Isolation of a Novel Bioactive Fraction from Saffron (Crocus sativus L.) Leaf Waste: Optimized Extraction and Evaluation of Its Promising Antiproliferative and Chemoprotective Effects as a Plant-Based Antitumor Agent
Abstract
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material
2.2. Materials and Reagents
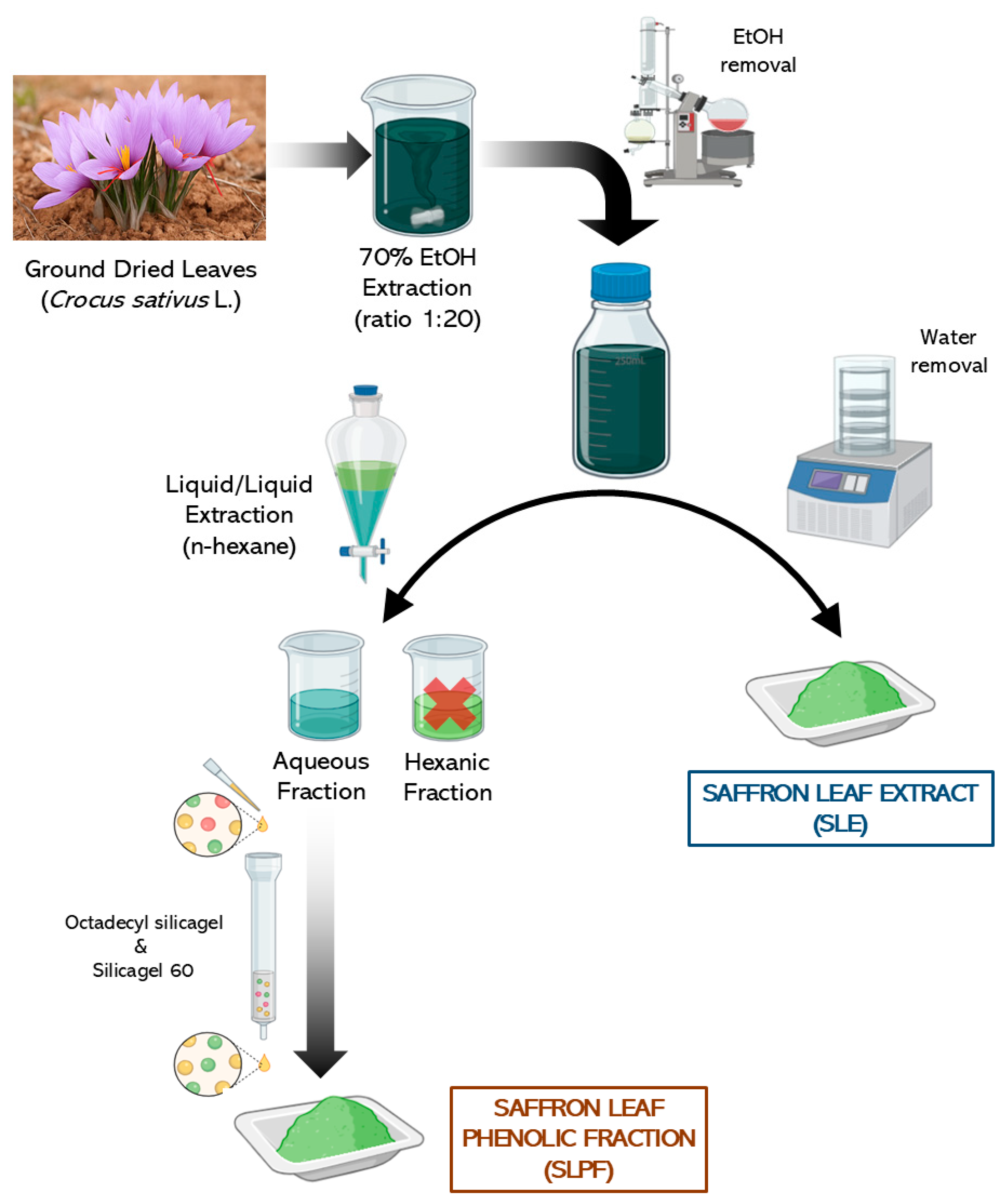
2.3. Saffron Leaf Extraction
2.4. Purification Protocol for Saffron Leaf Phenol-Rich Fraction
2.5. Identification and Quantification of Phenols by HPLC-DAD/ESI-MS
2.6. Cell Culture and Treatment
2.7. Iron- and Copper-Chelating Activities
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Phenolic Composition of Saffron Leaf Extracts
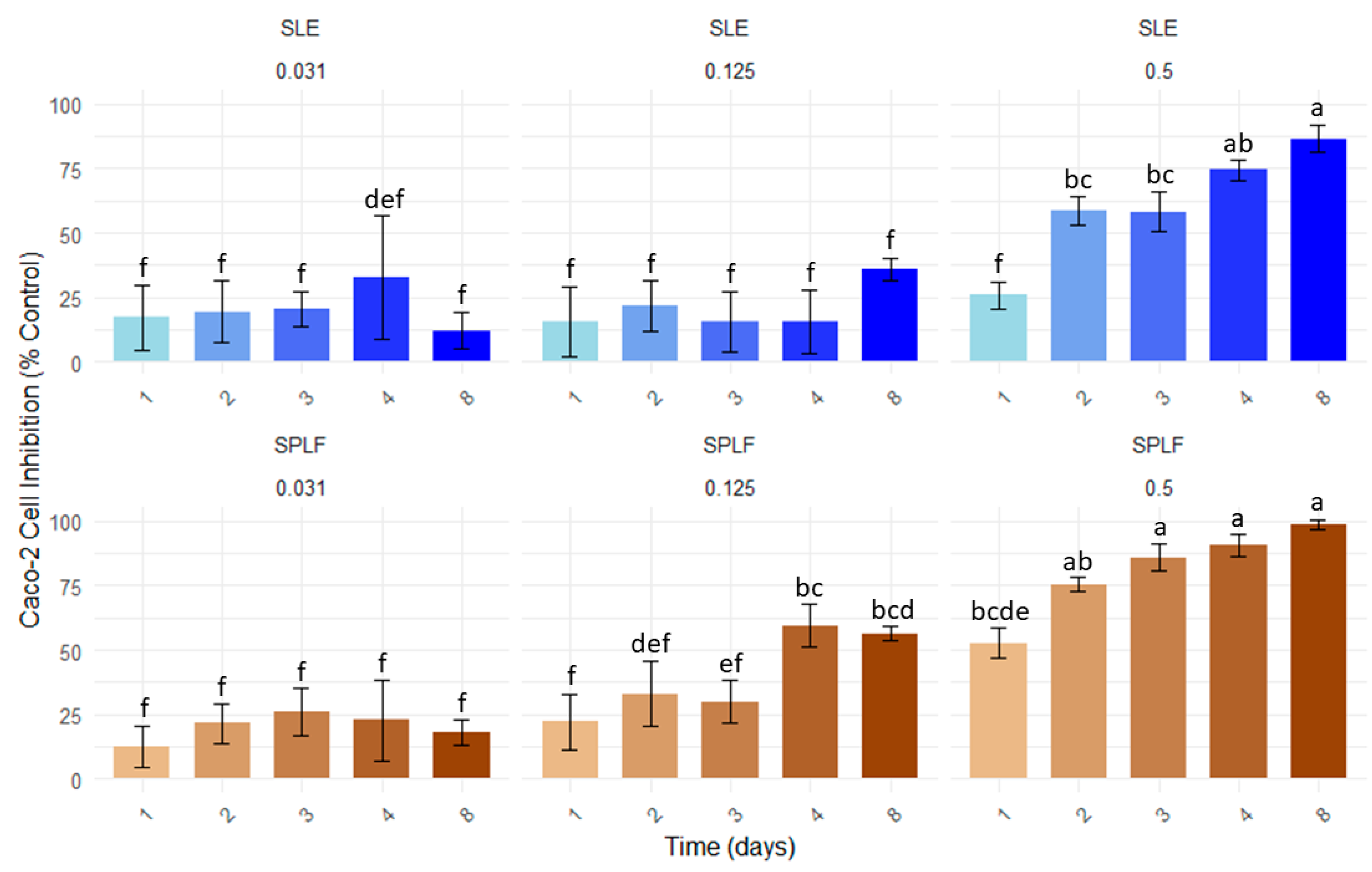
3.2. Effect of Saffron Leaf Extracts on Proliferation of Caco-2 Cells
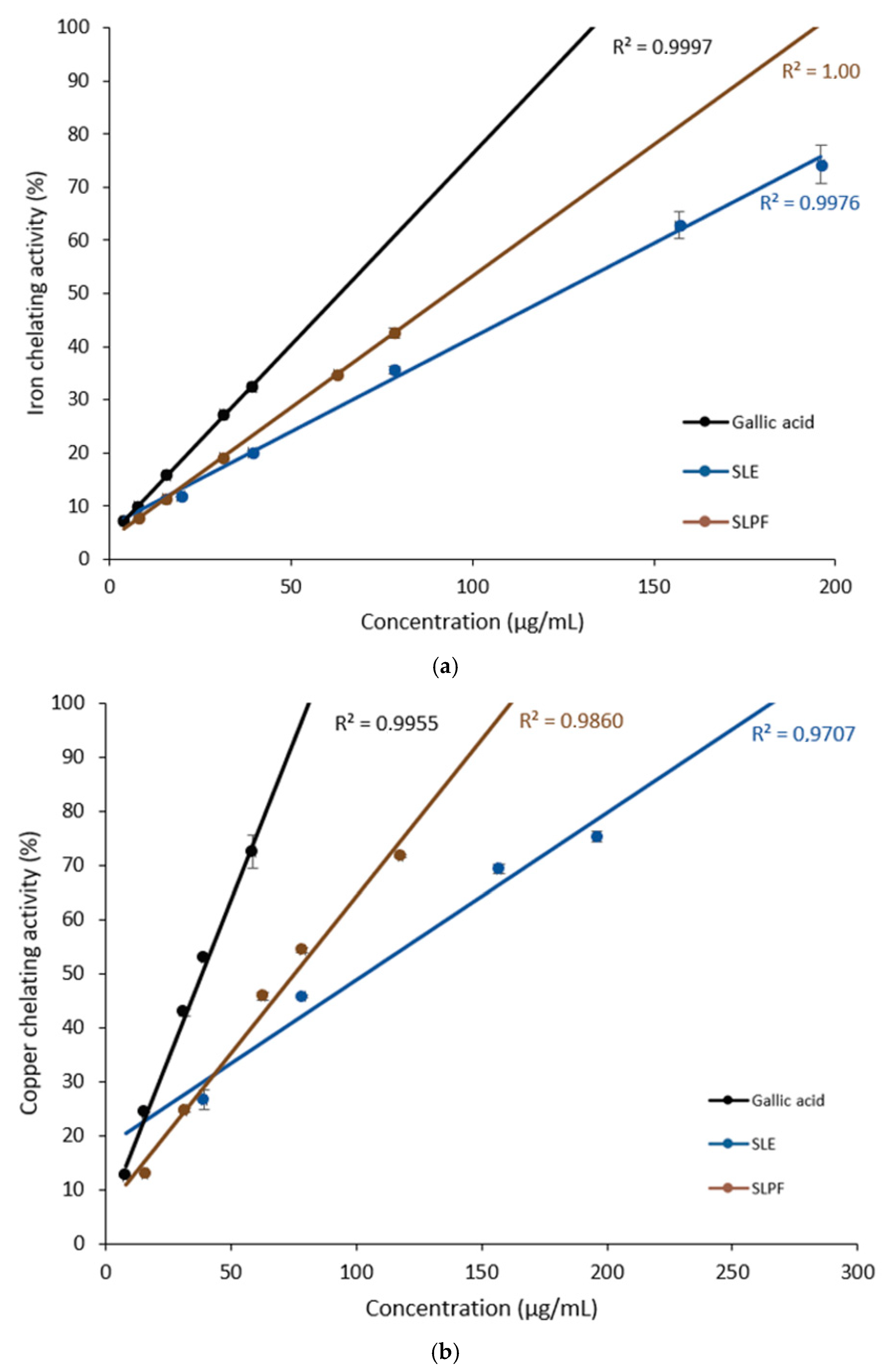
3.3. Iron- and Copper-Chelating Activities of Saffron Leaf Extracts
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Serrano-Díaz, J.; Sánchez, A.M.; Martínez-Tomé, M.; Winterhalter, P.; Alonso, G.L. Flavonoid Determination in the Quality Control of Floral Bioresidues from Crocus sativus L. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 3125–3133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrano-Díaz, J.; Sánchez, A.M.; Martínez-Tomé, M.; Winterhalter, P.; Alonso, G.L. A Contribution to Nutritional Studies on Crocus sativus Flowers and Their Value as Food. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2013, 31, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Díaz, J.; Sánchez, A.M.; Maggi, L.; Martínez-Tomé, M.; García-Diz, L.; Murcia, M.A.; Alonso, G.L. Increasing the Applications of Crocus sativus Flowers as Natural Antioxidants. J. Food Sci. 2012, 77, C1162–C1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Vioque, R.; Santana-Méridas, O.; Polissiou, M.; Vioque, J.; Astraka, K.; Alaiz, M.; Herraiz-Peñalver, D.; Tarantilis, P.A.; Girón-Calle, J. Polyphenol Composition and In Vitro Antiproliferative Effect of Corm, Tepal and Leaf from Crocus sativus L. on Human Colon Adenocarcinoma Cells (Caco-2). J. Funct. Foods 2016, 24, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahaiee, S.; Ranjbar, M.; Azizi, H.; Govahi, M.; Zare, M. Green Synthesis, Characterization, and Biological Activities of Saffron Leaf Extract-Mediated Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles: A Sustainable Approach to Reuse an Agricultural Waste. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2020, 34, e5705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soror, T.Y. Saffron Extract as Environmentally Safe Corrosion Inhibitors for Aluminium Dissolution in 2M HCl Solution. Eur. Chem. Bull. 2013, 2, 191–196. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Vioque, R.; Rodríguez-Conde, M.F.; Reina-Ureña, J.V.; Escolano-Tercero, M.A.; Herraiz-Peñalver, D.; Santana-Méridas, O. In Vitro Antioxidant and Metal Chelating Properties of Corm, Tepal and Leaf from Saffron (Crocus sativus L.). Ind. Crop Prod. 2012, 39, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, J.R.; Gonçalves, P.; Martel, F. Chemopreventive Effect of Dietary Polyphenols in Colorectal Cancer Cell Lines. Nutr. Res. 2011, 31, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatfat, M.; Merhi, R.A.; Rahal, O.; Stoyanovsky, D.A.; Zaki, A.; Haidar, H.; Kagan, V.E.; Gali-Muhtasib, H.; Machaca, K. Copper Chelation Selectively Kills Colon Cancer Cells through Redox Cycling and Generation of Reactive Oxygen Species. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, J.A.; Santana, O.; Guardiola, J.L.; Molina, R.V.; Heslop-Harrison, P.; Borbely, G.; Branca, F.; Argento, S.; Maloupa, E.; Talou, T.; et al. The World Saffron and Crocus Collection: Strategies for Establishment, Management, Characterisation and Utilisation. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2011, 58, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordán, M.J.; Lax, V.; Rota, M.C.; Lorán, S.; Sotomayor, J.A. Effect of the Phenological Stage on the Chemical Composition, and Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Properties of Rosmarinus Officinalis L Essential Oil and Its Polyphenolic Extract. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 48, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OpenAI ChatGPT-4o. Available online: https://chat.openai.com/chat (accessed on 10 April 2025).
- Girón-Calle, J.; Alaiz, M.; Vioque, J. Effect of Chickpea Protein Hydrolysates on Cell Proliferation and In Vitro Bioavailability. Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 1365–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Vioque, R.; Polissiou, M.; Astraka, K.; de los Mozos-Pascual, M.; Tarantilis, P.; Herraiz-Peñalver, D.; Santana-Méridas, O. Polyphenol Composition and Antioxidant and Metal Chelating Activities of the Solid Residues from the Essential Oil Industry. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 49, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallejo, F.; Tomás-Barberán, F.A.; Ferreres, F. Characterisation of Flavonols in Broccoli (Brassica Oleracea L. Var. Italica) by Liquid Chromatography-UV Diode-Array Detection-Electrospray Ionisation Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2004, 1054, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmona, M.; Sánchez, A.M.; Ferreres, F.; Zalacain, A.; Tomás-Barberán, F.; Alonso, G.L. Identification of the Flavonoid Fraction in Saffron Spice by LC/DAD/MS/MS: Comparative Study of Samples from Different Geographical Origins. Food Chem. 2007, 100, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goupy, P.; Vian, M.A.; Chemat, F.; Caris-Veyrat, C. Identification and Quantification of Flavonols, Anthocyanins and Lutein Diesters in Tepals of Crocus sativus by Ultra Performance Liquid Chromatography Coupled to Diode Array and Ion Trap Mass Spectrometry Detections. Ind. Crop Prod. 2013, 44, 496–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naim, N.; Bouymajane, A.; Oulad, Y.; Majdoub, E.; Ezrari, S.; Lahlali, R.; Tahiri, A.; Ennahli, S.; Lagan, R.; Cacciola, F.; et al. Crocus sativus L. Petal Extracts. 2023, 28, 186. [Google Scholar]
- Smolskaite, L.; Talou, T.; Fabre, N.; Venskutonis, P.R. Volarization of Saffron Industry by-Products: Bioactive Compounds from Leaves. In Proceedings of the 6th Baltic Conference on Food Science and Technology FOODBALT-2011, Jelgava, Latvia, 5–6 May 2011; pp. 67–72. [Google Scholar]
- Aisyah, L.S.; Yun, Y.F.; Herlina, T.; Julaeha, E.; Zainuddin, A.; Nurfarida, I.; Hidayat, A.T.; Supratman, U.; Shiono, Y. Flavonoid Compounds from the Leaves of Kalanchoe Prolifera and Their Cytotoxic Activity against P-388 Murine Leukimia Cells. Nat. Prod. Sci. 2017, 23, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes-Ricardo, M.; Moreno-García, B.E.; Gutiérrez-Uribe, J.A.; Aráiz-Hernández, D.; Alvarez, M.M.; Serna-Saldivar, S.O. Induction of Apoptosis in Colon Cancer Cells Treated with Isorhamnetin Glycosides from Opuntia Ficus-Indica Pads. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2014, 69, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Capanoglu, E.; Jassbi, A.R.; Miron, A. Advance on the Flavonoid C-Glycosides and Health Benefits. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 56, S29–S45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Min, J.W.; Kong, W.L.; He, X.H.; Li, J.X.; Peng, B.W. A Review on the Pharmacological Effects of Vitexin and Isovitexin. Fitoterapia 2016, 115, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, T.; Su, J.; Huang, C.; Yu, D.; Dai, S.; Huang, X.; Chen, B.; Zhou, M. Isoorientin Induces Apoptosis, Decreases Invasiveness, and Downregulates VEGF Secretion by Activating AMPK Signaling in Pancreatic Cancer Cells. OncoTargets Ther. 2016, 9, 7481–7492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labropoulou, E.P.; Datsis, A.; Kekelos, S.; Rogdakis, A.; Katsiki, E.; Labropoulou, C.M.; Spiliotis, J.; Christopoulou, A. The Presence and Significance of Iron in Neoplasia of the Colorectum. Tech. Coloproctol. 2004, 8, s211–s213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mladěnka, P.; MacÁková, K.; Filipský, T.; Zatloukalová, L.; Jahodář, L.; Bovicelli, P.; Silvestri, I.P.; Hrdina, R.; Saso, L. In Vitro Analysis of Iron Chelating Activity of Flavonoids. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2011, 105, 693–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Sun, S.; Cao, W.; Liang, Y.; Song, J. Antioxidant Property of Quercetin-Cr(III) Complex: The Role of Cr(III) Ion. J. Mol. Struct. 2009, 918, 194–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghan, G.; Khoshkam, Z. Tin(II)-Quercetin Complex: Synthesis, Spectral Characterisation and Antioxidant Activity. Food Chem. 2012, 131, 422–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Wang, B.; Zhu, L. DNA Binding and Oxidative DNA Damage Induced by a Quercetin copper(II) Complex: Potential Mechanism of Its Antitumor Properties. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2009, 14, 727–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasulewicz, A.; Mazur, A.; Opolski, A. Role of Copper in Tumour Angiogenesis—Clinical Implications. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2004, 18, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| #Peak | Rt (min) | UV-Vis (λmax; nm) | Mass (g/mol) | Fragmentation Ions (m/z) | Tentative Identification (UV + MS Data) | References | SLE (mg/g) | SLPF (mg/g) | Δ (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 18.68 ± 0.2 | 272/324 | (a) 950 (b) 934 | 949(100), 933(30), 771(10), 609(5), 447(5) | (a) Quercetin-3-O-sophotrioside-7-O-glucoside (tr.) (b) Kaempferol 3-O-glucoside-7-O-sophotrioside (c) Kaempferol 3-O-sophtrioside-7-O-glucoside | [15,16] | 1.42 | 5.06 | 256.01 |
| 2 | 19.77 ± 0.3 | 253/271sh/342 | 626 | 803(100), 625(90), 505(20), 445(5), 314(10) | Quercetin 3-O-sophoroside | [1,15,17] | 4.15 | 21.71 | 422.54 |
| 3 | 20.06 ± 0.0 | 271/337 | 787 | 787(100) | (a) Kaempferol-3-O-glucoside-7-O-sophoroside (b) Quercetin trihexoside (tr.) (c) Myricetin 3-rutinoside-7-glucoside | [4,16,18,19] | 25.63 | 132.97 | 418.71 |
| 4 | 21.89 ± 0.3 | 253/352 | (a) 964 (b) 772 | 963(15), 801(100), 771(55), 681(10) | (a) Isorhamnetin-3-O-sophotrioside-7-O-glucoside a (b) Kaempferol-3-O-glucoside-7-O-sophoroside (tr.) | [15] | 1.16 | 4.09 | 251.70 |
| 5 | 21.20 ± 0.6 | 272/334 | 610 | 609(100), 489(15), 429(10), 298(10) | Kaempferol 3-O-sophoroside | [1,15,17] | 1.90 | 7.68 | 305.26 |
| 6 | 22.64 ± 0.3 | 254/268sh/340 | 448 | 447(100), 357(95), 327(90), 298(55), 133(40) | Luteolin 6-C-glucoside (isoorientin) | [19]; Standard | 15.75 | 86.06 | 446.50 |
| 7 | 24.86 ± 0.4 | 284 | 772 | 771(100), 609(15), 429(10), 181(10) | Kaempferol-3-O-sophoroside-7-O-glucoside | [1,15,16,17] | 17.02 | 53.44 | 213.94 |
| 8 | 25.48 ± 0.2 | 272/330 | 432 | 431(100), 341(40), 311(90), 283(55), 117(25) | Apigenin-8-C-glucoside (vitexin) | [19]; Standard | 0.76 | 2.33 | 206.97 |
| 9 | 29.29 ± 0.7 | 284/330 | - | 401(20), 196(30), 181(100), 153(20) | Unknown | - | 7.53 | 16.65 | 121.08 |
| TOTAL | 75.33 | 330.00 | 438.07 | ||||||
| Sample | Multivariate Model (R2) | Linear Regression Model (Day 4) | EC50 (Day 4) | EC90 (Day 4) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Estimated (R2) 1 | Calculated (R2) 2 | Estimated 1 | Calculated | Estimated 1 | Calculated 2 | ||
| SLE | y = 95.82C + 2.84t + 3.48 (0.67) | y = 95.83x + 14.85 (1.00) | y = 100.35x + 19.15 (0.92) | 0.37 | 0.31 ± 0.02 (0.26–0.35) | 0.78 | 0.71 ± 0.05 (0.60–0.81) |
| SLPF | y = 124.82C + 3.45t + 7.43 (0.82) | y = 124.82x + 21.24 (1.00) | y = 135.33x + 19.87 (0.96) | 0.23 | 0.22 ± 0.01 (0.20–0.24) | 0.55 | 0.52 ± 0.03 (0.46–0.57) |
| Δ (%) | 37.84 | 29.03 | 29.48 | 26.76 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sánchez-Vioque, R.; Girón-Calle, J.; Alaiz, M.; Vioque-Peña, J.; Mena-Morales, A.; García-Romero, E.; Marchante-Cuevas, L.; Ortiz de Elguea-Culebras, G. Isolation of a Novel Bioactive Fraction from Saffron (Crocus sativus L.) Leaf Waste: Optimized Extraction and Evaluation of Its Promising Antiproliferative and Chemoprotective Effects as a Plant-Based Antitumor Agent. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 7376. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15137376
Sánchez-Vioque R, Girón-Calle J, Alaiz M, Vioque-Peña J, Mena-Morales A, García-Romero E, Marchante-Cuevas L, Ortiz de Elguea-Culebras G. Isolation of a Novel Bioactive Fraction from Saffron (Crocus sativus L.) Leaf Waste: Optimized Extraction and Evaluation of Its Promising Antiproliferative and Chemoprotective Effects as a Plant-Based Antitumor Agent. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(13):7376. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15137376
Chicago/Turabian StyleSánchez-Vioque, Raúl, Julio Girón-Calle, Manuel Alaiz, Javier Vioque-Peña, Adela Mena-Morales, Esteban García-Romero, Lourdes Marchante-Cuevas, and Gonzalo Ortiz de Elguea-Culebras. 2025. "Isolation of a Novel Bioactive Fraction from Saffron (Crocus sativus L.) Leaf Waste: Optimized Extraction and Evaluation of Its Promising Antiproliferative and Chemoprotective Effects as a Plant-Based Antitumor Agent" Applied Sciences 15, no. 13: 7376. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15137376
APA StyleSánchez-Vioque, R., Girón-Calle, J., Alaiz, M., Vioque-Peña, J., Mena-Morales, A., García-Romero, E., Marchante-Cuevas, L., & Ortiz de Elguea-Culebras, G. (2025). Isolation of a Novel Bioactive Fraction from Saffron (Crocus sativus L.) Leaf Waste: Optimized Extraction and Evaluation of Its Promising Antiproliferative and Chemoprotective Effects as a Plant-Based Antitumor Agent. Applied Sciences, 15(13), 7376. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15137376








