of the aggregate, the use of expensive or highly toxic solvents can pose a threat to the environment. When using these methods, the raw material and equipment loss is significant, the chemical reagents can easily pollute the environment, and the recycling effect is poor.
Surfactants—with their hydrophilic heads and hydrophobic tails—are widely used in oily sludge (OS) treatment to remove crude oil adsorbed onto solid particles. In addition, surfactant-enhanced OS cleaning technology is not only easily implemented but can also effectively remove oil from mineral surfaces at temperatures ranging from 50 °C to 70 °C [27]. Compared to cationic surfactants, anionic surfactants are less toxic to the environment. Sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) and sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate (SDBS) are common anionic surfactants, with oil removal efficiencies ranging from 26.99% to 96.69% [27,28,29,30,31]. However, research into surfactants in RAP treatment technology remains limited. There is a lack of relevant research on the process parameters of surfactants in the separation process for different RAP particle sizes, as well as systematic evaluations of the effects of gradation and aggregate morphology.
This study proposes a novel emulsification–separation method for RAP treatment, establishing optimal separation conditions for RAP clusters, evaluating the impacts on aggregate morphology and gradation, and demonstrating the environmental benefits of wastewater recycling.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. RAP Materials
The RAP material was obtained through the excavation of the upper layer of a road that had been in service for 10 years in Xi’an, Shaanxi Province, China. Ten years is a typical moderate aging state for RAP material. At this stage, asphalt hardening is obvious, and its performance is lower, but the integrity of the RAP quality aggregates is relatively good, making such a material suitable for evaluating the effectiveness of recycling technology.
The extracted gradation of the asphalt pavement was an AC-13 asphalt mixture with a nominal maximal aggregate size of 13.2 mm. Its gradation and asphalt content, which was 4.81%, were obtained by extractive testing. The aggregate was limestone, and its upper layer thickness was 5 cm. The crushing value of the coarse aggregate was 18.44, the abrasion value was 24.00, and the needle or plate content was 12.56, with an apparent specific gravity of 2.740 g/cm3. The aggregate gradation and the asphalt content of the RAP materials after the extraction are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Aggregate gradation and asphalt content of RAP materials after extraction.
The critical sieve sizes for 13.2–16, 9.5–13.2, 4.75–9.5, and 2.36–4.75 mm pretreatment RAP are respectively defined as 13.2, 9.5, 4.75, and 2.36 mm. It was observed that the passing percentages of the critical sieve of the RAP materials were high, which indicated that the extracted gradation of the RAP sources was relatively fine and that various sizes had agglomerated to varying degrees. It was also observed that the RAP asphalt content was relatively high for different sizes. This is due to the pretreatment screening of RAP material separated by heating; each size contains a large number of agglomerates, which are mainly composed of fine aggregates and oil sands. Their specific surface area is small, and they adsorb more asphalt content.
2.1.2. Anionic Surfactants
Three anionic surfactants were investigated: sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate (SDBS), sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS), and methyl ester sulfonate of fatty acids (MES). All surfactants were of analytical grade, with >99% purity. The appearance and molecular structure formulas of the surfactants are shown in Figure 1.
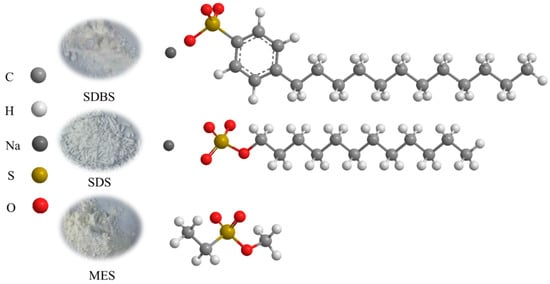
Figure 1.
Appearance and molecular structure formulas of surfactants.
2.2. Emulsification–Separation of RAP
2.2.1. RAP Pretreatment Experiments
According to the Chinese standard technical specification JTG/T T5521-2019 [32], RAP aggregates must be sieved into two parts before use. In this study, the CSE (crush and screen experiment) processing method was adopted, with the main purpose being to avoid the use of traditional mechanical processing, which can crush a large number of coarse aggregates and produce excess needle-like particles. In the CSE process, the large pieces of RAP are first dusted, then heated in the oven at 120 °C for 1 h, and finally kneaded and squeezed for separation. The CSE was used for the preliminary separation of the RAP aggregate, with the main purpose of separating the oversized particles (>16 mm) and then cooling them to obtain a large number of RAP clusters with different granular sizes.
For classification, the RAP material was pre-sieved into four particle sizes: 13.2–16, 9.5–13.2, 4.75–9.5, and 2.36–4.75 mm. Afterwards, RAP materials with different particle size ranges were identified based on the critical sieve size, such as 13.2–16 mm RAP, which was 13.2 mm RAP. The mortar with a particle size of less than 2.36 mm was collected without any separation, and the remaining four aggregates contained many agglomerates; in particular, the RAP larger than 9.5 mm had a high degree of agglomeration. Figure 2 shows the images of the RAP materials obtained using the CSE method.
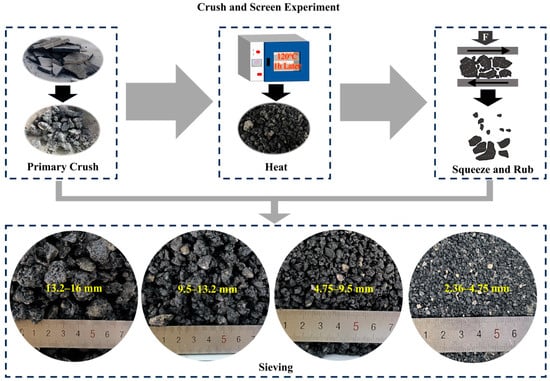
Figure 2.
Pretreatment processing of the RAP material.
2.2.2. RAP Emulsification–Separation Experiments
The emulsification–separation equipment used in this study was a mixing device modified from a drilling rig, where the drill bit of an ordinary drilling machine was replaced with a dispersion disk. For the emulsification–separation experimental process, the pretreated RAP was first preheated in an oven for about 30 min, during which time the emulsion was prepared. A certain amount of surfactant was weighed, poured into the tap water, stirred, and dispersed. After the RAP was preheated, it was gradually scooped into the container and stirred to disperse. During this process, the aggregates were placed near the container wall and were flipped and stirred every 10 min or so to sufficiently mix them. The asphalt foam and mineral foam in the upper layer of the emulsion surface were collected to prevent them from adhering again to the RAP. At the conclusion of the experiment, the aggregate was separated from the emulsion by sieving. After standing for 30 min, the emulsion was separated from the silt to obtain the recoverable residual emulsion. A flowchart of the emulsification–separation process is illustrated in Figure 3.

Figure 3.
Flowchart of RAP emulsification–separation.
The main function of the surfactants is to soften the asphalt. If their oil removal rate is the highest under identical conditions, their dispersing effect is the best, the agglomeration is easily dispersed, and their grading passing rate is the highest. In preliminary experiments, we chose 1800 RPM, 80 °C, and a 60 min rotation time; three different anionic surfactants, SDBS, SDS, and MES, were selected to study the effect of different concentrations (0–6 wt%) on the asphalt content. We then changed the emulsion/RAP to obtain the ratio with the highest oil removal efficiency.
The effects of different process parameters on RAP clusters varied, with speed (i.e., 280, 700, and 1800 RPM), temperature (i.e., 60, 80, and 90 °C), and time (i.e., 30, 60, and 90 min) all affecting the dispersion efficiency of agglomeration. Therefore, it was impossible to consider only changes in the asphalt content. The fineness modulus ratio (FMR) and degree of agglomeration (PL) were used as evaluation criteria to determine the best process parameters for lotion separation. The dispersion effect of RAP under the three process parameters was investigated using a three-factor, three-level orthogonal experiment, and the gray correlation method was used to determine the influence of the different process parameters on the dispersion effect. The three factors and three levels of the orthogonal experiment are shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Orthogonal test with three factors and three levels.
Owing to the significant influence of shear and collision on the dispersion of RAP particles of different sizes during mixing, this effect was refined after determining the relevant experimental parameters. Different sizes (13.2–16, 9.5–13.2, 4.75–9.5, and 2.36–4.75 mm) of pretreated RAP were selected to adjust the dispersing effect. First, RAPs of different sizes were handled separately; then, the sizes were adjusted, and RAPs of different sizes were gradually mixed in a 1:1 proportion to achieve the best size range for the dispersing effect.
2.3. Test Methods
2.3.1. Asphalt Content and Aggregate Gradation
The asphalt content of the RAP was determined using the conventional extraction method, and the asphalt content test was conducted for each RAP size to obtain its gradation and asphalt content, following the standard test method T0722 in the Standard Test Methods for Asphalt and Asphalt Mixtures for Highway Engineering (JTG E20-2019) [33]. Trichloroethylene was used as an eluent to remove the RAP asphalt from the samples, and then, the recycled aggregate and asphalt solutions were separated by centrifuge. After oven-drying the recycled aggregate, the initial and final weights of the samples were obtained, and the asphalt content was calculated.
2.3.2. Modulus of Fineness Method
The formula for calculating the fineness modulus is as follows [34]:
where uf is the fineness modulus and β1, β2, …, β5 are the cumulative sieve residue percentages of each sieve stage. β1 is the 13.2 cumulative sieve residue percentage, and β5 is the 0–2.36 mm cumulative sieve residue percentage. This study mainly investigated the dispersion of RAP above 2.36 mm; so, 100 was directly taken. The fineness modulus ratio (FMR) index of the extracted RAP aggregate to the emulsified RAP separation was calculated as follows:
where FMR is the fineness modulus ratio; ufaggregate is the fineness modulus of the old RAP material after the extraction test; and ufRAP is the fineness modulus of the RAP after emulsification–separation.
2.3.3. Improvement of the Loss Percentage Method
Xu et al. proposed a method to quantify the rate of RAP particle agglomeration at different sizes (ranging from 2.36 to about 19.0 mm) using sieve fraction tests [35]. We adapted it for quantitative evaluation in this article.
where PLi1 is the loss rate of the ith particle size following extraction (%), and pi is the fractionated sieve balance of the ith sieve after extraction. PLi2 is the loss rate of the ith particle size following emulsification–separation (%), and Ci is the fractionated sieve balance of the ith sieve after emulsification screening, with the ith sieve size not less than 2.36 mm.
The improved method considers the mass percentage of each particle size gradation. The total degree of agglomeration is calculated by summing the difference in loss rates for each block before and after extraction and emulsification–separation.
where PL is the agglomeration degree of RAP particles (%).
2.3.4. Angularity of Aggregates
Shape parameters, such as the axis, perimeter, and area of the processed RAP aggregates, can be obtained through IPP image acquisition. We sampled 100 particles of each size and calculated the average value, which was then subjected to arithmetic operations to obtain the axial coefficient and roundness quadratic parameters to determine the two-dimensional shape of the aggregates. Figure 4 presents aggregate images before and after RAP extraction and after emulsification–separation. The change in axial coefficient and roundness between the extracted RAP aggregate and the emulsified separated RAP was used to assess the effectiveness of the separation.
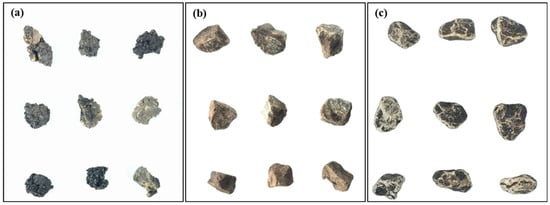
Figure 4.
Aggregate images before and after RAP extraction and after emulsification–separation: (a) original RAP before extraction; (b) RAP after extraction; and (c) RAP after emulsification–separation.
The axial coefficient is an indicator that describes the shape of the aggregate particles, which is the ratio of the longest axial length of the aggregate particle to the shortest axial length.
where Aspect is the axial coefficient; Axis (major) is the maximum axial length of the aggregate particles; and Axis (minor) is the shortest axial length of the aggregate particles.
Roundness describes the similarity of the shape of an aggregate particle to a circle.
where Roundness is the roundness of the aggregate particles; perimeter is the outer circumference of the 2D profile of the aggregate particles; and Area (polygon) is the area occupied by the 2D profile of the aggregate particles.
2.3.5. Aggregate Micro-Morphological Analysis
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM): The microstructure of 9.5 and 2.36 mm RAPs treated under optimal process conditions was obtained using scanning electron microscopy (JSM-IT 200 Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscope (FE-SEM) produced by JEOL Ltd., Tokyo, Japan with a working voltage of 20 kV, used as a secondary electron detector for imaging).
2.3.6. Recycling of the Remaining Emulsion
RAP was mixed with the upper clear emulsion after one treatment, and tap water or emulsion was added to the residual emulsion, such that the ratio of emulsion to RAP for each experiment was 1:2. The following experimental steps were the same as those for the emulsification–separation experiment, and the residual emulsion was collected again for the next recovery experiment. The emulsion recovery experiment was repeated six times.
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Influence of Anionic Surfactant Type and Content on Oil Removal Efficiency
The gradation data obtained after separation are detailed in Figure 5a. When the content was 2 wt% compared to other surfactants, SDBS had a better separation effect, and its passing rate of each block was higher than that of the other surfactants. Its gradation curve is closer to that of the extraction. MES and SDS, on the other hand, received poorer treatment, and both present large gaps between the gradation curves and the extracted gradations. Meanwhile, the clear water control group had extremely poor oil removal efficiency; with numerous agglomerates being unopened on its 13.2 mm sieve and a pass rate of less than 80%, the asphalt content was 3.26%. Figure 5b illustrates that SDBS had the best oil removal efficiency, reducing the asphalt content to 2.24% at a content of 2 wt%, which was more than half the reduction. The concentration of SDS must be increased to achieve a corresponding effect, while MES was less effective than the other two. Thus, only the emulsification–separation effect of SDBS on RAP was studied in subsequent experiments.
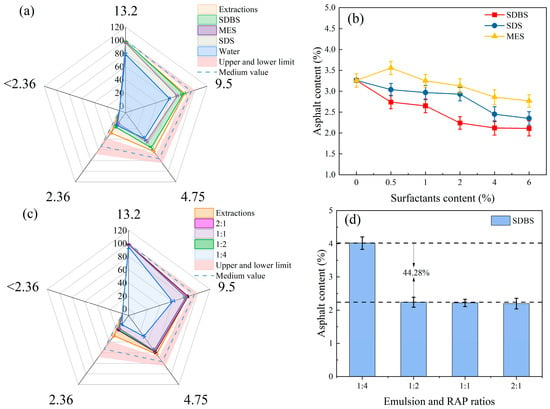
Figure 5.
Influence of anionic surfactant type and content on oil removal efficiency. Types and contents of surfactants: (a) gradation, (b) asphalt content and SDBS emulsion/RAP, (c) gradation, and (d) asphalt content.
Having determined the type of surfactant, the ratio of SDBS emulsion to RAP was varied to investigate the separating effect of different SDBS emulsion ratios on RAP. Figure 5c illustrates that when the ratio of SDBS emulsion to RAP was 1:4, the emulsion was too small, resulting in the eluted asphalt easily re-bonding to the RAP. Clusters were thus re-formed, and the passing rate was the lowest. Figure 5d shows that, as the ratio increased to 1:2, the asphalt content decreased by 44.28% as the solution increased, but the change was not significant as it continued to increase.
Based on the above results, SDBS had the best elution effect. The optimal doping amount was 2 wt%, and the ratio of SDBS emulsion to RAP was 1:2.
3.2. Influence of Process Parameters on the Emulsification–Separation Effect
An orthogonal test was used to study the effect of three factors—namely, temperature, time, and speed—on the PL, FMR, and asphalt content of RAP. As shown in Figure 6, with a decrease in temperature, the asphalt content showed an increasing trend, the FMR was also relatively low, the PL showed an increasing trend, and the peak of the PL appeared. Under the condition of same the temperature, with an increase in time and speed, the PL and asphalt content showed a decreasing trend; the FMR gradually increased, indicating that the longer the processing time and the higher the speed, the better the separation effect on RAP and the more asphalt removed. However, the corners of the aggregates were severely abraded as the time and speed increased; so, subsequent experimental conditions must also consider the angularity of the aggregate. Intuitive analysis was used to characterize the influence of different conditions on the emulsification–separation effects and determine the optimal conditions.
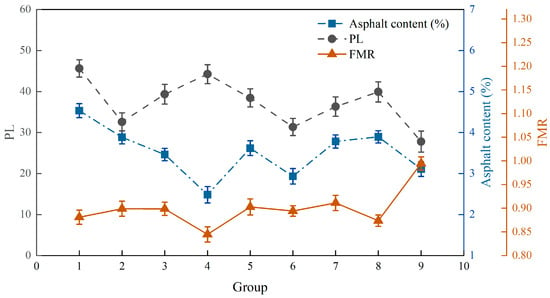
Figure 6.
Effect of different process parameters on RAP dispersion.
Table 3, Table 4 and Table 5 present an intuitive analysis of the asphalt content, FMR, and PL results obtained from the orthogonal test. K1, K2, and K3 represent the average test results obtained when factors were at the same level, and the magnitude of R indicates the degree to which different factors affect the separation effect.

Table 3.
Intuitive analysis of the asphalt content results of the orthogonal test.

Table 4.
Intuitive analysis of the FMR results of the orthogonal test.

Table 5.
Intuitive analysis of the PL results of the orthogonal test.
In Table 3, the primary and secondary factors affecting the asphalt content were temperature > rotation time > rotation speed. Temperature had the greatest impact on the RAP emulsification–separation effect, while time and rotation speed had similar effects. This is because asphalt is sensitive to temperature and can be softened by heating. In addition, as the temperature increases, the activation energy of the ionic surfactant significantly increases, and it is completely ionized in the solution system, enabling it to react with the asphalt and dissolve it. However, when the temperature is too high, the solution boils easily, the asphalt foam and mineral foam is reduced, and the latter is unlikely to float. The asphalt falling off in the system is likely to re-adhere, leading to an increase in asphalt content. Therefore, to reduce the asphalt content, the optimal combination is a speed of 1800 RPM, a temperature of 80 °C, and a time of 90 min.
In Table 4, the primary and secondary factors affecting the FMR are rotation speed > temperature > rotation time. Rotation speed and temperature had a greater impact, while time had a smaller impact. The FMR is a measure of the agglomeration of coarse and fine aggregates before and after emulsification–separation treatment. When the rotation speed and temperature reach a certain level, the fine aggregates can quickly detach from the coarse aggregates, and the coarse and fine emulsification–separation aggregates are basically consistent with the extracted aggregates. Therefore, to improve the FMR, the optimal combination is a rotation speed of 1800 RPM, a temperature of 90 °C, and a time of 90 min. In Table 3 and Table 4, the difference in R values between the asphalt content and FMR is relatively small, indicating that when the asphalt content and FMR decrease or increase, they become less sensitive (to a certain extent) to changes in factor combinations.
In Table 5, the order of factors affecting the PL is rotation time > rotation speed > temperature. Under the condition of constant speed and temperature, as the processing time extends, the mechanical action gradually causes collisions between aggregates, and more agglomerates are opened up. To reduce agglomeration, the optimal combination is a rotation speed of 1800 RPM, a temperature of 90 °C, and a time of 90 min.
Using gray correlation analysis based on temperature, time, and rotation speed, the correlation of temperature and time with the asphalt content, FMR, and PL was above 0.7, while the correlation with rotation speed was 0.5. In summary, compared to rotation speed, temperature and time had a greater impact on the dispersion effect of RAP.
Regarding RAP clusters and separation, the optimal separation parameters for emulsification–separation technology were 80 °C, 1800 RPM, and 90 min. However, because time mainly affects the asphalt content and PL, the increasing wear between aggregates over time was considered. After testing, the angularity of the aggregate treated for 90 min was basically the same as that of the aggregate treated with secondary emulsification–separation; the wear was severe, and, considering all factors, 60 min was ultimately chosen as the optimal treatment time.
Based on the above conclusion, the separation effect was the best and its asphalt content was reduced to 2.24 when the SDBS surfactant content was 2 wt%; the ratio of emulsion to RAP were 1:2, the rotation time was 60 min, the temperature was around 80 °C, and the rotation speed was determined to be 1800 RPM. The PL decreased to 26.9, and the FMR was 0.89.
3.3. Influence of RAP Particle Size on Emulsification–Separation
3.3.1. Effects of AC-13 Grading RAP on Emulsification–Separation
The AC-13 RAP aggregate process was conducted under the optimal conditions, as outlined in Section 3.2. A comparison was made between the process and the directly extracted grading curve. Under the optimal conditions shown in Figure 7, when the entire separation gradation curve was basically the same, we calculated the filling area between the emulsion sieve grading curve and the extraction grading curve, which had an area of 64.58. This indicated the emulsification of RAP sieving after false particle sizes were eliminated, but a gap in the aggregates below 4.75 mm existed, owing to the higher asphalt content. Thus, the emulsification–separation remained prone to agglomeration. To further optimize the experimental scheme, the effect of different particle sizes on the separation effect of RAP was refined. To further reduce the asphalt content and optimize the separation effect without increasing the cost and affecting the performance of the aggregates, the optimal RAP size was obtained by using the graded separation and its mixed separation comparison.
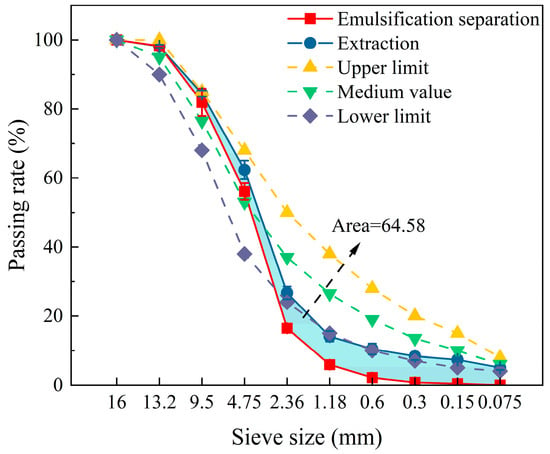
Figure 7.
Emulsification–separation of AC-13 RAP grading curves.
3.3.2. Emulsification–Separation Effects of Different Sizes of RAP Materials
The purpose of separately processing RAPs of different sizes is to refine the specific separating effect of different particle sizes during emulsification–separation and to obtain the PL between different particle sizes, thus preparing for the subsequent separation of mixed particle sizes. The gradation curves in Figure 8 indicate emulsification–separation clusters of different particle sizes. When treating RAP above 4.75 mm, the emulsification passing rate is almost the same as the extraction passing rate, but there remains a gap. The filling area between the emulsification–separation sieve grading curve and the extraction grading curve was calculated. According to the results, the best treatment effect was achieved with 13.2 mm RAP, which has an area of only 39.14, whereas the area of 2.36 mm RAP is 139.21, indicating a significant difference between its grading curve and the extraction grading curve. To refine the specific variations of the different sizes in the mixed separation, the different particle sizes were progressively paired within emulsification–separation.
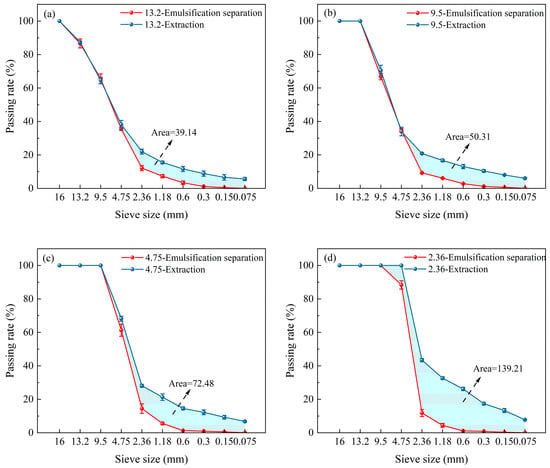
Figure 8.
Grading curves of emulsification–separation of different sizes of RAP: (a) 13.2 mm; (b) 9.5 mm; (c) 4.75 mm; and (d) 2.36 mm.
As shown in Figure 9, when different RAP sizes were treated separately, the separated asphalt content decreased significantly. The asphalt content of 9.5 mm RAP decreased by more than 60%, and the asphalt content of 13.2 and 4.75 mm RAP decreased by 50%. The FMR was higher than 0.9 for 4.75 mm RAP; the aggregate coarseness and fineness were the same as the original gradation. However, the asphalt content of 2.36 mm RAP was only reduced by about 18%, and its fineness modulus was only 0.798, which was poorly separated and required further separation.
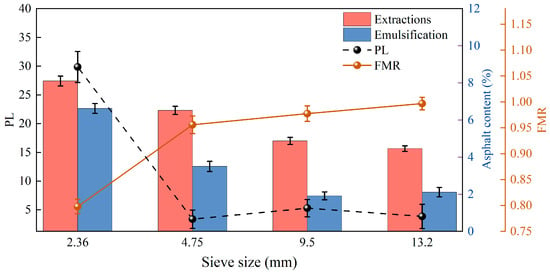
Figure 9.
Evaluation of emulsification–separation of different sizes of RAP.
Table 6 indicates the asphalt content after secondary separation, where it was further reduced, but its angular wear was more obvious through testing and observation. The gradation curve after one separation was basically the same; so, the difference in gradation after the second separation was small, and it met the requirements for use.

Table 6.
Asphalt content after secondary emulsification–separation.
3.3.3. Emulsification–Separation Effects of Different RAP Gradation Levels
A total of 300 g of pretreated RAP of different sizes was removed from each aggregate size, and 300 g of oversized aggregates with a diameter of 16 mm or more was taken. A total of 1500 g of RAP was emulsified and separated, and the optimum separation conditions in Section 3.2 were selected to determine the change in mass, thereby obtaining the increase or decrease in conditions for each aggregate. We defined the ratio of the mass change of each agglomerate of the aggregate before and after emulsification as the rate of change. A positive rate of change meant that the mass of this grade of aggregate was decreasing; a negative rate of change meant that the mass of this grade of aggregate was increasing.
In Figure 10, the quality of RAP aggregates above 9.5 mm is shown to be significantly reduced, especially the 16 mm RAP, with a sieve removal rate of 100%, and the 13.2 mm RAP, with a sieve removal rate of 88.11%. The sieve removal rate of the 9.5 mm RAP barely changed, with a rate of only 8.54%; correspondingly, aggregates below 9.5 mm increased, with the 4.75 mm aggregate increased by 31.73% and the 2.36 mm aggregate almost doubled, its sieve removal rate reaching 103.27%. From the rate of change of each grade, it can be preliminarily concluded that an aggregation larger than 9.5 mm contains numerous 4.75 and 2.36 mm aggregates, especially fine aggregates of 2.36 mm, with a very significant change rate. Aggregates of 2.36 mm can easily produce 4.75 mm clusters during processing because aggregates below 4.75 mm contain more asphalt, which is easily rebonded during the separation process. Therefore, no 2.36 mm RAP was added for subsequent separation, and only RAPs with a particle size above 4.75 mm were studied in mixed separation. To further explore the optimal separation, we used 500 g each of the same quality of 13.2, 9.5, and 4.75 mm coarse aggregates for emulsification–separation.
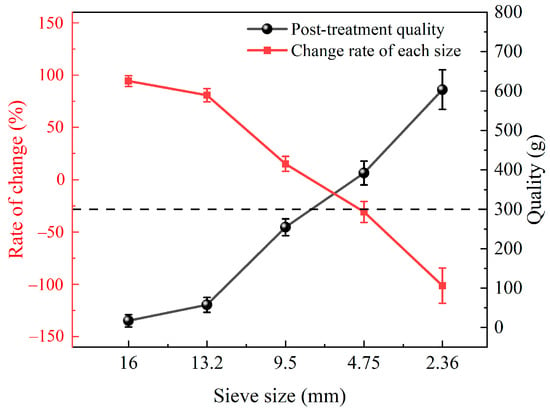
Figure 10.
Changes in mass after emulsification–separation of various RAP sizes.
Figure 11 shows that the sieve removal rate of the 9.5 mm aggregate reached about 40%, which was almost five times higher than the 8% rate for the average mixed processing of aggregates. Thus, it can be proved that the selection of coarse aggregate agglomerates with larger particle sizes makes it easier to open the agglomerates for separation.
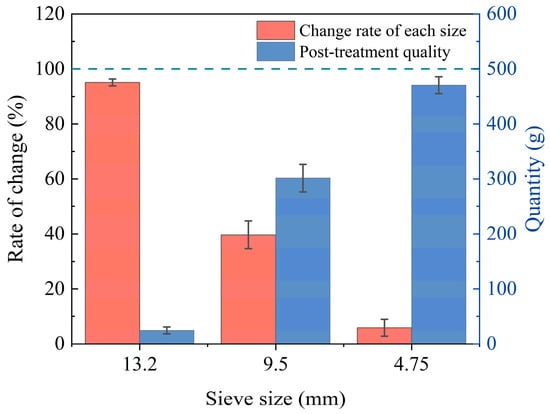
Figure 11.
Quality change in the emulsification–separation of RAP coarse aggregates above 4.75 mm in size.
As seen in Figure 12 and Table 7, when only 9.5–13.2 mm RAP was used, mixed in a 1:1 ratio for processing, the PL was only 18.06, the FMR reached 0.99, and the asphalt content was reduced to 1.6%, thus indicating that the mixing and separation effect is excellent when treating coarse aggregates of 9.5 mm or more. When only 4.75–9.5 mm RAP was used, the PL was only 15.67, the FMR was as low as 1.00, and the asphalt content was reduced to 1.8%, indicating an excellent separating effect. The filling area between the emulsification–separation sieve grading curve and the extraction grading curve was calculated. According to the results, the treatment effect for 9.5–13.2 mm RAP was the best, with an area of only 14.85. The separation effect for 4.75–9.5 mm RAP was also excellent, with an area of 26.48. The separation effect of mixed processing was significantly improved compared to single particle size processing. Based on the above conclusion, the 1:1 treatment of 13.2 and 9.5 mm RAPs yielded the best results.
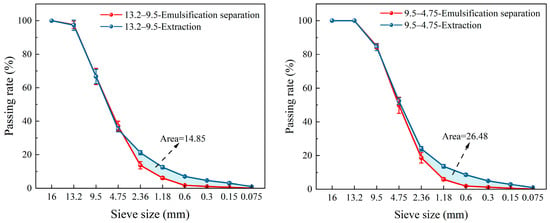
Figure 12.
Gradation curves for mixed separation of 9.5–13.2 mm and 4.75–9.5 mm RAP.

Table 7.
Effect of mixed separation of RAP aggregates.
3.4. Recovery of the Emulsion During Emulsification–Separation
A large amount of emulsion was collected from the emulsification–separation process, which was crucial to achieving the recycling of the emulsion. We repeated the processing conditions in Section 3.2 to treat 9.5–13.2 mm RAPs mixed in a 1:1 ratio. The effect of the number of emulsion cycles on the asphalt content of the aggregate is shown in Figure 13. As the number of emulsion cycles increased, the asphalt content of the aggregate remained at about 1.7% and barely changed. This indicated that the main effect of the emulsion was to reduce the viscosity of the RAP and promote the formation of bubbles. As a result, the emulsion collected from the RAP emulsification–separation process could be reused in the system, achieving zero effluent discharge.
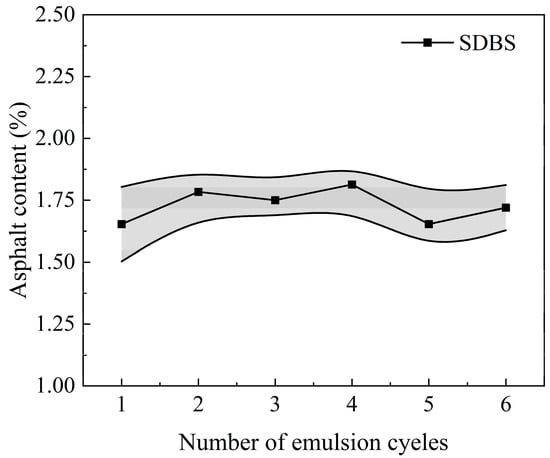
Figure 13.
Influence of the number of emulsion cycles on oil removal efficiency.
3.5. Angularity of Recycled Aggregates
Based on the experimental results, we selected the RAP treated with the best processing technology, observed the angularity of its coarse and fine aggregates, and repeated the separation to obtain the result of the secondary separation. V represents a lack of treatment, E1 represents preliminary emulsification–separation, and E2 represents secondary emulsification–separation.
After extraction–separation, the original aggregate had a relatively large axial ratio, which indicated a good needle-like property, which decreased after secondary emulsification–separation. The angularity between the aggregates deteriorated through extrusion and kneading and gradually tended to be spherical. As seen in Figure 14, the preliminary emulsification–separation RAP aggregate had a slight decrease in angularity, and its axial ratio was relatively small compared to the extracted aggregate, but the average reduction was only about 0.1. However, the sharpness of secondary emulsification–separation significantly decreased, and the 4.75 mm aggregate decreased by 0.3, approaching the critical value. Therefore, it is not recommended to carry out secondary emulsification–separation.
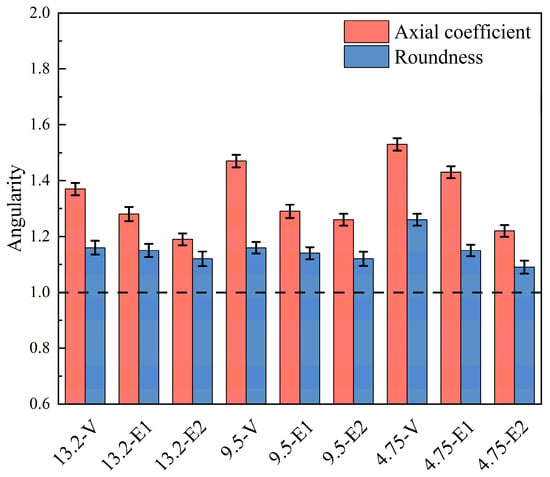
Figure 14.
Comparison of axial ratio roundness before and after RAP separation.
On the other hand, the surface of the aggregates was reshaped, but this can be understood in other ways. Figure 14 shows that the roundness of the aggregates changed after emulsification–separation. It can also be seen from the roundness parameter that the treated aggregate parameter was closer to 1, and the aggregate shape was closer to round. Compared to the secondary emulsification–separation, the changes in the preliminary emulsification–separation were smaller, with only a change of about 0.05, which is consistent with the extraction of aggregates.
3.6. Micro-Morphological Analysis Using SEM
Based on the test results, we selected RAPs treated with both the optimum and suboptimum processes to observe and compare the microstructure of the 9.5 and 2.36 mm aggregates. In the process of sieving the coarse aggregate material, we found that the asphalt coating was on the surface of the coarse aggregate material. According to the results of experimental processing, it was mainly divided into two cases: partial coating of the asphalt and extensive coating of the asphalt; the interfaces of the two surface asphalt coating cases are shown in Figure 15.
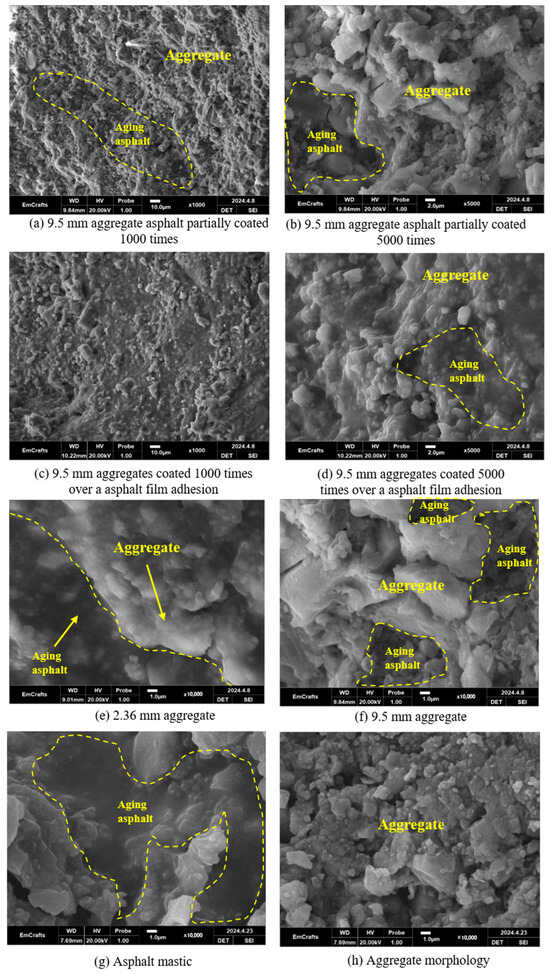
Figure 15.
SEM images of aggregates after emulsification–separation.
In Figure 15a,b, the asphalt partially wraps the 9.5 mm coarse aggregate, mainly showing its morphology, with only a small part of the asphalt remaining and with no asphalt mortar. Most of the coarse aggregates processed under optimal conditions exhibited this morphology. Part of the coarse aggregate surface adhered to the asphalt film. In Figure 15c,d, the surface of the large, wrapped part of the 9.5 mm coarse aggregate is also mainly covered by asphalt and asphalt mastic. However, it is a thin film, and the basic morphology of the aggregate can still be observed.
In Figure 15e,f, the 2.36 mm aggregate is completely wrapped by asphalt, and only part of the aggregate is exposed on the aggregate surface. The 9.5 mm aggregate’s morphology on the surface of the coarse aggregate is largely exposed. Figure 15g,h, illustrates that the asphalt part and the aggregate part of the aggregate surface are enlarged separately, which can be seen more closely, indicating the two adhesion patterns of the asphalt mortar and the aggregate. The black part is asphalt, and at 10,000 times magnification, asphalt is seen to adhere to the surface of some white aggregates.
3.7. Mechanism Analysis of RAP Emulsification–Separation
3.7.1. Action of Surfactants
In Figure 16, it can be observed that, after using anionic surfactants to formulate emulsions, the water–oil amphiphilicity of the surfactant in the emulsion effectively reduced the mutual exclusion phenomenon between the hydrophilic group of the surfactant and the hydrophobic pollutants and improved the solubilizing ability of the emulsion on the pollutants. The solubilizing effect of the lotion on the aged asphalt of the RAP surface gradually softened the asphalt. Then, as water penetrated, the adhesion between the aged asphalt and the aggregate was weakened, causing the asphalt to separate from the aggregate surface. The emulsification–separation method proved its effectiveness by destroying the colloidal structure of the aged asphalt with surfactants. It is recommended to apply it to modified asphalt, different types of matrix asphalt, etc. Its basis is derived from its amphiphilic molecular structure and its adsorption behavior at the interface. The specific effects of different materials will be explored in future research. The surface polarity of stone materials, such as basalt or granite, is strong, leading to an increase in reagent consumption, but the effect and change rule after treatment are basically the same as those of limestone.
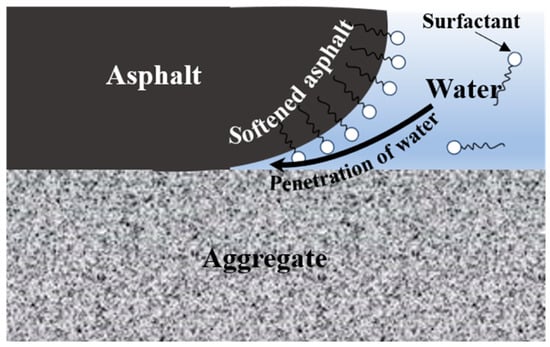
Figure 16.
Mechanism of surfactant action.
3.7.2. Influence of Process Parameters
The separation of asphalt and aggregate depends on the balance between the force separating the asphalt and aggregate and the force combining the asphalt and aggregate. This step is influenced by various factors, including temperature, processing time, stirring speed, etc. Figure 17 shows the mechanism of the process affecting the separation effect.
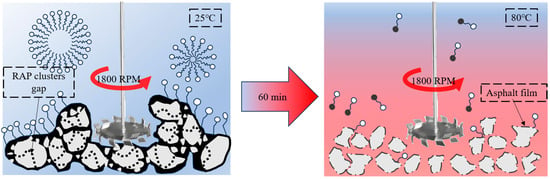
Figure 17.
Mechanism of the process affecting the dispersion effect.
The temperature significantly affects the separation of oil from the solid matrix, and an increase in temperature leads to a gradual decrease in the adhesion between the solid and asphaltene. Because of the strong bonding between the RAP aggregate at room temperature and the aggregate asphalt, it is necessary to soften the asphalt by heating. The ionic surfactant is weakened by temperature and becomes the formulation of choice. The hot washing process significantly increases ionic surfactant activation energy in the solution system and completely ionizes it, thus stabilizing the system. Surfactant molecules in ionic form are more likely to react with the strong electrolytes in asphalt, which, in turn, promotes the formation of gels. The ionic surfactant generates the gel molecule, and its hydrophobic group moves toward the inner gel; the inner core of the gel is attracted to the asphalt and draws it to the inner gel to exhibit a solubilizing effect.
The processing time and stirring speed can also affect the separation effect. If the stirring speed and time are insufficient, the surfactant and RAP will not mix evenly. However, at the same time, excessive rotation speed and time can lead to the destruction of aggregates and generate higher energy consumption. Through this experimental study, it was found that the processing time mainly affects the asphalt content and agglomeration degree, while the mixing speed mainly affects the FMR and agglomeration degree. As the processing time increases, the degree of wear between aggregates intensifies and the asphalt content decreases. The longer the time, the higher the mechanical collision efficiency between aggregates and the more clusters are opened. Therefore, the emulsification–separation is usually completed within 60 min, and it is not recommended to extend the processing time. At the same time, as the stirring speed increases, the mechanical force becomes stronger, and the effect of agglomeration opening improves. However, this study found that, from the perspective of the separation effect, the collision effect between aggregates is insufficient when the rotation speed is low, and all three indicators are poor. Increasing the rotation speed to 1800 RPM can achieve the best effect.
3.7.3. Influence of Aggregate Size
The PL of RAP varies with different sizes, and the size of the aggregate mainly affects its collision efficiency, which, in turn, affects the washing effect of the asphalt. The collision and shear behaviors between aggregates of different sizes during emulsification–separation are different; so, it is necessary to study the emulsification–separation effects for different particle sizes. Figure 18 shows the mechanism of RAP separation for different sizes. After comparing the emulsification–separation effects on a single particle size with the extraction effect, the emulsification–separation effect was found to be excellent when dealing with coarse aggregates larger than 4.75 mm. When processing 2.36 mm fine aggregate, a large amount of oil sand adheres to it. Owing to the larger specific surface area of fine aggregates, their asphalt film is thicker. After being softened by heating, the main effect of shear collision occurs on the softened asphalt, and only a portion of the asphalt is floated up. By studying the mixing of RAP of different sizes, it was found that the best treatment effect was achieved when mixing 13.2 and 9.5 mm RAP aggregates in a 1:1 ratio. After analysis, when there were more coarse aggregates larger than 9.5 mm in the mixed system, their dispersion effect was found to be better. When dealing with other gradations of RAP, it is recommended to mix the nominal maximum aggregate particle size with the RAP of the next level size for dispersion, for which a theoretical optimal solution can be obtained. Future research can investigate the peeling of the asphalt film on the surface of fine aggregates and elucidate the mechanism of differential dispersion effects between coarse and fine aggregates under shear fields.
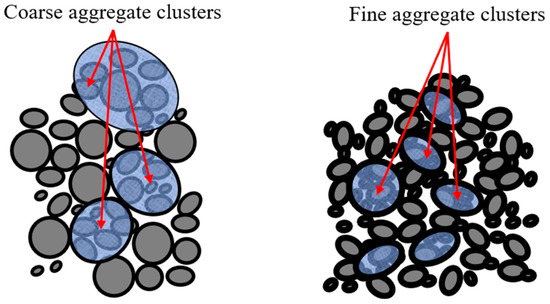
Figure 18.
Mechanism of the aggregate size affecting the dispersion effect.
4. Conclusions
This study developed and validated a novel emulsification–separation method for RAP treatment, achieving effective separation while maintaining the aggregate’s properties. The key findings are summarized as follows:
- Through orthogonal experiments, the following optimal separation conditions were established: 2 wt% SDBS surfactants, 1:2 emulsion-to-RAP ratio, 80 °C temperature, and 60 min processing at 1800 RPM. Under these conditions, the AC-13 RAP asphalt content was reduced to 2.24%, the PL decreased to 26.9, and the FMR reached 0.89. We processed RAP of different particle sizes separately and gradually mixed them to achieve the best results. The RAP of 9.5 mm achieved superior separation, with its asphalt content being 3.30%. Optimal results were achieved by mixing 13.2 and 9.5 mm RAPs in a 1:1 ratio, reducing the asphalt content to 1.67%, and the PL decreased to 18.06 with an FMR of 0.998.
- The angularity of the emulsification of the RAP aggregate was slight decrease and its axial ratio was relatively small compared to that of the extracted aggregate, which is a reduction of only about 0.1. The roundness of the aggregates was slightly reduced, but no difference was observed between them.
- The form of asphalt adhesion to the aggregate can also be observed from the microscopic morphology of the treated RAP aggregate surface. The asphalt on the surface of the better-treated coarse aggregate of 9.5 mm was basically washed off, and the morphology of the aggregate surface was exposed. The fine RAP aggregate of 2.36 mm, retained most of the asphalt mortar on its surface, further research will be conducted to address this.
- Under optimal processing conditions, as the number of emulsion cycles increased, the asphalt content of the aggregate reached about 1.7% and then did not change much. As a result, the emulsion collected from the RAP emulsification–separation process could be reused in the system, achieving zero effluent discharge.
Author Contributions
P.C.: Conceptualization, Methodology, and Review and Editing; K.Y.: Data Curation and Writing—Original Draft Preparation. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51978070), the Key Research and Development Plan Project of Shaanxi Province (2023-YBSF-110), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, CHD (300102313206).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Ali, A.W.; Mehta, Y.A.; Nolan, A.; Purdy, C.; Bennert, T. Investigation of the impacts of aging and RAP percentages on effectiveness of asphalt binder rejuvenators. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 110, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirhosseini, A.F.; Tahami, S.A.; Hoff, I.; Dessouky, S.; Ho, C.-H. Performance evaluation of asphalt mixtures containing high-RAP binder content and bio-oil rejuvenator. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 227, 116465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Liu, C.; Qu, J.; Lv, S.; Ju, Z.; Ding, S.; An, H.; Ren, K. Research on pavement performance of recycled asphalt mixture based on separation technology of asphalt and aggregate in RAP. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 393, 132103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Guo, C.; Chen, T.; Zhang, W.; Yao, K.; Fan, C.; Liang, M.; Guo, C.; Yao, Z. Evaluation on the mechanical performance of recycled asphalt mixtures incorporated with high percentage of RAP and self-developed rejuvenators. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 269, 121337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.; Chen, H.; Wang, H.; Shi, C.; Yang, J. The feasibility of using epoxy asphalt to recycle a mixture containing 100% reclaimed asphalt pavement (RAP). Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 319, 126122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Roque, R.; Hernando, D.; Lopp, G. Effect of reclaimed asphalt pavement and recycled asphalt shingles on fracture tolerance of asphalt binders. J. Test. Eval. 2019, 47, 3259–3274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Cao, J.; Gao, L.; Yi, J. Recent developments in asphalt-aggregate separation technology for reclaimed asphalt pavement. J. Road Eng. 2022, 2, 332–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalfattah, I.A.; Mogawer, W.S.; Stuart, K. Quantification of the degree of blending in hot-mix asphalt (HMA) with reclaimed asphalt pavement (RAP) using Energy Dispersive X-Ray Spectroscopy (EDX) analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 294, 126261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelaziz, A.; Masad, E.; Epps Martin, A.; Mercado, E.A.; Bajaj, A. Multiscale characterization of aging and rejuvenation in asphalt binder blends with high RAP contents. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2021, 33, 04021287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherif, R.; Eddhahak, A.; Gabet, T.; Hammoum, F.; Neji, J. Effect of the processing conditions on the viscoelastic properties of a high-RAP recycled asphalt mixture: Micromechanical and experimental approaches. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2021, 22, 708–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Yang, J.; Gao, J.; Zheng, M.; Song, L.; Xu, J.; Sun, C. RAP chunks produced in cold milling operation of asphalt pavement: Evaluation, mechanism, and engineering investigation in China. J. Traffic Transp. Eng. 2024, 11, 972–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Ding, Y.; Wang, J.; Shi, Y.; Cao, Z.; Sun, G.; Huang, B. Multiscale molecular simulations on the rejuvenation of recycled asphalt mixture: An insight into molecular impact of rejuvenators in aged asphalt binders. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 414, 137621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Hu, W.; Polaczyk, P.A.; Han, B.; Xiao, R.; Zhang, M.; Huang, B. Rheological and aging characteristics of the recycled asphalt binders with different rejuvenator incorporation methods. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 262, 121249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaumanis, M.; Boesiger, L.; Kunz, B.; Mazzoni, H.; Bruhin, P.; Mazor, S.; Poulikakos, L. Three indexes to characterise crushing and screening of reclaimed asphalt pavement. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2022, 23, 4977–4990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Tao, W.; Gao, J.; Yu, D.; Zhou, J.; He, L.; Yao, Y. Measurement of particle agglomeration and aggregate breakdown of reclaimed asphalt pavement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 296, 123681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Shen, J.; Kim, S. Effect of clustering of reclaimed asphalt pavement particles on rutting performance of asphalt mixtures containing RAP. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2023, 35, 04023239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, H.; Wang, K.; Huang, G.; Shen, Z.; Sun, L. Effect of recycled aggregate gradation on the degree of blending and performance of recycled hot-mix asphalt (HMA). J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 398, 136550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navaro, J.; Bruneau, D.; Drouadaine, I.; Colin, J.; Dony, A.; Cournet, J. Observation and evaluation of the degree of blending of reclaimed asphalt concretes using microscopy image analysis. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 37, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, T.; Liu, G.; Zhou, J.; Guo, P.; Zhao, Y. Optimization of gradation design of recycled asphalt mixtures based on fractal and Mohr-Coulomb theories. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 248, 118649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bressi, S.; Dumont, A.-G.; Pittet, M. Cluster phenomenon and partial differential aging in RAP mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 99, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, X.; Cao, J.; Feng, D.; Gao, L.; Hu, W.; Yi, J. Performance evaluation of recycled asphalt mixtures with various percentages of RAP from the rotary decomposition process. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 321, 126406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Tang, W.; Li, N.; Jiang, M.; Huang, J.; Wang, D. Refined decomposition: A new separation method for RAP materials and its effect on aggregate properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 358, 129452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, X.; Xiao, Y. Experimental evaluation of fatigue performance of recycled asphalt mixture using refined separation recycled aggregates. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 411, 134786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Huurman, M.; De Bruin, B.; Demmink, E.; Frunt, M. Towards 90% warm re-use of porous asphalt using foaming technology. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 190, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Liu, Y.; Xu, O.; Li, B. Influence of material characteristics on adhesion at interface between asphalt and aggregate. Chang. Daxue Xuebao/J. Chang. Univ. 2010, 30, 6–9. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, D.; You, Z.; Chen, S.; Liu, C.; Gao, J.; Lv, S. The performance of asphalt binder with trichloroethylene: Improving the efficiency of using reclaimed asphalt pavement. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 232, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Sun, D.; Chen, F.; Xu, H.; Xu, Z. New insights into interaction between oil and solid during hydrothermal treatment of oily sludge. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 471, 134358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Xu, H.; Cao, Y.; Wang, J.; Cui, J.; Sun, X. Advances in oil sludge separation technology and mechanism at normal temperature: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 114329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Ma, Y.; Feng, X.; Alheshibri, M.; Bu, X.; Ma, G.; Ni, M.; Li, Q.; Liu, A.; Niu, X. Optimization of an oil recovery process from oily sludge using a combined technique of froth flotation and centrifugal treatment. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 400, 136752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yin, Z.; Qin, J.; Yang, W.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, L. Role of surfactants in facilitating oil-solid separation in oily sludge treatment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 358, 130275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, D.; Jing, L.; Yong, Z.; Jin, L.; Tai, Y. Anionic/non-ionic surfactant system for washing oily sludge. Adv. Chem. Ind. 2014, 33, 2753–2757. [Google Scholar]
- JTG/T T5521-2019; Technical Specifications for Highway Asphalt Pavement Recycling. Ministry of Transport of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2019.
- JTG E20-2019; Standard Test Methods of Bitumen and Bituminous Mixtures for Highway Engineering. Ministry of Transport of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2019.
- Ling, H.J.; Wang, D.X.; Bai, H.E.; Wu, K.H. Evaluation and Control on Conglomeration of RAP in Cold Recycling Project of Asphalt Concrete Pavement. Highway 2008, 11, 221–225. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xu, G.; Ma, T.; Fang, Z. The evaluation method of particle clustering phenomena in RAP. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).