A Lightweight Network for Water Body Segmentation in Agricultural Remote Sensing Using Learnable Kalman Filters and Attention Mechanisms
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We proposed a learnable Kalman filter module, applied in the feature decoding stage, to enhance segmentation accuracy by stabilizing feature representations and suppressing complex noise through end-to-end optimization.
- We proposed a lightweight water body segmentation framework. By reducing the network depth and width, it achieves a favorable trade-off between accuracy and computational efficiency.
- Our method demonstrates strong performance on public datasets and effectively generalizes to UAV-captured images via transfer learning.
2. Materials and Methods
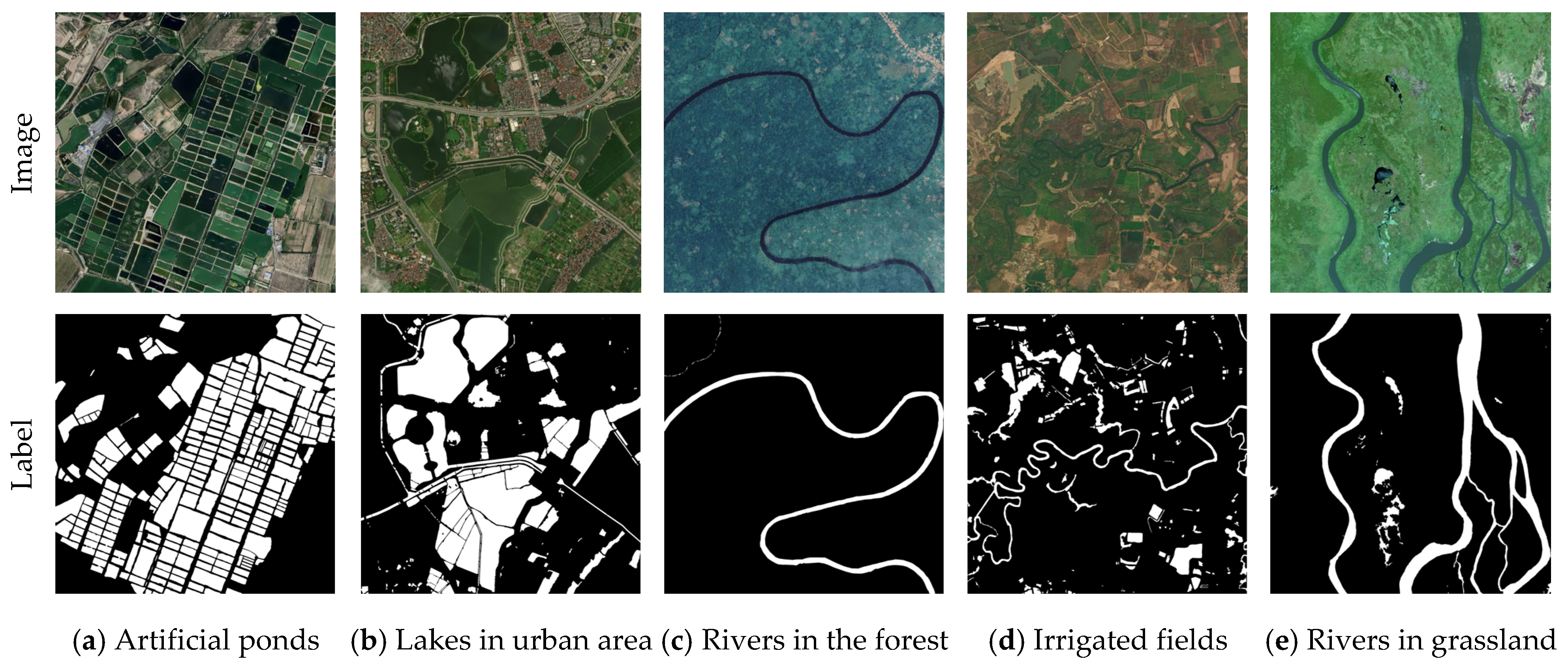
2.1. Datasets
2.1.1. GLH-Water Dataset Construction
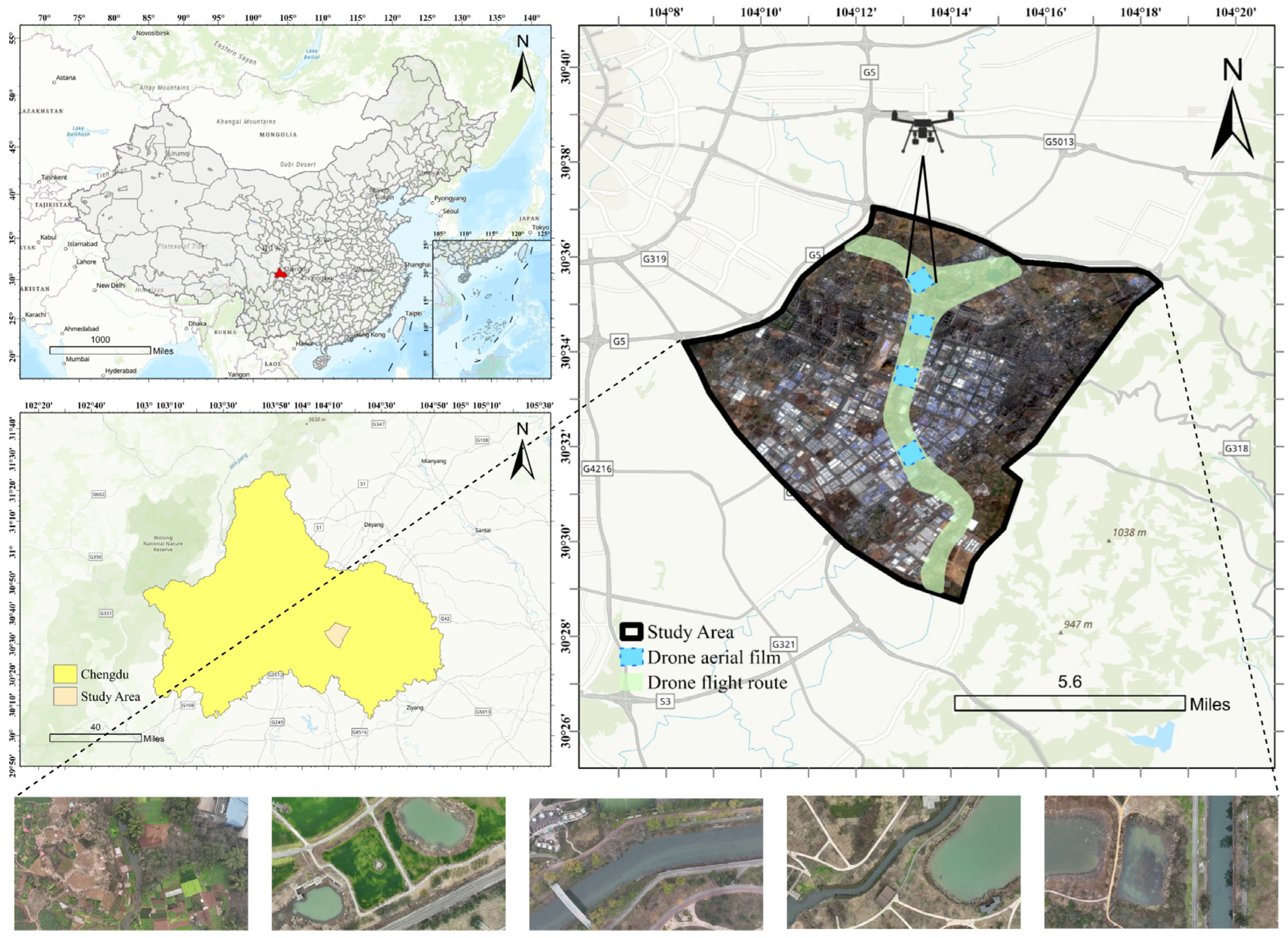
2.1.2. Self-Constructed UAV Dataset
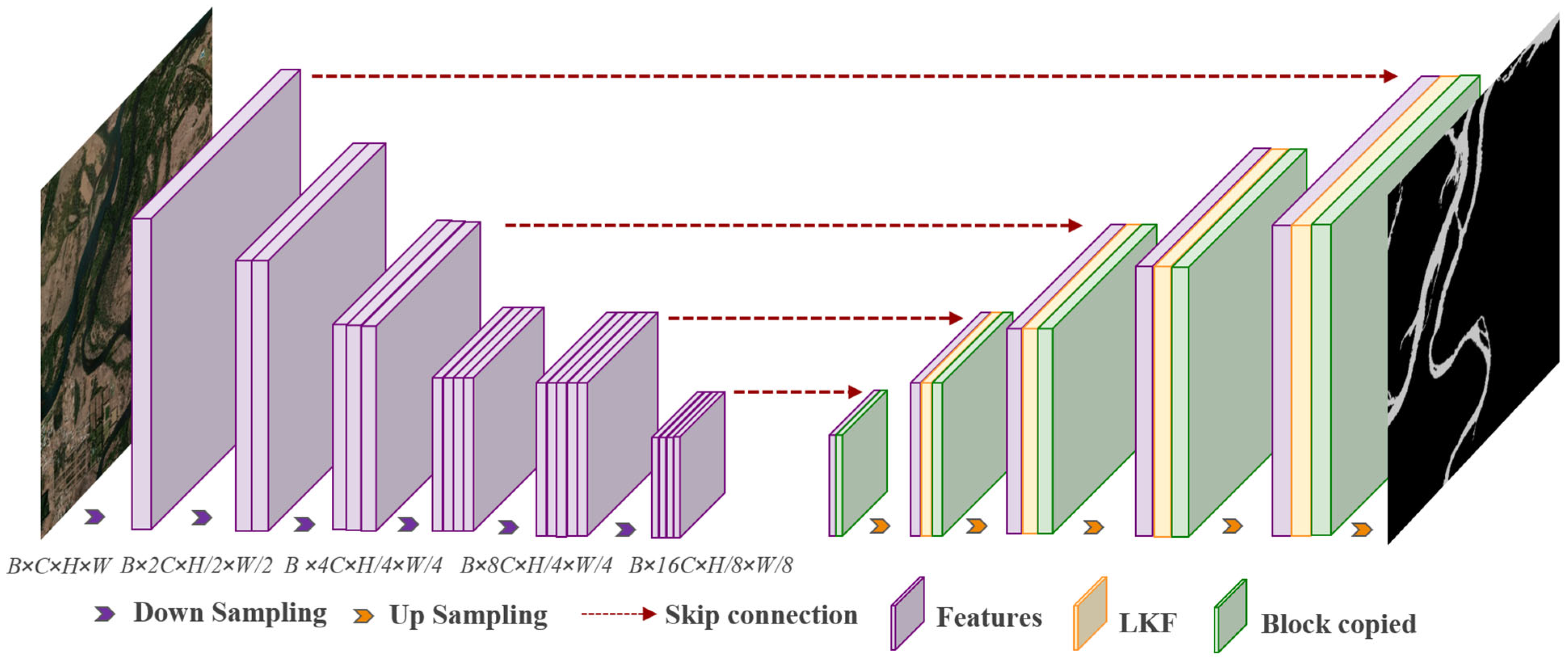
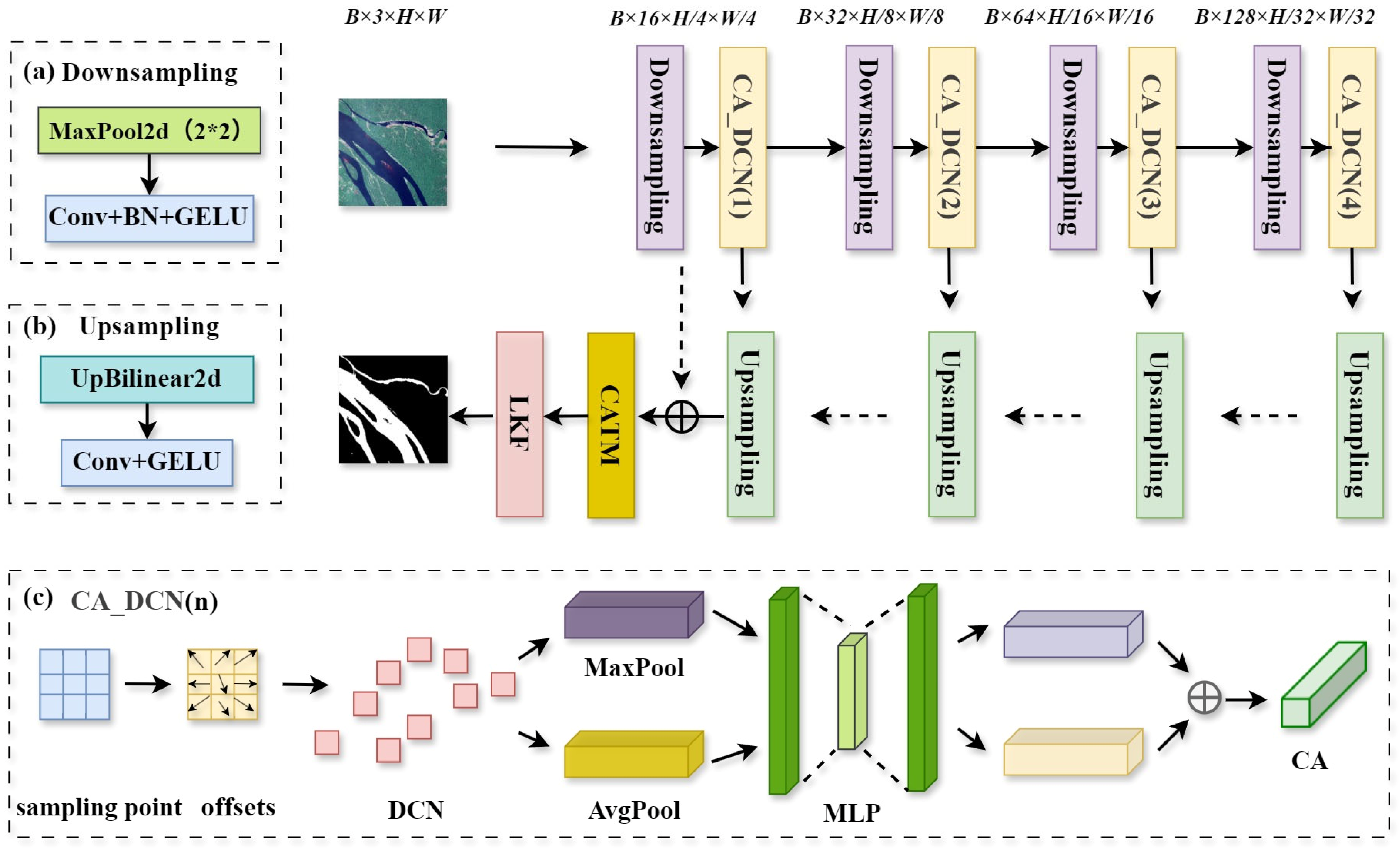
2.2. Overview of the Proposed Framework
2.3. Deep Water Body Segmentation Network
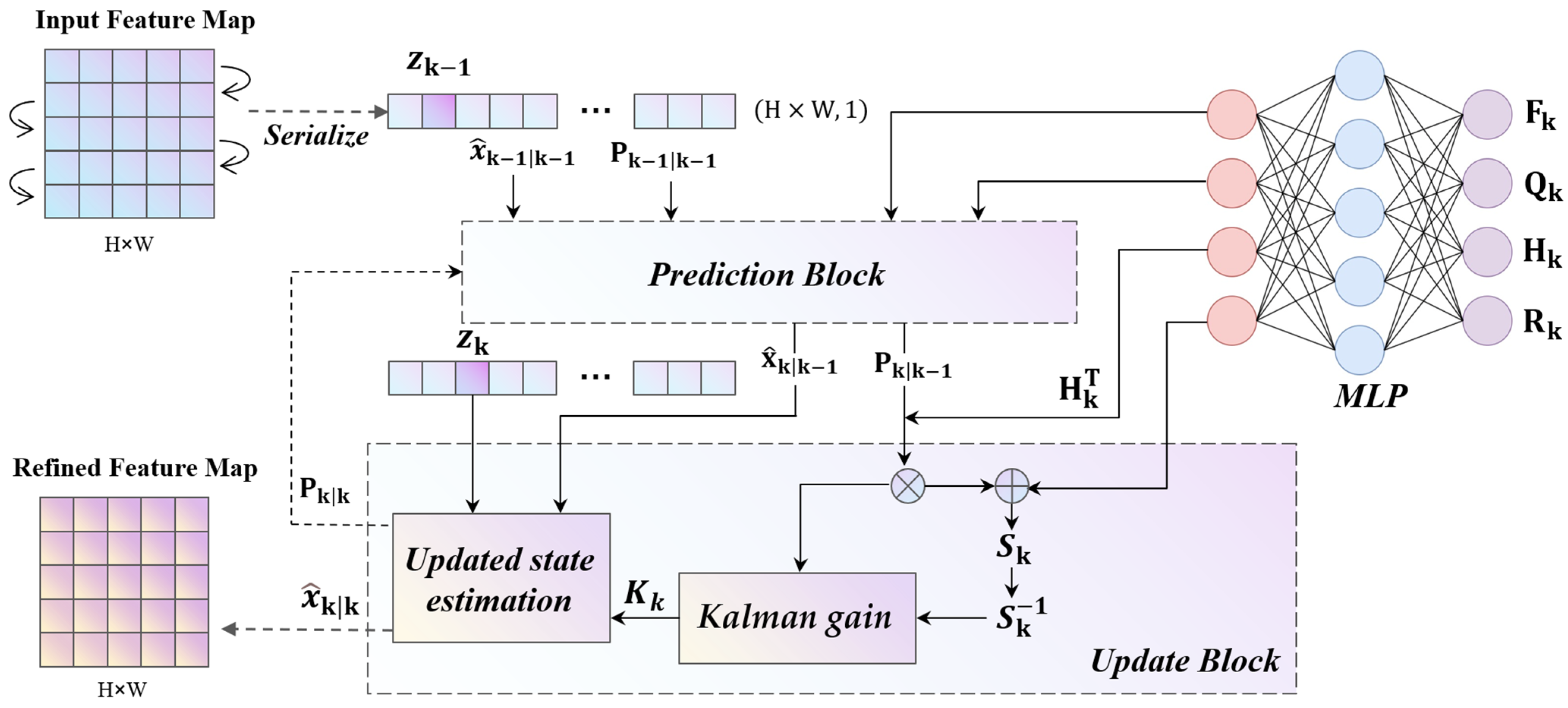
2.3.1. Learnable Kalman Filter Module
- (1)
- State Prediction Phase in LKF
- (2)
- State Update Phase in LKF
2.3.2. Encoder and Decoder
2.4. Lightweight Design of the Water Body Segmentation Network
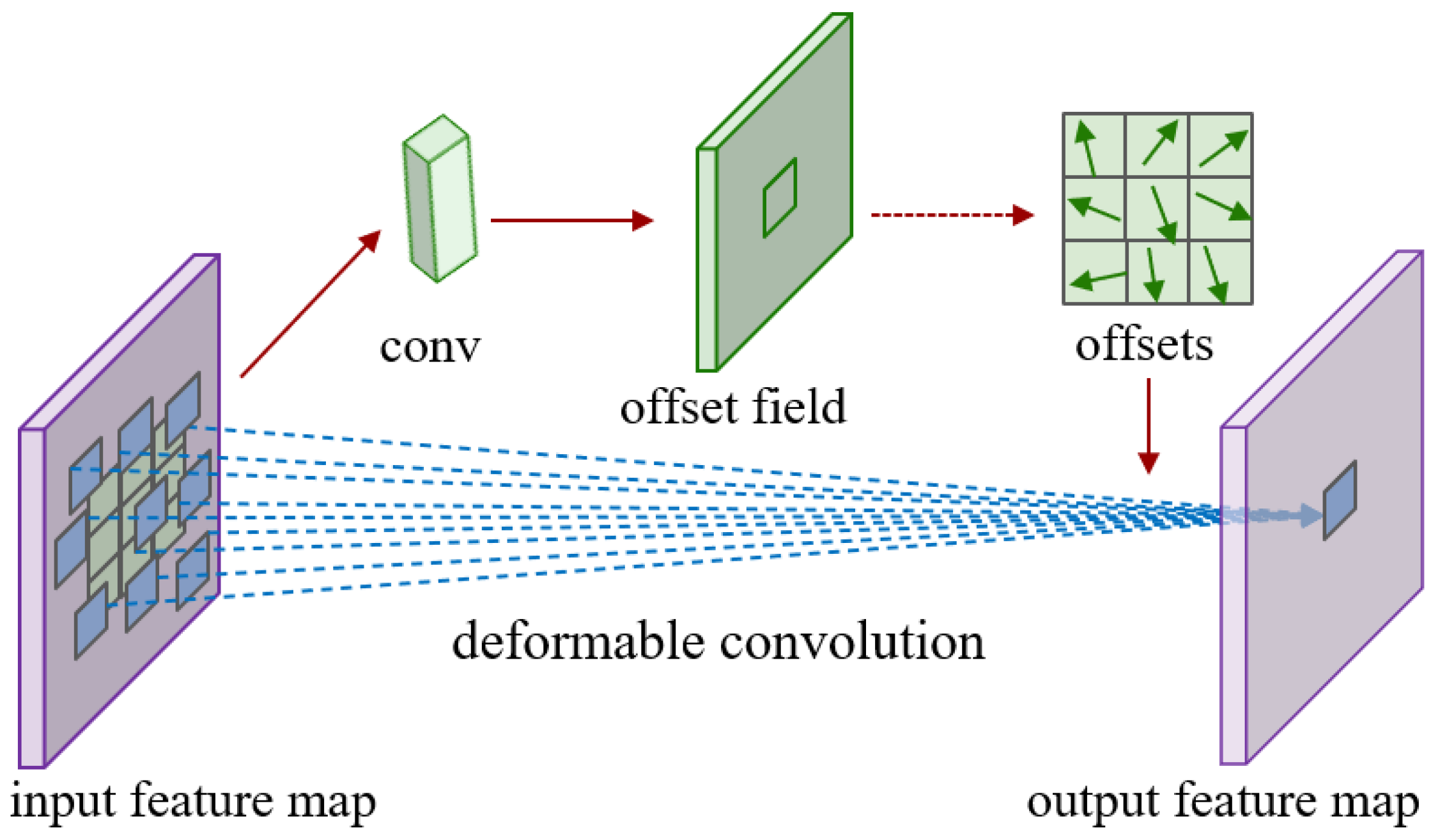
2.4.1. Encoder Based on CADCN
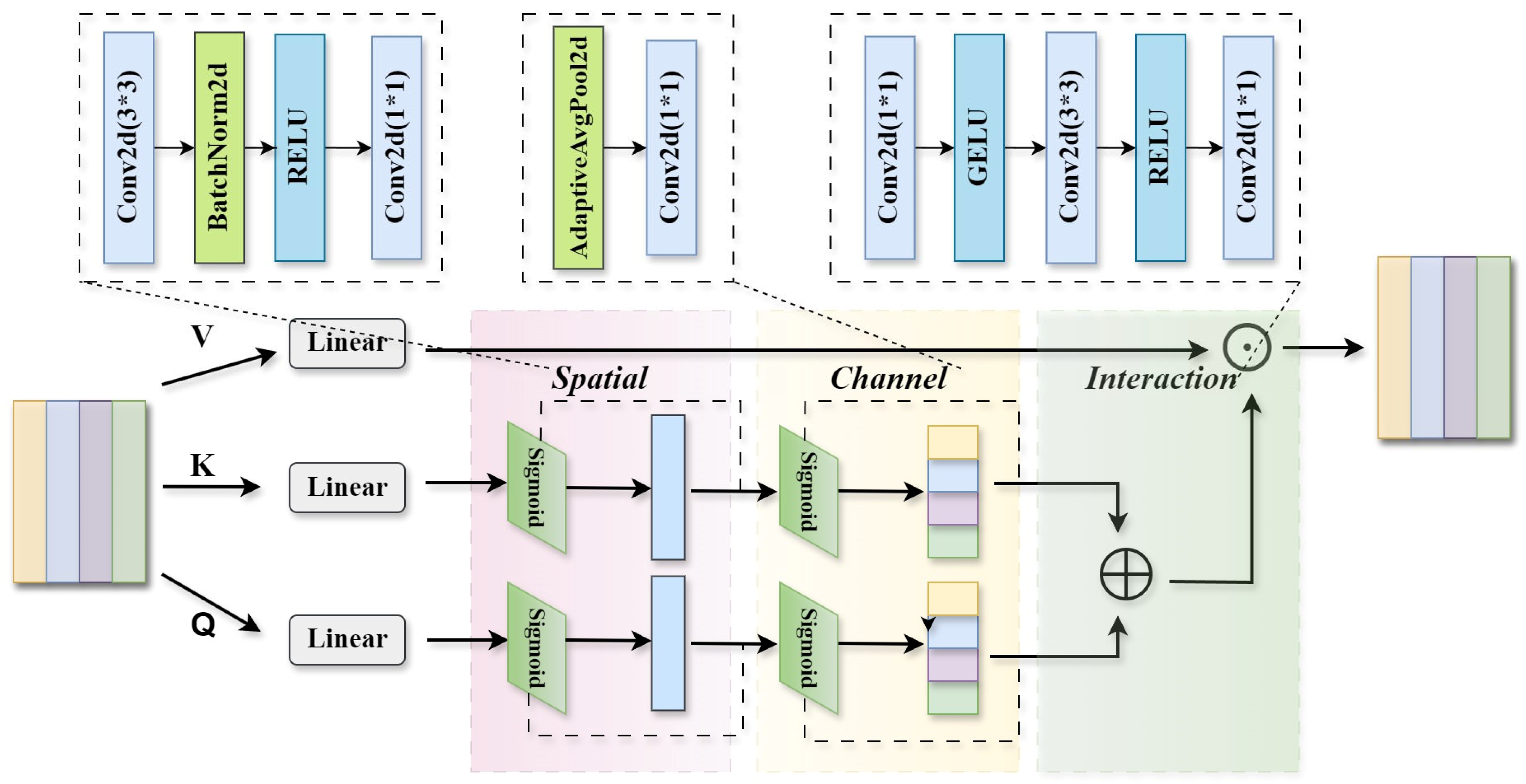
2.4.2. Decoder with CATM and LKF Module
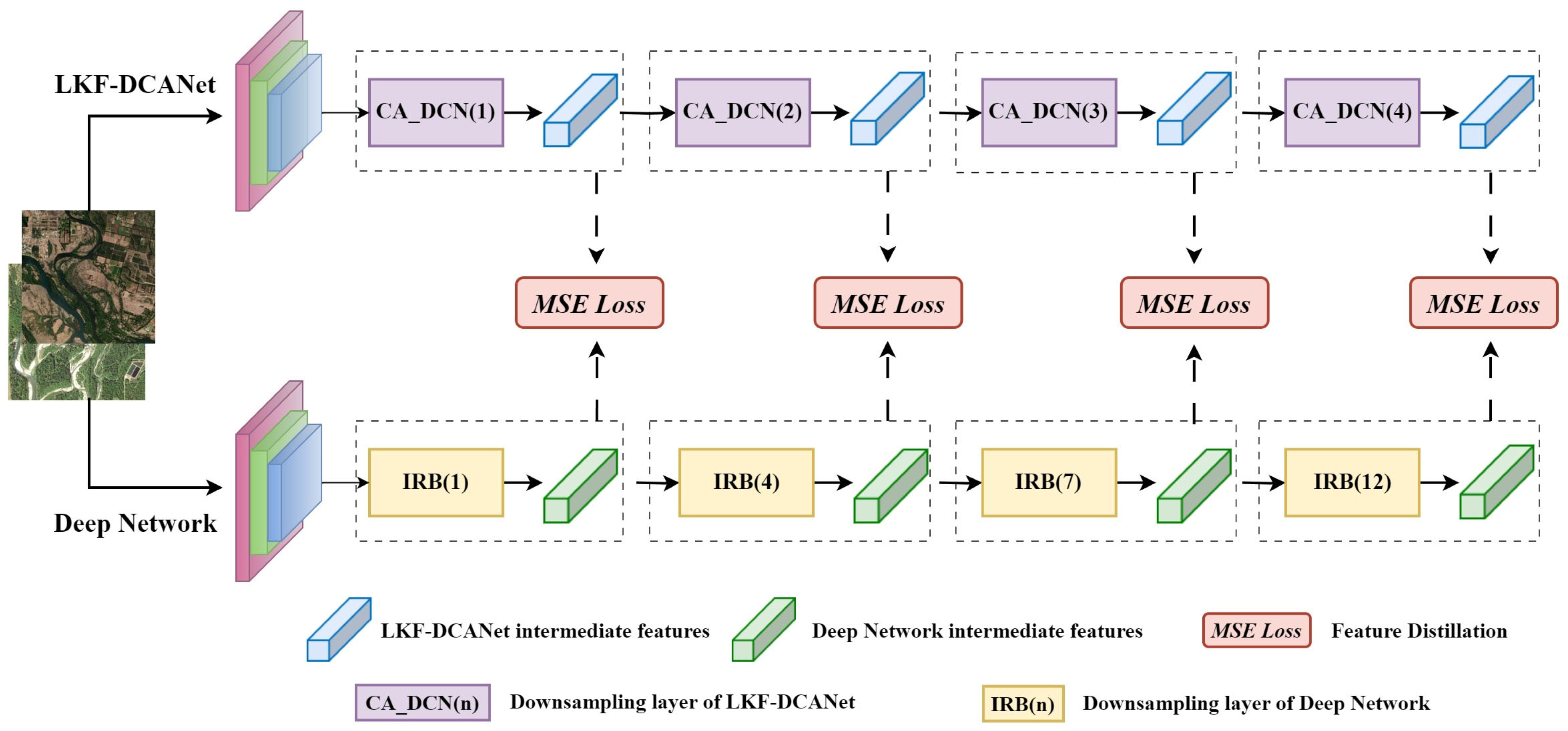
2.4.3. Feature-Based Knowledge Distillation Strategy
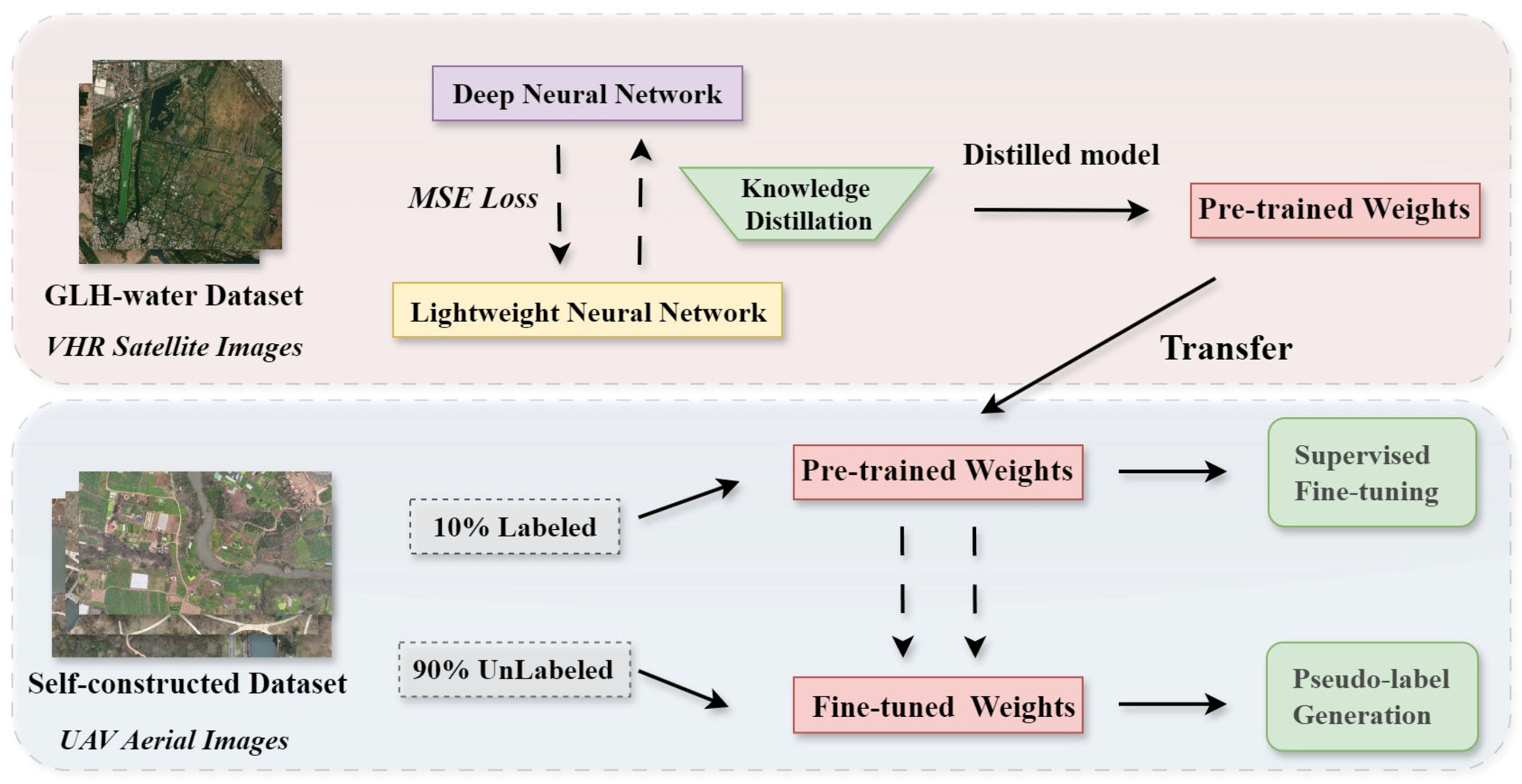
2.5. Training Strategy and Transfer Pipeline
3. Experiments and Results
3.1. Evaluation Metrics
3.2. Training Protocol
3.3. Experimental Results
3.3.1. Ablation Experiments
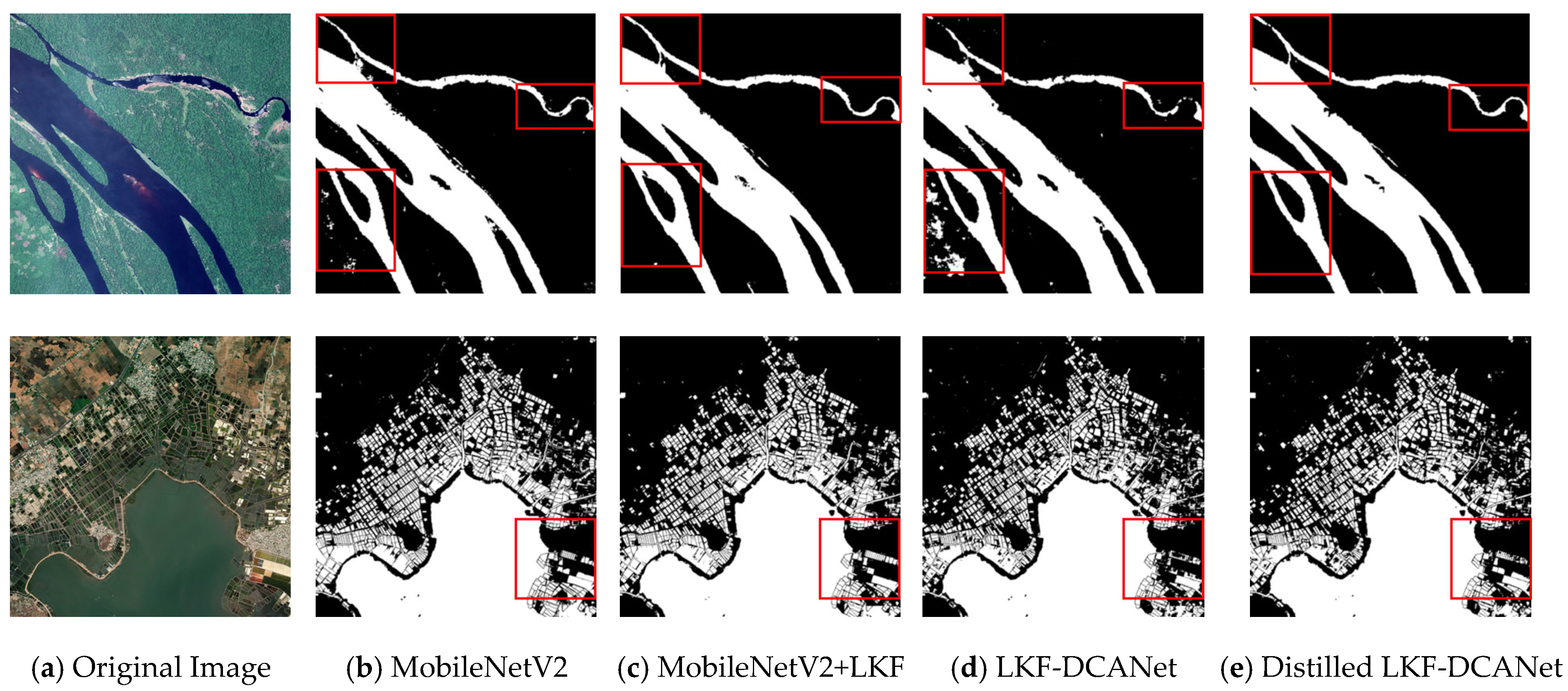
3.3.2. Distillation Experiment
3.3.3. Transfer Learning Experiment
4. Discussion
4.1. Theoretical Rationale and Design Motivation
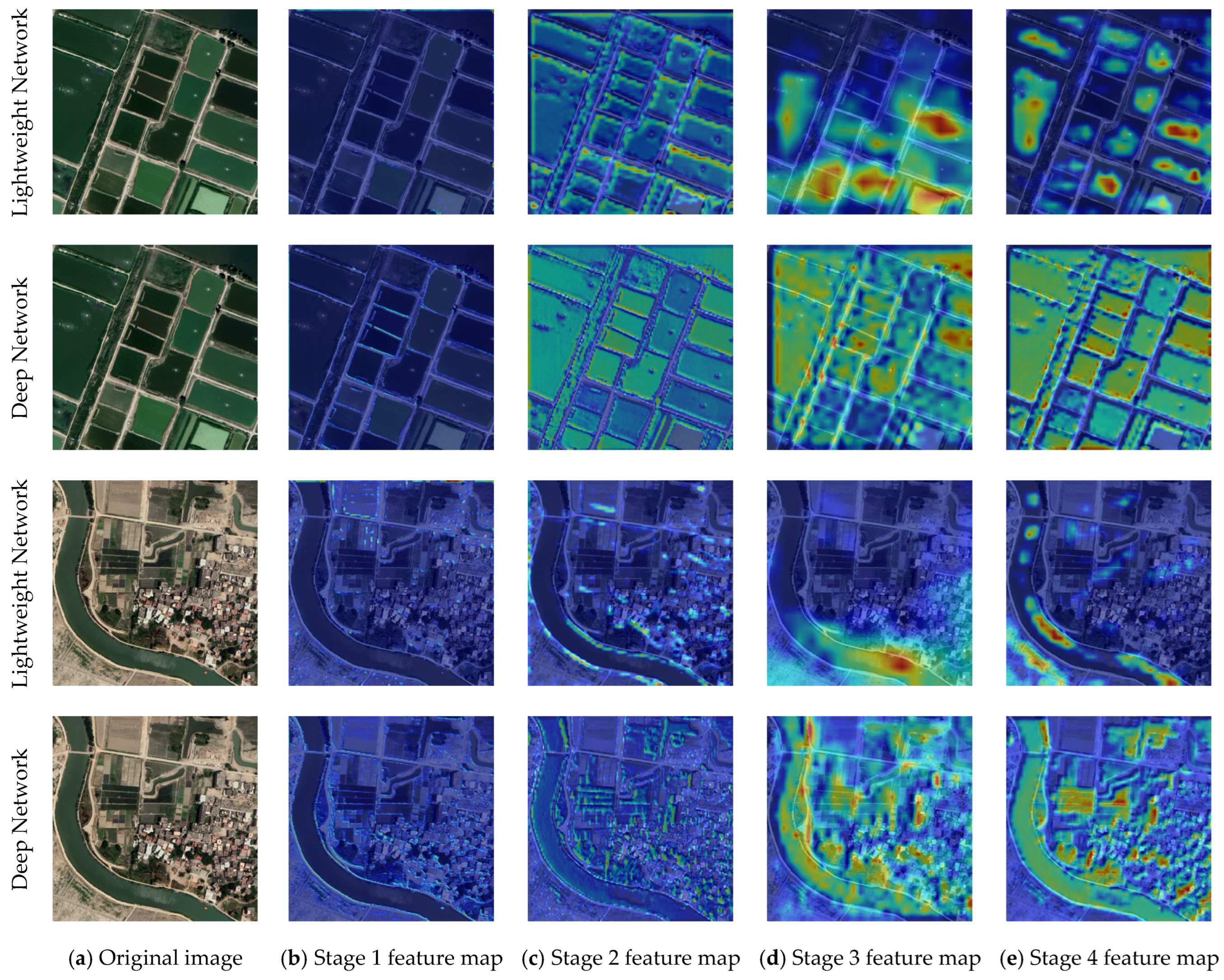
4.2. Multi-Module Collaboration and Feature Enhancement
4.3. Knowledge Distillation for Lightweight Accuracy Preservation
4.4. Cross-Platform Generalization and Data Efficiency
4.5. Computational Limitations and Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LKF-DCANet | Learnable Kalman Filter and Deformable Convolutional Attention Network |
| LKF | Learnable Kalman Filter |
| CADCN | Channel Attention-Enhanced Deformable Convolutional Network |
| CATM | Convolutional Additive Token Mixer |
| GELU | Gaussian Error Linear Unit |
| FLOPs | Floating Point Operations |
| Params | Parameters |
| IoU | Intersection over Union |
| F1 | F1-Score |
| UAV | Unmanned Aerial Vehicle |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
| DJI | Da Jiang Innovations |
| GPU | Graphics Processing Unit |
| CUDA | Compute Unified Device Architecture |
References
- Wen, D.; Huang, X.; Bovolo, F.; Li, J.; Ke, X.; Zhang, A.; Benediktsson, J.A. Change detection from very-high-spatial-resolution optical remote sensing images: Methods, applications, and future directions. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2021, 9, 68–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knox, J.W.; Kay, M.G.; Weatherhead, E.K. Water regulation, crop production, and agricultural water management—Understanding farmer perspectives on irrigation efficiency. Agric. Water Manag. 2012, 108, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpatne, A.; Khandelwal, A.; Chen, X.; Mithal, V.; Faghmous, J.; Kumar, V. Global Monitoring of Inland Water Dynamics: State-of-the-Art, Challenges, and Opportunities. In Computational Sustainability; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 121–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, P.; Yi, J.; Li, S.; Li, Y.; Lin, H. Agricultural surface water extraction in environmental remote sensing: A novel semantic segmentation model emphasizing contextual information enhancement and foreground detail attention. Neurocomputing 2025, 617, 129110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Dang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Du, Z. Water body classification from high-resolution optical remote sensing imagery: Achievements and perspectives. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2022, 187, 306–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFeeters, S.K. The use of the Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI) in the delineation of open water features. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1996, 17, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H. Modification of normalised difference water index (NDWI) to enhance open water features in remotelysensed imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 3025–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feyisa, G.L.; Meilby, H.; Fensholt, R.; Proud, S.R. Automated Water Extraction Index: A new technique for surface water mapping using Landsat imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 140, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, C.; Vapnik, V. Support-vector networks. Mach. Learn. 1995, 20, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, R.; Huang, J.F.; Wang, F.M. Research on extraction method of water body with DS spectral enhancement based on HJ-1 images. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2011, 31, 3064–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedl, M.A.; Brodley, C.E. Decision tree classification of land cover from remotely sensed data. Remote Sens. Environ. 1997, 61, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Wu, L.; Huang, Y.; Guo, Z.; Zhao, J.; Li, N. Water-body segmentation for SAR images: Past, current, and future. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Wang, L.; Yuan, Y.; Fan, L.; Wu, Y.; Sun, W.; Yang, G. Recognition of small water bodies under complex terrain based on SAR and optical image fusion algorithm. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 946, 174329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Bottou, L.; Bengio, Y.; Haffner, P. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proc. IEEE 1998, 86, 2278–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully Convolutional Networks for Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 3431–3440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2015: 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Part III. Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Shi, J.; Qi, X.; Wang, X.; Jia, J. Pyramid Scene Parsing Network. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2881–2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.C.; Zhu, Y.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Encoder-Decoder with Atrous Separable Convolution for Semantic Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 801–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A.L. Deeplab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected crfs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 40, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Rethinking Atrous Convolution for Semantic Image Segmentation. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.05587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Sun, K.; Cheng, T.; Jiang, B.; Deng, C.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, D.; Mu, Y.; Tan, M.; Wang, X.; et al. Deep high-resolution representation learning for visual recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 43, 3349–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Guan, H.; Peng, D.; Chen, Z. Multi-scale context extractor network for water-body extraction from high-resolution optical remotely sensed images. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 103, 102499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.H.; Cheng, M.M.; Zhao, K.; Zhang, X.Y.; Yang, M.H.; Torr, P. Res2net: A new multi-scale backbone architecture. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2019, 43, 652–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Chen, Z.; Wu, L.; Yang, X.; Zhou, Y. SADA-net: A shape feature Optimization and multiscale context information-based Water Body extraction method for high-resolution remote sensing images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 1744–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, D.; Zhang, X.; Wu, W.; Liu, H. Denseppmunet-a: A robust deep learning network for segmenting water bodies from aerial images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 4202611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wang, Y.; Yang, S.; Ji, X.; Wang, G. A K-Net-based hybrid semantic segmentation method for extracting lake water bodies. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 126, 106904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Du, S.; Bai, L.; Ouyang, S.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X. Water extraction from optical high-resolution remote sensing imagery: A multi-scale feature extraction network with contrastive learning. GIScience Remote Sens. 2023, 60, 2166396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, F.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Z.; Ji, J.; Xiong, Y.; Zhao, Q. FWENet: A deep convolutional neural network for flood water body extraction based on SAR images. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2022, 15, 345–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Lu, M.; Ji, S.; Yu, H.; Nie, C. Rich CNN features for water-body segmentation from very high resolution aerial and satellite imagery. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, H.F.; Sun, Q.; Sun, H.M.; Jia, R.S. NT-Net: A semantic segmentation network for extracting lake water bodies from optical remote sensing images based on transformer. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5627513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radford, A.; Kim, J.W.; Hallacy, C.; Ramesh, A.; Goh, G.; Agarwal, S.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; Mishkin, P.; Clark, J.; et al. Learning transferable visual models from natural language supervision. In Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Virtual, 18–24 July 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kirillov, A.; Mintun, E.; Ravi, N.; Mao, H.; Rolland, C.; Gustafson, L.; Xiao, T.; Whitehead, S.; Berg, A.C.; Lo, W.Y.; et al. Segment Anything. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023; pp. 4015–4026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keles, F.D.; Wijewardena, P.M.; Hegde, C. On the computational complexity of self-attention. In Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Algorithmic Learning Theory, PMLR, Singapore, 20–23 February 2023; pp. 597–619. [Google Scholar]
- Hinton, G.; Vinyals, O.; Dean, J. Distilling the knowledge in a neural network. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1503.02531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denil, M.; Shakibi, B.; Dinh, L.; Ranzato, M.A.; De Freitas, N. Predicting Parameters in Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, NV, USA, 5–10 December 2013; p. 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Siddiquee, M.M.R.; Tajbakhsh, N.; Liang, J. Unet++: Redesigning skip connections to exploit multiscale features in image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2019, 39, 1856–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jégou, S.; Drozdzal, M.; Vazquez, D.; Romero, A.; Bengio, Y. The one hundred layers tiramisu: Fully convolutional densenets for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, S.Y.; Hang, H.M.; Chan, S.W.; Lin, J.J. Efficient dense modules of asymmetric convolution for real-time semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the 1st ACM International Conference on Multimedia in Asia, Beijing, China, 15–18 December 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, S.; Hori, T.; Karita, S.; Hayashi, T.; Nishitoba, J.; Unno, Y.; Soplin, N.E.; Heymann, J.; Wiesner, M.; Chen, N.; et al. ESPnet: End-to-end speech processing toolkit. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.00015. [Google Scholar]
- Mehta, S.; Rastegari, M.; Shapiro, L.; Hajishirzi, H. Espnetv2: A light-weight, power efficient, and general purpose convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 9190–9200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaraj, R.; Kumar, L.S. Extraction of surface water bodies using optical remote sensing images: A review. Earth Sci. Inform. 2024, 17, 893–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Dang, B.; Li, W.; Zhang, Y. Glh-water: A large-scale dataset for global surface water detection in large-size very-high-resolution satellite imagery. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 20–27 February 2024; Volume 38, pp. 22213–22221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandler, M.; Howard, A.; Zhu, M.; Zhmoginov, A.; Chen, L.C. Mobilenetv2: Inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 4510–4520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chui, C.K.; Chen, G. Kalman Filtering; Springer International Publishing: Berlin, Germany, 2017; pp. 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revach, G.; Shlezinger, N.; Ni, X.; Escoriza, A.L.; Van Sloun, R.J.; Eldar, Y.C. KalmanNet: Neural network aided Kalman filtering for partially known dynamics. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2022, 70, 1532–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Yan, B.; Zhou, C.; Su, T.; Jin, X. State of art on state estimation: Kalman filter driven by machine learning. Annu. Rev. Control 2023, 56, 100909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Li, L.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, W.; Qian, C.; Hwang, J.N.; Ji, X. Cas-vit: Convolutional additive self-attention vision transformers for efficient mobile applications. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2408.03703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Dai, J.; Chen, Z.; Huang, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhu, X.; Hu, X.; Lu, T.; Lu, L.; Li, H.; et al. Internimage: Exploring large-scale vision foundation models with deformable convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 14408–14419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kweon, I.S. Cbam: Convolutional block attention module. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, B.; Kim, J.; Yun, S.; Park, H.; Kwak, N.; Choi, J.Y. A comprehensive overhaul of feature distillation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 1921–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Liu, L.; Gan, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, C.; Jiang, G.; Zhang, W.; Yi, R.; Ma, L.; et al. Isdnet: Integrating shallow and deep networks for efficient ultra-high resolution segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 4361–4370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, C.; Tran, A.T.; Luu, K.; Hoai, M. Progressive semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 16755–16764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, B.; Li, Y. MSResNet: Multiscale residual network via self-supervised learning for water-body detection in remote sensing imagery. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Yang, W.; Liu, W.; Yu, Y.; He, S. From contexts to locality: Ultra-high resolution image segmentation via locality-aware contextual correlation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 7252–7261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.; Lai, S.; Huang, J.; Wei, X.; Chai, Z.; Luo, J.; Wei, X. Rethinking bisenet for real-time semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 9716–9725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
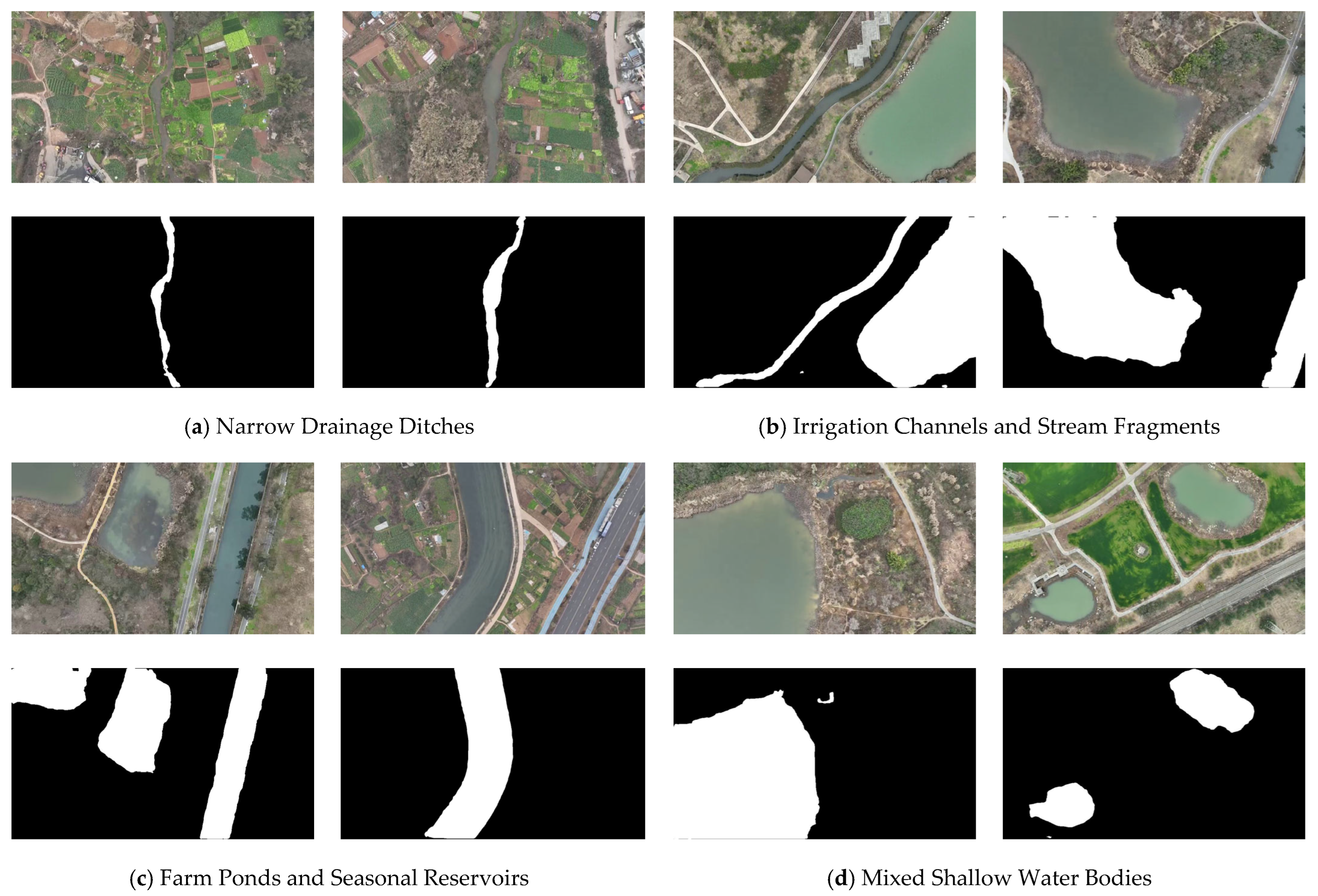

| Methods | IoU (%) | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|
| MECNet [30] | 44.67 | 61.75 |
| ISDNet [53] | 53.04 | - |
| MagNet [54] | 62.77 | - |
| MSResNet [55] | 69.76 | 82.18 |
| FCN8s [16] | 73.66 | 84.83 |
| FCtL [56] | 74.92 | 85.66 |
| MSCENet [23] | 74.81 | 85.58 |
| PSP-Net [18] | 75.19 | 85.84 |
| STDC-1446 [57] | 75.82 | 86.25 |
| HRNet-48 [22] | 78.6 | 88.01 |
| DeepLab-V3+ [21] | 79.8 | 88.76 |
| PCL [44] | 82.26 | 90.27 |
| Our Deep Network | 88.86 | 94.10 |
| Model Name | Params (M) | FLOPs (G) | IoU (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| MobileNetV2 [45] | 6.644 | 136.064 | 86.19 |
| MobileNetV2+LKF | 6.644 | 136.088 | 88.86 |
| CADCN+LKF | 0.10 | 72.908 | 81.62 |
| LKF-DCANet | 0.22 | 71.377 | 82.55 |
| Model Name | Params (M) | FLOPs (G) | IoU (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| DeepLab-V3+ [21] | 5.81 | 211.47 | 79.8 |
| PSP-Net [18] | 2.38 | 24.12 | 75.19 |
| MobileNetV2+LKF | 6.644 | 136.088 | 88.86 |
| LKF-DCANet | 0.22 | 71.377 | 82.55 |
| Distilled LKF-DCANet | 0.22 | 71.377 | 85.95 |
| Datasets | IoU (%) | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|
| GLH-Water [44] | 85.95 | 92.10 |
| Self-Constructed Dataset | 96.28 | 97.72 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liao, D.; Sun, J.; Deng, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Ou, D. A Lightweight Network for Water Body Segmentation in Agricultural Remote Sensing Using Learnable Kalman Filters and Attention Mechanisms. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 6292. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15116292
Liao D, Sun J, Deng Z, Zhao Y, Zhang J, Ou D. A Lightweight Network for Water Body Segmentation in Agricultural Remote Sensing Using Learnable Kalman Filters and Attention Mechanisms. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(11):6292. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15116292
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiao, Dingyi, Jun Sun, Zhiyong Deng, Yudong Zhao, Jiani Zhang, and Dinghua Ou. 2025. "A Lightweight Network for Water Body Segmentation in Agricultural Remote Sensing Using Learnable Kalman Filters and Attention Mechanisms" Applied Sciences 15, no. 11: 6292. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15116292
APA StyleLiao, D., Sun, J., Deng, Z., Zhao, Y., Zhang, J., & Ou, D. (2025). A Lightweight Network for Water Body Segmentation in Agricultural Remote Sensing Using Learnable Kalman Filters and Attention Mechanisms. Applied Sciences, 15(11), 6292. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15116292






