Classical Microbiological Diagnostics of Bacteremia: Are the Negative Results Really Negative? What is the Laboratory Result Telling Us About the “Gold Standard”?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Samples
2.3. Blood Purification, Pellets Separation, and Direct Smear Preparation
2.4. Gram Staining
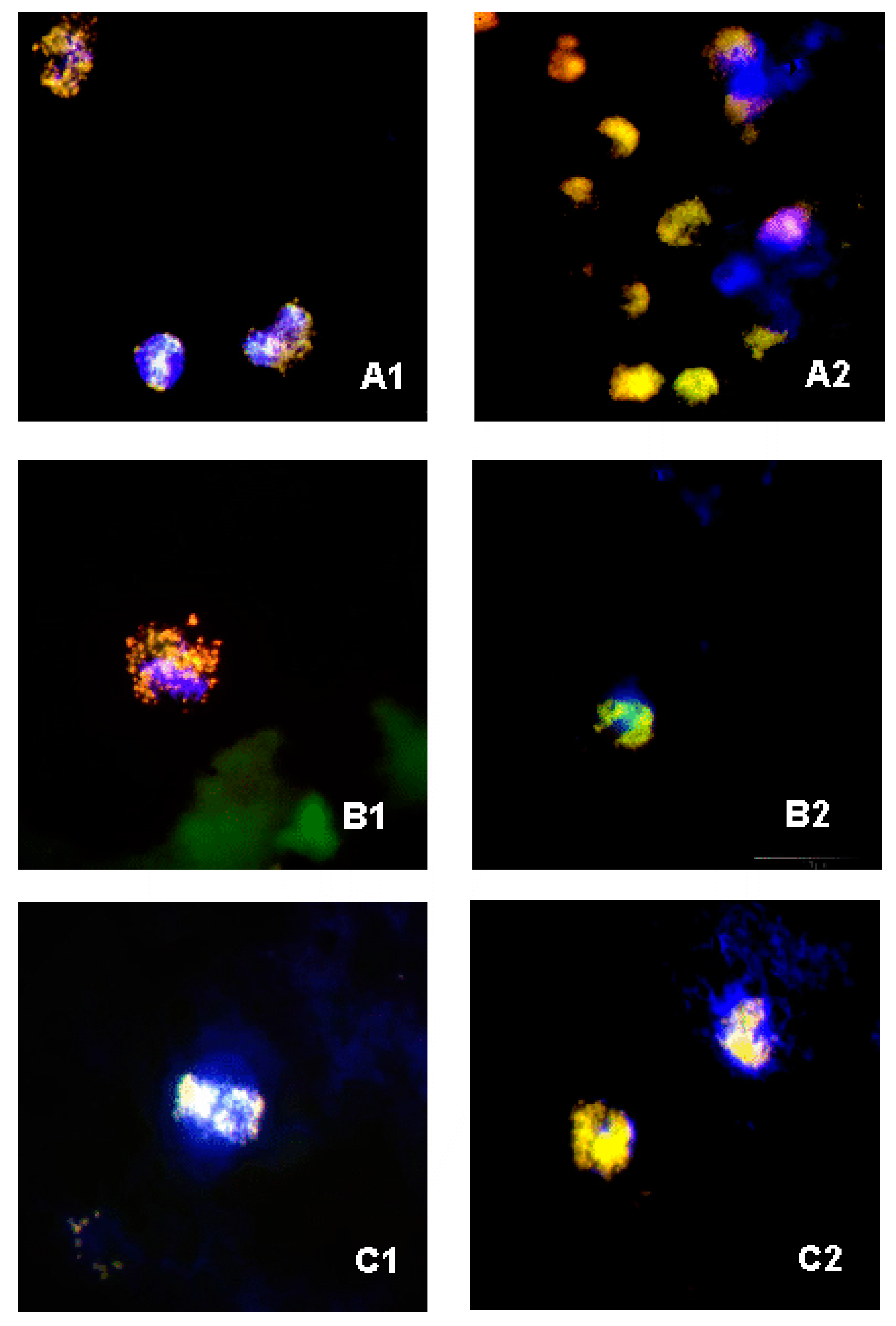
2.5. Fluorescence in-situ Hybridization (FISH).
2.6. Statistical Analysis
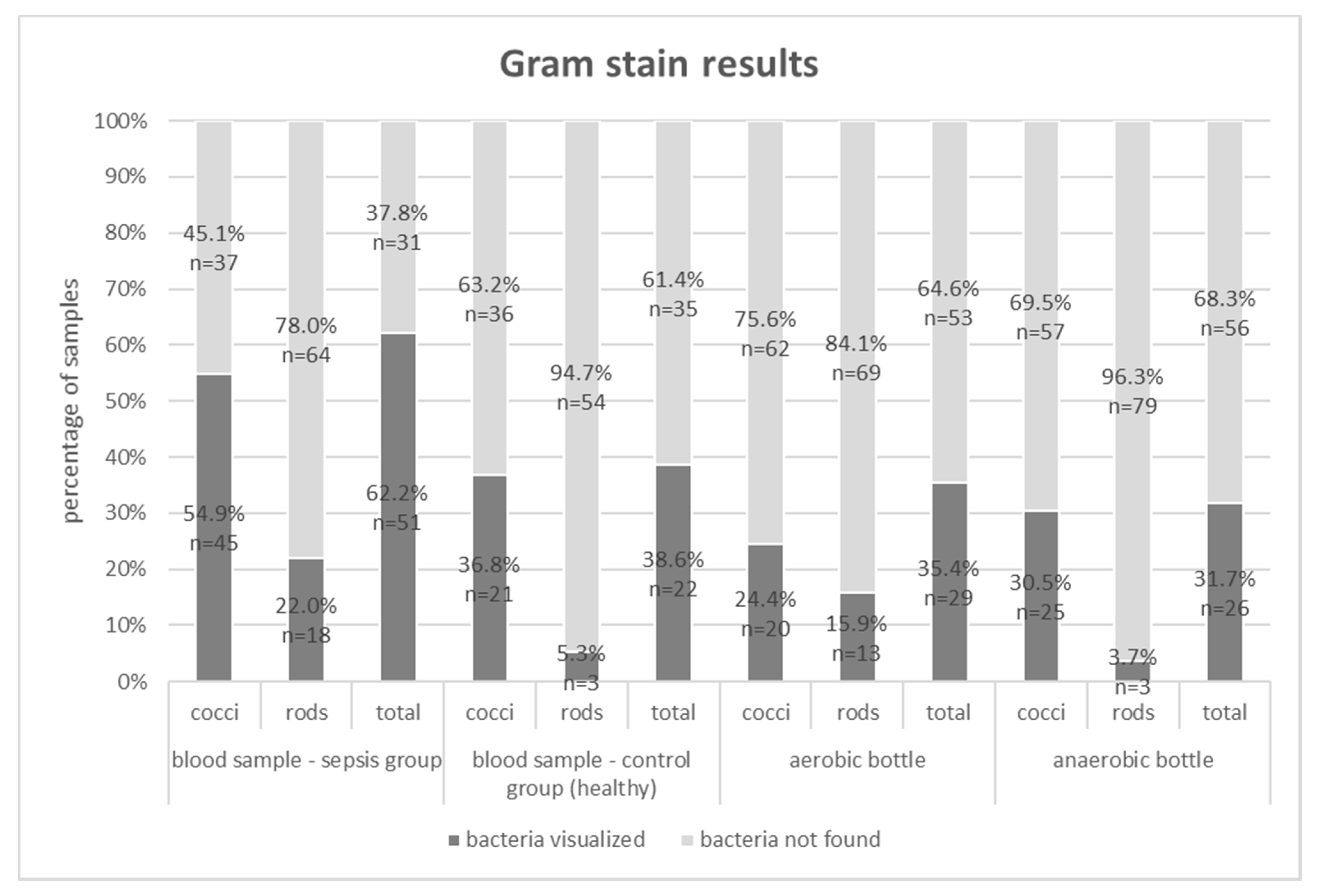
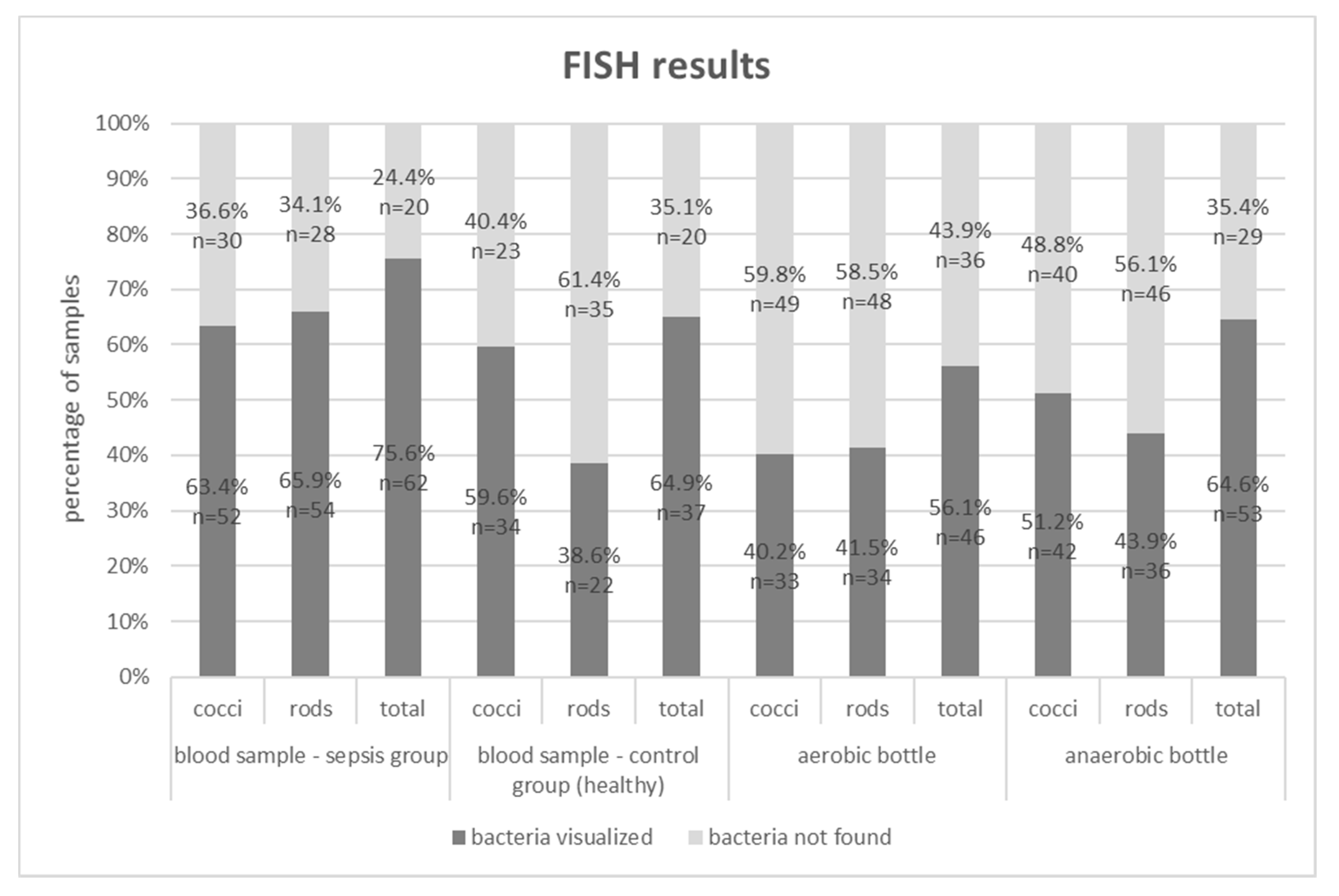
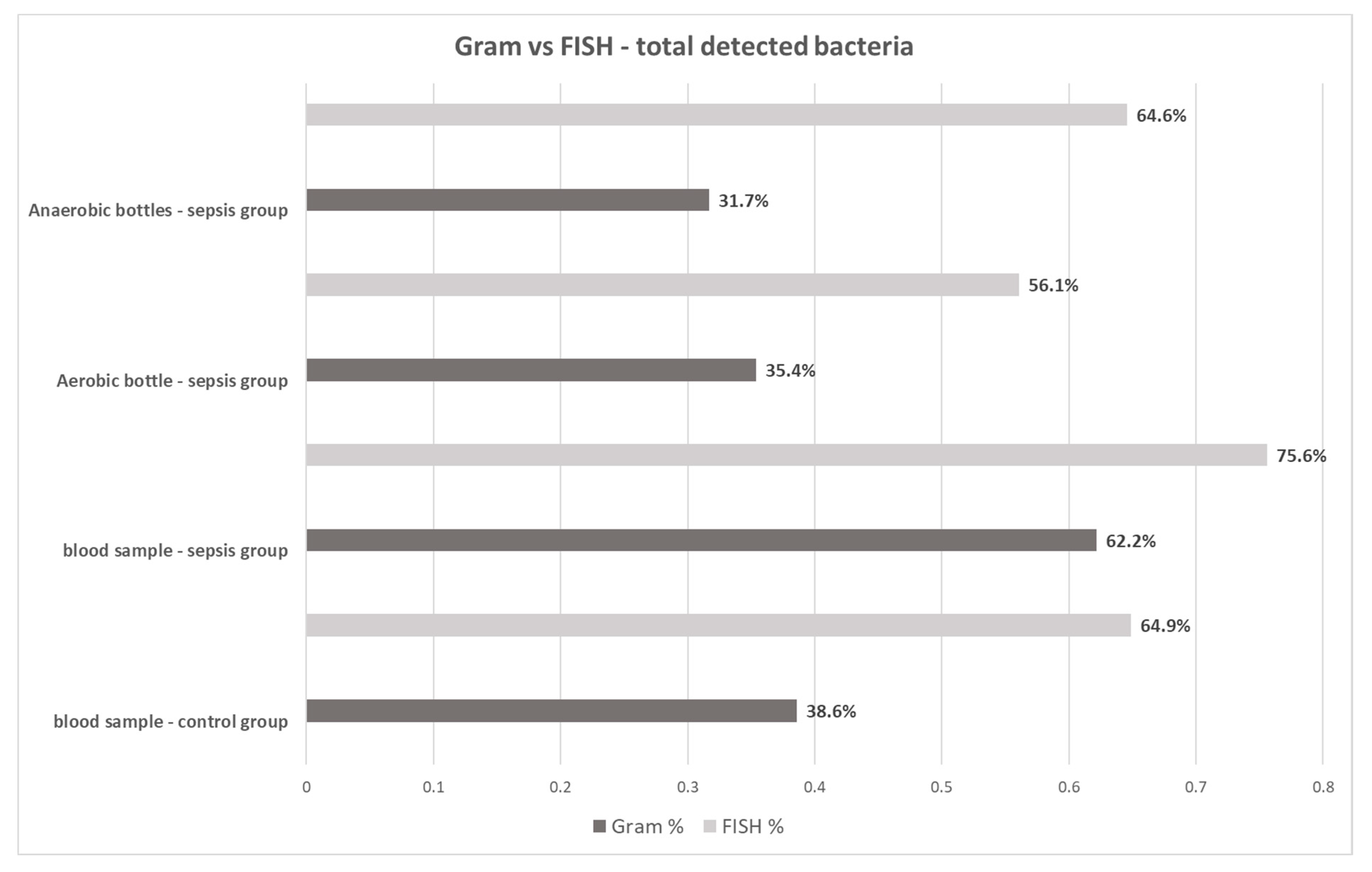
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hunfeld, K.-P.; Bingold, T.; Brade, V.; Wissing, H. Molecular biological detection of pathogens in patients with sepsis. Potentials, limitations and perspectives. Anaesthesist 2008, 57, 326–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singer, M.; Deutschman, C.S.; Seymour, C.W.; Shankar-Hari, M.; Annane, D.; Bauer, M.; Bellomo, R.; Bernard, G.R.; Chiche, J.-D.; Coopersmith, C.M.; et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA 2016, 315, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, J.S.; Cheng, A.C.; McMillan, M.; Humphrey, A.B.; Stephens, D.P.; Anstey, N.M. Sepsis in the tropical Top End of Australia’s Northern Territory: Disease burden and impact on Indigenous Australians. Med. J. Aust. 2011, 194, 519–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control (CDC). Increase in National Hospital Discharge Survey Rates for Septicemia--United States. JAMA 1990, 263, 937–938.
- Fleischmann, C.; Scherag, A.; Adhikari, N.K.J.; Hartog, C.S.; Tsaganos, T.; Schlattmann, P.; Angus, D.C.; Reinhart, K. Assessment of global incidence and mortality of hospital-treated sepsis current estimates and limitations. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 193, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Sakhuja, A.; Kumar, G.; McGrath, E.; Nanchal, R.S.; Kashani, K.B. Culture-Negative Severe Sepsis. Chest 2016, 150, 1251–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamal, W.; Tamaray, G.; Pazhoor, A.; Rotimi, V.O. Comparative evaluation of BacT/ALERT 3D and BACTEC systems for the recovery of pathogens causing bloodstream infections. Med. Princ. Pract. 2006, 15, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opal, S.M. Endotoxins and other sepsis triggers. Contrib. Nephrol. 2010, 167, 14–24. [Google Scholar]
- Dickson, K.; Lehmann, C. Inflammatory Response to Different Toxins in Experimental Sepsis Models. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, T.F.; Thompson, G.R.; Denning, D.W.; Fishman, J.A.; Hadley, S.; Herbrecht, R.; Kontoyiannis, D.P.; Marr, K.A.; Morrison, V.A.; Nguyen, M.H.; et al. Practice Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Aspergillosis: 2016 Update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 63, e1–e60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosiewski, T.; Flis, A.; Sroka, A.; Kedzierska, A.; Pietrzyk, A.; Kedzierska, J.; Drwila, R.; Bulanda, M. Comparison of nested, multiplex, qPCR; FISH; SeptiFast and blood culture methods in detection and identification of bacteria and fungi in blood of patients with sepsis. BMC Microbiol. 2014, 14, 2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gosiewski, T.; Ludwig-Galezowska, A.H.H.; Huminska, K.; Sroka-Oleksiak, A.; Radkowski, P.; Salamon, D.; Wojciechowicz, J.; Kus-Slowinska, M.; Bulanda, M.; Wolkow, P.P.P. Comprehensive detection and identification of bacterial DNA in the blood of patients with sepsis and healthy volunteers using next-generation sequencing method - the observation of DNAemia. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2017, 36, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Źródłowski, T.W.; Jurkiewicz-Badacz, D.; Sroka-Oleksiak, A.; Salamon, D.; Bulanda, M.; Gosiewski, T. Comparison of PCR, fluorescent in situ hybridization and blood cultures for detection of bacteremia in children and adolescents during antibiotic therapy. Polish J. Microbiol. 2018, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gosiewski, T.; Jurkiewicz-Badacz, D.; Sroka, A.; Brzychczy-Włoch, M.; Bulanda, M. A novel, nested, multiplex, real-time PCR for detection of bacteria and fungi in blood. BMC Microbiol. 2014, 14, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Klouche, M.; Schröder, U. Rapid methods for diagnosis of bloodstream infections. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2008, 46, 888–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderaro, A.; Martinelli, M.; Motta, F.; Larini, S.; Arcangeletti, M.C.; Medici, M.C.; Chezzi, C.; De Conto, F. Comparison of peptide nucleic acid fluorescence in situ hybridization assays with culture-based matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry for the identification of bacteria and yeasts from blood cultures and cerebrospina. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2014, 8, O468–O475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farina, C.; Perin, S.; Andreoni, S.; Conte, M.; Fazii, P.; Lombardi, G.; Manso, E.; Morazzoni, C.; Sanna, S. Evaluation of the peptide nucleic acid fluorescence in situ hybridisation technology for yeast identification directly from positive blood cultures: An Italian experience. Mycoses 2012, 55, 388–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parcell, B.J.; Orange, G. V PNA-FISH assays for early targeted bacteraemia treatment. J. Microbiol. Methods 2013, 95, 253–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loonen, A.J.M.; Wolffs, P.F.G.; Bruggeman, C.A.; van den Brule, A.J.C. Developments for improved diagnosis of bacterial bloodstream infections. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2014, 33, 1687–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Źródłowski, T.W.; Flis, A.; Ziętkiewicz, M.; Drwiła, R.; Gosiewski, T. Fluorescent in situ hybridization and Gram-stained smears of whole blood as complementary screening tools in the diagnosis of sepsis. Polish Arch. Intern. Med. 2017, 127, 122–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosiewski, T.; Brzychczy, M. Gosiewski Method for efficient isolation of microbial dna from blood. United States Patent US9879311 (B2), 30 January 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Gosiewski, T.; Szała, L.; Pietrzyk, A.; Brzychczy-Włoch, M.; Heczko, P.B.; Bulanda, M. Comparison of Methods for Isolation of Bacterial and Fungal DNA from Human Blood. Curr. Microbiol. 2014, 68, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amann, R.I.; Binder, B.J.; Olson, R.J.; Chisholm, S.W.; Devereux, R.; Stahl, D.A. Combination of 16S rRNA-targeted oligonucleotide probes with flow cytometry for analyzing mixed microbial populations. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1990, 56, 1919–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kempf, V.A.; Trebesius, K.; Autenrieth, I.B. Fluorescent In situ hybridization allows rapid identification of microorganisms in blood cultures. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 830–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedrich, U.; Van Langenhove, H.; Altendorf, K.; Lipski, A. Microbial community and physicochemical analysis of an industrial waste gas biofilter and design of 16S rRNA-targeting oligonucleotide probes. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 5, 183–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhodes, A.; Phillips, G.; Beale, R.; Cecconi, M.; Chiche, J.D.; De Backer, D.; Divatia, J.; Du, B.; Evans, L.; Ferrer, R.; et al. The Surviving Sepsis Campaign bundles and outcome: Results from the International Multicentre Prevalence Study on Sepsis (the IMPreSS study). Intensiv. Care Med. 2015, 41, 1620–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potgieter, M.; Bester, J.; Kell, D.B.; Pretorius, E. The dormant blood microbiome in chronic, inflammatory diseases. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 39, 567–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.-K.; Leung, R.K.-K.; Guo, H.-X.; Wei, J.-F.; Wang, J.-H.; Kwong, K.-T.; Lee, S.-S.; Zhang, C.; Tsui, S.K.-W. Detection and identification of plasma bacterial and viral elements in HIV/AIDS patients in comparison to healthy adults. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 1126–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wang, C.; Tang, C.; Zhao, X.; He, Q.; Li, J. Identification and Characterization of Blood and Neutrophil-Associated Microbiomes in Patients with Severe Acute Pancreatitis Using Next-Generation Sequencing. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingue, G.J.; Schlegel, J.U. Novel bacterial structures in human blood: Cultural isolation. Infect. Immun. 1977, 15, 621–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedeschi, G.G.; Bondi, A.; Paparelli, M.; Sprovieri, G. Electron microscopical evidence of the evolution of corynebacteria-like microorganisms within human erythrocytes. Experientia 1978, 34, 458–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devine, K.M. Bacterial L-forms on tap: An improved methodology to generate Bacillus subtilis L-forms heralds a new era of research. Mol. Microbiol. 2012, 83, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, M.; Jupe, J.; Mack, H.; Coleman, T.P.; Lawrence, S.M.; Fraley, S.I. Emerging technologies for molecular diagnosis of sepsis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 31, e00089-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delano, M.J.; Ward, P.A. Sepsis-induced immune dysfunction: Can immune therapies reduce mortality? J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lissauer, M.E.; Leekha, S.; Preas, M.A.; Thom, K.A.; Johnson, S.B. Risk factors for central line-associated bloodstream infections in the era of best practice. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2012, 72, 1174–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, M.-O.; Decker, S.G.; Allen-Bridson, K.; Hebden, J.N.; Leaptrot, D. Healthcare-associated infections studies project: An American Journal of Infection Control and National Healthcare Safety Network data quality collaboration: Location mapping. Am. J. Infect. Control 2018, 46, 577–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peretz, A.; Isakovich, N.; Pastukh, N.; Koifman, A.; Glyatman, T.; Brodsky, D. Performance of Gram staining on blood cultures flagged negative by an automated blood culture system. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2015, 34, 1539–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocoglu, M.E.; Bayram, A.; Balci, I. Evaluation of negative results of BacT/Alert 3D automated blood culture system. J. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 257–259. [Google Scholar]
- Greene, M.T.; Saint, S.; Ratz, D.; Kuhn, L.; Davis, J.; Patel, P.K.; Rogers, M.A.M. Role of transfusions in the development of hospital-acquired urinary tract-related bloodstream infection among United States Veterans. Am. J. Infect. Control 2019, 47, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, N.; Kryukov, K.; Nakagawa, S.; Takeuchi, J.S.; Takeshita, M.; Kirimura, Y.; Mitsuhashi, S.; Ishihara, T.; Aoki, H.; Inokuchi, S.; et al. Detection of pathogenic bacteria in the blood from sepsis patients using 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing analysis. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0202049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, A.; Wort, S.J.; Thomas, H.; Collinson, P.; David, E.D. Plasma DNA concentration as a predictor of mortality and sepsis in critically ill patients. Crit. Care 2006, 10, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garnacho-Montero, J.; Huici-Moreno, M.J.; Gutiérrez-Pizarraya, A.; López, I.; Márquez-Vácaro, J.A.; Macher, H.; Guerrero, J.M.; Puppo-Moreno, A. Prognostic and diagnostic value of eosinopenia, C-reactive protein, procalcitonin, and circulating cell-free DNA in critically ill patients admitted with suspicion of sepsis. Crit. Care 2014, 18, R116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grumaz, S.; Stevens, P.; Grumaz, C.; Decker, S.O.; Weigand, M.A.; Hofer, S.; Brenner, T.; von Haeseler, A.; Sohn, K. Next-generation sequencing diagnostics of bacteremia in septic patients. Genome Med. 2016, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benítez-Páez, A.; Álvarez, M.; Belda-Ferre, P.; Rubido, S.; Mira, A.; Tomás, I. Detection of transient bacteraemia following dental extractions by 16S rDNA pyrosequencing: A pilot study. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sepsis Group – Blood Cultures | Control Group (n = 57) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Negative (n = 82) | Positive (n = 8) | ||
| Sex (male/female) | 0.64 (± 0.2) | 0.85 (± 0.4) | 0.31 (± 0.1) |
| Age (year) | 69.4 (± 11.2) | 58.8 (± 9.4) | 39.6 (± 7.9) |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 22.7 (± 4.8) | 23.5 (± 3.8) | 24.5 (± 1.9) |
| SOFA score | 7.9 (± 4.1) | 6.6 (± 4.7) | N/A |
| WBC (109/L) | 17.2 (± 10.9) | 18.1 (± 11.3) | 4.5 (± 0.8) |
| CRP (mg/L) | 194.1 (± 140.5) | 175.5 (± 150.8) | 1.4 (± 0.6) |
| PCT (ng/mL) | 5.9 (± 0.6) | 5.2 (± 0.7) | N/A |
| [%] | FISH | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Gram stain | Blood Samples – Control Group | ||
| bacteria not found | bacteria visualized | ||
| bacteria not found | 35.1 | 26.3 | |
| bacteria visualized | 0.0 | 38.6 | |
| Blood Samples – Sepsis Group | |||
| bacteria not found | bacteria visualized | ||
| bacteria not found | 24.4 | 13.4 | |
| bacteria visualized | 0.0 | 62.2 | |
| Aerobic Bottles Samples – Sepsis Group | |||
| bacteria not found | bacteria visualized | ||
| bacteria not found | 43.9 | 20.7 | |
| bacteria visualized | 0.0 | 35.4 | |
| Anaerobic Bottles Samples – Sepsis Group | |||
| bacteria not found | bacteria visualized | ||
| bacteria not found | 24.4 | 45.3 | |
| bacteria visualized | 11.0 | 19.3 | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Źródłowski, T.; Sobońska, J.; Salamon, D.; McFarlane, I.M.; Ziętkiewicz, M.; Gosiewski, T. Classical Microbiological Diagnostics of Bacteremia: Are the Negative Results Really Negative? What is the Laboratory Result Telling Us About the “Gold Standard”? Microorganisms 2020, 8, 346. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8030346
Źródłowski T, Sobońska J, Salamon D, McFarlane IM, Ziętkiewicz M, Gosiewski T. Classical Microbiological Diagnostics of Bacteremia: Are the Negative Results Really Negative? What is the Laboratory Result Telling Us About the “Gold Standard”? Microorganisms. 2020; 8(3):346. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8030346
Chicago/Turabian StyleŹródłowski, Tomasz, Joanna Sobońska, Dominika Salamon, Isabel M. McFarlane, Mirosław Ziętkiewicz, and Tomasz Gosiewski. 2020. "Classical Microbiological Diagnostics of Bacteremia: Are the Negative Results Really Negative? What is the Laboratory Result Telling Us About the “Gold Standard”?" Microorganisms 8, no. 3: 346. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8030346
APA StyleŹródłowski, T., Sobońska, J., Salamon, D., McFarlane, I. M., Ziętkiewicz, M., & Gosiewski, T. (2020). Classical Microbiological Diagnostics of Bacteremia: Are the Negative Results Really Negative? What is the Laboratory Result Telling Us About the “Gold Standard”? Microorganisms, 8(3), 346. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8030346