Abstract
Even at historically low levels of air pollution, epidemiological time series studies carried out in cities across the globe have documented its substantial detrimental health effects. A time series analysis of counts of respiratory hospital admissions in Gjakova and outdoor air pollutants was performed, applying a General Additive Model with a Poisson distribution, controlling for time trends and meteorological factors over a 4-year period (2020–2023) with different time lags (0–7 days). The effects were further analyzed per age group (children and adults). We found significant associations between gaseous pollutants, mainly NO2, and respiratory disease-related hospital admissions in the city. The strongest association between NO2 and total hospital admissions was observed after a lag of 6 days, with an increase of 0.14 cases per 10 μg/m3 increase in concentration. The effects were stronger in adults. An adverse effect was also seen with SO2, but not particulate pollution. Our findings call for greater awareness regarding environmental protection and the implementation of effective measures to improve air quality, which may reduce the risk of adverse health effects.
1. Introduction
Air pollution is now recognized as the single greatest environmental threat to human health based on its notable contribution to the burden of disease [1]. Qualitatively, it has the same negative effects as smoking tobacco, putting everyone, including unborn children, women cooking over open fires, and children walking to school, at risk [2,3].
Air pollution is the most pressing environmental health risk facing the global population. Despite efforts to control and reduce air pollution in many countries, ambient air pollution in both urban and rural areas was estimated to have an association with up to 7 million premature deaths per year, and 92% of the world population lives in places where air quality levels exceed the World Health Organization’s (WHO) safety limits [4]. This assessment was still based on the older WHO air quality levels that had been updated and reduced in 2021 [1]. In light of the new data, the situation is even worse. According to the WHO [5], in 2019, 99% of the world’s population lived in places where air pollution levels exceeded WHO guideline limits, and according to Statista [6], more than 8 million people died in 2021 due to air pollution (outdoor and indoor).
Therefore, more research is needed to support better informed policies, particularly in low- and middle-income countries. Reducing hazards to public health due to air pollution through targeted emissions control techniques requires identifying the elements, physical attributes, and/or sources of air pollution that have the most severe effects on human health [7].
The potentially deleterious effect of episodes of high air pollution on health has been confirmed for more than 50 years, but the health effects of air pollution by source or environmental setting still require investigation [8]. A large number of recent research findings have strengthened the link between short- and long-term exposure to air pollution and the risk of hospitalization, morbidity, and mortality [9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20].
Exposure to outdoor air pollution is ubiquitous and has numerous adverse health effects, such as an increased risk of heart disease, respiratory infections, lung cancer, a shortened life expectancy, and mortality. The health of susceptible and sensitive individuals can be impacted even when air pollution indices are low. Genetics, comorbidities, nutrition, and socioeconomic factors also impact a person’s susceptibility to air pollution. In particular, people with a lower socioeconomic status are not only more vulnerable to a given concentration of pollutants but are also more likely to be exposed to higher concentrations. Children, the elderly, people with chronic diseases, people with low socioeconomic status, and people suffering from acute infectious diseases are most susceptible to polluted air [21].
Air pollution is positively associated with hospital admission for cardiovascular [22] and respiratory diseases [23]. Therefore, improving air quality can have long-term health benefits: lowering air pollution levels lowers the risk of stroke, heart disease, lung cancer, and both acute and chronic respiratory conditions, such as asthma [24].
Ambient pollution comprises several measurable pollutants, such as particulate matter (PM) of varying sizes (smaller than 2.5 or 10 µm in diameter, PM2.5 and PM10, respectively), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), sulfur dioxide (SO2), carbon monoxide (CO), and ozone (O3). Interest has increased in the extent of their effects on a host of health outcomes, ranging from low birth weight to cancer mortality [25,26]. Although the main focus of research is on particulate pollution, mounting evidence indicates that gaseous pollutants also affect health [27,28,29,30,31].
Even at relatively low levels, PM2.5 and NO2 can be used to predict acute and subacute fatal effects of urban air pollution [32] and hospitalization outcomes, suggesting the absence of a threshold. Deaths accrue over 14 days following an increase in air pollutants, even when harvesting is accounted for [33,34]. Associations between particulate air pollution and hospital admissions for respiratory causes have been investigated in numerous publications. Many of these studies applied a time series design in which the daily number of hospital admissions was linked to daily concentrations of outdoor air pollutants. Numerous epidemiological studies have shown associations between outdoor air pollution and adverse respiratory outcomes; in particular, traffic-related air pollution has been linked to severe respiratory health effects, especially in children [35,36,37,38,39,40].
The population of the Western Balkans and Eastern Europe is exposed to some of the highest air pollution concentrations in Europe; in addition to exceeding the WHO’s Air Quality Guideline, they may be up to five times higher than national and EU guideline levels [3,41]. Air quality has generally decreased due to large-scale urbanization and economic development that has largely relied on the burning of fossil fuels. Disparities in air pollution exposure are, therefore, increasing worldwide, including in Kosovo [42].
In Kosovo, indoor and outdoor air pollution have a considerable impact on public health. Despite this, they have received little attention in the past. Kosovo does not differ largely from other Balkan countries in this regard [43,44].
The main factors contributing to ambient air pollution in Kosovo have been identified as energy production in large, outdated, coal-fired power plants, industry, transportation, agriculture, waste disposal, and the consumption of solid fuels, mostly for domestic heating, in combination with unfavorable meteorological conditions for the distribution of emitted pollutants into the ambient air, especially during the winter (November to January) when smog episodes are frequent [45,46].
Kosovo, like several other Balkan countries, faces serious problems with ambient air quality, resulting in negative health effects for the entire population, for example, cardiovascular and respiratory diseases, and premature mortality. The selection of measures to reduce emissions requires a substantial scientific basis for informed decision-making, such as emission inventories and projections, emissions models, air quality measurements, data on the status of emissions reduction equipment, and the rates of implementation of these measures. The effective implementation of the selected measures will further depend on policy, i.e., existing and planned policy instruments, the readiness to harmonize national legislation with EU legislation, assigned responsibilities, practical mechanisms for implementing decisions, and the preconditions for introducing new policy instruments [47].
Each year, air pollution causes between 302 and 330 new cases of chronic bronchitis, 590–640 hospital admissions, and 11,300–12,500 emergency visits [48]. Other effects of air pollution in Kosovo include acute respiratory diseases; worsening condition of patients suffering from heart diseases, respiratory diseases, and asthma; cancer caused directly by pollutants; eye or nose irritation; stress; and a loss of welfare in general [46].
Despite ongoing problems with air quality in Kosovo, there is a scarcity of epidemiological studies conducted in the region, and effect estimates (as reported above) mostly depend on health impact assessments, making use of effect estimates from other regions.
Therefore, the purpose of this study was to evaluate the relationship between the effects of air pollution and the risk of hospitalization for total respiratory admissions. We postulated that the trend of increasing hospital admissions would be linked to increases in PM, O3, CO, NO2, and SO2 levels.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Admissions Data
The municipality of Gjakova ranks third in Kosovo in terms of surface area, with a total of 586.62 km2, and is situated at an altitude of 335 m. The municipality is characterized by a continental climate with hot summers and cold winters, where the hottest month is August and the coldest month is January. According to the last population census, the Municipality of Gjakova has a total of 78,699 inhabitants [49].
After receiving ethical approval from the Ethical Committee of the Faculty of Medicine in Gjakova, we obtained daily respiratory disease-related hospital admissions data for the period from 1 January 2020 to 31 December 2023. Due to a lack of electronic data, data on daily hospital admissions due to lung disease were obtained manually from the protocols of the Pediatric and Pulmonology Departments for children and adults, respectively, of the Regional Hospital “Isa Grezda” in Gjakovo. This hospital serves almost the entire population of Gjakova, Northern Albania, and the surrounding area.
The number of daily respiratory admissions of children, adults, and both were recorded based on the International Classification of Diseases, version 10 (ICD-10) codes; J00–J99 were used for total respiratory admissions.
2.2. Environmental Data
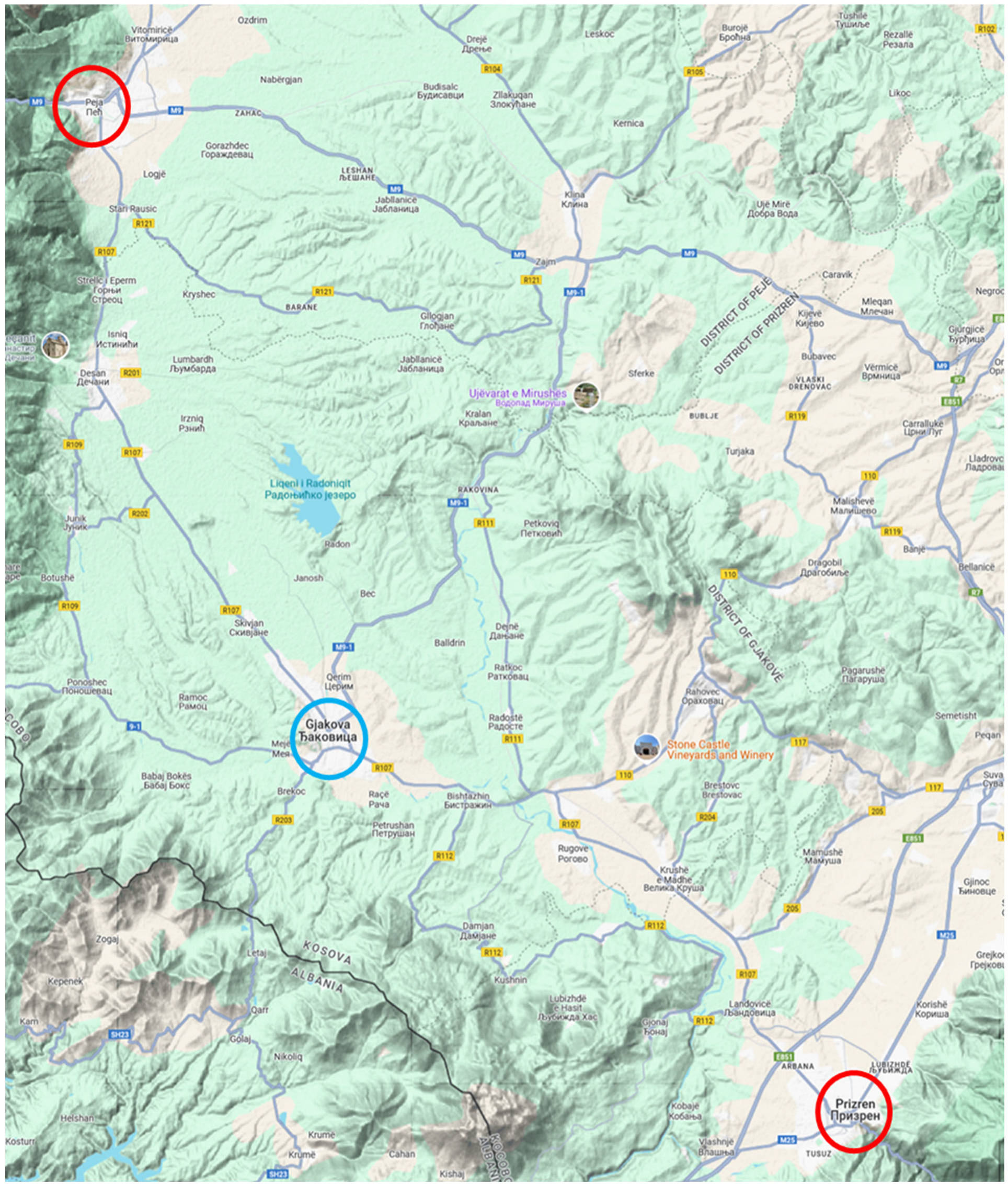
Daily data for carbon monoxide (CO), sulfur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), and particulate matter with a diameter of less than 10 or 2.5 µm (PM10 and PM2.5, respectively) were obtained from monitoring stations in Peja and Prizren because there is no station in the city of Gjakova, which is situated between these two locations. Although the maximal daily 8 h concentration was reported for O3, the daily average concentration was used for the other pollutants. All values were given in µg/m3 except for the CO concentration, which was reported in mg/m3. The locations of the monitoring stations in relation to Gjakova are shown in Figure A1.
Data from the monitoring network were provided by the Kosovo Hydro-Meteorological Institute (KHMI) and reported to the European Environment Agency (EEA) [50] and are published on the KHMI website [51].
This study primarily used data from the monitoring station in Prizren. To cope with missing data, data from the station in Peja were compared. The data from the two stations were sufficiently correlated, allowing for a calculation of the values missing from the Prizren data series. Unfortunately, complete lockdowns of the stations often occurred simultaneously. If the lockdown lasted a single day (which happened on three occasions), the missing data were calculated as the average of the data for the preceding and following days. On five occasions, gaps of more than 1 day occurred (28–30, 5, 2021; 9–11, 10, 2021; 12–13, 12, 2021; 9–10, 8, 2023; 14–27, 9, 2023). In these cases, the data remained unavailable.
The daily average temperature and humidity for Prizren station were obtained from annual meteorological reports [52]. Again, single missing days were interpolated, leaving no data gaps.
2.3. Statistical Analysis
The temporal association between air pollutants and case numbers was studied using R. For the main analysis, a general additive model (GAM) was used, assuming a Poisson distribution. The following parameters were considered possible confounders of the temporal association: (a) A long-term and seasonal trend modeled as a natural spline. As we discussed in our review on time series analysis [53], these models usually apply 3 to 7 knots per year. Therefore, we applied 5 knots per year or 20 knots in total. For sensitivity analysis, we examined the impact of different numbers of knots (10–40) on the strongest effect estimate. (b) The day of the week (categorical). (c) Temperature: we assumed that the temperature effect followed a spline with 3 knots and identified the lag with the best fit according to the AIC [54]. (d) Humidity (with the same considerations as for temperature). Air pollution is likely to first cause the onset or worsening of a disease. As a consequence, the patient will call for a doctor. When the doctor realizes that the treatment at home is too risky (or unlikely to be successful), a transfer to a hospital will be organized. Depending on the characteristics of the local health care system, the delay between exposure and admission will vary. Given that we expected a delay of 3 days in our previous study on hospital admissions of children in Pristina, we considered this lag the most likely contributor [55].
As an alternative, we analyzed single lags from 0 (the same day) to 7 days (a 1-week delay) separately. We primarily analyzed the number of hospital admissions for adults and children combined. If an effect was evident, we further investigated if the effect was driven by child or adult admissions or if it concerned admissions of individuals of all ages. As a proof-of-concept approach, for the effects that proved significant in the GAM, we also performed a (simpler) quasi-Poisson analysis controlling for the day (linear term) and month (categorical data) instead of the natural spline of time.
3. Results
The descriptive data are presented in Table 1. Over the 4 years (1461 days), on average, 1.29 pediatric and 1.54 adult patients were admitted because of respiratory diagnoses, adding up to 2.82 total cases per day. Although air pollution levels have witnessed a downward trend in recent years, daily concentrations still reach high levels during pollution episodes. Concentrations of PM10, PM2.5, and, to a somewhat lesser extent, NO2, O3, and CO were strongly correlated between the two monitoring stations. This was not the case with SO2 (Appendix A, Table A1). Like O3, most pollutants were positively correlated with each other (Appendix A, Table A2).

Table 1.
Environmental conditions and case numbers per day.
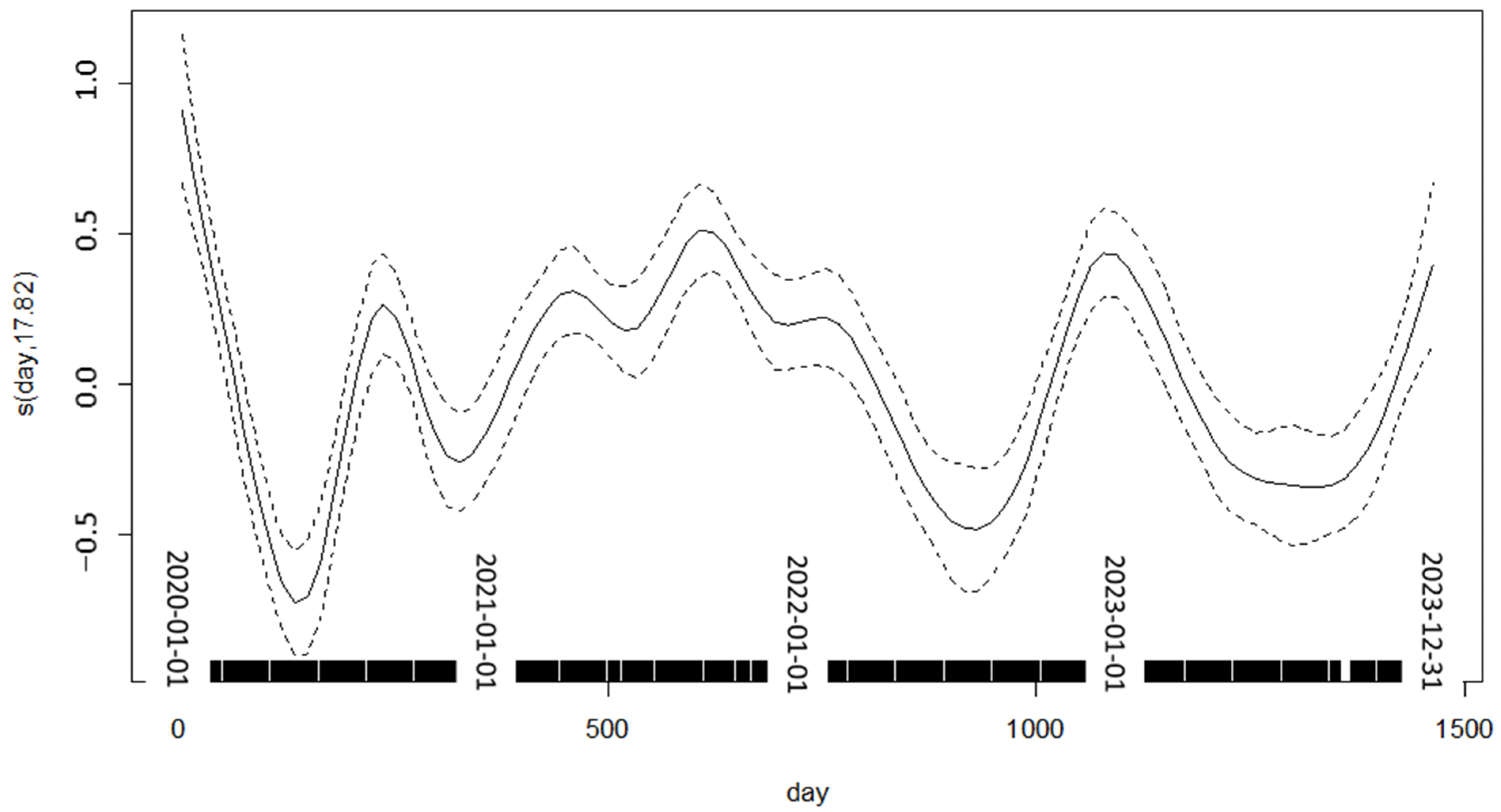
The daily number of all cases combined exhibited a clear seasonal variation, as depicted in Figure 1. Additionally, a significant drop in the number of cases was clearly visible in the summer of the first year, coinciding with the first surge and lockdown measures of the COVID-19 pandemic.
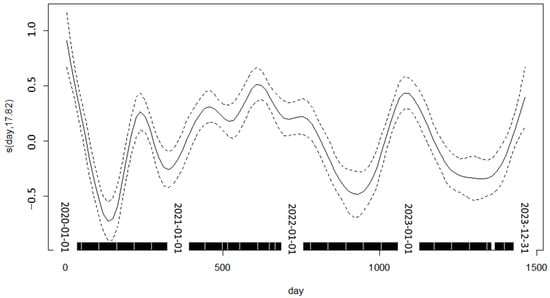
Figure 1.
Time-course of daily admissions (all ages), showing deviation from mean.
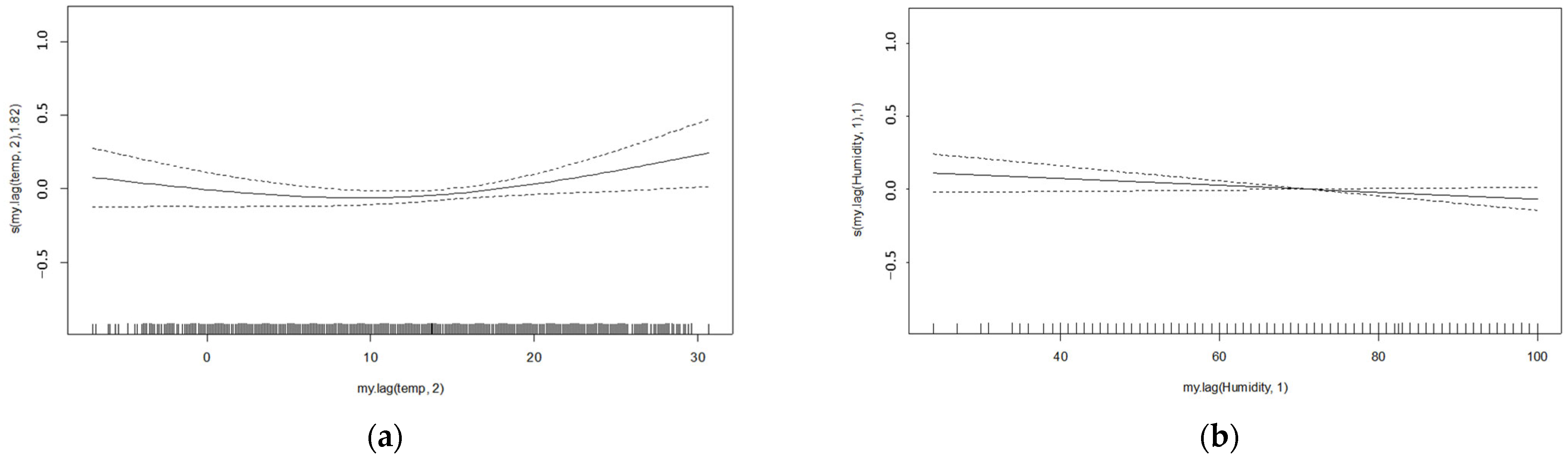
Temperature caused a small U-shaped variation in daily case numbers (Figure 2a), while case numbers declined slightly with increasing humidity (Figure 2b).
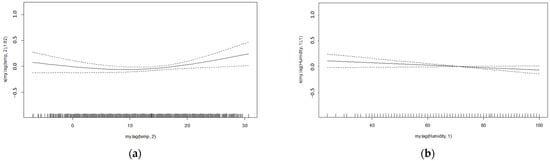
Figure 2.
Effect of temperature (lag 2, −7 to 30.6 °C, (a)) and relative humidity (lag 1, 24 to 100%, (b)) on total daily deaths, showing deviation from mean.
3.1. Impact of Air Pollution
3.1.1. General Additive Model (GAM)
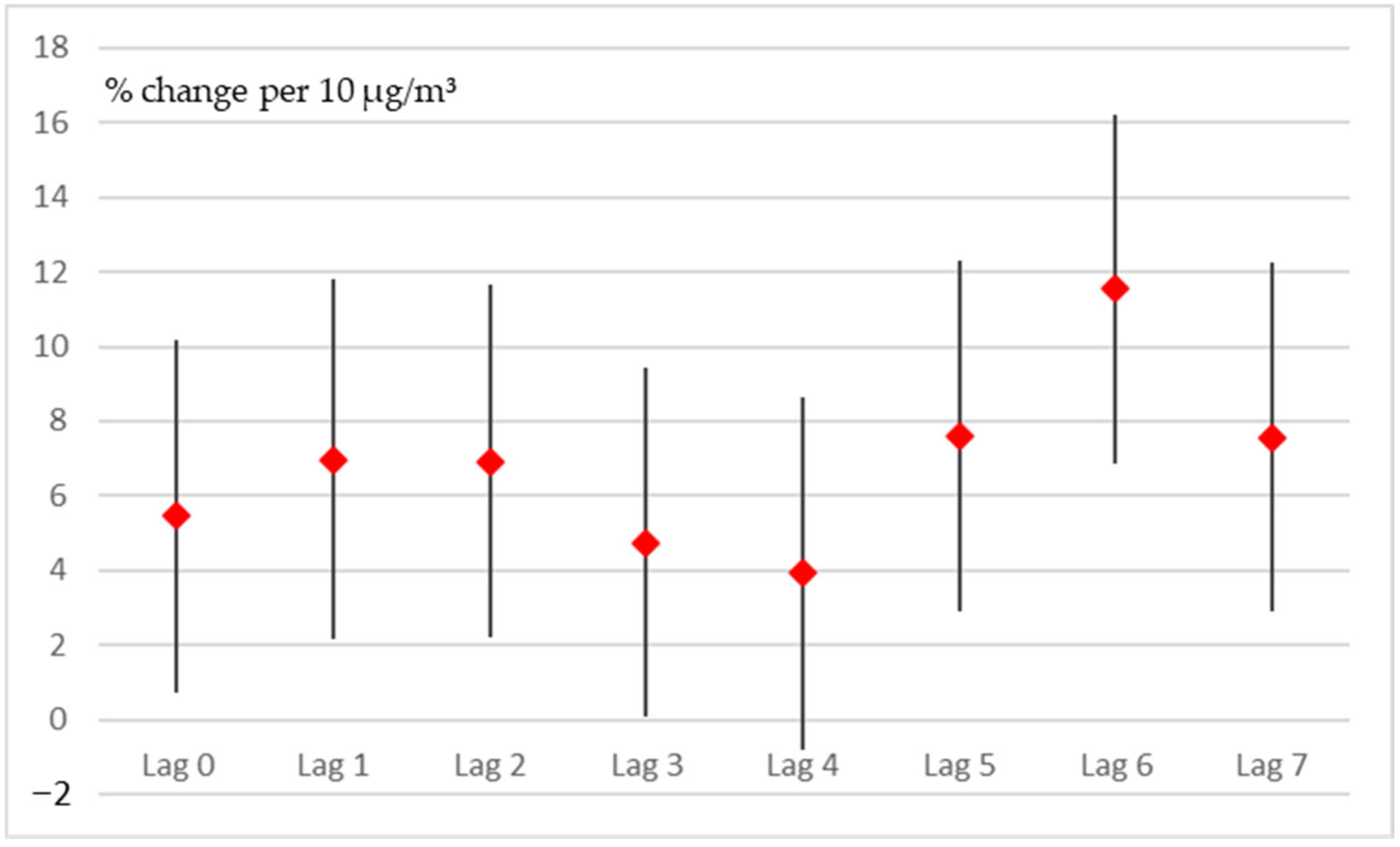
After controlling for long-term trends (20 knots), the day of the week, a lag of 2 days for temperature, and a lag of 1 day for relative humidity, only two gaseous pollutants, NO2 and SO2, displayed any significant impacts. Between them, only NO2 displayed a significant effect across most time lags, while SO2 was only significant for a lag of 3 days. The effect of SO2 was positive for most lags but usually small, with the highest increase (for lag 3, p = 0.027) being 0.1 cases per 10 µg/m3. The effects of NO2 were more consistent and peaked at a lag of 6 days (p < 0.01), with an increase of 0.12 cases per 10 µg/m3 (Figure 3). The effect was positive for all lags and significant for all but the 4-day lag.
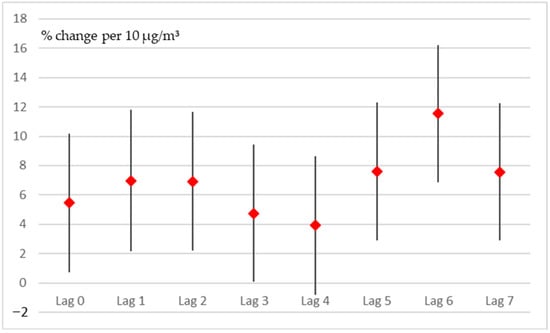
Figure 3.
Effect estimates (95% confidence intervals) for every lag (0–7) per 10 µg/m3 increase in NO2.
The significance of the effect of NO2 was mostly driven by adult admissions. For adult cases, significant effects were seen for all lags, while admissions of children, although mostly positively associated, reached significance (p < 0.05) only at lags of 0 and 6 days.
The effect estimates for the other pollutants are presented in Appendix A, Table A3, and the effect estimates for NO2 at lag 6, assuming different knots for the spline for the time trend, are presented in Table A4.
3.1.2. Quasi-Poisson Model
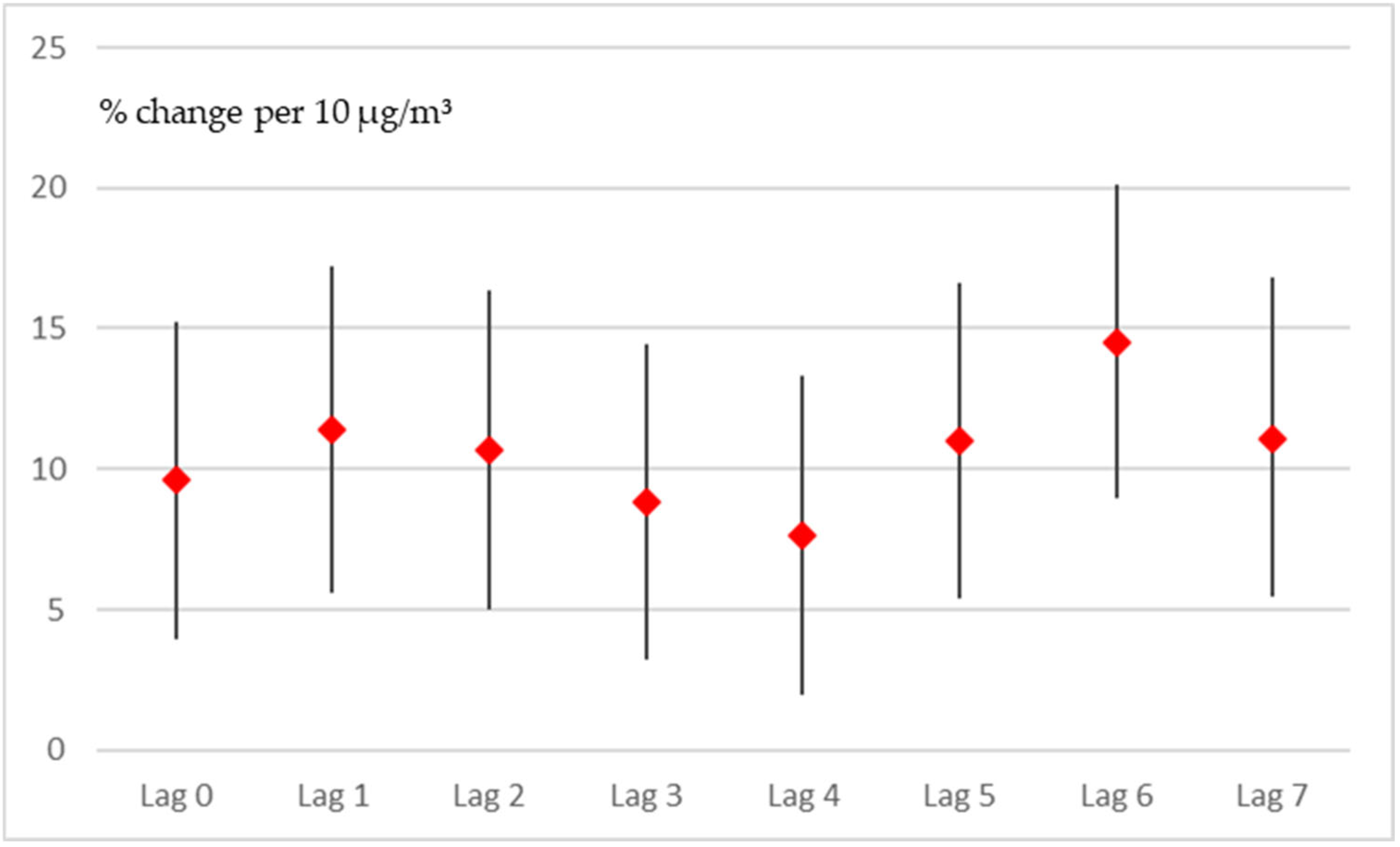
Before modeling seasonal and long-term trends with splines, we used the simpler quasi-Poisson model. In that model, we controlled for seasonal variation by including the “month” (a nominal variable, 1–12). This approach assumes that the months of consecutive years are similar after controlling for long-term (linear) trends. As seen in Figure 1, this assumption was violated by the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic in the years 2020 and 2021. Since the pandemic and lockdown measures are both associated with the number of hospital admissions and pollution levels, it is vital to correctly control for these impacts. Therefore, the simple approach might be biased due to the pandemic context; nevertheless, it aided in choosing the number of lag days and the relevant pollutants. As with the GAM, both NO2 and SO2 showed positive effects on the number of admissions. In both cases, the effects in the quasi-Poisson model were stronger than those in the GAM, as presented in Figure 4 for NO2. None of the other pollutants demonstrated any clear effect, even when the quasi-Poisson model was used. With the GAM, the other pollutants did not exhibit any clear adverse effects.
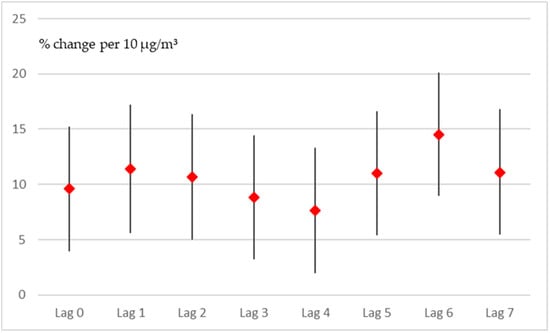
Figure 4.
Effect estimates (95% confidence intervals) for every lag (0–7) per 10 µg/m3 increase in NO2, quasi-Poisson model.
Although somewhat stronger effects were demonstrated, the general shape of the time course of the effects (lags of 0 to 7 days) was quite similar to that of the GAM results, with a first peak occurring for lags of 1 and 2 days and a second peak at a lag of 6 days.
4. Discussion
The chosen time interval (2020–2023) was certainly not optimal for a time series analysis. The COVID-19 pandemic caused an unusual variation in daily hospital admissions. This variation rendered a simple approach (controlling for linear long-term trends, the month of the year, and the day of the week instead of applying splines) inappropriate. When applying splines to control for long- and mid-term variations, the choice of the correct degree of freedom is always an issue. In previous studies, we chose the number of knots that minimized the absolute value of the partial autocorrelation of the residuals, as proposed by Katsouyanni et al. [56]. In previous studies, with an increasing number of knots, the partial autocorrelation declined until it turned from positive to negative; however, with the current data, the sum of the partial autocorrelation oscillated between positive and negative numbers, preventing us from choosing the optimal number of knots. Therefore, we had to resort to an arbitrary number of knots instead. Clearly, the larger the number of knots, the more “bumps” there are in short-term variations in daily cases. These are also covered by the spline until the true short-term effects of air pollution are obscured due to overadjustment. Too few knots, on the other hand, would result in a failure to fully represent the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic. Given the results in Figure 1, we are confident that the latter mistake was avoided.
As explained above, we had expected to find an effect of particulate matter. This expectation was not met. Even when using the simpler quasi-Poisson model, which may have been subject to residual bias from confounding effects of COVID-19, no effect of PM10 or PM2.5 was seen. In the simpler model, NO2 and SO2 were positively and significantly associated with the number of daily cases. Although the effect of the former remained in the GAM, the effects of the latter no longer reached significance for most lags but still tended to remain positive. When 40 to 50 years ago, SO2 still served as an indicator of industrial pollution, particularly due to coal-fired power plants, and detrimental health effects of SO2 (daily or weekly mortality) were also noted in Austria [57]. In more recent years, since approximately the turn of the century, these effects have not been visible, and in some instances, SO2 even appears to be protective [58]. The last decades of the 20th century saw a steep decline in SO2 concentrations in Austria. This was due to a large mitigation program [59] that eliminated all local sources of SO2. Rare days with higher SO2 concentrations, therefore, indicate the long-range transport of air masses. Therefore, we hypothesized that locally generated aerosols are more reactive and toxic than older aerosols that have the same mass concentration and derive from long-distance air movement. While SO2 concentrations now indicate a distant source of pollution, NO2 remains a valid indicator of local pollution sources [60]. In a country like Kosovo that still relies heavily on sulfur-rich coal for heating and energy production, SO2 still acts as an indicator of local pollution sources.
Clearly, the optimal location of monitoring stations presents a challenge [61]. The costs of each station must be taken into account when planning a monitoring system, which has several obligations to fulfill: confirming compliance with guideline values, providing information on sources and trends, and informing policy-makers and the general public about the air quality. The use of data for epidemiological research is usually a later consideration, which can pose problems for researchers. However, the outcomes of the current study, particularly the finding that the particulate pollutants and NO2 show sufficiently high correlations (R between 0.75 and 0.87) between the two closest monitoring sites. This would indicate that the temporal variation in concentrations, at least for these pollutants, is sufficiently representative of the temporal variation in exposure for the population considered in the study. Clearly, in a time series analysis of hospital admissions, that source population is not very well defined. However, it is obvious from the map (Figure A1) that this population mostly lives between the two monitoring sites.
Therefore, the locations of the monitoring stations do not provide any explanation for the unexpected null finding regarding particulate matter. There is some evidence [12] of a saturation effect at higher PM concentrations. This could play a role in our study if concentrations frequently fall into a range in which the slope of the dose–effect curve is already rather small.
In fact, particle mass may not be the best predictor of the health effects of particulate pollution. The number of particles [62] or the size of the particle surface [63] might be more relevant when assessing health effects, including hospital admissions. In the case of industrial pollution and coal burning, SO2 might serve as a valuable proxy of (nearby) particulate pollution sources, with fresh aerosols from nearby sources being more reactive and consisting of more and smaller particles than an aged aerosol from a more distant source. Similarly, NO2 might serve as a proxy for fresh particulate pollution due to motorized traffic.
Other studies [1,19] have also found effects of ozone, but since ozone is negatively correlated with the other pollutants and most strongly so with NO2, the effect of ozone is likely to be confounded by NO2. Indeed, in an ad-hoc two-pollutant model with O3 on a lag of 7 days and NO2 on a lag of 6 days, the effect of ozone (0.022 per 10 µg/m3) was nearly significant (p = 0.05525), and the effect of NO2 was even strengthened (0.114 per 10 µg/m3, p < 0.001).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.U.; methodology, H.M.; formal analysis, H.M.; investigation, R.X., F.T.H. and H.T.; resources, A.U.; data curation, A.U. and R.X.; writing—original draft preparation, H.M. and A.U.; supervision, A.U. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| PM | Particulate matter |
| PM2.5 | Particulate matter smaller than 2.5 µm in diameter |
| PM10 | Particulate matter smaller than 10 µm in diameter |
| NO2 | Nitrogen dioxide |
| SO2 | Sulphur dioxide |
| O3 | Ozone |
| CO | Carbon oxide |
| ICD-10 | International Classification of Diseases, version 10 |
| KHMI | Kosovo Hydro-Meteorological Institute |
| EEA | European Environment Agency |
| GAM | General Additive Model |
Appendix A

Table A1.
Correlation between two stations in Prizren and Peja.
Table A1.
Correlation between two stations in Prizren and Peja.
| Pollutant | Pearson’s R | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| PM10 | 0.8535 | <0.001 |
| PM2.5 | 0.8650 | <0.001 |
| NO2 | 0.7514 | <0.001 |
| O3 | 0.7347 | <0.001 |
| CO | 0.6927 | <0.001 |
| SO2 | 0.3875 | <0.001 |

Table A2.
Correlation between pollutants in Prizren (R, p-value).
Table A2.
Correlation between pollutants in Prizren (R, p-value).
| Pollutant | PM2.5 | NO2 | O3 | CO | SO2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM10 | 0.9780, <0.001 | 0.7835, <0.001 | −0.4997, <0.001 | 0.7524, <0.001 | 0.1215, <0.001 |
| PM2.5 | 0.7982, <0.001 | −0.5720, <0.001 | 0.8011, <0.001 | 0.0666, 0.0126 | |
| NO2 | −0.6792, <0.001 | 0.7086, <0.001 | 0.1756, <0.001 | ||
| O3 | −0.6189, <0.001 | 0.0418, 0.1193 | |||
| CO | −0.0639, 0.0169 |

Table A3.
Effect estimates of the other pollutants per 10 µg/m3 or, in the case of CO, per mg/m3 (p-value). Italics: p < 0.1; bold: p < 0.05.
Table A3.
Effect estimates of the other pollutants per 10 µg/m3 or, in the case of CO, per mg/m3 (p-value). Italics: p < 0.1; bold: p < 0.05.
| Lag | PM10 | PM2.5 | O3 | CO | SO2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lag 0 | 0.000 (0.974) | 0.005 (0.699) | 0.001 (0.957) | 0.0235 (0.506) | 0.037 (0.419) |
| Lag 1 | 0.005 (0.656) | 0.010 (0.435) | −0.016 (0.241) | −0.0088 (0.814) | 0.063 (0.173) |
| Lag 2 | 0.009 (0.392) | 0.016 (0.197) | −0.018 (0.150) | 0.0290 (0.419) | 0.019 (0.681) |
| Lag 3 | −0.003 (0.731) | −0.004 (0.718) | −0.009 (0.433) | −0.0224 (0.524) | 0.101 (0.027) |
| Lag 4 | −0.003 (0.7899) | −0.003 (0.816) | 0.003 (0.809) | −0.0088 (0.803) | −0.021 (0.647) |
| Lag 5 | 0.014 (0.140) | 0.016 (0.164) | −0.002 (0.867) | 0.0397 (0.246) | 0.040 (0.373) |
| Lag 6 | 0.018 (0.060) | 0.020 (0.087) | 0.005 (0.688) | 0.0634 (0.057) | −0.017 (0.703) |
| Lag 7 | 0.012 (0.241) | 0.011 (0.370) | 0.017 (0.137) | 0.0449 (0.195) | 0.000 (0.994) |

Table A4.
Effect estimates for NO2 at lag of 6 days, assuming different knots for time-trend spline.
Table A4.
Effect estimates for NO2 at lag of 6 days, assuming different knots for time-trend spline.
| Knots | Coefficient | Lower | Upper |
|---|---|---|---|
| per 10 µg/m3 | 95% confidence interval | ||
| 10 | 0.114 | 0.070 | 0.159 |
| 15 | 0.108 | 0.062 | 0.154 |
| 20 | 0.115 | 0.068 | 0.161 |
| 25 | 0.091 | 0.043 | 0.138 |
| 30 | 0.062 | 0.015 | 0.110 |
| 35 | 0.066 | 0.017 | 0.115 |
| 40 | 0.065 | 0.016 | 0.114 |
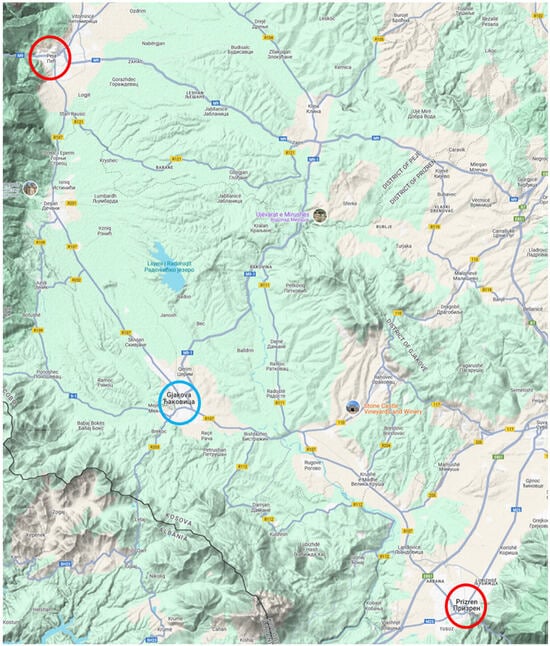
Figure A1.
Map (Google Maps) of the study area (blue circle) and the closest monitoring stations (red circles).
Figure A1.
Map (Google Maps) of the study area (blue circle) and the closest monitoring stations (red circles).
References
- World Health Organization (WHO). WHO Global Air Quality Guidelines. Particulate Matter (PM2.5 and PM 10), Ozone, Nitrogen Dioxide, Sulfur Dioxide and Carbon Monoxide; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021; Available online: https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/345329/9789240034228-eng.pdf?sequence=1 (accessed on 5 March 2025).
- United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP). Towards A Pollution-Free Planet Background Report; UNEP: Nairobi, Kenya, 2017; Available online: http://wedocs.unep.org/bitstream/handle/20.500.11822/21800/UNEA_towardspollution_long%20version_Web.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y (accessed on 5 March 2025).
- United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP). Air Pollution and Human Health: The Case of the Western Balkans; UNEP: Nairobi, Kenya, 2019; Available online: https://www.developmentaid.org/api/frontend/cms/file/2019/06/Air-Quality-and-Human-Health-Report_Case-of-Western-Balkans_preliminary_results.pdf (accessed on 5 March 2025).
- The World Bank. Air Pollution Deaths Cost Global Economy US$225 Billion; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2013; Available online: https://www.worldbank.org/en/news/press-release/2016/09/08/air-pollution-deaths-cost-global-economy-225-billion (accessed on 5 March 2025).
- World Health Organization (WHO). The Global Health Observatory. Air Pollution Data Portal. Available online: https://www.who.int/data/gho/data/themes/air-pollution (accessed on 8 May 2025).
- Statista. Annual Number of Deaths from Select Risk Factors Worldwide in 2021. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/1169367/worldwide-number-deaths-risk-factor/ (accessed on 8 May 2025).
- IQAir. 2019 World Air Quality Report. Region & City PM2.5 Ranking; IQAir: Steinach, Switzerland, 2020; Available online: https://www.iqair.com/dl/pdf-reports/2019-World-Air-Report-V8-20200318.pdf (accessed on 5 March 2025).
- Solomon, P.A.; Costantini, M.; Grahame, T.J.; Gerlofs-Nijland, M.E.; Cassee, F.R.; Russell, A.G.; Brook, J.R.; Hopke, P.K.; Hidy, G.; Phalen, R.F.; et al. Air pollution and health: Bridging the gap from sources to health outcomes: Conference summary. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2012, 5, 9–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Blasi, C.; Nobile, F.; Settembrini, A.M.; Stafoggia, M.; Davoli, M.; Michelozzi, P.; Renzi, M.; Mannucci, P.M. Association between long-term exposure to air pollution and incidence of peripheral artery disease: Evidence from a longitudinal study. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2025, 132, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Braun, D.; Christidis, T.; Cork, M.; Rodopoulou, S.; Samoli, E.; Stafoggia, M.; Wolf, K.; Wu, X.; Yuchi, W.; et al. Long-Term Exposure to Low-Level PM2.5 and Mortality: Investigation of Heterogeneity by Harmonizing Analyses in Large Cohort Studies in Canada, United States, and Europe. Environ. Health Perspect. 2023, 131, 127003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slama, A.; Śliwczyński, A.; Woźnica, J.; Zdrolik, M.; Wiśnicki, B.; Kubajek, J.; Turżańska-Wieczorek, O.; Gozdowski, D.; Wierzba, W.; Franek, E. Impact of air pollution on hospital admissions with a focus on respiratory diseases: A time-series multi-city analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2019, 26, 16998–17009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunekreef, B.; Strak, M.; Chen, J.; Andersen, Z.J.; Atkinson, R.; Bauwelinck, M.; Bellander, T.; Boutron, M.-C.; Brandt, J.; Carey, I.; et al. Mortality and Morbidity Effects of Long-Term Exposure to Low-Level PM2.5, BC, NO2, and O3: An Analysis of European Cohorts in the ELAPSE Project. Res. Rep. (Health Eff. Inst.) 2021, 208, 1–127. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, S.; Li, C.; Jin, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, R.; Mohamed, Z.A.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, Y. Air pollution and adult hospital admissions for ischemic stroke: A time-series analysis in Inner Mongolia, China. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2025, 30, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Cao, J.; Zhou, W.; Neophytou, A.M. Interactive Effect of Air Temperature and Fine Particulate Matter on the Hospital Admissions for Stroke in Shenzhen, China. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2025, 14, e037329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zama, D.; Paccapelo, A.; Betti, L.; Manieri, E.; Paglione, M.; Rinaldi, M.; Dondi, A.; Battelli, E.; Biagi, C.; Rizzolli, C.M.; et al. The influence of air pollutants on the risk of emergency department presentations of infants with bronchiolitis in an European air quality hotspot. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2025, 36, e70077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hales, S.; Atkinson, J.; Metcalfe, J.; Kuschel, G.; Woodward, A. Long term exposure to air pollution, mortality and morbidity in New Zealand: Cohort study. Sci Total Environ. 2021, 801, 149660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyaase, S.; Nyame, S.; Klipstein-Grobusch, K.; Asante, K.P.; Downward, G.S. Climate, Air Quality and Their Contribution to Cardiovascular Disease Morbidity and Mortality in Low- and Middle-Income Countries: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Glob. Heart 2025, 20, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.; Li, G.; Wang, Y.; Dong, P.; Yang, K.; Liu, H.; Xie, N.; Liu, J.; Chen, H.; Liu, X.; et al. Impacts of air pollutions on cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases through inflammation: A comprehensive analysis of one million Chinese and half million UK individuals. J. Transl. Med. 2025, 23, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, S.; Chen, Y.; Sun, X.; Dong, X.; He, G.; Pu, Y.; Fan, J.; Zhong, X.; Chen, Z.; Lin, Z.; et al. Long-term exposure to ambient ozone and cardiovascular diseases: Evidence from two national cohort studies in China. J. Adv. Res. 2024, 62, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, P.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Qiu, J.; Tang, X.; Ding, Z.; Xu, M.; Wang, C. Associations between short-term exposure to air pollution and acute exacerbation of chronic bronchitis: A time-stratified case-crossover study. Prev. Med. 2025, 191, 108217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, G.C.; Hajat, A.; Bird, C.E.; Cullen, M.R.; Griffin, B.A.; Miller, K.A.; Shih, R.A.; Stefanick, M.L.; Vedal, S.; Whitsel, E.A.; et al. Individual and neighborhood socioeconomic status and the association between air pollution and cardiovascular disease. Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 124, 1840–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Air Quality, Energy and Health. Health Impact. Available online: https://www.who.int/teams/environment-climate-change-and-health/air-quality-and-health/health-impacts (accessed on 5 March 2025).
- Bhaskaran, K.; Hajat, S.; Haines, A.; Herrett, E.; Wilkinson, P.; Smeeth, L. The effects of air pollution on the incidence of myocardial infarction—A systematic review. Heart 2009, 95, 1746–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina-Ramón, M.; Zanobetti, A.; Schwartz, J. The effect of ozone and PM10 on hospital admissions for pneumonia and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A national multicity study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2006, 163, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zare Sakhvidi, M.J.; Lequy, E.; Goldberg, M.; Jacquemin, B. Air Pollution Exposure and Bladder, Kidney and Urinary Tract Cancer Risk: A Systematic Review. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 267, 115328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekkar, B.; Pacheco, S.; Basu, R.; DeNicola, N. Association of Air Pollution and Heat Exposure with Preterm Birth, Low Birth Weight, and Stillbirth in the US: A Systematic Review. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e208243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, C.A.; Scotto, M.G.; do Carmo Freitas, M. Air Pollution and Emergency Admissions for Cardiorespiratory Diseases in Lisbon (Portugal). Quím Nova 2010, 33, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Health Effects Institute. State of Global Air 2024. Special Report; Health Effects Institute: Boston, MA, USA, 2024; Available online: https://www.stateofglobalair.org/sites/default/files/documents/2024-06/soga-2024-report_0.pdf (accessed on 5 March 2025).
- Wjst, M.; Reitmeir, P.; Dold, S.; Nicolai, T.; Von Loeffelholz Colberg, E.; Von Mutius, E. Road traffic and adverse effects on respiratory health in children. BMJ 1993, 307, 596–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oosterlee, A.; Drijver, M.; Lebret, E.; Brunekreef, B. Chronic respiratory symptoms of children and adults living along streets with high traffic density. Occup. Environ. Med. 1996, 53, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nitta, H.; Sato, T.; Nakai, S.; Maeda, K.; Aoki, S.; Ono, M. Respiratory health associated with exposure to automobile exhaust. I: Results of cross-sectional studies in 1979, 1982 and 1983. Arch. Environ. Health 1993, 48, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Healthy Environments for Healthier People; WHO Regional Office for Europe: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2018; Available online: https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/346127/WHO-EURO-2018-3004-42762-59655-eng.pdf?sequence=3 (accessed on 5 March 2025).
- Neuberger, M.; Rabczenko, D.; Moshammer, H. Extended effects of air pollution on cardiopulmonary mortality in Vienna. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 8549–8556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuberger, M.; Moshammer, H.; Rabczenko, D. Acute and Subacute Effects of Urban Air Pollution on Cardiopulmonary Emergencies and Mortality: Time Series Studies in Austrian Cities. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, 10, 4728–4751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Wang, Y.; Williams, C.; Xu, C.; Kartsonaki, C.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, P.; Yin, P.; Lam, K.B.H. The association between high particulate matter pollution and daily cause-specific hospital admissions: A time-series study in Yichang, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 5240–5250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Shi, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, N.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, T. Ambient air pollution and cause-specific risk of hospital admission in China: A nationwide time-series study. PLoS Med. 2020, 17, e1003188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manan, N.A.; Aizuddin, A.N.; Hod, R. Effect of Air Pollution and Hospital Admission: A Systematic Review. Ann. Glob. Health 2018, 84, 670–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.T.; Ramachandran, S.; Nguyen, D.; Roper, C. Investigating the acute effects of black carbon, PM2.5 exposure, and temperature on asthma and respiratory-related emergency department visits and hospitalizations in Mississippi. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 373, 126150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linares, C.; Díaz, J.; Navas, M.A.; Ruiz-Páez, R.; Saez, M.; Barceló, M.A.; López-Bueno, J.A. How air pollution and extreme temperatures affect emergency hospital admissions due to various respiratory causes in Spain, by age group: A nationwide study. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2025, 266, 114570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Qiu, J.; Kang, N.; Zhang, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Tang, X.; Yuchi, Y.; Xu, M.; Wang, C. Association of short-term exposure to PM2.5 and its components with hospital admission for asthma in Shanghai: A time-stratified case-crossover study. J. Asthma 2025, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The World Bank. Air Pollution Management in Kosovo; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2019; Available online: https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/handle/10986/33041. (accessed on 5 March 2025).
- Liu, J.; Clark, L.P.; Bechle, M.J.; Hajat, A.; Kim, S.Y.; Robinson, A.L.; Sheppard, L.; Szpiro, A.A.; Marshall, J.D. Disparities in Air Pollution Exposure in the United States by Race/Ethnicity and Income, 1990–2010. Environ. Health Perspect. 2021, 129, 127005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Air Q+: Burden of Disease Due to Air Pollution Manual; WHO Regional Office for Europe: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP). Healthier Kosovo (HK 2). Available online: https://www.undp.org/kosovo/projects/healthier-kosovo-hk-2 (accessed on 5 March 2025).
- Rees, N. Danger in the Air: How Air Pollution May be Affecting the Brain Development of Young Children Around the World; United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF): New York, NY, USA, 2017; Available online: https://www.unicef.org/sites/default/files/press-releases/glo-media-Danger_in_the_Air.pdf (accessed on 5 March 2025).
- Dreshaj, A.; Millaku, B.; Shala, S.; Selimaj, A.; Shabani, H. Sources of air pollution, environmental impacts and exploitation of natural resources in Kosovo. CBU Int. Conf. Proc. 2017, 5, 1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agjencioni për Mbrojtjen e Mjedisit të Kosovës (AMMK). Raporti Vjetor për Gjendjen e Ajrit 2023. 2024. Available online: https://ammk-rks.net/assets/cms/uploads/files/Raporti%20%20vjetor%20per%20cilesi%20te%20ajrti%202023%20-final%20alb.pdf (accessed on 15 April 2025).
- World Bank. Kosovo Country Environmental Analysis. Cost Assessment of Environmental Degradation, Institutional Review, and Public Environmental Expenditure Review. January 2013. Available online: https://documents1.worldbank.org/curated/en/282361468047686579/pdf/750290ESW0P1310LIC00Kosovo0CEA0Rprt.pdf (accessed on 15 April 2025).
- Agjencioni i Statistikës së Kosovës (ASK). Regjistrimi i Popullësis, Ekonomive Familjare, dhe Banesave në Kosovë. Rezultatet Parafinale 2024. Available online: https://ask.rks-gov.net/Rekos (accessed on 6 May 2025).
- European Environment Agency (EEA). Air Quality e-Reporting (AQ e-Reporting); EEA: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2021. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/data-and-maps/data/aqereporting-9 (accessed on 30 June 2022).
- KHMI. Data from Monitoring Stations. 2022. Available online: https://airqualitykosova.rks-gov.net/en/reports-for-themonitoring-stations/ (accessed on 30 June 2022).
- Vjetari Hidrometeorologjik. Available online: https://ihmk-rks.net (accessed on 30 June 2022).
- Gudziunaite, S.; Shabani, Z.; Weitensfelder, L.; Moshammer, H. Time series analysis in environmental epidemiology: Challenges and considerations. Int. J. Occup. Med. Environ. Health 2023, 36, 704–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samoli, E.; Schwartz, J.; Wojtyniak, B.; Touloumi, G.; Spix, C.; Balducci, F.; Medina, S.; Rossi, G.; Sunyer, J.; Bacharova, L.; et al. 2001. Investigating regional differences in short-term effects of air pollution on daily mortality in the APHEA project: A sensitivity analysis for controlling long-term trends and seasonality. Environ. Health Perspect. 2001, 109, 349–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabani Isenaj, Z.; Berisha, M.; Gjorgjev, D.; Dimovska, M.; Moshammer, H.; Ukëhaxhaj, A. Air Pollution in Kosovo: Short Term Effects on Hospital Visits of Children Due to Respiratory Health Diagnoses. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 10141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsouyanni, K.; Schwartz, J.; Spix, C.; Touloumi, G.; Zmirou, D.; Zanobetti, A.; Wojtyniak, B.; Vonk, J.M.; Tobias, A.; Pönkä, A.; et al. Short term effects of air pollution on health: A European approach using epidemiologic time series data: The APHEA protocol. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 1996, 50, S12–S18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friza, H.; Lax, F.; Neuberger, M. SO2—Ein kommunales Risiko in Wien? Untersuchungen über Beziehungen zwischen SO2 und Mortalität an Atemwegserkrankungen [SO2—A municipal risk in Vienna? Studies on the relationship between SO2 and mortality from respiratory diseases]. Forum Städte-Hyg. 1986, 37, 250–252. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- Neuberger, M.; Moshammer, H. Schwebstaub und Lungengesundheit [Suspended particulates and lung health]. Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 2004, 116, S8–S12. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- Umweltbundesamt: Dashboard Luftschadstoff-Emissionen und Luftqualität in Österreich. Available online: https://www.umweltbundesamt.at/umweltthemen/luft/luftschadstoffe/dashboard (accessed on 4 March 2025).
- Moshammer, H.; Poteser, M.; Kundi, M.; Lemmerer, K.; Weitensfelder, L.; Wallner, P.; Hutter, H.-P. Nitrogen-Dioxide Remains a Valid Air Quality Indicator. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofia, D.; Lotrecchiano, N.; Giuliano, A.; Barletta, D.; Poletto, M. Optimization of Number and Location of Sampling Points of an Air Quality Monitoring Network in an Urban Contest. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2019, 74, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, M.L.; Andersen, Z.J.; Massling, A.; Kindler, P.A.; Loft, S.; Amini, H.; Cole-Hunter, T.; Guo, Y.; Maric, M.; Nordstrøm, C.; et al. Short-term exposure to ultrafine particles and mortality and hospital admissions due to respiratory and cardiovascular diseases in Copenhagen, Denmark. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 336, 122396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Ryan, I.; Paul, S.; Deng, X.; Zhang, W.; Luo, G.; Dong, G.H.; Nair, A.; Yu, F. Particle surface area, ultrafine particle number concentration, and cardiovascular hospitalizations. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 310, 119795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).