Abstract
A large amount of bio-sulfur is generated during the process of refining landfill gas generated from landfills in metropolitan areas in Korea. Sulfurized concrete offers the advantages of reducing the amounts of CO2 generated, typically in large quantities, during the cement manufacturing process and accommodating a large amount of bio-sulfur generated during the process of refining landfill gas in the form of concrete, with a sulfur-modified binder replacing the commonly used cement paste. In this study, the potential of bio-sulfur as an additive was assessed by analyzing the compressive strength, sulfuric acid resistance, and hydration product generation metrics of cement manufactured using bio-sulfur as a cement additive. It was concluded as a result of the analysis that, when using bio-sulfur mixed into cement composites, if the addition is less than 2% a strength improvement is unlikely. In addition, it is suggested that it is necessary to closely review and analyze the economic feasibility and commercialization potential through research on prototype production with concrete producers.
1. Introduction
In 2019, a total of 497,238 tons/day of waste was generated in Korea, 89.7% of which was recycled, with the rest incinerated (5.2%) or sent to a landfill (6.1%) [1]. Landfill gas (LFG) is generated when organic substances are decomposed by microorganisms under anaerobic conditions in a landfill. LFG contains CH4 (40–55%), CO2 (35–50%), C6H14 (250–3000 ppm), chlorine compounds (30–300 mg/m3), and H2S (≤200 ppm), among other chemicals [2,3,4]. As LFG contains methane, it can cause serious global warming when discharged into the atmosphere. If it is captured, it can be used to produce electric power and thermal energy, and, because it can be used as fuel in a gaseous form, there is strong interest in its collection and effective use [5].
The H2S contained in LFG is generated by the reduction of sulfate by sulfate-reducing bacteria (SRB) under anaerobic conditions, as the gypsum contained in the cement among food waste and construction waste contains sulfur [5,6].
The mechanism for generating H2S using sulfates in SRB is shown in Figure 1. If the quantity of sulfates in landfills increases, SRB dominates, and most of the electrons generated from the decomposition of organic matter are used by sulfate-reducing bacteria to generate sulfide by means of the sulfate reduction process. As a result, the H2S concentration increases and the activity of methane bacteria decreases, resulting in lower methane gas production [7].
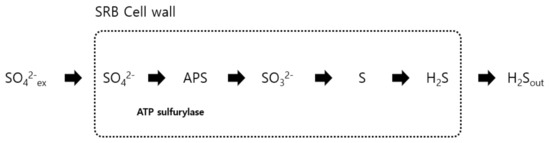
Figure 1.
Sulfate reduction reaction by sulfate-reducing bacteria (SRB). APS is an enzyme and ATP sulfurylase (ATPS) catalyzes the first committed step in the sulfate assimilation pathway, the activation of sulfate prior to its reduction.
Because H2S adversely affects health, causes odors, and promotes the corrosion of LFG utilization facilities [7,8], removing H2S is necessary. Physical, chemical, and biological desulfurization technologies are used as desulfurization technologies to remove H2S, but biological desulfurization is considered a feasible method in terms of economic and environmental considerations [9,10]. In particular, the desulfurization technology of Thiopaq, a leading company in the field of biological desulfurization technology, can recover sulfur components (bio-sulfur), while also accomplishing desulfurization, thus giving it an advantage [11,12].
According to Thiopaq’s desulfurization principle (Figure 2), when LFG flowing into the desulfurization facility comes into contact with the cleaning solution (NaOH), H2S and CO2 are converted from the gaseous to the liquid phase. Although the pH of the cleaning solution is decreased, the pH is maintained by continuously adding chemicals to control the alkalinity of the cleaning solution. The gas-to-liquid reaction in the scrubber proceeds as follows [12]:
H2S + NaOH → NaHS + H2O
CO2 + OH− → HCO3−
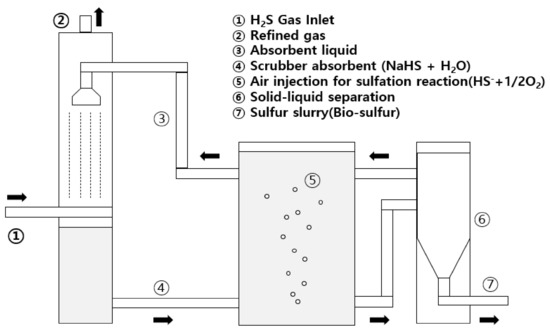
Figure 2.
Process diagram of the scheme for H2S removal from landfill gas. This system removes the H2S contained in Thiopaq’s LFG. When the landfill gas flows in, the refined gas is discharged, and H2S reacts with OH− and is converted to HS− liquid. The converted HS− is converted through the oxidation reaction of microorganisms in the bioreactor.
The collected landfill gas enters the washer from the bottom of the scrubber, passes through the filled column bed in the bioreactor, and comes into contact with the cleaning liquid. The cleaning liquid then absorbs the H2S in the LFG. LFG containing sulfides is converted into sulfur slurry in a biological process. The slurries are transferred to a settling tank through a pump, slowly settle at the bottom of the settling tank, and are finally discharged as sulfur-containing sludge. The sulfur from this process consists mainly of elemental sulfur but is discharged as a sludge containing small amounts of H2S2O3, SO42−, and Na2CO3. The bioreaction for conversion to elemental sulfur in the bioreactor is as follows [12].
HCO3− + OH− → CO32− + H2O
2NaHS + O2 → 2S°+ 2NaOH
HS− + 2O2 + OH− → SO42− + H2O
S°+ 2OH− + 32O2 → SO42− + H2O
SxS2- + O2 → (x + 1) S + O2
Thiopaq’s biological desulfurization technology is utilized to purify LFG generated at the Seoul Metropolitan Landfill (SML), the largest landfill in Korea, and the bio-sulfur generated is used as an organic agricultural material [13,14].
Different types of waste can be recycled from cement [15]. Coal bottom ash was found to enhance concrete strength [16]. There are also research results showing that the environmental load can be reduced by replacing raw materials or fuel with waste [17].
Sulfur is used in various areas, such as the chemical, rubber, plastics, and cement industries. Sulfur concrete produced using sulfur as a binder for cement is considered a building material with excellent chemical resistance, and cement as a basic industrial product can incorporate a large amount of sulfur as an additive [18].
In this study, the characteristics of bio-sulfur emitted from Thiopaq’s desulfurization facility, as applied to SML, were analyzed. The compressive strength, sulfuric acid resistance, and hydrate formation properties were evaluated to examine the possibility of its use as a cement admixture.
2. Results
2.1. Physico-Chemical Properties of Bio-Sulfur
Table 1 shows the results of the analysis of the physico-chemical properties of bio-sulfur. The pH was in the approximate range of 8.0–9.0, the average salinity of bio-sulfur was 2.5%, and the salinity of the supernatant after centrifugation was 4.8%. The supernatant was slightly alkaline due to the supply of NaOH, and Na+ was mostly present in a form combined with OH−. Because biosulfur improves the initial strength, it appears to be a useful material for addition to cement if an appropriate mixing ratio is maintained [19,20].

Table 1.
Characteristics of Bio-sulfur.
Figure 3 shows the particle size distribution characteristics of the microparticles in the bio-sulfur. The particle sizes of the fine particles determined by analysis were as follows: 1.75 μm for Dv (10), 5.3 μm for Dv (50), and 11.1 μm for Dv (90). The particle sizes of the fine particles dispersed in the bio-sulfur were relatively uniform at 5.3 μm, which corresponds to Dv (50), on average. This likely arose due to the sulfur, which has a relatively uniform particle size due to microbial metabolism. In general, it has been reported that cement develops higher reactivity as the content of particles 10 μm in size or less increases, as this results in faster setting times and increased heat of hydration due to rapid hydration [21].
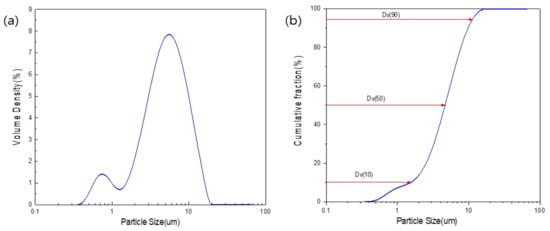
Figure 3.
Particle size distribution in bio-sulfur. Dv is volume-average diameter. (a,b) is shows each the distribution and the cumulative distribution of particle size. The graph indicates that the area under 10 um occupies 90% of the total size distribution.
Table 2 shows the results of quantitative analysis of the constituents using XRF (X-ray fluorescence) after the bio-sulfur was dried at 100 °C. Sulfur, the main component of bio-sulfur, was found to exist at the highest level, at 86.8%. In addition, Na+ (2.14%) and O2 (9.92%) were found. Bio-sulfur contains oxygen in addition to the sulfur component because oxygen is contained in the air supplied to the sulfated bacteria during the process of converting H2S to sulfur. In addition, C (1.14%) is presumed to derive from microorganisms remaining in the bio-sulfur or from polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) contained in the LFG. Due to the presence of PAHs, potential use in construction is limited given the possibilities of sick house syndrome and multiple chemical sensitivity (MCS) due to indoor air pollution [22].

Table 2.
The results of quantitative analysis of the constituents using XRF.
Figure 4 shows the XRD (X-ray diffraction) peak, which shows the crystal structures of the bio-sulfur and petroleum sulfur dried at 100 °C. It was confirmed that the petroleum sulfur was composed of S8, which has a stable bonding structure as a single sulfur structure; the structure of the sulfur contained in bio-sulfur was also found to be S8 and thus had the same bonding structure as the petroleum sulfur. In conclusion, from a qualitative standpoint, the petroleum sulfur and bio-sulfur are the same type of sulfur (S8), and it is considered that this product can be used as a substitute for petroleum sulfur.
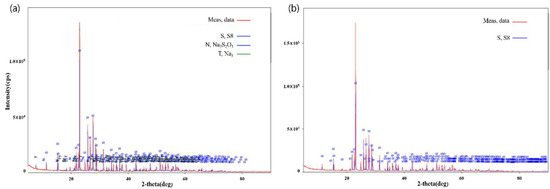
Figure 4.
XRD results of the dry bio-sulfur (a) and petroleum sulfur (b). The sulfur format in (a) is S8, with Na also present, and the sulfur format in (b) is S8.
2.2. Evaluation Outcomes of the Specimen Characteristics
2.2.1. Compressive Strength
Figure 5 shows the compressive strength evaluation results for each substitution method. Figure 5a shows bio-sulfur used instead of cement, and Figure 5b shows bio-sulfur added to cement. There were no significant differences in the compressive strength at 2.5% and 5% content for the substituted binder and substituted aggregate. At 5% and 10% content, the substituted aggregate case showed slightly higher strength. In the substituted aggregate case, which contained a relatively large amount of cement as a whole, the degree of strength reduction showed a similar tendency.
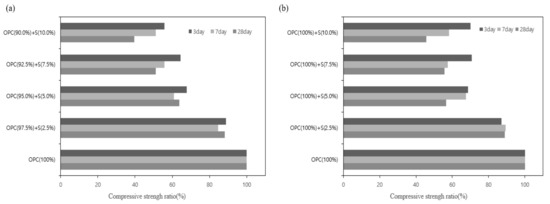
Figure 5.
Relative comparison of the compressive strength ratios for binder (a), aggregate (b) by OPC (100%). The figure shows that, as the mixing ratio of bio-sulfur increased, the compressive strength decreased, and the binder had lower compressive strength than the aggregate.
The reference standards for compressive strength for KS L 5201 Portland cement are 12.5 N/mm2, 22.5 N/mm2, and 42.5 N/mm2 or more, respectively, for 3 day, 7 day, and 28-day strength levels. The seven-day compressive strength levels of the specimen containing 2.5% bio-sulfur were equivalent to or greater than the KS standard but were lower than the standard for 28 days. However, even though the KS standard criteria were met at ages of three, seven, and 28 days, the overall strength decreased in the specimens with bio-sulfur compared to the reference specimen (OPC 100%). A typical cement mixture showed a black (dark gray)-based fracture surface, whereas the specimen containing bio-sulfur showed a yellow fracture surface, confirming that the bio-sulfur was mixed homogeneously. According to these results, it is inferred that the fine particles of bio-sulfur are helpful for mixing, whereas bio-sulfur does not have a positive effect on improving the degree of hydration. This appears to be due to the pH of the bio-sulfur. The hydration reaction of cement increases its compressive strength at pH 11–12, but with the added amount of bio-sulfur (pH of 8–9), which has a pH lower than that of cement, it becomes neutralized, and the specimen’s strength decreases [23].
2.2.2. Sulfuric acid Resistance Evaluation
Figure 6 shows the evaluation results for sulfuric acid resistance (weight loss rate and compressive strength change rate) after immersion in a 5% sulfuric acid solution for 7 days and 14 days. Overall, when no bio-sulfur was added, the weight reduction rate was the largest, and the weight reduction rate generally decreased with the addition of bio-sulfur. After 14 days of immersion in the 5% sulfuric acid aqueous solution, the weight loss rate was lowest when 7.5% bio-sulfur was utilized, indicating the best sulfuric acid resistance.
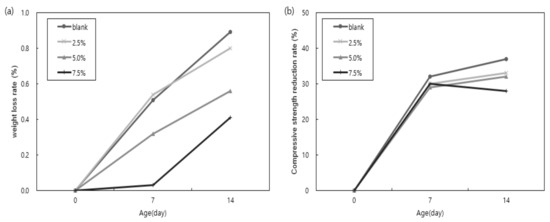
Figure 6.
Weight loss rate (a) and compression strength reduction rate (b) by immersion time in the aqueous sulfate solution. (a) is the weight loss rate after 7 days and 14 days. (b) is the rate of decrease in compressive strength after 7 days and 14 days.
Calcium-silicate-hydrate (C-S-H) can react with acids to form low-strength phases. In addition, CH reacting with sulfate radical ions can form gypsum, extending and damaging the C-S-H matrix. Gypsum can also react further with hydrated calcium aluminate to form ettringite [24]. The reason that the addition of bio-sulfur increases the sulfuric acid resistance, as shown in Figure 7, is thought to be because the components contained in bio-sulfur reduce the formation of gypsum or ettringite.
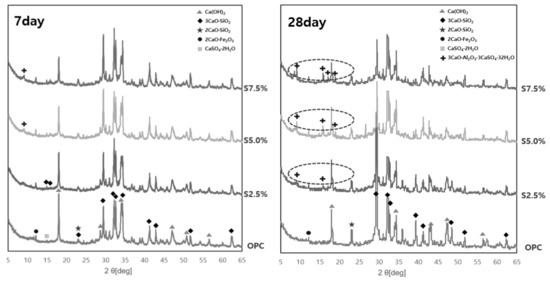
Figure 7.
Hydrate XRD changes after 7 and 28 days. The degree of hydrate formation by age according to the rate of binding resistance is shown. The left side represents results for the specimen 7 days after specimen preparation, and the right side results for the specimen 28 days after specimen preparation.
If the sulfuric acid resistance is excellent, it may be used in concrete structures and in structures where concerns over corrosion by sulfuric acid bacteria exist, such as water and sewage pipes [25]. Porous cement is inevitably more susceptible to sulfuric acid erosion, and its use as a binder may be considered for such cement [26].
Exposure of cement and concrete to sulfuric acid causes the formation of gypsum hydrate, which causes the structure to expand and weaken [27]. As shown in Figure 6, when immersed in the 5% sulfuric acid aqueous solution, the compressive strength of the samples decreased with age. When bio-sulfur was not added, the compressive strength reduction rate was evaluated to be the lowest, and, overall, when bio-sulfur was added, the compressive strength reduction rate was evaluated to be high.
2.2.3. Hydration Product Analysis
It was found that the major hydrates appearing in all specimens commonly contain Ca(OH)2, 3CaO·SiO2, and 2CaO·SiO2, which are the main hydrates of OPC. When biosulfur was added, the hydrate that appeared did not appear for seven days, whereas ettringite (3CaO·Al2O3·3CaSO4·32H2O) hydrate was observed on the 28th day. Ettringite is a functional material that induces the expansion of concrete by itself expanding during the cement hydration reaction process. It is used in the manufacture of expanded concrete. Therefore, it appears that it can be used as expanded concrete with the addition of bio-sulfur. However, as one of the side-effects of overproduction, it may cause a decrease in the compressive strength due to overexpansion [28]. As shown in Figure 7, the decrease in compressive strength was relatively small during the initial seven days due to the small amount of ettringite hydrate. This indicates that, even when used in the manufacture of expanded concrete, it is necessary to add bio-sulfur at an appropriate level to ensure compressive strength.
3. Discussion
As a result of a performance evaluation of cement composites made using bio-sulfur generated from power generation facilities in SML in Korea, the following conclusions can be drawn:
When bio-sulfur was incorporated into the cement composite, a decrease in strength was observed. At a rate of 2.5%, the smallest amount used here, the degree of strength reduction was relatively low and surface discoloration (turbidity) was observed due to the incorporation of bio-sulfur. However, the amount of discoloration was insignificant when a rate of 2.5% was used.
Overall, it was found that the sulfuric acid resistance of cement and concrete was improved by the incorporation of bio-sulfur and that the weight reduction rate was lowest when 7.5% of bio-sulfur was incorporated, leading to the best sulfuric acid resistance.
Regarding the addition of bio-sulfur, ettringite (3CaO·Al2O3·3CaSO4·32H2O) hydrate was observed on the 28th day, suggesting that sulfur contributes to hydrate formation to some extent.
Therefore, when using bio-sulfur mixed into cement composite materials, addition of less than 2% is appropriate; a major strength improvement is unlikely, but this amount may improve the sulfuric acid resistance properties. It is suggested that it is necessary to closely review and analyze the economic feasibility and commercialization potential through additional research on prototype production and other factors with concrete producers and other stakeholders.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Physico-Chemical Characterization of Bio-Sulfur
The bio-sulfur samples used for the analysis were collected during centrifugal dehydration at a biological desulfurization facility at SML. To ascertain the general properties of the collected samples, the ternary contents, salinity, pH, particle size, chemical composition and elemental composition were analyzed. The ternary contents and pH were measured according to waste process test standards (ES). Regarding the particle size, a particle size analyzer (micro-size, laser diffraction particle size analyzer) was used. XRF (X-ray fluorescence) was used to assess the chemical composition, and X-ray diffraction (XRD) was used to observe the forms of sulfur in the bio-sulfur and petroleum compounds. The elemental composition was analyzed using an elemental analyzer (MICRO) to determine the S content of the bio-sulfur.
4.2. Compressive Strength Evaluation
To evaluate the compressive strength, a test specimen was prepared and the characteristic change according to the addition ratio of bio-sulfur was confirmed. Portland cement was used as a control. According to the KS standard, ISO standard yarn was used; the mixing ratio of cement (binding material) and ISO standard yarn and water was 1:3:0.5, according to the KS standard. This ratio was used to prepare the test specimen here (Table 3a). The manufactured specimen was subjected to standard curing in water at 20 ± 2 °C; the strength evaluation was performed at 3, 7, and 28 days of curing. The compressive strength evaluation was carried out in accordance with the KS L ISO 679 (cement strength evaluation method) standard. The compressive strength tester is a domestic product manufactured by Company H with a maximum load of 100 tons. A type of tester generally used for cement quality control was used here.

Table 3.
Mixing ratios of the test samples. Indicates the composition ratio of the sample prepared to test the compressive strength (a) and sulfuric acid resistance (b).
4.3. Evaluation of Sulfuric Acid Resistance
To evaluate the sulfuric acid resistance outcomes, the test was conducted according to JSTM C 7401 (test method for chemical resistance of cement by solution deposition) (JSTM: Japanese standard test method). The water/cement ratio of the specimen was set to 0.4, and the bio-sulfur addition rates used here were 2.5%, 5%, and 7.5%, based on the amount of solid content used to prepare the specimens (Table 3b). Each produced specimen was subjected to standard water curing at a temperature of 20 ± 2 °C until 28 days of age. At 28 days of standard water curing, the specimen was immersed in 5% sulfuric acid solution for 7 days and 14 days, and the sulfuric acid resistance was evaluated by measuring the weight loss rate and compressive strength.
4.4. Assessment of the Effect of Bio-Sulfur on Cement Hydrate
The purpose of this study was to examine the effect of adding bio-sulfur to cement on cement hydrate. Differences in hydrate formation were evaluated when bio-sulfur was not mixed (OPC, ordinary Portland cement), and when bio-sulfur was added at rates of 2.5%, 5%, and 7.5%. The hydrated body was prepared using a binder and water at a ratio of 1:0.5; the hydrate was observed through XRD evaluations on the 7th and 28th days after preparation.
Author Contributions
Writing—original draft, D.K. and J.L.; Writing—review & editing, B.L. and C.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Korea Ministry of Environment (MOE) as Waste to Energy Recycling Human Resource Development Project.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ministry of Environment. National Waste Generation and Treatment Status; Ministry of Environment: Sejong City, Korea, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Bove, R.; Lunghi, P. Electric power generation from landfill gas using traditional and innovative technologies. Energy Convers. Manag. 2006, 47, 1391–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.E.; Jung, I.S.; Park, J.; Oh, C.B. A study on the determination of burning velocities of LFG and LFG-mixed fuels. Fuel 2002, 81, 1679–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchobanoglous, G.; Kreith, F. Handbook of Solid Waste Management, 2nd ed.; McGraw Hill Handbooks: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 14.1–14.77. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, J.J.; Yang, N.; Cen, D.Y.; Shao, L.M.; He, P.J. Odor compounds from different sources of landfill: Characterization and source identification. Waste Manag. 2012, 32, 1401–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaha, B.N.; Meeroff, D.E.; Kohn, K.; Townsend, T.G.; Schert, J.D.; Mayer, N.; Schultz, R.; Telson, J. Effect of electronic water treatment system on calcium carbonate scale formation in landfill leachate collection piping. J. Environ. Eng. 2019, 145, 04019052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.S.; Oh, S.E. Effect of Sulfate and Heavy Metals on Methanogenic Activation of in the Anaerobic Digestion of Tannery Wastes. J. Korea Org. Waste Recycl. Counc. 1996, 4, 13–21. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, H.S.; Kim, H.S.; Park, J.H.; Lee, Y.M. Study on In-situ Hydrogen Sulfide Reduction for Optimal Use of Landfill Gas (LFG). J. Korea Soc. Waste Manag. 2020, 37, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurul, N.Z.; Mohd, S.M.; Jamaliah, J.; Edy, H.M. Overview of H2S Removal Technologies from Biogas Production. Int. J. Appl. Eng. Res. 2016, 11, 10060–10066. [Google Scholar]
- Khoshnevisan, B.; Tsapekos, P.; Alfaro, N.; Díaz, I.; Fdz-Polanco, M.; Rafiee, S.; Angelidaki, I. A review on prospects and challenges of biological H2S removal from biogas with focus on biotrickling filtration and microaerobic desulfurization. Biofuel Res. J. 2017, 4, 741–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benschop, C. Shell-Paques® Bio-Desulfurization Process Directly and Selectively Removes H2S From High Pressure Natural Gas—Start-Up Report. 2007. Available online: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/SHELL-PAQUES%C2%AE-BIO-DESULFURIZATION-PROCESS-DIRECTLY-Benschop/d9f87c593dbbaf6ce0333d9e7ecfe505fa1d34f8 (accessed on 3 September 2022).
- Kim, Y.M.; Song, H.S.; Ahn, H.S.; Chun, S.K. Application of the Microbial Process for Hydrogen Sulfide Removal and Bio-Sulfur Production from Landfill Gas. New Renew. Energy 2020, 16, 68–76. [Google Scholar]
- Van Der Krieken, W.M.; Rutten, W.B.A.H. Novel Biosulfur Formulations. EP Patent No. 2629606A2, 26 April 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Available online: http://www.ycgmnews.com/news/articleView.html?idxno=21359 (accessed on 11 July 2021).
- Malek, B.; Iqbal, M.; Ibrahim, A. Use of selected waste materials in concrete mixes. Waste Manag. 2007, 27, 1870–1876. [Google Scholar]
- Watcharapong, W.; Pailyn, T.; Kedsarin, P.; Arnon, C. Compressive strength, flexural strength and thermal conductivity of autoclaved concrete block made using bottom ash as cement replacement materials. Mater. Des. 2012, 35, 434–439. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, M.U.; Poon, C.S.; Lo, I.M.; Cheng, J.C. Comparative LCA on using waste materials in the cement industry: A Hong Kong case study. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2017, 120, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.G.; Gwon, S.W.; Kim, S.W.; Cha, S.W. Physical Properties of Sulfur Concrete with Modified Sulfur Binder. KSCE J. Civ. Environ. Eng. Res. 2014, 34, 763–771. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, M.A.; Osbrone, G.J. Slag/fly ash cement. J. World Cem. Technol 1977, 1, 223–233. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Lin, Z. Effect of sodium hydroxide on the properties of phosphogypsum based cement. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mat. Sci. Ed. 2010, 25, 342–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, S.H.; Kim, H.C.; Kim, J.Y.; Choi, H.K.; Song, J.T. Effect of Cement Particle Size on Properties of Ordinary Portland Cement. J. Korean Ceram. Soc. 2010, 47, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, C.Y.; Kim, G.T.; Hwang, G.H. Study on the Seasonal Survey of the Indoor Air Quality in New Apartment Houses. LHI J. 2013, 4, 417–424. [Google Scholar]
- Sobhnamayan, F.; Sahebia, S.; Alborzi, A.; Ghorbani, S.; Shojaeea, N.S. Effect of Different pH Values on the Compressive Strength of Calcium-Enriched Mixture Cement. Iran Endod J. 2015, 10, 26–29. [Google Scholar]
- Wenkui, D.; Wengui, L.; Kirk, V.; Xuzhen, H.; Zhihui, S.; Daichao, S. Piezoresistivity deterioration of smart graphene nanoplate/cement-based sensors subjected to sulphuric acid attack. Compos. Commun. 2021, 23, 100563. [Google Scholar]
- Hewayde, E.; Nehdi, M.L.; Allouche, E.; Nakhla, G. Using concrete admixtures for sulphuric acid resistance. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng.—Constr. Mater. 2007, 160, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramyar, K.; İnan, G. Sodium sulfate attack on plain and blended cements. Build. Environ. 2007, 42, 1368–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.H.; Park, J.I.; Lee, K.M. Influence of Mineral Admixtures on the Resistance to Sulfuric Acid and Sulfate Attack in Concrete. J. Korea Concr. Inst. 2010, 22, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenk, H.R.; Monteiro, P.J.M.; Kunz, M.; Chen, K.; Tamura, N.; Lutterotti, L.; Del Arroz, J. Preferred orientation of ettringite in concrete fractures. J. Appl. Cryst. 2009, 42, 429–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).