Abstract
Ameloblastoma is an infiltrative benign neoplasm in the mandible or maxilla that is locally aggressive with rare metastasizing capacity. This lesion is the most common tumor of the odontogenic epithelium. However, its occurrence in children is low, representing only 10–15% of all reported ameloblastoma cases. In treating such benign neoplasms in pediatric patients, the preservation of vital structures such as the inferior alveolar nerve (IAN), deciduous teeth, tooth buds, and nerves with proper post-operative management to maintain normal mandibular growth is imperative. A five-year-old boy with painless swelling and displaced teeth in the right mandible was diagnosed with plexiform ameloblastoma. Instead of a radical approach, the patient was treated conservatively using decompression and routine irrigation along with long-term follow-up. Functional appliance treatment was provided using a Frankel appliance to preserve and induce normal growth of the jaw. After eight years, there was no recurrence of the ameloblastoma, and normal mandibular growth of the patient was observed. Pediatric plexiform ameloblastoma should be treated with a conservative approach considering the preservation of important anatomic structures and further mandibular growth. Moreover, functional appliance therapy should be considered as an integral part of treatment for pediatric ameloblastoma and other tumors in children to maintain and induce normal growth of the mandible.
1. Introduction
Ameloblastoma is an infiltrative benign neoplasm in the mandible or maxilla that is locally aggressive with rare metastasizing capacity [1]. Painless swelling of the affected jaw with facial asymmetry is the most common presentation of ameloblastoma. Although uncommon, pain can occur following fine needle aspiration (FNA). Moreover, tooth displacement which can cause malocclusion and root resorption are also reported [2]. This lesion is the most common benign epithelial odontogenic tumor, accounting for 1% of all tumors of the jaws and 11% of all odontogenic tumors. However, its occurrence in children is low, representing only 10–15% of all reported ameloblastoma cases [3,4]. According to the World Health Organization (WHO) in 2017, ameloblastomas are classified into three types: (1) conventional ameloblastoma (previously known as “multicystic/solid ameloblastoma”) including follicular, plexiform, acanthomatous, granular cell, basaloid, and desmoplastic histopathologic variants; (2) unicystic ameloblastoma including luminal, intraluminal, and mural variant; and (3) extraosseous/peripheral ameloblastoma [5]. In treating such benign neoplasms in pediatric patients, preservation of vital structures such as inferior alveolar nerve (IAN), deciduous teeth, tooth buds, and nerves with proper post-operative management to maintain normal mandibular growth is imperative. Therefore, in this long-term follow-up case report, we present the concept of conservative decompression with functional therapy for pediatric plexiform ameloblastoma.
2. Case Report
A five-year-old boy was referred to the Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery at Seoul National University Dental Hospital from another hospital with suspicion of ameloblastoma. Upon extraoral clinical examination, facial asymmetry was observed, with swelling on the right side of the mandible (Figure 1a). Meanwhile, the intraoral examination revealed buccal vestibule swelling and displaced teeth #82, #83, #84, and #85 (Figure 1b). The panoramic radiograph revealed a large unilocular radiolucency in the right mandible (Figure 1c). Computed tomography (CT) and 3D imaging Cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) showed an ovoid corticated lesion 37.06 × 20.44 mm in size, extending from the apex of #31 to #85 and expanded in the buccal and lingual directions (Figure 1d,e). Most of the lesion was filled with an enhanced solid portion, and partial fluid attenuation was observed. Anamnesis and lab result were negative for any history of serious medical conditions such as diabetes mellitus, hepatitis or drug allergy. The treatment was proceeded with the conservative surgery without pretreatment biopsy due to several considerations: (1) Radiographically, the growth pattern of the lesion represented benign characteristic, (2) the lesion was embedded in the bone, in which the required sufficient tissues for biopsy would be difficult to obtain, (3) the pretreatment biopsy would give additional injuries. Considering young patient’s low tolerance to postoperative pain can affect the cooperation to the upcoming treatment, the treatment stages should be as efficient as possible.
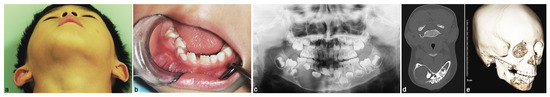
Figure 1.
Preoperative view. (a) Extraoral photograph. (b) Intraoral photograph. (c) Panoramic radiograph showed unilocular radiolucency extending from #31 to the mesial root of #46, surrounding the crown of the #43 tooth bud. (d) The axial CT radiograph. (e) The 3D imaging CBCT showed the extent of the lesion in the mandible.
Under general anesthesia, surgery was performed. The right mandibular vestibule was infiltrated with 2% lidocaine, 1:100.000 epinephrine. An incision was created in the right retromolar area using a #15 blade, and extended to #41 with a crevicular incision. A mucoperiosteal flap was elevated, and mass excision was performed with a molt curette (Figure 2a–c). After mass excision, the inferior alveolar nerve (IAN) was identified and carefully preserved. A silastic drain for decompression was inserted and sutured with 4-0 Polyglactin 910 Vicryl® (Johnson & Johnson Co., Johnson, NJ, USA) (Figure 2d,e). Primary closure with 4-0 Vicryl and pressure dressing was performed. Two days after surgery, a sensory assessment ensured the normal nerve function. Copious routine irrigation with warm saline was performed every day for one week after surgery and was repeated for every two weeks for seven months. The silastic drain was regularly changed to prevent infection.
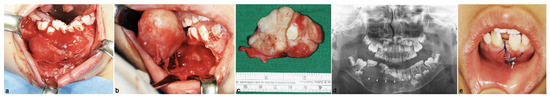
Figure 2.
Intraoperative and postoperative view. (a) The main mass of the tumor was identified after flap incision. (b) The obtained main mass of the tumor from the excision procedure; it can be seen that the cortical bone on the buccal part was already damaged by the tumor. (c) The excised gray-white mass 4.6 × 3.1 × 1.8 cm in size containing the permanent canine. (d) Post-operative panoramic view revealed the silastic drain inserted (arrowheads) for decompression after removal of the mass. (e)The clinical view of the drain (arrow) sutured along with the wound.
An excised gray-white mass containing tooth #43 4.6 × 3.1 × 1.8 cm in size was obtained (Figure 2c) and stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) for histopathologic examination. Microscopically, the excised mass was solid and surrounded by a thin fibrous capsule (Figure 3a). The tumor cells of odontogenic epithelial proliferated in long anastomosing cords bounded by columnar or cuboidal ameloblast like cells with inconspicuous stellate reticulum, forming a plexiform pattern. The stroma was composed of fibrous connective tissue with some cyst-like stromal degeneration in several areas (Figure 3b). Therefore, the final diagnosis was plexiform ameloblastoma.
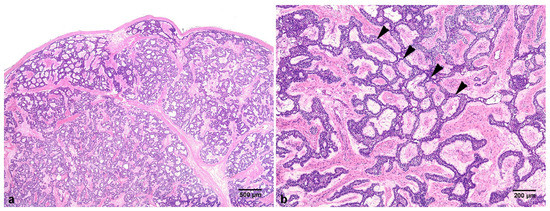
Figure 3.
Representative histopathological features. (a) Well-circumscribed, solid mass with a thin fibrous capsule. (b) Long, anastomosing cords of ameloblastic epithelium (arrowheads) in the fibrous stroma (H&E staining).
Monthly radiograph examination follow-ups were performed following the principle of as low as reasonably achievable (ALARA) for the first 10 months after surgery to evaluate healing of the right mandible (Figure 4a–c). By assessing the healing of the mandible through radiograph in the first 10 months, the progression of routine irrigation can be assessed, time for drain removal can be decided, the sign of early recurrence due to possible residual lesion can be monitored earlier, and finally, the next treatment step can be proceeded. Eight months after surgery, mandibular and maxillary arch impressions were created for fabrication of functional appliance, Frankel type, which was delivered to the patient one month later. The patient was instructed to wear the functional appliance for 19–20 h per day for myofunctional therapy to guide normal growth of the jaw (Figure 5a,b). In addition, appliance cleaning and oral hygiene maintenance was explained to the patient. Since the patient was in a growth period, regular adjustment of the functional appliance was required. Therefore, clinical and radiograph follow-up was performed at one month, and then on a trimonthly follow-up schedule. Follow-up comprised adjustment of the wire and acrylic components of the appliance and examination of the condition of the soft tissue surrounding the appliance, to observe signs of recurrence and to monitor the growth pattern (Figure 4d–g). The patient was cooperative and wore the functional appliance routinely for four years. At four years after surgery, the persistent #74, #75, and #85 teeth were extracted, and Augmentin 5cc syrup was prescribed three times per day for three days. Routine follow-up was scheduled to assess eruption of teeth. Eight years after surgery, radiographic examination revealed no recurrence of the lesion and eruption of permanent teeth. Teeth #43 and #44 were missing due to the ameloblastoma and further orthodontic therapy and prosthodontic management are required (Figure 4h and Figure 5c,d). Relevant data from this episode of care are organized as a timeline and presented in Figure 6.
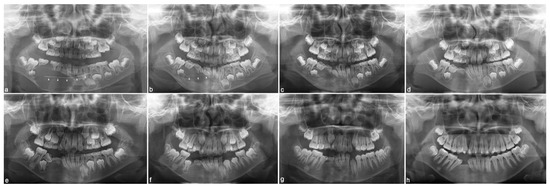
Figure 4.
Monthly radiograph examination follow-ups. (a) Panoramic view revealed the condition of the lesion four days after surgery. The lesion looked slightly smaller than before surgery, in which the daily copious irrigation through drain (arrowheads) was provided for one week following surgery. (b) Four months of copious irrigation through drain (arrowheads) showed the increased radiopacity of the cavity. (c) The 10-month follow-up showed an increase of radiopacity intensity, with the border of the cavity merging with the surrounding healthy bone indicating bone formation at the previous lesion site. (d) The 19-month follow-up showed no sign of lesion recurrence. (e) The 40-month follow-up showed no sign of recurrence and exhibited improvement of anterior tooth alignment in the jaw. (f) The 48-month follow-up showed normal eruption of the right mandibular posterior teeth with no sign of recurrence. (g) The 58-month follow-up showed complete posterior left mandibular teeth eruption with no sign of recurrence. (h) The 8-year follow-up showed normal dental development with healthy bone density in the site of the previous lesion.
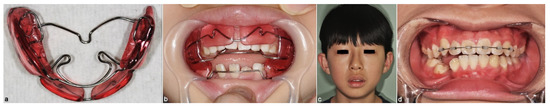
Figure 5.
Functional appliance therapy. (a) The upper view of the functional appliance, Frankel type. The vestibular shield on the right side was specifically extended to the occlusal as a bite riser to correct the teeth alignment and occlusion vertically, and create space for permanent teeth eruption into the right mandibular arch. (b) Intraoral application of the functional appliance. The upper lip shield of this appliance eliminated restrictive pressure of the upper lip; as a result, the maxilla growth was stimulated as well. (c) The extraoral view of the patient showed normal mandibular growth after conservative decompression and functional appliance therapy. Facial symmetry without mandibular deviation was observed. (d) The intraoral view eight years after treatment showed healthy soft tissue and normal permanent dentition. The previously displaced mandibular anterior teeth were in the correctly aligned and almost on the same occlusal plane. The permanent teeth on the right side of the mandible erupted into normal alignment as a result of the space obtained from the appliance.
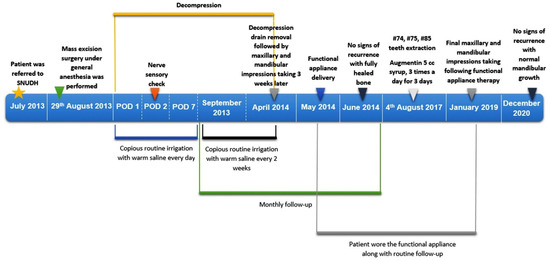
Figure 6.
The timeline of historical and current information from this episode of care. POD: Post-operative day.
3. Discussion
The conventional ameloblastoma is known as the most aggressive type of ameloblastoma, the most common histopathological variants of which are the follicular and plexiform patterns [2,3]. Furthermore, conventional ameloblastoma demonstrates a higher rate of recurrence, and predominates over the unicystic type from a histologic perspective [3].
Conventional ameloblastoma is most commonly associated with variably sized swellings of the jaw, which can be accompanied by facial deformity. Malocclusion and a loss of teeth also can be observed. However, pain or paresthesia is rare, and such a lesion might be associated with unerupted tooth [6,7]. In radiologic examination, conventional ameloblastoma can present in one of three patterns as a soap bubble appearance, beehive pattern, and the very important pattern for differential diagnosis, the unilocular form [7].
Upon histological analysis of this lesion, odontogenic epithelial islands can be observed. These islands are composed of hyperchromatic, palisading nuclei, showing reverse polarity. In addition, this lesion possess stellate reticulum-like cells and suprabasal cells, which compose loosely arranged angular cells [8]. The plexiform term refers to histologic appearance of basal cells in anastomosing strands with unobtrusive stellate reticulum, in which the stroma is usually delicate, and often with cyst like degeneration [9]. In immunohistochemistry analysis, plexiform ameloblastoma expresses cytokeratin 8 (CK8) in all outermost cells and stellate reticulum cells in the inner portion of the tumor nest. CK19 is found in the outermost and inner cells. AE1/AE3 positivity is expressed in all cells, including the outermost, inner, and stellate reticulum cells. Polyclonal keratin (PK) positivity can be found at the outermost tumor cells. Plexiform ameloblastoma also expresses Ki-67, which correlates with recurrence [10,11].
There are two types of treatment modalities for conventional ameloblastoma including conservative (marsupialization, enucleation, and curettage of the macroscopic lesion, simple bone resection, and decompression which was suggested by Huang), and radical (maxillectomy or segmental mandibulectomy) [4,12]. Due to the high recurrence of conventional ameloblastoma, the radical treatment approach has been suggested by several authors. Gardner suggested radical treatment for conventional ameloblastoma according to size and expansion. He suggested marginal resection for a small lesion, segmental resection for mandible inferior border expansion, and hemimandibulectomy for large lesion [13]. Troulis proposed en bloc resection, bone graft, implant placement, and prosthodontic reconstruction for aggressive pediatric ameloblastoma [14]. However, the radical treatment approach for pediatric patients remains controversial due to its effects on growth and craniofacial and dental development. Contrary to Gardner and Troulis, Huang et al. proposed conservative treatment for pediatric ameloblastoma using decompression followed by enucleation with peripheral osteotomy along with routine self-irrigation and follow-up. They do not suggest to treat pediatric ameloblastoma radically, due to the radical treatments do not guarantee the absence of recurrence and it will affect the dentocraniofacial development and growth. When pediatric ameloblastoma recurs after radical treatment, more extensive and thorough resection of the surrounding soft tissue will be needed. According to Huang, conservative treatment of pediatric ameloblastoma provides good results and in the event of recurrence, a second surgery can be successful [12]. Takahashi et al. suggested conservative treatment with long-term follow-up for pediatric conventional ameloblastoma, such as curettage with marsupialization, in which the marsupialization helps the evaluation of bone healing and recurrence. One consideration for conservative treatment in pediatric ameloblastoma is its histologic features. Plexiform type is considered to be the most common variant of conventional ameloblastoma in children. This variant is less aggressive than the follicular variant. Pediatric plexiform ameloblastoma remains in the primitive stage of tumor differentiation, whereas the follicular type is thought to undergo squamous differentiation. Furthermore, pediatric conventional ameloblastoma grows rapidly but does not differentiate into the follicular type in the remodeled bone of younger patients. In adult patients, the follicular is the most common variant, and the tumor which persists in the bone for long time, has a potential to progress to squamous metaplasia. In Takahashi’s study which included five cases of pediatric plexiform ameloblastoma and 1 pediatric follicular ameloblastoma with the longest follow-up period of 11 years 10 months, satisfactory results were obtained with no signs of recurrence [15]. Based on this consideration, we performed conservative decompression and copious warm saline irrigation treatment with long-term clinical and radiographic follow-up.
Decompression has a plethora of benefits, including bone formation, oral tissue preservation, pulp vitality maintenance, prevention of tooth extraction, important anatomic structure preservation, and a low risk of recurrence [16]. Castro-Nunez emphasized the cavity irrigation through the tube using normal saline as an integral part of decompression treatment for odontogenic cysts to facilitate the lavage of the cyst [17]. Gulsen et al., also reported successful outcome on calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumor treatment using decompression with a saline tube irrigation followed by enucleation [18]. According to the meta-analysis study on efficacy of continuous saline bladder irrigation following bladder tumor resection by Zhou et al., continuous saline irrigation after transurethral resection of bladder tumors can prevent the recurrence by washing away the floating cancer cells and prevent the adhesion of the cancer cells [19]. In another meta-analysis study on association of irrigation and local recurrence of anterior resection for rectal cancer by Zhou et al., the rectal washout using normal saline alone can reduce the rectal cancer local recurrence risk by 63%. The explanation for this is that the exfoliated malignant cells can be washed out through mechanical cleansing by saline since saline does not have cytocidal or tumoricidal effect. However, the saline washout is volume dependent and should be used copiously [20]. Furthermore, copious irrigation can keep the wound cavity clean and prevent infection, especially in aerodigestive tract [21,22]. Using this conservative treatment modality, the deciduous teeth and IAN can be preserved and the risk of recurrence as well as infection can be decreased.
The IAN is a sensory nerve, that carries not only sensory information, but also neuropeptides that are important in maintaining bone homeostasis. In an animal experimental study by Nemec et al., the transection of IAN caused changes in bone’s inorganic components including decrease in calcium, iron, and strontium, and increase in zinc. In a balanced condition, these inorganic components are essential for bone turnover and mineralization [23,24]. Moreover, Ghassemi-Tray found that IAN neurotomy affected mandibular growth in rat, with significant lower height and length of the mandible in neurotomized group than the control group [25].
As essential as IAN, deciduous teeth play an important role in development of facial muscles movement, eating skills, and speech abilities of children [26]. Deciduous teeth also guide eruption of permanent teeth and stimulate growth of the jaw [27]. In the absences of deciduous teeth during primary dentition period, food and nutrient intake as well as mastication activity are impaired. As a result, development and growth of the child will be compromised. Furthermore, teeth together with lips and tongue play an important role in production of sound and articulation [28]. During the primary dentition period (age 2.5–5 years), development of linguistic ability is important. Therefore, deciduous teeth should be maintained as long as possible until the exfoliation period and eruption of all permanent teeth.
To maintain normal growth of the jaws, we suggest use of a functional appliance as an integral part of treatment for pediatric ameloblastoma and other tumors. In this case, we used a Frankel functional appliance to induce the mandibular growth. The functional appliance was designed to act as a bite guide to increase the activity of the lateral pterygoid muscles attached to the heads of the condyles to move the mandible into a protrusive position and establish a centric relation [29]. Alio-Sanz et al. found that the functional appliance produced vertical orthopedic growth of the mandible [30]. The meta-analysis study by Perillo et al. also found that the functional appliance had a statistically significant effect on mandibular growth, specifically on total mandibular length [31]. Furthermore, Silvestrini-Biavati et al. found that the functional appliance had significant effects in the positioning of teeth, skeletal modifications, and soft tissue changes in prepubertal patients. The functional appliance prevented the worsening of progressive malocclusion and induced dentoalveolar, skeletal, functional, profile, and psychosocial improvements together with functional action on many dysfunctional causes of malocclusion [32]. In this eight-year follow-up case, no recurrence was observed, demonstrating good prognosis of conservative decompression treatment for pediatric plexiform ameloblastoma. Furthermore, with patient cooperation to wear the functional appliance for several years, the previously displaced teeth were repositioned and the permanent teeth erupted properly in the well-developed mandibular arch. Nevertheless, further orthodontic treatment and prosthetic management such as dental implants are required due to a loss of two teeth in the same quadrant caused by the pediatric plexiform ameloblastoma.
4. Conclusions
Pediatric plexiform ameloblastoma should be treated with a conservative approach considering further mandibular growth. Using the conservative decompression approach along with routine copious warm saline irrigation, important anatomic structures such as the IAN and deciduous teeth can be preserved, and the risk of recurrence can be reduced. Moreover, functional appliance therapy should be considered as an integral part of treatment for pediatric ameloblastoma and other tumors in children to maintain and induce normal growth of the mandible. In addition, routine and long-term follow-up along with patient cooperation are important to obtaining successful outcomes of treatment.
Author Contributions
K.R.M.: drafting and writing the manuscript; B.S.-I.: revising and editing the manuscript; M.-Y.E. and H.-J.Y.: acquisition of patient data and pathologic specimen; H.M. and S.-M.K.: concepting, drafting, acquisition of data, and revising the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
There is no funding related to this article.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Institutional Review Board of Seoul National University (S-D20200010).
Informed Consent Statement
Written informed consent was obtained from patient’s legal guardian for publication of this case report and accompanying images.
Data Availability Statement
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no data sets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (2017R1D1A1B04029339).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Rikhotso, R.E.; Premviyasa, V. Conservative treatment of ameloblastoma in a pediatric patient: A case report. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2019, 77, 1643–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClary, A.C.; West, R.B.; McClary, A.C.; Pollack, J.R.; Fischbein, N.J.; Holsinger, C.F.; Sunwoo, J.; Colevas, A.D.; Sirjani, D. Ameloblastoma: A clinical review and trends in management. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2016, 273, 1649–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheela, S.; Singer, S.R.; Braidy, H.F.; Alhatem, A.; Creanga, A.G. Maxillary ameloblastoma in an 8-year-old child: A case report with a review of the literature. Imaging Sci. Dent. 2019, 49, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laborde, A.; Nicot, R.; Wojcik, T.; Ferri, J.; Raoul, G. Ameloblastoma of the jaws: Management and recurrence rate. Eur. Ann. Otorhinolaryngol. Head Neck Dis. 2017, 134, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soluk-Tekkeşin, M.; Wright, J.M. The world health organization classification of odontogenic lesions: A summary of the changes of the 2017 (4th) edition. Turk. J. Pathol 2018, 34, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, L.D.R. World health organization classification of tumours: Pathology and genetics of head and neck tumours. Ear Nose Throat J. 2006, 85, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muddana, K.; Prakash Pasupula, A.; Reddy Dorankula, S.P.; Rao Thokala, M.; Krishna Muppalla, J.N. Pediatric odontogenic tumor of the jaw—A case report. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2014, 8, 250–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathology Outlines—Ameloblastoma. Available online: https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/mandiblemaxillaameloblastoma.html (accessed on 7 January 2021).
- Hertog, D.; Bloemena, E.; Aartman, I.H.A.; van-der-Waal, I. Histopathology of ameloblastoma of the jaws; some critical observations based on a 40 years single institution experience. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal. 2012, 17, e76–e82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wato, M.; Chen, Y.; Fang, Y.-R.; He, Z.-X.; Wu, L.-Y.; Bamba, Y.; Hida, T.; Hayashi, H.; Ueda, M.; Tanaka, A. Immunohistochemical expression of various cytokeratins in ameloblastomas. Oral Med. Pathol. 2006, 11, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yasuoka, S.; Kato, T. Histopathological and immunohistochemical characteristics of the progressive front of ameloblastoma. Int. J. Oral-Med. Sci. 2015, 13, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, I.Y.; Lai, S.T.; Chen, C.H.; Chen, C.M.; Wu, C.W.; Shen, Y.H. Surgical management of ameloblastoma in children. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endodontol. 2007, 104, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, D.G. A pathologist’s approach to the treatment of ameloblastoma. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 1984, 42, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troulis, M.J.; Williams, W.B.; Kaban, L.B. Staged Protocol for Resection, Skeletal Reconstruction, and Oral Rehabilitation of Children with Jaw Tumors. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2004, 62, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Miyauchi, K.; Sato, K. Treatment of ameloblastoma in children. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 1998, 36, 453–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.-S.; Song, I.-S.; Seo, B.-M.; Lee, J.-H.; Kim, M.-J. The effectiveness of decompression for patients with dentigerous cysts, keratocystic odontogenic tumors, and unicystic ameloblastoma. J. Korean Assoc. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2014, 40, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Núñez, J. An innovative decompression device to treat odontogenic cysts. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2016, 27, 1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gülşen, U.; Dereci, Ö.; Gülşen, E.A. Treatment of a calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumour with tube decompression: A case report. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2018, 56, 979–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Zhao, S.; Lu, Y.; Wu, J.; Li, Y.; Gao, Z.; Yang, D.; Cui, Y. Meta-analysis of efficacy and safety of continuous saline bladder irrigation compared with intravesical chemotherapy after transurethral resection of bladder tumors. World J. Urol. 2019, 37, 1075–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Ren, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, K.; He, J.; Chen, W.; Liu, P. Association between irrigation fluids, washout volumes and risk of local recurrence of anterior resection for rectal cancer: A meta-analysis of 427 cases and 492 controls. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, 5–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lodhia, K.A.; Dale, O.T.; Winter, S.C. Irrigation Solutions in Head and Neck Cancer Surgery: A Preclinical Efficacy Study. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2015, 124, 68–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Molon, R.S.; Verzola, M.H.; Pires, L.C.; Mascarenhas, V.I.; Da Silva, R.B.; Cirelli, J.A.; Barbeiro, R.H. Five years follow-up of a keratocyst odontogenic tumor treated by marsupialization and enucleation: A case report and literature review. Contemp. Clin. Dent. 2015, 6, S106–S110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Němec, I.; Smrčka, V.; Pokorný, J. The effect of sensory innervation on the inorganic component of bones and teeth; Experimental denervation—Review. Prague Med. Rep. 2018, 119, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nĕmec, I.; Smrčka, V.; Mihaljevič, M.; Hill, M.; Pokorný, J. Effect of inferior alveolar nerve transection on the inorganic component of bone of rat mandible. J. Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2020, 20, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ghassemi-Tary, B.; Cua-Benward, G.B. The effect of inferior alveolar neurotomy on mandibular growth in the rat. J. Clin. Pediatr. Dent. 1992, 17, 19–23. [Google Scholar]
- Le Révérend, B.J.D.; Edelson, L.R.; Loret, C. Anatomical, functional, physiological and behavioural aspects of the development of mastication in early childhood. Br. J. Nutr. 2014, 111, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Gómez, S.A.; Villalobos-Rodelo, J.J.; Ávila-Burgos, L.; Casanova-Rosado, J.F.; Vallejos-Sánchez, A.A.; Lucas-Rincón, S.E.; Patiño-Marín, N.; Medina-Solís, C.E. Relationship between premature loss of primary teeth with oral hygiene, consumption of soft drinks, dental care, and previous caries experience. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, N.C.; Sandy, J.R. Tooth position and speech—Is there a relationship? Angle Orthod. 1999, 69, 306–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianelly, A.A.; Brosnan, P.; Martignoni, M.; Bernstein, L. Mandibular growth, condyle position and Fränkel appliance therapy. Angle Orthod. 1983, 53, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alió-Sanz, J.J.; Kato, E.; Lorenzo-Pernía, J.; Iglesias-Conde, C.; Iglesias-Linares, A.; Solano-Reina, E. Study of mandibular growth in patients treated with Fränkel’s functional regulator (1b). Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal 2012, 17, e884–e892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Perillo, L.; Cannavale, R.; Ferro, F.; Franchi, L.; Masucci, C.; Chiodini, P.; Baccetti, T. Meta-analysis of skeletal mandibular changes during Fränkel appliance treatment. Eur. J. Orthod. 2011, 33, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestrini-Biavati, A.; Alberti, G.; Silvestrini-Biavati, F.; Signori, A.; Castaldo, A.; Migliorati, M. Early functional treatment in Class II division 1 subjects with mandibular retrognathia using Fränkel II appliance. A prospective controlled study. Eur. J. Paediatr. Dent. 2012, 13, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).