Abstract
Juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) is the most common rheumatic disease in children. Herein, we evaluated the relationship between the gut microbiome (GM) and disease phenotype by an integrated omics fused approach. In a multicenter, observational cohort study, stools from Italian JIA patients were collected at baseline, active, and inactive disease stages, and their GM compared to healthy controls (CTRLs). The microbiota metabolome was analyzed to detect volatile- and non-volatile organic compounds (VOCs); the data were fused with operational taxonomic units (OTUs) from 16S RNA targeted-metagenomics and classified by chemometric models. Non-VOCs did not characterize JIA patients nor JIA activity stages compared to CTRLs. The core of VOCs, (Ethanol, Methyl-isobutyl-ketone, 2,6-Dimethyl-4-heptanone and Phenol) characterized patients at baseline and inactive disease stages, while the OTUs represented by Ruminococcaceae, Lachnospiraceae and Clostridiacea discriminated between JIA inactive stage and CTRLs. No differences were highlighted amongst JIA activity stages. Finally, the fused data discriminated inactive and baseline stages versus CTRLs, based on the contribution of the invariant core of VOCs while Ruminococcaceae concurred for the inactive stage versus CTRLs comparison. In conclusion, the GM signatures enabled to distinguish the inactive disease stage from CTRLs.
1. Introduction
In recent years, many evidences have highlighted that alterations in the gut microbiome (GM) were frequently associated to the development of local and systemic inflammatory and autoimmune diseases [1], and thus, the role of GM in the pathogenesis of juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) has been also hypothesized [2]. In a recent multicenter observational cohort study, a GM dysbiosis for JIA patients was detected, in terms of richness and compositional deviation from age-matched healthy controls (CTRLs) [3]. Particularly, the study of van Dijkhuizen et al. [3] included a large cohort of treated-naive JIA Dutch and Italian patients in longitudinal follow up. This experimental design, which allowed us to compare the GM amongst patients versus CTRLs, revealed that age, geographic origin and disease status appeared to be determinant factors for the GM signature, regardless of the disease activity stage (i.e., baseline, inactive, active) and inflammation markers. In addition, a recent re-evaluation of previously published data derived from USA [4], Finland [5] and Indian [6] cohorts confirmed that the GM signature of JIA patients was different from CTRLs, on the basis of their geographical origin [7]. Moreover, training mathematical models built on a single cohort was unable to differentiate JIA patients from CTRLs [7]. Hence, while the JIA disease status is ascertained to be associated to a dysbiosis, the role of GM composition in the pathogenesis of the disease must be still deeply investigated, particularly for the aspects depending on geographical variability. The present study highlights a progression of a previous clinical study [3]; in particular, a well-defined Italian cohort of JIA patients at baseline, inactive and persistent stage conditions compared to CTRLs was studied to find possible associations amongst composition (operational taxonomic units OTUs at bacterial family level) and content of volatile organic compound (VOCs) and low weight molecules (Non-VOCs) in the stools. The multi-omic approach, achieved by the integration of different metabolomics and targeted-metagenomics data, might provide different profiles to better highlight the role of GM in the JIA disease.
2. Materials and Methods
Patient Enrollment and Omics Procedures
This observational prospective cohort study was conducted in Italy at the Ospedale Pediatrico Giannina Gaslini (OPGG) of Genoa and at the Ospedale Pediatrico Bambino Gesù (OPBG) of Rome, Italy. The consecutive 60 patients’ cohort, 46 from OPBG and 14 from OPGG, respectively, was recruited between October 2013 and December 2015 with a JIA diagnosis, according to International League Against Rheumatism (ILAR) criteria [8].
Patients, 16 males and 44 females, aged 1.7 to 16.6 years (average age 7.0 years SD ± 4.11), were aged-matched against a cohort of 25 CTRLs subjects, screened during a survey on GM programming at the OPBG Human Microbiome Unit (Table 1). Moreover, clinical data including the JADAS- 71 [9], CRP, ESR and the use of NSAIDs were collected (Table 1), as well as information on dietary habits and prebiotic, probiotic administration (Table S1). At the follow up visits, disease activity status was defined according to the Wallace criteria for inactive disease [10]. A previous study included more detailed information on the same patient’s cohort [3].

Table 1.
Clinical characteristics of the patients with JIA and CTRLs.
The study was approved by the OPBG ethics committees (Code 615/2013) on 6 May 2013 and was conducted in accordance with the Principles of Good Clinical Practice and the Declaration of Helsinki. Written informed consent was obtained from all participants.
Eighty-five fecal samples were collected at the reference node of the Biobanking and Biomolecular Resources Research Infrastructure of Italy (BBMRI) for human microbiome of the OPBG Human Microbiome Unit and stored at −80 °C until further meta-omics processing.
The 16S targeted-metagenomics data of the GM profiling, discussed in the previous study [3], were harmonized and combined for omics data integration to metabolomics data obtained by both solid phase micro-extraction coupled with gas-chromatography mass spectrometry (SPME/GC-MS) (Table S2) and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy (Table S3), obtained as described in the previous studies [11,12].
To integrate the multidimensional data, univariate and multivariate analyses were performed by MATLAB toolbox or by in-house written software. The OTUs and SPME/GC-MS raw data were reduced in order to obtain matrices considering only OTUs and metabolites detected in at least 70% of the entire dataset, including both JIA and CTRLs subjects. On the contrary, NMR raw data matrix did not need any reduction. Classification models were built according to Vernocchi et al. [13] and optimized for this specific application (Figure 1). Moreover, the partial least square-discriminant analysis (PLS-DA) was performed according to Szymańska et al. [14]; in particular, validation was carried out by means of a combination of double cross-validation (DCV) and permutation tests. Following DCV procedure, for each variable the geometric average was considered, and the non-parametric statistics rank product (RP) index was applied [15]. Low values of RP indicated variables highly contributing to the model and, accordingly, considered as candidate biomarkers.
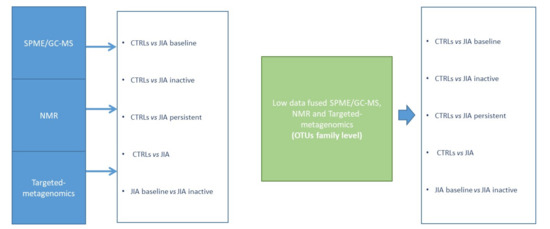
Figure 1.
Strategy for the multivariate analysis of targeted-metagenomics, gas-chromatography mass spectrometry SPME/GC-MS and nuclear magnetic resonance NMR based metabolomics data and low data fused (integrated platforms). Classification models, based on Partial least squares discriminant analysis(PLS-DA) in double cross-validation (DCV), were at first established considering the results for each omic platform and, in a second stage, according to a low-level data fusion strategy (targeted-metagenomics, SPME/GC-MS and NMR).
3. Results
3.1. Patients
Sixty JIA pediatric patients, (average age 7.0 years, SD ± 4.11), compared to 25 healthy age-paired subjects, were recruited in a previous study [3], to evaluate their microbiota signatures by metabolomics profiling and data fusion with microbiota composition. In according to the Juvenile Arthritis Disease Activity Score in 71 joints (JADAS-71) [9,16], the disease activity varied from moderate (mean value: 15.95) for baseline, to low (mean values 0.34) for inactive and persistent (mean values 7.19) disease stages, respectively. The mean values of C-reactive protein (CRP) showed low levels in the serum ranging from 0.24 to 1.38 mg/L. The erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) resulted higher at baseline (mean value 24.6 mm/hour), followed by ESR values at persistent (mean value 18.4 mm/h) and inactive disease stage (mean value 11.1 mm/h). Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) were mainly administered to patients at baseline (15/20), followed by patients with persistent (7/21) and inactive disease (3/19). No patients used any biologicals or synthetic antirheumatic drugs at baseline, whereas most patients were on methotrexate (MTX) in inactive (14/19) and during persistent (12/21) disease stages. Some patients used biological drugs (Table 1).
3.2. Omics Data and Fused Model Analysis
Different classification algorithms were created in order to achieve a functional model of the GM in JIA. Firstly, the analysis was conducted separately on the different data resulting from single platforms and generated variables: (i) targeted-metagenomics and OTUs; (ii) SPME/GC-MS and VOCs; (iii) NMR and Non-VOCs (Figure 1).
The PLS-DA models were created on single and low-level fused data generated from VOCs, OTUs, and Non-VOCs.
Focusing on VOCs, the average correct classification rate (CCR3) referring to CTRLs versus JIA patients (total variables) comparison ranged around 77% for each paired CTRLs-disease stage. Particularly, registered percentages were: 78.5 ± 2.6, CTRLs-JIA Baseline; 75.9 ± 4.9, CTRLs-JIA Inactive; 77.5 ± 3.2, CTRLs-JIA Persistent. Overall, CTRLs versus entire JIA phenotypes were classified by averaged CCR 3 62.9 ± 2.7% (Table 2).

Table 2.
PLS-DA models in DCV of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) data matrix.
Despite the partial CCR for each JIA disease stage was lower (CCR1 average around 55%) with respect to CTRLs group (CCR2 average around 95%), the CCR3 for the paired CTRLs-JIA disease stages represented a high value of classification. However, its value was principally due to CTRLs, hence characterizing this model as having a low predictive ability to identify JIA disease stage groups (Table 2). Nonetheless, an invariant core of metabolites such as Methyl-isobutyl-ketone, Ethanol, 2,6-Dimethyl-4-heptanone and Phenol were shared by the metabolomics profiles of patients at baseline and inactive disease stages, therefore resulting overrepresented in the patients’ profiles. The Methyl-isobutyl-ketone and the 1-Hexanol represented the highest and the lowest represented metabolite, respectively, in the JIA PLS-DA model (Table 3).

Table 3.
Metabolites derived from PLSA-DA models in DCV of VOCs data matrix.
Moreover, OTUs (Table 4 and Table 5) and Non-VOCs (Table 6) variables, evidenced values of CCRn that failed in the attempt to classify all groups of variables, including JIA, CTRLs and JIA at different disease stage.

Table 4.
PLS-DA models in DCV of operational taxonomic units (OTUs) at family level.

Table 5.
Microbial features derived from PLS-DA models in DCV of OTUs at family level.

Table 6.
PLS-DA models in DCV of Non-VOCs data matrix.
Concerning OTUs, the calculated values for each JIA disease stage (CCR1 average around 60%) and CTRLs (CCR2 average around 61%) resulted in a low prediction model (Table 4). Particularly, registered average percentages were: 53.3 ± 4.2, CTRLs-JIA Baseline; 69.4 ± 4.0, CTRLs-JIA Inactive; 58.1 ± 4.7, CTRLs-JIA Persistent. Therefore, the comparison between CTRLs and JIA Inactive stage (Table 4) was characterized by the highest CCRn value. The value was achieved by the concurrent contribution of the OTUs at family level, Ruminococcaceae, Lachnospiraceae, Clostridiaceae (Table 5).
Non-VOCs variables (Table 6) showed average and single CCRn values around 40–60%; hence the alone NMR platform data were considered not reliable to perform a group classification validation for both CTRLs, JIA patients and single JIA-disease stages.
Moving to the low-level fused data, the total classification ability of the model ranged from 57.6 to 81.2%. In particular, the grouping between JIA disease stage and CTRLs was classified by CCR 3 score whose average ranged from 68.1 to 72.8% (Table 7). For the comparison CTRLs/JIA ALL, the CCR 3 average value was the lowest value compared to the other CCR3, while, within disease phenotypes, the model recognized both JIA baseline (CCR3 71.6 ± 4.9) and JIA inactive stages (CCR3 72.8 ± 5.1) from CTRLs, as reported in Table 7.

Table 7.
PLS-DA models in DCV of low-level fused data matrix.
In the fused model, the variables OTUs and metabolites, which could be identified as significant and predictive compared to the CTRLs, were defined by the RP obtained by DCV procedure (Figure 2). Overall, the models built on the JIA patients at baseline, active and persistent disease stage identified high levels of alcohols, such as 1-Butanol and 1-Pentanol. Moreover, low abundance of Coriobacteriaceae represented an important variable for the discrimination from CTRLs of JIA Baseline and with less representativity of persistent disease stages’ children (Figure 2a).
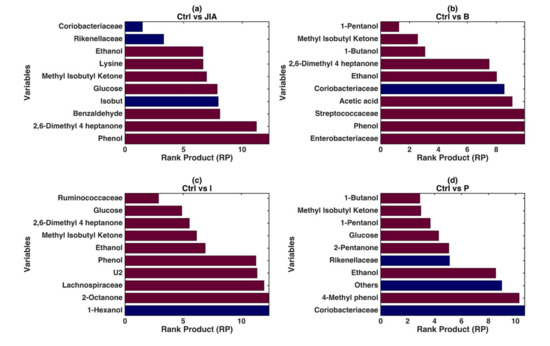
Figure 2.
PLS-DA modeling on the low-level fused data. Graphical illustration of the variables significantly contributing to the definition of the single models based on the values of RP resulting from the repeated DCV procedure. The four different panels show the RP values for the models: (a) CTRLs vs. JIA; (b) CTRLs vs. JIA Baseline; (c) CTRLs vs. JIA Inactive; (d) CTRLs vs. JIA Persistent. In each panel, the color of the bars indicates whether, on average, the variable is higher (red) or lower (blue) in the specific JIA disease stage with respect to the CTRLs.
The VOCs Ethanol, Methyl-isobutyl-ketone, 2,6-Dimethyl-4-heptanone and Phenol represented the metabolites discriminating JIA patients at both baseline and inactive stage from CTRLs in the PLS-DA (Figure 2b,c). These VOCs at JIA Baseline showed RP values ranging from 3 to 10, in the model discriminating CTRLs vs. JIA Baseline while in CTRLs vs. JIA Inactive RP values ranged from 6 to 12, identifying these molecules as highly contributing to the models, hence representing potential biomarkers (Figure 2b,c) of the disease stages. Streptococcaceae (RP: > 10) and Enterobacteriaceae (RP: > 10) were associated with JIA Baseline, despite low model values (Figure 2b). On the other site, Ruminococcaceae (RP: 4) well represented JIA Inactive stage, with also the low scored contribution of Lachnospiraceae (RP: 12.5) (Figure 2c).
In the JIA Persistent stage patients were characterized especially by 1-Butanol, Methyl-isobutyl-ketone, Glucose, 2-Pentanone which showed RP values ranging from 3.8 to 9. Regarding OTUs, Rikenellaceae group decreasing was significantly associated with the JIA Persistent disease stage (Figure 2d). Moreover, in order to achieve an insight on the relationship between omics fingerprints and clinics, different classification models based on clinical data were also established. However, none of these models were able to discriminate amongst JIA patients and reference CTRLs group but also amongst baseline, inactive and persistent disease stages (p-values > 0.05) (data not shown).
On the other hand, the information about the dietary habits and the use of prebiotics, probiotics (Table S1) did not allow to formulate any statistically meaningful hypothesis on the possible relation amongst these three factors and the observed discrimination. However, by inspecting the scores’ plot of the PLS-DA models discussed above, in light of the categorizations described by the three possible confounding factors (diet, prebiotics and probiotics), the distribution of JIA samples appeared not driven by any of these three effects (data not shown).
3.3. Univariate Analysis
Within the group referring to the JIA Inactive-stage, most of the patients were treated with MTX (14/19) similarly to the JIA Persistent-stage group (12/21), whereas at the JIA Baseline-stage the patients were treated with only NSAID (15/20). In order to evaluate the effects due to the pharmacological treatments, we compared the variables that resulted significant in the discrimination between patients and CTRLs, and between patients treated with either NSAID or MTX and those not treated. The results obtained from the univariate analysis (Mann–Whitney Rank Sum Test) showed no significant differences between patients treated and not, regardless therapy type (Text S1).
4. Discussion
The integrated metabolomics and targeted-metagenomics results suggest that the observed GM functional and compositional profiles can be specific for the subjects affected by JIA, rather than for each specific disease stage, and regardless of inflammation status, in agreement with previous results obtained by van Dijkhuizen et al. [3].
High levels of Ruminococcaceae, mainly associated to inactive JIA, were also detected in a polyarticular JIA and enthesitis-related arthritis patients (ERA) compared to CTRLs [11]. Moreover, Forbes et al. [17] revealed Ruminococcus lactaris and Lachnospiraceae as component of the microbiota profile in patients affected by rheumatoid arthritis (RA), along with other species such as Clostridium, Gordonibacter, Eggerthella, Bacteroides dentium, Lactobacillus spp.
The changes in the GM profile in JIA patients at the inactive disease stage resulted to have a higher predictive potentiality with respect to those at baseline and persistent disease stages. However, the high levels of Ethanol and Methyl-isobutyl-ketone had invariable characteristics observable in all PLS-DA models. Ethanol may be the end-product of fermentation of different carbohydrates by GM. Thus, several microbial species belonging to Ruminococcaceae, Lachnospiraceae and Clostridiaceae, as well as Enterobacteriaceae are able to produce ethanol [12]. In addition, the increased abundance of these bacterial families was associated with high levels of Ethanol. Ethanol has also been found in large amounts in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) patients [18]. Furthermore, peculiar changes observed in patients at baseline and persistent disease stage were linked to other alcohols such as 1-Pentanol and 1-Butanol, detected at high levels, compared to CTRLs. On the contrary, the differences between inactive and persistent disease stage patients were not statistically significant.
The higher level of 1-Pentanol and 1-Butanol were previously found in stools of children with NAFLD compared to CTRLs [19], but without any metabolic similarity between the GM of JIA and NAFLD patients. High levels of alcohols have also been observed in the stools of cystic fibrosis children [13], but this metabolic pattern could not define a specific microbial imbalanced activity in JIA patients. Probably, this imbalance could be related to the diet-linked intestinal environment or to a factor linked to an unspecific pathological event than with a metabolism of specific bacteria.
Zhang et al. [20] reported that after the modification of therapy with antirheumatic drugs, there was a partially improved dysbiosis in RA patients, but also highlighted a clinical amelioration.
Dong et al. [21] showed that anti-rheumatic treatments were linked with the partial reversion of dysbiosis. This suggests that the GM plays a crucial role in disease promotion and clinical course and that the intestinal homeostasis is fundamental for the host’s health. The results showed in the present study, in agreement with the previous data [3] carried out in a broad longitudinal study, evidenced that the GM composition and its metabolic activity were not affected by the disease stage.
These results could represent a characteristic phenotypic aspect of JIA individuals, which could be strongly correlated to geographic origin and diet, perfectly in agreement with that previously reported. In fact, dietary habits may represent one of the main variables contributing to the modulation of GM in terms of composition and metabolism [20]. However, we were not able to provide association between dietary habits and GM profiling in JIA patients due to a lack of clear dietary-induced GM modulation. The data fused suggested that the microbiome differences observed between inactive JIA and CTRLs might be related to an unspecific effect dependent on the therapy. Whether the GM composition in JIA Inactive disease was affected by the underlying disease process or past pharmacological treatments, it could not be determined in the present study. Indeed, a limitation of this study originates by an uneven distribution of the therapeutic interventions in different disease stages, as reported in the Results. In fact, the variance introduced by different treatments of the patient set could explain why we did not observe any significant variation between JIA Baseline and Persistent compared to JIA Inactive stages. Therefore, we could only consider the comparison of variables between a single subset of patients (e.g., MTX- or NSAID-treated patients) and related CTRLs.
5. Conclusions
The results supported the hypothesis that GM of JIA patients showed an imbalanced state respect to CTRLs in terms of composition and metabolic functionality. Methyl-isobutyl-ketone and Ethanol levels were higher in all JIA patients as compared to the healthy controls’ group. Furthermore, a predictive significant model discriminating JIA Inactive disease stage from healthy subjects was provided. At this point, it cannot be excluded that differences in GM arose owing to therapeutic interventions. Clearly, future investigations should be aimed at replicating these results in other populations, and in different disease stages, elucidating the potential causal role of GM in the pathogenesis of JIA and investigating the interaction amongst host genetics, microbiome and environmental factors that concur in the development of JIA.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2076-2607/8/10/1540/s1, Table S1: Dietary habits, prebiotics and probiotics administration; Table S2: GC-SPME raw data; Table S3: NMR raw data; Text S1: Univariate analysis.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization P.V., A.M. (Alfredo Miccheli), L.P.; Methodolody, F.M., P.V., F.D.C., E.H.P.v.D., C.M., G.C. (Giorgio Capuani), G.C. (Giorgia Conta), A.T.; Investigation F.M., A.M. (Alfredo Miccheli), P.V.; Validation, F.M., A.M. (Alfredo Miccheli); Visualization F.D.B., A.M. (Alberto Martini); Supervision, L.P., Writing—Original Draft Preparation P.V., A.M. (Alfredo Miccheli), F.M., L.P; Writing—Review and Editing, P.V., G.C. (Giorgia Conta), E.H.P.v.D., A.M. (Alberto Martini), B.D., L.P.; Funding acquisition L.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by: i) Fondazione Bambino Gesù, grant number 201903_FBG and Ricerca Corrente of the Minister of Italian Health, grant number 201905_genetica, to L.P; ii) European Commission’s Seventh Framework Programme (Information Communication Technologies Programme 600932).
Acknowledgments
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| JIA | Juvenile idiopathic arthritis |
| GM | Gut microbiome |
| CTRLs | Controls |
| OTUs | Operational taxonomic units |
| SPME/GC-MS | Solid phase microextraction/Gas-chromatography-mass spectrometry |
| 1H-NMR | Proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy |
| VOCs | Volatile organic compounds |
| JADAS | Juvenile Arthritis Disease Activity Score |
| CRP | C- reactive protein level |
| ESR | Erythrocyte sedimentation rate |
| NSAIDs | Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs |
| MSC | Number of misclassifications |
| ROC | Receiver operating characteristic |
| PLS-DA | Partial least squares discriminant analysis |
| RP | Rank product |
| CCR | Correct classification rate |
| DCV | Double cross-validation |
| ERA | Enthesitis-related arthritis patients |
| NAFLD | Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease |
| OPGG | Ospedale Pediatrico Giannina Gaslini |
| OPBG | Ospedale Pediatrico Bambino Gesù |
| ILAR | International League Against Rheumatism |
References
- Yeoh, N.; Burton, J.P.; Suppiah, P.; Reid, G.; Stebbings, S. The role of the microbiome in rheumatic diseases. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2013, 15, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verwoerd, A.; Ter Haar, N.M.; de Roock, S.; Vastert, S.J.; Bogaert, D. The human microbiome and juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Pediatr. Rheumatol. 2016, 14, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Dijkhuizen, E.H.P.; Del Chierico, F.; Malattia, C.; Russo, A.; Pires Marafon, D.; Ter Haar, N.M.; Magni-Manzoni, S.; Vastert, S.J.; Dallapiccola, B.; Prakken, B.; et al. Microbiome Analytics of the Gut Microbiota in Patients With Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis: A Longitudinal Observational Cohort Study. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 71, 1000–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoll, M.L.; Kumar, R.; Morrow, C.D.; Lefkowitz, E.J.; Cui, X.; Genin, A.; Cron, R.Q.; Elson, C.O. Altered microbiota associated with abnormal humoral immune responses to commensal organisms in enthesitis-related arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2014, 16, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tejesvi, M.V.; Arvonen, M.; Kangas, S.M.; Keskitalo, P.L.; Pirttilä, A.M.; Karttunen, T.J.; Vähäsalo, P. Faecal microbiome in new-onset juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2016, 35, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, A.; Sarangi, A.N.; Gaur, P.; Shukla, A.; Aggarwal, R. Gut microbiome in children with enthesitis-related arthritis in a developing country and the effect of probiotic administration. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2017, 187, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvonen, M.; Vänni, P.; Sarangi, A.N.; V Tejesvi, M.; Vähäsalo, P.; Aggarwal, A.; Stoll, M.L. Microbial orchestra in juvenile idiopathic arthritis: Sounds of disarray? Immunol. Rev. 2020, 294, 9–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petty, R.E.; Southwood, T.R.; Manners, P.; Baum, J.; Glass, D.N.; Goldenberg, J.; He, X.; Maldonado-Cocco, J.; Orozco-Alcala, J.; Prieur, A.-M.; et al. International League of Associations for Rheumatology classification of juvenile idiopathic arthritis: Second revision, Edmonton, 2001. J. Rheumatol. 2004, 31, 390–392. [Google Scholar]
- Consolaro, A.; Ruperto, N.; Bracciolini, G.; Frisina, A.; Gallo, M.C.; Pistorio, A.; Verazza, S.; Negro, G.; Gerloni, V.; Goldenstein-Schainberg, C.; et al. Defining criteria for high disease activity in juvenile idiopathic arthritis based on the juvenile arthritis disease activity score. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 73, 1380–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, C.A.; Giannini, E.H.; Huang, B.; Itert, L.; Ruperto, N.; Childhood Arthritis Rheumatology Research Alliance; Pediatric Rheumatology Collaborative Study Group; Paediatric Rheumatology International Trials Organisation. American College of Rheumatology provisional criteria for defining clinical inactive disease in select categories of juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Arthritis Care Res. 2011, 63, 929–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Paola, M.; Cavalieri, D.; Albanese, D.; Sordo, M.; Pindo, M.; Donati, C.; Pagnini, I.; Giani, T.; Simonini, G.; Paladini, A.; et al. Alteration of Fecal Microbiota Profiles in Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis. Associations with HLA-B27 Allele and Disease Status. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliphant, K.; Allen-Vercoe, E. Macronutrient metabolism by the human gut microbiome: Major fermentation by-products and their impact on host health. Microbiome 2019, 7, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vernocchi, P.; Del Chierico, F.; Russo, A.; Majo, F.; Rossitto, M.; Valerio, M.; Casadei, L.; La Storia, A.; De Filippis, F.; Rizzo, C.; et al. Gut microbiota signatures in cystic fibrosis: Loss of host CFTR function drives the microbiota enterophenotype. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0208171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymańska, E.; Saccenti, E.; Smilde, A.K.; Westerhuis, J.A. Double-check: Validation of diagnostic statistics for PLS-DA models in metabolomics studies. Metabolomics 2012, 8, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Carratore, F.; Jankevics, A.; Eisinga, R.; Heskes, T.; Hong, F.; Breitling, R. RankProd 2.0: A refactored bioconductor package for detecting differentially expressed features in molecular profiling datasets. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 2774–2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consolaro, A.; Ruperto, N.; Bazso, A.; Pistorio, A.; Magni-Manzoni, S.; Filocamo, G.; Malattia, C.; Viola, S.; Martini, A.; Ravelli, A.; et al. Development and validation of a composite disease activity score for juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 61, 658–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forbes, J.D.; Van Domselaar, G.; Bernstein, C.N. The Gut Microbiota in Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Diseases. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Baker, S.S.; Gill, C.; Liu, W.; Alkhouri, R.; Baker, R.D.; Gill, S.R. Characterization of gut microbiomes in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) patients: A connection between endogenous alcohol and NASH. Hepatology 2013, 57, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Chierico, F.; Nobili, V.; Vernocchi, P.; Russo, A.; De Stefanis, C.; Gnani, D.; Furlanello, C.; Zandonà, A.; Paci, P.; Capuani, G.; et al. Gut microbiota profiling of pediatric nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and obese patients unveiled by an integrated meta-omics-based approach. Hepatology 2017, 65, 451–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Sun, H.; Wang, X. Saliva metabolomics opens door to biomarker discovery, disease diagnosis, and treatment. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2012, 168, 1718–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.-Q.; Wang, W.; Li, J.; Ma, M.-S.; Zhong, L.-Q.; Wei, Q.-J.; Song, H.-M. Characterization of microbiota in systemic-onset juvenile idiopathic arthritis with different disease severities. World J. Clin. Cases 2019, 7, 2734–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).