Abstract
To elucidate ths chemical composition of Lilium brownii var. Viridulum Baker and the impact of primary processing on its quality, a comparison was made on the polysaccharide and extract contents of ten batches of Lilium from different regions, including Lilium lancifolium Thunb., Lilium brownii var. Viridulum Baker, and Lilium davidi var. unicdor cotton. The chemical composition differences of the three Lilium species mentioned above were compared using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) fingerprinting. The chemical components of Lilium brownii var. Viridulum Baker were analyzed by ultra-performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (UPLC-Q-TOF-MSE). The boiling time and drying temperature of fresh Lilium brownii var. Viridulum Baker were investigated using the comprehensive scoring method based on the polysaccharide and extract contents. The results showed that the polysaccharide content of ten batches of Lilium from different origins ranged from 13.34% to 34.00%, and the extract content ranged from 27.10% to 47.10%. The HPLC fingerprinting results showed that the similarity of the three Lilium species ranged from 0.796 to 0.999, and the chemical components of Lilium davidi var. unicdor cotton differed significantly from those of Lilium lancifolium Thunb. and Lilium brownii var. Viridulum Baker. UPLC-Q-TOF-MSE identified 22 phenolic compounds, 35 steroidal saponins, and 6 alkaloids in Lilium brownii var. Viridulum Baker. Boiling for 5 min and drying at 85 °C has the least effect on the quality of fresh Lilium.
1. Introduction
In China, Lilium is regarded as an agricultural product sharing the same origin as medicine and food. Lilium has biological activities, such as anti-inflammatory [1], antioxidant [2], anti-tumor [3], antidepressant [4], antibacterial [5], hypoglycemic [6], and anti-insomnia [7] properties. There are three common sources of Lilium plants: Lilium lancifolium Thunb., Lilium brownii var. Viridulum Baker, and Lilium davidi var. unicdor cotton. Among them, Lilium lancifolium Thunb. and Lilium brownii var. Viridulum Baker are primarily cultivated in Hunan Province, whereas Lilium davidi var. unicdor cotton is mainly produced in Gansu Province. Eight phenolic glycerides, four phenylpropanoids, and two flavonoids were isolated from Lilium lancifolium Thunb. [8]. The chemical constituents of Lilium davidi var. unicdor cotton mainly include 22 amino acids, polypeptides and their derivatives, 9 phospholipids, 7 sugars, 7 phenolic acids, 4 flavonoids, 4 natural vitamins, 3 phenolic amines, 2 coumarins, 2 alkaloids and 2 terpenoids [9]. In addition, 5 phenolic acids, 1 lignan compound, and 5 steroidal saponins were identified in Lilium brownii var. Viridulum Baker [10]. And 53 compounds were identified by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC-MS) in the weakly polar parts of Lilium produced in Yongxing Town, Jiangjin District, Chongqing Province [11]. Steroidal saponins with anti-hyperglycemic activity in Lilium were identified using liquid chromatography quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (LC-Q-TOF-MS/MS) [6]. A total of 331 components in Lilium lancifolium and Lilium brownii viridulum were identified by hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography (HILIC) and RPC18, among which phenylpropane derivatives and steroidal saponins were the most abundant [12]. The contents of regaloside A and regaloside B in Lilium lancifolium Thunb. and Lilium brownii var. Viridulum Baker were compared using metabolomics and transcriptome [13]. Lilium lancifolium Thunb., Lilium davidii var. unicolor, and Lilium trompeten were distinguished by headspace-gas chromatography-ion mobility spectrometry (HS-GC-IMS), in which 3-methylbutanal was the most abundant in Lilium Lancifolium Thunb., and butanone was the most abundant in Lilium davidii var. unicolor [14]. The analysis method for the chemical composition of Lilium lancifolium Thunb. using ultra-performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (UPLC-Q-TOF-MSE) was established [15]. However, the chemical composition of Lilium brownii var. Viridulum Baker has not been analyzed using the UPLC-Q-TOF-MSE method so far.
The 2020 edition of the Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China (hereinafter referred to as the Chinese Pharmacopoeia) [16] stipulates that the processing method of Lilium is “autumn harvesting, washing, peeling off scales, slightly scalding in boiling water, and drying”. However, there is no specific regulation on the duration of slight scalding in boiling water and drying. The impact of processing on the quality of Lilium has been reported in the relevant literature. Boiling water and steam hot treatment had a great influence on the physicochemical properties of Lilium lancifolium Thunb. [17]. The shredding and drying of Lilium could shorten the drying time and reduce energy consumption [18]. The comprehensive quality of Lilium brownii var. Viridulum Baker powder prepared by the combination of steam blanching and vacuum microwave drying process was obviously better than other process combinations [19]. Both boiling water scalding and steam scalding could effectively inhibit the activity of polyphenol oxidase and peroxidase of Lilium and affect its microstructure [20]. Heat shock treatment could effectively delay the quality deterioration of fresh-cut Lilium bulb slices and prolong the storage time [21]. To date, there have been no reports on the impact of the duration of slight scalding and drying on the quality of Lilium.
Through investigation and research on the processing methods of Lilium in their places of production, it is found that short-term boiling in water is mainly used for slight scalding in boiling water, and hot air drying is mainly used for the drying process. However, the uncertainty of the boiling time and drying temperature results in the uncontrollable quality of the Lilium. According to the market research on the application of Lilium, Lilium lancifolium Thunb. is mainly used in Traditional Chinese Medicine, Lilium davidi var. unicdor cotton is mainly used as food, and Lilium brownii var. Viridulum Baker can be used in both Traditional Chinese Medicine and food, with a wide range of applications. However, there are few reports on the chemical composition of Lilium brownii var. Viridulum Baker, and the impact of the primary processing on the quality of the fresh products has not been publicly reported. Therefore, the chemical composition of Lilium brownii var. Viridulum Baker was analyzed in this article. In addition, the effects of boiling time and drying temperature on the quality of fresh Lilium were investigated, so as to provide a reference for the primary processing of Lilium in their production areas.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Ten batches of Lilium samples from six producing areas, including Longhui, Lianqiao, Longshan, Hengshan, Xinhua in Hunan, and Lanzhou in Gansu, were collected from July to August 2022. They were identified by Professor Chen Yuxiu as dry succulent bulbs of Lilium lancifolium Thunb., Lilium brownii var. Viridulum Baker, and Lilium davidi var. unicdor cotton. The above ten batches of Lilium samples were sequentially numbered S1, S2, S3, S4, S5, S6, S7, S8, S9, and S10. Their varieties and origins are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
The varieties and origins information of ten batches of Lilium.
2.2. Determination of Extracts
The determination was carried out according to the cold soak method in the Chinese Pharmacopoeia (General Item 2201). The ten batches of Lilium samples were crushed, after which 4 g of each sample powder (10 meshes) was taken and put into 250 mL conical flasks with stoppers. Then 100 mL of water was precisely added, plugged tightly, and soaked in the cold. After being shaken constantly for 6 h, they were left still for 18 h. The mixtures were then filtered quickly with a drying filter. The continued filtrate (20 mL) was put into evaporating dishes, which were dried to constant weight, evaporated on a water bath at 105 °C for 3 h, and then cooled in a dryer. After drying for 30 min, the weight was quickly and accurately weighed. Unless otherwise specified, the water-soluble extract content (%) of the test product shall be calculated using the dry product.
2.3. Determination of Polysaccharides
The determination was carried out according to the Lilium in the Chinese Pharmacopoeia. The anhydrous glucose reference substance (50 mg), dried to a constant weight at 105 °C, was weighed accurately, placed in a 50 mL volumetric flask, dissolved in water and diluted to the scale, shaken well, and a solution of 1 mg of anhydrous glucose per 1 mL was obtained. The reference solution (2.0, 2.5, 3.0, 3.5, 4.0, and 4.5 mL) was placed in volumetric flasks of 50 mL. Water was added to the scale and shaken well. After that, 1 mL of each of the above solutions and 4.0 mL of 0.2% anthrone sulfuric acid solution were placed and mixed well in brown test tubes with stoppers, which were first quickly cooled in an ice water bath and then heated in a boiling water bath. After being heated for 10 min, the test tubes were placed in an ice water bath again for 5 min, and then placed at room temperature for 10 min. Using the corresponding reagent as a blank, absorbance was measured at a 580 nm wavelength on the UV-visible photometer (TU-1901, Beijing Puyang Universal Instrument Co., Ltd., Beijing, China). The standard curve was drawn with absorbance as the vertical axis and concentration as the horizontal axis. The dried Lilium powder (1 g) was precisely weighed and placed into a round-bottom flask using a 65-mesh sieve, and 100 mL of water was precisely added and weighed. The mixture was then heated and refluxed for 2 h, cooled, and weighed again. The lost weight was made up of water. Then the flask was shaken and centrifuged. The supernatant (1.5 mL) was taken and mixed with 7.5 mL of ethanol, shaken, and centrifuged again. The sediment was taken, dissolved in water, put into a 50 mL measuring flask, diluted to the scale, and shaken well. The solution (1 mL) was taken, the absorbance of which was determined starting from “adding 4.0 mL of 0.2% anthrone sulfuric acid solution”, according to the method under the preparation of the standard curve. The weight of the anhydrous glucose in the test solution can be read and calculated from the standard curve.
2.4. Fingerprint Analysis of Lilium from Different Regions
According to reference [22], 10 g of S1-S10 Lilium powder (24 mesh sieve) was precisely weighed and placed in a 150 mL conical flask with a stopper. Then, 50 mL of 70% ethanol solution (volume ratio) was added and the ultrasonic duration time was 15 min. The mixture was centrifugated at a speed of 5000 r/min for 10 min. The supernatant was filtered with a microporous membrane of 0.2 μm to provide the test solution. A high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) (1260 Infinity II, Agilent Technologies Inc., Santa Clara, CA, USA) fixed with a UV detector and a four-element liquid phase pump was utilized. The mobile phases of the Agilent 5 TC-C18 (2) chromatographic column (250 mm × 4.6 mm, 5 μm) were acetonitrile (A) and 0.1% phosphoric acid solution (B), and a gradient elution was performed within 0–20 min. The mobile phase changed from 20% (A) −80% (B) to 50% (A) −50% (B), and the detection wavelength was 308 nm; the injection volume was 10 μL, and the flow rate was 0.6 mL/min. The chromatograms obtained were analyzed with the software (2012.130723) “Similarity Evaluation System for Chromatographic Fingerprints of Traditional Chinese Medicine” (State Food and Drug Administration, Beijing, China), and the relative peak areas of the common peaks of the ten batches of Lilium fingerprints were analyzed with SPSS 27.0 (IBM, New York, NY, USA) software.
2.5. Composition Analysis of Lilium brownii var. Viridulum Baker
According to reference [23], the sample test solution was prepared using the same method as Section 2.4. The ultra-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry chromatograph (ACQUITY UPLC I—Class Xevo G2-S QTof MS, Waters Technology Co., Ltd., Milford, MA, USA) was used. The chromatography was performed on Waters Acquity UPLC BEH C18 column (2.1 mm × 50 mm, 1.7 μm) with a mobile phase of acetonitrile (A) −0.1% formic acid aqueous solution (B), gradient elution (0–2 min, 3% A; 2–6 min, 3–10% A; 6–9 min, 10–15% A; 9–12 min, 15% A; 12–16 min, 15–25% A; 16–18 min, 25–30% A; 18–22 min, 30–40% A; 22–25 min, 40–80% A; 25–27 min, 80–95% A; 27–30 min, 95% A; 30–36 min, 3% A), a column temperature of 35 °C, a flow rate of 0.3 mL/min, and an injection volume of 5 μL. The mass spectrum conditions were an electrospray ion source; the scanning range of the positive and negative ion detection mode was m/z 100–1200; the capillary voltage was 3.0 kV for the positive ion, 2.5 kV for the negative ion; the nozzle voltage was 40 V; the dry gas flow rate was 800 L/h; the ion source temperature was 120 °C; the collision gas was argon and the collision energy was 20–40 eV; and the experimental data were corrected in real-time using the Lock Mass pathway.
2.6. Subsection
2.6.1. Materials
The sample was fresh Lilium brownii var. Viridulum Baker, and the origin was Fengjia Town, Xinhua County, Loudi, Hunan Province, China (Longitude: 110.864121, Latitude: 27.791392). The samples were collected on 7 August 2022.
2.6.2. Influence of Boiling Time on the Quality of Lilium
Fresh Lilium was washed clean. The scales were peeled off, weighed (125 g), and put into a saucepan. Water was added until the scale surface was immersed to a depth of 1–2 cm. Eight groups of experiments were carried out, with a boiling time of 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, and 8 min, respectively. After boiling, the Lilium was quickly removed with a filter screen and put into an oven to dry at 65 °C until the weight was constant. The contents of extracts and polysaccharides were determined in accordance with the methods in Section 2.2 and Section 2.3, respectively.
2.6.3. Influence of Drying Temperature on the Quality of Lilium
Fresh Lilium was washed clean. The scales were peeled off, weighed (125 g), and put into a saucepan. Water was added to submerge the scale surface by 1–2 cm, and the boiling time was set to 5 min after the boiling of water. After boiling, the Lilium was quickly removed with a filter screen and put into an oven to dry at 45, 55, 65, 75, 85, 95, and 105 °C, respectively. The contents of extracts and polysaccharides were determined in accordance with the methods in Section 2.2 and Section 2.3, respectively.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Contents of Extracts and Polysaccharides of Lilium from Different Producing Areas
The contents of extracts and polysaccharides of ten batches of Lilium from different producing areas are summarized in Table 2. According to the regulations of the Chinese Pharmacopoeia, the extract content of Lilium should not be less than 18.0%. The results showed that the extract content of Lilium brownii var. Viridulum Baker S2 produced from Long Hui, Hunan, was 15.00%, and that of Lilium brownii var. Viridulum Baker S5 sourced from Lianqiao, Hunan, was 13.34%, both of which did not meet the standards of the Chinese Pharmacopoeia. Lilium brownii var. Viridulum Baker S9 produced in Xinhua, Hunan, with an extract content of 19.00%, met the standards of the Chinese Pharmacopoeia. According to the regulations of the Chinese Pharmacopoeia, the polysaccharides in Lilium should be measured by anhydrous glucose (C6H12O6), which should not be less than 21.0%. The results showed that the three batches of Lilium brownii var. Viridulum Baker collected in this study met the standards of the Chinese Pharmacopoeia.

Table 2.
The contents of extracts and polysaccharides of ten batches of Lilium.
3.2. Fingerprint of Lilium from Different Producing Areas
Establishment and Similarity Evaluation of the Fingerprint
Through software analysis, a total of nine common peaks were identified in ten batches of Lilium chromatograms. By comparing the peak areas, it can be seen that Peak 4 and Peak 7 were the main peaks. Among them, the peak areas of Peak 4 and Peak 7 in the Lilium S4 chromatogram were higher than those of other Lilium samples. Therefore, the chromatogram of Lilium S4 was selected as a reference. After multi-point correction, Mark peak self-matching was performed and a fingerprint overlay chart of Lilium with a spectral spacing of 100 was established, as shown in Figure 1. The control graph R was generated by the mean method, with a time width of 0.10 min, as shown in Figure 2. The relative peak area RSD ranged from 52.01% to 191.31%, with significant differences. The relative area and retention time of the common peaks are shown in Table 3. The similarity between the HPLC chromatograms of ten batches of Lilium and the control fingerprint was evaluated. The results showed that the similarity between the S1–S10 Lilium samples and the control fingerprint R ranged from 0.796 to 0.999. The similarity analysis results are shown in Table 4. The resemblance between Lilium brownii var. Viridulum Baker and Lilium lancifolium Thunb. was relatively high, whereas the dissimilarity between Lilium davidi var. unicdor cotton and the other varieties was significant. These results suggest that the chemical composition of Lilium davidi var. unicdor cotton differed significantly from the other two Lilium species.
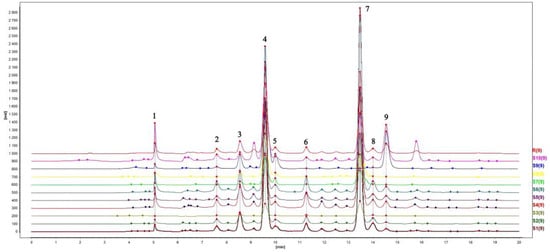
Figure 1.
A fingerprint overlay chart of ten batches of Lilium.
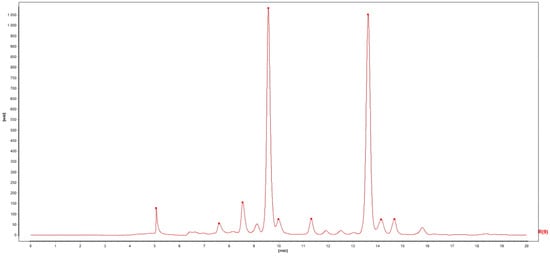
Figure 2.
The control graph R of Lilium.

Table 3.
The relative area and retention time of the common peaks of ten batches of Lilium.

Table 4.
The similarity analysis results of ten batches of Lilium.
SPSS 27.0 software was used to standardize the relative peak areas of the common peaks of ten batches of Lilium fingerprints. Custer analysis was carried out using the inter-group connection method, where the inter-sample distance was calculated by square Euclidean distance. The results are shown in Figure 3. When a clustering distance of 10 was applied, the data could be grouped into three main categories. The first category included S1, S2, S3, S4, S5, and S6, all of which belong to Lilium lancifolium Thunb. The second category comprised S7, S8, and S9, all of which are classified as Lilium brownii var. Viridulum Baker. The third category consisted of S10, identified as Lilium davidi var. unicdor cotton.
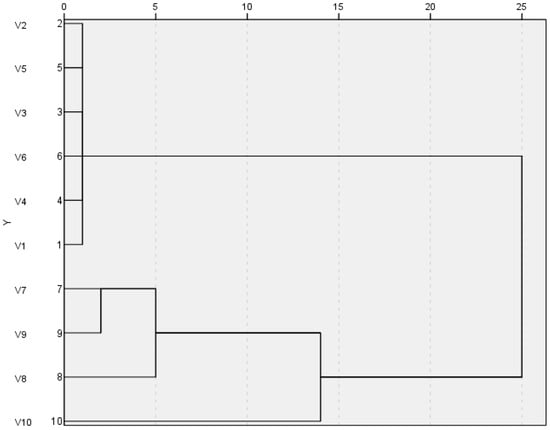
Figure 3.
The Custer analysis of ten batches of Lilium.
The HPLC gradient elution method was used to establish the fingerprints of 20 batches of fresh Lilium from Lilium lancifolium Thunb., Lilium brownii var. Viridulum Baker, and Lilium regale Wilson. The fingerprints were divided into two categories by cluster analysis, with a common peak similarity of 0.930–0.997 [24]. The fingerprint of 15 batches of C. dendron samples was established using the UPLC method, and the similarity was found to be above 0.910 [25]. This study compared the similarity of three kinds of Lilium, including Lilium davidi var. unicdor cotton, and further expanded the scope of comparison compared to the previously reported literature.
3.3. Chemical Composition of Lilium brownii var. Viridulum Baker
According to the method in Section 2.5, the S9 Lilium sample (Lilium brownii var. Viridulum Baker) was detected, and the ion flow diagrams of the Lilium sample in positive and negative ion modes were obtained, as shown in Figure 4 and Figure 5, respectively. Through the analysis of the precise relative molecular weight of the primary mass spectrometry and the cleavage information of the secondary mass spectrometry, identification and speculation were conducted in combination with the literature, as shown in Table 5 and Table 6. According to the data analysis method, a total of 70 compounds were speculated, including 22 phenolic compounds, 41 steroidal saponins, 6 alkaloids, and 1 flavonoid. The identification results are shown in Table 5 and Table 6.
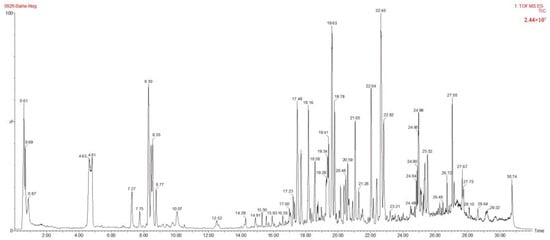
Figure 4.
The ion flow diagrams of the Lilium sample in negative ion modes.
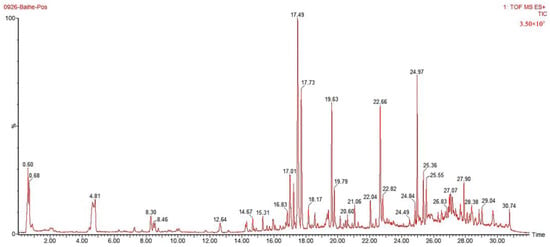
Figure 5.
The ion flow diagrams of the Lilium sample in positive ion modes.

Table 5.
The Chemical constituents of the Lilium sample in negative ion modes.

Table 6.
The Chemical constituents of the Lilium sample in positive ion modes.
3.4. Influence of Boiling Time on the Quality of Lilium
In the process of Lilium processing, the Lilium scales need to be cooked, but not gelatinized. According to observation, there was no significant change in the Lilium scales after boiling for 1–2 min. After boiling for 3–4 min, there were slight cracks on the Lilium scales. After boiling for 5–7 min, the cross-section of Lilium scales appeared pink. After boiling for 8 min, the Lilium scales were fully cooked, with a powdery cross-section that was easy to crush. Over 8 min, the Lilium scales were completely gelatinized. Therefore, the boiling time range was selected from 1 to 8 min. According to the method in Section 2.6, the polysaccharide and extract contents of fresh Lilium S9 were tested at different boiling times, as shown in Figure 6. The influence of boiling time on the quality of Lilium was evaluated according to two indicators: extract and polysaccharide contents.
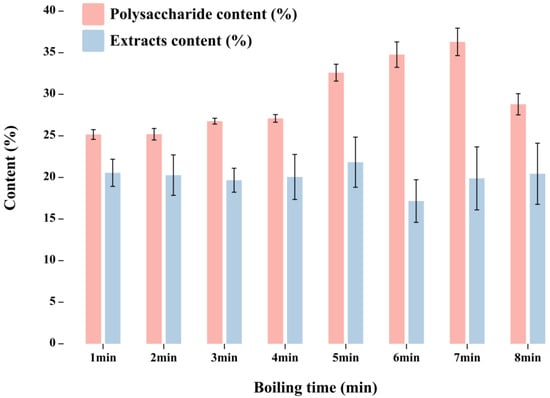
Figure 6.
The polysaccharide and extract contents of fresh Lilium S9 at different boiling times.
Lilium polysaccharide content (y1, weighing coefficient 0.5) and extract content (y2, weighing coefficient 0.5) were used as indicators for comprehensive evaluation. The comprehensive scores are shown in Table 7. The results showed that the comprehensive quality of Lilium was the best when the boiling time was 5 min.

Table 7.
The comprehensive scores of fresh Lilium S9 at different boiling times.
3.5. Influence of Drying Temperature on the Quality of Lilium
According to the method in Section 2.6, after boiling for 5 min, the polysaccharide and extract contents of Lilium S9 were detected at different drying temperatures, as shown in Figure 7. The effect of drying temperature on the quality of Lilium was evaluated according to two indicators: extract and polysaccharide contents.
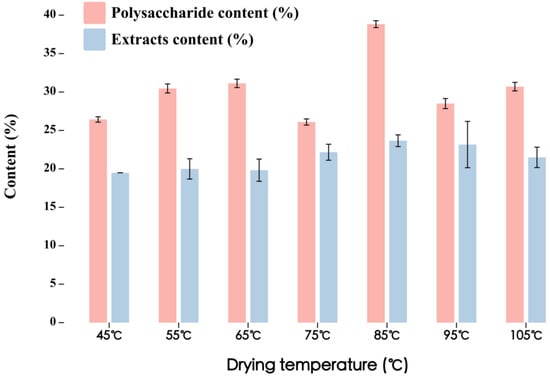
Figure 7.
The polysaccharide and extract contents of fresh Lilium S9 at different drying temperatures.
Lilium polysaccharide content (y1, weighing coefficient 0.5) and extract content (y2, weighing coefficient 0.5) were used as indicators for comprehensive evaluation. The comprehensive scores are shown in Table 8. The results showed that the overall quality of Lilium was the best when the drying temperature was 85 °C.

Table 8.
The comprehensive scores of fresh Lilium S9 at different drying temperatures.
In previous reports, Zhang et al. studied the effect of drying methods on the rehydration performance of scales of Lilium davidi var. unicdor cotton after drying [49]. Yuan et al. studied the effect of different drying processes on the changes in regaloside A content in fresh bulbs of Lilium [15]. Huang et al. studied the infrared drying characteristics and quality changes (color change, hardness, polyphenol, and flavonoid content) of Lilium bulbs before blanching treatment [50]. However, the contents of extracts and polysaccharides in the processing process were not measured according to the provisions of the Chinese Pharmacopoeia. This study improved the quality control of the primary processing of Lilium.
4. Conclusions
A total of ten batches of Lilium from three different sources were collected in this study, of which six batches were Lilium lancifolium Thunb., three were Lilium brownii var. Viridulum Baker, and one was Lilium davidi var. unicdor cotton.
HPLC fingerprinting analysis showed that the similarity between Lilium davidi var. unicdor cotton and other varieties was low, and the chemical composition differences were significant. The chemical composition of Lilium lancifolium Thunb. and Lilium brownii var. Viridulum Baker was relatively similar. According to the UPLC-Q-TOF-MSE analysis method, 70 compounds were identified, including 22 phenolic compounds, 41 steroidal saponins, 6 alkaloids, and 1 flavonoid.
The primary processing of fresh Lilium is a critical factor in ensuring its suitability for use in Traditional Chinese Medicine. This study investigated the effects of boiling time and drying temperature on the quality of Lilium based on the polysaccharide and extract content stipulated by the Chinese Pharmacopoeia and concluded that a boiling time of 5 min and a drying temperature of 85℃ had the least effect on the quality of fresh Lilium.
Author Contributions
Methodology, S.Z.; Software, M.H.; Validation, Y.C.; Formal analysis, Y.C.; Investigation, G.W.; Data curation, G.W.; Writing—original draft, M.H.; Writing—review & editing, S.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province Fund (2021JJ80054).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sim, W.S.; Choi, S.I.; Jung, T.D.; Cho, B.Y.; Choi, S.H.; Park, S.M.; Lee, O.H. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of lilium lancifolium bulbs extract. J. Food Biochem. 2020, 44, e13176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Zhang, T.; Jin, Z.; Xu, X.; Wang, J.; Zha, X.; Chen, H. Structural characterisation, physicochemical properties and antioxidant activity of polysaccharide from lilium lancifolium thunb. Food Chem. 2015, 169, 430–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Qin, H.Y.; An, R.F.; Zhang, W.J.; Liu, J.X.; Yu, Q.F.; Liu, W.; Huang, X.F. Isolation, purification, structural characterization and antitumor activities of a polysaccharide from lilium davidii var. Unicolor cotton. J. Mol. Struct. 2022, 1261, 132941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Han, X.L.; Qian, Z.B. Study on optimization of extraction process of saponins from bulbus lilii and their antidepressant effects. Asian J. Chem. 2014, 26, 5970–5972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, H.P.; Li, X.Z.; Jin, H.; Yang, X.Y.; Xin, A.Y.; Zhao, R.M.; Qin, B. Structural characterization, antioxidant and antibacterial activities of two heteropolysaccharides purified from the bulbs of lilium davidii var. Unicolor cotton. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 133, 306–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, M.D.; Luo, J.G.; Lv, H.W.; Kong, L.Y. Determination of anti-hyperglycaemic activity in steroidal glycoside rich fraction of lily bulbs and characterization of the chemical profiles by lc-q-tof-ms/ms. J. Funct. Foods 2014, 6, 585–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.Y.H.; Jin, L.; Zhang, J.B.; Niu, T.; Guo, T.; Chang, J. Chemical constituents from the bulbs of lilium davidii var. Unicolor and anti-insomnia effect. Fitoterapia 2022, 161, 105252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Shen, Y.; Du, L. Chemical constituents from fleshly scale leaves of lilium lancifolium. J. Chin. Med. Mater. 2021, 44, 2578–2583. [Google Scholar]
- Mi, L.; Wang, K.; Zhu, X.; Wang, X.; Yang, S.; Liao, X.; Xu, Z. The identification of phytochemical components in lilium davidii var. Unicolor using uhplc-qtof-ms. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2023, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, K.; Zhou, F.; Yan, S.-E.; Liu, D.-B.; Xie, H.-Q. The analysis of compounds from longya lily via hplc-q -tof-ms and hs-spme-gc-ms. Nat. Prod. Res. Dev. 2020, 32, 1331–1342. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S. Gc-ms identification of lilium brownii var.Viridulum bulb weak-polarity components and construction of it’s characteristic constituents tic fingerprints. J. Southwest Univ. 2014, 36, 53–61. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Hou, J.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, L.; Ni, H.; Qian, Y.; Wu, W.; Long, H.; Zhang, L.; Li, F.; et al. In-depth exploration and comparison of chemical constituents from two lilium species through offline two-dimensional liquid chromatography combined with multimode acquisition of high-resolution mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2022, 1670, 462980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Y.; Jin, J.; Zhou, R.R.; Fang, L.Z.; Liu, H.; Zhong, C.; Xie, Y.; Liu, P.A.; Qin, Y.H.; Zhang, S.H. Integrative analysis of metabolome and transcriptome provide new insights into the bitter components of lilium lancifolium and lilium brownii. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2022, 215, 114778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Z.Y.; Qu, H.Y.; Xie, M.Z.; Zeng, G.; Huang, H.Y.; Ren, F.; Chen, N.H. Direct authentication of three chinese materia medica species of the lilii bulbus family in terms of volatile components by headspace-gas chromatography-ion mobility spectrometry. Anal. Methods 2019, 11, 530–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.-Y.; Li, Z.-Y.; Zhao, H.-Q.; Gao, C.; Xiao, M.-W.; Jiang, X.-M.; Zhu, J.-P.; Huang, H.-Y.; Xu, G.-M.; Xie, M.-Z. Effects of different drying methods on the chemical constituents of lilium lancifolium thunb. Based on uhplc-ms analysis and antidepressant activity of the main chemical component regaloside a. J. Sep. Sci. 2021, 44, 992–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. People’s Republic of China Pharmacopoeia; China Medical Science Press: Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, R.; Wei, J.; Zhang, Q.; Gaoyang, L.; Shan, Y.; Ding, S. Nutrient composition, microstructure and functional properties of lily bulb flours during blanching. J. Chin. Inst. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 19, 164–174. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Li, M. Hot-air drying kinetics of lily. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2017, 38, 74. [Google Scholar]
- Yongxue, J.; Aihua, W.; Yubing, F.; Tao, Z.; Yiqiong, Z.; Hui, Z.; Yong, Y. Effect of steam blanching combined with vacuum microwave drying on the quality of lilium brownii var. Viridulum powder. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2021, 42, 144–150. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Ding, S.; Gao, W.; Xie, Q.; Li, G. Effect of blanching method on endogenous browning-related enzymes and microstructure of lily bulb. Food Sci. 2018, 39, 53–60. [Google Scholar]
- Jiani, C.; Yaohua, L.; Hui, K.; Ke, D.; Shuai, G.; Shenghua, D. Effect of heat shock treatment on the storage quality of fresh-cut lily bulb slices. Food Sci. 2023, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Chen, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhou, R.; Pei, G.; Chen, N. Establishment of hplc fingerprints of lilies from different sources. Chin. Tradit. Pat. Med. 2020, 42, 2195–2200. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, M.; Yuan, Z.; Zeng, Q.; He, Y.; Xiao, B.; Li, Y.; Du, Q.; Chen, N. Analysis of chemical constituent of lilium broumii by uplc-q-tof-mse. J. Hunan Univ. Chin. Med. 2020, 40, 964–973. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Y.; Xie, J.; Xin, E.; Cheng, F.; Song, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Dou, X. Based on hplc fingerprint and multi-component quantitative evaluation of fresh lily quality from different sources. Chin. Wild Plant Resour. 2023, 42, 60–67. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Q.; Deng, G.; Liang, Y.; Chen, F.; Liu, X.; Yang, W.; Tao, C. Study on quality evaluation of lily. J. Chin. Med. Mater. 2022, 45, 158–161. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Niu, L. Phenolic composition and antioxidant activity of polyphenols from bulbs of lilium lancifolium thunb. J. Northwest A F Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2015, 43, 150–154. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, L.; Zhang, Y.L.; Yan, L.M.; Guo, Y.L.; Niu, L.X. Phenolic compounds and antioxidant activity of bulb extracts of six lilium species native to China. Molecules 2012, 17, 9361–9378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mimaki, Y.; Sashida, Y. Steroidal and phenolic constituents of lilium-speciosum. Phytochemistry 1991, 30, 937–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mimaki, Y.; Sashida, Y.; Shimomura, H. Lipid and steroidal constituents of lilium-auratum var platyphyllum and lilium-tenuifolium. Phytochemistry 1989, 28, 3453–3458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munafo, J.P.; Gianfagna, T.J. Quantitative analysis of phenylpropanoid glycerol glucosides in different organs of easter lily (Lilium longiflorum Thunb.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 4836–4842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimomura, H.; Sashida, Y.; Mimaki, Y. Phenolic glycerides from lilium-auratum. Phytochemistry. 1987, 26, 844–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, Y.; Takaku, R.; Mimaki, Y. Novel steroidal glycosides from the bulbs of lilium pumilum. Molecules 2015, 20, 16255–16265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimomura, H.; Sashida, Y.; Mimaki, Y. Steroidal saponins, pardarinoside-a-g from the bulbs of lilium-pardarinum. Phytochemistry 1989, 28, 3163–3170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munafo, J.P.; Ramanathan, A.; Jimenez, L.S.; Gianfagna, T.J. Isolation and structural determination of steroidal glycosides from the bulbs of easter lily (Lilium longiflorum Thunb.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 8806–8813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mimaki, Y.; Satou, T.; Kuroda, M.; Sashida, Y.; Hatakeyama, Y. New steroidal constituents from the bulbs of lilium candidum. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1998, 46, 1829–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Shi, R.; Liu, B.; Xia, J.; Yin, W. Determination and structural analysis of sugar moieties of lily steroidal saponin by nmr. Nat. Prod. Res. Dev. 2012, 24, 307–311. [Google Scholar]
- Mimaki, Y.; Satou, T.; Kuroda, M.; Sashida, Y.; Hatakeyama, Y. Steroidal saponins from the bulbs of lilium candidum. Phytochemistry 1999, 51, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mimaki, Y.; Ishibashi, N.; Ori, K.; Sashida, Y. Steroidal glycosides from the bulbs of lilium-dauricum. Phytochemistry 1992, 31, 1753–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mimaki, Y.; Sashida, Y. Steroidal saponins and alkaloids from the bulbs of lilium brownii var. Colchesteri. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1990, 38, 3055–3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mimaki, Y.; Sashida, Y.; Nakamura, O.; Nikaido, T.; Ohmoto, T. Steroidal saponins from the bulbs of lilium-regale and l-henryi. Phytochemistry 1993, 33, 675–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mimaki, Y.; Nakamura, O.; Sashida, Y.; Satomi, Y.; Nishino, A.; Nishino, H. Steroidal saponins from the bulbs of lilium-longiflorum and their antitumor-promoter activity. Phytochemistry 1994, 37, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.-Y.; Duan, J.-A.; Qian, D.-W.; Wang, D.-W. Studies on chemical constituents in fresh fleshy scaleleaf of lilium lancifolium. China J. Chin. Mater. Medica 2007, 32, 1656–1659. [Google Scholar]
- Shimomura, H.; Sashida, Y.; Mimaki, Y.; Iitaka, Y. Studies on the chemical-constituents of lilium-henryi baker. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1988, 36, 2430–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ori, K.; Mimaki, Y.; Mito, K.; Sashida, Y.; Nikaido, T.; Ohmoto, T.; Masuko, A. Jatropham derivatives and steroidal saponins from the bulbs of lilium-hansonii. Phytochemistry 1992, 31, 2767–2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, X.; Chen, F. Studies on chemical constituents of lilium brownii. Yao Xue Xue Bao = Acta Pharm. Sinica 1998, 33, 923–926. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong-liu, Z.; Ren-bing, S.H.I.; Bin, L.I.U.; Xue-mei, W. Chemical constituents of juandan (Lilium lancifolium Thunb.). J. Beijing Univ. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2010, 33, 57–61. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.; Shi, R.; Liu, B.; Zou, J.; Yin, W.; Xia, J. Steroidal saponins and phenylic constituents from lilium lancifoliumand their anti-oxidant activities. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2011, 42, 21–24. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Gao, Y.X.; Zhou, X.J.; Hu, L.P.; Xie, T.Z. Chemical characterisation of polysaccharides from lilium davidii. Nat. Prod. Res. 2010, 24, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xue, L.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, C.; Liu, D. Insight into the effects of drying methods on lanzhou lily rehydration. Foods 2023, 12, 1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Yang, P.; Qin, Y.; Gong, G.; Tang, X.; Luo, W.; Luo, L.; Sunden, B. Infrared drying characteristics and quality variations of lily bulbs under blanching pretreatment. J. Therm. Sci. Eng. Appl. 2022, 14, 091005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).