Field Prevalence and Pathological Features of Edwardsiella tarda Infection in Farmed American Bullfrogs (Aquarana catesbeiana)
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Epidemiological Survey
2.2. Experimental Animals
2.3. Histopathology
2.4. Bacterial Isolation and Identification
2.5. Quantitative Detection of FV3 and E. tarda in Field Samples
2.6. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
2.7. Detection of Virulence Genes
2.8. Infection Model
2.8.1. Challenge Experiment
2.8.2. Disease Progression Analysis
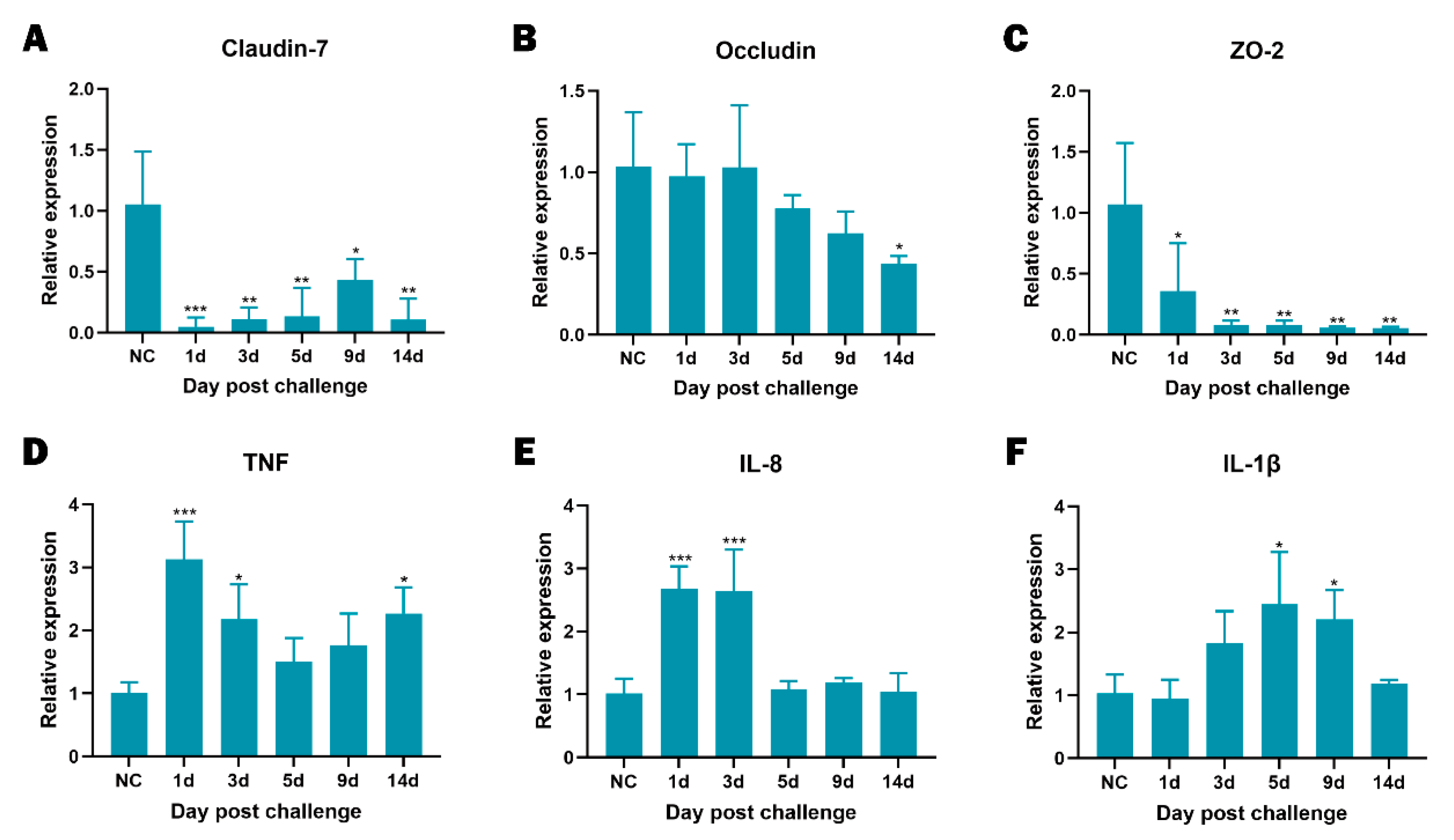
2.9. Intestinal Gene Expression
| Target Gene | Primer Sequence (5′-3′) | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| IL-1β | F: CAGTGATTAGACACCCAGGAACG | [19] |
| R: GACCTTCATTTCAGTGGAGCATTC | ||
| IL-8 | F: GCTTGTGCCACCCTTACCCTC | [19] |
| R: GCTCTACCCAAGAAGCAGAAGGA | ||
| TNF | F: CACAGCACCCAGGAGCAACT | XM_040323112.1 |
| R: GGGATGATGTGGAAGTGGAGC | ||
| ZO-2 | F: TGAGGATGGACATTTTGACCGTAG | [33] |
| R: CATAGCCTCGGTCTGGACTGGAT | ||
| Claudin-7 | F: GCTCTCCATTGTTCTCGGGGT | [33] |
| R: CCCAGCAGAAAGATGAAGCCTC | ||
| Occludin | F: GCTCTCCACCTGGCATCATCA | [33] |
| R: GCAAAACCCATTCCCATCTGAG | ||
| RNA 18S | F: CGTTGATTAAGTCCCTGCCCTT | [34] |
| R: GCCGATCCGAGGACCTCACTA | ||
| 16S rRNA | F: AGAGTTTGATCCTGGTCAGAACGAACGCT | [25] |
| R: TACGGCTACCTTGTTACGACTTCACCCC | ||
| gadB | F: ATTTGGATTCCCGCTTTGGT | [31] |
| R: GCACGACGCCGATGGTGTTC | ||
| mukF | F: TTGCTGGCTATCGCTACCCT | [31] |
| R: AACTCATCGCCGCCCTCTTC | ||
| citC | F: TTTCCGTTTGTGAATCAGGTC | [31] |
| R: AATGTTTCGGCATAGCGTTG | ||
| fimA | F: CTGTGAGTGGTCAGGCAAGC | [31] |
| R: TAACCGTGTTGGCGTAAGAGC | ||
| katB | F: CTTAGCCATCAGCCCTTCC | [31] |
| R: GCGAGTGCCGTAGTCCTT | ||
| EseD | F: TTCAGGGTGGTCAGTATCTCG | AY643478.1 |
| R: TCAACAGACGCAGCAAAGC | ||
| OmpA | F: ACCCGTCTGGACTATCAGTATGT | GQ259743.1 |
| R: GCGGCTGAGTAACTTCTTCTTT | ||
| FliC | F: CGCTGATGGCACAGAATAAC | AP040123.1 |
| R: TCAGATAGGGCTTTGTCCAG | ||
| rpoB | F: GCAGTGAAAGARTTCTTTGGTTC | [25] |
| R: GTTGCATGTTNGNACCCA | ||
| Et-gyrB | F: TGGCGACACCGAGCAGA | [26] |
| R: ACAAACGCCTTAATCCCACC | ||
| FV3-MCP | F: GACGAGAGACAGGCCATGAG | [27] |
| R: GGAAGGGTGTGTGACGTTCT | ||
| Probe: ACCTCCTGATCCA |
2.10. PCR and Quantitative PCR
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Features
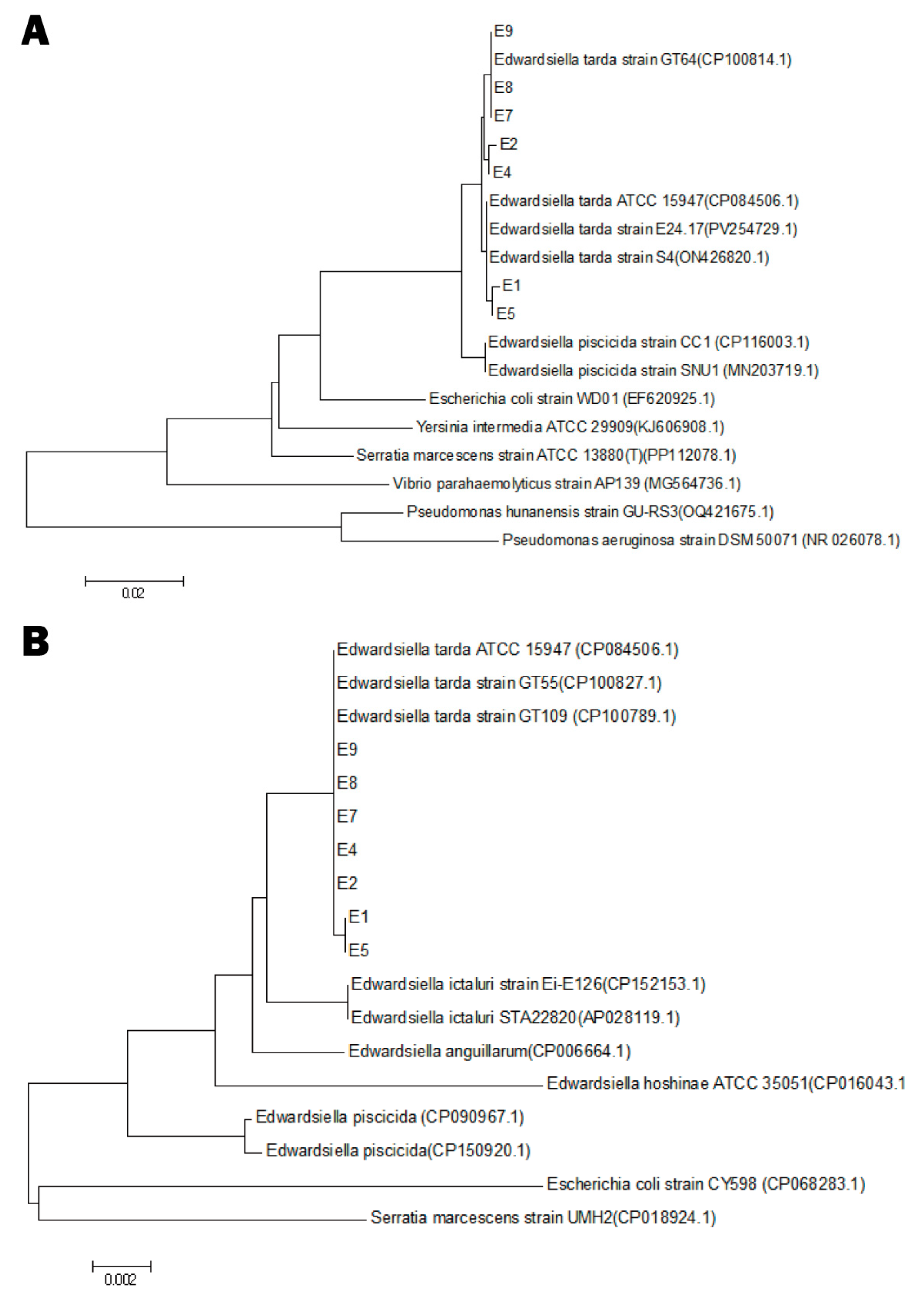
3.2. Molecular Identification
3.3. Prevalence and Bacterial Load
3.4. Virulence Gene Profiling
3.5. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Patterns
3.6. Challenge Experiment
3.7. Disease Progression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| E. tarda | Edwardsiella tarda |
| FV3 | Frog Virus 3 |
| rpoB | RNA Polymerase Subunit B |
| 16S rRNA | 16S Ribosomal RNA |
| CFU | Colony-Forming Unit |
| BHI | Brain Heart Infusion |
| CLSI | Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute |
| Ahp | Alkyl-Hydroperoxide Reductase |
| IL | Interleukin |
| TNF | Tumour Necrosis Factor |
| ZO-2 | Zonula Occludens-2 |
References
- Fujita, M.; Ito, H.; Oshida, J.; Kobayashi, D. Fulminant Edwardsiella tarda bacteremia following near-drowning episode in a patient without cirrhosis: A case report. J. Infect. Chemother. 2025, 31, 102591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, K.Y.; Wang, Q.; Zheng, X.; Zhuang, M.; Yang, Z.; Shao, S.; Achmon, Y.; Siame, B.A. Versatile lifestyles of Edwardsiella: Free-living, pathogen, and core bacterium of the aquatic resistome. Virulence 2022, 13, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, C.; Tanaka, T.; Nishiwada, S.; Kirihataya, Y.; Yoshimura, A. Acute cholecystitis with sepsis due to Edwardsiella tarda: A case report. Surg. Case Rep. 2023, 9, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, L.T.; Li, D.L.; Yang, D.X.; Peng, B. Taurine promotes Oreochromis niloticus survival against Edwardsiella tarda infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022, 129, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Wu, M.; Sun, Y.; Sun, L. Edwardsiella tarda TraT is an anti-complement factor and a cellular infection promoter. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.B.; Aoki, T.; Jung, T.S. Pathogenesis of and strategies for preventing Edwardsiella tarda infection in fish. Vet. Res. 2012, 43, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, F.; Chen, G.; Yang, B.; Chen, J.; Fang, Y.; Wang, K.; Hou, Y. Edwardsiella tarda induces enteritis in farmed seahorses (Hippocampus erectus): An experimental model and its evaluation. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 98, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Li, W.; Zhang, R.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, R.; Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Qing, B.; Duan, W.; et al. Edwardsiella tarda causing septicemia in a wild crested ibis (Nipponia nippon). J. Wildl. Dis. 2024, 60, 232–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, N.L.; Ware, C.; Griffin, M.J. Edwardsiella tarda isolated from a kidney mass in a common loon (Gavia immer). J. Wildl. Dis. 2023, 59, 804–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Ren, D.; Li, Y.; Gui, S. A case of septic shock caused by drug-resistant Edwardsiella tarda and literature review. BMC Infect. Dis. 2025, 25, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chida, R.; Iio, K.; Kaizuka, H.; Hirai, Y.; Ishida, Y.; Yamanaka, G. Chronic diarrhea associated with Edwardsiella tarda gastroenteritis: A case report and literature review. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2022, 41, e440–e442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owens, D.R.; Nelson, S.L.; Addison, J.B. Isolation of Edwardsiella tarda from swine. Appl. Microbiol. 1974, 27, 703–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Assche, J. Edwardsiella tarda infection in a puppy with possible parvovirus infection. Vet. Rec. 1991, 129, 475–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauel, M.J.; Miller, D.L.; Frazier, K.S.; Hines, M.E., II. Bacterial pathogens isolated from cultured bullfrogs (Rana catesbeiana). J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2002, 14, 431–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.X.; Huang, K.K.; Wang, L.; Song, K.; Zhang, L.; Li, P. Apparent digestibility coefficients and amino-acid availability of common protein ingredients in the diets of bullfrog (Rana/Lithobates catesbeiana). Aquaculture 2015, 437, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, Z.H.; Zheng, J.P.; Zhang, H.W.; Wang, X.; Guo, G.Y.; Lin, Y.Q.; Han, Q.; Li, R.S.; Yang, N.; Fan, L.X.; et al. Natural outbreaks and molecular characteristics of Streptococcus agalactiae infection in farmed American bullfrog (Rana catesbeiana). Aquaculture 2022, 551, 737885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, R.; Hou, G.; Sun, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, C.; Han, Y.; Li, Y.; Wu, T.; Shi, Q.; Zhu, Z.; et al. Outbreaks of Elizabethkingia miricola caused fatal meningitis-like disease in cultured bullfrogs. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2024, 2024, 4733320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.; Cheng, Y.; Xiao, S.; Liao, W.; Yu, Q.; Han, S.; Huang, S.; Shi, J.; Xie, Z.; Li, P. Natural occurrences and characterization of Elizabethkingia miricola infection in cultured bullfrogs (Rana catesbeiana). Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1094050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Zeng, G.; Yu, Y.; Li, H.; Chen, K.; Qin, Z.; Jiang, B.; Li, W.; Su, Y.; Li, L.; et al. Acute septicemia and diagnostic evaluation of Aeromonas veronii infection in American bullfrogs (Aquarana catesbeiana). Aquaculture 2023, 740, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoli, C.; Di Bianco, S.; Sigwalt, A.; Defois, J.; Dufay-Lefort, A.C.; Gambara, T.; Gabriac, M.S.; Leblanc Maridor, M.; Duvauchelle Waché, A. Informational resources used by farmers with ruminants and monogastrics for animal health monitoring: Importance of sensory indicators. Animal 2024, 18, 101053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semangoen, T.; Chotigawin, R.; Sangnim, T.; Chailerd, N.; Yodkeeree, S.; Pahasup-Anan, T.; Huanbutta, K. Antimicrobial efficacy of Mangosteen (Garcinia mangostana) peel extracts in airborne microbial control within livestock farming environments. Microb. Pathog. 2025, 204, 107618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Go, Y.Y.; Ho, J.H.P.; Tam, K.W.S.; Kamali, M.; Zhang, Y.; Lau, C.C.Y.; Li, S.H.; Wilson, M.T.; Guo, Z.; Li, R.; et al. Investigation of the first African swine fever outbreak in a domestic pig farm in Hong Kong. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2023, 2023, 1720474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Af Sandeberg, A.; Båge, R.; Nyman, A.K.; Agenäs, S.; Hansson, H. Linking animal health measures in dairy cows to farm-level economic outcomes: A systematic literature mapping. Animal 2023, 17, 100971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.E.; Park, J.S.; Park, H.T.; Shin, J.I.; Kim, K.M.; Park, S.R.; Choi, J.G.; Jung, M.; Kang, H.L.; Baik, S.C.; et al. Fetuin as a potential serum biomarker to detect subclinical shedder of bovine paratuberculosis. Microb. Pathog. 2022, 169, 105675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Chang, Q.; Zhang, D.F.; Li, K.B.; Wang, F.; Lin, M.H.; Shi, C.B.; Jiang, L.; Wang, Q.; Bergmann, S.M. Aeromonas shuberti as a cause of multi-organ necrosis in internal organs of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). J. Fish Dis. 2018, 41, 1529–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, X.; Liao, M.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, B.; Wang, L.; Chen, G. Development of an SYBR Green I real-time PCR assay for detection of Edwardsiella tarda and its application. J. Fish. China 2013, 37, 1829–1838. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liu, X.; Sun, J.; Lin, H.; Chen, K.; Hu, Y.; Jiang, M.; Jiang, B.; Li, W.; Su, Y.; et al. Frog virus 3: Prevalence survey and quantitative analysis in American bullfrogs using TaqMan MGB probe real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR. Aquaculture 2025, 605, 742527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CLSI. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 34th ed.; CLSI: Wayne, PA, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.M.; Yoshida, A.; Toutani, F.; Shimizu, T.; Oda, T.; Osatomi, K. Cloning, DNA sequence, and expression of flagellins from high- and low-virulence strains of Edwardsiella tarda and their macrophage-stimulating activities. Microb. Pathog. 2023, 176, 105993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Hu, Y.; You, Y.; Gao, Y.; Wang, X.; Qin, L. Functional analysis of OmpA and its contribution to pathogenesis of Edwardsiella tarda. Microb. Pathog. 2024, 193, 106760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yan, M.; Wang, Q.; Ding, L.; Li, F. Identification of Edwardsiella tarda isolated from duck and virulence-genes detection. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2012, 6, 4970–4975. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Mo, Z.L.; Xiao, P.; Li, J.; Zou, Y.X.; Hao, B.; Li, G.Y. EseD, a putative T3SS translocon component of Edwardsiella tarda, contributes to virulence in fish and is a candidate for vaccine development. Mar. Biotechnol. 2010, 12, 678–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Lin, H.; Sun, J.; Li, H.; Ma, J.; Qin, Z.; Jiang, B.; Li, W.; Wang, Q.; Su, Y.; et al. Archidendron clypearia extract: Modulating intestinal inflammation and enhancing disease resistance in aquacultured American bullfrogs (Aquarana catesbeiana). Aquac. Rep. 2025, 42, 102744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Feng, Y.; Tang, H.; Xiong, G.; Li, L.; Yang, Y.; Wang, K.; Ouyang, P.; Geng, Y.; Chen, D.; et al. Candidate animal disease model of Elizabethkingia spp. infection in humans, based on the systematic pathology and oxidative damage caused by E. miricola in Pelophylax nigromaculatus. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 6407524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Ma, J.; Sun, J.; Qin, Z.; Jiang, B.; Li, W.; Wang, Q.; Su, Y.; Lin, L.; Liu, C. Identification and characterization of Klebsiella pneumoniae from farmed American bullfrogs (Rana catesbeiana). Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0357922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Sun, J.; Li, H.; Chen, K.; Qin, Z.; Jiang, B.; Li, W.; Wang, Q.; Su, Y.; Lin, L.; et al. Enhanced virulence of Acinetobacter johnsonii at low temperatures induces acute immune response and systemic infection in American bullfrogs (Aquarana catesbeiana). Vet. Microbiol. 2025, 302, 110404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Xiong, N.X.; Ou, J.; Zhong, Z.R.; Xie, Q.; Huang, J.F.; Li, K.X.; Huang, M.Z.; Fang, Z.X.; Kuang, X.Y.; et al. Immunometabolic interplay in Edwardsiella tarda-infected crucian carp (Carassius auratus) and in vitro identification of the antimicrobial activity of apolipoprotein D. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 278, 134898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirarat, N.; Maita, M.; Endo, M.; Katagiri, T. Lymphoid apoptosis in Edwardsiella tarda septicemia in tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2007, 22, 608–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonosaki, K.; Yonenaga, K.; Mikami, T.; Mizuno, T.; Oyama, S. Acute cholecystitis, sepsis, and disseminated intravascular coagulation caused by Edwardsiella tarda in an elderly woman. Tokai J. Exp. Clin. Med. 2021, 46, 51–53. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, L.; Wu, X.; Lin, J.; Zhang, J.; Shi, H.; Hong, M.; Fang, Z. Butylparaben disordered intestinal homeostasis in Chinese, striped-necked turtles (Mauremys sinensis). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 262, 115193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Yang, D. Edwardsiella piscicida infection-induced tryptophan-kynurenine pathway impairs Th17 cells to drive intestinal inflammation in teleost. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2025, 163, 110425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Chen, Q.; Tang, M.; Wei, T.; Zou, J. Effects of TLR2/4 signalling pathway in western mosquitofish (Gambusia affinis) after Edwardsiella tarda infection. J. Fish Dis. 2023, 46, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macura, B.; Kiecka, A.; Szczepanik, M. Intestinal permeability disturbances: Causes, diseases and therapy. Clin. Exp. Med. 2024, 24, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, R.; Mathew, B.J.; Chourasia, R.; Singh, A.K.; Chaurasiya, S.K. Glutamate decarboxylase confers acid tolerance and enhances survival of mycobacteria within macrophages. J. Biol. Chem. 2025, 301, 108338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saint Martin, C.; Caccia, N.; Darsonval, M.; Gregoire, M.; Combeau, A.; Jubelin, G.; Dubois-Brissonnet, F.; Leroy, S.; Briandet, R.; Desvaux, M. Spatially localised expression of the glutamate decarboxylase gadB in Escherichia coli O157:H7 microcolonies in hydrogel matrices. npj Sci. Food 2023, 7, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seba, M.; Boccard, F.; Duigou, S. Activity of MukBEF for chromosome management in E. coli and its inhibition by MatP. eLife 2024, 12, RP91185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostiuk, B.; Becker, M.E.; Churaman, C.N.; Black, J.J.; Payne, S.M.; Pukatzki, S.; Koestler, B.J. Vibrio cholerae alkalizes its environment via citrate metabolism to inhibit enteric growth in vitro. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0491722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivasa Rao, P.S.; Yamada, Y.; Leung, K.Y. A major catalase (KatB) required for resistance to H2O2 and phagocyte-mediated killing in Edwardsiella tarda. Microbiology 2003, 149, 2635–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, J.; Chen, T.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y. Comparative roles of catalases KatB and KatG in fitness and pathogenesis of fish pathogen Edwardsiella tarda. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 54, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossainey, M.R.H.; Hauser, K.A.; Garvey, C.N.; Kalia, N.; Garvey, J.M.; Grayfer, L. A perspective into the relationships between amphibian (Xenopus laevis) myeloid cell subsets. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2023, 378, 20220124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaparla, A.; Popovic, M.; Hauser, K.A.; Rollins-Smith, L.A.; Grayfer, L. Amphibian (Xenopus laevis) macrophage subsets vary in their responses to the chytrid fungus Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis. J. Fungi 2025, 11, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, C.; Capilla-Lasheras, P.; Monaghan, P.; Burraco, P. Impact of chemical pollution across major life transitions: Meta-analysis on oxidative stress in amphibians. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2024, 291, 20241536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, R.; Chen, F.; Zhang, X.; Qin, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W. Immune-defence adaptation of Strauchbufo raddei population in heavy-metal-polluted area: Developmental and environmental perspectives. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 371, 123126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, L.; Nguyen, V.T.; Tamaoki, J.; Endo, Y.; Dong, G.; Sato, A.; Kobayashi, M. Genetic hyperactivation of Nrf2 causes larval lethality in Keap1a- and Keap1b-double-knockout zebrafish. Redox Biol. 2023, 62, 102673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, H.; Zhong, F.; Li, J.; Zhao, L. VBNC Cronobacter sakazakii survives in macrophages by resisting oxidative stress and evading recognition. BMC Microbiol. 2024, 24, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, M.; Hu, M.; Yang, M.; Peng, Z.; Li, D.; Zhao, Y. Characterization of oxidative-stress-induced cgahp, an alkyl hydroperoxide reductase gene, from Corynebacterium glutamicum. Biotechnol. Lett. 2023, 45, 1309–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.J.; Cui, R.; Liu, Y.Y.; Liu, W.R.; Wang, Z.L.; Li, C.M.; Ju, Y.X. Regulation of alkyl hydroperoxidase D by AhpD-R in the antioxidant system of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2025, 763, 151797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.G.; Gao, Y.P.; Jiang, S.J.; Jordan, R.W.; Yang, Y.F. Ecotoxicological risk of antibiotics and their mixtures to aquatic biota assessed with the DGT technique in sediments. Ecotoxicology 2023, 32, 536–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, X.; Qin, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, J.; Diao, X.; Altaf, M.M. Regional distribution differences of antibiotics in a tropical marine aquaculture area: Insights into antibiotic management and risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 954, 176391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarıçam İnce, S.; Akan, M. Distribution of antimicrobial resistance and virulence markers in chicken-origin Proteus mirabilis isolates. Acta Vet. Hung. 2024, 72, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salazar, C.; Giménez, M.; Riera, N.; Parada, A.; Puig, J.; Galiana, A.; Grill, F.; Vieytes, M.; Mason, C.E.; Antelo, V.; et al. Human microbiota drives hospital-associated antimicrobial resistance dissemination in the urban environment and mirrors patient case rates. Microbiome 2022, 10, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, C.; Céspedes, C.; Santibañez, N.; Ruiz, P.; Romero, A. Sub-inhibitory concentrations of florfenicol increase biofilm formation of Piscirickettsia salmonis. J. Fish Dis. 2023, 46, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colon, V.A.; Lugsomya, K.; Lam, H.K.; Wahl, L.C.; Parkes, R.S.V.; Cormack, C.A.; Horlbog, J.A.; Stevens, M.; Stephan, R.; Magouras, I. Serotype diversity and antimicrobial resistance profile of Salmonella enterica isolates from freshwater turtles sold for human consumption in wet markets in Hong Kong. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 912693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Wu, T.; Ma, K.; Cheng, Z.; Yi, Q.; Dai, Y.; Wang, B.; Chen, Y.; Wang, B.; et al. Characteristics of antibiotic resistance genes and microbial-community distribution in Wanfeng Lake, upper Pearl River, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 83214–83230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, P.; Zhai, J.; Yang, X.; Gao, J.; Ren, Z.; Guo, B.; Qi, P. Distribution and influencing factors of antibiotic resistance genes in two mussel species along the coasts of the East China Sea and the Yellow Sea. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 488, 137399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Strains | Virulence Factor Genes | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| gadB | mukF | citC | fimA | katB | eseD | ompA | fliC | |
| E1 | + | + | + | + | − | − | + | − |
| E2 | + | + | + | + | − | − | + | + |
| E4 | + | + | + | + | − | − | + | + |
| E5 | + | + | + | + | − | − | + | − |
| E7 | + | + | + | + | − | − | + | − |
| E8 | + | + | + | + | − | − | + | − |
| E9 | + | + | + | + | − | − | + | − |
| Classifications | Antibiotics | Content (µg) | Criteria (mm) | Isolation Sites/Isolated Strains/Inhibition Zone (mm) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Huizhou | Zhaoqing | Guangzhou | Yunfu | ATCC 25922 (CLSI Range) | ||||||||||
| R | I | SDD | S | E1 | E5 | E2 | E4 | E7 | E8 | E9 | ||||
| Cephalosporins | Ceftazidim | 30 | ≤17 | 18–20 | - | ≥21 | 25 S | 25 S | 22 S | 21 S | 27 S | 27 S | 28 S | 27 (25–32) |
| Cefepime | 30 | ≤18 | - | 19–24 | ≥25 | 26 S | 24 SDD | 28 S | 28 S | 28 S | 28 S | 30 S | 36 (31–37) | |
| Fluoroquinolones | Ciprofloxacin | 5 | ≤21 | 22–25 | - | ≥26 | 16 R | 18 R | 28 S | 28 S | 29 S | 29 S | 30 S | 29 (29–38) |
| Ofloxacin | 5 | ≤12 | 13–15 | - | ≥16 | 22 S | 20 S | 21 S | 22 S | 23 S | 20 S | 22 S | 30 (29–33) | |
| Chloramphenicol | Chloramphenicol | 30 | ≤12 | 13–17 | - | ≥18 | 13 I | 16 I | 15 I | 16 I | 18 S | 16 I | 16 I | 25 (21–27) |
| Aminoglycosides | Streptomycin | 10 | ≤11 | 12–14 | ≥15 | 18 S | 14 I | 18 S | 18 S | 16 S | 18 S | 16 S | 18 (12–20) | |
| Amikacin | 30 | ≤16 | 17–19 | - | ≥20 | 25 S | 21 S | 24 S | 22 S | 23 S | 22 S | 26 S | 21 (19–26) | |
| Gentamicin | 10 | ≤14 | 15–17 | ≥18 | 24 S | 22 S | 24 S | 24 S | 24 S | 26 S | 22 S | 22 (19–26) | ||
| Kanamycin | 30 | ≤13 | 14–17 | - | ≥18 | 14 I | 14 I | 16 I | 15 I | 18 S | 17 I | 17 I | 18 (17–25) | |
| Penicillin | Ampicillin | 10 | ≤13 | 14–16 | - | ≥17 | 0 R | 0 R | 0 R | 0 R | 0 R | 0 R | 0 R | 17 (15–22) |
| Carbapenem | Imipenem | 10 | ≤19 | 20–22 | - | ≥23 | 26 S | 30 S | 28 S | 28 S | 30 S | 28 S | 28 S | 28 (26–32) |
| Tetracycline | Tetracycline | 30 | ≤11 | 12–14 | - | ≥15 | 10 R | 15 S | 8 R | 8 R | 18 S | 22 S | 18 S | 23 (18–25) |
| Doxycycline | 30 | ≤10 | 11–13 | - | ≥14 | 10 R | 11 I | 10 R | 12 I | 10 R | 10 R | 11 R | 21 (18–24) | |
| Minocycline | 30 | ≤12 | 13–15 | - | ≥16 | 7 R | 10 R | 9 R | 9 R | 8 R | 9 R | 10 R | 20 (19–25) | |
| DHFR inhibitor | Trimethoprim | 5 | ≤10 | 11–15 | - | ≥16 | 0 R | 0 R | 0 R | 0 R | 0 R | 0 R | 0 R | 22 (21–28) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ye, Y.; Huang, Y.; Li, F.; Chen, Z.; Lin, H.; Chen, R. Field Prevalence and Pathological Features of Edwardsiella tarda Infection in Farmed American Bullfrogs (Aquarana catesbeiana). Animals 2025, 15, 2487. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15172487
Ye Y, Huang Y, Li F, Chen Z, Lin H, Chen R. Field Prevalence and Pathological Features of Edwardsiella tarda Infection in Farmed American Bullfrogs (Aquarana catesbeiana). Animals. 2025; 15(17):2487. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15172487
Chicago/Turabian StyleYe, Yongping, Yufang Huang, Furong Li, Ziyan Chen, Han Lin, and Ruiai Chen. 2025. "Field Prevalence and Pathological Features of Edwardsiella tarda Infection in Farmed American Bullfrogs (Aquarana catesbeiana)" Animals 15, no. 17: 2487. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15172487
APA StyleYe, Y., Huang, Y., Li, F., Chen, Z., Lin, H., & Chen, R. (2025). Field Prevalence and Pathological Features of Edwardsiella tarda Infection in Farmed American Bullfrogs (Aquarana catesbeiana). Animals, 15(17), 2487. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15172487





