Abstract
A comparative analysis of geodetic versus seismic moment-rate estimations makes it possible to distinguish between seismic and aseismic deformation, define the style of deformation, and also to reveal potential seismic gaps. This analysis has been performed for Egypt where the present-day tectonics and seismicity result from the long-lasting interaction between the Nubian, Eurasian, and Arabian plates. The data used comprises all available geological and tectonic information, an updated Poissonian earthquake catalog (2200 B.C.–2020 A.D.) including historical and instrumental datasets, a focal-mechanism solutions catalog (1951–2019), and crustal geodetic strains from Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) data. The studied region was divided into ten (EG-01 to EG-10) crustal seismic sources based mainly on seismicity, focal mechanisms, and geodetic strain characteristics. The delimited seismic sources cover the Gulf of Aqaba–Dead Sea Transform Fault system, the Gulf of Suez–Red Sea Rift, besides some potential seismic active regions along the Nile River and its delta. For each seismic source, the estimation of seismic and geodetic moment-rates has been performed. Although the obtained results cannot be considered to be definitive, among the delimited sources, four of them (EG-05, EG-06, EG-08, and EG-10) are characterized by low seismic-geodetic moment-rate ratios (<20%), reflecting a prevailing aseismic behavior. Intermediate moment-rate ratios (from 20% to 60%) have been obtained in four additional zones (EG-01, EG-04, EG-07, and EG-09), evidencing how the seismicity accounts for a minor to a moderate fraction of the total deformational budget. In the other two sources (EG-02 and EG-03), high seismic-geodetic moment-rates ratios (>60%) have been observed, reflecting a fully seismic deformation.
1. Introduction
For any seismic hazard assessment, earthquake occurrence rates represent an essential issue. Three types of data are available for the estimation of these rates: the historical earthquake record, the geological slip rates of known active faults, and the geodetic deformation rates [1]. Each approach has its limitations and generally provides a different perspective of the active tectonic forces, but in principle they should provide approximately similar estimates (see [1] for a general overview). In particular, estimations coming from geologic data take into account only known faults and usually require long time spans (e.g., 104 to 105 years). Estimations derived from geodesy include both elastic and anelastic components of deformation and suffer from network geometry and time spans (e.g., >2.5 years, [2]), while those coming from the seismic release capture the contribution of buried faults but only count the seismic component of deformation and largely suffer from both the temporal length and the completeness degree of available catalogs. Because of these different perspectives, the complementarity of the three approaches, along with other independent observations can provide reliable constraints on achieved estimations, therefore providing relevant insights for seismic hazard assessment and geological deformation studies [3,4,5,6,7]. However, because of the lack of spatially dense estimation of geological slip-rates of active outcropping faults and the poor knowledge of buried faults, earthquake occurrence rates and deformation budget comparisons are generally performed by taking into account only geodetic and seismic observations [4,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14]. Hence geodetic and seismic moment-rates comparison has enabled identification of regions in which the total deformation-rate budget is released completely by crustal earthquakes, or in the case that there is an excess of the budget, it could be released either as aseismic slip across faults or through large future earthquakes [7,9,11,12,13,15,16,17].
In the present study, an updated and Poissonian earthquake catalog for Egypt (historical and instrumental data within the period between 2200 B.C.–2020 A.D.), focal mechanism solutions coming from previous publications, and novel strain-rate field data were used to study the spatial patterns of seismic and geodetic moment-rates. The seismic moment-rates have been estimated by considering the truncated cumulative Gutenberg–Richter recurrence relationship [18] together with the characteristic earthquake model [19] when it was strictly required. The geodetic moment-rate was estimated by adopting the Savage and Simpson [20] approach.
The comparison of the geodetic and seismic moment-rates for a country such as Egypt with a relatively well-known historical seismic record and surrounding plate boundaries will provide additional insights into the seismic hazard and the seismotectonics of the region [7,21].
2. Tectonic Setting
The primary tectonic features of the surrounding plate boundaries of Egypt were studied and discussed by several researchers [22,23,24,25,26]. The Nubian–Eurasian plate margin in the north, and the Gulf of Suez–Red Sea plate margin, and the Gulf of Aqaba–Dead Sea Transform Fault system in the east represent the three main tectonic features in the vicinity of Egypt (Figure 1). On one hand, based on the analysis of fault systems, oceanic spreading, and earthquake slip vectors, the global kinematic models by DeMets et al. [27] show that across a wide zone in the Mediterranean Sea, both the Nubian and Eurasian plates are converging. The Nubian plate is moving in a northerly direction relative to the Eurasian plate at a rate of about 10 mm/year [27]. This form of closeness is translated in the form of the Cyprian and the Hellenic Arcs along the Eastern Mediterranean region (Figure 1). On the other hand, the Arabian plate is continuing to rotate away, in a northeastward divergent movement, from the Nubian plate along the Gulf of Suez–Red Sea Rift [28,29,30] (Figure 1). This rift is considered one of the premier examples of the creation of a new ocean and ongoing rifting. This rift system may extend further towards the north beneath the Suez Canal area, but this possible extension is probably masked by the alluvial Nile deposits [31]. Finally, the differential motion between the Nubian and the Arabian plates (about 15 mm/year) is thought to be taken up by the Gulf of Aqaba–Dead Sea Transform Fault System [32]. This is a seismically active 1100 km long left-lateral strike-slip transform boundary (Figure 1) that connects the northern Mediterranean triple junction in the north to the Red Sea spreading center in the south [33]. Geological evidence suggests that a pure strike-slip motion with slip rates between 5 and 10 mm/yr occurs along this transform fault [34,35,36]. This left-lateral sense of motion was recognized by the minor pull-apart in young sediments, cut and offset of man-made structures, and drainage lines [37,38,39,40,41,42].
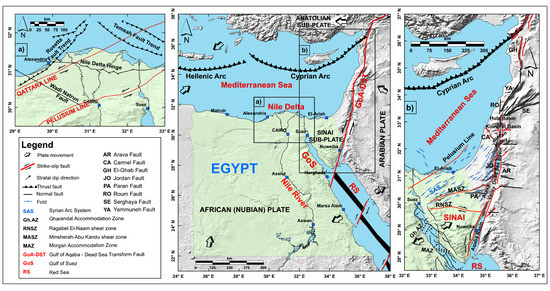
Figure 1.
Compiled global tectonic sketch for Egypt and its surrounding regions (the middle plot: after [43]), the Nile Delta region (the left plot (a): after [44]), and the Sinai Peninsula and the Dead Sea regions (the right plot (b): after [45,46,47]). Abbreviations for the geographic features, faults, and shear zones are included in the legend.
3. Preparation of an Updated and Unified Earthquake Catalog
As a first step towards the delimitation of areal seismic sources and the estimation of relevant seismicity parameters, an earthquake catalog was compiled from the beginning taking into account previous catalogs. A spatial region extending from 24° to 38° E longitudes and from 21° to 34° N latitudes was considered, within the period starting from 2200 B.C. until 2020. In the compilation, all shallow earthquakes (h < 35 km) above magnitude 3.0 on any magnitude scale were gathered. Several catalogs, bulletins, and publications were inspected and gathered to compile the dataset.
- The Poissonian earthquake catalog by Sawires et al. [48] for Egypt was considered as a priority since they considered both historical and instrumental earthquakes, covering large spatial (the whole territory of Egypt) and temporal extension (2200 B.C.–2014). The final number of earthquakes gathered from this catalog was 22,054 events.
- The local instrumental earthquake catalog of the Egyptian National Seismic Network was published by Abd El–Aal et al. [49]. They considered the time period from 1997 to 2019. A number of 1.543 earthquakes from this reference (including magnitudes equal to or greater than 3.0) was also included in our catalog.
- An additional number of earthquakes (4885 events) were collected from the Israel National Seismic Network (FDSN; https://www.fdsn.org/networks/detail/IS/; last accessed on 1 June 2021) in addition to other related publications (e.g., [50]).
- The instrumental earthquake catalog developed by Deif et al. [51] for the Arabian Peninsula was also considered, especially for the Red Sea region. Their catalog covers the period between 1900 and 2015, and 974 earthquakes from it were considered to be included in our database.
- Besides these local bulletins and catalogs (for Egypt, Israel, and the Arabian Peninsula), data from regional and international bulletins were also gathered. Within the period from 2014 until the present, a number of 393, 12, and 73 earthquakes in this region have been collected from the International Seismological Centre (ISC; http://www.isc.ac.uk/iscbulletin/search/; last accessed on 1 June 2021), the ISC-EHB bulletin (http://www.isc.ac.uk/isc-ehb/; last accessed on 1 June 2021), and the National Earthquake Information Center, United States Geological Survey (USGS; https://earthquake.usgs.gov/earthquakes/search/; last accessed on 1 June 2021), respectively.
When merging the previously mentioned data (a total of 29,934 earthquakes), it was crucial to avoid any possible duplication. The compiled dataset is described by the following parameters for each specific earthquake: year, month, and day for the date; hour, minute, and second for the time; longitude and latitude for the geographic location; depth value; and the reported magnitude(s) (body-wave “mb”, surface-wave “Ms”, moment “Mw”, duration “MD”, and local “ML” magnitudes). Duplicated earthquakes were identified, based on their geographic location and the date and time of their occurrence, and removed from the compiled dataset. In order to unify the different magnitude scale of the catalog into the moment magnitude one, the following magnitude-scaling relationships have been used:
- For those earthquakes compiled by Sawires et al. [48], ISC, EHB-ISC, and USGS bulletins, the same conversion relationships developed by these authors have been applied to convert macroseismic intensity values, mb, Ms, MD, and ML to Mw (Equations (1)–(5)).
- For those events gathered from Deif et al. [51] catalog for the Arabian Peninsula, the relationships by Sawires et al. [52] for developing a unified earthquake catalog for the surroundings of the United Arab Emirates were used, by converting the mb, Ms, and ML magnitudes to Mw (Equations (6)–(8)).
- Finally, since the data collected from the Israel National Seismic Network are reported in MD scale, the conversion relationship developed by Ataeva et al. [50] to do the conversion to the Mw scale has been used (Equation (9)).
In a successive step, to properly estimate the seismicity parameters (activity rate, b-value, and maximum expected magnitude), a declustering process of the catalog was performed. This step allows erasing of earthquake swarms and sequences which generally affect the activity rate and b-value estimations from the catalog. In this regard, the procedure by Gardner and Knopoff [53] has been applied. Given a certain magnitude, a scan within defined distance and time windows was performed for the whole unified catalog. Throughout this inspection, an earthquake having the largest magnitude is considered the mainshock or the independent one. Distance and time windows of 36 and 100 km and 100 and 600 days were applied for earthquakes with magnitudes Mw 4.0 and 8.0, respectively [54]. As a result, a final catalog with 3.419 earthquakes was obtained covering the geographic region between 21° and 34° N latitudes, and between 24° and 38° E longitudes, and within the period from 2200 B.C. to 2020, including both historical and instrumental earthquakes.
The completeness periods were estimated for the entire catalog. This was done by plotting the cumulative number of earthquakes for specific magnitude ranges against time (Figure 2). From the completeness analysis (Table 1), it was found that the catalog is complete for magnitudes above Mw 3.0, 4.0, 5.0, 6.0, and 7.0 broadly since the years 1995, 1980, 1925, 700 A.D., and 240 A.D., respectively. Some of the obtained completeness periods are closely related to the establishment or the improvement of some local and international networks. For instance, the years 1900, 1960, 1983, and 1993 are the approximates dates for the establishment of the Helwan Observatory in Cairo, the deployment of the World-Wide Standardized Seismograph Network (WWSSN), the installation of the Aswan Seismological Network around Nasser’s Lake, and the installation of the Egyptian National Seismic Network in Egypt after 12 October 1992, Mw 5.8 Cairo earthquake, respectively [55,56]. The given completeness periods for the current catalog indicate that our catalog is not as complete as could be desired. This is due mainly to the incomplete coverage of the seismic stations during the early instrumental period. Thus, some biases, underestimation, or overestimation for the seismicity parameters are expected during the computations.
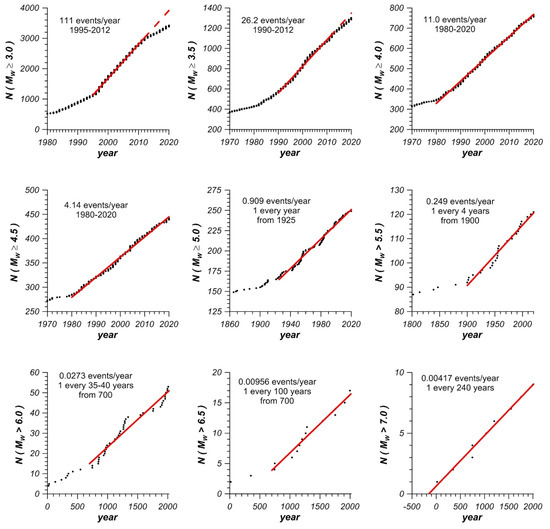
Figure 2.
Completeness analysis for the updated and declustered catalog. Completeness rates are also depicted.

Table 1.
Completeness periods and their corresponding activity rates for the current unified and declustered catalog. See Figure 2.
4. Seismicity of Egypt
Egypt is characterized by earthquakes of moderate magnitudes which mainly concentrate along the surrounding plate boundaries (the Gulf of Aqaba–Dead Sea transform fault, the Gulf of Suez-Red Sea rift, and the Nubian–Eurasian plate boundary). Available publications and catalogs of historical (pre-1900) earthquakes in Egypt [48,57,58,59,60] document the occurrence of only 83 earthquakes in the Egyptian lands (Figure 3). In addition, the population concentration along the Nile River and its delta creates imprecision in the proper identification of the location and the possible damage effects of historical earthquakes. In Figure 3, the historical earthquakes that occurred in and around Egypt have been imported mainly from Sawires et al. [48] earthquake catalog and were plotted in terms of the computed equivalent moment magnitude using the relationships shown above. They documented the occurrence of about 230 earthquakes in and around Egypt within the period between 2200 B.C. and 1899 A.D., and within the intensity range of III to XI (MMI Scale) [48].
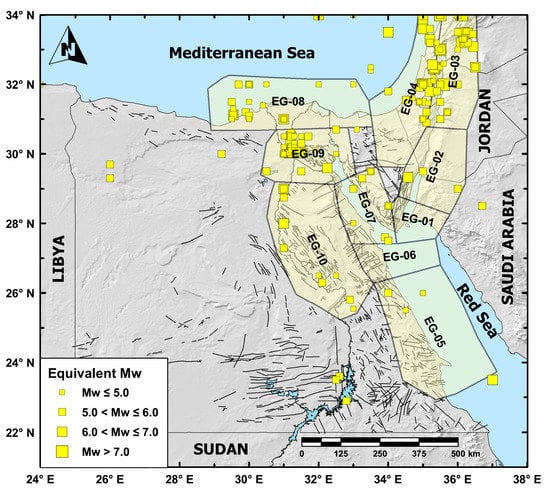
Figure 3.
Historical earthquakes (2200 B.C.–1899 A.D.) of Egypt and its surroundings (after [48,61]). Black lines refer to EGSA [62]. Polygons labeled from EG-01 to EG-10 refer to the delimited seismic sources in the current work.
On the other hand, regarding the instrumental events (1900–2020) (Figure 4), Egypt shows relatively moderate seismicity in comparison to other regions all over the world. However, it was affected by some damaging large earthquakes that originated mainly along the Hellenic and the Cyprian Arcs, as well as those from Southern Palestine [59]. The following points can be deduced from the plotting of seismicity: (a) a higher concentration for the instrumental seismicity appears on the northeastern parts of Egypt, especially along the triple junction of the Gulf of Suez, the Gulf of Aqaba and the Red Sea than those in southern Egypt, (b) the shallow seismic activity is mainly focused in the surrounding plate boundaries (the Gulf of Aqaba–Dead Sea fault system and the Gulf of Suez–Red Sea rift towards the east, and the Nubia–Eurasia plate boundary “the Hellenic and the Cyprian Arcs” towards the north) as well as on other active seismic zones (southwest Cairo, Cairo–Suez area, Abu Dabbab area on the Eastern Desert, offshore Delta region, west of Assiut and Sohag, and the surrounding of Nasser’s Lake), and (c) little dispersed seismicity could be noticed along the Western Desert of Egypt or on the southern parts of the Eastern Desert. Examples of those large earthquakes that affected Egypt through previous decades are the 12 November 1955 (Mw 5.5) Abu-Dabbab, the 31 March 1969 (Ms 6.9) Shedwan, the 14 November 1981 (Mw 5.8) Aswan, the 12 October 1992 (Mw 5.8) Cairo “Dahshour”, the 22 November 1995 (Mw 7.2) Gulf of Aqaba, and the 28 May 1998 (Mw 5.5) Ras El-Hikma earthquakes [48].
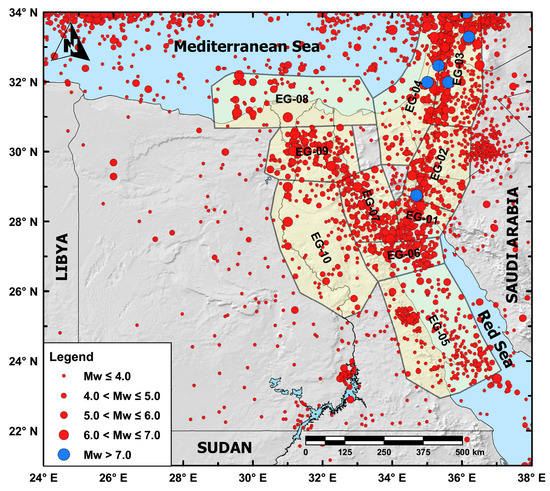
Figure 4.
Spatial distribution of declustered instrumental seismicity (1900–2020).
A recent database of focal mechanism solutions (1951–2019) has been provided in Rashwan et al. [61]. These focal mechanism solutions (Figure 5) have been used to study the seismotectonics pattern of the investigated region as well as to define and delimitate the studied seismic sources. Differentiation of the different faulting mechanisms based on their rake angle was considered (Figure 5), i.e., pure normal-faulting (NF), normal-faulting with strike-slip component (NS), pure strike-slip faulting (SS), pure reverse-faulting (TF), and reverse-faulting with strike-slip component (TS).
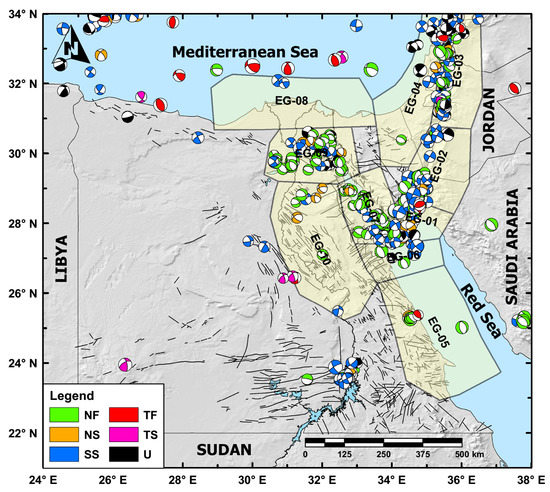
Figure 5.
Spatial distribution of lower hemisphere equal-area projection for the focal-mechanism solutions dataset (after [61]). Black lines refer to the faults defined by the EGSA [62]. Sizes and colors of the plotted focal mechanism are relative to their moment magnitudes and faulting types, respectively. NF: normal-faulting, NS: normal with a strike-slip component, SS: strike-slip faulting, TF: thrust faulting, TS: thrust with a strike-slip component, U: undefined.
5. Geodetic Data
A recent update of geodetic velocities and horizontal strain-rates for Egypt has been published by Rashwan et al. [61], therefore in the following, we refer to these results. The geodetic velocity field has been derived from a set of episodic and continuous GNSS observations collected during the 1995–2005 and 2000–2018 time spans, respectively. GNSS stations prevailing cover the eastern sector of Egypt, allowing measurement of the crustal deformation related to the most relevant tectonic elements of the region. In particular, Rashwan et al. In [61], it is evidenced that (i) the north-western coastal area and central Egypt show a pattern in agreement with the rigid motion of the Nubian Plate, (ii) the stations located along the western side of the Red Sea show a northward motion of ~1 mm/yr, (iii) the stations located on the north-eastern Sinai Peninsula show an NNW motion with rates larger than 1.6 mm/yr, and (iv) the stations on the Nile Delta show a complex pattern, both on the horizontal and vertical components, reflecting the general subsidence of the area.
Rashwan et al. [61] also estimated the horizontal strain-rate field over a regular 0.5° × 0.5° grid. Considering such a horizontal strain-rate field (Figure 6), values up to ~25 nstrain/yr can be observed along the Gulf of Aqaba–Dead Sea Transform Fault with extension along with the WSW–ENE orientation, passing to SW–NE attitudes along the Red Sea basin. Along the region between the Nile Valley and the Red Sea, the strain field shows a NNE–SSW attitude with rates progressively decreasing westward. The Gulf of Suez shows values ranging from ~20 nstrain/yr (southward) to ~8 nstrain/yr (northward), while on the northern sector of the Nile, the shortening strain axes show an E–W orientation with values up to ~8 nstrain/yr.
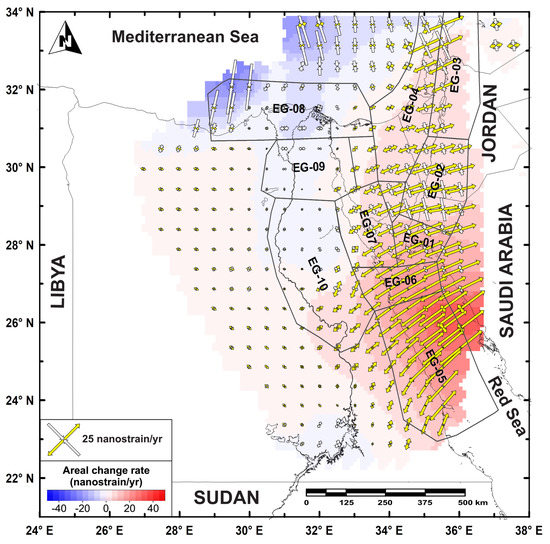
Figure 6.
Geodetic strain-rate field (after [61]) overlain by the defined seismic sources. Color scale range (from blue to red) in the background of the plot shows the areal change in the strain-rate field, while the arrows refer to the maximum extensional (in red) and maximum contractional (in blue) horizontal strain-rates.
6. Delimitation of Seismic Sources
Based on the geological and tectonic settings (Figure 1), the spatial distribution of historical and instrumental seismicity (Figure 3 and Figure 4), focal mechanism solutions and their related style of faulting (Figure 5), and also considering the distribution of GNSS data over the region, the studied region was subdivided into ten crustal seismic sources (h < 35 km), labeled from EG-01 to EG-10 (Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5). These sources are mainly covering the potential shallow active regions along the Gulf of Aqaba–Dead Sea Transform Fault, the Gulf of Suez–Red Sea Rift, and the Nile River and its delta. Some details about each seismic source are given in the following paragraphs.
6.1. Seismic Sources along the Gulf of Aqaba–Dead Sea Transform Fault System (EG-01 to EG-04)
The Gulf of Aqaba–Dead Sea Transform Fault (GoA–DST) can be divided into three main sectors [63] (see Figure 1b). The southern one (Jordan Rift) comprises the area from the junction of the Gulf of Aqaba with the Red Sea and extends through the Dead Sea and the Jordan Valley (Figure 1b). It is characterized by the presence of N12° E to N20° E striking left-lateral strike-slip faults. The central sector (Lebanese Splays) is running through Lebanon and southwest Syria (Figure 1b). It is characterized by about 200 km long NNE–SSW striking restraining bend [64]. Finally, the northern sector (El-Gharb Rift) of the GoA–DST is characterized by the occurrence of two N–S striking faults bounding the Ghab Valley and intersecting with both the East Anatolian Fault and the Cyprian Arc [42]. This intersection corresponds to the Hatay triple junction (Figure 1) between the Arabian, Nubian, and Anatolian plates [65].
The Gulf of Aqaba (Figure 1) forms the southernmost segment of the GoA–DST. It has experienced the largest recorded instrumental earthquake in Egypt (the 22 November 1995, Mw 7.2, earthquake). It comprises three elongated en-echelon basins transected by longitudinal faults [66]. Several tectonic basins were originated as a result of this en-echelon system, forming rhombic-shaped grabens (Figure 1b). These are the Tiran “Dakar” (from the south), Dakar, Aragonese, and Elat “Aqaba” (from the north) basins. The complex deformation pattern along the Gulf of Aqaba is related to a left-lateral strike-slip motion which dominates parallel to the main axis of the gulf, and a minor normal-slip component that dominates along the transverse faults [38,67,68,69,70].
In the current work, three main seismic sources (EG-01, EG-02, and EG-03; see Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5) were delimited along the GoA–DST, starting from the junction between the Gulf of Aqaba with the Red Sea (from the south) and reaching the northern latitude of 34° (from the north). The first defined seismic source is the EG-01 Tiran zone, which lies at the southern tip of the Gulf of Aqaba. No historical earthquakes are available for this source (Figure 3). The focal mechanism solutions inside this source is characterized by an average normal-faulting mechanism with a minor strike-slip component (Figure 5). The 3 August 1993 (Mw 6.1) earthquake represents the largest recorded magnitude (Figure 4) for the instrumental period within this source (Table 1).
The second delimited seismic source (EG-02) covers the region extending from the Aragonese Basin passing through the Aqaba “Elat” Basin (along the Gulf of Aqaba) to the Arava Valley (to the north) (Figure 1b). The Gulf of Aqaba has been the focus of the largest recorded earthquake in Egypt, the 22 November 1995 (Mw 7.2) earthquake. In addition, paleoseismological investigations by Shapira and Jarradat [71] deduced that border-faults of the Arava Valley could generate earthquakes bigger than Mw 6.0 for an average 1000–3000 years return period. Three historical earthquakes (Figure 3) have been reported in this source: the 18 March 1068 (felt intensity VIII, Mw 5.8), the 2 May 1212 (VII-IX, Mw 6.1), and the 4 January 1588 (VIII, Mw 5.8) earthquakes. The first one, in 1068, was reported in northern Hejaz, causing huge destruction along northwestern Saudi Arabia, and killing about 20,000 persons [59]. Available focal mechanisms show abundant strike-slip faulting solutions (Figure 5), while some few mechanisms are characterized by strike-slip faulting coupled with a minor normal component.
The third proposed source (EG-03; see Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5) was delimited to cover the seismicity along the Dead Sea Basin, Jordan Valley, Kineret–Hula Basin, and the Lebanese Splay in the southern and central sector of the GoA–DST (Figure 1b). The Dead Sea Basin is bounded by a double left-lateral strike-slip fault system, the Arava Fault (from the east) and the Jordan/Jericho Fault (from the west) [72] (see Figure 1b). The Jordan Valley links the Dead Sea Basin (from the south) and the Hula Basin (from the north) [23,38]. To the north, the Hula “Shamir–Almagor Fault” and Kineret “Kineret–Sheikh Ali Fault” Basins are located [73] (see Figure 1b). These two basins present seismic activity up to the Yammuneh Fault (Lebanese Splay). A number of 43 historical earthquakes, within the period from 1020 B.C. to 1802 are reported within this source (Figure 3). The largest observed historical earthquakes are the 746 (XI, Mw 7.7), 2 June 1201 (X-XI, Mw 7.4), and 30 October 1759 (X-XI, Mw 7.4) events (Figure 3). Most of the focal mechanism solutions within this seismic source reflect left-lateral strike-slip faulting solutions (Figure 5). However, some solutions also show normal-faulting mechanisms, reflecting the seismic activity along the N–S striking longitudinal normal faults extending along the Dead Sea Basin [33,38,74].
EG-04 (Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5) was defined to cover the seismic activity within the central-eastern part of the Sinai Peninsula, as well as the activity along the Mediterranean Sea coast of Palestine (see Figure 1). Among the active faults included in this source, there is the Themed Fault (Ragabet El-Naam shear zone in Figure 1b), an E–W striking right-lateral strike-slip fault, located in central Sinai [75]. It cuts the Tih Plateau in central Sinai, and links the Suez Rift (from the east) and the GoA–DST (from the west) [45]. Towards the north from the Themed Fault, a narrow ENE-oriented fault belt corresponds to Bartov et al. [34] central Sinai-Negev shear zone (Minsherah-Abu Kandu shear zone in Figure 1b). Although this source (EG-04) is located between the high seismic activity along the GoA-DST (EG-02 and EG-03) and the seismicity along the Cyprian Arc in the Eastern Mediterranean, it is characterized by relatively lower seismic activity than its surroundings. A number of 35 historical earthquakes (between 1180 B.C. and 1546) are reported within the boundaries of this source (Figure 3). The largest ones among them are the 748 (XI, Mw 7.7) and the 4 January 1034 (X-XI, Mw 7.4) earthquakes (Figure 3), in which the first one corresponds to the largest observed magnitude within the seismic record in this source (Figure 4). The focal mechanism solutions within this source are reflecting mostly strike-slip faulting solutions with a minority of the normal-faulting style (Figure 5).
6.2. Seismic Sources along the Gulf of Suez–Red Sea Rift (EG-05 to EG-07)
The Gulf of Suez-Red Sea (GoS-RS) NW-trending rift (Figure 1) extends from the Gulf of Aden (to the south) to the tip of the Gulf of Suez (to the north), for about 1900 km between the uplifted shoulders of the Nubian and Arabian plates. The GoS–RS region could be subdivided into four main zones, based on its morphology and structure, which reflects specific stages in the creation of the spreading center [76]. They are the southern Red Sea “active sea-floor spreading”, central Red Sea “transition zone”, northern Red Sea “late-stage continental rifting”, and the active rifting zones. The first zone is located between 15° and 20° N latitudes and is characterized by a well-developed axial trough developed through the normal seafloor spreading during the last 5 Ma [77] or at about 9–12 Ma [78]. The second zone is situated between 20° to about 23°20′ N latitudes, in which the axial trough of the rift becomes discontinuous and consists of a series of “deeps” alternating with shallow “inter-troughs” [79]. The third zone represents the northern Red Sea (Figure 1). However, there are small isolated “deeps/depressions”, which consist of a broad trough without a clear spreading center [76]. The last zone, that both could be added to the first one or could be considered as a separate one, is the future line along which the southern Red Sea is going to propagate through the Danakil Depression Afar (to the south).
To the north, the Gulf of Suez (Figure 1b) acts as the NW-trending divergent plate boundary between the Nubian plate (to the west) and the Sinai sub-plate (to the east) [80]. Together with the Gulf of Aqaba and the Red Sea, it acts as one of the three arms of the Sinai triple junction [31,63,81] (see Figure 1). The Gulf of Suez was interpreted by several researchers [82,83] to be composed of three half-grabens separated by two accommodation zones: Gharandal and Morgan accommodation zones [84] (see Figure 1b). Both accommodation zones show discrete normal, oblique, and strike-slip faults [85].
In the current work, the following seismic sources were delimited along the GoS–RS rift. Seismic source EG-05 (Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5) covers the seismic activity concentrating on the central Red Sea zone, as well as the dispersed seismicity on the Red Sea western coast and the Abu Dabbab region, in the Eastern Desert of Egypt. This zone is characterized by a relatively moderate seismic activity in comparison with the zones at the surroundings of the Sinai Peninsula (along the two arms of both gulfs). Only three slightly damaging historical earthquakes are reported to be located within this delimited source. They are the 997, 1887, and 1899 earthquakes (Figure 3). The largest observed magnitude within this seismic source is the 12 November 1955 (mb 6.2, Mw 5.7) earthquake (Figure 4). The few available focal mechanisms are characterized by prevailing normal-faulting features (Figure 5).
EG-06 covers the seismicity on the triple junction between the Red Sea, the Gulf of Aqaba, and the Gulf of Suez (Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5). This source is characterized by relatively higher seismicity than the previous one, which is mainly related to the juncture between these two gulfs [23,86]. No historical earthquakes have been reported within this source (Figure 3), while the recent 16 June 2020 (Mw 5.5) earthquake represents the maximum recorded magnitude (Figure 4, Table 1). Available focal mechanisms reflect both strike-slip and normal-faulting features (Figure 5). The first mechanism category may relate to earthquakes that originated along the transform faults crossing the main rift (Figure 1b), while the second one is related to those earthquakes that originated along the main rift itself [87,88].
EG-07 covers the seismic activity of the southern and central parts of the Gulf of Suez (Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5) and represents the northward prolongation of the previous source. It is distinguished by intensive structural deformation and relatively higher seismic activity [81,89]. This higher seismicity could be attributed to the crustal divergence between the Nubian plate (to the west), and both the Arabian plate and the Sinai sub-plate (to the east). Ten historical earthquakes (between 1220 B.C. and 1879) are reported within this seismic source (Figure 3). The largest ones among them are the 28 B.C. (VIII, Mw 5.8) and the 11 July 1897 (Mw 6.0) earthquakes. During the instrumental period (Figure 4), the largest recorded earthquake within this source was the 31 March 1969 (Ms 6.6, Mw 6.8) Shedwan Island earthquake (Table 1). Several researchers reported the occurrence of a seismic swarm (mb 4.5–5.2) preceding this mainshock [22,80,90,91]. The focal mechanism solutions for earthquakes located within this source mostly show normal-faulting behavior (e.g., the 6 March, Mw 6.8, and the 31 March 1900, Mw 6.1 earthquakes) with a negligible strike-slip component being parallel or sub-parallel to the main rift axis of the Gulf of Suez [86,92]. However, few focal mechanism solutions show normal-faulting with a slight strike-slip component to pure strike-slip faulting mechanisms (Figure 5). These solutions are mainly closer to the accommodation zones (Figure 1b) between three gulf provinces/half grabens [45,93].
6.3. Seismic Sources along the Nile Valley and the Nile Delta (EG-08 to EG-10)
The Nile Valley (Figure 1) is a N–S elongated Oligo–Miocene rift. Its origin is still a subject of controversy. Some researchers [94] deduced an erosional origin, while others [45,95] believe in its tectonic origin. Some of the supporting indicators for the latter origin are the fault scarps bounding the valley and the focal mechanisms of recent earthquakes [96,97]. From the structural point of view, both faults and joints are the dominant features that can be observed along the cliffs bordering the main stream of the Nile River [95,98]. The main trends of these structural features strike NW–SE and NNW–SSE, however, WNW–ESE, ENE–WSW, and NE–SW directions are also present. On the other hand, the Nile Delta (Figure 1a) can be subdivided by the E–W trending hinge zone (Nile Delta Hinge in Figure 1a) into two major structural sub-basins, the north and the south Nile Delta basins/blocks [98] (see Figure 1a). Three main fault trends comprise the structural pattern of the Nile Delta. They are the NW–SE Misfaq–Bardawil “Temsah” Fault (from the northeast side), the NE–SW Qantara–Eratosthenes “Rosetta” Fault (from the northwest side), and the E–W fault defining the Messinian salt basin [99] (see Figure 1a).
In the current study, the central part of the Nile Valley (to the north of latitude 25° N) and the Nile Delta was divided into three major seismic sources (EG-08, EG-09, and EG-10; see Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5). EG-08 covers the shallow crustal seismicity of the surroundings of the northern Nile Delta block (Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5). This zone is located adjacent to the west of the previous EG-04 seismic source. The southern boundary of this source is approximately coincident with the E–W trending hinge zone (Figure 1a). EG-08 is characterized by moderate seismic activity, located to the south of the active Eastern Mediterranean seismic belts (Hellenic and Cyprian arcs). Such seismicity could be attributed to the continental shelf and its associated deep faults, parallel to the Mediterranean coast [24,100]. Twenty-five historical earthquakes (between 24 B.C. and 1886) were located within the boundaries of this zone (Figure 3). The largest reported historical events correspond to the 15 September 951, and 31 August 1111 earthquakes, both with an estimated equivalent magnitude of Mw 6.2. However, the maximum observed magnitude within this zone belongs to the 12 September 1955 (mb 6.5, Mw 6.4) Alexandria earthquake (Figure 4). Only two focal-mechanism solutions are reported inside this source, belonging to 17 January 2013 (Mw 4.5) and 29 October 2016 (Mw 3.3) earthquakes (Figure 5), both exhibiting strike-slip faulting with a minor normal component.
EG-09 covers the seismic activity of the northern tip of the Gulf of Suez, the southern Nile Delta block, the Cairo-Suez region, as well as the west Cairo region (the epicentral area of 1992 Dahshour, Cairo destructive earthquake) (Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5). This zone contains 68 historical earthquakes (Figure 3) within the time between 2200 B.C. and 1895. Additionally, some significant instrumental events are located within this source, e.g., 29 April 1974 (mb 4.8, Mw 4.7) Abu Hammad, 29 March 1984 (mb 4.9, Mw 5.2) Wadi Hagul, 2 January 1987 (mb 5.0, Mw 5.0) Ismailia, and 12 October 1992 (Ms 5.9, Mw 5.8) Dahshour earthquakes (Figure 4). Focal mechanism solutions for this seismic source show mostly normal-faulting features with minor solutions with strike-slip faulting style (Figure 5). Abou Elenean [93] concluded that an NW–SE to WNW–ESE trending normal-faulting mechanism is dominant for the tip of the Gulf of Suez, which is, in general, in agreement with emergent faults crossing the Eastern Desert towards the Nile Valley (Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5). Abdel-Rahman and El-Etr [101] deduced that the Cairo–Suez region is affected by three main normal fault trends: E–W, ENE–WSW, and NW–SE. Abou Elenean [102] computed the focal mechanism solution of the 1992 Dahshour earthquake. He concluded that the nodal planes are characterized by a normal-faulting mechanism with a large strike-slip component (Figure 5).
EG-10 covers the seismicity along the Nile Valley between 25° and 29° N latitudes (Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5). It lies to the west and adjacent to the EG-06 and EG-07 sources. Few historical and instrumental scattered earthquakes are located within the boundaries of this source (Figure 3 and Figure 4). Only nine historical earthquakes are reported here (felt intensities in the range V–VIII), during the period from 600 B.C. to 1850. The maximum observed magnitude within the boundaries of this zone corresponds to the April 857 A.D. (VIII, Mw 6.2), and the 20 February 1264 A.D. (VIII, Mw 6.2) earthquakes (Figure 3 and Figure 4). Different faulting mechanisms (thrust, normal and strike-slip faulting) could be concluded from the available focal mechanism solutions within this zone (Figure 5), which are mainly related to the dominant structural fault trends.
Finally, despite the occurrence of seismicity at the southern parts of Egypt (e.g., in the surroundings of Nasser’s Lake), the northwestern coast of Egypt, and the Western Desert of Egypt, the lack of GNNS data in these regions prevent us from estimating a reliable geodetic moment-rate. Hence, no further seismic sources were defined for these regions.
7. Estimation of Seismicity Parameters and Seismic Moment-Rates
The magnitude–frequency recurrence relationship (Equation (10)) by Gutenberg and Richter [18] describes the seismic activity within a certain seismic source.
N(m) is the annual number of earthquakes equal to or greater than a specific magnitude m, and a- and b-parameters characterize the seismicity within the source. The a-value indicates the seismicity level during a certain period, while the b-value provides indications about the low- to large-magnitude earthquakes ratio. The later parameter typically lies between 0.6 and 1.5 [48,103,104].
In order to estimate the seismicity parameters, separate earthquake sub-catalogs were created for each delimited source, considering only crustal earthquakes, i.e., earthquakes with depth less than 35 km. The seismicity recurrence parameters for the defined sources were estimated by applying the linear least-square method, taking into account the completeness period for each magnitude range [105] (Table 1 and Table 2). This method, as stated by the author, is the maximum likelihood estimation of the a- and b-parameters extended to the case of events grouped in magnitude with each group observed over individual periods. Additionally, the maximum expected magnitude (mmax) and its variance have been also determined following the Robson–Whitlock–Cooke methodology [106,107,108] (Equations (11) and (12)). It is an optimal approach when seismicity data, as happens to be the case for this region, are scarce or incomplete. Given an ordered set including n recorded magnitudes, m1 ≤ … ≤ mn−1 ≤ , maximum estimated magnitude (mmax) and its uncertainty (σ) are given by

Table 2.
Number of earthquakes (Mw ≥ 4.0), maximum recorded/observed magnitudes, D50 and D90 depth values, activity rates (≥Mw 4.0), and b-values of the Gutenberg–Richter relationship, maximum expected magnitudes (mmax), and the estimated seismic moment-rates for the proposed seismic sources. See the text for more explanation.
σM being the standard deviation of the maximum observed magnitude.
All estimated parameters for each seismic source and their associated uncertainties are reported in Table 2. Depths D50 and D90, the depths above which 50% and 90% of the earthquakes occur, respectively, were also computed. To do that, depths that seem to be artificial (equal to 0, 10, 30, and 33 km) were removed before the computation. Finally, D90 (in Table 2 and Table 3) has been proposed as the seismogenic depth for each source. Concerning uncertainty in the mmax value, when computing the model uncertainty given by Equation (12), it was considered conservatively that uncertainties () are equal to 0.6 previously to the year 1900, 0.5 in the period 1900–1962, 0.3 in the period 1962–2002, and 0.2 since 2002 [109].

Table 3.
Area of the proposed sources, seismogenic thickness (D90) with 10% variation for both lower and upper ranges, maximum strain (nanostrain/year), and their corresponding geodetic moment-rates. Seismic coupling coefficients (SCC %) estimated from the geodetic-seismic moment-rates ratio are also included.
Two sources need some additional explanation. In the EG-10 source, the largest magnitude values, corresponding to the 857 A.D. and 1264, Mw 6.2, earthquakes, do not follow the Gutenberg–Richter model (Table 2). Then, these two earthquakes have been considered as characteristic earthquakes. To include them, a constant seismic rate equal to 0.001 earthquakes by year (2 earthquakes every ~2000 years) in the magnitude interval [19] has been considered, being in this case equal to Mw 6.2, the biggest recorded magnitudes in the source, and equal to 0.6, the individual uncertainty for earthquakes before 1900. The second source is the EG-02 zone, initially presenting the same problem as the EG-10 one. In addition, the obtained b-value presents an odd high value, above 1.5, then providing an unrealistic seismic moment-rate. This is clearly due to the incompleteness of the seismic catalog in this source. Then, a rough seismic moment-rate estimation has been computed for this source by adding the individual seismic moment of earthquakes that occurred in the last 50 years; a time interval that includes some of the largest earthquakes that happened in this source, in addition to the biggest one, the 22 November 1995, Mw 7.2, earthquake. To compute it, the well-known relationship between seismic moment and moment magnitude by Hanks and Kanamori [110] has been used:
is the seismic moment, is the moment magnitude, and and are constants equal to 1.5 and 9.1, respectively, when defining in N·m.
In order to compute the seismic moment-rate for the rest of the delimited sources (EG-01, and from EG-03 to EG-09), the exact relationship by Youngs and Coppersmith [19] has been used, rewritten as the following:
The first term in the equation corresponds to the contribution of the Gutenberg–Richter exponential magnitude recurrence relationship, while the second one belongs to the characteristic earthquake model, considered uniformly distributed in the magnitude range . This second term is only considered for the source EG-10, for which, as quoted previously, the two largest recorded earthquakes have been considered as characteristic events. In order to compute this equation, b-value is obtained from Equation (10), , c comes from Equation (13), and and define the range in which the Gutenberg–Richter relationship is valid (Table 2), being the so-called threshold magnitude. In our assessment, has been set to zero, being then . In addition, is estimated using Equation (13), and is the annual rate for earthquakes exceeding magnitude .
Seismic moment-rate results from Equation (14) have been multiplied by the stochastic correction factor proposed by Hyndman and Weichert [111], that considers the asymmetry of the moment–magnitude relation, recognizing this as an important source of uncertainty. Obtained results are tabulated in Table 2.
8. Geodetic Moment-Rates
As mentioned above in the following computation, we refer to the results recently published by Rashwan et al. [61]. For each of the previously defined seismic source zones, the geodetic moment-rate was estimated by adopting the Savage and Simpson [20] formulation:
where μ is the shear modulus of the rocks (a constant value of 3.0 × 1010 N/m2 for the crustal rocks is used for all sources), Hs·A is the volume of the source zone with Hs representing its seismogenic thickness (D90, as stated before); εHmax and εhmin are the principal horizontal strain-rates (Figure 6 and Figure 7) as defined in Rashwan et al. [61], and Max is a function returning the largest of the arguments. Strain-rates values are almost homogeneous for most of the seismogenic source zones; however, additional considerations are required for the EG-03, EG-08, and EG-10 zones. In particular, the strain-rate estimation for EG-03 source is only concentrated on the western side of the region, while no estimations are available for the eastern side. Besides, strain-rates values are not homogeneous for EG-10 either, with values increasing southward. Due to this factor, the largest obtained strain-rate value in each source has been considered in the geodetic moment-rate computation. Furthermore, the north-western corner of EG-08 is characterized by large strain-rates, which could represent a computational boundary effect (due to stations located in Cyprus), being these values larger with respect to the well-constrained ones of the southern sector of the zone. Therefore, for this source, the largest strain-rate value used in the computation has been estimated by excluding the values inferred for the north-western area.
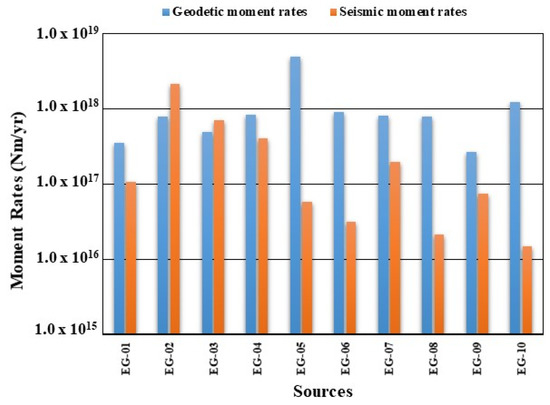
Figure 7.
Comparison between the estimated values of the geodetic and seismic moment-rates.
Keeping in mind these considerations, geodetic moment-rates for the EG-03, EG-08, and EG-10 sources should be considered with caution. Parameters and achieved results are reported in Table 3. Estimated values range in the interval 2.64 × 1017–4.93 × 1018 N·m/yr, with high values inferred for EG-05 and EG-10 seismic source zones, while low values were computed for sources EG-01 and EG-09.
9. Seismic-Geodetic Moment-Rates Ratio
The seismic-geodetic moment-rate ratios (in percentages) for the proposed seismic sources in Egypt are referred to herein as the “seismic coupling coefficient; SCC” [6,12]. The seismic moment-rate is a measure of the elastic unloading rate, and the geodetic moment-rate is a measure for both elastic and anelastic loading rates [6]. The resulting ratio between the seismic and geodetic moment-rates (SCC) theoretically ranges between 0 and 100%. Closer percentages to 100% reflect that a large amount of the deformation budget was released by earthquakes, however, lower percentages suggest either accumulating strain not released by earthquakes or a significant proportion of aseismic deformation [6]. The SCC exceeds the 100% value when seismic moment-rate values are greater than the geodetic ones, and is usually observed in areas where the seismic catalogs cover a relatively short time and contain large earthquakes [12].
The completeness period of the used seismic catalog, as well as its temporal span, may affect seismic moment-rate estimations for a studied region [1]. In other words, to estimate reliable seismic moment-rates, the average earthquake recurrence interval should be shorter than the duration of the catalog [9,12]. Available historical datasets for Egypt highlight the occurrence of large earthquakes (M ≥ 6.0) since 590 B.C. that could be considered to be complete for the same magnitude since the year 700 (0.0273 events/year; see Figure 2 and Table 1). Taking into consideration that the earthquake occurrences and their statistics are not steady-state over the entire time of the studied catalog, and being familiar that the truncated Gutenberg–Richter law allows the consideration of possible incompleteness of the used catalog [1], our seismic moment-rates for most of the defined source could be considered as reliable estimations. Regarding the geodetic moment-rate estimations, the GNSS measurements sample a relatively large spatial region, so that the data are not significantly affected by the local strain accumulation on any individual fault. Also, they cover a long enough temporal period, so that the uncertainties have a minimal effect on the velocity estimations, and hence they sample seismic, aseismic, and long-term deformation transients [6]. Recently, Sasajima et al. [112] observed an increase of the subsidence rate in the forearc region during the late period of the Mw 9.0 2021 Tohoku earthquake, therefore evidencing possible temporal variation of crustal deformation rates during the interseismic period of very large earthquakes. Moreover, Hussain et al. [112], pointed out that strain-rates derived from geodetic measurements around major transform faults are constant during the interseismic period, except for the ~10 years period following an earthquake. These observations suggest that significant temporal variations of crustal deformation rates would occur in fast convergent tectonic settings where very large earthquakes are expected, while in other tectonic settings, such as the one considered in this study, short-term geodetic observations can provide realistic contributions to long-term seismic hazard assessment.
In the following paragraphs we are going to discuss, compare and frame our results carefully with available geological and geophysical data.
The obtained seismic-geodetic moment-rates ratios (SCC%) are depicted in Figure 8 and tabulated in Table 3. Based on the estimated SCC results, we could consider three principal ratio ranges in the current study. Four delimited seismic sources are characterized by lower SCC values (less than 20%). They are the EG-05, EG-06, EG-08, and EG-10 seismic sources. They cover the seismicity along the central Red Sea region, the triple junction between the Gulf of Suez, Gulf of Aqaba, and the Red Sea, the northern Nile Delta block, and the central part of the Nile Valley, respectively (Figure 8). Such a result suggests that in these sectors, deformation occurs prevailingly in an aseismic mode. As mentioned above, moment-rates estimations for EG-08 and EG-10 must be considered with caution, being the computed strain-rates not homogeneously distributed within the seismic zones. Since the moment-rates estimations have been performed by taking into account the largest strain-rate values for both zones, we performed an additional computation by considering the average strain-rate value. Achieved results do not significantly alter the previous considerations, being the new SCC values increasing of a factor of 1.3 and 2.2 for the EG-08 and EG-10 zones, respectively.
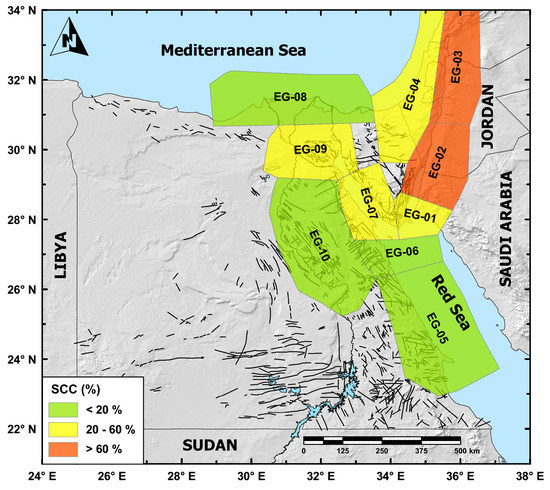
Figure 8.
Seismic coupling coefficient (SCC) is depicted as percentage of the seismic-geodetic moment-rate ratio.
Another ratio range is observed for the sources EG-01, EG-04, EG-07, and EG-09 (Figure 8), characterized by moderate SCC values (between 20% and 60%). They defined the seismic activity along the southern Gulf of Aqaba, northeastern Sinai and eastern Mediterranean coast, the southern and central parts of the Gulf of Suez, and the Cairo–Suez district and northern Gulf of Suez, respectively (Figure 8). Therefore, these moderate SCC values are suggesting that these areas account for only an intermediate seismic fraction from the total budget of the deformation rate. Some of these seismic regions are characterized by well-known active faults that frequently generate moderate seismic activity such as in the Cairo-Suez district, the southern and central half-grabens of the Gulf of Suez.
Finally, the highest SCC values (actually >100%, labeled as >60% in Figure 8) have been reached in the current study for the EG-02 and EG-03 seismic sources. Both zones are located along the GoA–DST which extends in the NE–SW direction. Such results suggest that the crustal deformation is mostly released through seismic activity. As mentioned above, strain-rate estimation for EG-03 concentrated only on the western side of the source, while no estimations are available for the eastern side. The high SCC value (Table 3) in this source points to an underestimation of the geodetic rates or an overestimation of the seismic ones, as discussed previously. The high seismic rate is well constrained because of the long-time interval covered by the catalog as well as the occurrence of some M ≥ 6.0 earthquakes (since 590 A.D.). Moreover, an underestimation of geodetic rates could be possible because of the existence of very few stations within the seismic zone, which therefore would not be enough to properly constrain the deformation pattern of active faults. Regarding the EG-02 source, seismic moment-rate, as explained previously, was computed from individually recorded earthquakes in the last 50 years. This implies that the obtained result must be also considered with care.
10. Summary and Conclusions
Although the comparison between the seismic and geodetic moment-rates implies several assumptions and approximations, it provides important insights into the seismic hazard of potential active tectonic regions. Despite the different approaches operated by several authors for different studied regions worldwide, their estimations and comparisons enabled the achievement of valuable results which sometimes document the agreements between geodetic and seismic moment-rates, and other times the larger values of the geodetic moment-rates against the seismic ones.
In the current work, an updated and Poissonian earthquake catalog (2200 B.C.–2020 A.D.) for Egypt, focal mechanism solutions (1951–2019) coming from previous publications, and the original GNSS data were used to study the spatial and temporal seismic and geodetic moment patterns. An attempt has been made to compare the seismic and geodetic moment-rates in order to provide a statistical estimation for the deformation budget in the surroundings of Egypt and therefore to give more insights into the seismic hazard of the studied region. Considering the geological and tectonic settings of the studied region as well as the previously mentioned data (seismicity, focal mechanisms, and GNSS data), ten broad shallow crustal seismic sources (EG-01 to EG-10; h < 35 km) have been delimited. These zones mainly cover the potential shallow active seismic regions along the GoA–DST, the Gulf of Suez–Red Sea Rift, and the Nile River and its delta. The lack of GPS data in other regions (e.g., Aswan region, northwestern coast, and the Western Desert of Egypt) prevent us from estimating the geodetic moment-rate, hence no further seismic sources were defined for these regions. The different seismicity parameters (average annual activity rate, maximum observed magnitude, seismogenic depth, b-value, and maximum expected magnitude) were estimated for the proposed sources both for the Gutenberg–Richter and the characteristic earthquake models, when necessary, taking into account the completeness period for each magnitude range. The seismic and geodetic moment-rates have been computed, using the previously mentioned algorithms, for the delimited seismic sources.
The estimation of such rates was challenging for several reasons. The heterogeneous coverage of the GNSS data in some regions (e.g., strain-rate estimation for EG-03, EG-08, and EG-10 sources), the incompleteness of the earthquake sub-catalog (e.g., unexpected high b-values for EG-02 and EG-05 zones), and the own computation of seismic moment-rate for some sources (EG-02 and EG-10) were the most difficult problems in this work. Keeping in mind these considerations, geodetic and seismic moment-rates for some sources should be considered with caution.
Based on the computed seismic-geodetic moment-rate ratio (seismic coupling coefficient “SCC”) for the studied sources, three main categories were differentiated according to their seismic behavior in and around Egypt. The first region/category comprises a large sector of the delimited sources: the Red Sea, the Gulf of Aqaba, the Nile Delta, and the Nile Valley (EG-05, EG-06, EG-08, and EG-10 sources). They are characterized by low SCC values (<20%), evidencing the aseismic deformation behavior. The second region, characterized by moderate SCC values (between 20% and 60%), comprises the southern Gulf of Aqaba, northeastern Sinai and the Eastern Mediterranean coast, the Gulf of Suez, and the Cairo–Suez district (EG-01, EG-04, EG-07, and EG-09 sources). Such moderate SCC values confirm that the crustal earthquake activity for this region accounts only for a moderate fraction of the total budget of deformation. Finally, the third region that has higher SCC values extends along the GoA–DST (EG-02 and EG-03 sources). These values highlight a fully seismic deformation behavior in this region.
In conclusion, the results obtained in the current study provide the basis of the evaluation of the completeness periods of the earthquake catalog, guide the spatial delimitation, definition, and characterization of the potential seismic active sources for future seismotectonics and probabilistic seismic hazard assessment studies, and motivation for the integration of geodetic data with the seismic data for seismic hazard studies.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, all authors; methodology, R.S., J.A.P. and M.P.; software, R.S., J.A.P. and M.P.; validation, J.A.P. and M.P.; formal analysis, R.S., J.A.P. and M.P.; investigation, R.S., J.A.P. and M.P.; resources, R.S., A.M.R. and M.R.; data curation, R.S., J.A.P. and M.P.; writing—original draft preparation, R.S.; writing—review and editing, R.S., J.A.P., F.S. and M.P.; visualization, R.S.; supervision, R.S., J.A.P. and M.P.; project administration, J.A.P. and M.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research has been partially funded in the frame of the Programa Operativo FEDER Andalucía 2014–2020-call made by the University of Jaén, 2018.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the authors.
Acknowledgments
Authors are grateful to the staff members of both the Egyptian National Seismic Network (Seismology Department) and the Crustal Movement Laboratory (Geodynamics Department) of the National Research Institute of Astronomy and Geophysics (NRIAG), Cairo, Egypt, for providing access to local seismic data and helping with GNSS data acquisition.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ward, S.N. On the consistency of earthquake moment rates, geological fault data, and space geodetic strain: The United States. Geophys. J. Int. 1998, 134, 172–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blewitt, G.; Lavallée, D. Effect of annual signals on geodetic velocity. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2002, 107, ETG 9-1–ETG 9-11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palano, M.; Imprescia, P.; Agnon, A.; Gresta, S. An improved evaluation of the seismic/geodetic deformation-rate ratio for the Zagros Fold-and-Thrust collisional belt. Geophys. J. Int. 2018, 213, 194–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palano, M.; Cannavò, F.; Ferranti, L.; Mattia, M.; Mazzella, M.E. Strain and stress fields in the Southern Apennines (Italy) constrained by geodetic, seismological and borehole data. Geophys. J. Int. 2011, 187, 1270–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferranti, L.; Palano, M.; Cannavò, F.; Mazzella, M.E.; Oldow, J.S.; Gueguen, E.; Mattia, M.; Monaco, C. Rates of geodetic deformation across active faults in southern Italy. Tectonophysics 2014, 621, 101–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparacino, F.; Palano, M.; Peláez, J.A.; Fernández, J. Geodetic deformation versus seismic crustal moment-rates: Insights from the Ibero-Maghrebian region. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Masson, F.; Chéry, J.; Hatzfeld, D.; Martinod, J.; Vernant, P.; Tavakoli, F.; Ghafory-Ashtiani, M. Seismic versus aseismic deformation in Iran inferred from earthquakes and geodetic data. Geophys. J. Int. 2005, 160, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilham, R.; Ambraseys, N. Apparent Himalayan slip deficit from the summation of seismic moments for Himalayan earthquakes, 1500–2000. Curr. Sci. 2005, 88, 1658–1663. [Google Scholar]
- Pancha, A.; Anderson, J.G.; Kreemer, C. Comparison of seismic and geodetic scalar moment rates across the Basin and Range province. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2006, 96, 11–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rontogianni, S. Comparison of geodetic and seismic strain rates in Greece by using a uniform processing approach to campaign GPS measurements over the interval 1994–2000. J. Geodyn. 2010, 50, 381–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mazzotti, S.; Leonard, L.J.; Cassidy, J.F.; Rogers, G.C.; Halchuk, S. Seismic hazard in western Canada from GPS strain rates versus earthquake catalog. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palano, M.; Imprescia, P.; Gresta, S. Current stress and strain-rate fields across the Dead Sea Fault System: Constraints from seismological data and GPS observations. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2013, 369–370, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chousianitis, K.; Ganas, A.; Evangelidis, C.P. Strain and rotation rate patterns of mainland Greece from continuous GPS data and comparison between seismic and geodetic moment release. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2015, 120, 3909–3931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bos, A.G.; Spakman, W. Kinematics of the southwestern U.S. deformation zone inferred from GPS motion data. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2005, 110, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- D’Agostino, N. Complete seismic release of tectonic strain and earthquake recurrence in the Apennines (Italy). Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 1155–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, V.L.; Avouac, J.P. Millenary Mw > 9.0 earthquakes required by geodetic strain in the Himalaya. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 1118–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gutenberg, B.; Richter, C.F. Seismicity of the Earth; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1954. [Google Scholar]
- Youngs, R.R.; Coppersmith, K.J. Implications of fault slip rates and earthquake recurrence models to probabilistic seismic hazard estimates. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. Geomech. Abstr. 1986, 23, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savage, J.C.; Simpson, R. Surface strain accumulation and the seismic moment tensor. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 1997, 87, 1345–1353. [Google Scholar]
- Zolfaghari, M.R. Geodetic deformation vs. seismic strain deduced by historical earthquakes across the Alborz Mountains. J. Seismol. 2009, 13, 647–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenzie, D. Active Tectonics of the Mediterranean Region. Geophys. J. Int. 1972, 30, 109–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ben-Menahem, A.; Nur, A.; Vered, M. Tectonics, seismicity and structure of the Afro-Eurasian junction—The breaking of an incoherent plate. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 1976, 12, 1–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Avraham, Z.; Nur, A.; Giuseppe, C. Active transcurrent fault system along the North African passive margin. Tectonophysics 1987, 141, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WCC-Woodward Clyde Consultants. Earthquake Activity and Stability Evaluation for the Aswan High Dam; Submitted to Aswan High Dam Authority; Ministry of Irrigation: Aswan, Egypt, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Kebeasy, R. Seismicity. In The Geology of Egypt; A.A. Balkerma: Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 1990; pp. 51–59. [Google Scholar]
- DeMets, C.; Gordon, R.G.; Argus, D.F. Geologically current plate motions. Geophys. J. Int. 2010, 181, 1–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coleman, R.G. Geologic background of the Red Sea. In The Geology of Continental Margins; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1974; pp. 743–751. [Google Scholar]
- Hempton, M.R. Constraints on Arabian Plate motion and extensional history of the Red Sea. Tectonics 1987, 6, 687–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosworth, W.; Mcclay, K. Structural and stratigraphic evolution of the Gulf of Suez Rift, Egypt: A synthesis. In Peri-Tethys Memoir 6: Peri-Tethyan Rift/Wrench Basins and Passive Margins; Ziegler, P.A., Cavazza, W., Robertson, A.H.F., Crasquin-Soleau, S., Eds.; French National Museum of Natural History: Paris, France, 2001; pp. 567–606. ISBN 2-85653-528-3. [Google Scholar]
- Schlumberger. Geology of Egypt. In Well Evaluation Conference; Schlumberger: Cairo, Egypt, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Freund, R.; Garfunkel, Z.; Zak, I. The Shear along the Dead Sea Rift. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. 1970, 267, 107–130. [Google Scholar]
- Salamon, A.; Hofstetter, A.; Garfunkel, Z.; Ron, H. Seismotectonics of the Sinai subplate—The eastern Mediterranean region. Geophys. J. Int. 2003, 155, 149–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bartov, Y.; Steinitz, G.; Eyal, M.; Eyal, Y. Sinistral movement along the Gulf of Aqaba—Its age and relation to the opening of the Red Sea. Nature 1980, 285, 220–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joffe, S.; Garfunkel, Z. Plate kinematics of the circum Red Sea—A re-evaluation. Tectonophysics 1987, 141, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sneh, A. The Dead Sea Rift: Lateral displacement and downfaulting phases. Tectonophysics 1996, 263, 277–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marco, S.; Agnon, A.; Ellenblum, R.; Eidelman, A.; Basson, U.; Boas, A. 817-Year-old walls offset sinistrally 2.1 m by the Dead Sea transform, Israel. J. Geodyn. 1997, 24, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garfunkel, Z.; Zak, I.; Freund, R. Active faulting in the dead sea rift. Tectonophysics 1981, 80, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zilberman, E.; Amit, R.; Heimann, A.; Porat, N. Changes in Holocene Paleoseismic activity in the Hula pull-apart basin, Dead Sea Rift, northern Israel. Tectonophysics 2000, 321, 237–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amit, R.; Zilberman, E.; Porat, N.; Enzel, Y. Relief Inversion in the Avrona Playa as Evidence of Large-Magnitude Historical Earthquakes, Southern Arava Valley, Dead Sea Rift. Quat. Res. 1999, 52, 76–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinger, Y.; Avouac, J.P.; Abou Karaki, N.; Dorbath, L.; Bourles, D.; Reyss, J.L. Slip rate on the Dead Sea transform fault in northern Araba valley (Jordan). Geophys. J. Int. 2000, 142, 755–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gomez, F.; Meghraoui, M.; Darkal, A.N.; Hijazi, F.; Mouty, M.; Suleiman, Y.; Sbeinati, R.; Darawcheh, R.; Al-Ghazzi, R.; Barazangi, M. Holocene faulting and earthquake recurrence along the Serghaya branch of the Dead Sea fault system in Syria and Lebanon. Geophys. J. Int. 2003, 153, 658–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sawires, R.; Peláez, J.A.; Fat-Helbary, R.E.; Panzera, F.; Ibrahim, H.A.; Hamdache, M. Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Deaggregation for Selected Egyptian Cities. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2017, 174, 1581–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamel, H.; Eita, T.; Sarhan, M. Nile delta hydrocarbon potentiality. In Proceedings of the 14th Egyptian General Petroleum Corporation Exploration and Production Conference, Cairo, Egypt, 15–18 October 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Meshref, W. Tectonic framework. In The Geology of Egypt; Said, R., Ed.; A.A. Balkerma: Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 1990; pp. 113–155. [Google Scholar]
- Younes, A.I.; McClay, K. Development of accommodation zones in the Gulf of Suez-Red Sea Rift, Egypt. Am. Assoc. Pet. Geol. Bull. 2002, 86, 1003–1026. [Google Scholar]
- Heidbach, O.; Ben-Avraham, Z. Stress evolution and seismic hazard of the Dead Sea Fault System. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2007, 257, 299–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sawires, R.; Peláez, J.A.; Fat-helbary, R.E.; Ibrahim, H.A. An earthquake catalogue (2200 B.C. to 2013) for seismotectonic and Seismic Hazard Assessment Studies in Egypt. In Earthquakes and Their Impact on Society; D’Amico, S., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 97–136. ISBN 9783319217536. [Google Scholar]
- Abd El–Aal, A.E.-A.K.; AbdelHafiez, H.E.; Saadalla, H.; Soliman, M.S. A homogenous moment magnitude and local magnitude scaling relation for earthquakes in Egypt. NRIAG J. Astron. Geophys. 2020, 9, 532–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ataeva, G.; Shapira, A.; Hofstetter, A. Determination of source parameters for local and regional earthquakes in Israel. J. Seismol. 2015, 19, 389–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deif, A.; Al-Shijbi, Y.; El-Hussain, I.; Ezzelarab, M.; Mohamed, A.M.E. Compiling an earthquake catalogue for the Arabian Plate, Western Asia. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2017, 147, 345–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawires, R.; Peláez, J.A.J.A.; AlHamaydeh, M.; Henares, J. A state-of-the-art seismic source model for the United Arab Emirates. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2019, 186, 104063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, J.K.; Knopoff, L. Is the sequence of earthquakes in Southern California, with aftershocks removed, Poissonian? Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 1974, 64, 1363–1367. [Google Scholar]
- Sawires, R.; Santoyo, M.A.; Peláez, J.A.; Corona Fernández, R.D. An updated and unified earthquake catalog from 1787 to 2018 for seismic hazard assessment studies in Mexico. Sci. Data 2019, 6, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- AbdelHafiez, H.E.; Tawfiek, A. A review of the Egyptian National Seismological Network after 20 years of operation. NRIAG J. Astron. Geophys. 2020, 9, 330–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moustafa, S.S.R.; Deif, A. A magnitude scale for Egyptian National Seismic Network (ENSN). NRIAG J. Geophys. 2009, 32, 633–651. [Google Scholar]
- Poirier, J.P.; Taher, M.A. Historical seismicity in the near and Middle East, North Africa, and Spain from Arabic documents (VIIth-XVIIIth century). Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 1980, 70, 2185–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maamoun, M.; Allam, A.; Megahed, A. Seismicity of Egypt. Bull. Helwan Inst. Astron. Geophys. 1984, 4, 109–160. [Google Scholar]
- Ambraseys, N.N.; Melville, C.P.; Adams, R.D. The Seismicity of Egypt, Arabia and the Red Sea: A Historical Review; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Badawy, A. Historical seismicity of Egypt. Acta Geod. Geophys. Hung. 1999, 34, 119–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashwan, M.; Sawires, R.; Radwan, A.M.; Sparacino, F.; Peláez, J.A.; Palano, M. Crustal Strain and Stress Fields in Egypt from Geodetic and Seismological Data. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EGSA Egyptian Geological Survey Authority. Geological Map of Egypt; Egyptian Geological Survey: Cairo, Egypt, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Garfunkel, Z. Internal structure of the Dead Sea leaky transform (rift) in relation to plate kinematics. Tectonophysics 1981, 80, 81–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girdler, R.W. The Dead Sea transform fault system. Tectonophysics 1990, 180, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, Y.; Masson, F.; Meghraoui, M.; Cakir, Z.; Alchalbi, A.; Yavasoglu, H.; Yönlü, O.; Daoud, M.; Ergintav, S.; Inan, S. Kinematic study at the junction of the East Anatolian fault and the Dead Sea fault from GPS measurements. J. Geodyn. 2013, 67, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyal, M.; Eyal, Y.; Bartov, Y.; Steinitz, G. The tectonic development of the western margin of the Gulf of Elat (Aqaba) rift. Tectonophysics 1981, 80, 39–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Fattah, A.K.; Hussein, H.M.; Ibrahim, E.M.; El Atta, A.S.A. Fault plane solutions of the 1993 and 1995 Gulf of Aqaba earthquakes and their tectonic implications. Ann. Geophys. 1997, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinar, A.; Türkelli, N. Source inversion of the 1993 and 1995 Gulf of Aqaba earthquakes. Tectonophysics 1997, 283, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofstetter, A.; Thio, H.K.; Shamir, G. Source mechanism of the 22/11/1995 Gulf of Aqaba earthquake and its aftershock sequence. J. Seismol. 2003, 7, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, H.M.; Abou Elenean, K.M.; Marzouk, I.A.; Korrat, I.M.; Abu El-Nader, I.F.; Ghazala, H.; ElGabry, M.N. Present-day tectonic stress regime in Egypt and surrounding area based on inversion of earthquake focal mechanisms. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2013, 81, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapira, A.; Jarradat, M. Earthquake Risk and Loss Assessment in Aqaba and Eilat Regions; Submitted to the U.S. Aid-Merc Program; 1995; Available online: https://scholar.google.com/scholar?hl=en&as_sdt=0%2C5&q=Earthquake+Risk+and+Loss+Assessment+in+Aqaba+and+Eilat+Regions+1995&btnG= (accessed on 23 August 2021).
- Reches, Z.; Hoexter, D.F. Holocene seismic and tectonic activity in the Dead Sea area. Tectonophysics 1981, 80, 235–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimann, A. The Development of the Dead Sea Rift and Its Margins in Northern Israel in the Pliocene and Pleistocene; The Hebrew University of Jerusalem: Jerusalem, Israel, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Gardosh, M.; Reches, Z.; Garfunkel, Z. Holocene tectonic deformation along the western margins of the Dead Sea. Tectonophysics 1990, 180, 123–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinitz, G.; Bartov, Y.; Hunziker, J.C. K-Ar age determinations of some Miocene–Pliocene basalts in Israel: Their significance to the tectonics of the Rift Valley. Geol. Mag. 1978, 115, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cochran, J.R.; Martinez, F.; Steckler, M.S.; Hobart, M.A. Conrad deep: A new northern Red Sea deep. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1986, 78, 18–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roeser, H.A. A detailed magnetic survey of the Southern Red Sea—Hans Albert Roeser—Google Books. Geol. Jahrb. 1975, 13, 131–153. [Google Scholar]
- Makris, J.; Rihm, R. Shear-controlled evolution of the Red Sea: Pull apart model. Tectonophysics 1991, 198, 441–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Searle, R.C.; Ross, D.A. A Geophysical Study of the Red Sea Axial Trough between 20*5 and 22 N. Geophys. J. Int. 1975, 43, 555–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McKenzie, D.P.; Davies, D.; Molnar, P. Plate Tectonics of the Red Sea and East Africa. Nature 1970, 226, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosworth, W.; Taviani, M. Late Quaternary reorientation of stress field and extension direction in the southern Gulf of Suez, Egypt: Evidence from uplifted coral terraces, mesoscopic fault arrays, and borehole breakouts. Tectonics 1996, 15, 791–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustafa, A.R. Internal structure and deformation of an accommodation zone in the northern part of the Suez rift. J. Struct. Geol. 1996, 18, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyberis, N. Tectonic evolution of the Gulf of Suez and the Gulf of Aqaba. Tectonophysics 1988, 153, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosworth, W. A high-strain rift model for the southern Gulf of Suez (Egypt). Geol. Soc. Spec. Publ. 1995, 80, 75–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chorowicz, J.; Sorlien, C. Oblique extensional tectonics in the Malawi Rift, Africa. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1992, 104, 1015–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daggett, P.H.; Morgan, P.; Boulos, F.K.; Hennin, S.F.; El-Sherif, A.A.; El-Sayed, A.A.; Basta, N.Z.; Melek, Y.S. Seismicity and active tectonics of the Egyptian Red Sea margin and the northern Red Sea. Tectonophysics 1986, 125, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurukawa, N.; Seto, N.; Inoue, H.; Nishigami, K.; Marzouk, I.; Megahed, A.; Ibrahim, E.M.; Murakami, H.; Nakamura, M.; Haneda, T.; et al. Seismological Observations in and around the Southern Part of the Gulf of Suez, Egypt. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2001, 1994, 708–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-fattah, A.K. An approach to investigate earthquake source processes. Acta Geol. Pol. 2003, 51, 257–269. [Google Scholar]
- Gergawi, A.; El-Khashab, A. Seismicity of U.A.R. Bull. Helwan Inst. Astron. Geophys. 1986, 76. [Google Scholar]
- Fairhead, J.D.; Girdler, R.W. The seismicity of the Red Sea, Gulf of Aden and Afar Triangle. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. 1970, 267, 49–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maamoun, M.; El-Khashab, H.M. Seismic studies of the Shedwan (Red Sea) earthquake. Bull. Helwan Inst. Astron. Geophys. 1978, 171, 22–46. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, J.; McKenzie, D. Active tectonics of the Alpine–Himalayan Belt between western Turkey and Pakistan. Geophys. J. R. Astron. Soc. 1984, 77, 185–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou Elenean, K.M. Focal Mechanisms of Small and Moderate Size Earthquakes Recorded by the Egyptian National Seismic Network (ENSN), Egypt. NRIAG J. Geophys. 2007, 6, 117–151. [Google Scholar]
- Sandford, K.S. Paleolithic man and the Nile Valley in Upper and Middle Egypt. Chic. Univ. Orient. Inst. Publ. 1934, 18, 1–131. [Google Scholar]
- Said, R. The Geology of Egypt; Elservier: New York, NY, USA, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Issawi, B. Geology of the South Western Desert of Egypt. Ann. Geol. Surv. Egypt 1981, 2, 57–66. [Google Scholar]
- Philobbos, E.R.; Riad, S.; Omran, A.A.; Othman, A.B. Stages of fracture development controlling the evolution of the Nile Valley in Egypt. Egypt J. Geol. 2000, 44, 503–532. [Google Scholar]
- Said, R. The Geological Evolution of the River Nile; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel Aal, A.; El-Barkooky, A.; Gerrites, M.; Meyer, H.; Schwander, M.; Zaki, H. Tectonic evolution of the Eastern Mediterranean Basin and its significance for hydrocarbon productivity in the ultra-deep water of the Nile Delta. In Proceedings of the Mediterranean Offshore Conference, Alexandria, Egypt, 15–17 October 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Maamoun, M.; Ibrahim, E.M. Tectonic activity in Egypt as indicated by earthquakes. Bull. Helwan Inst. Astron. Geophys. 1978, 170, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Rahman, M.A.; El-Etr, H.A. The orientational characteristics of the structure grain of the eastern desert of Egypt. In Proceedings of the Symposium of the Evolution and Mineralization of the Arabian-Nubian Shield, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia, 3–5 February 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Abou Elenean, K.M. Seismotectonics of Egypt in Relation to the Mediterranean and Red Sea Tectonics. Ph.D. Thesis, Ain Shams University, Cairo, Egypt, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, P.K.; Ghosh, M.; Chakraborty, P.P.; Mukherjee, D. Seismic b-Value and the Assessment of Ambient Stress in Northeast India. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2011, 168, 1693–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pelaez, J.A.; Hamdache, M.; Sanz de Galdeano, C.; Sawires, R.; Garcia Hernandez, M.T. Forecasting moderate earthquakes in Northern Algeria and Morocco. In Earthquakes and Their Impact on Society; D’Amico, S., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 81–95. ISBN 9783319217536. [Google Scholar]
- Weichert, D.H. Estimation of the earthquake recurrence parameters for unequal observation periods for different magnitudes. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 1980, 70, 1337–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robson, D.S.; Whitlock, J.H. Estimation of a truncation point. Biometrika 1964, 51, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, P. Statistical inference for bounds of random variables. Biometrika 1979, 66, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kijko, A.; Singh, M. Statistical Tools for Maximum Possible Earthquake Magnitude Estimation. Acta Geophys. 2011, 59, 674–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sawires, R.; Peláez, J.A.; Ibrahim, H.A.; Fat-Helbary, R.E.; Henares, J.; Hamdache, M. Delineation and characterization of a new seismic source model for seismic hazard studies in Egypt. Nat. Hazards 2016, 80, 1823–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanks, T.C.; Kanamori, H. A moment magnitude scale. J. Geophys. Res. 1979, 84, 2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyndman, R.D.; Weichert, D.H. Seismicity and rates of relative motion on the plate boundaries of Western North America. Geophys. J. Int. 1983, 72, 59–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sasajima, R.; Shibazaki, B.; Iwamori, H.; Nishimura, T.; Nakai, Y. Mechanism of subsidence of the Northeast Japan forearc during the late period of a gigantic earthquake cycle. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hussain, E.; Wright, T.J.; Walters, R.J.; Bekaert, D.P.S.; Lloyd, R.; Hooper, A. Constant strain accumulation rate between major earthquakes on the North Anatolian Fault. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).