Simple Summary
The digestive system of ruminants contains billions of microorganisms that help them digest plants and obtain energy. Different Cervid species have evolved unique ways to adapt to their environments, but how their gut microbes and body metabolism differ remains unclear. In this study, we compared three deer species—Sika deer, Reindeer, and Milu deer—raised on the same diet. We analyzed the rumen microbiota, the fermentation products, and metabolites in serum. We found that although they were fed same diet, rumen microbiota and metabolic profiles were different among three ruminants. Milu deer had higher levels of blood fats, while Reindeer and Sika deer showed higher levels of blood proteins and specific liver enzymes. We also found that the blood genes regulate host metabolism. These findings reveal the specific metabolic adaptations of each species and provide insights for improving their feeding management and conservation strategies.
Abstract
Rumen microbiota is pivotal for nutrient metabolism and physiological adaptation in ruminants. This study investigated the rumen microbial community, fermentation parameters, and serum biochemistry of three Cervid species—Sika deer (Cervus nippon), Reindeer (Rangifer tarandus), and Milu deer (Elaphurus davidianus) (n = 5/group)—fed an identical diet. Using 16S rRNA sequencing and biochemical analyses, we found that while Bacteroidota, Firmicutes, and Proteobacteria were dominant phyla across species. Sika deer and Milu deer exhibited significantly higher microbial diversity and abundance of carbohydrate-digesting genera (e.g., Butyrivibrio, Saccharofermentans), and pathways of carbohydrate digestion and absorption, starch and sucrose metabolism compared to Reindeer. Conversely, Reindeer showed increased abundances of Lachnospiraceae ND3007 and butyrate metabolism pathway, and significantly elevated rumen volatile fatty acid concentrations, particularly acetate and butyrate. Serum profiling revealed that Milu deer had significantly higher lipid levels (CHO, TG, LDL-C) but lower total protein and AST levels compared to other species. Notably, WGCNA linked these blood lipid traits to host genes enriched in PI3K-Akt, MAPK, and bile secretion pathways. These findings demonstrate distinct species-specific rumen fermentation patterns and host metabolic adaptations, suggesting a coordinated regulation between the rumen microbiome and host genetics in Cervid.
1. Introduction
Ruminants are distinguished from other herbivores by their unique gastric structure, the rumen, which hosts one of the most complex and diverse ecosystems [1]. This microbial ecosystem, composed of bacteria, archaea, protozoa, and fungi, efficiently converts plant fibers and non-protein nitrogen into high-value nutrients such as milk and meat [2]. The fermentation process driven by these microbes produces volatile fatty acids (VFAs) [3], which provide up to 70% of the energy requirements for the host [4]. Among these microorganisms, bacteria are the most abundant and metabolically active, constituting approximately 50% to 70% of the total rumen microbiota [5]. Consequently, the rumen microbiota serves as a critical indicator of rumen health and is intrinsically linked to the nutrient metabolism and physiological well-being of ruminants [1,6]. Growing evidence suggests that rumen microbial composition is shaped by a complex interplay of factors, including age, gender, diet, geographical location, and host genetics [6,7,8,9]. While diet is often considered the primary driver of microbial shifts [7,8,9,10]. While diet is often considered the primary driver of microbial shifts [11], the host’s genetic background plays a pivotal role in selecting and maintaining specific microbial communities. For instance, rumen content exchange studies in beef cattle have shown that the host significantly influences the re-establishment of microbiota after transplantation [12]. Furthermore, recent genomic studies indicate that host genes regulate heritable components of the rumen microbiota by creating unique ecological niches [13,14]. Therefore, exploring the rumen microbiota across different ruminant species is essential for understanding host-specific metabolic adaptations.
Cervidae represents a diverse group of large ruminants inhabiting a wide range of ecological environments, from tropical zones to high-altitude and arctic regions [15]. Different deer species have evolved distinct physiological traits to adapt to their specific niches. For example, Reindeer (Rangifer tarandus) possess exceptional lipid storage capabilities and harbor a rumen microbiota highly efficient in fiber digestion and nitrogen recycling to survive in extreme northern environments [16,17]. In contrast, Sika deer (Cervus nippon) have been found to host specific tannin-degrading bacteria (e.g., Streptococcus) in winter, conferring a stronger ability to utilize tannin-rich forage compared to cattle [18]. However, information regarding the rumen microbiota of Milu deer (Elaphurus davidianus) remains limited, with only a few reports identifying specific methanogens such as Methanocorpusculum sp. as dominant species [19]. Given these distinct ecological backgrounds, we hypothesize that Reindeer, Sika deer, and Milu deer harbor species-specific rumen microbial profiles that contribute to differences in their fermentation pattern.
Beyond rumen fermentation, blood biochemical parameters reflect the systemic metabolic status of the host. These metabolic profiles are closely tied to species-specific phenological rhythms, particularly antler growth. Unlike other cervids, both male and female Reindeer grow antler [17]. Furthermore, the timing of antler genesis varies significantly among species; for instance, it occurs in winter for Milu deer [20] but in summer for Sika deer [21]. Previous studies have established that circulating hormones (e.g., GH, IGF-1) and metabolites (e.g., triglycerides, cholesterol) are critical regulators of antler development [22,23,24]. Li et al. [25] also showed that rumen microbiota composition shifts across different antler growth stages. However, a comparative analysis integrating rumen microbiota, fermentation parameters, and blood metabolites across these three deer species is lacking. Therefore, the objective of this study is to compare the rumen microbiota and blood biochemical parameters of Reindeer, Milu deer, and Sika deer, aiming to elucidate the species-specific host-microbe interactions and metabolic characteristics that underlie their adaptation and physiological functions.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals, Experimental Design, and Sample Collection
This study was conducted using fifteen three-year-old males, comprising five Reindeer, five Milu deer, and five Sika deer. Specifically, the Sika deer, Milu deer, and Reindeer in our study had been maintained at a farm in Changchun for over two years. The feeding trial lasted for eight weeks (September to November). During the initial two weeks, the animals were gradually transitioned from their original diet to a total mixed ration (TMR) of roughage and concentrate (50:50, dry matter basis; Table S1). The animals were fed twice a day (07:00 a.m. and 16:00 p.m.), with Ad libitum access to fresh drinking water. All animal-specific procedures were approved and authorized by the Animal Ethics Committee of Jilin Agricultural University (Approval No. 20220317001).
On 10 November 2022, the animals were anesthetized after morning feed, and then 5 mL of blood was collected through the jugular vein using procoagulant tube. Subsequently, approximately 150 mL of rumen fluid was collected using an oral stomach tube and the first 50 mL was discarded to minimize saliva contamination. The pH of the remaining rumen fluid was immediately measured using a portable pH meter. The samples were then snap-frozen in liquid nitrogen for downstream analysis.
2.2. Measurement of Serum Biochemical Parameters and Rumen VFAs
Bloods were centrifuged at 3000× g for 15 min at 4 °C to obtain serum. The serum concentrations of glucose (GLU), triglycerides (TG), total cholesterol (TC), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), alkaline phosphatase (ALP), total protein (TP), and albumin (ALB) were quantified using commercial kits (Jiancheng Bioengineering Institute, Nanjing, China) with an automatic biochemical analyzer (Mindray, Shenzhen, China). For volatile fatty acid (VFA) analysis, rumen fluids were centrifuged at 10,000× g for 10 min at 4 °C. The supernatant was analyzed using gas chromatography (6890GC, Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA) equipped with a flame ionization detector (FID) and a DB-FFAP column according to previous method [26].
2.3. DNA Extraction, Sequencing, and Bioinformatics Analysis
Total microbial DNA was extracted from rumen fluids using the MoBio Power Fecal DNA Isolation Kit (QIAGEN, Valencia, CA, USA) following the manufacturer’s protocol. The V3–V4 regions of the bacterial 16S rRNA gene were amplified using primers 341F (5′-CCTACGGGAGGCAGCAG-3′) and 806R (5′-GGACTACHVGGGTWTCTAAT-3′). The resulting amplicons were purified using the QIAquick PCR Purification Kit (QIAGEN, Valencia, CA, USA) and sequenced on the Illumina NovaSeq 6000 platform to generate paired-end reads. Raw paired-end reads were merged using FLASH [27] and subsequently processed using the QIIME 2 [28]. The DADA2 plugin was employed to denoise sequences and generate amplicon sequence variants (ASVs) [29]. Taxonomy was assigned to representative ASVs against the SILVA database (release 138.1) [30]. To normalize sequencing depth, each sample was rarefied to a minimum depth of 19,228 reads. Alpha diversity indices were calculated to assess within-sample diversity. Beta diversity was evaluated using principal coordinate analysis (PCoA) based on Bray–Curtis dissimilarity, as well as Unweighted and Weighted UniFrac distance matrices. Analysis of Similarities (ANOSIM) was performed to test for significant differences in microbial community structure among groups, while the Adonis test was used to quantify the variation explained by grouping factors (999 permutations). Tax4Fun2 was used to predict the functional profiles of the rumen microbiota based on SILVA database (v132) [31].
2.4. Network and Correlation Analysis
Visual association networks between differential bacterial genera and fermentation parameters were constructed using the Fruchterman-Reingold layout algorithm in Gephi (v0.10.1) [32]. Additionally, we performed a weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA) [33]. This analysis integrated the serum biochemical indices obtained in the current study with differentially expressed genes (DEGs) identified in the blood transcriptome of the same species from our previous study (BioProject PRJNA1373567) [34]. Correlations were assessed using the Spearman coefficient. Functional enrichment analysis of gene modules, including Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathways, was performed using KOBAS [35], with p-values adjusted using the Benjamini–Hochberg method.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
All statistical analyses were performed using R software (v4.3.1). The Kruskal–Wallis test was used to assess overall differences among the three groups. Where significant differences were detected, post hoc pairwise comparisons were conducted using the Wilcoxon rank-sum test. p-values were adjusted for multiple comparisons using the Benjamini–Hochberg false discovery rate (FDR) method. A p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Data are expressed as the mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM).
3. Results
3.1. Comparison of Rumen Microbiota and Potential Functions Among Sika Deer, Reindeer, and Milu Deer
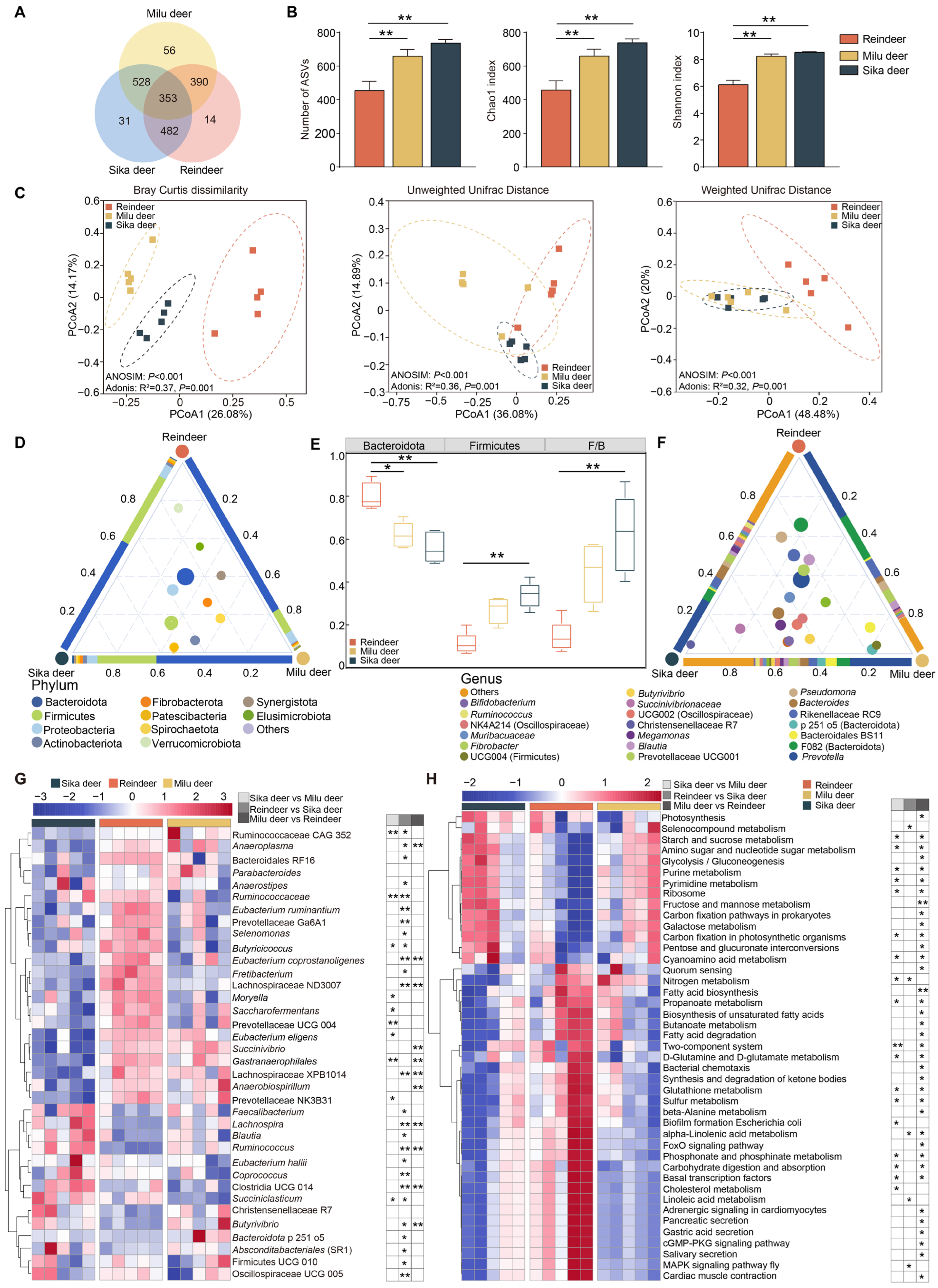
The rumen bacterial communities were characterized based on 16S rRNA gene sequencing, yielding a total of 1617 ASVs from a sequencing depth ranging from 72,522 to 84,986 reads per sample. Venn diagram analysis revealed that 353 ASVs were shared among the three cervid species, while 14, 56, and 31 ASVs were unique to Reindeer, Milu deer, and Sika deer, respectively (Figure 1A). Alpha diversity analysis indicated that the number of observed ASVs, Chao1 index, and Shannon index were significantly higher in Sika deer and Milu deer compared to Reindeer (Figure 1B, p < 0.01). Furthermore, PCoA based on Bray–Curtis dissimilarity, unweighted UniFrac, and weighted UniFrac distances demonstrated distinct clustering, indicating significant differences in microbial community structure among the three species (Figure 1C).
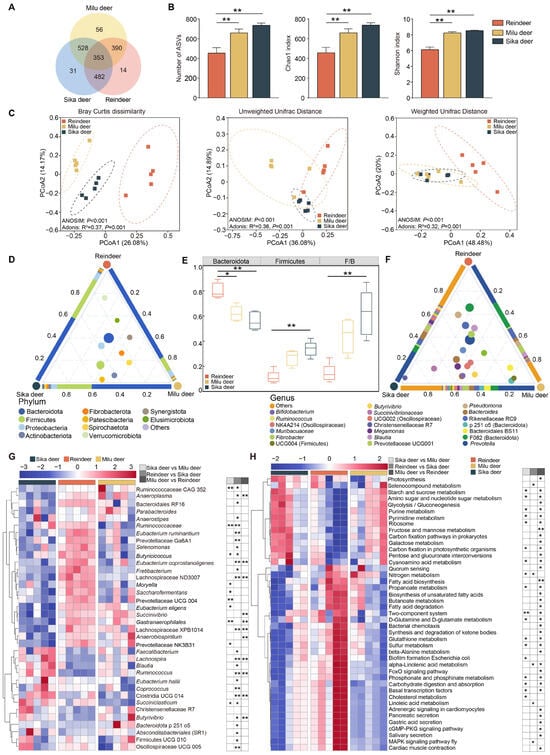
Figure 1.
Rumen bacterial community composition and predicted functional profiles. (A) Venn diagram showing shared and unique bacterial ASVs among Sika deer, Reindeer, and Milu deer. (B) Comparison of alpha diversity indices of the rumen microbiota among the three species. (C) PCoA plots based on Bray–Curtis dissimilarity, unweighted UniFrac, and weighted UniFrac distances at the ASV level. The colored dashed ellipses indicate the 95% confidence intervals for each group. (D) Ternary plot displaying the average relative abundance of the top ten bacterial phyla. The three vertices represent the three species. Inner circles represent bacterial phyla, with size proportional to abundance. Proximity to a vertex indicates higher abundance of that phylum in the corresponding species. The colors of three triangle sides and inner circles represent different bacterial phyla as defined in the legend. (E) Comparison of the relative abundances of Bacteroidota and Firmicutes, and F/B ratio among the three species. (F) Average relative abundance of the top twenty bacterial genera among the three species. The colors of three triangle sides and inner circles represent different bacterial genera as defined in the legend. (G) Heatmap showing differentially abundant genera among the three species. The color scale represents normalized relative abundance, ranging from low (blue) to high (red). (H) Heatmap showing differentially enriched KEGG pathways (Level 3) among the three species. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01.
Taxonomic classification identified 15 phyla across all samples (Figure 1D). Bacteroidota was the predominant phylum (Sika deer = 56.1 ± 3.3%, Reindeer = 80.1 ± 2.8%, Milu deer = 62.0 ± 2.7%), followed by Firmicutes (Sika deer = 33.9 ± 2.7%, Reindeer = 11.2 ± 2.3%, Milu deer = 26.8 ± 2.8%) and Proteobacteria (Sika deer = 6.0 ± 1.4%, Reindeer = 5.5 ± 2.0%, Milu deer = 4.7 ± 0.3%). Comparative analysis revealed that the relative abundance of Bacteroidota was significantly higher in Reindeer than in Milu deer (p < 0.05) and Sika deer (p < 0.01). Conversely, both the relative abundance of Firmicutes and the Firmicutes/Bacteroidota (F/B) ratio were significantly lower in Reindeer compared to Sika deer (p < 0.01, Figure 1E). At the genus level, 160 genera were identified (Figure 1F). Prevotella was the most abundant genus across all groups (Sika deer = 12.1 ± 3.2%, Reindeer = 24.5 ± 8.2%, Milu deer = 21.4 ± 8.4%), followed by Bacteroidales F082 (Sika deer = 5.2 ± 0.9%, Reindeer = 21.1 ± 6.0%, Milu deer = 5.7 ± 0.7%). Notably, Bacteroides (6.0 ± 1.4%) was prevalent in Sika deer, while Bacteroidales BS11 (5.0 ± 2.8%) was enriched in Milu deer. In Reindeer, Rikenellaceae RC9 (8.5 ± 1.9%) and Bacteroidales RF16 (5.9 ± 0.5%) showed high relative abundances.
Differential abundance analysis identified 36 genera that varied significantly among the three species (p < 0.05, Figure 1G). The relative abundances of Ruminococcus, Butyrivibrio, Lachnospira, Absconditabacteriales (SR1), Eubacterium coprostanoligenes, Lachnospiraceae XPB1014, and Saccharofermentans were significantly lower in Reindeer compared to Milu deer and Sika deer (p < 0.05). In contrast, Fretibacterium, Lachnospiraceae ND3007, Bacteroidales RF16, and Moryella were significantly enriched in Reindeer compared to the other groups. Functional prediction analysis using Tax4Fun2 revealed significant differences in 43 metabolic pathways among the three groups (p < 0.05, Figure 1H). Specifically, pathways related to starch and sucrose metabolism, amino sugar and nucleotide sugar metabolism, carbohydrate digestion and absorption, purine metabolism, and pyrimidine metabolism were significantly less abundant in Reindeer compared to Milu deer and Sika deer. Conversely, pathways associated with propanoate metabolism, butanoate metabolism, signal transduction, and sulfur metabolism were significantly enriched in Reindeer.
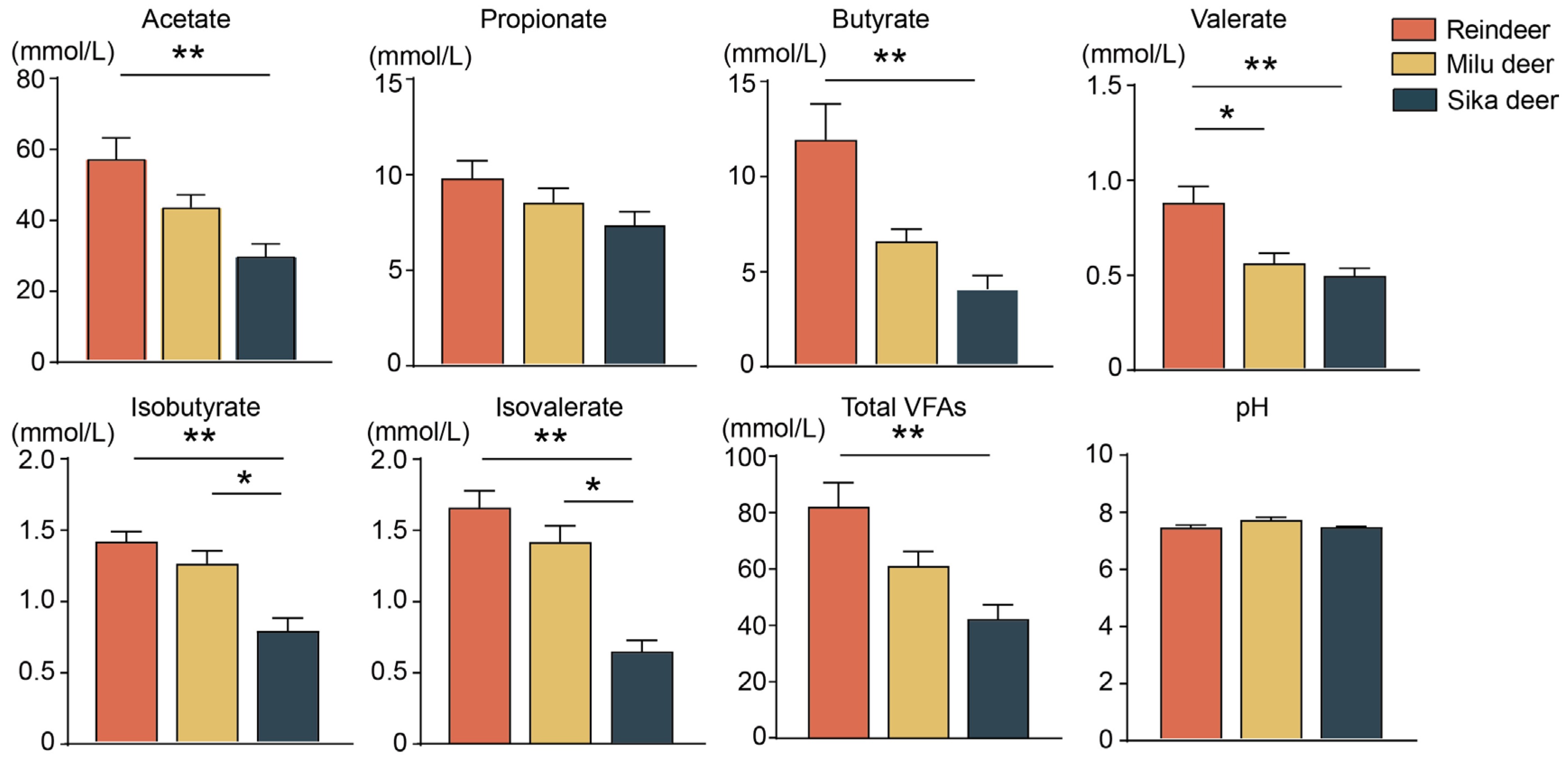
3.2. Comparison of Rumen Fermentation Parameters Among the Three Cervid Species
Analysis of rumen fermentation parameters revealed distinct VFA profiles among the species (Figure 2). Specifically, the concentrations of acetate, butyrate, isobutyrate, valerate, isovalerate, and total VFAs were significantly higher in Reindeer compared to Sika deer (p < 0.01). Furthermore, Reindeer exhibited significantly higher valerate concentrations than Milu deer (p < 0.05). Comparisons between Milu deer and Sika deer showed that the concentrations of isobutyrate and isovalerate were significantly higher in Milu deer. In contrast, no significant differences were observed in rumen pH values among the three species.
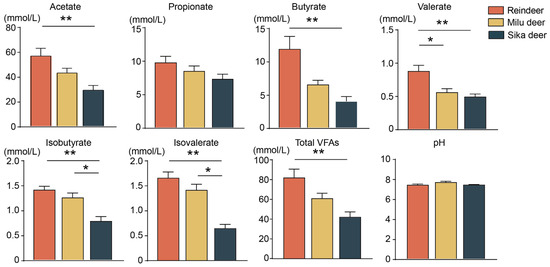
Figure 2.
Comparison of fermentation parameters in the rumen fluid among Reindeer, Milu deer, and Sika deer. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01.
3.3. Correlation Analysis Between Rumen Microbiota and Fermentation Parameters
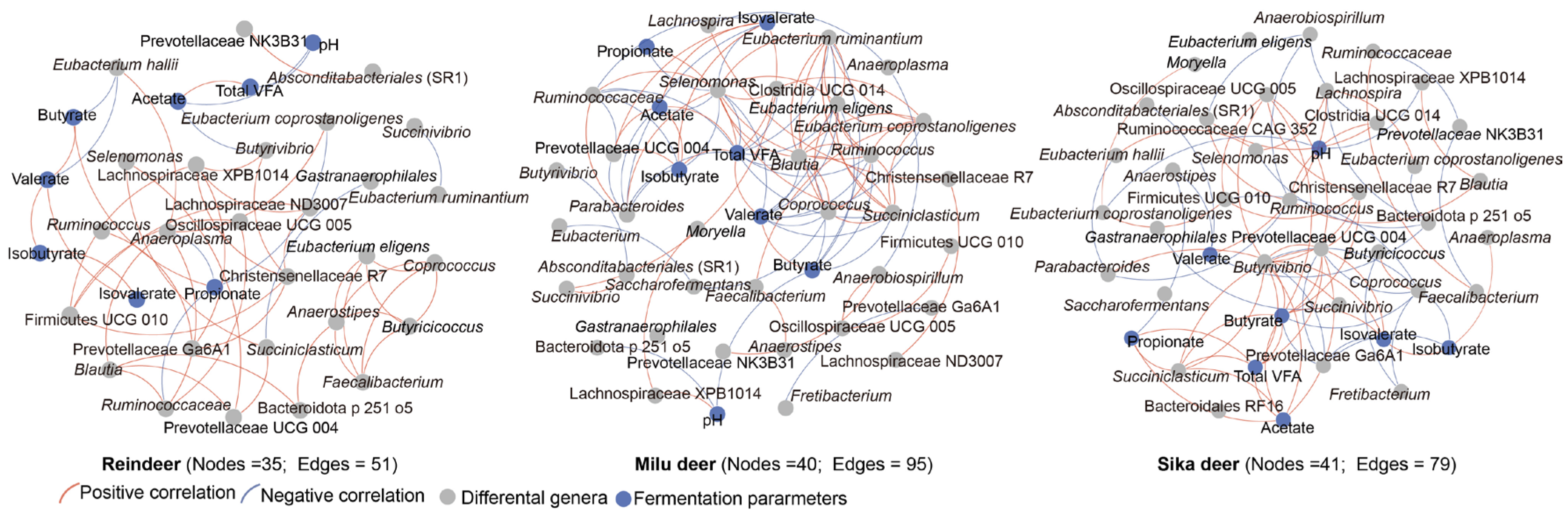
Network analysis was performed to evaluate the associations between differential bacterial genera and fermentation parameters (Figure 3). The resulting correlation networks exhibited distinct topological structures for each species: Sika deer (41 nodes, 79 edges), Reindeer (35 nodes, 51 edges), and Milu deer (40 nodes, 95 edges). Notably, the Milu deer network displayed the highest average degree of connectivity, whereas the Reindeer network was the least complex.
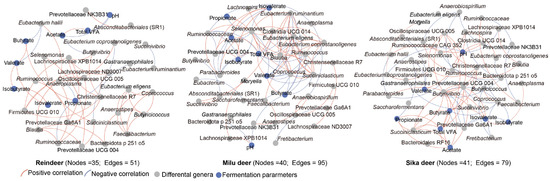
Figure 3.
Association networks between fermentation parameters and differentially abundant genera in Sika deer, Reindeer, and Milu deer. Circular nodes represent fermentation parameters (blue) and bacterial genera (gray). Edges denote correlations between nodes, with red lines indicating positive correlations and blue lines indicating negative correlations.
In Sika deer, a stable and densely connected module of positive correlations was identified, comprising Butyrivibrio, Succiniclasticum, Prevotellaceae UCG-004, Christensenellaceae R7, Oscillospiraceae UCG-005, and key fermentation parameters (total VFA, acetate, butyrate, and isovalerate). For Reindeer, positive correlations were primarily observed among Christensenellaceae R7, Oscillospiraceae UCG-005, Lachnospiraceae XPB1014, and Anaeroplasma. In the Milu deer network, a robust correlation module was observed linking Ruminococcus, Clostridia UCG-014, Coprococcus, Selenomonas, Eubacterium ruminantium, Eubacterium eligens, and total VFA (Figure 3).
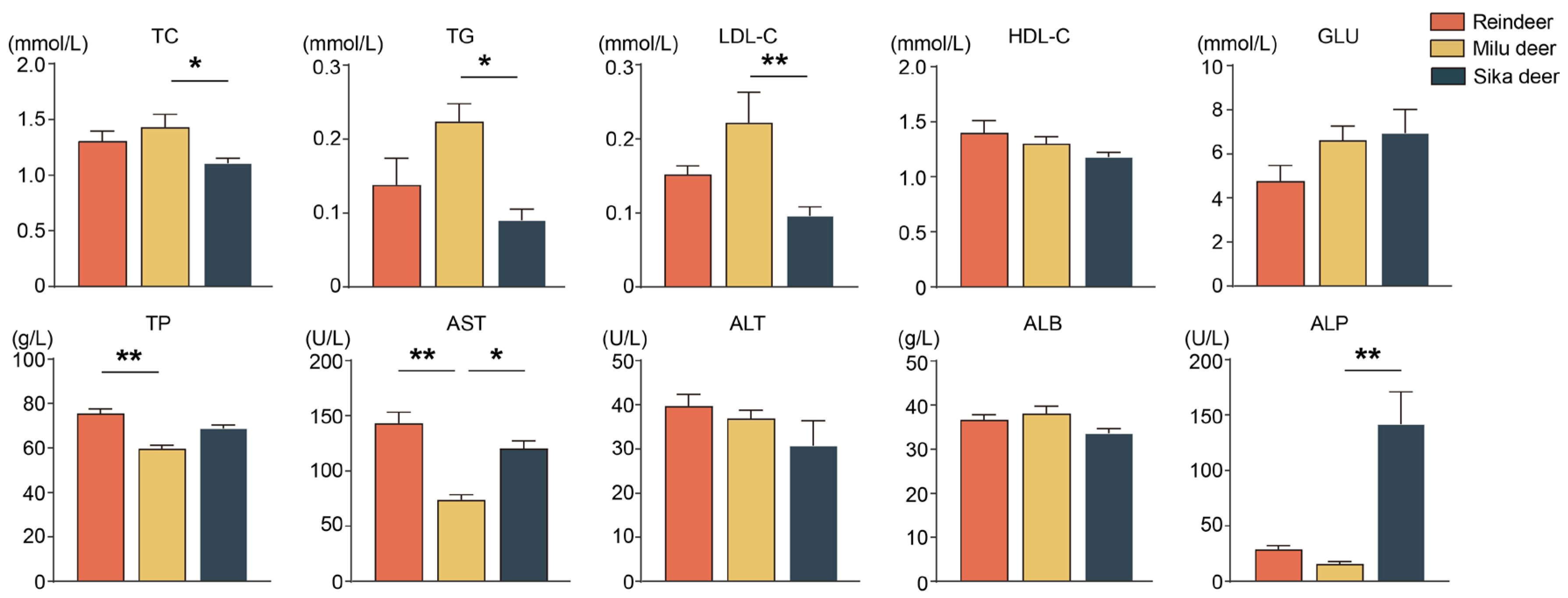
3.4. Comparison of Serum Biochemical Parameters Among the Three Cervid Species
Analysis of serum biochemical profiles revealed significant interspecies differences (Figure 4). Specifically, serum concentrations of total cholesterol (TC), triglycerides (TG), and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) were significantly higher in Milu deer compared to Sika deer (p < 0.05). Reindeer exhibited significantly higher levels of aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and total protein (TP) compared to Milu deer (p < 0.01). Furthermore, serum AST and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) levels were significantly elevated in Sika deer compared to Milu deer (p < 0.05).
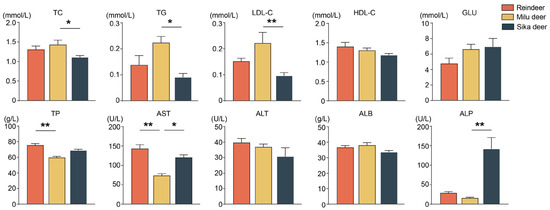
Figure 4.
Comparison of serum biochemical parameters among Reindeer, Milu deer, and Sika deer. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01.
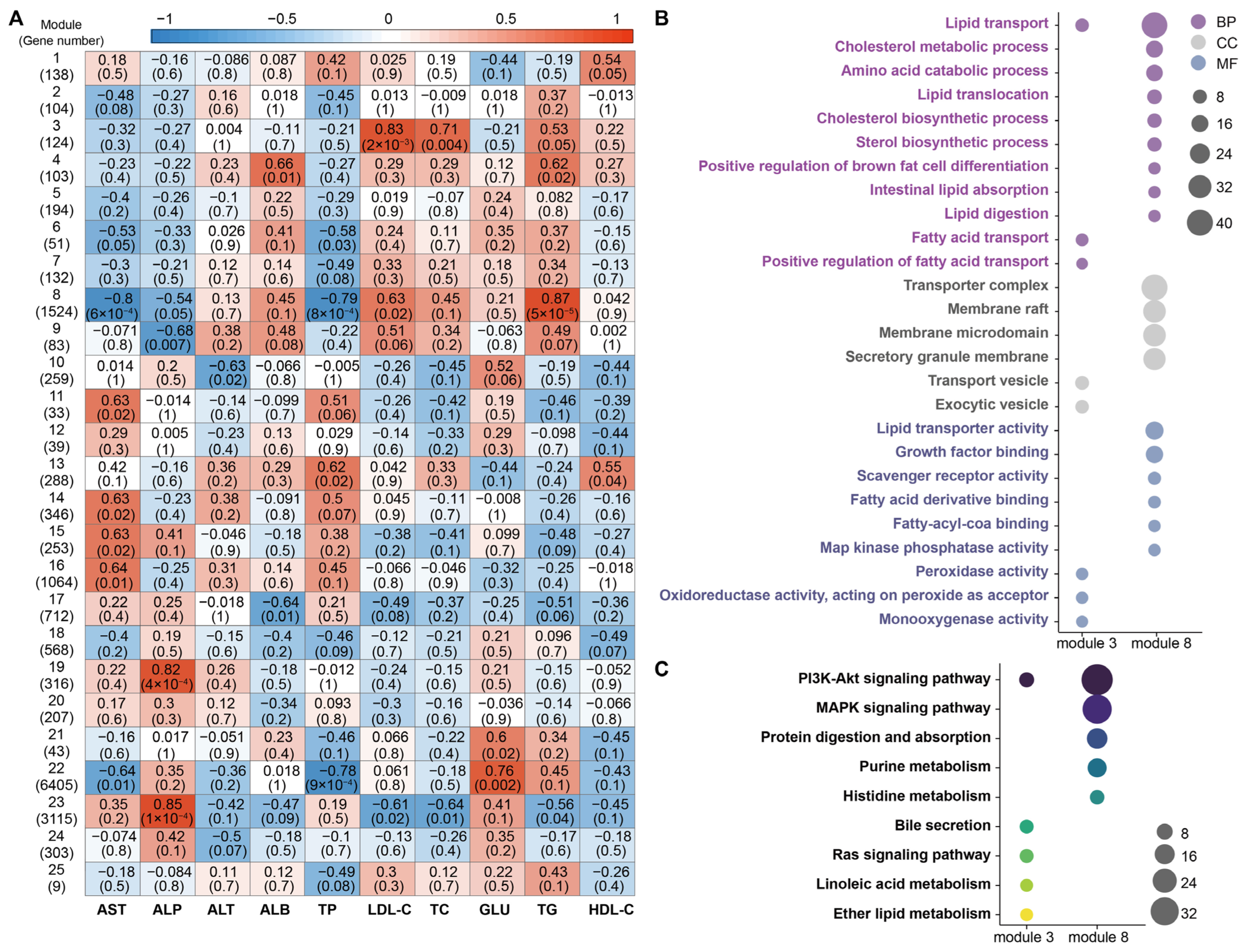
3.5. WGCNA Between Serum Biochemical Parameters and DEGs in Blood
In our previous study, we investigated distinct blood gene expression profiles among Sika deer, Reindeer, and Milu deer [34]. Building on this, we performed WGCNA to integrate the current serum biochemical parameters with the previously identified blood differentially expressed genes (DEGs). This analysis identified 25 co-expression modules (Figure 5A). We observed significant positive correlations between lipid metabolism-related parameters (specifically LDL-C and TC) and Modules 3 and 8. Module 3, which contains genes such as ERFE, CYP4F2, PLA2G1B, and BMP4, showed significant positive correlations with LDL-C, TG, and TC (p < 0.05). Similarly, Module 8 (containing MAPK14, METRNL, and PTGS2) was positively correlated with TG and LDL-C (p < 0.05).
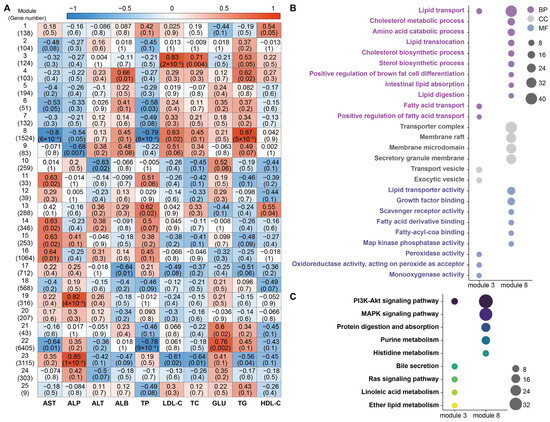
Figure 5.
WGCNA identifying associations between blood DEGs and serum biochemical parameters. (A) Heatmap displaying correlation coefficients between 25 co-expression modules (rows) and 13 serum biochemical parameters (columns). In each cell, the upper value represents the correlation coefficient, and the lower value represents the corresponding significance level (p-value). The color gradient ranges from blue (negative correlation) to red (positive correlation), with intensity reflecting the strength of the correlation. (B) GO enrichment analysis of genes within Modules 3 and 8. Dot size is proportional to the number of genes annotated to each GO term, while dot color denotes the GO category: Biological Process (BP, purple), Cellular Component (CC, grey), and Molecular Function (MF, blue). (C) KEGG pathway enrichment analysis for Modules 3 and 8. Dot size reflects the number of genes enriched in each pathway. Dot color indicates statistical significance, ranging from yellow (lower significance) to dark purple (higher significance).
Subsequent GO and KEGG pathway enrichment analyses were conducted on these two key modules. For Module 3, DEGs were primarily enriched in biological processes related to lipid and fatty acid transport; cellular components including transport vesicles and exocytic vesicles; and molecular functions such as peroxidase and monooxygenase activities. For Module 8, DEGs were significantly enriched in biological processes, including lipid transport and the positive regulation of brown fat cell differentiation. Enriched cellular components for Module 8 included transporter complexes and membrane rafts, while molecular functions involved lipid transporter activity and fatty acid derivative binding (Figure 5B). KEGG pathway analysis revealed that DEGs in Module 3 were mainly associated with the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway, bile secretion, and the Ras signaling pathway. DEGs in Module 8 were enriched in pathways including PI3K-Akt signaling, MAPK signaling, and protein digestion and absorption (Figure 5C).
4. Discussion
Our results demonstrated that Bacteroidota, Firmicutes, and Proteobacteria were the dominant phyla in the rumen of Sika deer, Reindeer, and Milu deer, consistent with previous findings in other cervid species, including roe deer, Sika deer, and red deer [9,26,36]. At the genus level, Prevotella and Bacteroidales F082 were the most dominant taxa across all three species. Prevotella has been identified as a core genus in the rumen of numerous cervids, such as Tarim red deer, moose, and Sika deer [37,38,39]. This genus is capable of degrading various polysaccharides to generate propionate, an essential substrate for hepatic gluconeogenesis [40]. Previous studies have indicated that Bacteroidales F082 likely plays a role similar to that of Bacteroides in carbohydrate decomposition and organic matter fermentation, possibly contributing to propionate production [36,41]. These findings highlight the fundamental roles of these microorganisms in the rumen function of Cervidae.
Despite identical dietary conditions, we observed significant differences in the abundance, diversity, and structure of the rumen microbiota among Sika deer, Reindeer, and Milu deer. This is consistent with our previous observation that the rumen microbiota of hybrid offspring (Sika deer × Red deer) remained highly similar to that of their parents [7], suggesting that the structure and composition of the rumen microbiota are strongly influenced by the host genetic background. Notably, the F/B ratio was significantly lower in Reindeer compared to Sika deer and Milu deer. It has been demonstrated that a decrease in Firmicutes or an increase in Bacteroidota is associated with increased total VFA concentrations [42], which indicates enhanced fermentation efficiency and energy supply to host [43]. Accordingly, the concentrations of total VFAs in the rumen of Reindeer were higher than those in Milu deer and Sika deer. Given that alterations in the metabolic activity of the Reindeer digestive tract may constitute a compensatory mechanism for energy and nutrient expenditure [44], these results suggest that the rumen microbiota contributes significantly to the adaptation of Reindeer to the Arctic environment.
Comparative analysis revealed that the relative abundances of Bacteroidales RF16 and Lachnospiraceae ND3007, as well as pathways related to butyrate metabolism, were elevated in the rumen of Reindeer. A significant decrease in Bacteroidales RF16 has previously been observed in the gastrointestinal tract of diarrheal Milu deer compared to healthy individuals [45], suggesting a role for this taxon in maintaining gastrointestinal health. Lachnospira, belonging to the family Lachnospiraceae, is widely reported in the cervid digestive tract and is involved in fiber degradation and butyrate production [46,47,48,49]. Butyrate produced by the gut microbiota is involved in regulating bone mineral density, particularly in response to exercise [50]. Notably, our previous study demonstrated that butyrate-producing fermentation was significantly upregulated during the rapid antler growth phase of Sika deer [51]. Given the elevated abundance of butyrate-producing bacteria and increased butyrate metabolism in rumen of Reindeer, it is plausible that the rumen microbiota promotes antler development by modulating host metabolic and physiological pathways.
Conversely, Saccharofermentans, Butyrivibrio, and Parabacteroides were significantly more abundant in the rumen of Sika deer and Milu deer relative to Reindeer. Saccharofermentans plays a crucial role in carbohydrate fermentation, generating fumarate, lactate, and acetate [52]. Members of Parabacteroides possess polysaccharide utilization loci that facilitate carbohydrate utilization with the production of acetate, propionate, and butyrate [53]. Butyrivibrio is known to degrade hemicellulose, participate in protein breakdown, and facilitate the biohydrogenation of fatty acids [54,55,56]. Functional prediction analysis indicated that pathways related to starch and sucrose metabolism, carbohydrate digestion and absorption, and amino sugar and nucleotide sugar metabolism were enriched in the rumen of Sika deer and Milu deer. These findings indicate that the composition of the rumen microbial community plays a critical role in determining fermentation patterns.
Network analysis revealed distinct interaction patterns among the species. The Reindeer microbiome exhibited higher degree of positive correlations, whereas Sika deer and Milu deer networks showed higher degree of negative correlations. Recent evidence demonstrates that core taxa produce essential metabolites and encode crucial fiber-degrading enzymes, engaging in cross-feeding to provide non-core microbes with vital nutrients [57]. In dairy cows, strong microbial cooperation has been linked to better adaptability to nutritional changes [58]. Our results suggest potential cooperation among rumen microbiota in Reindeer, contrasting with the competitive dynamics in Sika deer and Milu deer. Furthermore, Prevotellaceae UCG-004 and Christensenellaceae R-7 were identified as key taxa in the networks of both Sika deer and Reindeer, while Eubacterium was central in Milu deer. Prevotellaceae UCG-004 contributes to polysaccharide degradation, enhancing rumen fermentation capacity and promoting rumen epithelium development, and is positively correlated with acetate and butyrate concentrations [59,60,61]. The Christensenellaceae R-7 is important for maintaining gut structure and function and is primarily involved in amino acid, peptide, and lipid metabolism [62]. Members of Eubacterium, such as E. coprostanoligenes, E. ruminantium, and E. eligens, are potential probiotics known for cholesterol-lowering effects and cellulose degradation [63,64,65]. These findings reveal that microbial interactions and cross-feeding mechanisms differ among the three cervid species even under the same dietary conditions.
The levels of TC, TG, and LDL-C were significantly higher in Milu deer than in Reindeer and Sika deer. Total cholesterol (TC) is a key product of lipid metabolism, and elevated levels may indicate a lower utilization rate of body fat [66]. LDL-C transports cholesterol from the liver to peripheral tissues, whereas HDL-C facilitates reverse transport [67]. These results suggest a species-specific tendency towards enhanced lipid synthesis and storage in Milu deer. In contrast, serum AST and TP levels were lower in Milu deer compared to the other two species. Increased TP indicates improved absorption and utilization efficiency of amino acids and proteins, as well as enhanced hepatic protein synthesis and metabolic function [68]. ALT is produced by liver and plays an important role in amino acid metabolism [69]. Together, these distinct blood biochemical profiles reflect species-specific adaptations regarding lipid mobilization efficiency and protein metabolic dynamics.
WGCNA revealed significant correlations between lipid metabolism genes (including ERFE, CYP4F2, PLA2G1B, MAPK14, METRNL, and PTGS2) and serum TG and LDL-C levels. ERFE has been reported to suppress excessive abdominal fat accumulation and improve glucose tolerance [70]. High expression of CYP4F2 contributes to the metabolism of arachidonic acid and omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids [71]. PLA2G1B facilitates dietary fat absorption and can promote diet-induced obesity [72]. METRNL is a cold-induced circulating hormone that stimulates energy expenditure and the “browning” of white adipose tissue [73]. Similarly, PTGS2 (encoding COX-2) is a crucial downstream effector in the induction of beige adipocytes [74], and MAPK14 (p38 MAPK) serves as a central signaling hub for activating the thermogenic program in response to cold stress [75]. The enrichment of these positive regulators suggests that adult Reindeer may retain the plasticity to recruit thermogenic adipocytes to cope with extreme cold environments. Moreover, the PI3K-Akt and MAPK signaling pathways were enriched in Modules 3 and 8, while bile secretion was enriched in Module 3. Both PI3K-Akt and MAPK signaling pathways have been reported to be involved in antler stem cell proliferation and growth [21,76]. Bile acids play a crucial role in lipid digestion and absorption, and our previous study revealed their role in promoting antler stem cell proliferation [24]. These findings suggest a potential mechanistic connection between lipid metabolism—particularly bile acid-related processes—and antler development.
5. Conclusions
Our study reveals significant interspecific divergence in the rumen microbiota, fermentation patterns, and host metabolic profiles among Sika deer, Reindeer, and Milu deer maintained under identical dietary conditions. Specifically, Milu deer exhibit a metabolic signature characterized by enhanced lipid storage, whereas Reindeer and Sika deer display traits indicative of active protein turnover. Furthermore, integrated WGCNA highlights a potential regulatory network linking lipid metabolism genes to key signaling pathways, such as PI3K-Akt and MAPK, which may underlie the observed physiological phenotypes. These findings underscore the distinct metabolic adaptations evolved by these cervid species, providing insights for optimizing species-specific nutritional strategies and advancing our understanding of cervid physiology. Moreover, these findings offer insights for developing nutritional strategies (e.g., supplementing with polysaccharides, oligosaccharides, and amino acids) that could affect the gastrointestinal tract and host metabolism, contributing to the conservation of endangered species such as the Milu deer and the improvement of productivity. In future studies, isolating butyrate-producing microbes and investigating metabolic profiles based on shotgun sequencing and metabolomics would be valuable for understanding the roles of the gastrointestinal microbiome in host adaptation and metabolism, particularly by including a larger sample size.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/ani16010116/s1, Table S1: Ingredients and chemical compositions of the experimental diets.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.L.; methodology, Z.L., W.Q., Y.Z., and H.S.; software, Y.Z., S.C., and Y.C.; validation, Y.Z., S.C. and Y.C.; formal analysis, Y.Z. and Y.C.; investigation, Y.Z., S.C., Y.C., and H.S.; resources, Z.L.; data curation, Y.Z., S.C., Y.C., W.Q., and Z.L.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.Z., Y.C. and H.S.; writing—review and editing, W.Q. and Z.L.; visualization, Y.Z. and Y.C.; supervision, W.Q. and Z.L.; project administration, Z.L.; funding acquisition, Z.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study is supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2023YFD1302000), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (U24A20434), and the Natural Science Foundation of Jilin Province (20240101012JJ) to Z.L.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The animal study protocol was approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of Jilin Agricultural University (No. 20220317001; approved on 17 March 2022).
Data Availability Statement
Blood bulk RNA-seq data and 16S rRNA sequencing data have been deposited in NCBI under accession numbers PRJNA1373567 and PRJNA1373525, respectively.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| TC | total cholesterol |
| TG | triglyceride |
| LDL-C | low-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| GLU | glucose |
| HDL-C | high-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| AST | aspartate aminotransferase |
| ALT | aminotransferase |
| ALP | alkaline phosphatase |
| TP | total protein |
| ALB | albumin |
| PCoA | principal coordinates analyses |
| ANOSIM | analysis of similarities |
| DEGs | differently expressed genes |
| GO | gene ontology |
| KEGG | kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes |
| SEM | standard error of the mean |
| VFA | volatile fatty acid |
| WGCNA | weighted correlation network analysis |
References
- Mizrahi, I.; Jami, E. The compositional variation of the rumen microbiome and its effect on host performance and methane emission. Animal 2018, 12, s220–s232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seshadri, R.; Leahy, S.C.; Attwood, G.T.; Teh, K.H.; Lambie, S.C.; Cookson, A.L.; Eloe-Fadrosh, E.A.; Pavlopoulos, G.A.; Hadjithomas, M.; Varghese, N.J. Cultivation and sequencing of rumen microbiome members from the Hungate1000 Collection. Nat. Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergman, E. Energy contributions of volatile fatty acids from the gastrointestinal tract in various species. Physiol. Rev. 1990, 70, 567–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armentano, L.E. Ruminant Hepatic Metabolism of Volatile Fatty Acids, Lactate and Pyruvate1. J. Nutr. 1992, 122, 838–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newbold, C.; Ramos-Morales, E. Review: Ruminal microbiome and microbial metabolome: Effects of diet and ruminant host. Animal 2020, 14, s78–s86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Zhou, L.; You, X.; Han, H.; Chen, X.; Huang, X. Production performance and rumen bacterial community structure of Hu sheep fed fermented spent mushroom substrate from Pleurotus eryngii. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 8696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wright, A.D.G.; Si, H.; Wang, X.; Qian, W.; Zhang, Z.; Li, G. Changes in the rumen microbiome and metabolites reveal the effect of host genetics on hybrid crosses. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2016, 8, 1016–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, T.; Yang, C.; Li, B.; Huang, X.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, X.; Tian, L.; Zhang, E. High-energy diet modify rumen microbial composition and microbial energy metabolism pattern in fattening sheep. BMC Vet. Res. 2023, 1, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eto, M.; Yahara, T.; Kuroiwa, A.; Shioya, K.; Flores, G.E.; Hamamura, N. Dynamics of rumen microbiome in sika deer (Cervus nippon yakushimae) from unique subtropical ecosystem in Yakushima Island, Japan. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 21623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, H.; Mo, Q.; Wu, H.; Zhao, D. How do living conditions affect the gut microbiota of endangered Père David’s deer (Elaphurus davidianus)? Initial findings from the warm temperate zone. PeerJ 2023, 11, e14897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, S.C.; Jeong, C.D.; Mamuad, L.L.; Kim, S.H.; Kang, S.H.; Kim, E.T.; Cho, Y.I.; Lee, S.S.; Lee, S.S. Diet transition from high-forage to high-concentrate alters rumen bacterial community composition, epithelial transcriptomes and ruminal fermentation parameters in dairy cows. Animals 2021, 11, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Peng, Y.-J.; Chen, Y.; Klinger, C.M.; Oba, M.; Liu, J.-X.; Guan, L.L. Assessment of microbiome changes after rumen transfaunation: Implications on improving feed efficiency in beef cattle. Microbiome 2018, 6, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Li, C.; Chen, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, C.; Irving, B.; Fitzsimmons, C.; Plastow, G.; Guan, L.L. Host genetics influence the rumen microbiota and heritable rumen microbial features associate with feed efficiency in cattle. Microbiome 2019, 7, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasson, G.; Kruger Ben-Shabat, S.; Seroussi, E.; Doron-Faigenboim, A.; Shterzer, N.; Yaacoby, S.; Berg Miller, M.E.; White, B.A.; Halperin, E.; Mizrahi, I. Heritable bovine rumen bacteria are phylogenetically related and correlated with the cow’s capacity to harvest energy from its feed. mBio 2017, 8, e00703-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, B.A.; D’Angelo, G.J. A Review of Cervidae Visual Ecology. Animals 2024, 14, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orpin, C.G.; Mathiesen, S.D.; Greenwood, Y.; Blix, A.S. Seasonal changes in the ruminal microflora of the high-arctic Svalbard reindeer (Rangifer tarandus platyrhynchus). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1985, 50, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.; Chen, L.; Chen, X.; Zhong, Y.; Yang, Y.; Xia, W.; Liu, C.; Zhu, W.; Wang, H.; Yan, B. Biological adaptations in the Arctic cervid, the reindeer (Rangifer tarandus). Science 2019, 364, eaav6312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawabe, Y.; Yamano, H.; Koike, S.; Kobayashi, Y. Isolation and characterization of tannin-degrading bacteria from the rumen of wild Hokkaido sika deer (Cervus nippon yezoensis). Anim. Sci. J. 2024, 95, e13918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Wang, X.; Alberdi, A.; Deng, J.; Zhong, Z.; Si, H.; Zheng, C.; Zhou, H.; Wang, J.; Yang, Y.; et al. Comparative Microbiome Analysis Reveals the Ecological Relationships Between Rumen Methanogens, Acetogens, and Their Hosts. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Xia, Z.; Shan, Y.; Li, J.; Hu, H.; Xiao, X.; Bai, J.; Zhong, Z.; Meng, X.; Zhang, F.; et al. Effects of light duration times on the ecological overflow of antler growth and reproductive dominance of male Père David’s deer (Elaphurus davidianus). Acta Ecol. Sin. 2024, 44, 4368–4376. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, T.; Zhang, G.; Zheng, Y.; Li, S.; Yuan, Y.; Li, Q.; Hu, M.; Si, H.; Wei, G.; Gao, X.; et al. A population of stem cells with strong regenerative potential discovered in deer antlers. Science 2023, 379, 840–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suttie, J.M.; Fennessy, P.F.; Corson, I.D.; Laas, F.J.; Crosbie, S.F.; Butler, J.H.; Gluckman, P.D. Pulsatile growth hormone, insulin-like growth factors and antler development in red deer (Cervus elaphus scoticus) stags. J. Endocrinol. 1989, 121, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Si, H.; Li, S.; Nan, W.; Sang, J.; Xu, C.; Li, Z. Integrated Transcriptome and Microbiota Reveal the Regulatory Effect of 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Supplementation in Antler Growth of Sika Deer. Animals 2022, 12, 3497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Deng, R.; Sang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Ma, C.; Nan, W.; Wang, T.; Si, H.; Li, Z. Integrated microbial and metabolic coordination orchestrates antler growth induced by guar gum and xylo-oligosaccharides. Carbohydr. Polym. 2026, 373, 124586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Mu, R.; Zhu, Y.; Zhao, F.; Qiu, Q.; Si, H.; Wright, A.-D.G.; Li, Z. Shifts in the microbial community and metabolome in rumen ecological niches during antler growth. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2024, 23, 1608–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Li, S.; Mu, R.; Zhao, F.; Yan, X.; Si, H.; Li, Z. Roe deer produce less methane and harbor distinct gut microbiota. Fermentation 2023, 9, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magoč, T.; Salzberg, S.L. FLASH: Fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, M.; Beiko, R.G. 16S rRNA gene analysis with QIIME2. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1849, 113–129. [Google Scholar]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wemheuer, F.; Taylor, J.A.; Daniel, R.; Johnston, E.; Meinicke, P.; Thomas, T.; Wemheuer, B. Tax4Fun2: Prediction of habitat-specific functional profiles and functional redundancy based on 16S rRNA gene sequences. Environ. Microbiome 2020, 15, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastian, M.; Heymann, S.; Jacomy, M. Gephi: An open source software for exploring and manipulating networks. Proc. Int. AAAI. Conf. Weblogs Soc. Media 2009, 3, 361–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langfelder, P.; Horvath, S. WGCNA: An R package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Sang, J.; Zhao, F.; Si, H.; Zhao, Q.; Li, Z. Comparison of Blood Transcriptome among Sika Deer, Reindeer and Père David’s Deer. J. Econ. Anim. 2024, 28, 165–172. [Google Scholar]
- Bu, D.; Luo, H.; Huo, P.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, S.; He, Z.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, L.; Liu, J.; Guo, J. KOBAS-i: Intelligent prioritization and exploratory visualization of biological functions for gene enrichment analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W317–W325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Sheng, Y.; Xue, P.; Guan, P.; Ren, J.; Qian, W. Characteristics of bacterial community and volatile fatty acids in the gastrointestinal tract of Tarim wapiti. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2024, 23, 259–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, T.; Wang, X.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zheng, Y. Gastrointestinal Biogeography of Luminal Microbiota and Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Sika Deer (Cervus nippon). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2022, 17, e0049922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, W.; Li, Z.; Ao, W.; Zhao, G.; Li, G.; Wu, J. Bacterial community composition and fermentation in the rumen of Xinjiang brown cattle (Bos taurus), Tarim red deer (Cervus elaphus yarkandensis), and Karakul sheep (Ovis aries). Can. J. Microbiol. 2017, 63, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishaq, S.L.; Wright, A.-D. High-throughput DNA sequencing of the ruminal bacteria from moose (Alces alces) in Vermont, Alaska, and Norway. Microb. Ecol. 2014, 68, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.-C.; Wang, W.-K.; Zhang, F.; Li, W.-J.; Wang, Y.-L.; Lv, L.-K.; Yang, H.-J. Dietary cysteamine supplementation remarkably increased feed efficiency and shifted rumen fermentation toward glucogenic propionate production via enrichment of Prevotella in feedlot lambs. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, T.; Wu, W.; Tu, Y.; Zhang, N.; Diao, Q. Resveratrol affects in vitro rumen fermentation, methane production and prokaryotic community composition in a time-and diet-specific manner. Microb. Biotechnol. 2020, 13, 1118–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Jiao, J.; Wang, H.; Degen, A.A.; Gou, N.; Li, S.; Bai, Y.; Shang, Z. The effects of supplementing sweet sorghum with grapeseeds on dry matter intake, average daily gain, feed digestibility and rumen parameters and microbiota in lambs. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2021, 272, 114750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minich, D.; Madden, C.; Evans, M.V.; Ballash, G.A.; Barr, D.J.; Poulsen, K.P.; Dennis, P.M.; Hale, V.L. Alterations in gut microbiota linked to provenance, sex, and chronic wasting disease in white-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus). Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 13218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, E.; Ilina, L.; Laptev, G.; Filippova, V.; Brazhnik, E.; Dunyashev, T.; Dubrovin, A.; Novikova, N.; Tiurina, D.; Tarlavin, N. The structure and functional profile of ruminal microbiota in young and adult reindeers (Rangifer tarandus) consuming natural winter-spring and summer-autumn seasonal diets. PeerJ 2021, 9, e12389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, J.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yuan, X.; Wang, L.; Shen, H.; Liu, P.; Chen, Y. Effect of different dietary regimes on the gut microbiota and fecal metabolites of Père David’s deer. Animals 2022, 12, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.-H.; Liu, H.-Y.; Liu, B.; Yuan, B.-D.; Lu, C.-H. Analysis of the gut microbiome of wild and captive Père David’s deer. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 485029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, S.; Sandfort, R.; Pinior, B.; Mann, E.; Wetzels, S.U.; Stalder, G. Impact of supplemental winter feeding on ruminal microbiota of roe deer Capreolus capreolus. Wildl. Biol. 2019, 2019, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahl, S.-A.; Seifert, J.; Camarinha-Silva, A.; Hernández-Arriaga, A.; Windisch, W.; König, A. “Get the best out of what comes in”–adaptation of the microbiota of chamois (Rupicapra rupicapra) to seasonal forage availability in the Bavarian Alps. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1238744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geirnaert, A.; Calatayud, M.; Grootaert, C.; Laukens, D.; Devriese, S.; Smagghe, G.; De Vos, M.; Boon, N.; Van de Wiele, T. Butyrate-producing bacteria supplemented in vitro to Crohn’s disease patient microbiota increased butyrate production and enhanced intestinal epithelial barrier integrity. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dou, X.; Fu, P.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ning, K.; Yang, B.; Yang, X.; Niu, Y.; Wang, D.-E.; Xu, H. Gut microbiota-derived butyrate enhances exercise-induced bone mineral density in humans. Mechanobiol. Med. 2025, 3, 100124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, S.; Zhu, Y.; Mu, R.; Wang, T.; Zhen, Y.; Si, H.; Du, R.; Li, Z. In vitro dynamics of rumen microbiota and fermentation profiles with Antler growth of Sika deer. Microbiol. Spectr. 2025, 13, e02829-24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, A.A.; Zhang, J.; Liang, Z.; Du, M.; Yang, Y.; Zheng, J.; Yan, P.; Long, R.; Tong, B.; Han, J. Age-dependent variations in rumen bacterial community of Mongolian cattle from weaning to adulthood. BMC Microbiol. 2022, 22, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X.; Yi, Y.; Shan, Y.; Liu, B.; Zhou, Y.; Lü, X. Roles of intestinal Parabacteroides in human health and diseases. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2022, 369, fnac072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miron, J.; Ben-Ghedalia, D. Digestion of cell-wall monosaccharides of ryegrass and alfalfa hays by the ruminal bacteria Fibrobacter succinogenes and Butyrivibrio fibrisolvens. Can. J. Microbiol. 1993, 39, 780–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blackburn, T.; Hobson, P. Further studies on the isolation of proteolytic bacteria from the sheep rumen. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1962, 29, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKain, N.; Shingfield, K.J.; Wallace, R.J. Metabolism of conjugated linoleic acids and 18: 1 fatty acids by ruminal bacteria: Products and mechanisms. Microbiology 2010, 156, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tovar-Herrera, O.E.; Grinshpan, I.; Sorek, G.; Lybovits, I.; Levin, L.; Moraïs, S.; Mizrahi, I. Core rumen microbes are functional generalists that sustain host metabolism and gut ecosystem function. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2025. online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Ouyang, T.; Wang, W.; Wang, Y.; Cao, Z.; Yang, H.; Guan, L.L.; Li, S. Competitive Analysis of Rumen and Hindgut Microbiota Composition and Fermentation Function in Diarrheic and Non-Diarrheic Postpartum Dairy Cows. Microorganisms 2023, 12, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.; Wang, D.; Mao, K.; Wang, M.; Wang, J.; Xun, W.; Huang, S. Exploring the Rumen Microbiota and Serum Metabolite Profile of Hainan Black Goats with Different Body Weights before Weaning. Animals 2024, 14, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takizawa, S.; Shinkai, T.; Saito, K.; Fukumoto, N.; Arai, Y.; Hirai, T.; Maruyama, M.; Takeda, M. Effect of rumen microbiota transfaunation on the growth, rumen fermentation, and microbial community of early separated Japanese Black cattle. Anim. Sci. J. 2023, 94, e13876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinritz, S.N.; Weiss, E.; Eklund, M.; Aumiller, T.; Louis, S.; Rings, A.; Messner, S.; Camarinha-Silva, A.; Seifert, J.; Bischoff, S.C. Intestinal microbiota and microbial metabolites are changed in a pig model fed a high-fat/low-fiber or a low-fat/high-fiber diet. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154329. [Google Scholar]
- Waters, J.L.; Ley, R.E. The human gut bacteria Christensenellaceae are widespread, heritable, and associated with health. BMC Biol. 2019, 17, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, A.; Lordan, C.; Ross, R.P.; Cotter, P.D. Gut microbes from the phylogenetically diverse genus Eubacterium and their various contributions to gut health. Gut Microbes 2020, 12, 1802866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wade, W.G. The genus Eubacterium and related genera. Prokaryotes 2006, 4, 823–835. [Google Scholar]
- Freier, T.A.; Beitz, D.C.; Li, L.; Hartman, P.A. Characterization of Eubacterium coprostanoligenes sp. nov., a cholesterol-reducing anaerobe. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1994, 44, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, A.; Zhang, P.; Abubakari, A.-H.; Elemba, E.; Zhong, Q.; Sun, Z. Reclamation of Astragalus by-product through dietary inclusion in ruminant diets: Effects on growth performance, nutrient digestibility, rumen fermentation, blood biochemical parameters, and humoral immune response in sheep. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2019, 2019, 8530961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, R.; Fang, Y.; Zhou, D.; Sun, X.; Zhou, C.; He, Y. Pelleted total mixed ration improves growth performance of fattening lambs. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2018, 242, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Qu, Y.-h.; Guo, P.-t.; Xu, C.-c.; Ma, Y.; Luo, H.-l. Effects of dietary supplementation with alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) saponins on lamb growth performance, nutrient digestibility, and plasma parameters. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2018, 236, 98–106. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Tan, Z.; Jiao, J.; Long, D.; Zhou, C.; Yi, K.; Liu, C.; Kang, J.; Wang, M.; Duan, F. Supplementation with fat-coated rumen-protected glucose during the transition period enhances milk production and influences blood biochemical parameters of liver function and inflammation in dairy cows. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2019, 252, 92–102. [Google Scholar]
- Hilton, C.; Sabaratnam, R.; Neville, M.; Karpe, F. Plasma Erythroferrone is negatively correlated with total body fat. Endocr. Abstr. 2022, 86, P76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarrar, Y.B.; Lee, S.-J. Molecular functionality of cytochrome P450 4 (CYP4) genetic polymorphisms and their clinical implications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cash, J.G.; Kuhel, D.G.; Goodin, C.; Hui, D.Y. Pancreatic acinar cell-specific overexpression of group 1B phospholipase A2 exacerbates diet-induced obesity and insulin resistance in mice. Int. J. Obes. 2011, 35, 877–881. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, R.R.; Long, J.Z.; White, J.P.; Svensson, K.J.; Lou, J.; Lokurkar, I.; Jedrychowski, M.P.; Ruas, J.L.; Wrann, C.D.; Lo, J.C. Meteorin-like is a hormone that regulates immune-adipose interactions to increase beige fat thermogenesis. Cell 2014, 157, 1279–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vegiopoulos, A.; Müller-Decker, K.; Strzoda, D.; Schmitt, I.; Chichelnitskiy, E.; Ostertag, A.; Diaz, M.B.; Rozman, J.; Hrabe de Angelis, M.; Nüsing, R.M.; et al. Cyclooxygenase-2 Controls Energy Homeostasis in Mice by de Novo Recruitment of Brown Adipocytes. Science 2010, 328, 1158–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, W.; Daniel, K.W.; Robidoux, J.; Puigserver, P.; Medvedev, A.V.; Bai, X.; Floering, L.M.; Spiegelman, B.M.; Collins, S. p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase is the central regulator of cyclic AMP-dependent transcription of the brown fat uncoupling protein 1 gene. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004, 24, 3057–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Zhao, H.-P.; Wang, D.-T.; McMahon, C.; Li, C.-Y. Differential effects of the PI3K/AKT pathway on antler stem cells for generation and regeneration of antlers in vitro. Front. Biosci. 2018, 23, 1848–1863. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.