Abstract
The growing prevalence of pharmaceutical compounds in the environment raises significant concerns due to their potential impacts on ecological and human health. This present manuscript focuses on the methods used to extract and determine these pharmaceuticals in water samples. It provides a comprehensive analysis of the extraction techniques and analytical approaches employed for the identification and quantification of pharmaceuticals in environmental water. Due to their chemical properties and widespread use, pharmaceuticals persist in the environment and contaminate water bodies, soil, and sediments. The presence of pharmaceuticals in the aquatic environment has been linked to several adverse effects on aquatic organisms, including the disruption of physiological processes and reproductive impairment. Furthermore, pharmaceuticals in the environment can affect human health through food and drinking water contamination and contribute to antibiotic resistance. The analysis of pharmaceutical contaminants in water samples presents several challenges due to the complex matrix and low concentrations of target substances. Various sample preparation techniques and protocols, including solid-phase extraction (more than 76% of the studied literature) and QuEChERS (quick, easy, cheap, effective, rugged, and safe), coupled with liquid chromatography–tandem-mass spectrometry, are commonly used for their determination. These methods offer high sensitivity, selectivity, and efficiency in identifying and quantifying pharmaceuticals in environmental samples. It is, therefore, essential that ongoing research is conducted in order to develop more efficient analytical methods and mitigation strategies to address pharmaceutical contamination in the environmental water effectively. It is also crucial that increased awareness and regulatory measures are put in place in order to minimize the environmental and human health risks associated with pharmaceutical pollutants.
1. Introduction
Pharmaceutical substances are indispensable components of contemporary medicine and veterinary practice. They are primarily used to treat and prevent disease in humans and animals, and their beneficial effects on food production and economic prosperity are widely recognized. The growing global population, advances in research, investments in the pharmaceutical industry, and the ubiquitous availability of pharmaceuticals on the global market contribute to a significant increase in drug consumption [1]. According to a report by the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), global antibiotic consumption for livestock is expected to rise by 67% by 2030. Furthermore, drug consumption in industrialized nations such as Germany could rise by up to 67% by 2045 due to demographic changes [2].
Pharmaceuticals do not represent a new group of contaminants; their research in the environment has been dealt with worldwide and for a long time by many development researchers and workers; however, their specific occurrence according to actual medical situations, concentration levels, and variability in effluents is changing.
Although pharmaceuticals are not a novel class of contaminants, their presence in aquatic environments is becoming increasingly prevalent. These substances enter these ecosystems via a number of different pathways, including direct discharge from wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) [3], agricultural runoff, and the improper disposal of unused medications [4]. The persistence and extensive distribution of these compounds give rise to concerns regarding their potential environmental and health impacts—the full extent of which is yet to be determined.
It is estimated that between 70 and 80 percent of this pollution originates from treated wastewater, while the remaining 20 to 30 percent is attributable to industrial waste [5], the improper disposal of unused or expired medications, and agricultural runoff. The pervasive occurrence of these contaminants underscores the inadequacy of conventional wastewater treatment processes in effectively removing pharmaceutical compounds. Despite numerous endeavors, current wastewater treatment methods frequently prove incapable of degrading or eliminating pharmaceutical substances, their metabolites, and byproducts [6].
Another significant source of contamination is the runoff from livestock farms and aquaculture, which utilize pharmaceuticals such as antibiotics and hormones [7]. The improper disposal of pharmaceuticals from households, hospitals, and healthcare facilities, in addition to landfill leachates, contributes further to the issue [8]. Despite the advent of novel advanced treatment methods, including biological processes and electrocoagulation, their overall efficiency remains constrained [9,10,11]. On the other hand, the occurrence and concentration of drugs in wastewater depend on the physicochemical properties of the pharmaceutical compounds (logKow, volatility, etc.), the characteristics of the wastewater influent (i.e., alkalinity and acidity), the sorption of drugs onto suspended particles, and the treatment processes used [8]. Recently, novel treatment methods were introduced for the elimination of pharmaceuticals using advanced materials, such as micromotors and solar evaporation techniques [12,13], and Phoslock TM as a P&N-inactivation agent was also applied [14].
A selection of the most frequently occurring groups of monitored pharmaceutical substances in environmental water samples is shown in Figure 1. The pharmaceuticals that were identified in the aquatic environment belong to a number of different chemical classes. These include non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), antibiotics, antiepileptics, β-blockers, steroid estrogens, and psychiatric medications [15,16,17,18,19,20]. Among the pharmaceuticals most often detected in the aquatic environment include (1) NSAIDs—such pharmaceuticals as ibuprofen, diclofenac, and naproxen are frequently detected due to their extensive use in the treatment of pain, inflammation, and fever [21]. (2) Antibiotics, including penicillin, macrolides, and sulfonamides, are prevalent due to their extensive application in human and veterinary medicine. Antibiotics are often detected in water due to their incomplete metabolism and disposal through agricultural runoff, improper waste management, and excretion from treated animals [22,23]. (3) Antiepileptic drugs and drugs for the treatment of mental disorders (antipsychotics) are a group of substances that do not contain a carboxyl group in their structure and are separable in a reverse-phase system. Such analytes can show a weak basic character due to the presence of the NH2 group or nitrogen in the cycle, such as carbamazepine or 10,11-epoxycarbamazepine (a drug for the treatment of mental disorders), diazepam [24], and others. Antiepileptics like carbamazepine, known for their persistence in wastewater treatment processes, are often used as indicators of pharmaceutical contamination [25,26].
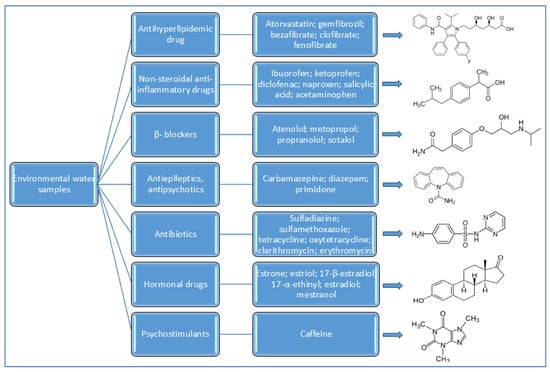
Figure 1.
The most commonly detected pharmaceuticals in water samples and their chemical structures of the first representant in the group.
The group of steroid estrogens are hormonal drugs, which include estrogens (hormonal contraceptives). With uncontrolled entry from the environment into living organisms, they can act as endocrine disruptors, i.e., disrupt the proper functioning of the organism. The structure of these compounds is formed by a phenolic core and possibly several hydroxyl groups. Estrogens are divided into natural (17-β-estradiol, estrone, estriol) and synthetic (17-α-ethinylestradiol, mestranol) types, and both types are lipophilic substances [27,28].
The concentrations of pharmaceuticals in the environment typically range from nanograms to micrograms per liter (ng/L to µg/L) [8,29], with over 600 pharmaceutical compounds detected globally [30]. The low levels of pharmaceuticals in the environment, combined with the complex nature of water matrices, present a significant challenge to their detection. Solid-phase extraction (SPE) is a commonly employed sample preparation technique due to its capacity to extract analytes by sorption onto a solid material from large volumes of water samples and subsequently elute them with a minimal volume of organic solvent, thereby achieving the preconcentration of target compounds [31]. Combining SPE, which preconcentrates the analytes and eliminates the interferents from environmental samples, with liquid chromatography separation and tandem-mass spectrometric detection (LC–MS/MS) provides a highly efficient analytical method for trace and ultra-trace analyses of pharmaceutical pollutants in environmental samples with high selectivity and sensitivity [32].
The physicochemical properties of pharmaceuticals exhibit considerable variation, which in turn affects their behavior in the environment. Lipophilic compounds tend to sorb onto particulate matter, whereas hydrophilic substances exhibit a greater propensity to disperse in aqueous solutions [4]. NSAIDs are persistent in the environment, where they can cause oxidative stress and reproductive harm to aquatic species. For example, diclofenac has been associated with cardiovascular damage in fish [33,34].
Considering antibiotics, such compounds contribute to the development of antibiotic resistance, which represents a significant environmental and public health concern. The exposure of organisms to sub-lethal concentrations of antibiotics in the environment has been demonstrated to promote the development and spread of antibiotic-resistant genes (ARGs) [35].
Meanwhile, steroid estrogens and the use of these hormonal drugs in contraception have been linked to endocrine disruption in aquatic organisms, which can result in reproductive abnormalities and population declines [36].
Antiepileptic and psychiatric medications, such as pharmaceutical agents carbamazepine and fluoxetine, have been demonstrated to exert an influence on the behavior of aquatic species while also causing neurotoxicity [37].
The toxic effects of these pharmaceuticals are not limited to the effects of individual compounds [38]. The combined effects of pharmaceuticals with other environmental contaminants can be additive or synergistic, leading to an exacerbation of the harm they cause to aquatic life.
Pharmaceuticals in the environment rarely exist in isolation. Instead, they form complex mixtures, which include active parent compounds, metabolites, and degradation products. These mixtures pose a greater risk than individual compounds, as they may interact with one another, leading to enhanced toxicity. Consequently, ecotoxicological studies are increasingly focusing on these combined effects, though assessing and managing such risks remains challenging [38].
The presence of pharmaceutical mixtures in aquatic environments gives rise to a number of significant regulatory and treatment challenges. The current wastewater treatment plants are not equipped to fully remove these complex compounds, which have the potential to exert long-lasting effects on ecosystems and human health [3,6].
This manuscript aims to raise awareness about pharmaceuticals’ widespread presence and risks in the environment, emphasizing the need for improved monitoring, detection, and extraction methods for these contaminants in water samples. One of the main focuses of this manuscript is to address the challenges and complexities involved in accurately identifying and quantifying pharmaceuticals in environmental waters. Therefore, this manuscript highlights the importance of developing advanced analytical techniques, including optimized extraction modes, preconcentration procedures, and more sensitive detection methods such as high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC–MS), liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry (LC–MS), and solid-phase extraction (SPE). These techniques are essential for identifying pharmaceuticals at low concentrations and ensuring that their presence and risks are accurately assessed.
2. Methodology
The main focus of this manuscript is to provide a review of the sample preparation and determination techniques used for pharmaceutical analysis in water samples. Table 1 contains a review of the publications for determining pharmaceuticals in water samples. A systematic literature search was conducted across multiple databases, including Web of Science, PubMed, ScienceDirect, and Google Scholar, to ensure a comprehensive and up-to-date review. The search was performed using a combination of key terms such as “pharmaceuticals in aquatic environment”, “pharmaceutical contamination in water”, “pharmaceutical occurrence in water bodies”, “environmental impacts of pharmaceuticals”, “analytical methodologies for pharmaceutical detection”, and “sample preparation techniques for water analysis”. The literature search was restricted to peer-reviewed articles, reviews, and relevant reports published between 2010 and 2023 to ensure that the review incorporates the most relevant findings and technological advances. The extracted data were synthesized to provide a comprehensive overview of the current knowledge on pharmaceutical contamination in water bodies. The studies were compared to identify common trends, methodologies, and findings, and critical insights were drawn.

Table 1.
Overview of extraction techniques and analytical methods for the determination of selected pharmaceuticals in different types of water.
3. Determination of Pharmaceuticals in Environmental Samples
One of the current challenges associated with the analysis of pharmaceutical contaminants in waters, such as wastewater from treatment plants and surface waters, is the complexity of the sample matrix. Analytes are often present in trace amounts along with other organic, inorganic, and/or biological interferents. Therefore, highly sensitive and selective analytical methods are used to reliably detect, identify, and quantify the target analytes. The developed analytical method for the trace to ultra-trace level analyses consists of sampling, sample preparation (i.e., isolation of the target analytes from the matrix), and analyte separation and detection [32].
3.1. Sample Preparation Techniques
Sample preparation is the first step of the analytical method and is crucial for the accurate and correct determination of analytes.
Suitable pretreatment methods are selected for different analytes in various environmental samples based on the physicochemical properties of the substances. In complex environmental matrices, analytes are converted into forms that can be easily extracted and purified. The result of sample preparation is the reduction of matrix interferences and the concentration of the analyte [51]. SPE has gradually replaced the traditionally used liquid–liquid extraction (LLE) method for the sample treatment, used to isolate organic compounds from the aqueous matrix into the organic layer. SPE is suitable for many types of environmental samples, allows for the analysis of the sample as a whole, and can also be automatized, ultimately enabling the processing of a large number of samples in a set time [10].
3.1.1. Solid-Phase Extraction (SPE)
SPE was developed in the 1970s [51] and is the most used extraction technique for the isolation of pharmaceuticals from environmental samples (Table 1). The mechanism employed in the extraction procedure is somewhat similar to that of liquid chromatography but occurs in several steps. The first step is to condition the sorbent by washing it to maximize analyte sorption by increasing the effective surface area. In the next step, the sample is applied to the sorbent, with the sorbent capacity depending on the sorbent type. For example, the sorbent capacity based on SiO2 is 5 to 10% of its weight. Higher sorbent loading can lead to inefficient extraction. The third step involves washing out interferents, substances that did not bind to the sorbent or have significantly lower interactions with the sorbent than the analyte–sorbent interactions. The wash solution is a solvent that selectively removes unwanted components while not disrupting the analyte–sorbent bond. Several reagents or their mixtures may be used to achieve the desired sample purity. In the final step, the analytes are eluted from the sorbent surface. The eluent has a greater elution strength than the wash solution. The result is an analyte concentration by reducing the volume relative to the sample volume applied to the SPE device [32].
By using columns with various types of sorbents and selecting suitable eluents, a degree of analyte preconcentration sufficient for further determination by various detection techniques can be achieved. Depending on the analyte properties, silica-based composites, polymeric materials, organic–inorganic hybrid materials, natural sorbents, and carbon-based materials have been successfully used [7]. Some commonly used SPE sorbents include C8, aluminum oxide, C18, and silica [51]. Oasis HLB is widely used as an SPE sorbent because it can extract a wide range of pharmaceuticals from different types of water [52]. Oasis HLB columns with various particle sizes are capable of extracting both polar and non-polar compounds over a wide pH range due to their chemical compositions (a combination of lipophilic divinylbenzene and hydrophilic N-vinylpyrrolidone polymers) [53]. Strata-X is a surface-modified styrene-divinylbenzene polymer that, similar to Oasis HLB, can retain a wide range of analytes through hydrophilic and hydrophobic interactions. It is almost a universal sorbent for acidic, basic, and neutral analytes [54].
Although SPE is predominantly used offline, online coupling is also possible using column switching. Online SPE allows the automation of the analytical procedure, resulting in increased process efficiency, reduced sample handling, and prevention of cross-contamination [55].
The online SPE technique represents an automated continuous solid-phase extraction method, most often in a SPE–LC–MS/MS chromatographic system. In this type of solid-phase extraction, the same types of sorbents are used for the SPE columns in the “offline” system. Most often, conventional non-polar sorbents (C18 or C8 bound to a carrier, such as silica gel), whose sorption uses hydrophobic interactions, van der Waals interactions between the hydrophobic part of the analyte and the hydrophobic part of the sorbent are the most popular. The first analytes that were extracted in the online SPE system were pesticides in water, and later, the application was also developed for pharmaceuticals [24]. An essential advantage of online SPE compared to the classic “offline” SPE is the timesaving and elimination of manual operations from preparation to elution of the analytes since all sub-operations of SPE take place in a closed system (within high-performance liquid chromatographic (HPLC) and ultra-high-performance liquid chromatographic (UHPLC) systems), thereby eliminating losses of the target analytes. Idder et al. [24] developed and validated a multi-residue method for the determination of 40 pharmaceutical substances, where online SPE preconcentration was chosen as the sample preparation technique. For the extraction of surface water and drinking water samples, they used the SPE columns Strata-X (20 mm × 2 mm, 25 μm) for the analytes subsequently detected in positive ionization mode by the LC–MS/MS. A volume of 1 mL of surface water sample was satisfactory for analysis. The recoveries achieved by online SPE preparation (compared to direct injection of the sample, without preconcentration and with an injection volume of 20 μL) for most monitored analytes were in the range of 90–120%, with the exception of the acetaminophen and trimethoprim analytes, where they reached recoveries in the range of 70–80%. They verified and confirmed that the usability of the selected online SPE columns was up to 400 injections without changing the sensitivity, accuracy, or repeatability of the method.
Camilleri et al. [56] used online SPE for the preparation of surface water samples for the determination of 37 multi-residual xenobiotics (medicinal substances, pesticides, steroid hormones, UV filters, alkylphenols, and other contaminants). A volume of 2.5 mL of a portion of the sample (acidified with formic acid, pH = 1.6) and Oasis HLB SPE columns (20 × 2.1 mm, 5 μm) were used. Developing the method, the authors optimized the sample volume for online SPE, the SPE sorbent type, composition, and volume elution solvents, as well as the step of cleaning the sorbent after the elution of the analytes from the SPE column. By choosing online SPEs, they appear to significantly achieve low limits of determination at ultra-trace concentration levels (within the limit of quantification (LOQ) range from 0.1 ng/L to 10 ng/L). Other advantages of this are the eliminated sample handling, low solvent consumption, time aspect, and cost of analysis. The recoveries achieved by the online SPE preparation were in the range of 85–110% for all determined analytes.
Axel et al. [26] proposed an analytical method for the determination of 17 antibiotics in surface water samples. A combination of an online SPE system with LC–ESI–MS/MS was proposed. The target analytes were selected according to the recommendation of the Finnish Medicines Agency (FIMEA) and were the anticonvulsant carbamazepine and the antibiotics sulfadiazine, sulfamethoxazole, clarithromycin, oxytetracycline, tetracycline, trimethoprim, and others. The online SPE columns used PLRP-S with the parameters 2.1 × 12.5 mm and 15–20 μm and a composition of macroporous polystyrene and divinylbenzene. Axel et al. [26] tested the addition of different additives (formic acid, acetic acid, and ammonium formate) in the elution process after online SPE extraction. They found that a 0.1% addition of formic acid increased the sensitivity of the method in the positive ionization mode for the monitored analytes the most. They also tested the extraction volume of the sample and finally used a 1.8 mL portion of the surface water sample. The method showed satisfactory linearity (with determination coefficients of 0.989–0.999) in the tested range, and the achieved LOQ values were 1 to 50 ng/L.
Alternative Sorption Materials
In recent years, new extraction materials such as carbon nanotubes (CNTs), magnetic nanoparticles, magnetic cellulose nanoparticles, graphene, metal–organic frameworks (MOFs), restricted access material (RAM), and molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs) have come to the forefront (Figure 2) [56].
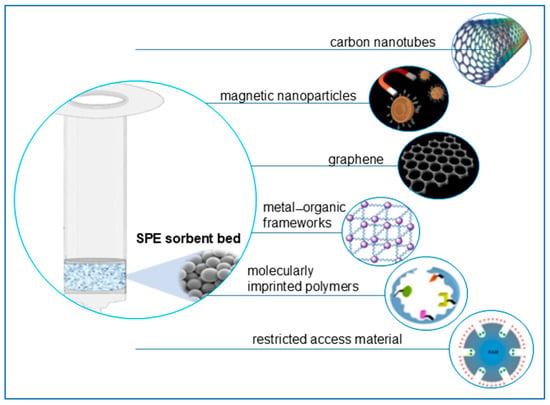
Figure 2.
Advanced types of SPE sorbents used for the isolation of pharmaceuticals from water samples.
Among the various SPE sorbents, MIPs are capable of selectively extracting one molecule or a group of analytes by utilizing their unique properties, such as functional groups, molecular shapes, and sizes. MIPs represent a specific type of sorbent that offers a highly selective retention mechanism to the extracted molecule of the target analyte or a group of structurally similar compounds [57]. This approach reduces the matrix effect and allows analysis using cost-effective analytical equipment such as liquid chromatography with a diode array detector. MIPs demonstrate increased selectivity toward target analytes and also allow for reuse [31]. However, in samples with a high matrix effect, MIPs tend to lose their recognition abilities after a few extractions. Using a porous membrane as a protective shell is a simple approach to prevent matrix interferents from accessing the sorbent. The combination known as membrane-assisted solvent extraction with molecularly imprinted polymers (MASE–MIP) is very advantageous, combining the membrane’s separation ability (filtering high-molecular-weight interfering compounds and solid particles) with the high selectivity of MIPs. Khulu et al. used MASE–MIP to extract pharmaceuticals from river water, achieving limits of detection (LODs) of 0.09–0.2 ng/mL [44]. Martinez-Sena et al. [58] applied MIPs to the selective extraction of NSAIDs (ibuprofen, ketoprofen, diclofenac, and naproxen) from environmental and biological samples. Sample preparation using MIPs consisted of sorbent conditioning (1 mL of acetonitrile, 1 mL of methanol, and 1 mL of 10 mM ammonium formate), application of 1 mL of the sample, washing of the interfering components from MIPs (1 mL of deionized water and 1 mL of 40% (v/v) acetonitrile in water), and NSAID elution (1 mL of methanol). The extract was finally filtered with a 0.22 μm polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) filter and analyzed by HPLC with a diode array detector (DAD) and LC–MS/MS. The achieved MIP extraction recoveries for biological samples ranged from 102 to 113%.
Magnetic SPE represents a new type of SPE technique, which is based on the use of magnetic or magnetically modified sorbents [48,49]. Magnetic nanoparticles offer high extraction yields in a short time and with minimal adverse impact on the environment. Nanoparticles show advantageous properties: they are stable, do not undergo oxidation, do not agglomerate (without the formation of agglomerates), and are easily separated by an external magnet after extraction, making them reusable. They can be modified with functional groups of inorganic or organic molecules such as polymers with intrinsic conductivity, MIPs, etc. [58].
With the current development of nanotechnology, the synthesis of nanomolecules with a precisely defined structure and size, which can function as building blocks of nanotechnological processes, is being promoted in synthetic chemistry. Dendrimers (2–20 nm) are synthetic macromolecules, highly branched with a defined globular structure. In the surface part, dendrimers have multiple functional groups. Magnetic dendrimer polyamidoamine (PAMAM), a new type of sorbent for the extraction of NSAIDs in environmental water samples, was applied by Alinezhad et al. [48]. Magnetic PAMAM (Fe3O4@PAMAM) combines magnetic nanoparticles (Fe3O4) with a commercially available PAMAM dendrimer. The advantages are properties such as an excellent extraction capacity, structural homogeneity, high internal porosity, controlled composition, integrity, and biocompatibility [59]. Another nano-sorbent for magnetic SPE—a composite of Fe3O4/graphene—has been used for the extraction of cytostatic pharmaceuticals used in chemotherapy and applied to wastewater analysis [60].
Abujaber et al. [61] proposed magnetic cellulose nanoparticles as an equivalent of the classic SPE sorbents for the extraction of pharmaceuticals (paracetamol, ibuprofen, naproxen, and diclofenac) in water. Magnetic nanoparticles show a negative charge on the surface, thus giving room for a type of retention mechanism, such as electrostatic interactions. Such “magnetic SPE material” is suitable for the extraction of inorganic as well as organic analytes. In addition, the microcrystalline cellulose base of the nanoparticles is a non-toxic and renewable polymer. The nanoparticles were covered with a layer of ionic liquid (1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate). A water sample (acidified, pH 1.5) was added to the vial along with magnetic nanoparticles coated with a layer of ionic liquid (vortex, 5 min). After extraction, the nanoparticles were separated from the solution with the help of a magnet, and the desorption of the target analytes took place using 250 μL of 0.5 M phosphate buffer (ultrasound, 10 min). The achieved extraction yields were in the range of 85–116% [61].
As a basis for magnetic nanoparticles, modified sporopollenin was invented [62]. Sporopollenin is a natural biopolymer isolated from the outer cell wall of Lycopodium clavatum spores. They bound/immobilized magnetite (Fe3O4) to the surface structure of sporopollenin and subsequently substituted the hydroxyl functional group with silica gel derivatives (3-cyanopropyltriethoxysilane, tetraethylorthosilicate) in order to ensure and increase the extraction yield of pharmaceuticals (ketoprofen, diclofenac, ibuprofen, and mefenamic acid) from surface and wastewater samples. Abd Wahib et al. [62] reported that the synthesized sporopollenin sorption material can be used up to seven times in the sorption–desorption cycle without changing the response of the target analytes analyzed by the HPLC–UV method [62].
Marasco et al. first described an automated method that allows the direct injection of wastewater samples for the simultaneous determination of six pharmaceuticals using RAM for online sample preparation. A laboratory-made RAM column with bovine serum albumin (RAM-BSA) was prepared for this purpose. In this case, RAM functions as a precolumn responsible for analyte preconcentration and extraction, with a switching valve connecting it to the analytical column. RAM carriers enable the separation of analytes based on a combination of size exclusion and conventional hydrophobic or ion-exchange interactions, allowing small molecules to pass through while restricting the macromolecules from accessing the extraction phase. Compared to traditional SPE sorbents, RAM sorbents offer many advantages, including a long lifespan, high separation efficiency, reduced analyte loss, low organic waste production, and low overall analysis costs. Marasco et al. achieved LODs of 0.01–3 μg/L using this method [47].
An interesting alternative sorbent for SPE sorbents is carbon nanotubes (CNT), formed by single-walled carbon nanotubes or several layers of graphite (multi-walled carbon nanotubes), with a diameter of several nm and several μm long, rolled into a cylinder shape [63]. They find application in microextractions in the environmental analysis of waters.
Abujaber et al. [64] replaced the rod used for adsorptive microextraction—BAμE with a CNT rod covered with multiple layers of carbon material. A CNT rod (15 mm length × 2 mm inner diameter × 3 mm outer diameter) was inserted into a 25 mL portion of the sample (pH 5.5) and stirred for 3 h (1000 rpm) at room temperature. The extraction was followed by desorption in 100 μL of methanol (ultrasound, 30 min). LOQ values of 80 ng/L for all monitored pharmaceuticals in this type of microextraction were achieved [64].
3.1.2. QuEChERS
An alternative, less explored strategy for determining pharmaceuticals in environmental samples is the use of extraction methods based on QuEChERS (quick, easy, cheap, effective, rugged, and safe) (Table 1). This method is commonly used as a preliminary preparation of solid samples in the multi-residue analysis of polar and non-polar pesticides. The QuEChERS method is based on solid–liquid extraction with an organic solvent, followed by liquid–liquid partitioning using a suitable salt mixture. Dispersive solid-phase extraction (d-SPE) is usually used for the clean-up [42]. Acetonitrile is used as the extraction solvent, and interfering compounds contained in the extract are removed in the clean-up step [65].
Due to its high versatility, the QuEChERS method has recently been successfully used to extract 19 pharmaceuticals and personal care products in surface and wastewater using acetate buffer and achieved LODs of 0.001–0.167 ng/mL [66]. Martínez-Piernas et al. performed wastewater analysis based on the QuEChERS extraction procedure for more than 100 contaminants, including compounds with various physicochemical properties such as pharmaceuticals, antibiotics, and pesticides [42].
3.1.3. Microextraction Techniques
Microextraction techniques are highly favored in current analytical practice due to miniaturization and the possibility of automation or the use of small volumes of extraction solvents. The advantage of microextraction techniques is also the elimination of the risk of sample contamination in the sample pretreatment process [67].
Liquid microextraction using hollow fiber (HF–LPME) represents a microextraction technique based on extraction in the pores of the hollow fiber walls. The pores are filled with an organic solvent. Due to the porosity, the target analytes of the sample have a large contact area with the extraction agent, making the extraction process efficient.
Saleh et al. [17] introduced HF–LPME as a purification and preconcentration technique for monitoring selected pharmaceuticals (ketoprofen, diclofenac, ibuprofen, and naproxen) in treated sewage sludge samples. HF–LPME was also applied to the microextraction of other pharmaceuticals, such as benzodiazepines [68,69], sulfonamides in water, etc. [68,70]. Hydrophobic polymer (polypropylene) hollow fiber represents a carrier with an applied liquid phase (e.g., ammonium carbonate 0.1 M, organic solvents), which is immobilized in the fiber. The fiber used by Saleh et al. [17] for HF–LPME was with the following parameters: 25 μL volume, 10 cm U-shaped, 600 μm I.D., 200 μm fiber wall thickness, and 0.2 μm pore size. The fiber was immersed in the sample, resp. to 100 mL of pressurized hot water extract (PHWE), and the HF–LPME microextraction lasted 120 min with constant stirring with a magnetic stirrer. The resulting 10 μL of fiber extract was analyzed directly by LC–ESI–MS/MS. This preparation of the samples achieved a significant elimination of the effect of suppressing or increasing the resulting signal during electrospray ionization, and the use of organic solvents of a small volume (a few μL of di-n-hexyl ether) was also an advantage [17].
Guan et al. [19] used dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction (DLLME) to isolate pharmaceuticals from water. DLLME is a technique using a three-component extraction system and is based on the dispersion of the solvent in the sample [71]. Guan et al. monitored six pharmaceuticals from the NSAID group (e.g., ketoprofen, naproxen, sulindac, piroxicam, mefenamic acid, and tolfenamic acid) and six antibiotics (tinidazole, cefuroxime-axetil, ciprofloxacin, sulfamethoxazole, sulfadiazine, and chloramphenicol). Surface water samples after collection were filtered (0.45 μm nylon filter). A 5 mL portion of the sample was used for the extraction, which was subsequently acidified (HCl 0.1 mol/L, pH 4), and a mixture of solvents, such as methanol/acetonitrile (1200 μL, 1:1, v/v) and dichloromethane, was added as a dispersion solvent (800 μL of dichloromethane, vortex for 60 s, ultrasound for 10 min). The phases were separated by centrifugation (4000 rpm, 10 min). The supernatant was separated with a microsyringe and the residual sediment phase was evaporated with a stream of N2. The residue was reconstituted with a mixture of acetonitrile/water (1:1, v/v), while 5 μL of the filtered extract was analyzed by the UPLC–ESI–MS/MS method. The method was applied to real samples of surface water analysis and achieved LODs of 0.006–0.091 ng/mL, thus ranking among the works of authors who achieved significantly low values of LODs [19].
Bar adsorptive microextraction (BAμE) was proposed for the microextraction of pharmaceuticals from water samples. BAμE represents a type of extraction technique for the determination of ultra-trace polar and non-polar analytes in water samples. Moreover, the combination of BAμE and microfluidic desorption provides a “green chemistry” technique compared to the traditional extraction methods [67]. BAμE was applied to the analysis of pharmaceuticals, e.g., ketoprofen, diclofenac, mefenamic acid [58], or sulfonamide antibiotics [24,68].
The extraction of pharmaceuticals by BAμE—diclofenac, ketoprofen, gemfibrozil, and mefenamic acid with multi-walled carbon nanotubes (5–20 μm length, 30 ± 15 nm film layer, 95% purity) used as the sorption material was proposed, and LOQs lower than 0.35 μg/L were achieved [64].
Abd Wahib et al. [62] selected the dispersive-micro-solid-phase extraction (d-μ-SPE) technique for the extraction of pharmaceuticals from the NSAID group (ketoprofen, diclofenac, ibuprofen, and mefenamic acid). Surface water and drinking water samples were filtered and acidified (HCl; 0.1 M) after collection. For d-μ-SPE extraction, an amount of 40 mg of derivatized sporopollenin sorbent and 15 mL of a water sample (vortex, 5 min) were applied. After separating the sample solution and modified sporopollenin, 250 μL of isopropanol was used for the desorption of the analytes from the sorbent (ultrasound, 5 min). This technique, in combination with LC–MS/MS, achieved LODs in the range of 220–510 ng/L [62].
Stir bar sorptive extraction (SBSE) represents a type of microextraction technique based on the sorption of analytes, most often on a layer of polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) applied to a magnetic stirrer. Tanwar et al. [70] used the SBSE technique with a commercially available type of PDMS sorbent to analyze NSAIDs in surface water samples. PDMS is suitable for the extraction of non-polar and semi-polar substances from various matrices and is a relatively widespread and used type of sorbent for SBSE [67,71]. SBSE sorbents such as polyacrylate (PA), polyethylene glycol (EG), or polyethylene glycol-modified silicone (EG-SIL) are suitle for the extraction of polar analytes, and they find application in the extraction of pharmaceutical substances, e.g., in wastewater [71]. The resulting extraction conditions—40 mL of the sample, pH 2, extraction time of 3 h (500 rpm), desorption time, and elution solvent volume of acetonitrile being 800 μL (ultrasound 40 min)—provided satisfactory LOD values for diclofenac 11 ng/L, mefenamic acid 7.5 ng/L, and ibuprofen 8 ng/L, as well as for ketoprofen 60 ng/L and naproxen 71 ng/L using the EG-SIL sorbent, which was more suitable for the monitored analytes with a polar character [71].
Aparicio et al. [72] compared the use of SBSE sorbents—EG-SIL and PDMS—for the extraction of pharmaceuticals (diclofenac, bezafibrate, ethinylestradiol, estrone, ibuprofen, ketoprofen, gemfibrozil, etc.) in surface waters. Compared to the PDMS sorbent, the highest recoveries were achieved with the EG-SIL type sorbent, which was more favorable for analytes with both polar and non-polar character. The LOD values ranged from 5.6 to 23 ng/L for pharmaceuticals in surface waters [72].
Manzo et al. [73] used sorption microextraction with the MIP phase immobilized on rotating disks (RDSE) to isolate pharmaceuticals (diclofenac and mefenamic acid) from wastewater. The methods developed for the synthesis of the MIP fibers for solid-phase microextractions or MIP stir rods for SBSE are relatively simple and robust, and therefore, their use and applications in analytical laboratories can be foreseen in the coming years. RDSE represents an alternative to microextractions or purification techniques. RDSE offers a large extraction surface, and rotating disks can be stirred at higher speeds than stirring bars in SBSE extraction, during which they can be damaged [73]. Higher rotational speeds in RDSE help and facilitate mass transfer to the sorption surface. Manzo et al. used Teflon rotating disks (diameter 1.5 cm) that were inserted into vials with the prepared MIP phase (3000 rpm, 60 min, laboratory temperature). After extraction, the disk was transferred to a vial with 10 mL of methanol, where the target analytes were desorbed (2000 rpm, 5 min), and the extract was evaporated to dryness under a stream of nitrogen and reconstituted with ethyl acetate to a volume of 0.5 mL. The extract was derivatized because they used gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC–MS) for the analysis. The achieved RDSE recoveries with the synthesized MIP phase were from 99 to 100% for diclofenac and mefenamic acid with an RSD of less than 6%. The LOQ for the pharmaceuticals reached 220 ng/L for diclofenac and 200 ng/L for mefenamic acid in wastewater [73].
3.2. Instrumental Separation and Detection Technique
Purified and concentrated extracts containing pharmaceuticals are further analyzed using instrumental analytical techniques such as HPLC and, less commonly, gas chromatography (GC). The main requirement for the analysis of molecules using GC is high volatility. Most pharmaceutical pollutants are not sufficiently volatile and are not directly compatible with GC. However, several examples of pharmaceutical derivatization have been recorded, allowing for their analysis using GC–MS. Some examples of derivatizing agents used for the analysis of pharmaceuticals in environmental samples by GC–MS include pentafluorobenzyl bromide, methyl chloromethane, methanol/boron trifluoride (BF3), and tetrabutylammonium salts. The main advantage of GC–MS is that the ionization techniques, such as electron ionization (EI) or chemical ionization (CI), are less affected by the sample matrix compared to the ionization techniques used in LC–MS [32]. HPLC and the more advanced UHPLC–MS/MS with ultra-high-performance rapid flow rates and MS detection are alternative methods offering several advantages, including fast separation, absence of the need for derivatization, good sample stability, and small sample size [74].
Reverse-phase HPLC is widely used for multicomponent analysis with C18-based chromatographic columns. The typical column size parameters are as follows: (i) a length ranging from 10–25 cm, (ii) an internal diameter of 2.1–4.6 mm, and (iii) a particle size of 3–5 mm [75]. Most LC–MS/MS applications use electrospray ionization (ESI), which is generally compatible with lower mobile phase flow rates, from 0.1 to 0.5 mL/min. Due to these low flow rates, LC columns with narrow diameters (i.e., 2–3 mm) are more popular compared to the conventional analytical columns with a diameter of 4.6 mm. Narrower diameter columns also provide high separation efficiency and sensitivity and are less susceptible to matrix effects. Acidic and neutral pharmaceuticals are typically analyzed using columns longer than 15 cm [76].
Gradient elution represents the most common strategy for separating multiple classes of pharmaceuticals. Organic solvents such as acetonitrile and methanol are commonly used as mobile phases. Mobile phase modifiers, buffers, and acids are often used to achieve effective analyte retention in the column and improve MS detection sensitivity. Common modifiers include ammonium acetate, ammonium formate, tri-n-butylamine (TNBA), formic acid, and acetic acid [75,77]. Typical salt concentrations range from 2 to 20 mM, as higher concentrations have been observed to reduce signal intensity [56,75].
Among the detection techniques, MS and MS/MS are the most commonly used. Spectrophotometric detection in the ultraviolet–visible (UV–VIS) region is used less frequently. MS is often employed due to its high specificity and sensitivity. The triple-quadrupole (QqQ) mass analyzer is frequently used in combination with LC and has become the standard for many pharmaceuticals in various environmental samples. The QqQ mass analyzer uses multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) modes to achieve high selectivity and provide very low LODs [51]. The identification and quantification of pharmaceutical residues are also performed using high-resolution MS techniques such as time-of-flight (TOF) MS and quadrupole time-of-flight (Q-TOF) MS [74].
The most frequently detected pharmaceuticals in surface and wastewater are antibiotics, analgesics, beta-blockers, and estrogens. LODs are generally in the range of ng/L to μg/L [77]. The detected concentrations range from a few ng/L to 100 μg/L [75]. However, LC–MS/MS analysis can be affected by matrix effects (i.e., co-eluting components), which influence the ionization efficiency of target analytes and reduce method sensitivity and reproducibility [78]. These effects are most frequently observed in complex matrices such as sewage, wastewater, and solid samples [75].
Togunde et al. used the QuEChERS procedure to extract drugs from wastewater samples, reporting that the matrix effects are more pronounced in ESI than atmospheric pressure chemical ionization (APCI) [78]. Matrix effects can also be minimized or eliminated using HRMS. When using LC with HRMS, Q-TOF and Q-Orbitrap are used. Q-Orbitrap is more advantageous for the identification of unknown analytes due to its higher resolving power, mass accuracy, and long-term stability [77]. Recent studies show that coupling the Q-Orbitrap to the LC with online SPE provides the simultaneous determination of polar and non-polar contaminants. Thus, the wide-scope screening of pharmaceuticals in water samples is possible, although concentrations may be higher compared to the conventional method due to the lack of certified standards in HRMS libraries. However, the quantitative results of target analytes obtained by LC–MS/MS and LC–HRMS are comparable [77,78].
Many studies have documented the occurrence of pharmaceuticals and their transformation products in effluents, surface waters, groundwater, and drinking water [79]. Antibiotics such as sulfonamides, penicillin, tetracyclines, and macrolides are some of the most frequently detected pharmaceuticals in aquatic environments. Diclofenac and ibuprofen, among NSAIDs, are the most commonly detected in wastewater effluents [80]. Psychiatric drugs such as fluoxetine and carbamazepine are often detected in surface waters and effluents. To improve the understanding of the occurrence of pharmaceuticals in surface waters, various pharmaceutical residues in river water from different locations around the world were analyzed. The overall frequency of detection was 63.1% for all pharmaceuticals, including NSAIDs, antibiotics, psychiatric drugs, and β-blockers. The detection frequencies for diclofenac, carbamazepine, and propranolol were 75.5%, 45.4%, and 40.5%, respectively. Among the antibiotics analyzed, the frequency of detection was highest for erythromycin and trimethoprim, at 57.5% and 51.4%, respectively. The antibiotics trimethoprim and ciprofloxacin, the NSAID diclofenac, the psychiatric drug carbamazepine, and the β-blocker propranolol were among the most frequently detected contaminants worldwide [79].
Pharmaceutical pollution in the aquatic environment has become a global issue, and there is a continuous effort to improve methods for the detection, identification, and quantification of these contaminants. Advanced sample preparation techniques, along with sophisticated analytical instruments such as UHPLC–MS/MS, have significantly enhanced our capability to monitor these pollutants, contributing to a better understanding of their occurrence, distribution, and potential risks. It is crucial to continue developing more efficient, sensitive, and selective analytical methods to accurately assess the presence and impact of pharmaceuticals in the environment and to devise strategies to mitigate their harmful effects.
An overview of the analytical methods for pharmaceutical detection in environmental samples is given in Table 1.
4. Conclusions and Future Remarks
The presence of pharmaceutical compounds in the environment represents a complex and multifaceted issue with significant implications for ecosystems and human health. The key constraints include the ongoing release of pharmaceuticals from wastewater, improper disposal, and agricultural activities, which contribute to their accumulation and slow degradation. The adverse effects on aquatic life, such as physiological disruptions and antibiotic resistance, highlight the need for effective regulatory measures and sustainable practices. This manuscript has highlighted the widespread occurrence of pharmaceuticals in various environmental compartments, the adverse effects they pose to living organisms, and the methodologies used for their detection and quantification.
Analytical techniques such as SPE and LC–MS/MS play a crucial role in the detection and quantification of pharmaceuticals in environmental samples. These methods offer high sensitivity, selectivity, and efficiency, enabling researchers to identify complex mixtures of pharmaceuticals at trace levels.
Future research should focus on refining these methods, implementing stricter regulations, and fostering interdisciplinary collaboration. Greater attention is needed in developing advanced degradation technologies, improving wastewater treatment processes, and promoting responsible pharmaceutical use and disposal practices. These efforts are essential for mitigating environmental and health risks and ensuring the protection of ecosystems and public health.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.S. and S.H.; Funding acquisition, S.H. and N.V.; Investigation, L.V. and Z.K.; Methodology, A.S. and S.H.; Project administration, S.H. and N.V.; Supervision, A.S. and S.H.; Writing—original draft, A.S.; Writing—review and editing, S.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Slovak Research and Development Agency under Contract No. APVV-19-0149, by the STU Young Researchers Support Program and by the STU Program for support of excellent teams of young researchers.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data are summarized in this manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Beek, T.; Weber, F.A.; Bergmann, A.; Hickmann, S.; Ebert, I.; Hein, A.; Küster, A. Pharmaceuticals in the environment—Global occurrences and perspectives. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2016, 35, 823–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OECD. Pharmaceutical Residues: Freshwater: Hazards and Policy Responses. Available online: https://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/environment/pharmaceutical-residues-in-freshwater_c936f42d-en (accessed on 15 March 2024).
- Samal, K.; Mahapatra, S.; Ali, M.H. Pharmaceutical wastewater as Emerging Contaminants (EC): Treatment technologies, impact on environment and human health. Energy Nexus 2022, 6, 100076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brausch, J.M.; Connors, K.A.; Brooks, B.W.; Rand, G.M. Human pharmaceuticals in the aquatic environment: A review of recent toxicological studies and considerations for toxicity testing. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2012, 218, 1–99. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Patrolecco, L.; Ademollo, N.; Greni, P.; Tolomei, A.; Caraciollo, A.B.; Capri, S. Simultaneous determination of human pharmaceuticals in water samples by solid phase extraction and HPLC with UV-fluorescence detection. Microchem. J. 2013, 107, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.; Ashique, S.; Hassan, M.Z.; Afzal, O.; Asiri, Y.I.; Kumar, P.; Dua, K.; Webster, T.J.; Altamimi, A.S.A.; Altamimi, M.A. Pharmaceutical contaminants in aquatic systems, conventional and green strategies, recent updates, challenges and policies, and potential outcomes. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 389, 122905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratulat, A.; Sousa, É.M.L.; Calisto, V.; Lima, D.L. Solid phase extraction using biomass-based sorbents for the quantification of pharmaceuticals in aquatic environments. Microchem. J. 2023, 188, 108465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khasawneh, O.F.S.; Palaniandy, P. Occurrence and removal of pharmaceuticals in wastewater treatment plants. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 150, 532–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeoye, J.B.; Tan, Y.H.; Lau, S.Y.; Tan, Y.Y.; Chiong, T.; Mubarak, N.M.; Khalid, M. Advanced oxidation and biological integrated processes for pharmaceutical wastewater treatment: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 353, 120170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horváth, G.; Szalay, Z.; Šimo, F.; Vidová, B.; Hlavanda, P.; Szarka, A.; Hrouzková, S.; Debnárová, S.; Zažímal, F.; Homola, T. Sustainable remediation of paint factory wastewater using electrocoagulation. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2024, 10, 702–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyriakopoulos, G.; Xiarchos, I.; Doulia, D. Treatment of contaminated water with pesticides via adsorption. Int. J. Environ. Technol. Manag. 2006, 6, 515–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, K.; Gong, J.; Qu, J.; Niu, R. Dual-Mode-Driven Micromotor Based on Foam-like Carbon Nitride and Fe3O4 with Improved Manipulation and Photocatalytic Performance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 44271–44281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, J.; Liu, Z.; Li, Q.; Chen, L.; Gong, J.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Qu, J.; Niu, R. Harnessing Synchronous Photothermal and Photocatalytic Effects of Substoichiometric MoO3–x Nanoparticle-Decorated Membranes for Clean Water Generation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 18855–18866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamparas, M.; Kyriakopoulos, G.; Kapsalis, V.; Drosos, M.; Kalavrouziotis, I. Application of novel composite materials as sediment capping agents: Column experiments and modelling. Desalin. Water Treat. 2019, 170, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loos, R.; Gawlik, B.M.; Locoro, G.; Rimaviciute, E.; Contini, S.; Bidoglio, G. EU-wide survey of polar organic persistent pollutants in European river waters. Environ. Pol. 2009, 157, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peake, B.M.; Braund, R.; Tong, A.Y.C.; Tremblay, L.A. Detection and presence of pharmaceuticals in the environment. In The Life-Cycle of Pharmaceuticals in the Environment; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 77–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, A.; Larsson, E.; Yamini, Y.; Jönsson, J.Ä. Hollow fibre liquid phase microextraction as a preconcentration and clean-up step after pressurized hot water extraction for the determination of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in sewage sludge. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 1331–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Serna, R.; Petrovic, M.; Barceló, D. Development of a fast instrumental method for the analysis of pharmaceuticals in environmental and wastewaters based on ultra high performance liquid chromatography (UHPLC)-tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS). Chemosphere 2011, 85, 1390–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, J.; Zhan, C.; Wang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Huang, P.; Zhao, L. Simultaneous determination of 12 pharmaceuticals by ultrasound-assisted dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction coupled with ultra-high performance liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry. J. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 8099–8109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Shi, H.; Adams, C.D.; Gamagedara, S.; Stayton, I.; Timmons, T.; Ma, Y. Investigation of pharmaceuticals in Missouri natural and drinking water using high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Water. Res. 2011, 45, 1818–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, S.; Kumar, D. Ibuprofen as an emerging organic contaminant in environment, distribution and remediation. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kónyová, Z.; Czifruszová, M.; Nikš, M.; Purgelová, A.; Horniačková, M.; Göböová, M.; Komjáthy, H.; Slimáková, L. Štandardný diagnostický a terapeutický postup pre implementáciu antimikrobiálnej politiky v ústavných zdravotníckych zariadeniach; Ministerstvo zdravotníctva Slovenskej republiky: Bratislava, Slovakia, 2019; Available online: https://www.mzsr.sk/Zdroje?/Sources/dokumenty/SDTP/standardy/1-6-2020/096_KM_Standardny_diagnosticky_a_terapeuticky_postup_pre_implementaciu_antimikrobialnej_politiky.pdf (accessed on 15 June 2024).
- Proctor, K.; Petrie, B.; Barden, R.; Arnot, T.; Kasparzyk-Hordern, B. Multi-residue ultra-performance liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry method for comprehensive multi-class anthropogenic compounds of emerging concern analysis in catchment-based exposure-driven study. J. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 7061–7086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idder, S.; Ley, L.; Mazellier, P.; Budzinski, H. Quantitative on-line preconcentration-liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry method for the determination of pharmaceutical compounds in water. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 805, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klančar, A.; Trontelj, J.; Roškar, R. Development of a Multi-Residue Method for Monitoring 44 Pharmaceuticals in Slovene Surface Water by SPE-LC-MS/MS. Water Air Soil Poll. 2018, 229, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axel, M.; Kortesmäki, E.; Brozinski, J.M.; Kronberg, L. An online SPE LC-MS/MS method for the analysis of antibiotics in environmental water. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 8692–8699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avar, P.; Zrínyi, Z.; Maász, G.; Takátsy, A.; Lovas, S.; Tóth, L.; Pirger, Z. β-Estradiol and ethinyl-estradiol contamination in the rivers of the Carpathian Basin. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 11630–11638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uraipong, C.D.; Allan, R.; Chunchua, L.R.; Kennedy, I.; Wong, V.; Lee, N.A. A survey of 17α-ethinylestradiol and mestranol residues in Hawkesbury River, Australia, using a highly specific enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) demonstrates the levels of potential biological significance. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2017, 144, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spilsbury, F.D.; Inostroza, P.A.; Svedberg, P.; Cannata, C.; Ragas, A.M.J.; Backhaus, T. Defining the data gap: What do we know about environmental exposure, hazards and risks of pharmaceuticals in the European aquatic environment? Water Res. 2024, 251, 121002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küster, A.; Adler, N. Pharmaceuticals in the environment: Scientific evidence of risks and its regulation. Philos. Trans. R Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2014, 369, 1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madikizela, L.M.; Ncube, S.; Chimuka, L. Analysis, occurrence and removal of pharmaceuticals in African water resources: A current status. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 253, 109741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, A.; Miller, S.E. Advances in Green and Sustainable Chemistry. In Contemporary Chemical Approaches for Green and Sustainable Drugs; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 27–45. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, H.K.; Rehman, M.Y.A.; Malik, R.N. Fate and toxicity of pharmaceuticals in water environment: An insight on their occurrence in South Asia. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 271, 111030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Świacka, K.; Michnowska, A.; Maculewicz, J.; Caban, M.; Smolarz, K. Toxic effects of NSAIDs in non-target species: A review from the perspective of the aquatic environment. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 273, 115891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayaz, T.; Renuka, N.; Ratha, S.K. Antibiotic occurrence, environmental risks, and their removal from aquatic environments using microalgae: Advances and future perspectives. Chemosphere 2024, 349, 140822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlson, J.C.; Stefan, M.I.; Parnis, J.M.; Metcalfe, C.H.D. Direct UV photolysis of selected pharmaceuticals, personal care products and endocirne disruptors in aqueos samples. Water Res. 2015, 84, 350–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brezovšek, P.; Eleršek, T.; Filipič, M. Toxicities of four anti-neoplastic drugs and their binary mixtures tested on the green alga Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata and the cyanobacterium Synechococcus leopoliensis. Water Res. 2014, 52, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kümmer, K. The presence of pharmaceuticals in the environment due to human use--present knowledge and future challenges. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 2354–2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Gautam, L.; Hall, S.W. The detection of drugs of abuse and pharmaceuticals in drinking water using solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Chemosphere 2019, 223, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera-Herrera, A.V.; Hernánder-Borges, J.; Borges-Miquel, T.; Rodríguez-Delgado, M.Á. Dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction combined with ultra-high performance liquid chromatography for the simultaneous determination of 25 sulfonamide and quinolone antibiotics in water samples. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2013, 75, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Tenorio, R.; Guzmán-Mar, J.L.; Hinojosa-Reyes, L. Determination of Pharmaceuticals Discharged in Wastewater from a Public Hospital Using LC-MS/MS Technique. J. Mex. Chem. Soc. 2021, 65, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Piernas, A.B.; Plaza-Bolanos, P.; Gilabert, A.; Agüera, A. Application of a fast and sensitive method for the determination of contaminants of emerging concern in wastewater using a quick, easy, cheap, effective, rugged and safe-based extraction and liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1653, 462396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papageorgiou, M.; Zioris, I.; Danis, T.; Bikiaris, D.; Lambropoulou, D. Comprehensive investigation of a wide range of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in urban and hospital wastewaters in Greece. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 694, 133565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khulu, S.; Ncube, S.; Nuapia, Y.; Madikizela, L.M.; Tutu, H.; Richards, H.; Ndungu, K.; Mavhunga, E.; Chimuka, L. Multivariate optimization of a two-way technique for extraction of pharmaceuticals in surface water using a combination of membrane assisted solvent extraction and a molecularly imprinted polymer. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omotola, E.O.; Olatunji, O.S. Quantification of selected pharmaceutical compounds in water using liquid chromatography-electrospray ionisation mass spectrometry (LC-ESI-MS). Heliyon 2020, 6, e05787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiszkiel-Taudul, I. Determination of Antihistaminic Pharmaceuticals in Surface Water Samples by SPE-LC-MS/MS Method. Microchem. J. 2021, 162, 105874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marasco Júnior, C.A.; Sartore, D.M.; Lamarca, R.S.; da Silva, B.F.; Santos-Neto, J.; Gomes, P.C.F.d.L. On-line solid-phase extraction of pharmaceutical compounds from wastewater treatment plant samples using restricted access media in column-switching liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2021, 1180, 122896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascale, R.; Bianco, G.; Coviello, D.; Lafiosca, M.C.; Masi, S.; Mancini, I.M.; Bufo, S.A.; Scrano, L.; Caniani, D. Validation of a liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry method for the determination of drugs in wastewater using a three-phase solvent system. J. Sep. Sci. 2019, 43, 886–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Althakafy, J.T.; Kulsing, C.; Grace, M.R.; Marriott, P.J. Liquid chromatography—Quadrupole Orbitrap mass spectrometry method for selected pharmaceuticals in water samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1515, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, A.A.; Tanimu, A.; Alhooshani, K. Iron and cobalt-containing magnetic ionic liquids for dispersive micro-solid phase extraction coupled with HPLC-DAD for the preconcentration and quantification of carbamazepine drug in urine and environmental water samples. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 336, 116370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Liu, H.; Liu, Y.; Di, S.; Bao, Y.; Zhai, Y.; Zhu, S. Recent advances in sample preparation and chromatographic analysis of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in environment. Trends Analyt. Chem. 2023, 164, 117112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midikizela, L.M.; Ncube, S.; Tutu, H.; Richards, H.; Newman, B.; Ndungu, K.; Chimuka, L. Pharmaceuticals and their metabolites in the marine environment: Sources, analytical methods and occurrence. Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 2020, 28, e00104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Liu, H.; Ma, Y.; Huang, G.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, B.; Xie, D.; Huang, K.; Wang, R. Reproducibility in nontarget screening (NTS) of environmental emerging contaminants: Assessing different HLB SPE cartridges and instruments. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 168971. [Google Scholar]
- Qureshi, M.; Stecher, G.; Huck, C.; Bonn, G.K. Preparation of polymer based sorbents for solid phase extraction of polyphenolic compounds. Open Chem. 2011, 9, 206–212. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Yan, X.; Zhou, X.; Peng, P.; Sun, Q.; Zhao, F. Advances in the on-line solid-phase extraction-liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis of emerging organic contaminants. Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 160, 116976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camillieri, J.; Baudot, R.; Wiest, L.; Vulliet, E.; Cren-Olivé, C.; Daniele, G. Multiresidue fully automated online SPE-HPLC-MS/MS method for the quantification of endocrine-disrupting and pharmaceutical compounds at trace level in surface water. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2014, 95, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, B.; Zohrabi, P.; Shamsipur, M. Recent developments and applications of different sorbents for SPE and SPME from biological samples. Talanta 2018, 187, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Sena, T.; Armenta, S.D.L.; Guardia, M.; Esteve-Turillas, F.A. Determination of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in water and urine using selective molecular imprinted polymer extraction and liquid chromatography. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2016, 131, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alinezhad, H.; Amiri, A.; Tarahomi, M.; Maleki, B. Magnetic solid-phase extraction of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs from environmental water samples using polyamidoamine dendrimer functionalized with magnetite nanoparticles as a sorbent. Talanta 2018, 183, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arvand, M.; Hemmati, S. Magnetic nanoparticles embedded with graphene quantum dots and multiwalled carbon nanotubes as a sensing platform for electrochemical detection of progesterone. Sens. Actuators B 2017, 238, 346–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abujaber, F.; Zougagh, M.; Jodeh, S.; Rios, Á.; Guzmán, B.F.J.; Martin-Doimeadios, R.C.R. Magnetic cellulose nanoparticles coated with ionic liquid as a new material for the simple and fast monitoring of emerging pollutants in waters by magnetic solid phase extraction. Microchem. J. 2018, 137, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd Wahib, S.M.; Wan Ibrahim, W.A.; Marsin Sanagi, M.; Afzal Kamboh, M.; Abdul Keyon, A.S. Magnetic sporopollenin-cyanopropyltriethooxysilane-dispersive micro-solid phase extraction coupled with high performance liquid chromatography for the determination of selected non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in water samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1532, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.Y.; Chen, J.; Shi, Y.P. Different configurations of carbon nanotubes reinforced solid-phase microextraction techniques and their applications in the environmental analysis. Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 86, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abujaber, F.; Ahmad, S.M.; Neng, N.R.; Rodríguez Martin-Doimeadios, R.C.; Guzmán Bernardo, F.J.; Nogueira, J.M.F. Bar adsorptive microextraction coated with multi-walled carbon nanotube phases—Application for trace analysis of pharmaceuticals in environmental waters. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1600, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kim, C.; Hong, Y.; Lee, W.; Lee, S.; Chung, H.; Kim, H.; Jeong, D.-H. Determination of pharmaceuticals in solid samples in municipal wastewater treatment plants by online SPE LC–MS/MS using QuEChERS extraction. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kachhawaha, A.S.; Nagarnaik, P.M.; Jadhav, M.; Pudale, A.; Labhasetwar, P.K.; Banerjee, K. Optimization of a modified QuEChERS method for multiresidue analysis of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in sewage and surface water by LC-MS/MS. J. AOAC Int. 2017, 100, 592–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrouzková, S.; Szarka, A.; Zichová, S. Pokroky a využitie mikroextrakčných techník na analýzu rezíduí pesticídov v potravinách. Chem. Listy 2018, 112, 165–174. [Google Scholar]
- Carasek, E.; Mores, L.; Merib, J. Basic principles, recent trends and future directions of microextraction technique for the analysis of aqueous environmental samples. Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 2018, 19, e00060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezai, F.; Yamini, Y.; Moradi, M.; Daraei, B. Supramolecular solvent-based hollow fiber liquid phase microextraction of benzodiazepines. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 804, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, A.Y.C.; Peake, B.M.; Braund, R. Disposal practices for unused medications around the world. Environ. Int. 2011, 37, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanwar, S.; Di Carro, M.; Magi, E. Innovative sampling and extraction methods for the determination of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in water. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2015, 106, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aparicio, I.; Martin, J.; Santos, J.L.; Malvar, J.L.; Alonso, E. Stir bar sorptive extraction and liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry determination of polar and non-polar emerging and priority pollutants in environmental waters. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1500, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzo, V.; Ulisse, K.; Rodríguez, I.; Pereir, E.; Richter, P. A moleculary imprinted polymer as a sorptive phase imobilized in a rotating disk extraction device for the determination of diclofenac and mefenamic acid in wastewater. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 889, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landmark, C.J.; Johannessen, S.I. Chapter 10.7—Therapeutic monitoring of antiepileptic drugs. In Handbook of Analytical Separations; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 225–256. [Google Scholar]
- Petrović, M.; Gros, M.; Barceló, D. Chapter 2.4—Multi-residue analysis of pharmaceuticals using LC-tandem MS and LC-hybrid MS. In Comprehensive Analytical Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 157–183. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, X.S.; Metcalfe, C.D. Chapter 2.3—Analysis of neutral and acidic pharmaceuticals by liquid chromatography mass spectrometry. In Comprehensive Analytical Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 133–156. [Google Scholar]
- Sabourian, R.; Mirjalili, S.Z.; Namini, N.; Chavoshy, F.; Hajimahmoodi, M.; Safavi, M. HPLC methods for quantifying anticancer drugs in human samples: A systematic review. Anal. Biochem. 2020, 610, 113891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Togunde, O.P.; Cudjoe, E.; Oakes, K.D.; Mirnaghi, F.S.; Servos, M.R.; Pawliszyn, J. Determination of selected pharmaceutical residues in wastewater using an automated open bed solid phase microextraction system. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1262, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosma, C.I.; Nannou, C.I.; Boti, V.I.; Albanis, T.A. Psychiatrics and selected metabolites in hospital and urban wastewaters: Occurrence, removal, mass loading, seasonal influence and risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 659, 1473–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, G.; Lu, D.; Liu, C.; Hower, D. Analytical challenges and recent advances in the identification and quantitation of extractables and leachables in pharmaceutical and medical products. Trends Analyt. Chem. 2021, 141, 116286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).